Abstract
Two novel aspochalasins, tricochalasin A (1) and aspochalasin A2 (2), along with three known compounds (3–5) have been isolated from the different culture broth of Aspergillus sp., which was found in the gut of a marine isopod Ligia oceanica. Compound 1 contains a rare 5/6/6 tricyclic ring fused with the aspochalasin skeleton. The structures were determined on the basis of electrospray ionisation mass spectroscopy (ESIMS), nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectral data, and the absolute configurations were further confirmed by modified Mosher’s method. Cytotoxicity against the prostate cancer PC3 cell line were assayed by the MTT method. Compound 3 showed strong activity while the remaining compounds showed weak activity.
1. Introduction
Aspochalasins constitute a subgroup within the small group of cytochalasans, which are fungal secondary metabolites known for varieties of biological activities [1]. These include cytotoxic [2,3,4], anti human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) [5], immunomodulatory [6], and nematicidal activity [7]. So far, more than 200 cytochalasan analogues have been reported [1]. Structurally, this group of compounds contains one isoindole unit fused with one macrocyclic ring. Isotope-labeling experiments have revealed that cytochalasans originate from an acetyl- and methionine-derived polyketide chain and the attachment of an amino acid precursors such as Leu, Phe, Ala and Trp [8,9]. With diverse oxygenated regions in the macrocyclic ring, there are several unusual analogues among these known compounds including chaetochalasin A [10], aspergillin PZ [11], spicochalasin A [12], epicochalasines A and B [13]. In our ongoing search for new bioactive metabolites of marine fungi, some new compounds have been purified from the marine-derived fungus Z4 [14,15,16,17], and one strain isolated from the gut of the marine isopod Ligia oceanica. In order to find more novel natural products from this fungus, we employed the OSMAC (one strain, many compounds) approach by varying the culture conditions of Z4. Two new cytochalasans, aspochalasins 1 and 2, in addition to three known cytochalasans, aspochalasins 3–5 (Figure 1) were purified when cultured in media 2216E and rice. Herein we present the isolation, structure elucidation, and cytotoxic activity of these aspochalasins.
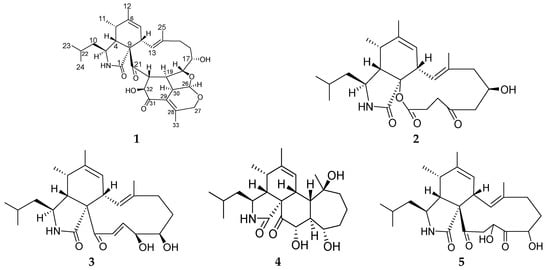
Figure 1.
Structures of compounds 1–5.
2. Results and Discussion
Compound 1 was purified as a colorless solid. The molecular formula C32H43NO7 with 12 degrees of unsaturation was established by the positive mode quasi-molecular ion peaks at m/z 554.3107 for [M + H]+ (calcd. 554.3073 for C32H44NO7) and m/z 576.2930 for [M + Na]+ (calcd. 576.2893 for C32H43NO7Na) combined with 1D nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) data. The 1H NMR spectrum recorded in CDCl3 together with heteronuclear single quantum coherence (HSQC) spectra revealed six methyl groups [δH 0.93 (3H, d, J = 6.4 Hz), 0.96 (3H, d, J = 6.4 Hz), 1.18 (3H, d, J = 7.1 Hz), 1.57 (3H, s), 1.77 (3H, s), 1.85 (3H, s)], two olefinic protons [δH 5.45 (1H, br s), δH 5.70 (1H, d, J = 11.4 Hz)], three oxygenated methine hydrogen atoms [δH 4.35 (1H, d, J = 6.29 Hz), δH 4.42 (1H, dd, J = 3.6, 11.1 Hz), δH 3.86 (1H, d, J = 11.3 Hz)], one oxygenated methylene proton [δH 4.79 (2H, m)], one proton of acetal group [δH 5.91 (1H, d, J = 3.9 Hz)] and other 18 aliphatic protons. The 13C NMR and distortionless enhancement by polarization transfer (DEPT) spectra of 1 indicated 32 carbon resonances ascribed to two ketone carbonyl, one amide carbonyl, six olefinic carbons, five oxygenated carbons including one acetal carbon, 12 aliphatic carbon atoms and six methyl carbons (Table 1). These features characteristically revealed the structure of 1 to be an aspochalasin skeleton. The excess number of carbon atoms when compared to the previously isolated and reported aspochalasin derivatives [18,19], indicated that 1 was an unusual one.

Table 1.
Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopic data of compounds 1 and 2 in CDCl3.
The planar structure of 1 was elucidated by 2D NMR spectrum. The 1H-1H correlation spectroscopy (COSY) cross peaks (Figure S8 in Supplementary Materials) of Me-23 (δH 0.93)/Me-24 (δH 0.96)/H-22 (δH 1.53)/H-10 (δH 1.49, 1.25)/H-3 (δH 2.97)/H-4 (δH 2.81)/H-5 (δH 2.67)/Me-11 (δH 1.18), H-7 (δH 5.45)/H-8 (δH 3.61)/H-13 (δH 5.70), H-15 (δH 2.07)/H-16 (δH 1.50, 1.30)/H-17 (δH 4.35) and heteronuclear multiple bond correlation (HMBC) correlations (Figure S9) from Me-12 (δH 1.77) to C-5 (δC 35.9), C-6 (δC 140.6) and C-7 (δC 125.6), from Me-25 (δH 1.57) to C-13 (δC 125.1), C-14 (δC 135.9) and C-15 (δC 36.9) established unit A, possessing a (2-methylpropyl) isoindolone moiety, which had two positions vacant to be linked, R1 and R2 (Figure 2). 11 carbon signals remained. The 1H-1H COSY cross peaks of H-26 (δH 5.91)/H-30 (δH 3.59)/H-19 (δH 2.25)/H-18 (δH 3.86) and H-19/H-20 (δH 3.51)/H-32 (δH 4.42)/OH-32 (δH 4.58), together with HMBC interactions from Me-33 (δH 1.85) to C-29 (δC 127.6), C-28 (δC 158.1) and C-31 (δC 197.0), from H-20 and OH-32 to C-31 were preliminarily attributed to unit B (Figure 2). Furthermore, the HMBC correlations from H-19 and H-20 to C-21 (δC 214.2), from H-18 to C-16 (δC 29.3), C-17 (δC 68.6) and C-19 connected R1 with R4, and R2 with R3 respectively. To satisfy the unsaturation, R5 and R6 were linked. Thus, the gross planar structure of 1 was established.
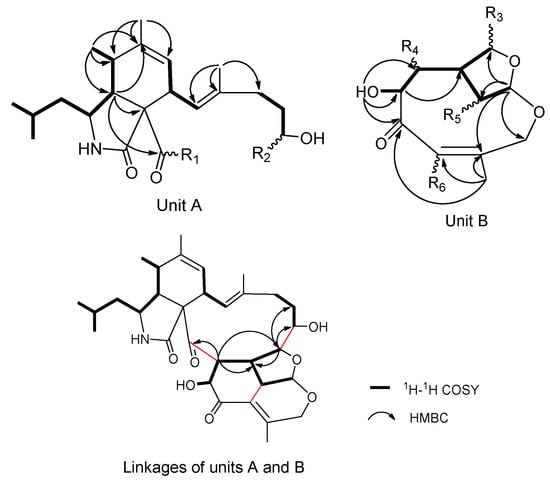
Figure 2.
Partial structures of 1 based on 1H-1H correlation spectroscopy (COSY) and heteronuclear multiple bond correlation (HMBC) spectra.
The relative stereochemistry of 1 was determined with the help of 1H NMR coupling constants, nuclear Overhauser effect spectroscopy (NOESY) experiments, and comparison with those of reported aspochalasins. The NOESY cross peaks (Figure S10) among H-5, H-4 and H-8 demonstrated the relative configurations of the isoindolone moiety in accordance with those of reported cytochalasans [20,21]. For the macrocyclic part, the NOESY correlations of H-17, H-18 and H-20 suggested they were cofacial. The double peak of H-18 with big coupling constants between H-19 reflected the trans-orientation of these two atoms. For the penta-heterocycle moiety, both H-19 and H-30 were located at the joint of three cycles, which elucidated the axial bond in these two atoms. Additionally, the NOESY correlations between H-19, H-30, H-26 and H-32 established that these moieties had the same orientation (Figure 3). The modified Mosher’s method using (S)/(R)-α-methoxy-α-(trifluoromethyl) phenylacetyl (MPTA)-Cl was applied to assign the absolute configuration of 1. The positive and negative value disposition (ΔδS-R) of the Mosher’s ester derivatives (1a and 1b) established the absolute configuration of C-17 as S (Figure 4). It is noteworthy that in all natural cytochalasans, so far, the stereochemistry of perhydroisoindol-1-one moiety is the same [4,21] which assigned the absolute configurations for C-3, C-4, C-5,C-8 and C-9 as 3S, 4R, 5S, 8S, 9S, respectively. Therefore, the complete absolute stereochemistry of 1 could be assigned as 3S, 4R, 5S, 8S, 9S, 17S, 18R, 19R, 20R, 26R, 30S, 32S and named as Tricochalasin A.
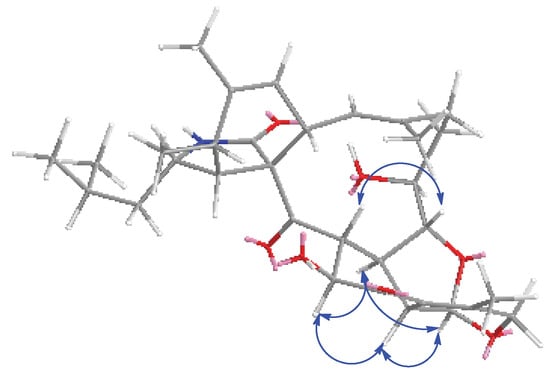
Figure 3.
Key nuclear Overhauser effect spectroscopy (NOESY) correlations of 1.
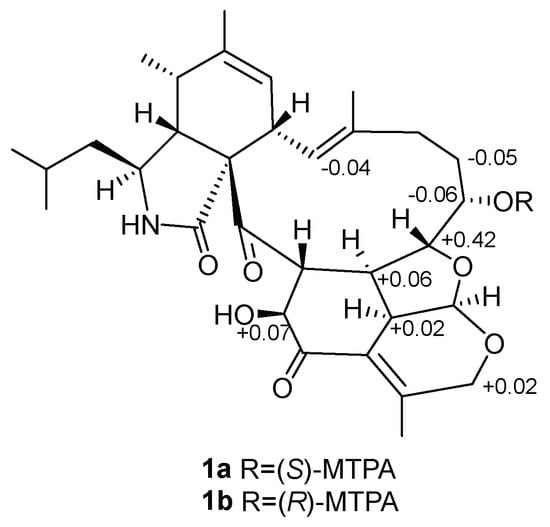
Figure 4.
Δδ values (in ppm) = δS-δR obtained for (S)- and (R)-α-methoxy-α-(trifluoromethyl) phenylacetyl (MPTA)-Cl esters 1a and 1b.
Compound 2 was isolated as a white solid. Its molecular formula was deduced to be C24H35NO5 (8 degrees of unsaturation) by positive-mode high-resolution electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (HR-ESIMS) ion peaks at m/z 418.2589 [M + H]+ (calcd. 418.2549 for C24H36NO5) and m/z 440.2406 [M + Na]+ (calcd. 440.2368 for C24H35NO5Na), combined with 1D NMR data. Analysis of the 1H NMR and 13C NMR spectrum data recorded in CDCl3 revealed the presence of (2-methylpropyl) isoindolone moiety similar to those found in 1. 13C NMR and DEPT spectra showed 24 carbon resonances including one ketone carbonyl (δC 208.9), one ester/lactone carbonyl (δC 171.9), one amide carbonyl (δC 172.4), four olefinic carbon (δC 123.5, 123.8, 138.2 and 140.9), five aliphatic methylene carbons (δC 46.8, 33.1, 32.3, 29.0 and 34.1), six aliphatic methine carbons (δC 25.6, 52.3, 52.4, 34.8, 41.1 and 75.1), five methyl signals (δC 21.1, 23.8, 14.3, 20.1 and 17.7) and one quaternary carbon (δC 86.5) (Table 1). These features characteristically suggested 2 belongs to the same structural family as 1. Comparison with reported aspochalasin derivatives indicated that 2 was similar to aspochalasin A1 [22]. The planar structure of 2 was elucidated by 1H-1H COSY and 1H-13C HMBC experiments (Figure 5). 1H-1H COSY cross peaks (Figure S20) of the H-15 (δH 2.14, 2.27)/H-16 (δH 4.42)/H-17 (δH 2.04, 2.28) established the position of the hydroxyl group at C-16 (δC 75.1) and the H-19 (δH 2.32, 3.02)/H-20 (δH 2.44, 2.62) pairs located the ketone carbonyl group at C-18 (δC 208.9). The key HMBC correlations (Figure S21) from H-17 to C-16 and C-18, from H-15 to C-16 and C-14 (δC 138.2) and from H-19, H-20 to C-18 and C-21 (δC 171.9) also demonstrated the structural features.
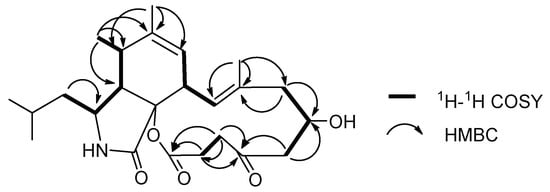
Figure 5.
1H-1H COSY and key HMBC correlations of 2.
The absolute configuration of C-16 in 2 was established by the convenient Mosher’s ester. The difference in chemical shift values of the easters 2a and 2b was calculated to assign the absolute configuration at C-16 as R (Figure 6). Thus, the absolute configuration of 2 was deduced as 3S, 4R, 5S, 8S, 9S, 16R and named as aspochalasin A2.
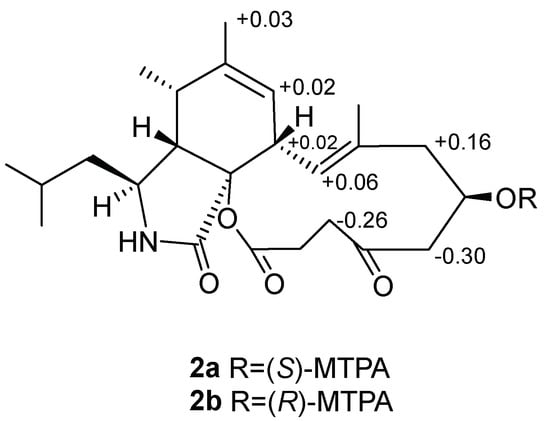
Figure 6.
Δδ values (in ppm) = δS-δR obtained for (S)- and (R)-MPTA esters 2a and 2b.
NMR data of compounds 3–5 was in full agreement with the previously reported values for aspochalasins D (3) [23], aspergilluchalasin (4) [24] and aspochalasins T (5) [25].
All compounds were tested for their in vitro cytotoxicity against the prostate cancer PC3 cell lines by the MTT method, using doxorubicin (ADR) as positive control. As shown in Table 2, compound 3 showed strong activity against PC3 cell line, while others showed weak activities against it.

Table 2.
Growth inhibition of 1–5 against prostate cancer PC3 cell line.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
Optical rotations were measured on a Jasco P-1010 polarimeter. The ultraviolet (UV) absorption spectra were measured in MeOH on a METASH UV-8000 spectrophotometer. The infrared (IR) spectra were recorded using a Bruker Vector 22 spectrometer (film) and an Avatar 370 Fourier-transform–infrared (FT–IR) spectrometer (KBr disk). NMR spectra were recorded in Chloroform-d (ALDRICH, St. Louis, MO, USA) with tetramethylsilane as an internal standard or Pyridine-d5 (ALDRICH, St. Louis, MO, USA), using a Bruker AVANCE-III 500 MHz NMR spectrometer (Brucker, Ettlingen, Germany). HR-ESIMS data were obtained on an Agilent 6224 TOF LC/MS (Agilent, Santa Clara, CA, USA) (positive mode; infusion rate: 0.6 mL/min; capillary voltages: 4000 V; nebulizer: 50 psig; drying gas: 10mL/min; gas temperature: 325 °C).
Column chromatography (CC) was performed with silica (100–200 and 200–300 mesh, Qingdao Haiyang Chemical Co., Ltd., Qingdao, China).
3.2. Fungal Material
The fungal colony (Z4) was isolated from marine isopod Ligia oceanica which was collected in seaside of Dinghai in Zhoushan, Zhejiang Province of China in December 2011. The fungal Z4 was determined as Aspergillus sp. by 18S rDNA analysis and preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC No.M2013631).
3.3. Fermentation, Extraction, and Isolation of Strain Z4
Two different media were used: A—500 mL Erlenmeyer-flasks (400 × 200 mL, a total of 80 L) each containing 200 mL of 2216E liquid media (QingDao Hopebio-Technology Co., Ltd., Qingdao, China) and B—40 500 mL Erlenmeyer-flasks each containing 40 g of rice with 45 mL 3% artificial seawater. Both medium were incubated at 28 °C for 30 days in static condition.
Medium A was filtered and extracted with equivoluminal EtOAc for 3 times to yield 5 g of extract, which was fractioned by silica gel column chromatography (CC) eluted in gradient from petroleum ether-EtOAc (100:1–2:1) to CH2Cl2-MeOH (50:1–0:100). 8 fractions were collected based on thin layer chromatography (TLC) analysis. Fr. 5 (2.5 g) was fractionated by CC over silica gel using a gradient of CH2Cl2-MeOH (100:1–0:100) as a mobile phase to provide eight subfractions (Frs. 5-1 to 5-8). Fr. 5-4 (0.5 g) was further purified by CC over silica gel using a gradient of cyclohexane(C)-E(3:1–1:1) to yield nine subfractions (Frs. 5-4-1 to 5-4-9). Fr. 5-4-5 (90 mg) were purified by semi-preparative octadecyl-silica high-performance liquid chromatography (ODS-HPLC) (COSMOSIL PACKED COLUMN, 5C18-MS-II column, 10ID × 250 mm, 3 mL/min, 54% acetonitrile in H2O) to obtain compound 2 (3 mg). Fr. 5-4-9 (37 mg) were purified by semi-preparative ODS-HPLC (3 mL/min, 52% MeOH in H2O) to obtain compound 5 (17 mg). Each flask of B medium was extracted 3 times with EtOAc (60 mL) yielding 39 g of extract. CC over silica gel using a gradient of CH2Cl2-MeOH (100:1–0:100) as the eluents to afforded seven fractions based on TLC analysis. Fr. 3 (900 mg) was then purified by CC over silica gel with a CH2Cl2-MeOH gradient from 100:1–10:1 to afford 10 subfractions (Frs. 3-1 to 3-10), among which, Fr. 3-6 (28 mg) was further purified by semi-preparative ODS-HPLC (4 mL/min, 75% MeOH in H2O) to obtain compounds 1 (3 mg). Fr. 6 (4 g) was purified by CC over silica gel with a CH2Cl2-MeOH gradient from 50:1–5:1 to afford six subfractions (Frs. 6-1 to 6-6). Fr. 6-2 (76 mg) was purified by semi-preparative ODS-HPLC (4 mL/min, 75% MeOH in H2O) to obtain compounds 4 (13 mg). Fr. 6-3 (28 mg) was purified by semi-preparative ODS-HPLC (4 mL/min, 80% MeOH in H2O) to yield compound 3 (1 mg).
- Tricochalasin A (1): colorless solid; −2.39 (c 0.67, MeOH); UV (MeOH) λmax (log ε) 204 (3.4), 245 (1.6) nm; IR(film) νmax 3391, 2931, 1753, 1681, 1452, 1380, 1189, 1095 cm−1; 1H and 13C data see Table 1; HR-ESIMS m/z 554.3107 [M + H]+, calcd. 554.3073 for C32H44NO7.
- Aspochalasin A2 (2): colorless solid; 8.08 (c 0.98, CHCl3); UV (MeOH) λmax (log ε) 202 (3.6) nm; IR(KBr) νmax 3454, 3273, 2924, 2852, 1709, 1435, 1384, 1324, 1263, 1142 cm−1; 1H and 13C data see Table 1; HR-ESIMS m/z 418.2589 [M + H]+, calcd. 418.2549 for C24H36NO5.
- Aspochalasins D (3): colorless solid; UV (MeOH) λmax (log ε) 204 (3.1) nm.
- Aspergillulactone (4): colorless solid; UV (MeOH) λmax (log ε) 204 (3.6), 245 (1.3) nm.
- Aspochalasins T (5): colorless solid; UV (MeOH) λmax (log ε) 205 (3.7) nm.
3.4. Preparation of MTPA Esters
Compound 1 was transferred into two clean NMR tubes (0.5 mg in each tube) and dried completely under vacuum. Deuterated pyridine (400 μL) was added to dissolve the sample and (R)-MTPA-Cl/(S)-MTPA-Cl (8μL) were quickly added into the tubes, respectively. All contents were mixed thoroughly by shaking the tubes carefully. The reaction was performed at room temperature for 4h to obtained the S-MTPA and the R-MTPA ester (1a and 1b), respectively. The chemical shift differences (Δδ = δS − δR) calculated from the 1H NMR spectra of the two diastereomeric esters 1a and 1b, obtained without purification, enabled us to determine the absolute configuration of C-17 as S.
Similarly, the S-MTPA and R-MTPA ester (2a and 2b) of compound 2 was obtained. 1H NMR data of 2a and 2b were run without further purification and the chemical shift differences (Δδ = δS − δR) enabled us to determine the absolute configuration of C-16 as R.
- 1a:1H NMR (500 MHz, pyridine-d5): δ 6.68 (1H, H-13), δ 1.37 (1H, H-16a), δ 7.86 (1H, H-17), δ 4.51 (1H, H-18), δ 2.77 (1H, H-19), δ 4.95 (1H, H-27a), δ 4.03 (1H, H-30), δ 4.32 (1H, H-32).
- 1b:1H NMR (500 MHz, pyridine-d5): δ 6.72 (1H, H-13), δ 1.42 (1H, H-16a), δ 7.92 (1H, H-17), δ 4.09 (1H, H-18), δ 2.71 (1H, H-19), δ 4.93 (1H, H-27a), δ 4.01 (1H, H-30), δ 4.25 (1H, H-32).
- 2a:1H NMR (500 MHz, pyridine-d5): δ 5.42 (1H, H-7), δ 3.26 (1H, H-8), δ 1.79 (3H, H-12), δ 6.61 (1H, H-13), δ 2.35 (1H, H-15a), δ 2.25 (1H, H-17a), δ 2.14 (1H, H-19a).
- 2b:1H NMR (500 MHz, pyridine-d5): δ 5.40 (1H, H-7), δ 3.24 (1H, H-8), δ 1.76 (3H, H-12), δ 6.55 (1H, H-13), δ 2.19 (1H, H-15a), δ 2.55 (1H, H-17a), δ 2.40 (1H, H-19a).
3.5. Cytotoxicity Bioassays
The cytotoxicity was measured by the MTT assay against the prostate cancer PC3 cell line. Tumor cell lines were seeded in 96-well plates (4 × 103 per well in 100 μL). After 24 h of incubation, the cells were treated with gradient concentrations (100 μM, 50 μM, 25 μM, 12.5 μM, 6.25 μM, 3.125 μM) for another 72 h. Afterwards, MTT solution (5.0 mg/mL in RPMI-1640 media, Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA) was added (20 μL/well) and the plates were incubated for another 4 h at 37 °C. The compounds were dissolved in DMSO and cell growth inhibition assay was performed as reported previously [26]. The growth inhibitory ability of the compounds were calculated and expressed using the IC50 value by dose-effect analysis software. Doxorubicin (ADR) was used as a positive control.
4. Conclusions
A chemical investigation was carried out on the marine fungus Z4, which resulted in the isolation of two novel aspochalasins (compounds 1 and 2) along with three known aspochalasins (compounds 3–5). The planar structures were determined and compound 1 contains a rare 5/6/6 tricyclic ring fused with the aspochalasin skeleton. Furthermore, the absolute configurations were established by modified Mosher’s method. Cytotoxicity against the prostate cancer PC3 cell line were assayed by MTT method. Compound 3 showed strong activity while others showed weak activity.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at http://www.mdpi.com/1660-3397/16/10/343/s1, Figure S1: IR spectrum of 1; Figures S2 and S3: HR-ESI-MS spectrum of 1; Figures S4–S10: 1H, 13C, DEPT, HSQC, COSY, HMBC, NOESY NMR data of 1 in CDCl3; Figures S11 and S12: 1H NMR data of 1a and 1b in pyridine-d5; Figure S13: IR spectrum of 2; Figures S14 and S15: HR-ESI-MS spectrum of 2; Figures S16–S22: 1H, 13C, DEPT, HSQC, COSY, HMBC, NOESY NMR data of 2 in CDCl3; Figures S23 and S24: 1H NMR data of 2a and 2b in pyridine-d5; Figures S25 and S26: 1H and 13C NMR data of 3 in CDCl3; Figures S27 and S28: 1H and 13C NMR data of 4 in CDCl3; Figures S29 and S30: 1H and 13C NMR data of 5 in CDCl3.
Author Contributions
J.X. designed the experiment. X.L. performed the experiment, determined the structures and prepare the manuscript. W.D. tested the biological activities. P.W. isolated and identified the fungus.
Funding
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC No. 41406141).
Acknowledgments
We thank Jianyang Pan (Pharmaceutical Informatics Institute, Zhejiang University) for performing NMR spectroscopy for structure elucidation.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Scherlach, K.; Boettger, D.; Remme, N.; Hertweck, C. The chemistry and biology of cytochalasans. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2010, 27, 869–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Ge, H.; Xie, D.; Chen, R.; Zou, J.H.; Tao, X.; Dai, J. Periconiasins A–C, new cytotoxic cytochalasans with an unprecedented 9/6/5 tricyclic ring system from endophytic fungus periconia sp. Org. Lett. 2013, 15, 1674–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knudsen, P.B.; Hanna, B.; Ohl, S.; Sellner, L.; Zenz, T.; Dohner, H.; Stilgenbauer, S.; Larsen, T.O.; Lichter, P.; Seiffert, M. Chaetoglobosin A preferentially induces apoptosis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells by targeting the cytoskeleton. Leukemia 2014, 28, 1289–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, G.X.; Wijeratne, E.M.K.; Bigelow, D.; Pierson, L.S.; Vanetten, H.D.; Guantilaka, A.A.L. Aspochalasins I, J, and K: Three new cytotoxic cytochalasans of Aspergillus flavipes from the rhizosphere of Ericameria laricifolia of the sonoran desert. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 328–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rochfort, S.; Ford, J.; Ovenden, S.; Wan, S.S.; George, S.; Wildman, H.; Tait, R.M.; Meurer-Grimes, B.; Cox, S.; Coates, J.; et al. A novel aspochalasin with HIV-1 integrase inhibitory activity from Aspergillus flavipes. J. Antibiot. 2005, 58, 279–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, C.Y.; Yang, Y.H.; Sun, L.; Dou, H.; Tan, R.X.; Hou, Y.Y. Chaetoglobosin F, a small molecule compound, possesses immunomodulatory properties on bone marrow-derived dendritic cells via TLR9 signaling pathway. Immunobiology 2013, 218, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Zhang, W.P.; Zhang, P.; Ruan, W.B.; Zhu, X.D. Nematicidal Activity of Chaetoglobosin A Poduced by Chaetomium globosum NK102 against Meloidogyne incognita. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, K.J.; Chooi, Y.H.; Tang, Y. Identification and engineering of the cytochalasin gene cluster from Aspergillus clavatus NRRL 1. Metab. Eng. 2011, 13, 723–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schumann, J.; Hertweck, C. Molecular basis of cytochalasan biosynthesis in fungi: Gene cluster analysis and evidence for the involvement of a PKS-NRPS hybrid synthase by RNA silencing. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 9564–9565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, H.; Swenson, D.C.; Gloer, J.B.; Wicklow, D.T.; Dowd, P.F. Chaetochalasin A: A new bioactive metabolite from Chaetomium brasiliense. Tetrahedron. Lett. 1998, 39, 7633–7636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, T.; Pei, Y.H.; Hua, H.M.; Feng, B.M. Aspergillin PZ, a novel isoindole-alkaloid from Aspergillus awamori. J. Antibiot. 2002, 55, 693–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Z.J.; Zhu, T.J.; Wei, H.J.; Zhang, G.J.; Wang, H.; Gu, Q.Q. Spicochalasin A and New Aspochalasins from the Marine-Derived Fungus Spicaria elegans. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2009, 18, 3045–3051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.C.; Chen, C.M.; Tong, Q.Y.; Li, X.N.; Yang, J.; Xue, Y.B.; Luo, Z.W.; Wang, J.P.; Yao, G.M.; Zhang, Y.H. Epicochalasines A and B: Two bioactive merocytochalasans bearing caged epicoccine dimer units from Aspergillus flavipes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 3486–3490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhao, Z.; Ding, W.; Ye, B.; Wang, P.; Xu, J. Aspochalazine A, a novel polycyclic aspochalasin from the fungus Aspergillus sp. Z4. Tetrahedron Lett. 2017, 58, 2405–2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, S.; Ding, W.; Wang, P.; Yang, X.; Xu, J. Methylthio-aspochalasins from a marine-derived fungus Aspergillus sp. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 5124–5131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.Z.; Zhao, S.Z.; Yang, X.W. A new cyclopeptide metabolite of marine gut fungus from Ligia oceanica. Nat. Prod. Res. 2014, 28, 994–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.M.; Zhao, S.Z.; Liu, Y.; Ding, W.J.; Qiu, F.; Xu, J.Z. Asperginine, an unprecedented alkaloid from the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus sp. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2015, 10, 1363–1364. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Pei, Y.h. Two novel trichothecenes from Myrothecium roridum. Med. Chem. Res. 2007, 16, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, G.; Wang, H.; Li, L.; Chen, A.J.; Chen, L.; Chen, H.; Zhang, H.; Liu, X.; Zou, Z. Trichoderones A and B: Two pentacyclic cytochalasans from the plant endophytic fungus Trichoderma gamsii. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2012, 2012, 2516–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Gu, Q.; Zhu, W.; Cui, C.; Fan, G.; Fang, Y.; Zhu, T.; Liu, H. 10-Phenyl-[12]-cytochalasins Z7, Z8, and Z9 from the marine-derived fungus Spicaria elegans. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 871–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Tong, Q.; Zhu, H.; Tan, D.; Zhang, J.; Xue, Y.; Yao, G.; Luo, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; et al. Nine new cytochalasan alkaloids from Chaetomium globosum TW1-1 (Ascomycota, Sordariales). Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 18711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, C.J.; Shao, C.L.; Wu, L.Y.; Chen, M.; Wang, K.L.; Zhao, D.L.; Sun, X.P.; Chen, G.Y.; Wang, C.Y. Bioactive phenylalanine derivatives and cytochalasins from the soft coral-derived fungus, Aspergillus elegans. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 2054–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomikawa, T.; Shin-ya, K.; Kinoshita, T.; Miyajima, A.; Seto, H.; Hayakawa, Y. Selective cytotoxicity and stereochemistry of aspochalasin D. J. Antibiot. 2001, 54, 379–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rukachaisirikul, V.; Rungsaiwattana, N.; Klaiklay, S.; Phongpaichit, S.; Borwornwiriyapan, K.; Sakayaroj, J. γ-Butyrolactone, cytochalasin, cyclic carbonate, eutypinic acid, and phenalenone derivatives from the soil fungus Aspergillus sp. PSU-RSPG185. J. Nat. Prod. 2014, 77, 2375–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Z.J.; Zhu, T.J.; Chen, L.; Gu, Q.Q. Three new aspochalasin derivatives from the marine-derived fungus Spicaria elegans. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2010, 21, 824–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Hua, H.M.; Pei, Y.H.; Chen, D.; Jing, Y.K. Triterpenoids from the resin of Styrax tonkinensis and their antiproliferative and differentiation effects in human leukemia HL-60 cells. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 807–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).