Isolation, Amino Acid Sequences, and Plausible Functions of the Galacturonic Acid-Binding Egg Lectin of the Sea Hare Aplysia kurodai
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
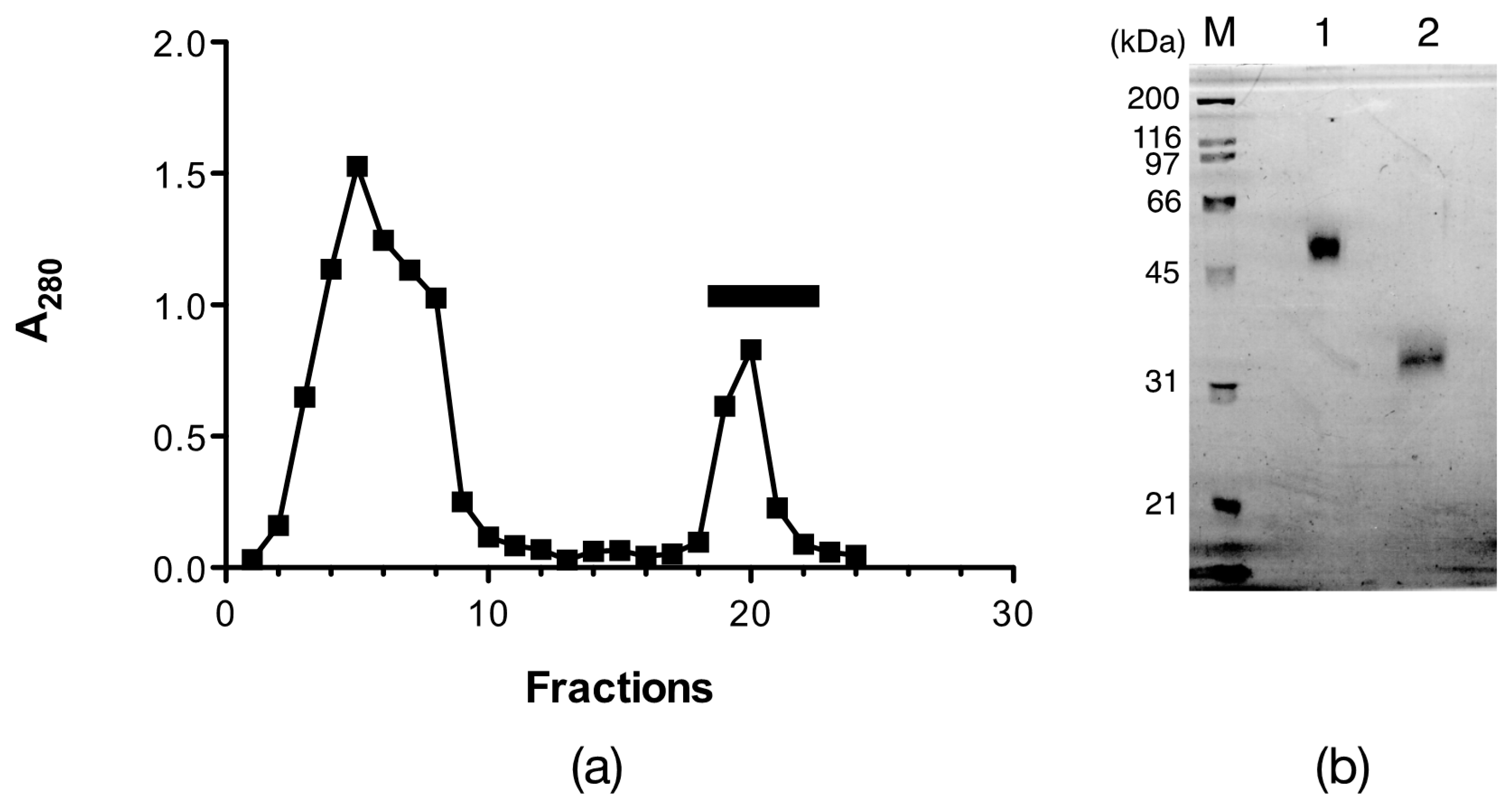
2.1. Isolation of Egg Lectins
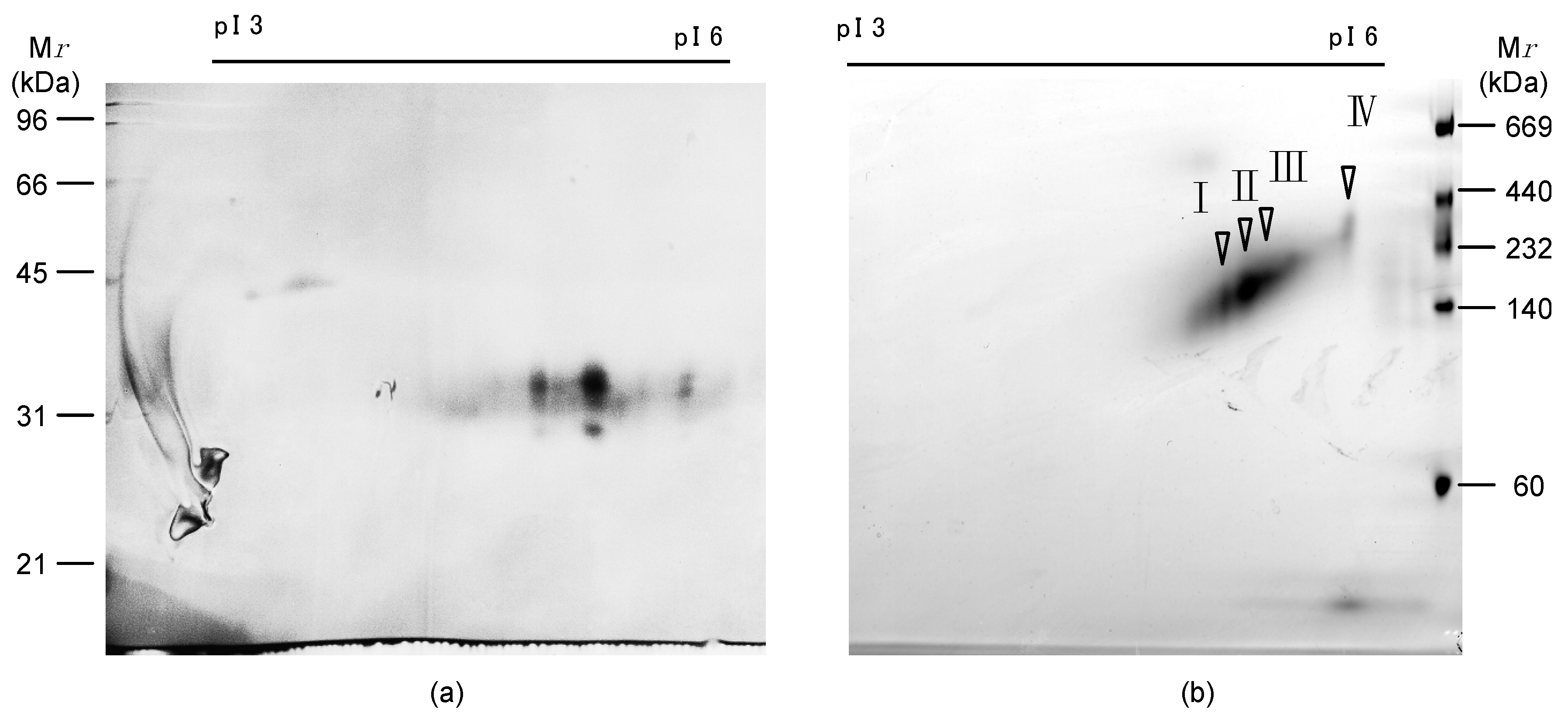
2.2. The N-Terminal and Partial Amino Acid Sequence of AKL
2.3. Sugar Inhibition of AKL
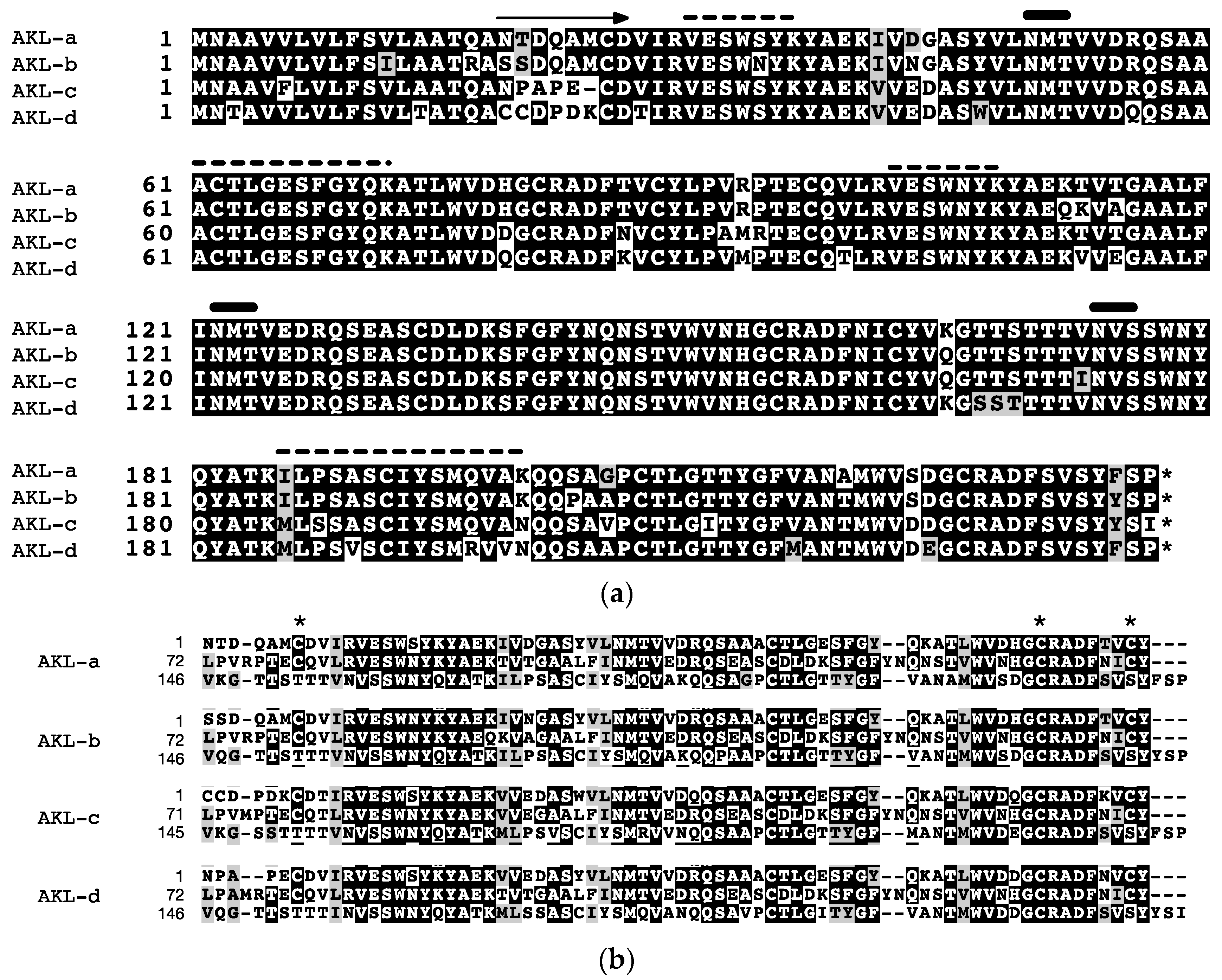
2.4. Primary Structure of AKL
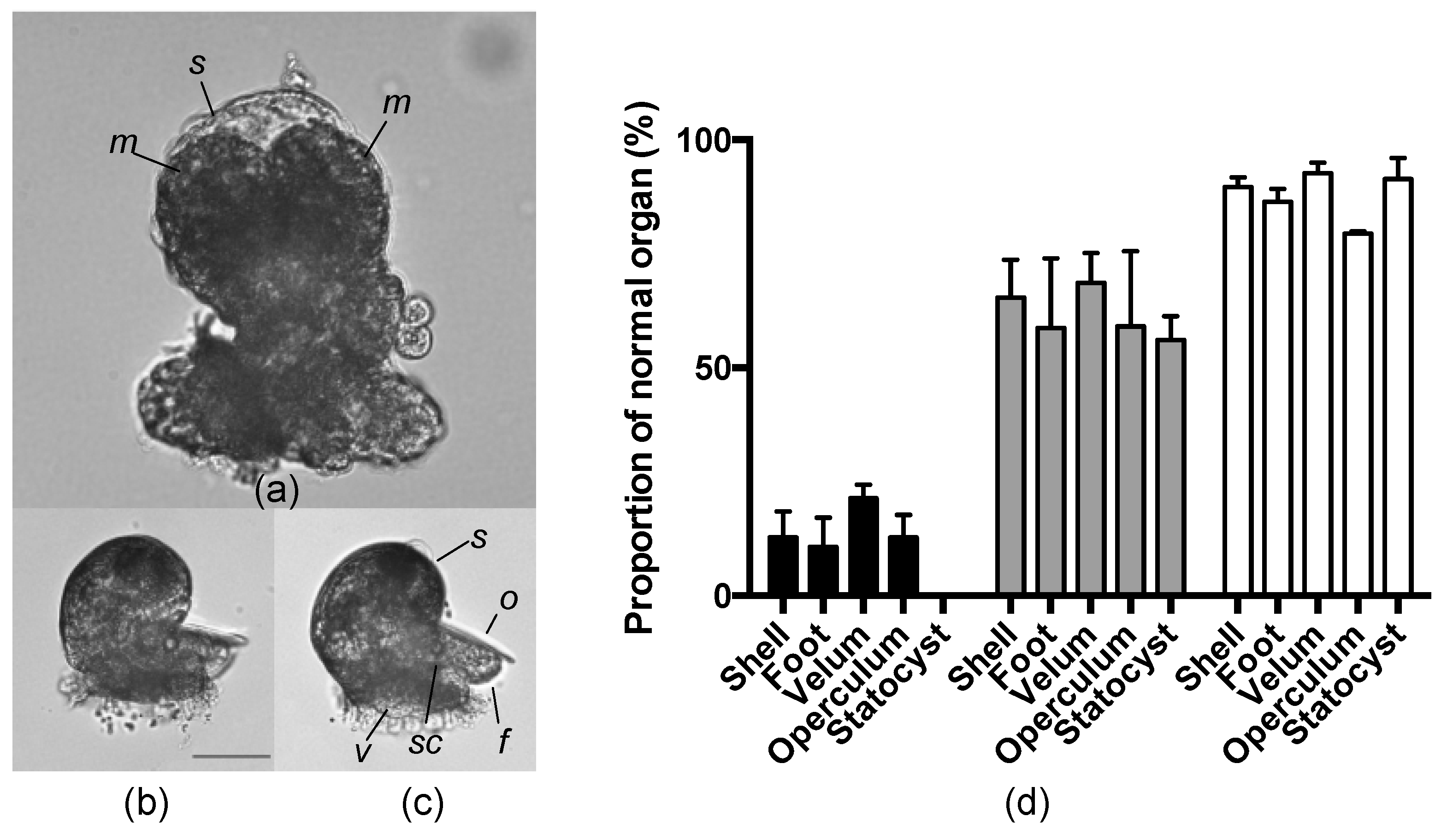
2.5. Effects of an AKL Inhibitor on Larval Morphology
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Isolation of A. kurodai Egg Lectin
4.3. Hemagglutination Testing
4.4. Inhibition of Hemagglutination by Sugars
4.5. Electrophoresis
4.6. Protein Quantification
4.7. Amino Acid Sequence Determination
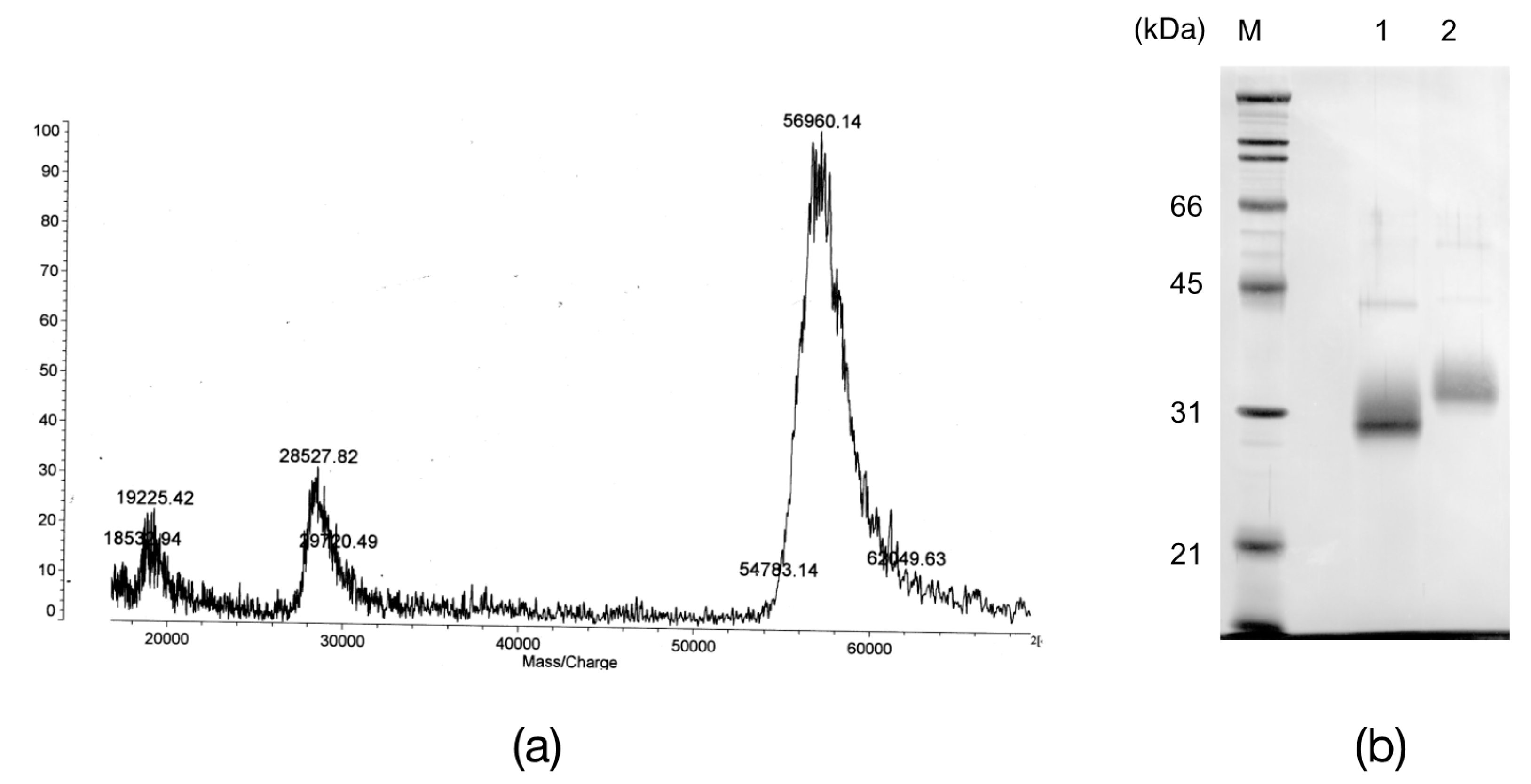
4.8. Molecular Mass Determination of AKL
4.9. Deglycosylation of AKL
4.10. Preparation of cDNA
4.11. Determination of the cDNA of AKLs
4.12. Effects of Uronic Acids on Larvae at Different Embryonic Stages
4.13. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chang, B.Y.; Peavy, T.R.; Wardrip, N.J.; Hedrick, J.L. The Xenopus laevis cortical granule lectin: cDNA cloning, developmental expression, and identification of the egg lectin family of lectins. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A 2004, 137, 115–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimbo, M.; Yamashita, H.; Koike, K.; Sakai, R.; Kamiya, H. Effects of lectin in the scleractinian coral Ctenactis echinata on symbiotic zooxanthellae. Fish. Sci. 2010, 76, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koike, K.; Jimbo, M.; Sakai, R.; Kaeriyama, M.; Muramoto, K.; Ogata, T.; Maruyama, T.; Kamiya, H. Octocoral chemical signaling selects and controls dinoflagellate symbionts. Biol. Bull. 2004, 207, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyes-Grajeda, J.P.; Moreno, A.; Romero, A. Crystal structure of ovocleidin-17, a major protein of the calcified Gallus gallus eggshell: Implications in the calcite mineral growth pattern. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 40876–40881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueda, T.; Nakamura, Y.; Smith, C.M.; Copits, B.A.; Inoue, A.; Ojima, T.; Matsunaga, S.; Swanson, G.T.; Sakai, R. Isolation of novel prototype galectins from the marine ball sponge Cinachyrella sp. guided by their modulatory activity on mammalian glutamate-gated ion channels. Glycobiology 2013, 23, 412–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidal-Dupiol, J.; Adjeroud, M.; Roger, E.; Foure, L.; Duval, D.; Mone, Y.; Ferrier-Pagès, C.; Tambutte, E.; Tambutte, S.; Zoccola, D.; et al. Coral bleaching under thermal stress: Putative involvement of host/symbiont recognition mechanisms. BMC Physiol. 2009, 9, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamiya, H.; Muramoto, K.; Goto, R.; Sakai, M.; Ida, H. Properties of a Lectin in Chum Salmon Ova. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 1990, 56, 1139–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tateno, H.; Saneyoshi, A.; Ogawa, T.; Muramoto, K.; Kamiya, H.; Saneyoshi, M. Isolation and characterization of rhamnose-binding lectins from eggs of steelhead trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) homologous to low density lipoprotein receptor superfamily. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 19190–19197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimbo, M.; Usui, R.; Sakai, R.; Muramoto, K.; Kamiya, H. Purification, cloning and characterization of egg lectins from the teleost Tribolodon brandti. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B 2007, 147, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nitta, K.; Takayanagi, G.; Kawauchi, H.; Hakomori, S. Isolation and characterization of Rana catesbeiana lectin and demonstration of the lectin-binding glycoprotein of rodent and human tumor cell membranes. Cancer Res. 1987, 47, 4877–4883. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, H.; Aketa, K. Purification and distribution of a lectin in sea urchin (Anthocidaris crassispina) egg before and after fertilization. Exp. Cell Res. 1981, 135, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamiya, H.; Shimizu, Y. A natural agglutinin inhibitable by d-galacturonic acid in the sea hare Aplysia eggs: Characterization and purification. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 1981, 47, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishihara, T.; Wyrick, R.E.; Working, P.K.; Chen, Y.H.; Hedrick, J.L. Isolation and characterization of a lectin from the cortical granules of Xenopus laevis eggs. Biochemistry 1986, 25, 6013–6020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Outenreath, R.L.; Roberson, M.M.; Barondes, S.H. Endogenous lectin secretion into the extracellular matrix of early embryos of Xenopus laevis. Dev. Biol. 1988, 125, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tateno, H.; Ogawa, T.; Muramoto, K.; Kamiya, H.; Hirai, T.; Saneyoshi, M. A novel rhamnose-binding lectin family from eggs of steelhead trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) with different structures and tissue distribution. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2001, 65, 1328–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tateno, H.; Yamaguchi, T.; Ogawa, T.; Muramoto, K.; Watanabe, T.; Kamiya, H.; Saneyoshi, M. Immunohistochemical localization of rhamnose-binding lectins in the steelhead trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2002, 26, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levi, G.; Teichberg, V.I. Patterns of expression of a 15K beta-D-galactoside-specific lectin during early development of the avian embryo. Development 1989, 107, 909–921. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ghaskadbi, S.; Ghaskadbi, S.; Patwardhan, V.; Patwardhan, V.; Chakraborthy, M.; Chakraborthy, M.; Agrawal, S.; Agrawal, S.; Verma, M.K.; Verma, M.K.; et al. Enhancement of vertebrate cardiogenesis by a lectin from perivitelline fluid of horseshoe crab embryo. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2008, 65, 3312–3324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawsar, S.M.A.; Matsumoto, R.; Fujii, Y.; Yasumitsu, H.; Dogasaki, C.; Hosono, M.; Nitta, K.; Hamako, J.; Matsui, T.; Kojima, N.; et al. Purification and biochemical characterization of a D-galactose binding lectin from Japanese sea hare (Aplysia kurodai) eggs. Biochemistry 2009, 74, 709–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawsar, S.M.A.; Matsumoto, R.; Fujii, Y.; Matsuoka, H.; Masuda, N.; Chihiro, I.; Yasumitsu, H.; Kanaly, R. A.; Sugawara, S.; Hosono, M.; et al. Cytotoxicity and glycan-binding profile of a d-galactose-binding lectin from the eggs of a Japanese sea hare (Aplysia kurodai). Protein J. 2011, 30, 509–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilboa-Garber, N.; Susswein, A.J.; Mizrahi, L.; Avichezer, D. Purification and characterization of the gonad lectin of Aplysia depilans. FEBS Lett. 1985, 181, 267–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilboa-Garber, N.; Sudakevitz, D.; Levene, C. A comparison of the Aplysia lectin anti-I specificity with human anti-I and several other I-detecting lectins. Transfusion 1999, 39, 1060–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- PINCDATA FUCATA VER VAR2.0. Available online: http://marinegenomics.oist.jp/pearl/viewer/info?project_id=36 (accessed on 1 June 2017).
- Wilson, M.P.; Carrow, G.M.; Levitan, I.B. Modulation of growth of Aplysia neurons by an endogenous lectin. J. Neurobiol. 1992, 23, 739–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, J.F. Biochemical and structural analysis of Helix pomatia agglutinin: A hexameric lectin with a novel fold. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 20171–20180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carneiro, R.F.; Torres, R.C.F.; Chaves, R.P.; de Vasconcelos, M.A.; de Sousa, B.L.; Goveia, A.C.R.; Arruda, F.V.; Matos, M.N.C.; Mathews-Cascon, H.; Freire, V.N.; et al. Purification, biochemical characterization, and amino acid sequence of a novel type of lectin from Aplysia dactylomela eggs with antibacterial/antibiofilm potential. Mar. Biotechnol. 2017, 19, 49–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiggins, F.M.; Kim, K.W. A screen for immunity genes evolving under positive selection in Drosophila. J. Evol. Biol. 2007, 20, 965–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hori, K.; Sato, Y.; Ito, K.; Fujiwara, Y.; Iwamoto, Y.; Makino, H.; Kawakubo, A. Strict specificity for high-mannose type N-glycans and primary structure of a red alga Eucheuma serra lectin. Glycobiology 2007, 17, 479–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimbo, M.; Yamaguchi, M.; Muramoto, K.; Kamiya, H. Cloning of the Microcystis aeruginosa M228 lectin (MAL) gene. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 273, 499–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niehrs, C. Regionally specific induction by the Spemann-Mangold organizer. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2004, 5, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkinson, J.W. Organogenesis in normal and lobeless embryos of the marine prosobranch gastropod Ilyanassa obsoleta. J. Morphol. 1971, 133, 339–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimbo, M.; Yanohara, T.; Koike, K.; Sakai, R.; Muramoto, K.; Kamiya, H. The d-galactose-binding lectin of the octocoral Sinularia lochmodes: Characterization and possible relationship to the symbiotic dinoflagellates. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 2000, 125, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Patron, C.; Castellanos-Serra, L.; Rodriguez, P. Reverse staining of sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gels by imidazole-zinc salts: Sensitive detection of unmodified proteins. BioTechniques 1992, 12, 564–573. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kuniya, N.; Jimbo, M.; Tanimoto, F.; Yamashita, H.; Koike, K.; Harii, S.; Nakano, Y.; Iwao, K.; Yasumoto, K.; Watabe, S. Possible involvement of Tachylectin-2-like lectin from Acropora tenuis in the process of Symbiodinium acquisition. Fish. Sci. 2015, 81, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beardsley, R.L.; Reilly, J.P. Optimization of guanidination procedures for MALDI mass mapping. Anal. Chem. 2002, 74, 1884–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.; Nie, S.; Mi, W.; Wang, X.-C.; Liang, S.-P. De novo sequencing of tryptic peptides sulfonated by 4-sulfophenyl isothiocyanate for unambiguous protein identification using post-source decay matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2004, 18, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strohalm, M.; Kavan, D.; Novák, P.; Volný, M.; Havlíček, V. mMass 3: A cross-platform software environment for precise analysis of mass spectrometric data. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 4648–4651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Doucette, A.; Li, L. Two-layer sample preparation method for MALDI mass spectrometric analysis of protein and peptide samples containing sodium dodecyl sulfate. Anal. Chem. 2001, 73, 2968–2975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altschul, S.F.; Madden, T.L.; Schaffer, A.A.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Miller, W.; Lipman, D.J. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: A new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 3389–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchler-Bauer, A.; Zheng, C.; Chitsaz, F.; Derbyshire, M.K.; Geer, L.Y.; Geer, R.C.; Gonzales, N.R.; Gwadz, M.; Hurwitz, D.I.; Lanczycki, C.J.; et al. CDD: Conserved domains and protein three-dimensional structure. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D348–D352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sievers, F.; Wilm, A.; Dineen, D.; Gibson, T.J.; Karplus, K.; Li, W.; Lopez, R.; McWilliam, H.; Remmert, M.; Söding, J.; et al. Fast, scalable generation of high-quality protein multiple sequence alignments using Clustal Omega. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2011, 7, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McWilliam, H.; Li, W.; Uludag, M.; Squizzato, S.; Park, Y.M.; Buso, N.; Cowley, A.P.; Lopez, R. Analysis Tool Web Services from the EMBL-EBI. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, W597–W600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- BoxShade. Available online: http://www.ch.embnet.org/software/BOX_form.html (accessed on 1 June 2017).

| Sample | Amino Acid Sequence |
|---|---|
| SDS | N/S Q/P G/D D/P A/E M/D T/D V/D G/V I/V |
| I | S G D Q A M C D V I VESWNYKXA |
| II | N Q D Q A M C D V I VESXNYKXA |
| III | N Q D Q A M C D V I VESWXYKYA |
| IV | N Q D Q A C D V I VES |
| m/z | Amino Acid Sequence |
|---|---|
| 1155 | VESWSYK |
| 1182 | VESWNYK |
| 1932 | T I/L W HPXQYAK |
| 1939 | I/L I/L PSASX I/L YSMQVAK |
| 1941 | T I/L WSFGYQK |
| 1975 | ACT I/L GESFGYQK |
| 1989 | T I/L GESFGYQK |
| 1990 | T I/L WSFGYQK |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Motohashi, S.; Jimbo, M.; Naito, T.; Suzuki, T.; Sakai, R.; Kamiya, H. Isolation, Amino Acid Sequences, and Plausible Functions of the Galacturonic Acid-Binding Egg Lectin of the Sea Hare Aplysia kurodai. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 161. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15060161
Motohashi S, Jimbo M, Naito T, Suzuki T, Sakai R, Kamiya H. Isolation, Amino Acid Sequences, and Plausible Functions of the Galacturonic Acid-Binding Egg Lectin of the Sea Hare Aplysia kurodai. Marine Drugs. 2017; 15(6):161. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15060161
Chicago/Turabian StyleMotohashi, Shoko, Mitsuru Jimbo, Tomohiro Naito, Takefumi Suzuki, Ryuichi Sakai, and Hisao Kamiya. 2017. "Isolation, Amino Acid Sequences, and Plausible Functions of the Galacturonic Acid-Binding Egg Lectin of the Sea Hare Aplysia kurodai" Marine Drugs 15, no. 6: 161. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15060161
APA StyleMotohashi, S., Jimbo, M., Naito, T., Suzuki, T., Sakai, R., & Kamiya, H. (2017). Isolation, Amino Acid Sequences, and Plausible Functions of the Galacturonic Acid-Binding Egg Lectin of the Sea Hare Aplysia kurodai. Marine Drugs, 15(6), 161. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15060161





