Asperlin Stimulates Energy Expenditure and Modulates Gut Microbiota in HFD-Fed Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
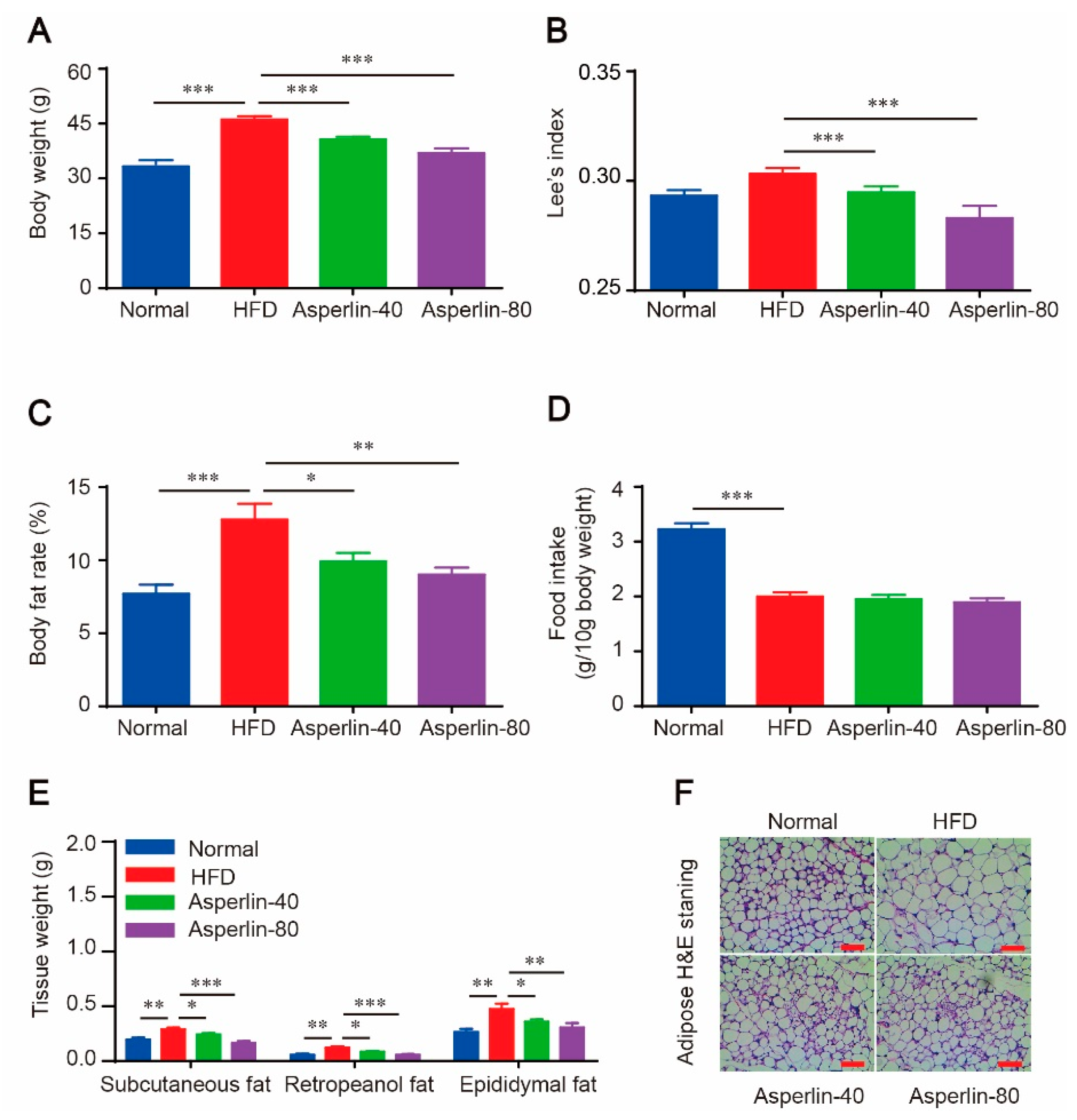
2.1. Oral Administration of Asperlin Prevents HFD-Induced Obesity
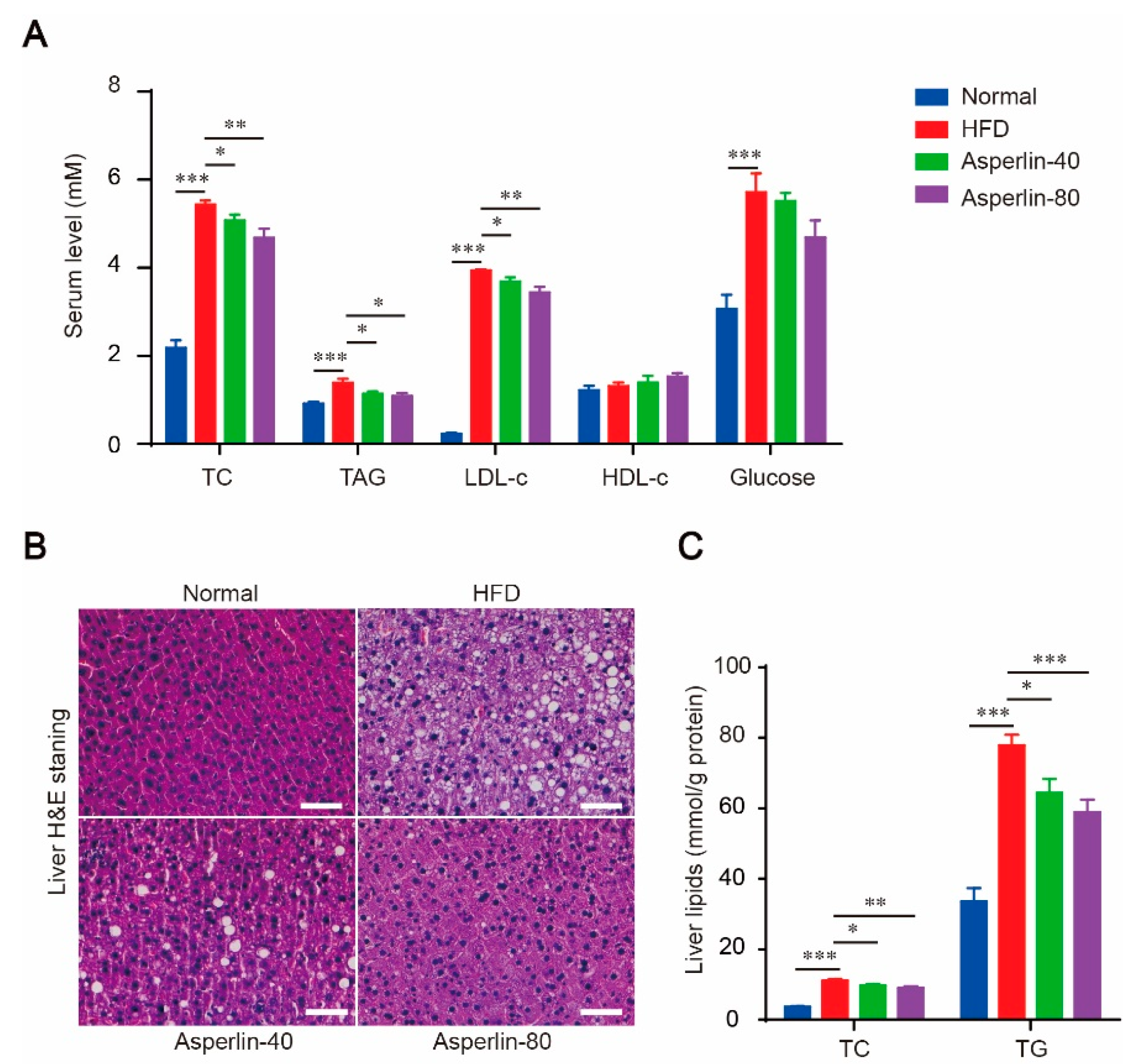
2.2. Asperlin Improved Serum Lipid Profile and Ameliorated Liver Steatosis
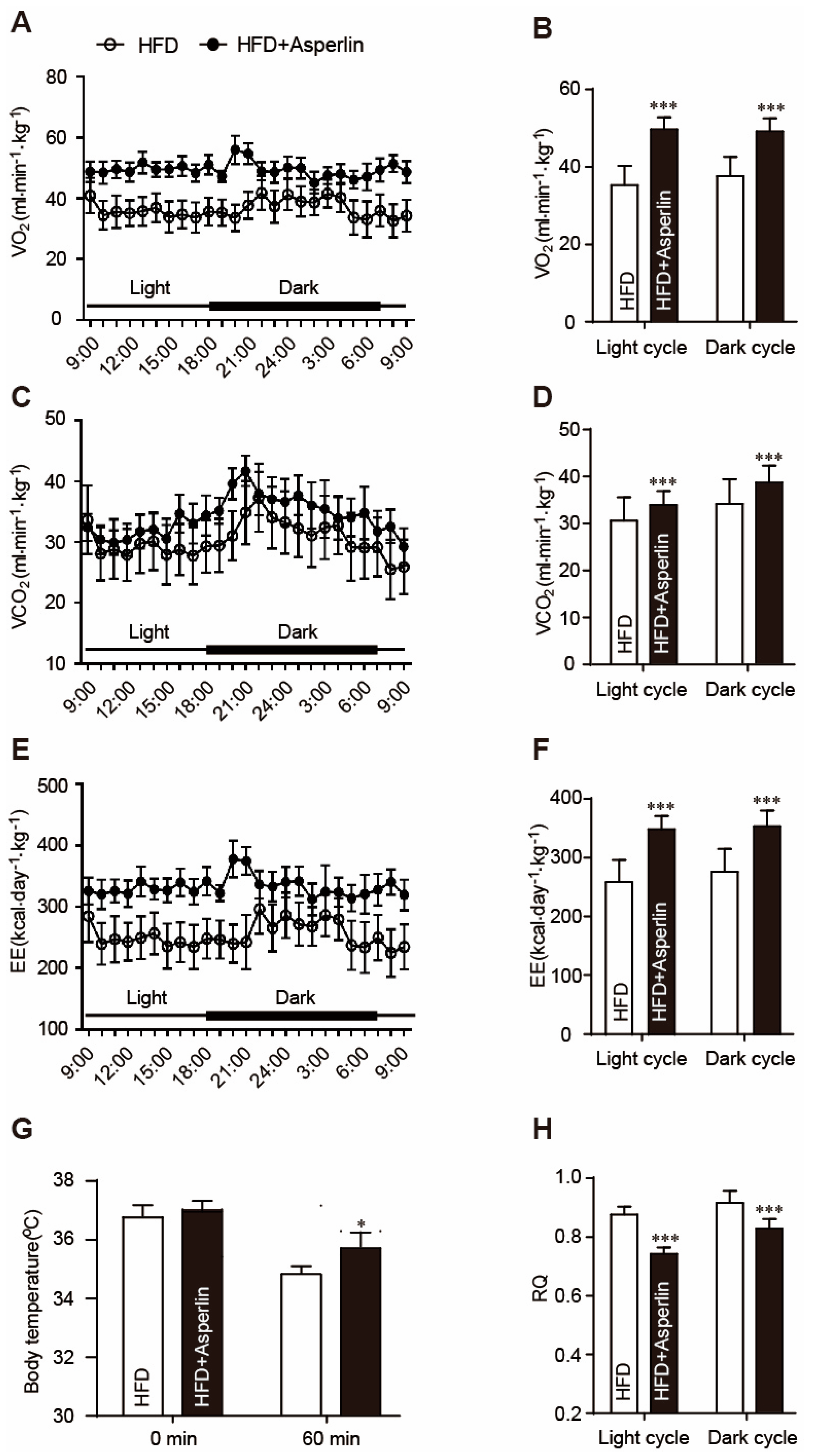
2.3. Asperlin Enhanced Energy Expenditure
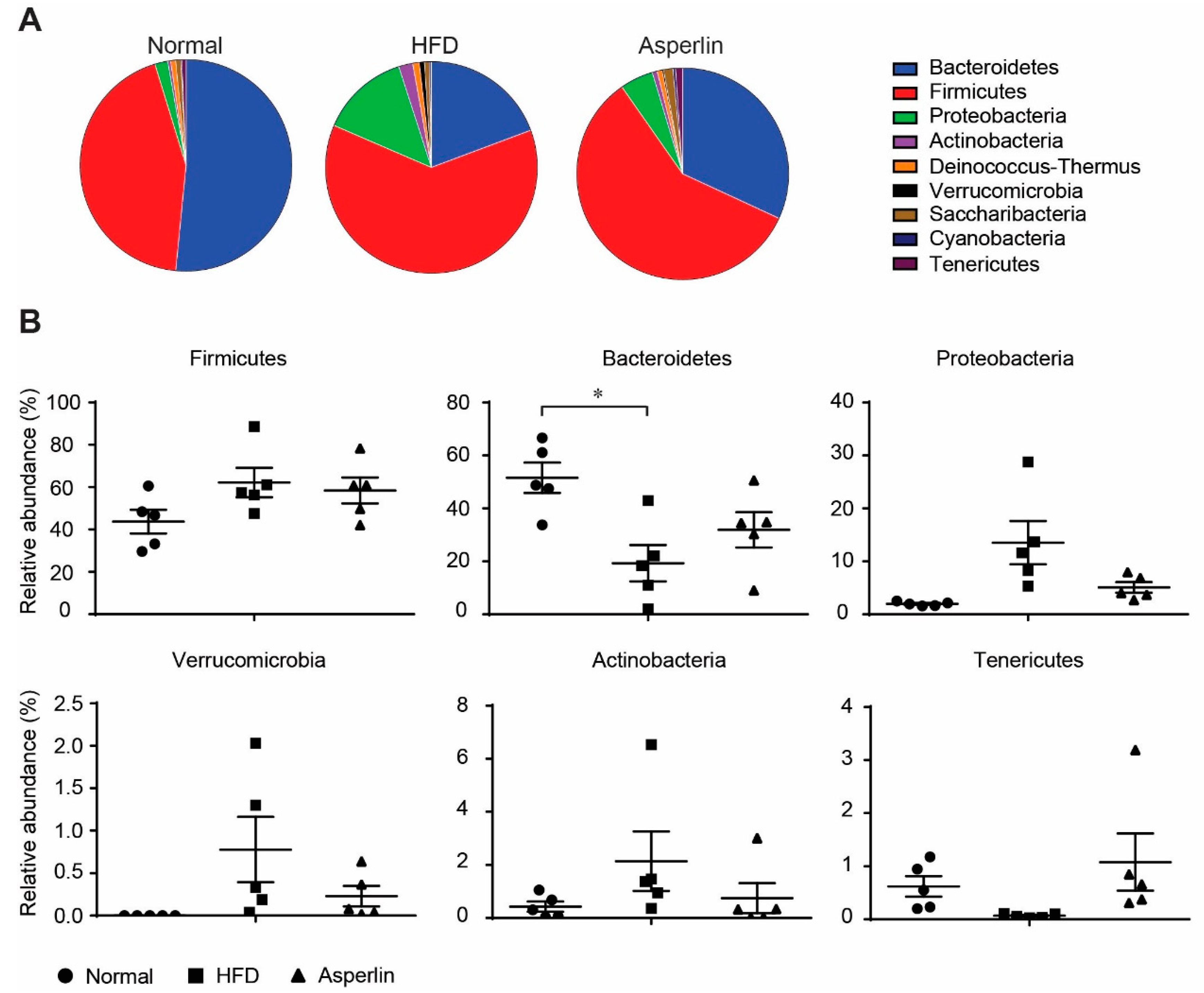
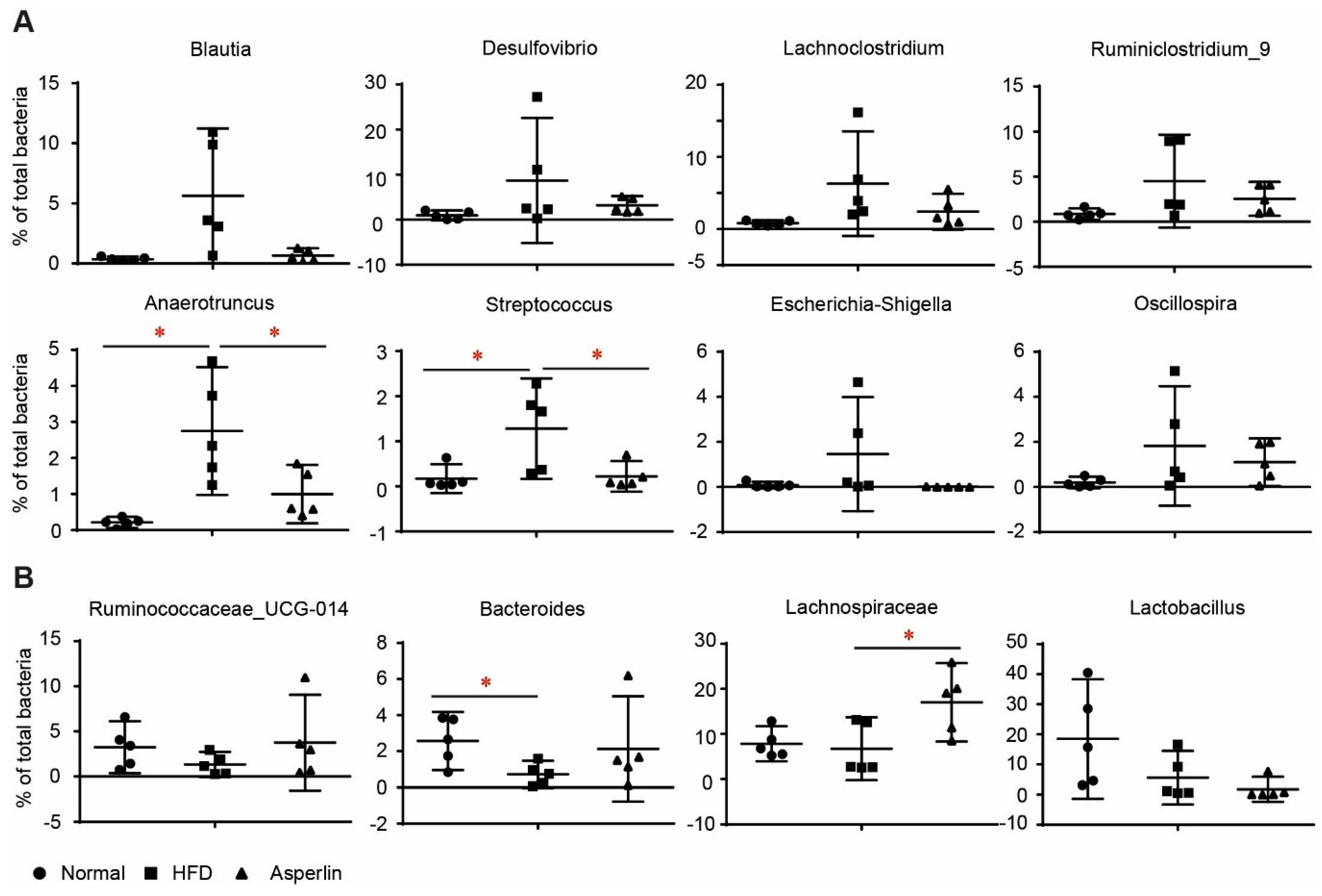
2.4. Asperlin Shifted the Gut Microbiota Structure
2.5. Key Phylotypes of Gut Microbiota Responding to Asperlin
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Asperlin Preparation
4.2. Animals and Experiment Design
4.3. Metabolic Rate and Physical Activity
4.4. Cold Tolerance Test
4.5. Histology Analysis
4.6. Quantitative Realtime-PCR Analysis
4.7. Phylogenetic Analysis
4.8. Phylogenetic Data Analysis
4.9. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saltiel, A.R.; Olefsky, J.M. Inflammatory mechanisms linking obesity and metabolic disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwong, E.; Li, Y.; Hylemon, P.B.; Zhou, H. Bile acids and sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 2 in hepatic lipid metabolism. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2015, 5, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrow, J.S. Energy imbalance in obesity is not “just a hypothesis”. BMJ 2013, 346, f3079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.R.; Jang, H.J.; Choi, S.S.; Lee, Y.H.; Lee, G.H.; Seo, Y.K.; Choi, J.H.; Park, D.; Koh, A.; Kim, I.S.; et al. Obesity resistance and increased energy expenditure by white adipose tissue browning in Oga(+/−) mice. Diabetologia 2015, 58, 2867–2876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, P. Wasting Energy to Treat Obesity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 2298–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, Y.H.; Cypess, A.M.; Kahn, C.R. Cellular bioenergetics as a target for obesity therapy. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2010, 9, 465–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Q.; Chen, W.D.; Wang, Y.D. Gut Microbiota: An Integral Moderator in Health and Disease. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butel, M.J.; Waligora-Dupriet, A.J.; Wydau-Dematteis, S. The developing gut microbiota and its consequences for health. J. Dev. Orig. Health Dis. 2018, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao, M.C.; Clement, K. Gut microbiota and obesity: Concepts relevant to clinical care. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2018, 48, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibbo, S.; Ianiro, G.; Dore, M.P.; Simonelli, C.; Newton, E.E.; Cammarota, G. Gut Microbiota as a Driver of Inflammation in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Mediators Inflamm. 2018, 2018, 9321643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sircana, A.; De Michieli, F.; Parente, R.; Framarin, L.; Leone, N.; Berrutti, M.; Paschetta, E.; Bongiovanni, D.; Musso, G. Gut Microbiota, Hypertension and Chronic kidney Disease: Recent advances. Pharmacol. Res. 2018, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De la Cuesta-Zuluaga, J.; Mueller, N.T.; Corrales-Agudelo, V.; Velasquez-Mejia, E.P.; Carmona, J.A.; Abad, J.M.; Escobar, J.S. Metformin Is Associated With Higher Relative Abundance of Mucin-Degrading Akkermansia muciniphila and Several Short-Chain Fatty Acid-Producing Microbiota in the Gut. Diabetes Care 2017, 40, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, N.R.; Lee, J.C.; Lee, H.Y.; Kim, M.S.; Whon, T.W.; Lee, M.S.; Bae, J.W. An increase in the Akkermansia spp. population induced by metformin treatment improves glucose homeostasis in diet-induced obese mice. Gut 2014, 63, 727–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anhe, F.F.; Roy, D.; Pilon, G.; Dudonne, S.; Matamoros, S.; Varin, T.V.; Garofalo, C.; Moine, Q.; Desjardins, Y.; Levy, E.; et al. A polyphenol-rich cranberry extract protects from diet-induced obesity, insulin resistance and intestinal inflammation in association with increased Akkermansia spp. population in the gut microbiota of mice. Gut 2015, 64, 872–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.J.; Lin, C.S.; Lu, C.C.; Martel, J.; Ko, Y.F.; Ojcius, D.M.; Tseng, S.F.; Wu, T.R.; Chen, Y.Y.; Young, J.D.; et al. Ganoderma lucidum reduces obesity in mice by modulating the composition of the gut microbiota. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Nan, M.H.; Oh, H.C.; Kim, Y.H.; Jang, J.H.; Erikson, R.L.; Ahn, J.S.; Kim, B.Y. Asperlin induces G(2)/M arrest through ROS generation and ATM pathway in human cervical carcinoma cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 409, 489–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.S.; Jeong, G.S.; Li, B.; Lee, S.U.; Oh, H.; Kim, Y.C. Asperlin from the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus sp. SF-5044 exerts anti-inflammatory effects through heme oxygenase-1 expression in murine macrophages. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2011, 116, 283–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Chen, R.; Liu, D.; Wu, C.; Guo, P.; Lin, W. Asperlin Inhibits LPS-Evoked Foam Cell Formation and Prevents Atherosclerosis in ApoE(-/-) Mice. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenhill, C. Obesity: Role for creatine metabolism in energy expenditure. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2017, 13, 624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerard, P. Gut microbiota and obesity. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 147–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yang, S.; Lei, R.; Gu, W.; Qin, Y.; Ma, S.; Chen, K.; Chang, Y.; Bai, X.; Xia, S.; et al. Oral administration of rutile and anatase TiO2 nanoparticles shifts mouse gut microbiota structure. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 7736–7745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Esteve, E.; Tremaroli, V.; Khan, M.T.; Caesar, R.; Manneras-Holm, L.; Stahlman, M.; Olsson, L.M.; Serino, M.; Planas-Felix, M.; et al. Metformin alters the gut microbiome of individuals with treatment-naive type 2 diabetes, contributing to the therapeutic effects of the drug. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 850–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Wang, L.; Cheng, Y.; Xia, Z.; Liao, Y.; Cao, J. Efficacy of orlistat in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Biomed. Rep. 2018, 9, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, G.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yu, J.; Li, X.; Cao, X.; Wu, C.; Guo, P. Cordycepin promotes browning of white adipose tissue through an AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK)-dependent pathway. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2018, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Li, B.; Meng, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, S.; Ma, Q.; Jin, L.; Yang, J.; et al. Berberine activates thermogenesis in white and brown adipose tissue. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beiroa, D.; Imbernon, M.; Gallego, R.; Senra, A.; Herranz, D.; Villarroya, F.; Serrano, M.; Ferno, J.; Salvador, J.; Escalada, J.; et al. GLP-1 agonism stimulates brown adipose tissue thermogenesis and browning through hypothalamic AMPK. Diabetes 2014, 63, 3346–3358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lone, J.; Choi, J.H.; Kim, S.W.; Yun, J.W. Curcumin induces brown fat-like phenotype in 3T3-L1 and primary white adipocytes. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2016, 27, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basolo, A.; Votruba, S.B.; Heinitz, S.; Krakoff, J.; Piaggi, P. Deviations in Energy Sensing Predict Long-term Weight Change in Overweight Native Americans. Metabolism 2018, 82, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glatt, H.; Jung, R.; Oesch, F. Bacterial mutagenicity investigation of epoxides: Drugs, drug metabolites, steroids and pesticides. Mutat. Res. 1983, 111, 99–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridaura, V.K.; Faith, J.J.; Rey, F.E.; Cheng, J.; Duncan, A.E.; Kau, A.L.; Griffin, N.W.; Lombard, V.; Henrissat, B.; Bain, J.R.; et al. Gut microbiota from twins discordant for obesity modulate metabolism in mice. Science 2013, 341, 1241214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, E.F.; Cotter, P.D.; Hogan, A.; O’Sullivan, O.; Joyce, A.; Fouhy, F.; Clarke, S.F.; Marques, T.M.; O’Toole, P.W.; Stanton, C.; et al. Divergent metabolic outcomes arising from targeted manipulation of the gut microbiota in diet-induced obesity. Gut 2013, 62, 220–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Everard, A.; Matamoros, S.; Geurts, L.; Delzenne, N.M.; Cani, P.D. Saccharomyces boulardii administration changes gut microbiota and reduces hepatic steatosis, low-grade inflammation, and fat mass in obese and type 2 diabetic db/db mice. MBio 2014, 5, e01011–e01014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, E.; Gaudier, F.L.; Hearing, L.R.; Del Valle, G.O.; Jenkins, S.; Briones, D. Group B streptococcus colonization in pregnant diabetic women. Obstet. Gynecol. 1997, 89, 257–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, M.; Pang, X.; Xu, J.; Kang, C.; Li, M.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Structural changes of gut microbiota during berberine-mediated prevention of obesity and insulin resistance in high-fat diet-fed rats. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardis, L.L.; Patterson, B.D. Correlation between ‘Lee index’ and carcass fat content in weanling and adult female rats with hypothalamic lesions. J. Endocrinol. 1968, 40, 527–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Feng, J.; Wang, R.; Liu, H.; Yang, H.; Rodriguez, P.L.; Qin, H.; Liu, X.; Wang, D. HRS1 acts as a negative regulator of abscisic acid signaling to promote timely germination of Arabidopsis seeds. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Lei, R.; Li, X.; Xiong, F.; Zhang, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, S.; Chang, Y.; Chen, K.; Gu, W.; et al. The antihyperlipidemic effects of fullerenol nanoparticles via adjusting the gut microbiota in vivo. Part Fibre Toxicol. 2018, 15, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, C.; Zhou, Y.; Qi, G.; Liu, D.; Cao, X.; Yu, J.; Zhang, R.; Lin, W.; Guo, P. Asperlin Stimulates Energy Expenditure and Modulates Gut Microbiota in HFD-Fed Mice. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17010038
Wu C, Zhou Y, Qi G, Liu D, Cao X, Yu J, Zhang R, Lin W, Guo P. Asperlin Stimulates Energy Expenditure and Modulates Gut Microbiota in HFD-Fed Mice. Marine Drugs. 2019; 17(1):38. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17010038
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Chongming, Yue Zhou, Guihong Qi, Dong Liu, Xiaoxue Cao, Jiaqi Yu, Rong Zhang, Wenhan Lin, and Peng Guo. 2019. "Asperlin Stimulates Energy Expenditure and Modulates Gut Microbiota in HFD-Fed Mice" Marine Drugs 17, no. 1: 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17010038
APA StyleWu, C., Zhou, Y., Qi, G., Liu, D., Cao, X., Yu, J., Zhang, R., Lin, W., & Guo, P. (2019). Asperlin Stimulates Energy Expenditure and Modulates Gut Microbiota in HFD-Fed Mice. Marine Drugs, 17(1), 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17010038





