Abstract
Cyanobacteria are found globally due to their adaptation to various environments. The occurrence of cyanobacterial blooms is not a new phenomenon. The bloom-forming and toxin-producing species have been a persistent nuisance all over the world over the last decades. Evidence suggests that this trend might be attributed to a complex interplay of direct and indirect anthropogenic influences. To control cyanobacterial blooms, various strategies, including physical, chemical, and biological methods have been proposed. Nevertheless, the use of those strategies is usually not effective. The isolation of natural compounds from many aquatic and terrestrial plants and seaweeds has become an alternative approach for controlling harmful algae in aquatic systems. Seaweeds have received attention from scientists because of their bioactive compounds with antibacterial, antifungal, anti-microalgae, and antioxidant properties. The undesirable effects of cyanobacteria proliferations and potential control methods are here reviewed, focusing on the use of potent bioactive compounds, isolated from seaweeds, against microalgae and cyanobacteria growth.
1. Introduction
Over the last two decades, there has been a growing concern about the impact of microalgae and cyanobacteria blooms due to increasing pollution and eutrophication. Harmful effects, including the development of high biomass and scums, which decrease the water quality and adversely affect the aquatic ecosystems, the aquaculture industry as well as the environmental and human health, have been reported [1]. Therefore, the control of cyanobacterial blooms is important and urgently required. Various strategies, including physical, chemical, and biological methods have been proposed for controlling or mitigating Harmful Algal Blooms (HABs). Chemical agents such us copper sulfate [2], potassium chloride [3], and endothall [4] have been used. Mechanical control involves the use of filters, pumps, and barriers [5]. Biological agents include herbivorous fishes [6], algae [7], and microorganisms [6]. However, the application of these strategies in the aquatic environment is not usually effective due to their nonselective toxicity to many aquatic organisms [8], high cost, energy expenditure, and low efficiency [9].
Recently, the isolation of natural compounds from many aquatic and terrestrial plants and seaweeds has been regarded as an environmentally friendly alternative approach for controlling harmful algae and cyanobacteria in aquatic systems [10]. These compounds include a variety of bioactive molecules such us ethyl 2-methylacetoacetate isolated from an emergent macrophyte Phragmites communis [11]; α-linolenic acid, oleic acid, and palmitic acid purified from Botryococcus braunii [12]; cyclic sulfur [13], and rutacridone epoxide [14].
Seaweeds are the most primitive group of vegetation and they have gained great importance as a promising source of bioactive compounds that can be used for drug development. Seaweeds can produce a variety of bioactive compounds, with a wide range of biological activity, including antibacterial, antifungal, antimicroalgae, antioxidant, and others [15,16,17,18]. Several live marine macroalgae (Corallina pilulifera, Enteromorpha clathrata, Undaria pinnatifida, Laminaria japonica, Porphyra tenera, Ulva pertusa, Sargassum thunbergii) have been found to inhibit bloom-forming microalgae such as Cochlodinium polykrikoides, Skeletonema costatum, Heterosigma akashiwo, and Prorocentrum micans [8,19,20].
2. Cyanobacteria
2.1. General Characteristics
Cyanobacteria, for a long time considered as blue-green algae on account of their ability to conduct photosynthesis, are Gram-negative bacteria. They are from a monophyletic group composed of almost 2000 species divided into 150 genera [21]. Cyanobacteria are among the oldest organisms to have appeared on our planet and are one of the most abundant and largely distributed [22]. They are present in a broad range of ecosystems such as aquatic environments (from fresh waters to hyper-saline water) and deserts [23]. They also may grow in symbiosis with algae (marine and freshwater diatoms), fungi to form lichens, with animals like protozoa, sponges or sea squirts, or with plants such as aquatic ferns, gymnosperms, and angiosperms [24]. The majority of the cyanobacteria species are aerobic photoautotrophs but some species, like Synechocystis sp. PCC6803 are optional heterotrophs [25]. They are responsible for about half of the earth’s oxygen atmosphere [26].
Cyanobacteria have a considerable morphological diversity. They can be solitary (unicellular), or colonial, or organized in trichomes (without sheath) or filaments (with sheath) with very varied forms (e.g., ovoid, spherical). In addition to their vegetative cells, specialized cells give them great advantages; gas vacuoles which regulate floating, the akinets which allows their conservation and dissemination, and the heterocysts which have the ability to convert dinitrogen directly (N2) in an available form (ammonium NH4+) through the nitrogenase. These latter types of cells are found in many kinds of cyanobacteria such as: Microcoleus, Gloeothece, Nostoc, Anabaena, Aphanizomenon [27,28]. Cyanobacteria can produce a variety of bioactive components, which have broad biological activity, including antibacterial, antifungal, antioxidant, and anticancer compounds [29,30,31]. According to several researchers, 40% of species of cyanobacteria are supposed to be toxigenic [32]. The toxins are classified into four large categories: neurotoxins, hepatotoxins, cytotoxins, and irritant toxins such as lipopolysaccharides [33]. Moreover, cyanobacteria also have the ability to synthesize allelopathic substances which tend to target the other competitive species directly and can induce reactions of avoidance, deteriorate their aspect, or cause their mortality [34,35].
2.2. Blooms of Cyanobacteria
Eutrophication is caused by an excessive load of nutritive elements which leads to changes in the aquatic environment, materialized by the proliferation of cyanobacteria blooms [36]. This situation is influenced by many factors such as temperature, pH, luminosity, and high concentrations of inorganic nutrients (nitrogen and/or phosphorus) which are often limiting elements in water bodies [36,37], as well as the stability of the water column [38].
In temperate climates, during the summer and at the beginning of the autumn, cyanobacteria blooms can form in a few days and last for one to several weeks [22], often inducing scums and leading to intense discoloration of the water bodies. The development of cyanobacteria in eutrophic mediums is supported by their reduced capacity to capture carbon dioxide (CO2) [39,40], the skill to use bicarbonates (HCO3−) even with raised pH, the faculty to fix and use dinitrogen (N2), combined with their capacity to position themselves vertically in the water column [37].
Cyanobacteria have the advantage of not being easily digested by zooplankton unlike other members of phytoplankton [41]. They secrete siderophores (hydroxamates) enabling them to capture the surrounding Fe3+ ions limiting the growth of potential competitors [42]. Cyanobacterial populations end up dominating the phytoplankton in eutrophic lakes. Even if blooms constitute a natural phenomenon, their frequency and their severity are increased by eutrophication, often related to anthropic activities (domestic or industrial wastewater discharge, intensive agriculture, both rich in nitrogen and phosphates). Moreover, global warming seems to act as a catalyst for cyanobacterial proliferations [43,44,45].
2.3. Undesirable Effects of Cyanobacteria Blooms
The harmful blooms of cyanobacteria have multiple consequences on ecosystems including the lethality of some species. Cyanobacteria massive growth can lead to two types of problems, one associated with a strong production of biomass and the other associated with the production of toxins that can result from a very low density of producing organisms [46].
The low consumption of cyanobacteria by zooplankton could disturb these trophic networks by limiting the transfers of matter and energy towards higher levels. Blooms also increase pH and water turbidity, reducing transparency and therefore light penetration. Light is then no longer available for photosynthetic activity below the surface level. In depth zones, anoxia develops and subsequently limits the growth of primary benthic producers such as macrophytes, epiphytes, and metaphyton [47]. The death of primary producers increases organic matter that causes the proliferation of decomposers (bacteria, fungi). These microorganisms mineralize organic material and use for their metabolism, dissolved oxygen which limits its access to many other organisms such as zooplankton and fish, causing significant mortalities [48], and dramatic changes in the species composition of aquatic communities [22]. Cyanobacterial blooms typically involve a considerable loss of biodiversity in the phytoplankton community [48].
The harmful blooms of cyanobacteria also generate nuisances compromising the use of water for various activities. Moreover, some cyanobacteria such as Anabaena, Aphanizomenon, Lyngbya, Microcystis, Oscillatoria, Phormidium, Schizothrix and Symploca [49], produce non-toxic volatile organic secondary metabolites, geosmin (E1, 10-dimethyl-E-9-decalol) and MIB (2-methyl isoborneol), which cause bad tastes and foul-smelling odors with significant economic consequences in fish farming [50,51,52]. Furthermore, more than 100 species belonging to 40 genera of cyanobacteria are able to synthesize toxins that can have harmful impacts on aquatic fauna and flora as well as the health of land animals and humans [1]. Among these genera, Microcystis is the most prevalent in the formation of toxic blooms, namely in Moroccan lakes [53,54,55]. Toxins are classified into four categories according to the effects they cause in mammals and vertebrates: hepatotoxins such as hepatotoxic microcystins (targeting the liver), neurotoxins (targeting the nervous system), cytotoxins and irritating toxins such as lipopolysaccharides (dermatotoxins) [33,56]. Furthermore, toxic cyanobacteria blooms in lakes may not only pose a significant threat to the drinking water supply, but may also result in significant economic losses associated with mitigation of the blooms and lake restoration [57,58]. It is estimated in the United States that the annual economic costs of eutrophication in freshwaters is over $2.2 billion [57]. In addition, the use of contaminated water by cyanotoxins in irrigation could have negative effects on the development and metabolism of seeds and plants, influencing agricultural production [59,60].
2.4. Methods Applied in Cyanobacterial Bloom Control
Mechanical, physical, chemical, and biological methods are used to prevent and control the blooms of cyanobacteria, the chemical ones being the most used. Copper sulfate (CuSO4·5H2O) used to be the most popular algicide. Although the treatment was usually effective by killing cyanobacteria, side effects occurred: copper is toxic to many other aquatic organisms including fish [2] and the increase in dead algal biomass led to oxygen depletion and an increase in the release of phosphorus from the sediments, resulting in the reoccurrence of the blooms.
Research showed that cyanobacteria can develop resistance to copper [61,62]. There are many other inorganic chemicals highly toxic to cyanobacteria such as potassium chloride (K+) [3], endothall (7-oxabicyclo(2.2.1)eptane-2,3-dicarboxylic acid) [4], and diuron (3-[3,4-dichlorophenyl]-1,1-dimethylurea) [63]. Moreover, their application to the aquatic environment is not advisable due to the nonselective toxicity to many aquatic organisms; in addition, affected populations may build up resistance to these compounds [64].
Mechanical control involves the use of filters, pumps, and barriers (curtains, floating booms) to remove or exclude algal blooms, dead fish, or other bloom-related materials from impacted waters [5]. Cyanobacterial booms can also be limited by the dilution of lake water, by lake flushing or ultrasonic radiation [65]. The object of these methods is both the augmentation of the water exchange rate and the decrease of nutrient concentration [66]. The mechanical and physical treatment of algae removal is energy intensive and tends to be of low efficiency [9]. It is applied mainly to surface scums and only a small part of the cyanobacterial population in the lake can be removed by mechanical techniques [67]. Other work however, showed that it could be effective even on a whole lake [68]. In addition, lesions caused to non-target organisms by these techniques, also limit the application in the field of such approaches in large scale.
Biological control such as biomanipulation tends to be environmentally friendly and a promising method for controlling algal blooms, being highly specific to the target organism, with no destruction of other organisms and with no direct chemical pollution. Biomanipulation involves the introduction of new grazers and competitors of cyanobacteria to control the phytoplankton development in eutrophic lakes [69]. Many organisms are used such as macrophytes and periphyton [70,71], herbivorous fishes (silver and bighead carp) [6], algae [7], and microorganisms (viruses, bacteria, fungi, and protozoa) [6]. However, the introduction of new species in an environment can have negative consequences on other species, with an imbalance of the trophic chain [72,73].
Over the last two decades, as an alternative to synthetic algicidal agents, natural compounds have been tested for controlling harmful algae in aquatic systems [10]. Research has shown that extracts and essential oils of many aquatic and terrestrial plants and seaweeds inhibit the growth of cyanobacteria. Aquatic plants, such as Phragmites communis [74], Myriophyllum spicatum [75], Typha latifolia and Arundo donax [76], Ceratophyllum demersum [77], Potamogeton cristatus, Potamogeton maackianus, Potamogeton lucens, Vallisneria spinulosa, Ceratophyllum demersum, Hydrilla verticillata [78] and Sagittaria trifolia [79], inhibit the growth of cyanobacteria. The extracts and essential oils of many terrestrial plants also show inhibitory effects against cyanobacteria, such as Ailanthus altissima [80], Rosmarinus officinalis [81], Callicarpa americana [82]. Moreover, several studies have demonstrated the effects of seaweeds extracts in microalgae. Sun et al. and Sun et al. [83,84], indicated that Ulva intestinalis, Gracilaria lemaneiformis, and Ulva prolifera inhibit the growth of various microalgae species such as Prorocentrum micans, Prorocentrum donghaiense and Heterosigma akashiwo.
3. Macroalgae
3.1. General Characteristics
Macroalgae, also known as seaweeds, are conspicuous and dominant features in marine ecosystems. They differ from other plants, in that algae lack roots, leafy shoots, flowers, and vascular tissues. According to differences in pigmentation, macroalgae include three different phyla: Chlorophyta, or green seaweeds are a diverse group with more than 7000 species widespread in various habitats (marine, freshwater and terrestrial ecosystems) [85]. Green algae are characterized by the dominance of two photosynthetic pigments chlorophyll a and b, chloroplasts with no outer endoplasmic reticulum, thylakoids typically in stacks of two to six, and cellulosic walls or scales. Phaeophyta, or brown seaweeds, the principal pigments in which are xanthophyll and fucoxanthin that mask chlorophyll a and c, which give them a dark shade [86]. Brown algae are distinguished by chloroplasts that have four surrounding membranes, thylakoids in stacks of three and with a richness of polysaccharides that possess importance biological activities [87]. They are exclusive to the marine habitat, under 1% of the species occur in truly freshwater habitats. Rhodophyta, or red seaweeds, the presence of two principal pigments phycoerythrin and phycocyanin, chloroplasts without external endoplasmic reticulum, unstacked thylakoids, and absence of flagella, are the principle characters of these phyla. They are prevalently marine in distribution; just roughly 3% of more than 5000 species are from fresh water [88].
Morocco due to its specific geographical position: the Mediterranean Sea to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, accommodates a large bio-ecological diversity. However, the investigation of benthic kelp exhibited a particular wealth of 489 species [89] distributed between 303 species of Rhodophyceae (red algae), 99 species of Phaeophyceae (brown algae), and 87 species of Chlorophyceae (green algae). Their geographical distribution reveals the presence of 381 species (75%) on the Mediterranean coast and 323 species (64%) on the Atlantic coast, none of these algal species is endemic and only the Gelidium sesquipedale is currently exploited in Morocco [90].
3.2. Potential Use of Macroalgal Compounds
In recent years, macroalgae have gained significant importance as a new promising source of novel bioactive compounds that can be used for drug development. Seaweeds may produce a variety of bioactive compounds, which have a wide range of biological activities, including antibacterial, antifungal, antioxidant, and anti-microalgal compounds [15,16,17,18].
3.2.1. Production of Antimicrobial Substances
The urgent need to find new therapeutic drugs from natural products has increased during the last decade owing to the increase of emerging multidrug-resistant microorganisms. The discovery of new bioactive substances with potent effects against resistant pathogenic and toxic microorganisms is an important aspect of the bioactive substance research today. The diversity of natural products makes it one of the most important sources of novel structures, which have been found to possess useful biological activities [91].
Generally, the antimicrobial activity of macroalgae has been extensively studied. However, the exploitation of seaweeds as a source for the discovery of new bioactive substance is still at an early stage, despite the fact that numerous novel antimicrobial compounds have been isolated over the last few years (Table 1).

Table 1.
Novel antimicrobial compounds isolated from seaweeds.
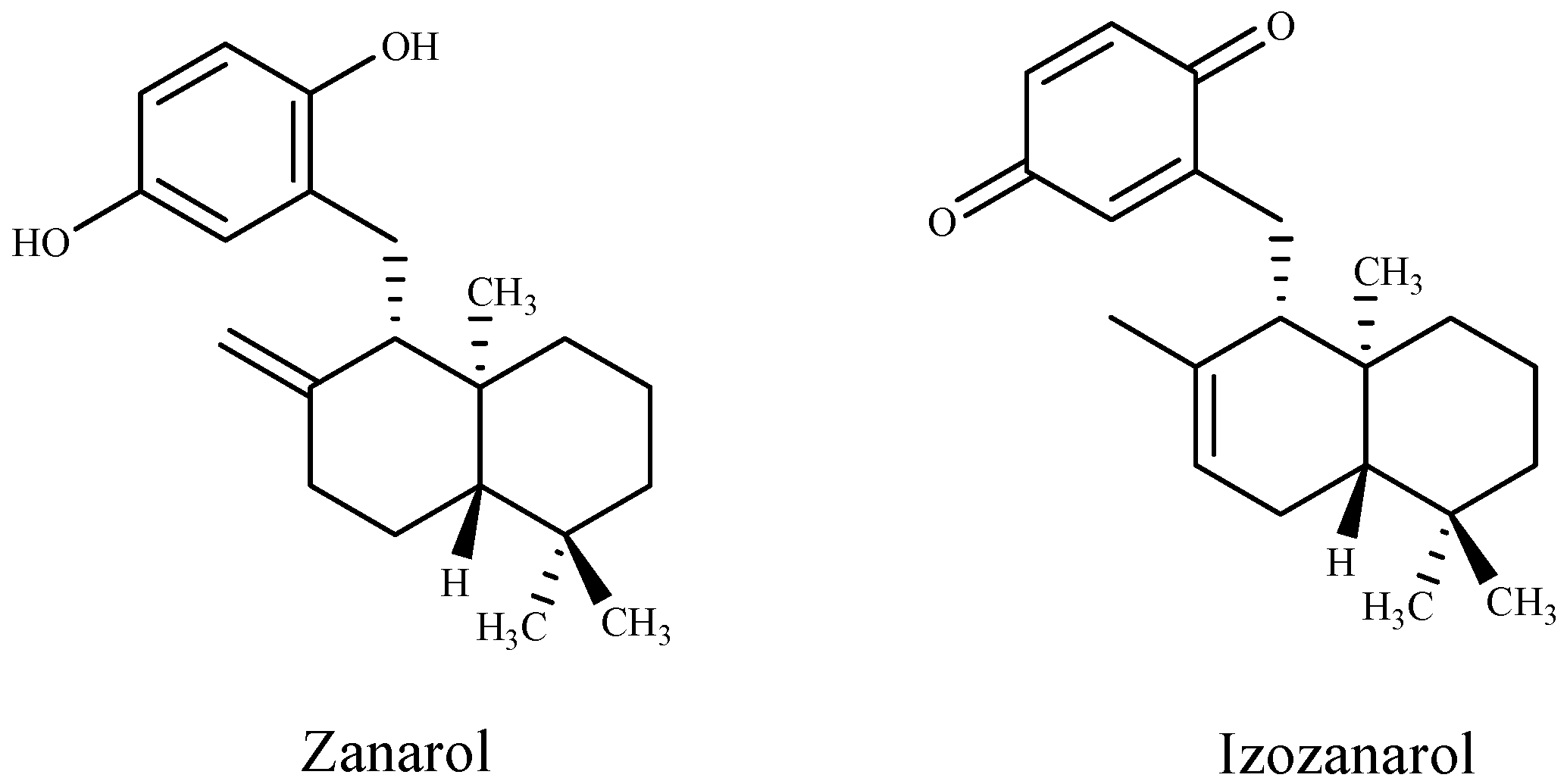
Kamei et al. [96] found a novel antibacterial terpenoid compound, the diterpene sargafuran, from the methanolic extract of the marine brown algae Sargassum macrocarpum. The results of antibacterial activity show that sargafuran was bactericidal and killed Propionibacterium acnes by lysing bacterial cells. Also, zonarol and isozonarol sesquiterpenes (Figure 1) isolated from Dictyopteris zonarioides have been shown to exhibit a strong inhibitory effect against plant pathogenic fungi [95]. A few sesquiterpenoid hydroquinones occasionally incorporating halogens such as tiomanene and acetylmajapolene A and B isolated from Malaysian Laurencia sp. have been found to exert potent antimicrobial efficacy [93].
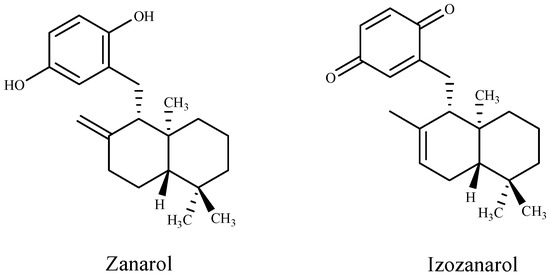
Figure 1.
Structures of terpenoid compounds from Dictyopteris zonarioides.
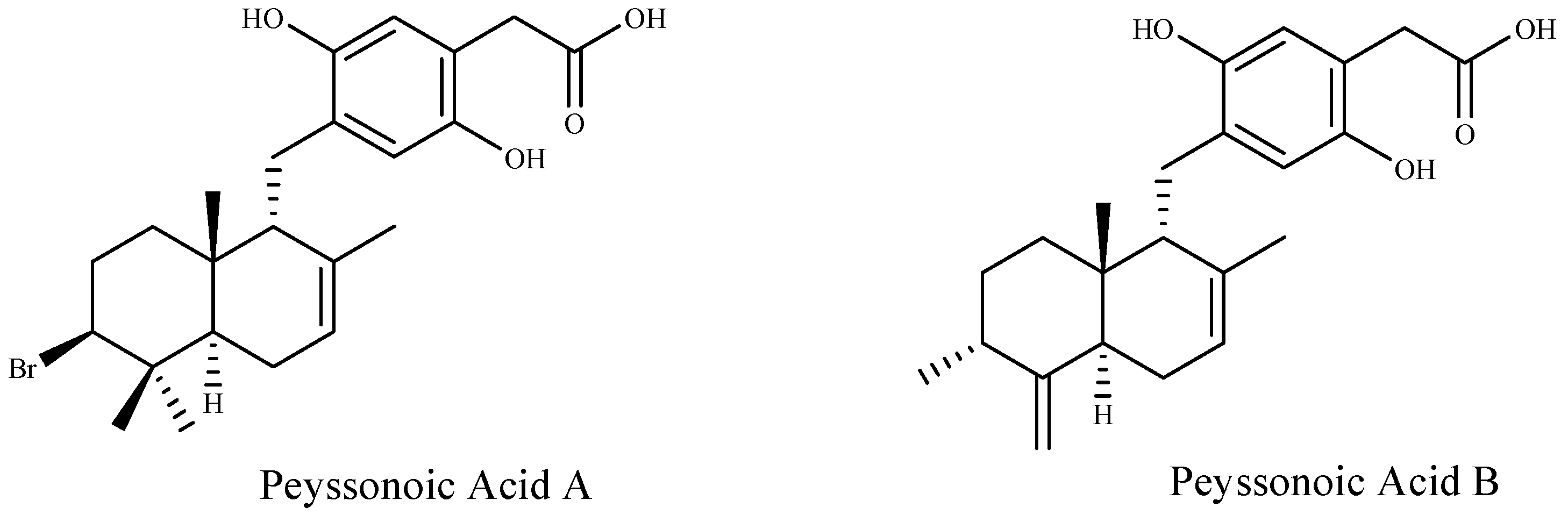
Furthermore, two new sesquiterpene hydroquinones, peyssonoic acids A and B (Figure 2) have been isolated from the crustose red alga Peyssonnelia sp. at ecologically realistic concentrations, and both compounds inhibited the growth of bacterial and fungal pathogens, Pseudoalteromonas bacteriolytica and Lindra thalassiae, from marine algae origin [92].
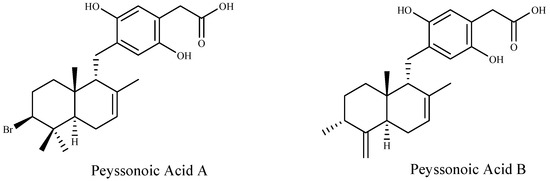
Figure 2.
Structures of the two new sesquiterpene hydroquinones.
The antimicrobial activity may be influenced by some factors such as the habitat and the season of algal collection, different growth stages of macroalgae, experimental methods etc. Moreover the variation in antimicrobial activity may be due to the method of extraction including the solvent used in the extraction [98,99].
The potential of seaweeds as a source of active compounds against pathogenic microorganisms has been confirmed in different studies (Table 2). Taskin et al. [100] indicated that the methanolic extracts of five marine algae, Cystoseira barbata, Dictyota dichotoma, Halopteris filicina, Cladostephus spongiosus f. verticillatus, and Ulva rigida collected from the North Aegean Sea (Turkey) showed inhibition against Staphylococcus aureus, the most effective being Ulva rigida extract. Moreover, the highest inhibition activity was shown in Enterobacter aerogenes (34.00 ± 1.00 mm) by Corralina officinalis and it was followed by Escherichia coli and Enterococcus faecalis. Cortés et al. [101] found that the dichloromethane extract of Ceramium rubrum was active on Yersinia ruckeri (Gram-negative). The identification of extract composition showed that it contains fatty acids, fatty acid esters, one hydrocarbon, and phytol. In addition, they found that the antibacterial activity of the extract has a synergistic effect of its constituents because the pure compounds only showed a weak effect, which suggests a strong synergistic effect among the components. Moreover, Salvador et al. [102] screened 82 marine algae as fresh and lyophilized forms against bacterial and fungal pathogens. Of the algae 67% were active against at least one of the microorganisms tested. Among the species tested Pseudomonas aeruginosa was the most resistant and Bacillus cereus was the most sensitive. In this study, they reported that the members of the red algal order, Bonnemaisoniales were the most active. Additionally, they showed that Phaeophyceae and Rhodophyceae autumn samples exhibited the most important antimicrobial activity, while the maximum activity of chlorophyceae extracts was observed for summer samples.

Table 2.
Antibacterial and antifungal activity of different solvent extracts from seaweeds.
According to their solubility and polarity, solvents show different antimicrobial activity. Therefore, it is necessary to select the best extraction solvents for each species of macroalgae in order to optimize extraction of the maximum chemical compounds. Methanol extracts have higher antimicrobial activity than extracts obtained with other solvents [103,104,105,106,107]. Shanmughapriya et al. [108] used fresh and dried materials of fourteen seaweeds for the extraction. They found that dried samples have less or no effects on microorganism tests in comparison to the fresh seaweed extracts. In addition, the antimicrobial principle from marine algae was found to be lipophilic. They also demonstrated that methanol extracts had higher antibacterial activity whereas ethanolic extracts had no antibacterial activity. This result was consistent with those reported by ref. [109] which showed that the methanol extraction yields had higher antimicrobial activity than ethyl acetate and hexane. They found that all seaweeds were active against at least one of the bacteria tested, on the other hand only five algal extracts showed antifungal activity. Contrary wise, Baleta et al. [110] indicated that the extraction of antimicrobials from Sargassum oligocystum and Sargassum crassifolium was solvent dependent, ethanol being the best solvent for isolation of antimicrobial compounds. Also, they revealed the presence of flavonoids, tannins, phenolics, sterols, and terpenoids which could be responsible for the observed antimicrobial property.
Radhika et al. [111] studied the antifungal activities of Acanthophora spicifera, Padina tetrastomatica, and Caulerpascal pelliformis against five fungal strains, namely Aspergillus terrus, Aspergillus fumigatus, Gibberline sp., Alternaria sp., and Ganoderma sp. The ethanol extracts showed the best antifungal activity followed by acetone and then methanol extracts. Aspergillus fumigatus was the most susceptible fungal species while Ganoderma sp. was the most resistant. However, Tüney et al. [112] investigated the antimicrobial activities of the extracts from 11 seaweed species prepared by methanol, acetone, diethyl ether, and ethanol against Candida sp., Enterococcus faecalis, Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus epidermidis, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Escherichia coli. The highest activities were obtained by the diethyl ether prepared extracts. They reported that the most active algal species was Cystoseira mediterranea, Enteromorpha linza, Ulva rigida, Gracilaria gracilis, and Ectocarpus siliculosus against all test organisms. Furthermore, Moorthi et al. [113] found that acetone and chloroform extracts of the Sargassum muticum exhibited higher antibacterial activity compared to other solvent extracts. Cox et al. [114] revealed that methanol was the better solvent for extraction of antimicrobials from Phaeophyceae; whereas acetone was good for chlorophyceae. A variety of metabolites and natural bioactive compounds groups from seaweeds, such as polysaccharides, tannins, flavonoids, phenolic acids, bromophenols, and carotenoids have been reported to be bacterial inhibitors [115,116].
Depending on their constitution and concentration, phenol compounds, chemical components of algal cells, could have an activating or inhibiting effect on microbial development [117,118]. Furthermore, seaweeds have been reported to act as inhibitors of the oxidative phosphorylation and factor cell lysis due to their ability to bind with bacterial proteins such as enzymes and those of cell membranes [116]. Wei et al. [119] reported that low molecular weight phlorotannins extracted from Sargassum thunbergii damaged the wall and the permeability membrane of Vibrio parahaemolyticus cell. Nagayama et al. [120] identified bacterial activity of phlorotannins from the brown alga Ecklonia kurome against 35 bacterial strains.
Marine macroalgae have been found to produce diverse bioactive compounds with antialgal activities [18,142,143] that can prevent the development of microalgae or even kill them (Table 3).

Table 3.
Anti-microalgal activity of different extracts from seaweeds.
Manilal et al. [144] reported that a methanol extract of Stoechospermum marginatum showed significant algicidal effect and produced 90% of cell lysis of Oscillatoria sp. at 600 mg/L by the seventh day of treatment.
The GC-MS profile of this algal extract demonstrated the presence of diethyl phthalate as a major constituent (84.45%). Chowdhury et al. [145] investigated the toxic effect of the brown alga Ecklonia cava on Cochlodinium polykrikide and Heterosigma akashiwo with total growth inhibition, revealing that the maximum algicidal activity was attained after 24 h of exposition. Ecklonia cava potent algicidal activity against microalgae tests was maximized at a temperature of 25 °C or above. Nan et al. [146] showed that the growth of eight phytoplankton species was significantly (p < 0.01) suppressed in batch co-cultures with Ulva pertusa and the percentage of growth reduction varied between 42% and 100%. Moreover, Wang et al. [143] showed that the growth of Heterosigma akashiwo was strongly inhibited by using fresh tissue, dry powder or dry tissue of Enteromorpha intestinalis, Ulva pertusa, Ulva linza. Aqueous and methanol extracts had strong inhibitory effects on the growth of H. akashiwo, the effective concentration was 1.6 × 10−12 and 0.2 × 10−12 for the aqueous and the methanolic extract respectively with no apparent inhibitory effect of the other three organic solvent extracts (acetone, ether, and chloroform). Recently, Sun et al. [147] studied the effect of green alga Ulva prolifera on the growing of red tide microalgae and feed microalgae. The effects of Ulva prolifera methanolic extract partitions (FA, FB, FC, and FD) on several microalgae at the concentrations of 115.2 μg/mL FA and FB showed significant antialgal activity against most of the red tide microalgae tests, especially Heterosigma akashiwo and Prorocentrum donghaiense. They reported that the inhibitory activity of the fraction FA on Karenia mikimito was lower than that on Skeletonema costatum; 50.3% and 100% in day 12 at 14.4 μg/m; respectively, with no biological toxicity against feed microalgae. Furthermore, after screening 27 species of seaweeds, the methanol extracts of the brown alga Ishige sinicola showed significant growth inhibition of more than 30% against tissue, spores, zyogote and germling of Entermorpha prolifera. The water extracts of two seaweeds Codium fragile and Monostroma nitidum showed significant growth inhibition of more than 40% against tissue of Entermorpha prolifera, and only one seaweed Porphyra yezoensis showed significant inhibition of more than 30% against zygote of Entermorpha prolifera [148].
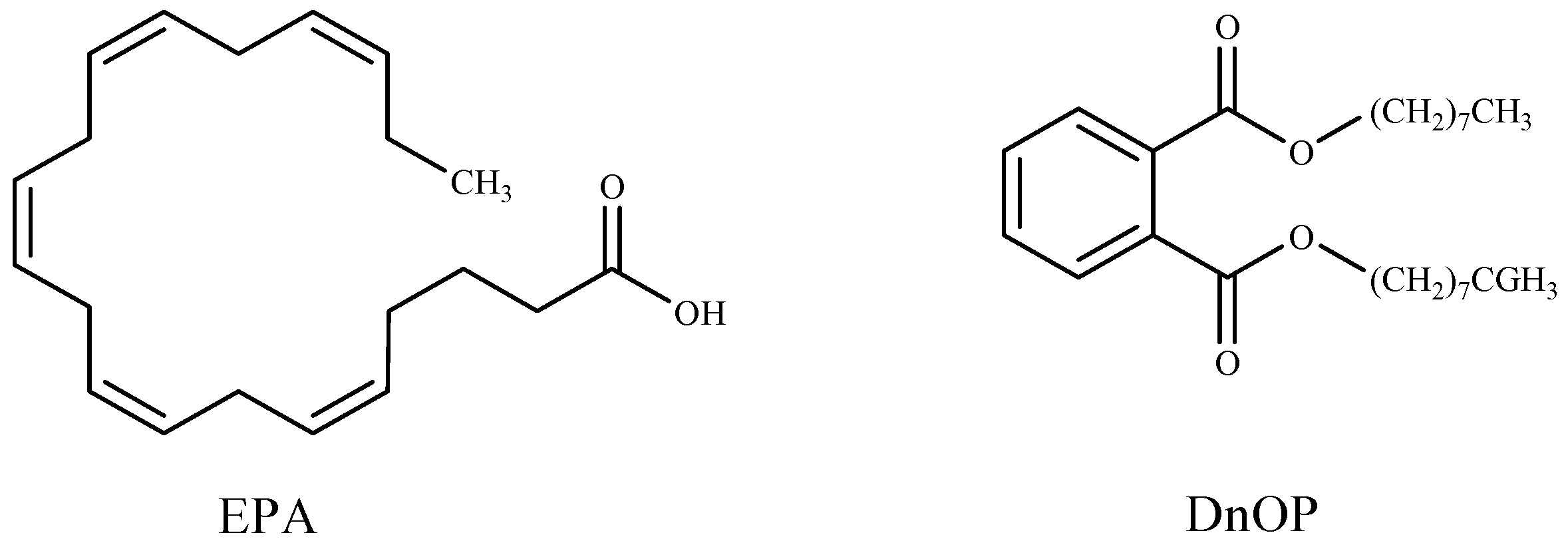
Researchers have described methods of controlling cyanobacteria harmful blooms by using algicidal compounds extracted from seaweeds, such as octadeca-6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z-tetraenoic acid (ODTA) isolated from the brown alga Cladosiphon okamuranus [160]; α-linolenic acid, oleic acid, and palmitic acid isolated from green alga Botryococcus braunii [12]; hexadeca-4,7,10,13-tetraenoic acid (HDTA), octadeca-6,9,12,15-tetraenoic acid (ODTA), and α linolenic acid isolated from the green alga Ulva fasciata [142]; (6E,9E,12E)-(2-acetoxy-β-d-glucose)-octadecatrienoic acid ester separated from green alga Ulva intestinalis [83]; gossonorol, 7,10-epoxy-ar-bisabol-11-ol, glycerol monopalmitate, stigmasterol, 15-hydroxymethyl-2,6,10,18,22,26,30-heptamethyl-14-methylene-17-hentriacontene, 4-hydroxyphenethyl alcohol, and margaric acid were obtained from the ethanolic extract of the red alga Gracilaria lemaneiformis [84]; 5,8,11,14,17-eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and di-n-octylphthalate (DnOP) (Figure 3) purified from the methanol extract of the red alga Corallina pilulifera [157].
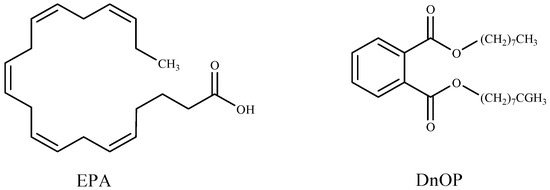
Figure 3.
Algicidal substances isolated from Corallina pilulifera.
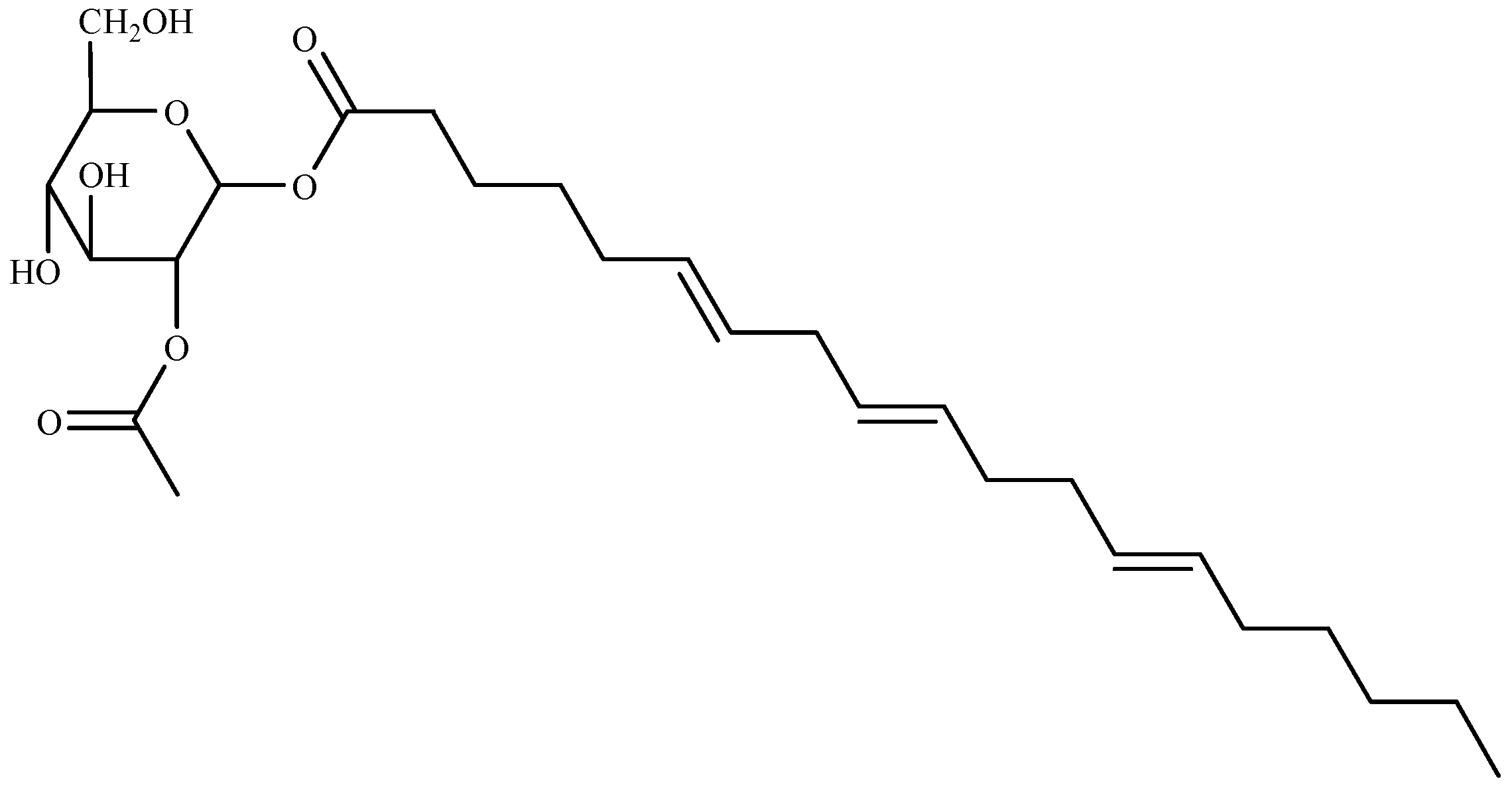
Recently, three algicidal compounds in the ethyl acetate (EtOAc) extracts were successfully isolated from green algae Ulva intestinalis as 15-ethoxy-(6Z,9Z,12Z)-hexadecatrienoic acid (I), (6E,9E,12E)-(2-acetoxy-β-d-glucose)-octadecatrienoic acid ester (II), and hexadecanoic acid (III). Compound I and III showed moderate algicidal activity. Whereas compound II (Figure 4) displayed the most potent algicidal activity with IC50 values of 4.9 and 14.1 μg/mL for Heterosigma akashiwo and Prorocentrum micans, respectively [83].
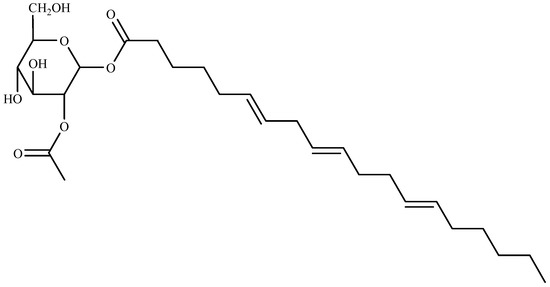
Figure 4.
Structure of compound II isolated from Ulva intestinalis.
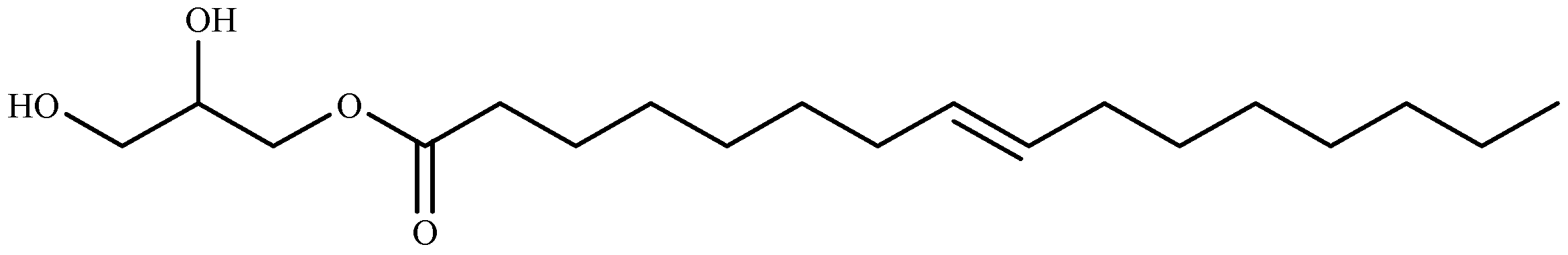
Ten compounds were identified for the first time from green algae Ulva prolifera as three glycoglycerolipids: 1-o-octadecanoic acid-3-o-β-d-galactopyranosyl glycerol (2), 1-o-palmitoyl-3-o-β-d-galactopyranosyl glycerol (4), and 1-o-palmitoyl-2-Ooleoyl-3-o-β-d-galactopyranosyl glycerol (5); two monoglycerides: glycerol monopalmitate (1), 9-hexadecenoic acid, 2,3-dihydroxypropyl ester (3); two terpenoids: loliolide (6), and lsololiolide (7); one lipid-soluble pigments: zeaxanthin (8); one sterol: cholest-5-en-3-ol (9); and one alkaloid: pyrrolopiperazine-2,5-dione (10). Their algicidal activity reveal that compounds 3, 6, and 7 showed the stronger activity. The results also prove that compound 3 (9-hexadecenoic acid, 2,3-dihydroxypropyl ester) (Figure 5), was isolated for the first time from marine macroalgae [147].
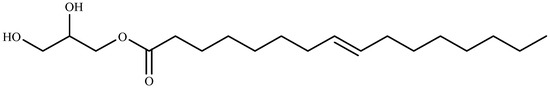
Figure 5.
Structure of 9-hexadecenoic acid, 2,3-dihydroxypropyl ester isolated from Ulva prolifera.
3.2.2. Antioxidant Activity
Among all the compounds contained in macroalgae, antioxidants are the most abundant. They can be classified into two groups, exogenous (vitamin C, vitamin E, and polyphenols) and endogenous antioxidants (enzymes and proteins) [161]. Seaweeds, like all photosynthesizing plants, are exposed to free radical and strong oxidizing agents due to a combination of high light and high oxygen concentration [162,163]. However, the absence of structural damage in the cells of macroalgae and their stability to oxidation during storage, suggests that these cells have protective antioxidative mechanisms and compounds [164,165].
Several studies have investigated the antioxidant activity of natural products in seaweeds. Chang and Teo [161] studied the antioxidant activity of Eucheuma cottonii extract by 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) scavenging method. The result showed that the total phenolic content value for the seaweed extract was 3.40 ± 0.013 mg GAE/g, and the IC50 of E. cottonii crude extract on DPPH was 38.82 ± 0.99 mg/mL. The antioxidant activity of extracts of 48 species of seaweed collected from the coasts of Yucatan and Quintana Roo (Mexico) was evaluated by DPPH scavenging method. All species exhibited a DPPH radical scavenging activity, and Avrainvillea longicaulis demonstrated the largest antioxidant potential with a very low oxidation index EC50 (1.44 ± 0.01 mg/L) with high phenolic content (3.36 ± 0.05% dry wt.), while the lowest antioxidant activity was observed in Enteromorpha intestinalis (43.23 ± 0.28) [166]. The in vitro antioxidant activities of methanol extracts of five selected species (Codium tomentosum, Enteromorpha linza, Gelidium sesquipedale, Cystoseira spicata, and Padina pavonica) of Libyan algae were evaluated by Alghazeer et al. [139]. They found that the maximum antioxidant activity was exhibited significantly by the methanol extract of Cystoseira spicata 199.38 ± 12.73 (199.38 mg of ascorbic acid/g of seaweed dry weight) with a significant high amount of phenolics, flavonoids, and condensed tannins compared with the other extracts whereas, the extract of the green algae Enteromorpha linza exhibited the lowest antioxidant activity (144.05 mg of ascorbic acid/g of seaweed dry weight). Lee et al. [167] studied the in vivo antioxidant activities of fucosterol isolated from the marine algae Pelvetia siliquosa. The results showed that fucosterol produced a significant increase of free radical scavenging enzyme activities such as hepatic cytosolic superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase, and glutathione peroxide (GSH-px) activities by 33.89%, 21.56%, and 39.24%, respectively.
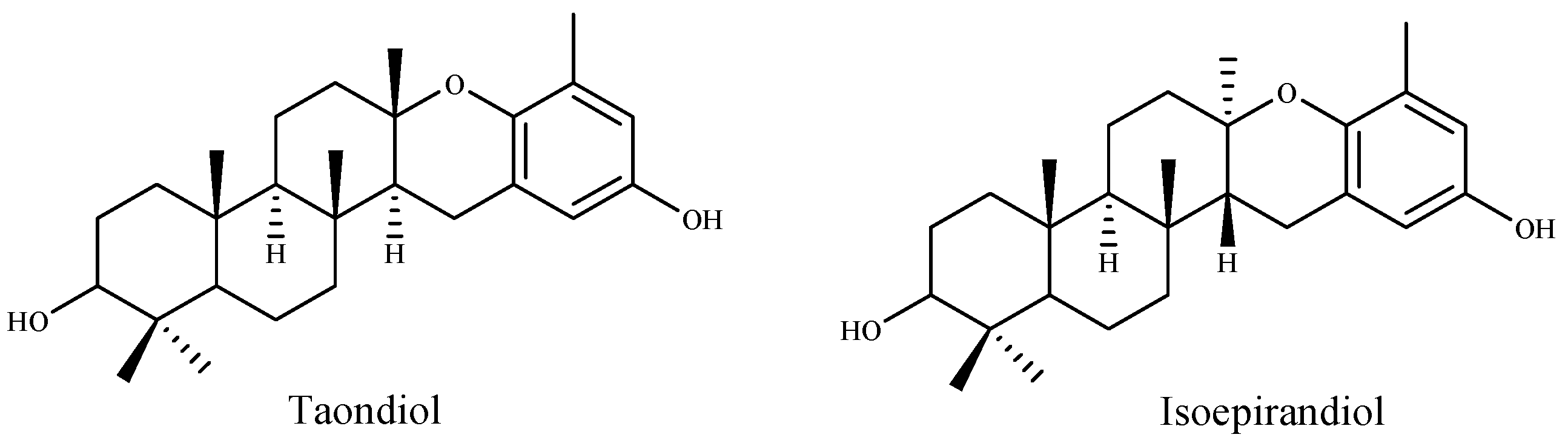
Many researchers have indicated a relation between total phenolic and flavonoid content and high antioxidant activity. Farasat et al., Chai et al. and Alghazeer et al. [168,169,170] reported a positive correlation between antioxidation capacity and the total phenolic and flavonoid contents. Pinteus et al. [171] attributed the strong antioxidant activity to the high phenolic content. They also suggested that high antioxidant activity is not directly linked to a high cytoprotective potential. Contrariwise, Lim et al. and Mamelona et al. [165,172] demonstrated that the antioxidant capacity is not directly correlated with the total phenolic contents. Also, Cho et al. [173] suggested that the antioxidant activity of the extracts from the green algae Enteromorpha prolifera was related to the chlorophyll compound pheophorbide, and not to total phenolic contents. According to ref. [137] the free radical scavenging activity on DPPH was found to be increased with the increase of concentration of methanolic extract of Ulva lactuca. In this study, the IC50 value was lower (81.36 µg/mL) compared to other reported values [161]. Recently, Raja et al. [174] suggested that the antioxidant potential of Eisenia arborea was the most effective followed by Ulva lactuca and Codium fragile. The methanolic extracts were found to contain high phenolic and flavonoid contents with higher antioxidant activities compared to their aqueous extract. Nahas et al. [175] tested the radical scavenging activity (RSA) of thirteen algae from the Aegean Sea by using the DPPH test and chemi-luminescence (CL). The results indicated that the extracts of the brown alga Taonia atomaria exhibited the best RSA in comparison to the other algae extracts. Moreover, they suggested that two metabolites, taondiol and isoepitaondiol (Figure 6), were responsible for the extract antioxidant activity.
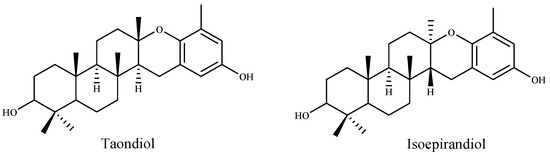
Figure 6.
Antioxidant metabolites of the brown alga Taonia atomaria.
4. Conclusions
Enhanced growth of aquatic vegetation or phytoplankton and algal blooms disrupts normal functioning of aquatic ecosystems all over the world. When toxic microalgae and cyanobacteria are involved in these eutrophication consequences, a variety of ecological, economical, and sanitary health problems could arise. Most of the recent studies on the control of the HABs have focused on the use of chemical, physical, and biological treatment agents but these processes show serious environmental consequences. Among the biological agents, a variety of extracts from aquatic and terrestrial plants, which contain many bioactive compounds, with a wide range of applications and biocides activities have been experimented.
With respect to bioactive compounds extracted from seaweeds, most of them have been applied for their biocidal (anti-fungi, anti-bacteria) and pharmaceutical activities. However, very few reports have focused on their algicide and anti-cyanobacterial activities. In order to explore macroalgae as an alternative and an available natural source of bioactive compounds, we recommend that works could be oriented on the research of new natural products extracted from seaweeds. Seaweed extracts show interesting potential against many harmful microalgae and cyanobacteria species but not much is yet known, namely the structure and mechanisms of action of the effective substances. These substances should be tested for their biocide activities against micro-algae growth in general and particularly against cyanobacteria growth. Research on novel biomolecules is needed in order to better control the phytoplankton excessive growth in a sustainable way, and to maintain the ecological equilibrium and the stability of the aquatic ecosystems.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by FCT Project UID/Multi/04423/2013,by the Structured Program of R&D&I INNOVMAR—Innovation and Sustainability in the Management and Exploitation of Marine Resources (reference NORTE-01-0145-FEDER-000035, Research Line NOVELMAR), funded by the Northern Regional Operational Program (NORTE2020) through the European Regional Development Fund (ERDF) and by the project CVMar+I (0302_CVMAR_I_1_P) funded by the program Interreg V A Espanha—Portugal (POCTEP) 2014-2020.
Author Contributions
All authors wrote the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Catherine, Q.; Susanna, W.; Isidora, E.S.; Mark, H.; Aurelie, V.; Jean-Franeois, H. A review of current knowledge on toxic benthic freshwater cyanobacteria—Ecology, toxin production and risk management. Water Res. 2013, 47, 5464–5479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seder-Colomina, M.; Burgos, A.; Maldonado, J.; Solé, A.; Esteve, I. The effect of copper on different phototrophic microorganisms determined in vivo and at cellular level by confocal laser microscopy. Ecotoxicology 2013, 22, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandrini, G.; Huisman, J.; Matthijs, H.C.P. Potassium sensitivity differs among strains of the harmful cyanobacterium Microcystis and correlates with the presence of salt tolerance genes. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2015, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holdren, C.; Jones, W.; Taggart, J.; Holdren, C.W.; Jones, J. Taggart Managing Lakes and Reservoirs; Terrene Institute: Alexandria, VA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Visser, P.M.; Ibelings, B.W.; Mur, L.R.; Walsby, A.E. The Ecophysiology of the Harmful Cyanobacterium Microcystis. Harmful Cyanobact. 2005, 3, 109–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demeke, A. Cyanobacteria blooms and biological control Methods. Int. J. Fauna Boil. Stud. 2016, 3, 32–38. [Google Scholar]
- Pajdak-Stós, A.; Fiałkowska, E.; Fyda, J. Phormidium autumnale (Cyanobacteria) defense against three ciliate grazer species. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2001, 23, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.H.; Jin, H.J.; Sohn, C.H.; Suh, K.H.; Hong, Y.K. Algicidal activity of the seaweed Corallina pilulifera against red tide microalgae. J. Appl. Phycol. 2000, 12, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Xie, L. Analysis of the influence of meteorological condition on cyanobacterial bloom and treatment methods in Taihu Lake. China Resour. 2011, 29, 35–38. [Google Scholar]
- Schrader, K.K. Natural Algicides for the Control of Cyanobacterial-Related Off-Flavor in Catfish Aquaculture; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.M.; Hu, H.Y. Allelopathic effects of different macrophytes on the growth of Microcystis aeruginosa. Allelopath. J. 2005, 15, 145–151. [Google Scholar]
- Chiang, I.-Z.; Huang, W.-Y.; Wu, J.-T. Allelochemicals of botryococcus braunii (chlorophyceae). J. Phycol. 2004, 40, 474–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Greca, M.; Fiorentino, A.; Monaco, P.; Pinto, G.; Pollio, A.; Previtera, L. Action of antialgal compounds from Juncus effusus L. on Selenastrum capricornutum. J. Chem. Ecol. 1996, 22, 587–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meepagala, K.M.; Schrader, K.K.; Wedge, D.E.; Duke, S.O. Algicidal and antifungal compounds from the roots of Ruta graveolens and synthesis of their analogs. Phytochemistry 2005, 66, 2689–2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belattmania, Z.; Engelen, A.H.; Pereira, H.; Serrão, E.A.; Barakate, M.; Elatouani, S.; Zrid, R.; Bentiss, F.; Chahboun, N.; Reani, A.; et al. Potential uses of the brown seaweed Cystoseira humilis biomass: 2-Fatty acid composition, antioxidant and antibacterial activities. J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 2016, 7, 2074–2081. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.S.; Kim, J.Y.; Choi, W.H.; Lee, S.S. Effects of seaweed supplementation on blood glucose concentration, lipid profile, and antioxidant enzyme activities in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nutr. Res. Pract. 2008, 2, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumari, P.; Kumar, M.; Gupta, V.; Reddy, C.R.K.; Jha, B. Tropical marine macroalgae as potential sources of nutritionally important PUFAs. Food Chem. 2010, 120, 749–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, N.; Dobretsov, S.; Rohde, S.; Schupp, P.J. Comparison of antifouling properties of native and invasive Sargassum (Fucales, Phaeophyceae) species. Eur. J. Phycol. 2017, 52, 116–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Z.; Wang, Z.; Li, F.; Tian, Z.; Hu, H. Allelopathic inhibition on red tide microalgae Skeletonema costatum by five macroalgal extracts. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. China 2008, 2, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Wang, Y.; Tang, X. Identification of the toxic compounds produced by Sargassum thunbergii to red tide microalgae. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2012, 30, 778–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reviers, B. Biologie et Phylohgénie des Algues; Belin Education: Paris, France, 2003; ISBN 2-7011-3512-5. [Google Scholar]
- Paerl, H.W.; Fulton, R.S.; Moisander, P.H.; Dyble, J. Harmful Freshwater Algal Blooms, with an Emphasis on Cyanobacteria. Sci. World J. 2001, 1, 76–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seckbach, J. Algae and Cyanobacteria in Extreme Environments; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Rowell, P.; Kerby, N.W. Cyanobacteria and Their Toxins; Study Plant Science: London, UK, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Stanier, R.Y.; Deruelles, J.; Rippka, R.; Herdman, M.; Waterbury, J.B. Generic Assignments, Strain Histories and Properties of Pure Cultures of Cyanobacteria. Microbiology 1979, 111, 1–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schopf, J.W. The Fossil Record: Tracing the Roots of the Cyanobacterial Lineage. In The Ecology of Cyanobacteria; Potts, M., Whitton, B.A., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2002; pp. 13–35. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.C.; Laurent, S.; Sakr, S.; Peng, L.; Bédu, S. Heterocyst differentiation and pattern formation in cyanobacteria: A chorus of signals. Mol. Microbiol. 2006, 59, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Du, Y.; Khudyakov, I.; Fan, Q.; Gao, H.; Ning, D.; Wolk, C.P.; Xu, X. A gene cluster that regulates both heterocyst differentiation and pattern formation in Anabaena sp. strain PCC 7120. Mol. Microbiol. 2007, 66, 1429–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burja, A.M.; Banaigs, B.; Abou-Mansour, E.; Grant Burgess, J.; Wright, P.C. Marine cyanobacteria—A prolific source of natural products. Tetrahedron 2001, 57, 9347–9377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oufdou, K.; Oudra, B. Substances bioactives élaborées par des cyanobactéries isolées de certains écosystèmes aquatiques marocains. Afr. Sci. 2009, 5, 260–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, E.; Idris, A.; Saparon, A. Papr reduction using scs-slm technique in stfbc mimo-ofdm. ARPN J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2017, 12, 3218–3221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayatissa, L.P.; Silva, E.I.L.; McElhiney, J.; Lawton, L.A. Occurrence of toxigenic cyanobacterial blooms in freshwaters of Sri Lanka. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2006, 29, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearson, L.A.; Neilan, B.A. The molecular genetics of cyanobacterial toxicity as a basis for monitoring water quality and public health risk. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2008, 19, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leflaive, J.; Ten-Hage, L. Algal and cyanobacterial secondary metabolites in freshwaters: A comparison of allelopathic compounds and toxins. Freshw. Biol. 2007, 52, 199–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leão, P.N.; Vasconcelos, M.T.S.; Vasconcelos, V.M. Allelopathic activity of cyanobacteria on green microalgae at low cell densities. Eur. J. Phycol. 2009, 44, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havens, K.E. Cyanobacterial blooms: Effects on aquatic ecosystems. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2008, 619, 733–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millie, D.F.; Weckman, G.R.; Fahnenstiel, G.L.; Carrick, H.J.; Ardjmand, E.; Young, W.A.; Sayers, M.J.; Shuchman, R.A. Using artificial intelligence for CyanoHAB niche modeling: Discovery and visualization of Microcystis—Environmental associations within western Lake Erie. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2014, 71, 1642–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertani, I.; Obenour, D.R.; Steger, C.E.; Stow, C.A.; Gronewold, A.D.; Scavia, D. Probabilistically assessing the role of nutrient loading in harmful algal bloom formation in western Lake Erie. J. Gt. Lakes Res. 2016, 42, 1184–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Cornwell, J.C.; Stoecker, D.K.; Owens, M.S. Influence of cyanobacteria blooms on sediment biogeochemistry and nutrient fluxes. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2014, 59, 959–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verspagen, J.M.H.; Van De Waal, D.B.; Finke, J.F.; Visser, P.M.; Van Donk, E.; Huisman, J. Rising CO2 levels will intensify phytoplankton blooms in eutrophic and hypertrophic lakes. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e104325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sigee, D.C. Freshwater Microbiology: Biodiversity and Dynamic Interactions of Microorganisms in the Aquatic Environment; John Wiley Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Castenholz, R.W. General Characteristics of the Cyanobacteria. In Bergey’s Manual of Systematics of Archaea and Bacteria; John Wiley Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2001; pp. 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Paerl, H.W.; Huisman, J. CLIMATE: Blooms Like It Hot. Science 2008, 320, 57–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeppesen, E.; Brucet, S.; Naselli-Flores, L.; Papastergiadou, E.; Stefanidis, K.; Nõges, T.; Nõges, P.; Attayde, J.L.; Zohary, T.; Coppens, J.; et al. Ecological impacts of global warming and water abstraction on lakes and reservoirs due to changes in water level and related changes in salinity. Hydrobiologia 2015, 750, 201–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasil, J.; Attayde, J.L.; Vasconcelos, F.R.; Dantas, D.D.F.; Huszar, V.L.M. Drought-induced water-level reduction favors cyanobacteria blooms in tropical shallow lakes. Hydrobiologia 2016, 770, 145–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masó, M.; Garcés, E. Harmful microalgae blooms (HAB); problematic and conditions that induce them. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2006, 53, 620–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrantes, N.; Antunes, S.C.; Pereira, M.J.; Gonçalves, F. Seasonal succession of cladocerans and phytoplankton and their interactions in a shallow eutrophic lake (Lake Vela, Portugal). Acta Oecol. 2006, 29, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zingone, A.; Oksfeldt Enevoldsen, H. The diversity of harmful algal blooms: A challenge for science and management. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2000, 43, 725–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.L.; Boyer, G.L.; Zimba, P.V. A review of cyanobacterial odorous and bioactive metabolites: Impacts and management alternatives in aquaculture. Aquaculture 2008, 280, 5–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robin, J.; Cravedi, J.P.; Hillenweck, A.; Deshayes, C.; Vallod, D. Off flavor characterization and origin in French trout farming. Aquaculture 2006, 260, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jüttner, F.; Watson, S.B. Biochemical and ecological control of geosmin and 2-methylisoborneol in source waters. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 4395–4406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, J.L.; Loftin, K.A.; Meyer, M.T.; Ziegler, A.C. Cyanotoxin mixtures and taste-and-odor compounds in cyanobacterial blooms from the midwestern united states. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 7361–7368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oudra, B.; Loudiki, M.; Vasconcelos, V.; Sabour, B.; Sbiyyaa, B.; Oufdou, K.; Mezrioui, N. Detection and quantification of microcystins from cyanobacteria strains isolated from reservoirs and ponds in Morocco. Environ. Toxicol. 2002, 17, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loudiki, M.; Oudra, B.; Sabour, B.; Sbiyyaa, B.; Vasconcelos, V. Taxonomy and geographic distribution of potential toxic cyanobacterial strains in Morocco. Ann. Limnol. Int. J. Limnol. 2002, 38, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douma, M.; Ouahid, Y.; Campo, F.F.; del Loudiki, M.; Mouhri, K.; Oudra, B. Identification and quantification of cyanobacterial toxins (microcystins) in two Moroccan drinking-water reservoirs (Mansour Eddahbi, Almassira). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2010, 160, 439–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, I.; Schluter, P.J.; Shaw, G.R. Cyanobacterial lipopolysaccharides and human health—A review. Environ. Health 2006, 5, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dodds, W.K.; Bouska, W.W.; Eitzmann, J.L.; Pilger, T.J.; Pitts, K.L.; Riley, A.J.; Schloesser, J.T.; Thornbrugh, D.J. Policy Analysis Eutrophication of U.S. Freshwaters: Damages. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibelings, B.W.; Chorus, I. Accumulation of cyanobacterial toxins in freshwater “seafood” and its consequences for public health: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2007, 150, 177–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Khalloufi, F.; El Ghazali, I.; Saqrane, S.; Oufdou, K.; Vasconcelos, V.; Oudra, B. Phytotoxic effects of a natural bloom extract containing microcystins on Lycopersicon esculentum. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2012, 79, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Khalloufi, F.; Oufdou, K.; Bertrand, M.; Lahrouni, M.; Oudra, B.; Ortet, P.; Barakat, M.; Heulin, T.; Achouak, W. Microbiote shift in the Medicago sativa rhizosphere in response to cyanotoxins extract exposure. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 539, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shavyrina, O.B.; Gapochka, L.D.; Azovskii, A.I. Development of tolerance for copper in cyanobacteria repeatedly exposed to its toxic effect. Biol. Bull. 2001, 28, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Villada, L.; Rico, M.; Altamirano, M.; Sánchez-Martín, L.; López-Rodas, V.; Costas, E. Occurrence of copper resistant mutants in the toxic cyanobacteria Microcystis aeruginosa: Characterisation and future implications in the use of copper sulphate as algaecide. Water Res. 2004, 38, 2207–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magnusson, M.; Heimann, K.; Quayle, P.; Negri, A.P. Additive toxicity of herbicide mixtures and comparative sensitivity of tropical benthic microalgae. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2010, 60, 1978–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prosecka, J.; Orlov, A.V.; Fantin, Y.S.; Zinchenko, V.V.; Babykin, M.M.; Tichy, M. A novel ATP-binding cassette transporter is responsible for resistance to viologen herbicides in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. FEBS J. 2009, 276, 4001–4011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, T.J.; Nakano, K.; Matsumura, M. A novel strategy for cyanobacterial bloom control by ultrasonic irradiation. Water Sci. Technol. 2002, 46, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cooke, G.D.; Welch, E.B.; Peterson, S.; Nichols, S.A. Restoration and Management of Lakes and Reservoirs; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Klapper, H. Technologies for lake restoration. J. Limnol. 2003, 62, 73–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wu, G.; Ao, H.; Qiu, C. Mechanical removal of heavy cyanobacterial bloom in the hyper-eutrophic lake Dianchi. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 2004, 28, 131–136. [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro, J.; Lamarra, V.; Lynch, M. Biomanipulation: An Ecosystem Approach to Lake Restoration; Limnological Research Center, University of Minnesota: Minneapolis, MN, USA, 1975; pp. 85–96. [Google Scholar]
- Van Donk, E.; Van de Bund, W.J. Impact of submerged macrophytes including charophytes on phyto- and zooplankton communities: Allelopathy versus other mechanisms. Aquat. Bot. 2002, 72, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erhard, D.; Gross, E.M. Allelopathic activity of Elodea canadensis and Elodea nuttallii against epiphytes and phytoplankton. Aquat. Bot. 2006, 85, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.H.; Chung, I.M.; Ahmad, A.; Kim, B.H.; Hwang, S.J. Growth inhibition of unicellular and colonial Microcystis strains (Cyanophyceae) by compounds isolated from rice (Oryza sativa) hulls. Aquat. Bot. 2009, 90, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Liu, B.; Wang, J.; Gao, Y.; Wu, Z. Study on the mechanism of allelopathic influence on cyanobacteria and chlorophytes by submerged macrophyte (Myriophyllum spicatum) and its secretion. Aquat. Toxicol. 2010, 98, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Hu, H. Isolation and Characterization of a Novel Antialgal Allelochemical from Phragmites communis. Society 2005, 71, 6545–6553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, S.; Jiao, L.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y. Physiological response of a submerged plant (Myriophyllum spicatum) to different NH4Cl concentrations in sediments. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 58, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liang, F.; Qiao, N.; Dong, J.; Zhang, L.; Guo, Y. Chemical Composition of Volatile Oil from Two Emergent Plants and Their Algae Inhibition Activity. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2014, 23, 2371–2374. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, J.; Yang, K.; Li, S.; Li, G.; Song, L. Submerged vegetation removal promotes shift of dominant phytoplankton functional groups in a eutrophic lake. J. Environ. Sci. 2014, 26, 1699–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Liang, F.; Zhang, L. Composition and anti-cyanobacterial activity of essential oils from six different submerged macrophytes. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2015, 24, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, P.; Zeng, G.; Cai, X.; Liu, S.; Yin, Y.; Hu, X.; Hu, X.; Tan, X. Growth inhibition and oxidative damage of Microcystis aeruginosa induced by crude extract of Sagittaria trifolia tubers. J. Environ. Sci. 2016, 43, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, P.; Pei, H.; Hu, W.; Liu, Z.; Li, X.; Xu, H. Allelopathic effects of Ailanthus altissima extracts on Microcystis aeruginosa growth, physiological changes and microcystins release. Chemosphere 2015, 141, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najem, A.M.; Abed, I.J.; Al-haidari, A.M.D. Evaluation the Activity of Rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis L.) Essential Oil Against Some Cyanobacteria. Iraqi J. Biotechnol. 2016, 15, 97–102. [Google Scholar]
- Tellez, M.R.; Dayan, F.E.; Schrader, K.K.; Wedge, D.E.; Duke, S.O. Composition and some biological activities of the essential oil of Callicarpa americana (L.). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 3008–3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Jin, H.; Zhang, L.; Hu, W.; Li, Y.; Xu, N. Screening and isolation of the algicidal compounds from marine green alga Ulva intestinalis. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2016, 34, 781–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.Y.; Meng, K.; Su, Z.; Guo, G.L.; Pu, Y.F.; Wang, C. Isolation and purification of antialgal compounds from the red alga Gracilaria lemaneiformis for activity against common harmful red tide microalgae. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 4964–4972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagarajan, S.; Mathaiyan, M. Emerging novel anti HIV biomolecules from marine Algae: An overview. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 5, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Sullivan, L.; Murphy, B.; McLoughlin, P.; Duggan, P.; Lawlor, P.G.; Hughes, H.; Gardiner, G.E. Prebiotics from marine macroalgae for human and animal health applications. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 2038–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siriwardhana, N.; Jeon, Y.-J.; Kim, S.-H.; Ha, J.-H.; Heo, S.-J.; Lee, K.-W. Enzymatic Hydrolysis for Effective Extraction of Antioxidative Compounds from Hizikia fusiformis. Algae 2004, 19, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, Y.; Rasoul-Amini, S.; Morowvat, M.H. Algae for the Production of SCP; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 163–184. [Google Scholar]
- Laouina, A. Prospective “Maroc 2030”: Gestion Durable des Ressources Naturelles de la Biodiversité au Maroc; Haut-Commissariat au Plan (HCP): Casablanca, Marocco, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Chalabi, A.; Semroud, R.; Grimes, S. Plan d’Action Stratégique pour la Conservation de la Diversité Biologique en Région Méditerranéenne; National PAS-BIO Algérie, Ministère de l’Aménagement du Territoire et de l’Environnement: Algiers, Algérie, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Sasidharan, S.; Aravindran, S.; Latha, L.Y.; Vijenthi, R.; Saravanan, D.; Amutha, S. In vitro antioxidant activity and hepatoprotective effects of lentinula edodes against paracetamol-induced hepatotoxicity. Molecules 2010, 15, 4478–4489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lane, A.L.; Mular, L.; Drenkard, E.J.; Shearer, T.L.; Fredericq, S.; Fairchild, C.R.; Prudhomme, J.; Roch, K.; Hay, M.E.; Aalbersberg, W.; et al. Ecological leads for natural product discovery: Novel sesquiterpene hydroquinones from the red macroalga Peyssonnelia sp. Tetrahedron 2011, 66, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vairappan, C.S.; Suzuki, M.; Ishii, T.; Okino, T.; Abe, T.; Masuda, M. Antibacterial activity of halogenated sesquiterpenes from Malaysian Laurencia spp. Phytochemistry 2008, 69, 2490–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodgkin, H.; Craige, S.J.; Mcinnes, G. The occurrence of 2,3-dibromobenzyl alcohol 4,5-disulfate, dipotassium salt, in Polysiphonia lanosa. Can. J. Chem. 1966, 44, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenical, W.; Sims, J.J.; Wing, R.M.; Radlick, P.C. Zonarene, a sesquiterpene from the brown seaweed Dictyopteris zonarioides. Phytochemistry 1972, 11, 1161–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamei, Y.; Sueyoshi, M.; Hayashi, K.; Terada, R.; Nozaki, H. The novel anti-Propionibacterium acnes compound, Sargafuran, found in the marine brown alga Sargassum macrocarpum. J. Antibiot. 2009, 62, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, N.Y.; Li, X.M.; Li, K.; Ding, L.P.; Gloer, J.B.; Wang, B.G. Diterpenes, sesquiterpenes, and a C15-acetogenin from the marine red alga Laurencia mariannensis. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 1901–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosaline, X.D.; Sakthivelkumar, S.; Rajendran, K.; Janarthanan, S. Screening of selected marine algae from the coastal Tamil Nadu, South India for antibacterial activity. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2012, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, J.K.; Srinivas, T.; Sawhney, S. Antibacterial Activity of Seaweed Halimeda Opuntia From the coasts of south andaman. Glob. J. Biosci. Biotechnol. 2016, 5, 345–348. [Google Scholar]
- Taskin, E.; Ozturk, M.; Kurt, O. Antibacterial activities of some marine algae from the Aegean Sea (Turkey). Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2007, 6, 2746–2751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortés, Y.; Hormazábal, E.; Leal, H.; Urzúa, A.; Mutis, A.; Parra, L.; Quiroz, A. Novel antimicrobial activity of a dichloromethane extract obtained from red seaweed Ceramium rubrum (Hudson) (Rhodophyta: Florideophyceae) against Yersinia ruckeri and Saprolegnia parasitica, agents that cause diseases in salmonids. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 2014, 17, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvador, N.; Garreta, A.G.; Lavelli, L.; Ribera, M.A. Antimicrobial activity of Iberian macroalgae. Sci. Mar. 2007, 71, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangaiah, G.S.; Lakshmi, P.; Sruthikeerthi, K. Antimicrobial activity of the crude extracts of Chlorophycean seaweeds Ulva, Caulerpa and Spongomorpha sps. against clinical and phytopathogens. Drug Invent. Today 2010, 2, 311–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seenivasan, R.; Indu, H.; Archana, G.; Geetha, S. The Antibacterial Activity of Some Marine Algae from South East Coast of India. Environ. Sci. 2010, 9, 480–489. [Google Scholar]
- Lavanya, R.; Veerappan, N.; Nadu, P.-T. Antibacterial Potential of Six Seaweeds Collected from Gulf of Mannar of Southeast Coast of India. Adv. Biol. Res. 2011, 5, 38–44. [Google Scholar]
- Pandian, P.; Selvamuthukumar, S.; Manavalan, R. Screening of antibacterial and antifungal activities of red marine algae Acanthaphora spicifera (Rhodophyceae). J. Biomed. Sci. Res. 2011, 3, 444–448. [Google Scholar]
- Kausalya, M.; Rao, G.M.N. Antimicrobial activity of marine Algae. J. Algal Biomass Util. 2015, 6, 78–87. [Google Scholar]
- Shanmughapriya, S.; Manilal, A.; Sujith, S.; Selvin, J.; Kiran, G.S.; Natarajaseenivasan, K. Antimicrobial activity of seaweeds extracts against multiresistant pathogens. Ann. Microbiol. 2008, 58, 535–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolsi, R.B.A.; Frikha, D.; Jribi, I.; Hamza, A.; Feki, L.; Belghith, K. Screening of antibacterial and antifongical activity in marine macroalgae and magnoliophytea from the coast of Tunisia. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 7, 47–51. [Google Scholar]
- Baleta, F.N.; Bolaños, J.M.; Ruma, O.C.; Baleta, A.N.; Cairel, J.D. Phytochemicals screening and antimicrobial properties of Sargassum oligocystum and Sargassum crassifolium Extracts. J. Med. Plants 2017, 5, 382–387. [Google Scholar]
- Radhika, D.; Priya, R. Antifungal Activity of Acanthophora Spicifera, Padina Tetrastomatica and Caulerpa Scalpelliformis Against Some Fungal Pathogens in Crude and Fractionated. World J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 5, 1155–1162. [Google Scholar]
- Tüney, I.; Çadirci, B.H.; Ünal, D.; Sukatar, A. Antimicrobial Activities of the Extracts of Marine Algae from the Coast of Urla (Izmir, Turkey). Turk. J. Biol. 2006, 30, 171–175. [Google Scholar]
- Moorthi, P.V.; Balasubramanian, C. Antimicrobial properties of marine seaweed, Sargassum muticum against human pathogens. J. Coast. Life Med. 2015, 3, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, S.; Abu-Ghannam, N.; Gupta, S. An assessment of the antioxidant and antimicrobial activity of six species of edible Irish seaweeds. Int. Food Res. J. 2010, 17, 205–220. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues, D.; Freitas, A.C.; Pereira, L.; Rocha-Santos, T.A.P.; Vasconcelos, M.W.; Roriz, M.; Rodríguez-Alcalá, L.M.; Gomes, A.M.P.; Duarte, A.C. Chemical composition of red, brown and green macroalgae from Buarcos bay in Central West Coast of Portugal. Food Chem. 2015, 183, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez, M.J.; Falqué, E.; Domínguez, H. Antimicrobial action of compounds from marine seaweed. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reguant, C.; Bordons, A.; Arola, L.; Rozès, N. Influence of phenolic compounds on the physiology of Oenococcus oeni from wine. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2000, 88, 1065–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberto, M.R.; Farías, M.E.; Manca De Nadra, M.G. Effect of gallic acid and catechin on Lactobacillus hilgardii 5w growth and metabolism of organic compounds. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 4359–4363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; Liu, Q.; Xu, C.; Yu, J.; Zhao, L.; Guo, Q. Damage to the Membrane Permeability and Cell Death of Vibrio parahaemolyticus Caused by Phlorotannins with Low Molecular Weight from Sargassum thunbergii. J. Aquat. Food Prod. Technol. 2016, 25, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagayama, K.; Shibata, T.; Fujimoto, K.; Honjo, T.; Nakamura, T. Algicidal effect of phlorotannins from the brown alga Ecklonia kurome on red tide microalgae. Aquaculture 2003, 218, 601–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameer, J.; Begum, M.; Selvaraju, P.; Vijayakumar, A. Evaluation of antifungal activity of seaweed extract (Turbinaria conoides) against Fusarium oxysporum. Chem. Sci. Rev. Lett. 2016, 9411, 2014–2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kosanić, M.; Ranković, B.; Stanojković, T. Biological potential of marine macroalgae of the genus Cystoseira. Acta Biol. Hung. 2015, 66, 374–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xavier, D.R. Antibacterial activity of the seaweeds Chaetomorpha linum and Padina gymnospora on human bacterial pathogens. J. Environ. Biotechnol. Res. 2017, 6, 43–52. [Google Scholar]
- Moubayed, N.M.S.; Al Houri, H.J.; Al Khulaifi, M.M.; Al Farraj, D.A. Antimicrobial, antioxidant properties and chemical composition of seaweeds collected from Saudi Arabia (Red Sea and Arabian Gulf). Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2017, 24, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhagavathy, S.; Sumathi, P.; Jancy Sherene Bell, I. Green algae Chlorococcum humicola—A new source of bioactive compounds with antimicrobial activity. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2011, 1, S1–S7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Saif, S.S.A.; Abdel-Raouf, N.; El-Wazanani, H.A.; Aref, I.A. Antibacterial substances from marine algae isolated from Jeddah coast of Red sea, Saudi Arabia. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2014, 21, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renata, C.C.; Paula, F.F.; Isabel, R.A.; Ana, P.S.; Vera, L.; Maria, T.; Alexandre, G. Antimicrobial activity of seaweeds of Pernambuco, northeastern coast of Brazil. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2016, 10, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Shafay, S.M.; Ali, S.S.; El-Sheekh, M.M. Antimicrobial activity of some seaweeds species from Red sea, against multidrug resistant bacteria. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2016, 42, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khelil-Radji, F.; Belhouari, M.Y.; Chemlal-Kherraz, D.; Matallah-Boutiba, A.; Boutiba, Z. Antimicrobial activity of aqueous and ethanol extracts of two marine algae collected from Algerian west coast. Electron. J. Environ. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 6655, 100–104. [Google Scholar]
- Genovese, G.; Leitner, S.; Minicante, S.A.; Lass-Flörl, C. The Mediterranean red alga Asparagopsis taxiformis has antifungal activity against Aspergillus species. Mycoses 2013, 56, 516–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Eom, S.; Lee, E.; Jung, Y.; Kim, H.; Jo, M.; Son, K.; Lee, H.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, M.; et al. In vitro antibacterial and synergistic effect of phlorotannins isolated from edible brown seaweed Eisenia bicyclis against acne-related bacteria. Algae 2014, 29, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nithya, P.; Dhanalakshmi, B. Antibacterial activity of methanol extracts from selected seaweed of south east coast of India. Int. J. Adv. Res. 2016, 2, 714–718. [Google Scholar]
- Sahnouni, F.; Benattouche, Z.; Matallah-Boutiba, A.; Benchohra, M.; Moumen Chentouf, W.; Bouhadi, D.; Boutiba, Z. Antimicrobial activity of two marine algae Ulva rigida and Ulva intestinalis collected from Arzew gulf (Western Algeria). J. Appl. Environ. Biol. Sci. 2016, 6, 242–248. [Google Scholar]
- Shobier, A.H.; Abdel Ghani, S.A.; Barakat, K.M. GC/MS spectroscopic approach and antifungal potential of bioactive extracts produced by marine macroalgae. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2016, 42, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-zahrani, A.; Omer, H.; Al-judaibi, A. Impact of Antibacterial Activity of Physical Storage Extracts on Pathogenic Bacteria. J. Biosci. Med. 2016, 4, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daisy, A.; Indra, V.; Geetha, S.; Seetharaman, S.; Selvamuthu, B.; Nadu, T. Phytochemical Profiling and Antibacterial Activity of Seaweeds Collected From Pulicate Lake, Coramandal Coast of South India. World J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 5, 740–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alagan, V.; Valsala, R.; Rajesh, K. Bioactive Chemical Constituent Analysis, in vitro Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Activity of Whole Plant Methanol Extracts of Ulva lactuca Linn. Br. J. Pharm. Res. 2017, 15, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, V.; Jawahar, P.; Shakila, R.J.; Srinivasan, A. Antibacterial Activity of Some Brown Seaweeds of Gulf Of Mannar, South East Coast of India. J. Pharm. Biosci. 2017, 4, 14–21. [Google Scholar]
- Alghazeer, R.; Whida, F.; Abduelrhman, E.; Gammoudi, F.; Azwai, S. Screening of antibacterial activity in marine green, red and brown macroalgae from the western coast of Libya. Nat. Sci. 2013, 5, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebaaly, C.; Kassem, S.; Grishina, E.; Kanaan, H.; Sweidan, A.; Chmit, M.S.; Kanaan, H.M. Anticoagulant and antibacterial activities of polysaccharides of red algae Corallina collected from lebanese coast. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 4, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rameshkumar, S.; Kolidoss, R.; Arasan, S. Antibacterial activity of four Gracilaria species of red seaweeds collected from Mandapam Coast, Gulf of Mannar Marine Biosphere Reserve, India. J. Coast. Life Med. 2016, 4, 703–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamsjah, M.A.; Hirao, S.; Ishibashi, F.; Fujita, Y. Isolation and structure determination of algicidal compounds from Ulva fasciata. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2005, 69, 2186–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Feng, L.; Tang, X.; Wang, J.; Dong, S. Allelopathic growth inhibition of Heterosigma akashiwo by the three Ulva spcieces (Ulva Pertusa, Ulva Linza, Enteromorpha intestinalis) under laboratory conditions. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2012, 31, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manilal, A.; Sujith, S.; Seghal Kiran, G.; Selvin, J.; Panikkar, M.V.N. Evaluation of seaweed bioactives on common aquatic floral and faunal weeds of shrimp ponds. Thalassas 2011, 27, 47–56. [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury, M.T.H.; Bangoura, I.; Kang, J.-Y.; Cho, J.Y.; Joo, J.; Choi, Y.S.; Hwang, D.S.; Hong, Y.-K. Comparison of Ecklonia cava, Ecklonia stolonifera and Eisenia bicyclis for phlorotannin extraction. J. Environ. Biol. 2014, 35, 713. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nan, C.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, G. Allelopathic interactions between the macroalga Ulva pertusa and eight microalgal species. J. Sea Res. 2004, 52, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, H.; Guo, G.; Pu, Y.; Yan, B.; Wang, C. Isolation, purification, and identification of antialgal substances in green alga Ulva prolifera for antialgal activity against the common harmful red tide microalgae. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 1449–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, J.Y.; Kwon, E.H.; Choi, J.S.; Hong, S.Y.; Shin, H.W.; Hong, Y.K. Antifouling activity of seaweed extracts on the green alga Enteromorpha prolifera and the mussel Mytilus edulis. J. Appl. Phycol. 2001, 13, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Xia, Y.; Xu, N.; Cai, X. Inhibitory effects of marine alga Enteromorpha intestinalis on the growth of the red tide microalga Prorocentrum micans. In Proceedings of the World Automation Congress, Puerto Vallarta, Mexico, 24–28 June 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Zhou, B.; Tang, X. Effects of two species of macroalgae—Ulva pertusa and Gracilaria lemaneiformis—On growth of Heterosigma akashiwo (Raphidophyceae). J. Appl. Phycol. 2009, 21, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, C.; Zhang, M. Allelopathic Effect of Macroalga Gracilaria Tenuistipitata (Rhodophyta) on the Photosynthetic Apparatus of Red-tide Causing Microalga Prorocentrum micans. IERI Procedia 2013, 5, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.Z.; Gobler, C.J. The green macroalga, Ulva lactuca, inhibits the growth of seven common harmful algal bloom species via allelopathy. Harmful Algae 2011, 10, 480–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Xiao, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, W.; Tang, X. Effects of three macroalgae, Ulva linza (Chlorophyta), Corallina pilulifera (Rhodophyta) and Sargassum thunbergii (Phaeophyta) on the growth of the red tide microalga Prorocentrum donghaiense under laboratory conditions. J. Sea Res. 2007, 58, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manilal, A.; Sujith, S.; Sabarathnam, B.; Kiran, G.S.; Selvin, J.; Shakir, C.; Lipton, A.P. Bioactivity of the red algae Asparagopsis taxiformis collected from the southwestern coast of India. Braz. J. Oceanogr. 2010, 58, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramitha, V.S.; Lipton, A.P. Growth responses of microalgae, chlorella salina and isochrysis galbana exposed to extracts of the macroalga, Hypnea musciformis. Indian J. Fish. 2011, 58, 95–99. [Google Scholar]
- Ying, S.; Hui, W.; Gan, G.; Yin, P.; Bin, Y.; Chang, W. Green Alga Ulva pertusa—A new source of bioactive compounds with antialgal activity. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 10351–10359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, M.Y.; Lee, S.B.; Jin, D.H.; Hong, Y.K.; Jin, H.J. Isolation of algicidal compounds from the red Alga Corallina pilulifera against red tide microalgae. J. Appl. Phycol. 2010, 22, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamouda, M.H.H.; Karim-Eldeen, N.E. Potentiality and Biological Activities of the Polysaccharide. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 6, 373–392. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Sun, J.; Tang, X. Algicidal activity of Ulva pertusa and Ulva prolifera on Prorocentrum donghaiense under laboratory conditions. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2013, 7, 4389–4396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakisawa, H.; Asari, F.; Kusumi, T.; Toma, T.; Sakurai, T.; Oohusa, T.; Hara, Y.; Chiharai, M. An allelopathic fatty acid from the brown alga Cladosiphon okamuranus. Phytochemistry 1988, 27, 731–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, V.S.; Teo, S.S. Evaluation of heavy metal, antioxidant and anti-tyrosinase activities of red seaweed (Eucheuma cottonii). Int. Food Res. J. 2016, 23, 2370–2373. [Google Scholar]
- Shalaby, E.A.; Shanab, S.M.M.; El-Fayoumy, E.A. Enteromorpha compressa exhibits potent antioxidant activity. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2011, 2011, 726405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mole Megha, N.; Sabale Anjali, B. Antioxidant Potential of Seaweeds from Kunakeshwar along the West Coast Maharashtra. Asian J. Biomed. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 3, 45–50. [Google Scholar]
- Matsukawa, R.; Dubinsky, Z.; Kishimoto, E.; Masaki, K.; Masuda, Y.; Takeuchi, T.; Chihara, M.; Yamamoto, Y.; Niki, E.; Karube, I. A comparison of screening methods for antioxidant activity in seaweeds. J. Appl. Phycol. 1997, 9, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.N.; Cheung, P.C.K.; Ooi, V.E.C.; Ang, P.O. Evaluation of antioxidative activity of extracts from a brown seaweed, Sargassum siliquastrum. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 3862–3866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zubia, M.; Robledo, D.; Freile-Pelegrin, Y. Antioxidant activities in tropical marine macroalgae from the Yucatan Peninsula, Mexico. J. Appl. Phycol. 2007, 19, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Lee, Y.S.; Jung, S.H.; Kang, S.S.; Shin, K.H. Anti-oxidant activities of fucosterol from the marine algae Pelvetia siliquosa. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2003, 26, 719–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farasat, M.; Khavari-Nejad, F.A.; Nabavi, S.M.B.; Namjooyan, F. Antioxidant Properties of two Edible Green Seaweeds from northern coasts of the Persian Gulf. Jundishapur J. Nat. Pharm. Prod. 2013, 8, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, T.T.; Kwek, M.T.; Ismail, N.I.M.; Ooi, J.L.S.; Amri, A.Y.; Manan, F.A.; Law, Y.C.; Wong, F.C. Antioxidant Activities of Methanol Extract and Solvent Fractions of Marine Macroalga, Avrainvillea Erecta (Berkeley) a. Gepp and E.S. Gepp (Dichotomosiphonaceae). Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2015, 14, 503–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghazeer, R.; Elmansori, A.; Sidati, M.; Gammoudi, F.; Azwai, S. In Vitro Antibacterial Activity of Flavonoid Extracts of Two Selected Libyan Algae against Multi-Drug Resistant Bacteria Isolated from Food Products. J. Biosci. Med. 2017, 5, 27–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinteus, S.; Silva, J.; Alves, C.; Horta, A.; Fino, N.; Rodrigues, A.I.; Mendes, S.; Pedrosa, R. Cytoprotective effect of seaweeds with high antioxidant activity from the Peniche coast (Portugal). Food Chem. 2017, 218, 591–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamelona, J.; Pelletier, É.; Girard-Lalancette, K.; Legault, J.; Karboune, S.; Kermasha, S. Quantification of phenolic contents and antioxidant capacity of Atlantic sea cucumber, Cucumaria frondosa. Food Chem. 2007, 104, 1040–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, M.; Lee, H.S.; Kang, I.J.; Won, M.H.; You, S. Antioxidant properties of extract and fractions from Enteromorpha prolifera, a type of green seaweed. Food Chem. 2011, 127, 999–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raja, R.; Hemaiswarya, S.; Arunkumar, K.; Carvalho, I.S. Antioxidant activity and lipid profile of three seaweeds of Faro, Portugal. Braz. J. Bot. 2016, 39, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahas, R.; Abatis, D.; Anagnostopoulou, M.A.; Kefalas, P.; Vagias, C.; Roussis, V. Radical-scavenging activity of Aegean Sea marine algae. Food Chem. 2007, 102, 577–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).