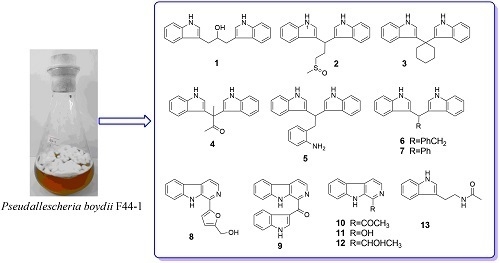
Exploration of Indole Alkaloids from Marine Fungus Pseudallescheria boydii F44-1 Using an Amino Acid-Directed Strategy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
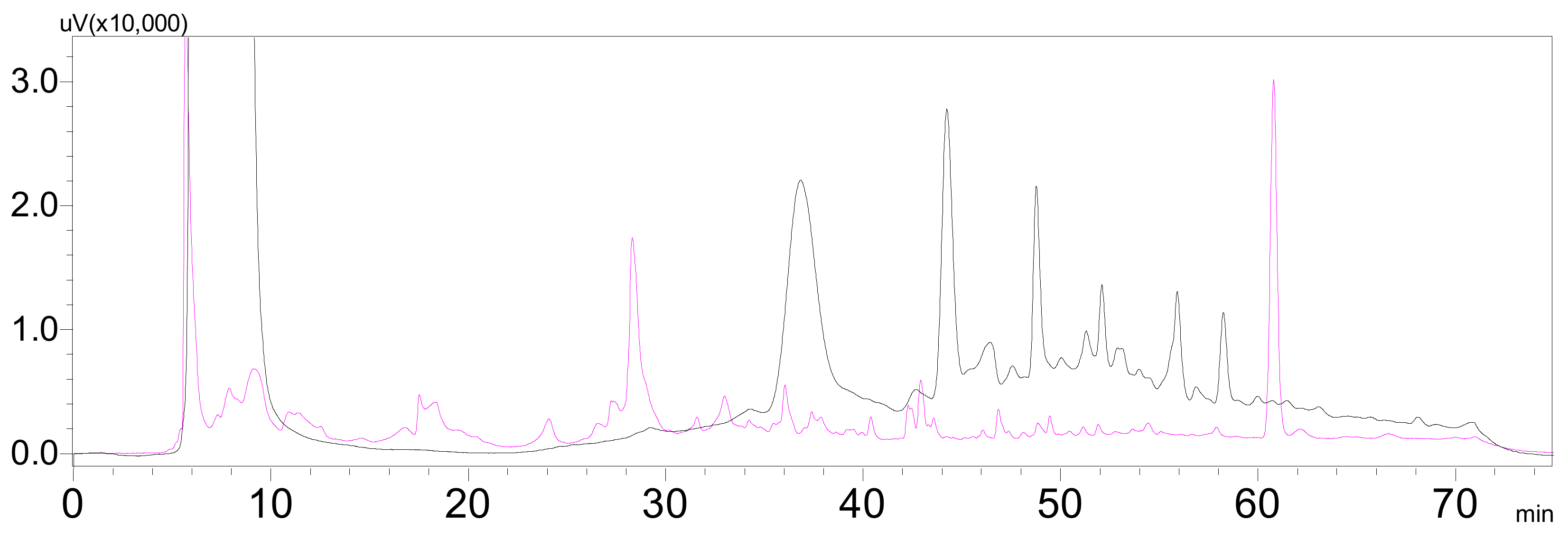
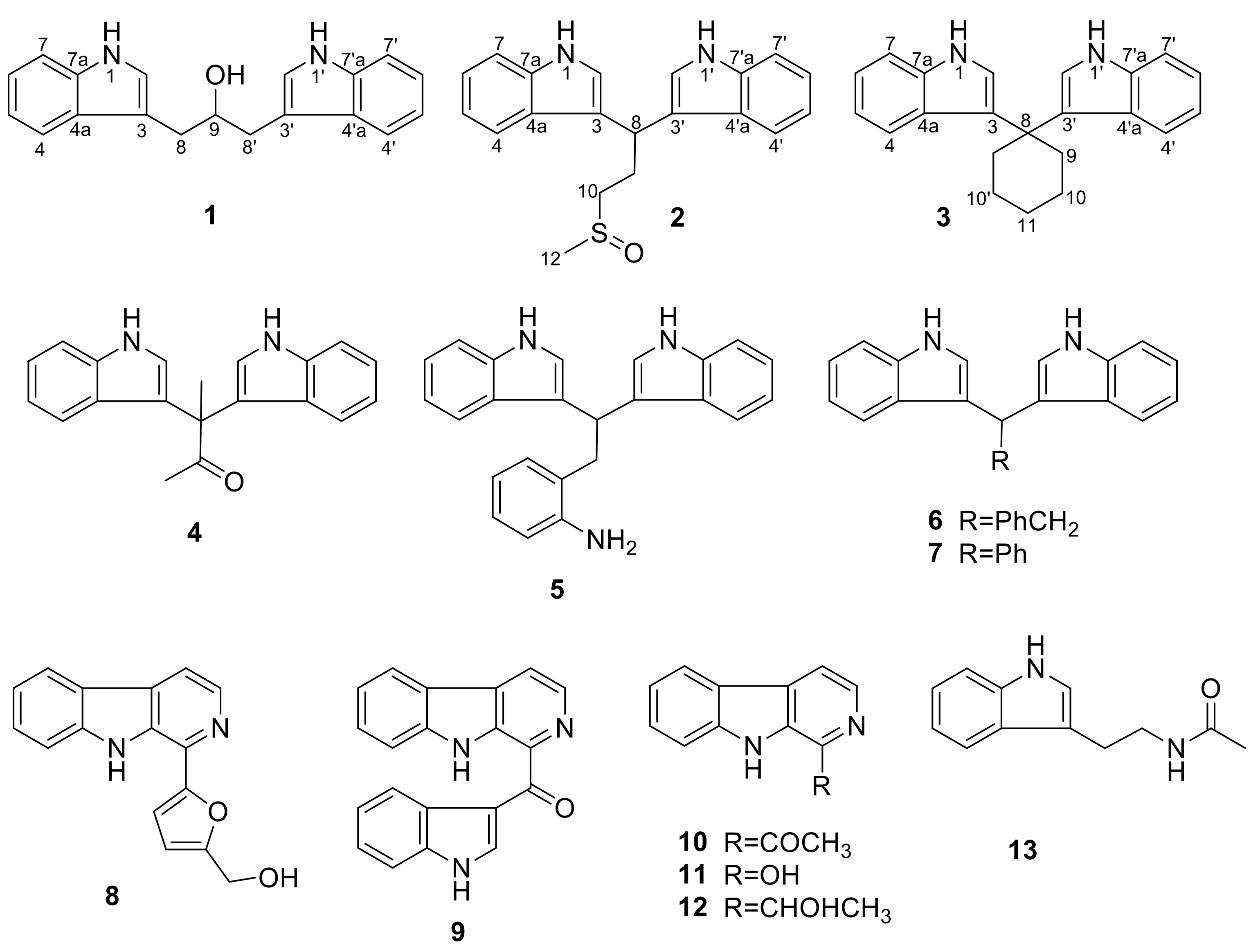
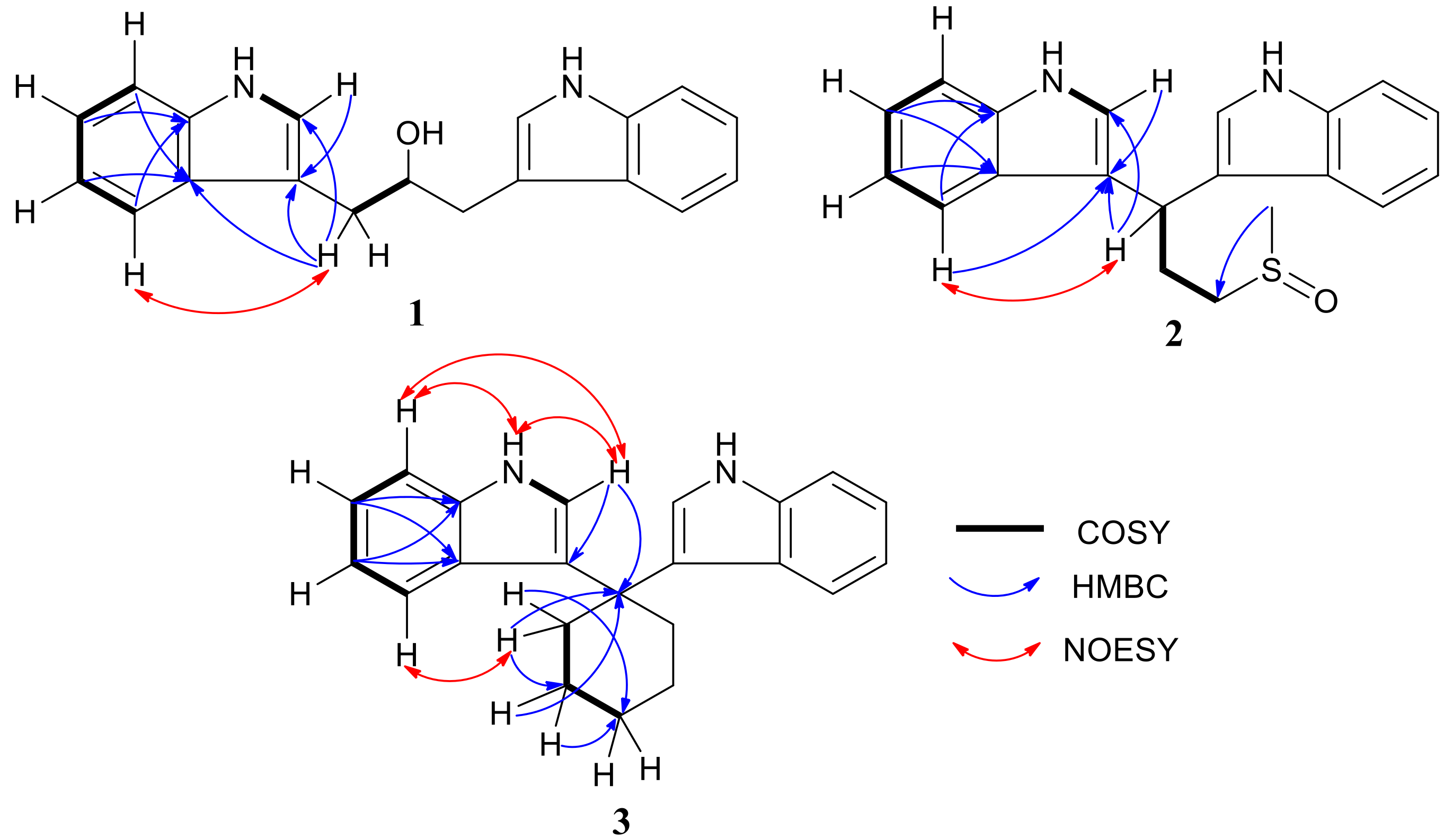
2.1. Structural Elucidation
2.2. Biological Activity
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Procedures
3.2. Fungal Strain and Culture Method
3.3. Extraction and Isolation
3.4. Cytotoxicity Assay
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Netz, N.; Opatz, T. Marine indole alkaloids. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 4814–4914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, T.P.; Singh, O.M. Recent progress in biological activities of indole and indole alkaloids. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 2018, 18, 9–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chadha, N.; Silakari, O. Indoles as therapeutics of interest in medicinal chemistry: Bird’s eye view. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 134, 159–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.G.; Huang, H.; Jiang, B. Progress in studies of novel marine bis (indole) alkaloids. Curr. Org. Chem. 2004, 8, 1691–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, L.; Talwar, A.; Chauhan, P.M.S. Bis and tris indole alkaloids from marine organisms: new leads for drug discovery. Curr. Med. Chem. 2007, 14, 1789–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.H.; Xu, M.Y.; Li, H.J.; Li, J.Q.; Chen, Y.X.; Ma, W.Z.; Li, Y.P.; Xu, J.; Yang, D.P; Lan, W.J. Amino acid-directed strategy for inducing the marine-derived fungus Scedosporium apiospermum F41-1 to maximize alkaloid diversity. Org. Lett. 2017, 19, 4888–4891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.X.; Xu, M.Y.; Li, H.J.; Zeng, K.J.; Ma, W.Z.; Tian, G.B.; Xu, J.; Yang, D.P.; Lan, W.J. Diverse secondary metabolites from the marine-derived fungus Dichotomomyces cejpii F31-1. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 339–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.L.; Li, H.J.; Duncan, R.S.; Janejira, J.; Xia-Fu-Kai-Ti, X.K.E.; Ma, W.Z.; Guo, Y.W.; Dong, J.; Shen, J.; Yang, D.P.; et al. Polyketides and alkaloids from the marine-derived fungus Dichotomomyces cejpii F31-1 and the antiviral activity of scequinadoline A against dengue virus. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, W.J.; Liu, W.; Liang, W.L.; Xu, Z.; Le, X.; Xu, J.; Lam, C.K.; Yang, D.P.; Li, H.J.; Wang, L.Y. Pseudaboydins A and B: Novel isobenzofuranone derivatives from marine fungus Pseudallescheria boydii associated with starfish Acanthaster planci. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 4188–4199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.F.; Lan, W.J.; Wang, K.T.; Huang, L.; Jiang, C.W.; Li, H.J. Two chlorinated benzofuran derivatives from the marine fungus Pseudallescheria boydii. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2015, 10, 621–622. [Google Scholar]
- Lan, W.J.; Wang, K.T.; Xu, M.Y.; Zhang, J.J.; Lam, C.K.; Zhong, G.H.; Xu, J.; Yang, D.P.; Li, H.J.; Wang, L.Y. Secondary metabolites with chemical diversity from the marine-derived fungus Pseudallescheria boydii F19-1 and their cytotoxic activity. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 76206–76213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Li, H.J.; Xu, M.Y.; Ju, Y.C.; Wang, L.Y.; Xu, J.; Yang, D.P.; Lan, W.J. Pseudellones A–C, three alkaloids from the marine-derived fungus Pseudallescheria ellipsoidea F42-3. Org. Lett. 2015, 17, 5156–5159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.T.; Xu, M.Y.; Liu, W.; Li, H.J.; Xu, J.; Yang, D.P.; Lan, W.J.; Wang, L.Y. Two additional new compounds from the marine-derived fungus Pseudallescheria ellipsoidea F42-3. Molecules 2016, 21, 442–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noguchiy Yachide, T.; Tetsuhashi, M.; Aoyama, H.; Hashimoto, Y. Enhancement of chemically-induced HL-60 cell differentiation by 3,3’-diindolylmethane derivatives. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2009, 57, 536–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taheri, A.; Lai, B.B.; Cheng, C.G.; Gu, Y.L. Bronsted acid ionic liquid-catalyzed reductive Friedel-Crafts alkylation of indoles and cyclic ketones without using an external reductant. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 812–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veluri, R.; Oka, I.; Wagner-Dobler, I.; Laatsch, H. New indole alkaloids from the North Sea bacterium Vibrio parahaemolyticus bio249. J. Nat. Prod. 2003, 66, 1520–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.X.; Li, D.H.; Zhu, T.J.; Wang, F.P.; Xiao, X.; Gu, Q.Q. Two new indole alkaloids from the marine-derived bacterium Aeromonas sp. CB101. Helv. Chim. Acta 2010, 93, 791–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.L.; Han, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.H.; Zhu, W.M. Bis- and tris- indole alkaloids from Edwardsiella tarda. Microbiology China 2010, 37, 1325–1330. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, M.M.; Kirk, L.P. β-Carboline derivatives and diphenols from soy sauce are in vitro quinone reductase (QR) inducers. J. Agr. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 2332–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liew, L.P.P.; Fleming, J.M.; Longeon, A.; Mouray, E.; Florent, I.; Bourguet-Kondracki, M.L.; Copp, B.R. Synthesis of 1-indolyl substituted β-carboline natural products and discovery of antimalarial and cytotoxic activities. Tetrahedron 2014, 70, 4910–4920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillman, R.L.; Cardellina II, J.H. Aromatic secondary metabolites from the sponge Tedania ignis. J. Nat. Prod. 1991, 54, 1056–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, W.H.; Gao, H.; Li, C.Y.; Zhou, G.X.; Kitanaka, S.; Ohmura, A.; Yao, X.S. β-Carboline alkaloids from the stems of Picrasma quassioides. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2010, 48, 490–495. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Anouhe, J.B.S.; Adima, A.A.; Niamke, F.B.; Stien, D.; Amian, B.K.; Blandinieres, P.A.; Virieux, D.; Pirat, J.L.; Kati-Coulibaly, S.; Amusant, N. Dicorynamine and harmalan-N-oxide, two new β-carboline alkaloids from Dicorynia guianensis amsh heartwood. Phytochem. Lett. 2015, 12, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, X.F.; Kim, D.S.; Choi, H.D.; Son, B.W. Indole alkaloid derivatives, Nb-acetyltryptamine and oxaline from a marine-derived fungus. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2003, 26, 21–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SPSS, student version 13.0 for Windows; Statistical Program for Social Sciences, IBM Company: New York, NY, USA, 2001.
| No. | 1 | 2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| δC, Type | δH, Mult. (J, Hz) | δC, Type | δH, Mult. (J, Hz) | ||
| 1, 1′ | NH | 8.10, brs | NH | 8.11, d (2.4) | |
| 2, 2′ | 122.8, CH | 7.03, d (2.0) | 121.77, CH | 7.01, d (2.4) | |
| 3, 3′ | 112.4, C | 118.67/118.40, C | |||
| 4a, 4′a | 127.6, C | 126.80/126.71, C | |||
| 4, 4′ | 118.9, CH | 7.61, brd (8.0) | 119.29, CH | 7.04, d (7.6) | |
| 5, 5′ | 119.3, CH | 7.12, ddd (8.0, 8.0, 0.8) | 119.37, CH | 7.55, dd (7.6, 7.6) | |
| 6, 6′ | 122.0, CH | 7.21, ddd (8.0, 8.0, 0.8) | 122.01/121.99, CH | 7.16, dd (8.0, 7.6) | |
| 7, 7′ | 111.1, CH | 7.34, brd (8.0) | 111.24, CH | 7.34, d (8.0) | |
| 7a, 7′a | 136.3, C | 136.60/136.56, C | |||
| 8 | 32.9, CH2 | 2.95, dd (14.4, 8.0) 3.09, dd (14.4, 4.8) | 33.2, CH | 4.64, t (7.6,) | |
| 9 | 71.5, CH | 4.30, dddd (8.0, 8.0, 4.8, 4.8) | 28.3, CH2 | 2.69, m | |
| 10 | OH | 2.08, brs | 53.0, CH2 | 2.81, m; 2.73, m | |
| 11 | S = O | ||||
| 12 | 38.4, CH3 | 2.47, s | |||
| No. | In CDCl3 | In acetone-d6 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| δC, Type | δH, Mult. (J, Hz) | δC, Type | δH, Mult. (J, Hz) | ||
| 1, 1′ | NH | 7.92 brs | NH | 9.95, brs | |
| 2, 2′ | 122.0, CH | 7.10, d (1.8) | 123.0, CH | 7.34, d (2.4) | |
| 3, 3′ | 123.7 C | 123.7, C | |||
| 4a, 4′a | 126.3, C | 127.4, C | |||
| 4, 4′ | 121.5, CH | 7.56, d (8.0) | 121.9, CH | 7.46, d (8.4) | |
| 5, 5′ | 118.5, CH | 6.90, dd (8.0, 8.0) | 121.3, CH | 6.91, ddd (8.4, 8.4, 0.6) | |
| 6, 6′ | 121.2, CH | 7.06, dd (8.0, 8.0) | 118.6, CH | 6.72, ddd (8.4, 8.4, 0.6) | |
| 7, 7′ | 111.0, CH | 7.30, d (8.0) | 112.0, CH | 7.28, d (8.4) | |
| 7a, 7′a | 137.1, C | 138.5, C | |||
| 8 | 39.5, C | 40.1, C | |||
| 9, 9′ | 36.8, CH2 | 2.55, t (6.0) | 37.9, CH2 | 2.55, t (6.0) | |
| 10, 10′ | 23.0, CH2 | 1.66, m | 23.8, CH2 | 1.68, m | |
| 11 | 26.8, CH2 | 1.58, m | 27.6, CH2 | 1.57, m | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuan, M.-X.; Qiu, Y.; Ran, Y.-Q.; Feng, G.-K.; Deng, R.; Zhu, X.-F.; Lan, W.-J.; Li, H.-J. Exploration of Indole Alkaloids from Marine Fungus Pseudallescheria boydii F44-1 Using an Amino Acid-Directed Strategy. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 77. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17020077
Yuan M-X, Qiu Y, Ran Y-Q, Feng G-K, Deng R, Zhu X-F, Lan W-J, Li H-J. Exploration of Indole Alkaloids from Marine Fungus Pseudallescheria boydii F44-1 Using an Amino Acid-Directed Strategy. Marine Drugs. 2019; 17(2):77. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17020077
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuan, Mei-Xiang, Yi Qiu, Yan-Qin Ran, Gong-Kan Feng, Rong Deng, Xiao-Feng Zhu, Wen-Jian Lan, and Hou-Jin Li. 2019. "Exploration of Indole Alkaloids from Marine Fungus Pseudallescheria boydii F44-1 Using an Amino Acid-Directed Strategy" Marine Drugs 17, no. 2: 77. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17020077
APA StyleYuan, M.-X., Qiu, Y., Ran, Y.-Q., Feng, G.-K., Deng, R., Zhu, X.-F., Lan, W.-J., & Li, H.-J. (2019). Exploration of Indole Alkaloids from Marine Fungus Pseudallescheria boydii F44-1 Using an Amino Acid-Directed Strategy. Marine Drugs, 17(2), 77. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17020077