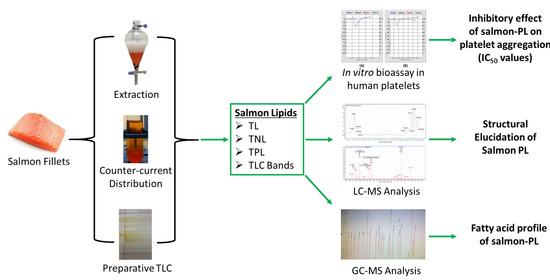
Structural Elucidation of Irish Organic Farmed Salmon (Salmo salar) Polar Lipids with Antithrombotic Activities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. TL, TPL, and TNL Content of Salmon Fillet Samples
2.2. TLC Analysis of Irish Organic Farmed Salmon Fillets Total Polar Lipids
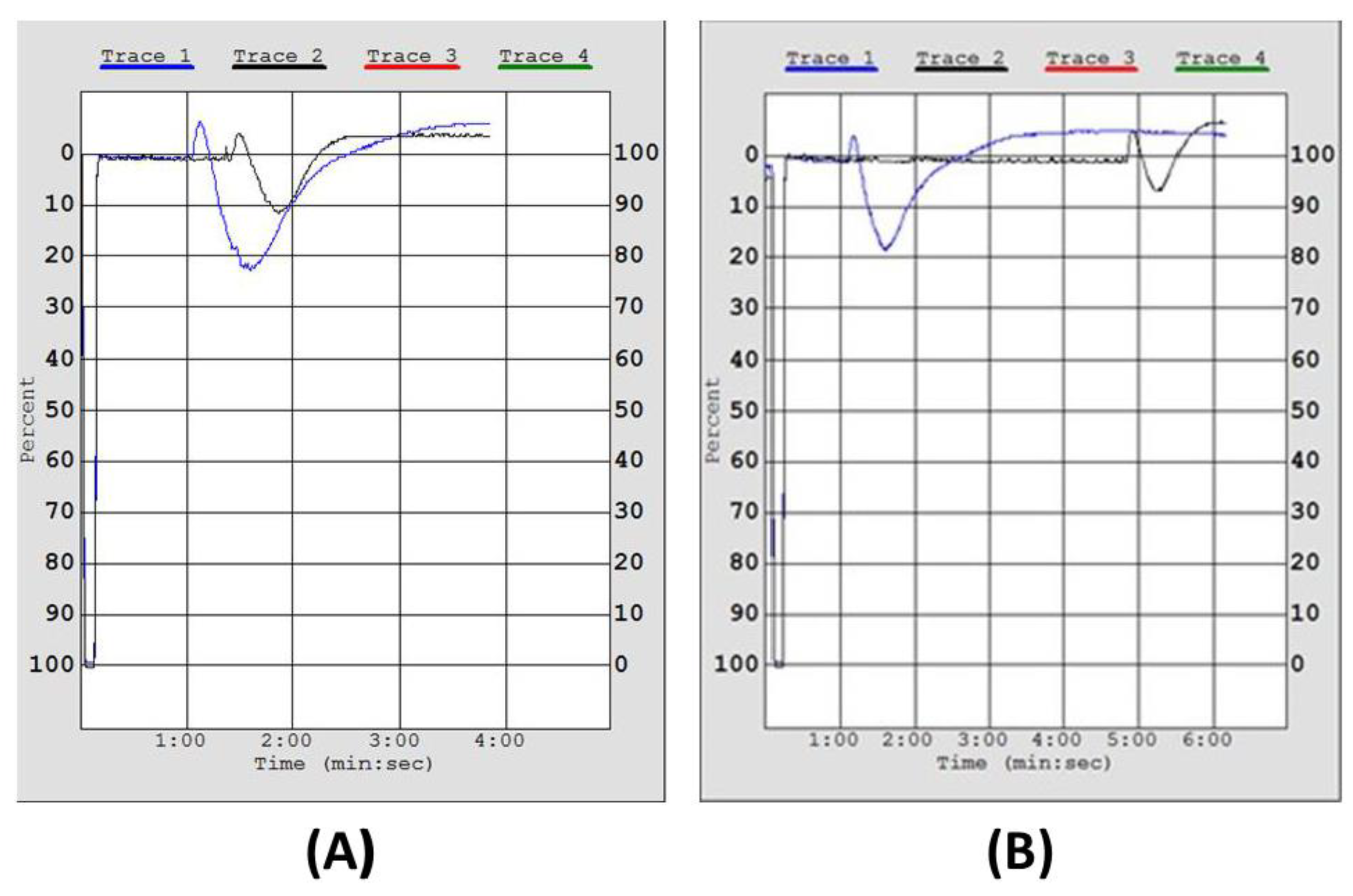
2.3. Inhibitory Effect of Irish Organic Farmed Salmon Fillets Polar Lipids Towards Aggregation of Human Platelet-Rich Plasma (hPRP)
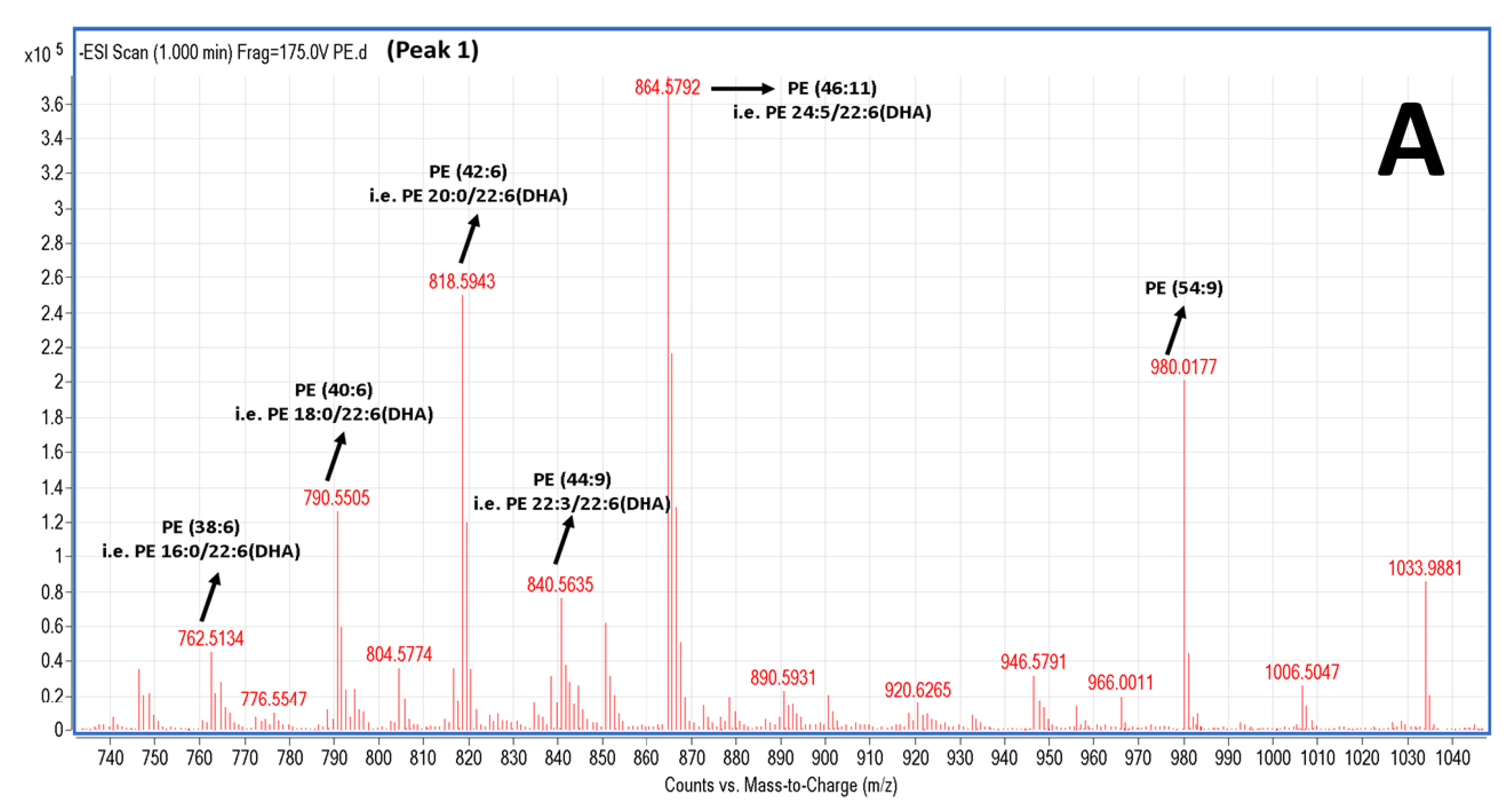
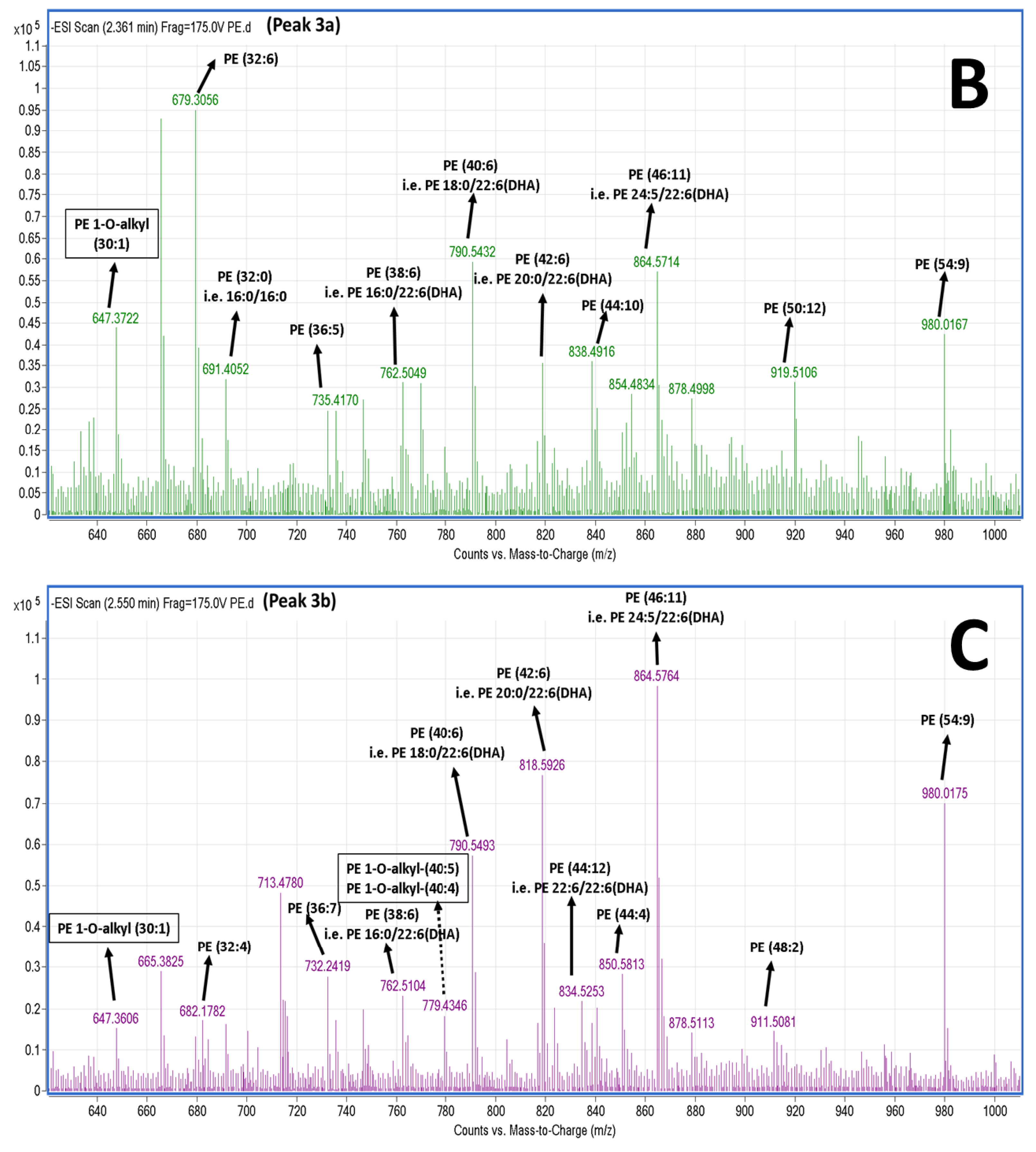
2.4. GC-MS Analysis of Salmon Polar Lipids
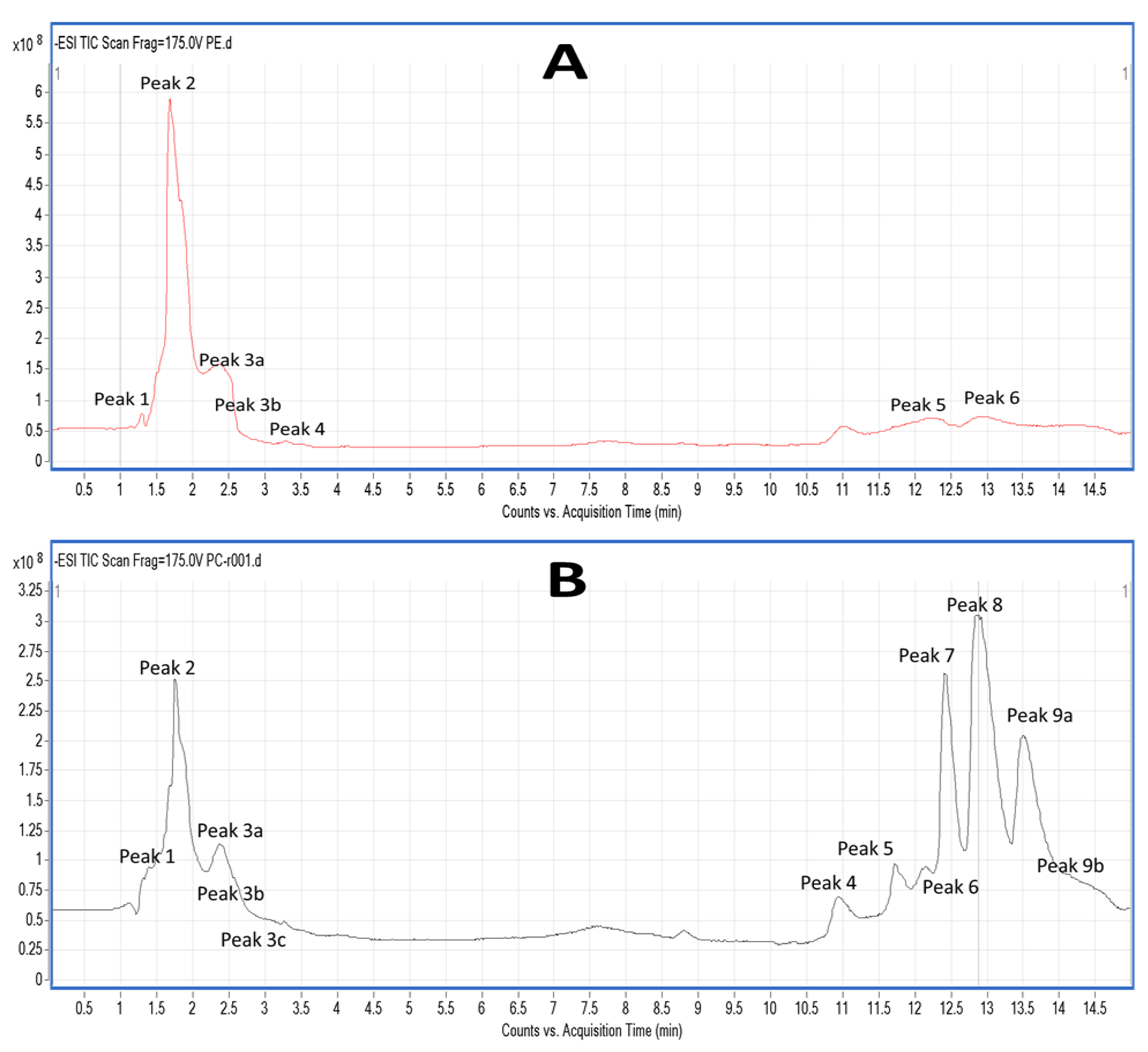
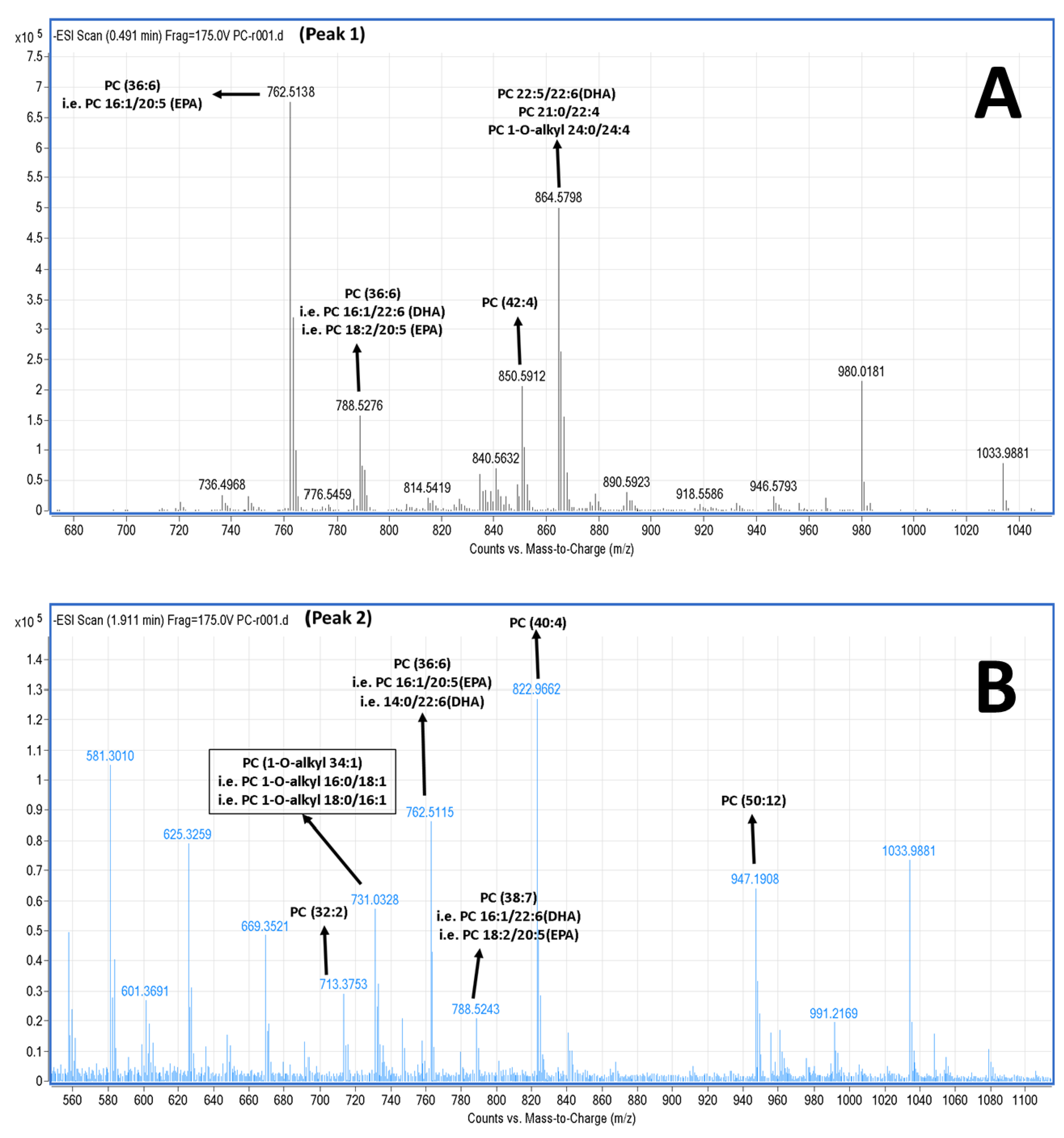
2.5. LC-MS Analysis of Salmon Polar Lipids
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials and Instrumentation
4.2. Isolation of Salmon Total Lipids, Total Polar, and Total Neutral Lipids
4.3. Fractionation of Salmon TPL by Thin-Layer Chromatography
4.4. Human Platelet-Rich Plasma (hPRP) Aggregation Studies of Salmon Polar Lipids
4.5. GC-MS Analysis of Salmon Polar Lipids
4.6. LC-MS Analysis of Salmon Polar Lipids
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mori, T.A. Marine OMEGA-3 fatty acids in the prevention of cardiovascular disease. Fitoterapia 2017, 123, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simopoulos, A.P. The importance of the omega-6/omega-3 fatty acid ratio in cardiovascular disease and other chronic diseases. Exp. Biol. Med. 2008, 233, 674–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lordan, R.; Tsoupras, A.; Zabetakis, I. Phospholipids of animal and marine origin: Structure, function, and anti-inflammatory properties. Molecules 2017, 22, 1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasopoulou, C.; Tsoupras, A.B.; Karantonis, H.C.; Demopoulos, C.A.; Zabetakis, I. Fish polar lipids retard atherosclerosis in rabbits by down-regulating PAF biosynthesis and up-regulating PAF catabolism. Lipids Health Dis. 2011, 10, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsoupras, A.B.; Iatrou, C.; Frangia, C.; Demopoulos, C.A. The implication of platelet-activating factor in cancer growth and metastasis: Potent beneficial role of PAF-inhibitors and antioxidants. Infect. Disord. Drug Targets 2009, 9, 390–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsoupras, A.B.; Chini, M.; Tsogas, N.; Fragopoulou, E.; Nomikos, T.; Lioni, A.; Mangafas, N.; Demopoulos, C.A.; Antonopoulou, S.; Lazanas, M.C. Anti-platelet-activating factor effects of highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART): A new insight in the drug therapy of HIV infection? AIDS Res. Hum. Retrovir. 2008, 24, 1079–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demopoulos, C.A.; Karantonis, H.C.; Antonopoulou, S. Platelet-activating factor—A molecular link between atherosclerosis theories. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2003, 105, 705–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoupras, A.; Lordan, R.; Zabetakis, I. Inflammation, not cholesterol, is a cause of chronic disease. Nutrients 2018, 10, 604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lordan, R.; Zabetakis, I. Invited review: The anti-inflammatory properties of dairy lipids. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 4197–4212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lordan, R.; Tsoupras, A.; Mitra, B.; Zabetakis, I. Dairy fats and cardiovascular disease: Do we really need to be concerned? Foods 2018, 7, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Megson, I.L.; Whitfield, P.D.; Zabetakis, I. Lipids and cardiovascular disease: Where does dietary intervention sit alongside statin therapy? Food Funct. 2016, 7, 2603–2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zabetakis, I. Food security and cardioprotection: The polar lipid link. J. Food Sci. 2013, 78, 1101–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasopoulou, C.; Karantonis, H.C.; Perrea, D.N.; Theocharis, S.E.; Iliopoulos, D.G.; Demopoulos, C.A.; Zabetakis, I. In vivo anti-atherogenic properties of cultured gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata) polar lipid extracts in hypercholesterolaemic rabbits. Food Chem. 2010, 120, 831–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sioriki, E.; Nasopoulou, C.; Demopoulos, C.A.; Zabetakis, I. Comparison of sensory and cardioprotective properties of olive-pomace enriched and conventional gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata): The effect of grilling. J. Aquat. Food Prod. Technol. 2015, 24, 782–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasopoulou, C.; Smith, T.; Detopoulou, M.; Tsikrika, C.; Papaharisis, L.; Barkas, D.; Zabetakis, I. Structural elucidation of olive pomace fed sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) polar lipids with cardioprotective activities. Food Chem. 2014, 145, 1097–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasopoulou, C.; Psani, E.; Sioriki, E.; Demopoulos, C.A.; Zabetakis, I. Evaluation of sensory and in vitro cardio protective properties of sardine (Sardina pilchardus): The effect of grilling and brining. Food Nutr. Sci. 2013, 4, 940–949. [Google Scholar]
- Nasopoulou, C.; Nomikos, T.; Demopoulos, C.; Zabetakis, I. Comparison of antiatherogenic properties of lipids obtained from wild and cultured sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) and gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata). Food Chem. 2007, 100, 560–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panayiotou, A.; Samartzis, D.; Nomikos, T.; Fragopoulou, E.; Karantonis, H.C.; Demopoulos, C.A.; Zabetakis, I. Lipid fractions with aggregatory and antiaggregatory activity toward platelets in fresh and fried cod (Gadus morhua): Correlation with platelet-activating factor and atherogenesis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 6372–6379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rementzis, J.; Antonopoulou, S.; Argyropoulos, D.; Demopoulos, C.A. Biologically active lipids from S. scombrus. In Platelet-Activating Factor and Related Lipid Mediators 2; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1996; pp. 65–72. [Google Scholar]
- Fragopoulou, E.; Nomikos, T.; Tsantila, N.; Mitropoulou, A.; Zabetakis, I.; Demopoulos, C.A. Biological activity of total lipids from red and white wine/must. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 5186–5193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fragopoulou, E.; Antonopoulou, S.; Tsoupras, A.; Tsantila, N.; Grypioti, A.; Gribilas, G.; Gritzapi, H.; Konsta, E.; Skandalou, E.; Papadopoulou, A. Antiatherogenic properties of red/white wine, musts, grape-skins, and yeast. In Proceedings of the 45th International Conference on the Bioscience of Lipids, University of Ioannina, Ioannina, Greece, 25–29 May 2004; p. 66. [Google Scholar]
- Megalemou, K.; Sioriki, E.; Lordan, R.; Dermiki, M.; Nasopoulou, C.; Zabetakis, I. Evaluation of sensory and in vitro anti-thrombotic properties of traditional greek yogurts derived from different types of milk. Heliyon 2017, 3, e00227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berdeaux, O.; Juaneda, P.; Martine, L.; Cabaret, S.; Bretillon, L.; Acar, N. Identification and quantification of phosphatidylcholines containing very-long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acid in bovine and human retina using liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 7738–7748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zabetakis, I. Marine Oils (From Sea to Pharmaceuticals); Nova Science: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Raatz, S.K.; Johnson, L.K.; Rosenberger, T.A.; Picklo, M.J. Twice weekly intake of farmed atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) positively influences lipoprotein concentration and particle size in overweight men and women. Nutr. Res. 2016, 36, 899–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, C.; Li, L.; Man, Q.; Song, P.; Meng, L.; Du, Z.Y.; Frøyland, L. Inclusion of atlantic salmon in the chinese diet reduces cardiovascular disease risk markers in dyslipidemic adult men. Nutr. Res. 2010, 30, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagen, I.V.; Helland, A.; Bratlie, M.; Brokstad, K.A.; Rosenlund, G.; Sveier, H.; Mellgren, G.; Gudbrandsen, O.A. High intake of fatty fish, but not of lean fish, affects serum concentrations of TAG and HDL-cholesterol in healthy, normal-weight adults: A randomised trial. Br. J. Nutr. 2016, 116, 648–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalum, A.; Tangen, R.; Falk, K.; Hordvik, I.; Rosenlund, G.; Torstensen, B.; Koppang, E.O. Coronary changes in the atlantic salmon Salmo salar L.: Characterization and impact of dietary fatty acid compositions. J. Fish Dis. 2016, 39, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raatz, S.K.; Golovko, M.Y.; Brose, S.A.; Rosenberger, T.A.; Burr, G.S.; Wolters, W.R.; Picklo, M.J. Baking reduces prostaglandin, resolvin, and hydroxy-fatty acid content of farm-raised atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 11278–11286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLennan, P.L.; Owen, A.J.; Slee, E.L.; Theiss, M.L. Myocardial function, ischaemia and n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids: A membrane basis. Eur. J. Cardiovasc. Med. 2007, 8, S15–S18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizos, E.C.; Ntzani, E.E.; Bika, E.; Kostapanos, M.S.; Elisaf, M.S. Association between omega-3 fatty acid supplementation and risk of major cardiovascular disease events: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA 2012, 308, 1024–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enns, J.E.; Yeganeh, A.; Zarychanski, R.; Abou-Setta, A.M.; Friesen, C.; Zahradka, P.; Taylor, C.G. The impact of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid supplementation on the incidence of cardiovascular events and complications in peripheral arterial disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2014, 14, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwak, S.; Myung, S.; Lee, Y.; Seo, H. Efficacy of omega-3 fatty acid supplements (eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid) in the secondary prevention of cardiovascular disease: A meta-analysis of randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials. Arch. Intern. Med. 2012, 172, 686–694. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Walz, C.P.; Barry, A.R.; Koshman, S.L. Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid supplementation in the prevention of cardiovascular disease. Can. Pharm. J. 2016, 149, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, R.; Stevens, S.; Gorman, D.; Pan, A.; Warnakula, S.; Chowdhury, S.; Ward, H.; Johnson, L.; Crowe, F.; Hu, F.B. Association between fish consumption, long chain omega-3 fatty acids, and risk of cerebrovascular disease: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ 2012, 345, e6698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanagita, T.; Nagao, K. Functional lipids and the prevention of the metabolic syndrome. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 17, 189–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Küllenberg, D.; Taylor, L.A.; Schneider, M.; Massing, U. Health effects of dietary phospholipids. Lipids Health Dis. 2012, 11, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verouti, S.N.; Tsoupras, A.B.; Alevizopoulou, F.; Demopoulos, C.A.; Iatrou, C. Paricalcitol effects on activities and metabolism of platelet activating factor and on inflammatory cytokines in hemodialysis patients. Int. J. Artif. Organs 2013, 36, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsoupras, A.B.; Chini, M.; Mangafas, N.; Tsogas, N.; Stamatakis, G.; Tsantila, N.; Fragopoulou, E.; Antonopoulou, S.; Gargalianos, P.; Demopoulos, C.A. Platelet-activating factor and its basic metabolic enzymes in blood of naive HIV-infected patients. Angiology 2012, 63, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Lopez, N.; Stubhaug, I.; Ipharraguerre, I.; Rimbach, G.; Menoyo, D. Positional distribution of fatty acids in triacylglycerols and phospholipids from fillets of atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) fed vegetable and fish oil blends. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 4255–4269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beppu, F.; Yasuda, K.; Okada, A.; Hirosaki, Y.; Okazaki, M.; Gotoh, N. Comparison of the distribution of unsaturated fatty acids at the sn-2 position of phospholipids and triacylglycerols in marine fishes and mammals. J. Oleo Sci. 2017, 66, 1217–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, J.; Larondelle, Y.; Pham, D.; Ackman, R.G.; Rollin, X. Polyunsaturated fatty acid profiles of whole body phospholipids and triacylglycerols in anadromous and landlocked atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) fry. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2003, 134, 335–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simopoulos, A. An increase in the omega-6/omega-3 fatty acid ratio increases the risk for obesity. Nutrients 2016, 8, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeung, E.H.; Robledo, C.; Boghossian, N.; Zhang, C.; Mendola, P. Developmental origins of cardiovascular disease. Curr. Epidemiol. Rep. 2014, 1, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Flaherty, J.T.; Tessner, T.; Greene, D.; Redman, J.R.; Wykle, R.L. Comparison of 1-O-alkyl-, 1-O-alk-1′-enyl-, and 1-O-acyl-2-acetyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamines and -3-phosphocholines as agonists of the platelet-activating factor family. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1994, 1210, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsantila, N.; Karantonis, H.C.; Perrea, D.N.; Theocharis, S.E.; Iliopoulos, D.G.; Antonopoulou, S.; Demopoulos, C.A. Antithrombotic and antiatherosclerotic properties of olive oil and olive pomace polar extracts in rabbits. Mediat. Inflamm. 2007, 2007, 36204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, H.; Tanaka, Y.; Hibino, H.; Umeda, Y.; Kawamitsu, H.; Fujimoto, H.; Amakawa, T. Beneficial effect of salmon roe phosphatidylcholine in chronic liver disease. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 1999, 15, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukunaga, K.; Hossain, Z.; Takahashi, K. Marine phosphatidylcholine suppresses 1,2-dimethylhydrazine-induced colon carcinogenesis in rats by inducing apoptosis. Nutr. Res. 2008, 28, 635–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, Z.; Konishi, M.; Hosokawa, M.; Takahashi, K. Effect of polyunsaturated fatty acid-enriched phosphatidylcholine and phosphatidylserine on butyrate-induced growth inhibition, differentiation and apoptosis in caco-2 cells. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2006, 24, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bligh, E.G.; Dyer, W.J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can. J. Biochem. Phys. 1959, 37, 911–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galanos, D.S.; Kapoulas, V.M. Isolation of polar lipids from triglyceride mixtures. J. Lipid Res. 1962, 3, 134–136. [Google Scholar]
- Tsantila, N.; Tsoupras, A.B.; Fragopoulou, E.; Antonopoulou, S.; Iatrou, C.; Demopoulos, C.A. In vitro and in vivo effects of statins on platelet-activating factor and its metabolism. Angiology 2011, 62, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasopoulou, C.; Stamatakis, G.; Demopoulos, C.A.; Zabetakis, I. Effects of olive pomace and olive pomace oil on growth performance, fatty acid composition and cardio protective properties of gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata) and sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax). Food Chem. 2011, 129, 1108–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otero, P.; Saha, S.K.; Gushin, J.M.; Moane, S.; Barron, J.; Murray, P. Identification of optimum fatty acid extraction methods for two different microalgae phaeodactylum tricornutum and haematococcus pluvialis for food and biodiesel applications. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2017, 409, 4659–4667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qandil, A. Prodrugs of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDS), more than meets the eye: A critical review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 17244–17274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| TL | TNL | TPL | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lipid Content * (g) ± SD | 5.51 ± 1.90 | 4.66 ± 2.08 | 0.86 ± 0.36 |
| IC50 † (µg) ± SD towards PAF inhibition | 170 ± 32 | 432 ± 44 | 45 ± 22 |
| IC50 † (µg) ± SD towards thrombin inhibition | 451 ± 56 | 682 ± 62 | 382 ± 39 |
| Fatty Acids | % FAs | mg/kg of Salmon |
|---|---|---|
| 12:0 | 0.018 ± 0.001 | 1.3574 ± 0.096 |
| 14:0 | 2.107 ± 0.138 | 159.71 ± 15.33 |
| 14:1ω7 c9 | 0.098 ± 0.008 | 7.4086 ± 0.806 |
| 16:0 | 22.56 ± 0.658 | 1711.2 ± 95.30 |
| 16:1ω7 c9 | 1.992 ± 0.659 | 151.63 ± 55.74 |
| 18:0 | 6.331 ± 0.040 | 480.22 ± 38.98 |
| 18:1ω9 c9 | 13.31 ± 0.904 | 1009.8 ± 122.7 |
| 18:2ω6 c9, c12 | 6.938 ± 0.378 | 526.18 ± 50.54 |
| 18:2ω6 c11, c14 | 0.113 ± 0.008 | 8.5675 ± 0.275 |
| 18:3ω6 c6, c9, c12 | 0.047 ± 0.014 | 3.5902 ± 1.186 |
| 18:3ω3 c9, c12, c15 | 2.139 ± 0.123 | 161.78 ± 5.438 |
| 18:4ω3 c6, c9, c12, c15 | 0.695 ± 0.047 | 200.20 ± 257.0 |
| 20:0 | 0.157 ± 0.053 | 9.4081 ± 0.545 |
| 20:1ω9 c9 | 3.512 ± 0.208 | 265.62 ± 8.865 |
| 20:2ω6 c11, c14 | 0.890 ± 0.114 | 67.497 ± 10.30 |
| 20:3ω9 c5, c8, c11 | 0.771 ± 0.042 | 58.644 ± 7.951 |
| 20:4ω6 c5, c8, c11, c14 | 2.091 ± 0.120 | 158.41 ± 13.02 |
| 20:4ω3 c8, c11, c14, c17 | 0.347 ± 0.127 | 26.416 ± 10.45 |
| 20:5ω3 c5, c8, c11, c14, c17 | 10.02 ± 0.344 | 765.56 ± 37.49 |
| 22:1 c11 | 4.458 ± 0.590 | 339.03 ± 59.87 |
| 22:5ω6 c4, c7, c10, c13, c16 | 0.424 ± 0.116 | 32.176 ± 9.535 |
| 22:6ω3 c4, c7, c10, c13, c16, c19 | 12.94 ± 0.418 | 981.66 ± 92.63 |
| Total SFA | 32.54 ± 0.211 | 2425.5 ± 160.0 |
| Total MUFA | 24.08 ± 0.639 | 1835.3 ± 187.9 |
| Total ω7 FA | 2.448 ± 0.069 | 186.24 ± 58.80 |
| Total ω9 FA | 17.59 ± 0.927 | 1334.1 ± 187.9 |
| Total PUFA | 37.85 ± 0.527 | 3005.9 ± 366.4 |
| Total ω3 PUFA | 26.42 ± 0.419 | 2135.6 ± 317.2 |
| Total ω6 PUFA | 10.50 ± 0.131 | 796.43 ± 59.56 |
| ω6/ω3 | 0.37 ± 0.08 |
| Fatty Acids | PC | PE |
|---|---|---|
| 12:0 | 0.060 ± 0.004 | 0.034 ± 0.012 |
| 14:0 | 2.210 ± 0.212 | 5.424 ± 0.198 |
| 16:0 | 30.00 ± 0.488 | 20.76 ± 0.947 |
| 16:1ω7 c9 | 2.211 ± 0.121 | 1.883 ± 0.054 |
| 16:4ω3 c6, c9, c12, c15 | 0.290 ± 0.023 | ND |
| 18:0 | 8.171 ± 0.568 | 9.157 ± 0.543 |
| 18:1ω9 c9 | 7.937 ± 0.365 | 11.40 ± 0.044 |
| 18:1ω5 c13 | 2.369 ± 0.003 | 2.181 ± 0.269 |
| 18:2ω6 c9,c12 | 3.578 ± 0.068 | 2.298 ± 0.036 |
| 18:3ω3 c9, c12, c15 | 1.470 ± 0.033 | 1.562 ± 0.044 |
| 20:0 | 0.133 ± 0.029 | 0.945 ± 0.200 |
| 20:1ω9 c9 | 0.408 ± 0.011 | 1.054 ± 0.012 |
| 20:1ω7 c13 | 1.213 ± 0.097 | 6.670 ± 0.832 |
| 20:2ω6 c11, c14 | 0.516 ± 0.016 | 0.408 ± 0.001 |
| 20:3ω9 c5, c8, c11 | 0.252 ± 0.008 | ND |
| 20:4ω6 c5, c8, c11, c14 | 2.128 ± 0.139 | 1.012 ± 0.089 |
| 20:4ω3 c8, c11, c14, c17 | 0.785 ± 0.007 | 1.233 ± 0.030 |
| 20:5ω3 c5, c8, c11, c14, c17 | 9.289 ± 0.729 | 2.936 ± 0.123 |
| 22:1ω9 c11 | 2.203 ± 0.193 | 7.913 ± 0.716 |
| 22:5ω6 c4, c7, c10, c13, c16 | 2.553 ± 0.020 | ND |
| 22:6ω3 c4, c7, c10, c13, c16, c19 | 21.57 ± 1.407 | ND |
| SFA | 40.58 ± 1.301 | 36.32 ± 1.501 |
| Total MUFA | 16.34 ± 0.398 | 31.59 ± 0.247 |
| Total ω7 FA | 3.424 ± 0.218 | 2.937 ± 0.041 |
| Total ω9 FA | 10.80 ± 0.175 | 20.36 ± 0.747 |
| Total PUFA | 42.43 ± 2.172 | 9.449 ± 0.233 |
| Total ω3 PUFA | 33.41 ± 2.219 | 5.731 ± 0.109 |
| Total ω6 PUFA | 6.222 ± 0.054 | 3.718 ± 0.125 |
| ω6/ω3 | 0.186 ± 0.075 | 0.649 ± 0.053 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsoupras, A.; Lordan, R.; Demuru, M.; Shiels, K.; Saha, S.K.; Nasopoulou, C.; Zabetakis, I. Structural Elucidation of Irish Organic Farmed Salmon (Salmo salar) Polar Lipids with Antithrombotic Activities. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 176. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16060176
Tsoupras A, Lordan R, Demuru M, Shiels K, Saha SK, Nasopoulou C, Zabetakis I. Structural Elucidation of Irish Organic Farmed Salmon (Salmo salar) Polar Lipids with Antithrombotic Activities. Marine Drugs. 2018; 16(6):176. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16060176
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsoupras, Alexandros, Ronan Lordan, Martina Demuru, Katie Shiels, Sushanta Kumar Saha, Constantina Nasopoulou, and Ioannis Zabetakis. 2018. "Structural Elucidation of Irish Organic Farmed Salmon (Salmo salar) Polar Lipids with Antithrombotic Activities" Marine Drugs 16, no. 6: 176. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16060176
APA StyleTsoupras, A., Lordan, R., Demuru, M., Shiels, K., Saha, S. K., Nasopoulou, C., & Zabetakis, I. (2018). Structural Elucidation of Irish Organic Farmed Salmon (Salmo salar) Polar Lipids with Antithrombotic Activities. Marine Drugs, 16(6), 176. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16060176