Abstract
A new 14-membered homodimeric macrodiolide, brevidiolide (3), along with four known aromatic compounds (1, 2, 4 and 5) were obtained by heterologous expression of the recombinant plasmid pWLI823 expressing the G231L variant of VioA in the marine-derived Brevibacterium sp. 7002-073. The structures of 1–5 were elucidated on the basis of LC-MS and 2D NMR spectroscopic analyses. In the evaluation for the antibacterial activities of the compounds against multi-drug resistant (MDR) strains, 5 showed notable growth inhibition against Staphylococcus aureus CCARM 3090 and Klebsiella pneumoniae ATCC 13883, with a minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) value of 3.12 µg/mL.
1. Introduction
Marine-derived actinomycetes, with their extreme living environment featuring low temperatures and high pressure as well as poor nutrient availability, are considered to have great potential to generate structurally novel and biologically active secondary metabolites [1,2]. However, the actinomycete-derived compounds reported to date are just the tip of an iceberg: a large number of the molecules are cryptic due to the silent genes [3]. Thus, activating the silent genes becomes an important key to entering the locked world of inaccessible compounds generated by marine actinomycetes.
Since the 1980s, a wide range of approaches have been used to activate/modulate silent genes in microbes [4,5], among which cell-cell communication by signaling molecules has attracted increasing attention [6]. Small molecules produced by a microbe may act as signal molecules to regulate gene expression in other microbes depending on the treating concentration [7], thus triggering the production of related compounds in the heterologous hosts.
In our previous study, we identified a series of antibiotic violapyrone derivatives, which are encoded by the type III polyketide synthetase VioA, from deep sea-derived Streptomyces somaliansis SCSIO ZH66 [8]. The chemical skeleton of violapyrones is quite similar to reported α-pyrone type photopyrones that serve as signal molecules at low nanomolar concentrations (Figure S1) [9], thus, we assumed that the violapyrones might play a similar function, providing the possibility for their potential of activation/regulation of gene expression in the heterologous hosts.
Brevibacterium sp. 7002-073 (GenBankID: KY770501.1) was isolated from the cyanobacterium Synechococcus sp. PCC7002 collected off the coast of China in the Yellow Sea near Qingdao. Brevibacterium is an obligate aerobic, catalase-positive and spore-free Gram-positive actinomycete. Some Brevibacterium strains are very useful in industry. B. linens is one of the most important surface bacteria in the cheese-making process due to its role in the surface coloring and its typical flavoring activity [10]. B. flavum has been used in the mass production of the essential amino acid L-valine [11]. However, the secondary metabolites from Brevibacterium have not been reported much, except for a handful of peptides, fatty acids and glycolipids [12,13,14].
In this study, to test the possibility of the violapyrones being signal molecules, the recombinant plasmid pWLI823 expressing the G231L variant of VioA (impaired activity, unpublished data), which is a pWLI807 derivative [15], was introduced into Brevibacterium sp. 7002-073 by electroporation. In the recombinant strain 7002-073/pWLI823, compound 2 was overproduced 20-fold as compared to in the wild-type strain, and compounds 1 and 3–5 were newly accumulated, among which 3 was a new compound with an unusual 14-membered symmetric macrodiolide ring (Figure 1). Herein, we describe the isolation and structure identification of compounds 1–5 from the 7002-073/pWLI823 recombinant strain. Moreover, the antibacterial activities of 1–5 against multi-drug resistant (MDR) strains were evaluated as well.
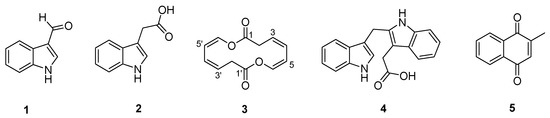
Figure 1.
Structures of compounds 1–5.
2. Results and Discussion
To introduce heterologous gene into Brevibacterium sp. 7002-073, the genetic system of Brevibacterium sp. 7002-073 was firstly established using pMT3 as vector and electroporation as transformation method. Competent cells were prepared as described in the Experimental Section, and then pMT3 (control) and pWLI823 (harboring VioA-G231L) were introduced to generate recombinant strains 7002-073/pMT3 and 7002-073/pWLI823, respectively (Figure S2).
Interestingly, the color of the culture broth of 7002-073/pWLI823 was quite different from that of the wild type, indicating the possible changes in their metabolite production (Figure S3). The fermentation broth of wild-type and recombinant strains (7002-073/pMT3 and 7002-073/pWLI823) of the Brevibacterium sp. 7002-073 were extracted with EtOAc. In the HPLC profile of the Brevibacterium/pWLI823 strain, we observed that compounds 1 and 3–5 were newly generated, and compound 2 was overproduced by 20-fold as compared to the wild-type strain (Figure 2). These results indicated that insertion of the recombinant plasmid pWLI823 led to the compound activation in Brevibacterium sp. 7002-073. With the large-scale fermentation of the 7002-073/pWLI823 strain, which was sequentially subjected to EtOAC extraction and reversed-phase chromatographic fractionation as well as HPLC purification, compounds 1–5 were obtained.
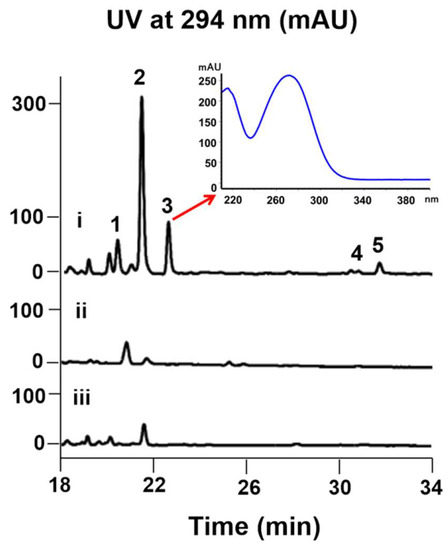
Figure 2.
Comparative HPLC analysis of the compound production in the culture extracts of wild-type and recombinant strains of Brevibacterium sp. 7002-073; (i) 7002-073/pWLI823; (ii) 7002-073/pMT3; (iii) wild-type 7002-073.
Compound 3 was isolated as a yellowish amorphous solid. The molecular formula of 3 was established as C12H12O4 on the basis of the HR-ESIMS data ([M + HCOOH − H]− at m/z 265.1467 calcd 265.0712) (Figure S4). The structure of 3 was elucidated by 1D and 2D (COSY, HSQC, HMBC and NOESY) NMR spectroscopic analysis (Figures S5–S9). The 1H and HSQC spectra of 3 disclosed a methylene (δH 3.66) and four olefinic protons (δH 5.95, 6.04, 5.48 and 6.60), which sequentially comprise a spin system of H-2/H-3/H-4/H-5/H-6 according to the COSY spectrum (Figure 3A). In the HMBC spectrum, except for the corresponding carbon signals of C-2~C-6, only one additional carbonyl carbon C-1 (δC 167.4) was observed, which showed correlations with H-2, and H-6 (Figure 3A). The conformations of two double bonds were confirmed to be cis by combination of the coupling constant values and NOE correlations of H-4/H-5 and H-5/H-6 (Table 1 and Figure 3B). Thus, compound 3 was deduced to be cyclic oxepin-2(3H)-one. However, the molecular formula of oxepin-2(3H)-one (C6H6O2) does not match with the experimental HR-ESIMS data of 3, in which each number of atoms was double of the supposed structure, revealing the formation of a symmetric homodimer. Thus, compound 3 was finally identified as a new 14-membered homodimeric macrodiolide, named brevidiolide. This conclusion was further supported by the chemical shift estimation with ChemDraw 15.0. The 1H and 13C NMR chemical shift values of 3 are shown in Table 1.
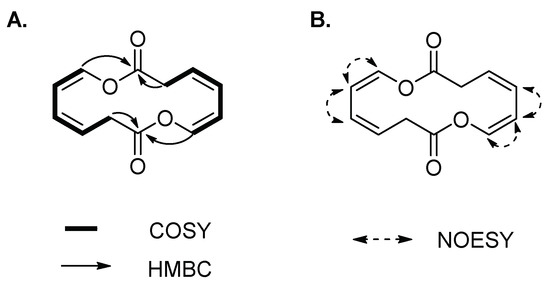
Figure 3.
(A) 1H-1H COSY, key HMBC and (B) NOE correlations of 3.

Table 1.
The 1H (600 MHz) and 13C (150 MHz) NMR chemical shifts of 3 in CD3OD.
Compounds 1, 2, 4 and 5 were isolated as yellowish amorphous solids. The HR-ESIMS analysis disclosed that the molecular formulas of 1, 2, 4 and 5 were C9H7NO, C10H9NO2, C19H16N2O2 and C11H8O2 with molecular ion peaks at m/z 146.0598 [M + H]+, 176.0706 [M + H]+, 303.1132 [M − H]− and 173.1170 [M + H]+, respectively (Figures S10, S15, S17 and S22). The structures of 1, 2, 4 and 5 were determined by NMR data assignment and comparison with the reported literatures [16,17,18,19], which were identified as indole-3-carboxaldehyde, indole-3-acetic acid, 2-(1H-indol-3-ylmethyl)-1H-indole-3-acetic acid, and 2-methyl-1,4-naphthalenedione, respectively (Figure 1). The 1H and 13C NMR chemical shift values of 1, 2, 4 and 5 are listed in Tables S1–S4.
The heterologous expression of the recombinant plasmid pWLI823 expressing the G231L variant of VioA in the Brevibacterium sp. 7002-073 activated the production of a novel 14-membered macrodiolide (3). Macrodiolides are a class of unusual microbe-derived natural products that are grouped into homodimers and heterodimers according to the building block symmetry [20,21,22]. Among the reported macrodiolide structures, the 14-membered ring is rather rare, with only one heterodimeric colletodiol family being discovered from the fungus Clonostachys cylindrospora [23]. To the best of our knowledge, compound 3 is the first 14-membered homodimeric macrodiolide obtained from nature. These results indicated the possibility of the violapyrones acting as signal molecules for activation of the silent microdiolide biosynthetic gene cluster in Brevibacterium sp. 7002-073.
In our investigation for potent antibacterial activity of compounds 1–5 against MDR strains, 5 exhibited notable inhibitions against Staphylococcus aureus CCARM 3090 and Klebsiella pneumoniae ATCC 13883 with a minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) value of 3.12 µg/mL. Compounds 1–4 showed null inhibition against all of the tested MDR strains up to 12.5 µg/mL (Table 2).

Table 2.
Antibacterial activities of compounds 1–5 against multi-drug resistant (MDR) strains (MIC, unit: µg/mL).
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
1H, 13C, COSY, HSQC, HMBC, and NOESY (mixing time = 142 ms) NMR spectra were recorded on Bruker Avance III 600 spectrometers at 298 K. The mixing time used for the NOESY spectrum was 142 ms. Chemical shifts were reported with reference to the respective solvent peaks and residual solvent peaks (δH 3.31 and δC 49.0 for CD3OD; δH 2.50 and δC 39.5 for DMSO-d6). HR-ESIMS data were obtained on a Q-TOF Ultima Global GAA076 LC-MS spectrometer. Optical density (OD) measurements of ELISA experiments were recorded on a TECAN infinite M1000 Pro multi-detection microplate reader. High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) was performed on an Agillent 1260 Infinity apparatus with a diode array detector (DAD).
3.2. Strains, Plasmids, and Culture Conditions
Brevibacterium sp. 7002-073 (GenBank accession No: KY770501.1) was isolated from the cyanobacterium Synechococcus sp. PCC7002, which was collected off the coast of China in the Yellow Sea near Qingdao, China. The multi-drug resistant (MDR) bacterial strains Staphylococcus aureus CCARM 3090, Escherichia coli CCARM 1009, Enterococcus faecalis CCARM 5172, Enterococcus faecium CCARM 5203, and Salmonella typhimurium CCARM 8250 were bought from the Culture Collection of Antimicrobial Resistant Microbes (Seoul Women’s University of Korea), and Acinetobacter baumannii ATCC 19606 and Klebsiella pneumoniae ATCC 13883 were bought from the American Type Culture Collection. The plasmids used in this study are listed in Table S5.
The Brevibacterium sp. 7002-073 strain was routinely cultured at 30 °C in the brain heart infusion broth (BHI) liquid medium or on BHI agar plate. BHI medium supplemented with 2% glycine and 10% sodium succinate was used for electro-competent cell preparation. The Brevibacterium sp. 7002-073 transformants harboring plasmid were incubated in the BHI medium with thiostrepton (5 µg/mL). The fermentation medium (M8) consists of 2% soluble starch, 1% glucose, 0.2% meat extract, 0.2% yeast extract, 0.3% CaCO3 and 0.4% casein (pH = 7.0). The MDR bacterial strains were cultured in Luria-Bertani (LB) medium at 37 °C.
3.3. Transformation Procedures
The transformation procedures for Brevibacterium sp. 7002-073 was established with reference to the literature [24]. When the OD570 reading reached 1.3–1.5, the cell culture was cooled on ice for 10 min, followed by centrifugation at 4 °C, 5000× g for 10 min. After washing twice with 20 mL of cold sucrose (0.8 M), the cells were resuspended in 1/100 volume of the same solution and were frozen in liquid nitrogen for 30 s. The competent cells (100 μL) were mixed with 100 ng of plasmid DNA and loaded into a prechilled 2-mm gap electroporation cuvette. After 10 min of incubation on ice, the cell-DNA mixture was shocked by a single 25 kV/cm pulse generated by Bio-Rad Gene Pulser apparatus (Bio-Rad laboratories, USA). The 0.7 mL of recovery medium (BHI medium supplemented with 0.5 M sucrose) was added to the cells right after the pulse delivery. After incubation at 30 °C for 90 min, the cells were then spread onto BHI agar plates supplemented with thiostrepton (5 μg/mL), and incubated at 30 °C for 2 days. Transformants were verified by PCR with the primer pairs listed in Table S6.
3.4. Isolation and Purification
The fermentation broth (50 mL) of the Brevibacterium sp. 7002-073 in M8 medium was extracted with EtOAc, and was subsequently subjected to the HPLC analysis. Analytical HPLC was performed with a linear gradient from 5% to 80% B/A in 40 min (phase B: 100% ACN + 0.1% HCOOH; phase A: H2O + 0.1% HCOOH; YMC-Pack ODS-A column 150 mm × 4.6 mm, i.d. 5 µm; wavelength: 210 nm) to analyze the production changes between the wild-type and recombinant strains. The culture broth (16 L) of 7002-073/pWLI823 was extracted with EtOAc at room temperature, which was partitioned between 90% MeOH and n-hexane to remove nonpolar components. Then the MeOH layer was subjected to a stepped-gradient open column (ODS-A, 120 Å, S-30/50 mesh) eluting with 20–100% MeOH to yield 13 fractions. Compounds 1–3 (0.39, 8.76 and 0.57 mg, respectively) were obtained from fraction 3 on a reversed-phase HPLC (YMC-Triart C18 column 250 mm × 10 mm, i.d. 5 µm; wavelength: 210 nm) eluting with 70% MeOH + 0.1% HCOOH (v/v) (1.5 mL/min). Compound 4 (0.85 mg) was obtained from the fraction 5 eluting with 75% MeOH + 0.1% HCOOH (v/v) (1.5 mL/min). Compound 5 (1.18 mg) was obtained from fraction 6 eluting with 70% MeOH + 0.1% HCOOH (v/v) (1.5 mL/min).
Brevidiolide (3): yellow amorphous solid; UV (MeOH) λmax (log ε) 207 (3.75), 236 (3.27), 262 (3.45), 310 (2.58) nm; 1H and 13C NMR data, see Table 1; HR-ESIMS m/z 265.1467 [M + HCOOH − H]− (calcd. for C12H12O4, 220.0736).
3.5. Antibacterial Activity Assay
The antibacterial activities of compounds 1–5 against MDR bacterial strains were tested by the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) method [8]. The MDR strains were seeded in LB medium and then incubated at 37 °C for 18 h. After dilution with LB broth to 106 cfu/mL, the 190 μL of cell suspension was dispensed into 96-well plates. Different concentrations of sample solutions in MeOH were dispensed into 96-well plates. The LB broth was used as a blank, and the methanol and tetracycline were used as a negative and a positive control, respectively. The growth of MDR strains was measured after 18 h of incubation at 37 °C on a microplate reader (Epoch2, Biotech) at the wavelength of 600 nm. Each assay was performed in triplicate.
4. Conclusions
In summary, we introduced the recombinant plasmid pWLI823 into the marine-derived Brevibacterium sp. 7002-073, leading to accumulation of five compounds (1–5), among which 3 was a novel compound with an unusual 14-membered homodimeric macrodiolide skeleton. In the test of their potent antibacterial activity against MDR strains, compound 5 exhibited notable inhibition against S. aureus and K. pneumoniai. These results demonstrated that the current strategy provides new opportunities for the discovery of novel cryptic compounds from marine actinomycetes, and furthermore, it may be used as an efficient tool for antibiotic lead compound digging as well.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at http://www.mdpi.com/1660-3397/16/6/191/s1. Supporting Figures S1−S26 and Tables S1−S4, including HR-ESIMS and NMR spectra of 1–5; plasmids and primer lists.
Author Contributions
Experimental Performance: X.H., L.H., and J.H.; Writing—Original Draft Preparation: X.H.; NMR Data Assignment: H.L.; Bacterial Isolation: Y.Z.; Supervision: H.L. and W.L. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21502180, 31570032 and 41506157), the NSFC-Shandong Joint Fund for Marine Science Research Centers (U1706206 and U1406403), and the Scientific and Technological Innovation Project Financially Supported by Qingdao National Laboratory for Marine Science and Technology (2015ASKJ02).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Subramani, R.; Aalbersberg, W. Marine actinomycetes: An ongoing source of novel bioactive metabolites. Microbiol. Res. 2012, 167, 571–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, S.S.U.; Shaikh, A.L. Marine actinobacteria as a drug treasure house. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 87, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelmohsen, U.R.; Grkovic, T.; Balasubramanian, S.; Kamel, M.S.; Quinn, R.J.; Hentschel, U. Elicitation of secondary metabolism in actinomycetes. Biotechnol. Adv. 2015, 33, 798–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopwood, D.A.; Chater, K.F. Fresh approaches to antibiotic production. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sciet. 1980, 290, 313–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Challis, G.L. Mining microbial genomes for new natural products and biosynthetic pathways. Microbiology 2008, 154, 1555–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keller, L.; Surette, M.G. Communication in bacteria: An ecological and evolutionary perspective. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2006, 4, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero, D.; Traxler, M.F.; López, D.; Kolter, R. Antibiotics as signal molecules. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 5492–5505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Hou, L.; Li, H.; Qiu, Y.; Ju, J.; Li, W. Activation of a plasmid-situated type III PKS gene cluster by deletion of awblgene in deepsea-derived Streptomyces somaliensis SCSIO ZH66. Microb. Cell Fact. 2016, 15, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brachmann, A.O.; Brameyer, S.; Kresovic, D.; Hitkova, I.; Kopp, Y.; Manske, C.; Schubert, K.; Bode, H.B.; Heermann, R. Pyrones as bacterial signaling molecules. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2013, 9, 573–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rattray, F.P.; Fox, P.F. Aspects of enzymology and biochemical properties of Brevibacterium linens relevant to cheese ripening: A review. J. Dairy Sci. 1999, 82, 891–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Tan, Y.; Huan, X.; Hu, X.; Wang, X. Construction of a novel shuttle vector for use in Brevibacterium flavum, an industrial amino acid producer. J. Microbiol. Methods 2010, 80, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.X.; Guo, Q.; Peng, G.T.; He, X.X.; Chen, X.J.; Lei, L.F.; Deng, Y.; Su, X.J.; Zhang, C.X. New cyclic tetrapeptide from the coral-derived endophytic bacteria Brevibacterium sp. L-4 collected from the South China Sea. Nat. Prod. Res. 2016, 30, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiran, G.S.; Lipton, A.N.; Priyadharshini, S.; Anitha, K.; Suárez, L.E.; Arasu, M.V.; Choi, K.C.; Selvin, J.; Al-Dhabi, N.A. Antiadhesive activity of poly-hydroxy butyrate biopolymer from a marine Brevibacterium casei MSI04 against shrimp pathogenic vibrios. Microb. Cell Fact. 2014, 13, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiran, G.S.; Sabarathnam, B.; Selvin, J. Biofilm disruption potential of a glycolipid biosurfactant from marine Brevibacterium casei. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2010, 59, 432–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, L.; Huang, H.; Li, H.; Wang, S.; Ju, J.; Li, W. Overexpression of a type III PKS gene affording novel violapyrones with enhanced anti-influenza A virus activity. Microb. Cell Fact. 2018, 17, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashour, M.A.; Elkhayat, E.S.; Ebel, R.; Edrada, R.; Proksch, P. Indole alkaloid from the red sea sponge Hyrtios erectus. Arkivoc 2007, 2007, 225–231. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, X.; Qiu, F.; Sun, H.; Bai, L.; Wang, W.X.; Xiang, W.; Xiao, H. A self-assembled oligopeptide as a versatile NMR alignment medium for the measurement of residual dipolar couplings in methanol. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2017, 56, 12857–12861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, Y.; Kawarada, A. Products of peroxidase catalyzed oxidation of indolyl-3-acetic acid. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1978, 42, 1315–1321. [Google Scholar]
- Lebrasseur, N.; Fan, G.J.; Oxoby, M.; Looney, M.A.; Quideau, S. λ3-Iodane-mediated arenol dearomatization. Synthesis of five-membered ring-containing analogues of the aquayamycin ABC tricyclic unit and novel access to the apoptosis inducer menadione. Tetrahedron 2005, 61, 1551–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.T.; Wei, Y.J.; Ge, H.M.; Jiao, R.H.; Tan, R.X. Acaulins A and B, trimeric macrodiolides from Acaulium sp. H-JQSF. Org. Lett. 2018, 20, 2490–2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutiérrez, M.; Andrianasolo, E.H.; Shin, W.K.; Goeger, D.E.; Yokochi, A.; Schemies, J.; Jung, M.; France, D.; Cornell-kennon, S.; Lee, E.; et al. Structural and synthetic investigations of tanikolide dimer, a SIRT2 selective inhibitor, and tanikolide seco-acid from the madagascar marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya majuscula. J. Org. Chem. 2009, 74, 5267–5275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, P.; Wang, X.; Li, W.; Zhang, W.; Liu, X.; Liu, H.W.; Keller, N.P.; An, Z.; et al. Polyketide production of pestaloficiols and macrodiolide ficiolides revealed by manipulations of epigenetic regulators in an endophytic fungus. Org. Lett. 2016, 18, 1832–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grabley, S.; Hammann, P.; Thiericke, R.; Wink, J.; Philipps, S.; Zeeck, A. Secondary metabolites by chemical screening. 21. Clonostachydiol, a novel anthelmintic macrodiolide from the fungus Clonostachys cylindrospora (strain FH-A 6607). J. Antibiot. 1993, 46, 343–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nardi, M.; Sextius, P.; Bonnarme, P.; Spinnler, H.E.; Monnet, V.; Irlinger, F. Genetic transformation of Brevibacterium linens strains producing high amounts of diverse sulphur compounds. J. Dairy Res. 2005, 72, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).