Sulfated Galactan from Palisada flagellifera Inhibits Toxic Effects of Lachesis muta Snake Venom
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Neutralization of Coagulation

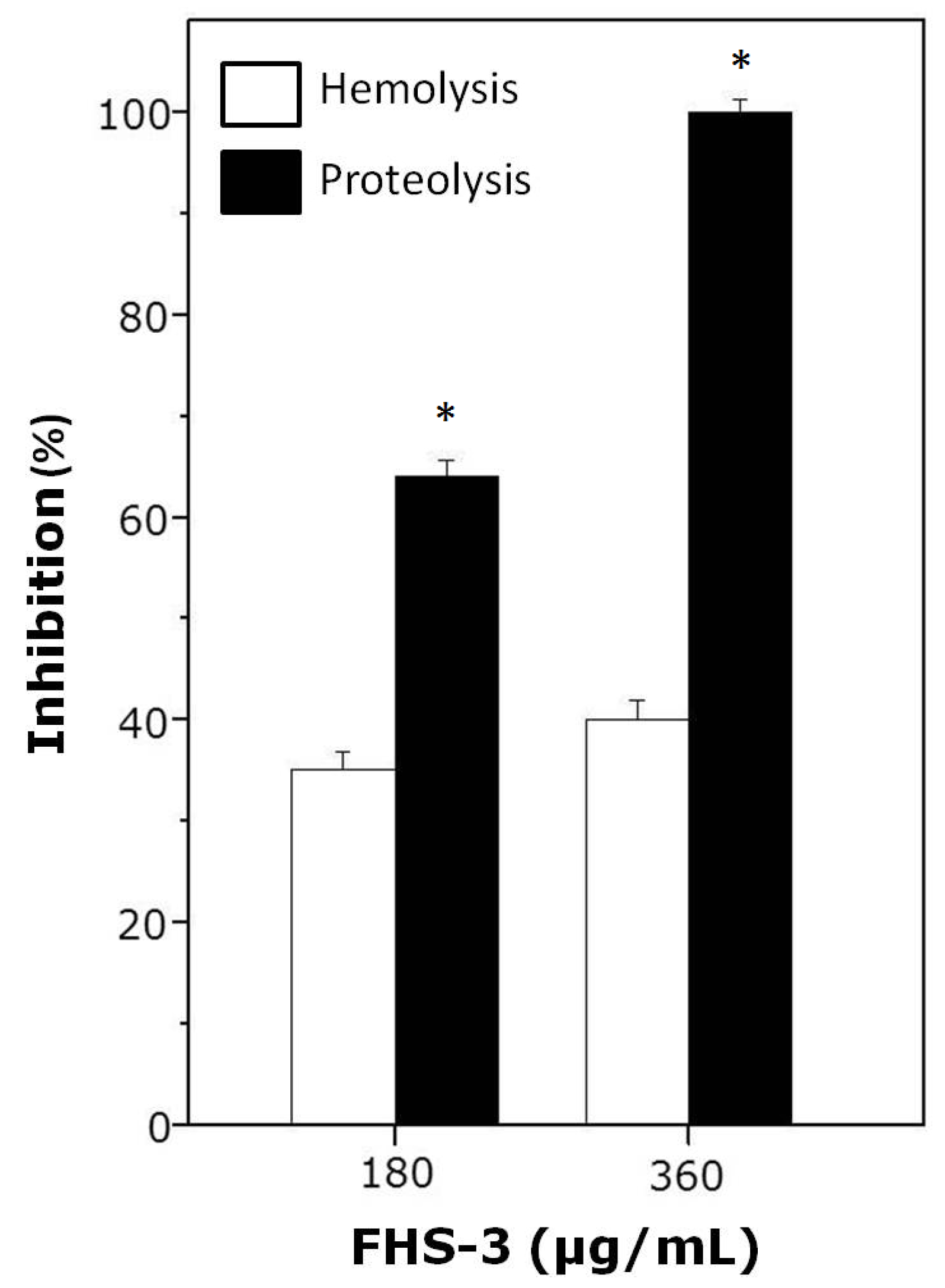
2.2. Neutralization of Hemolysis and Proteolysis
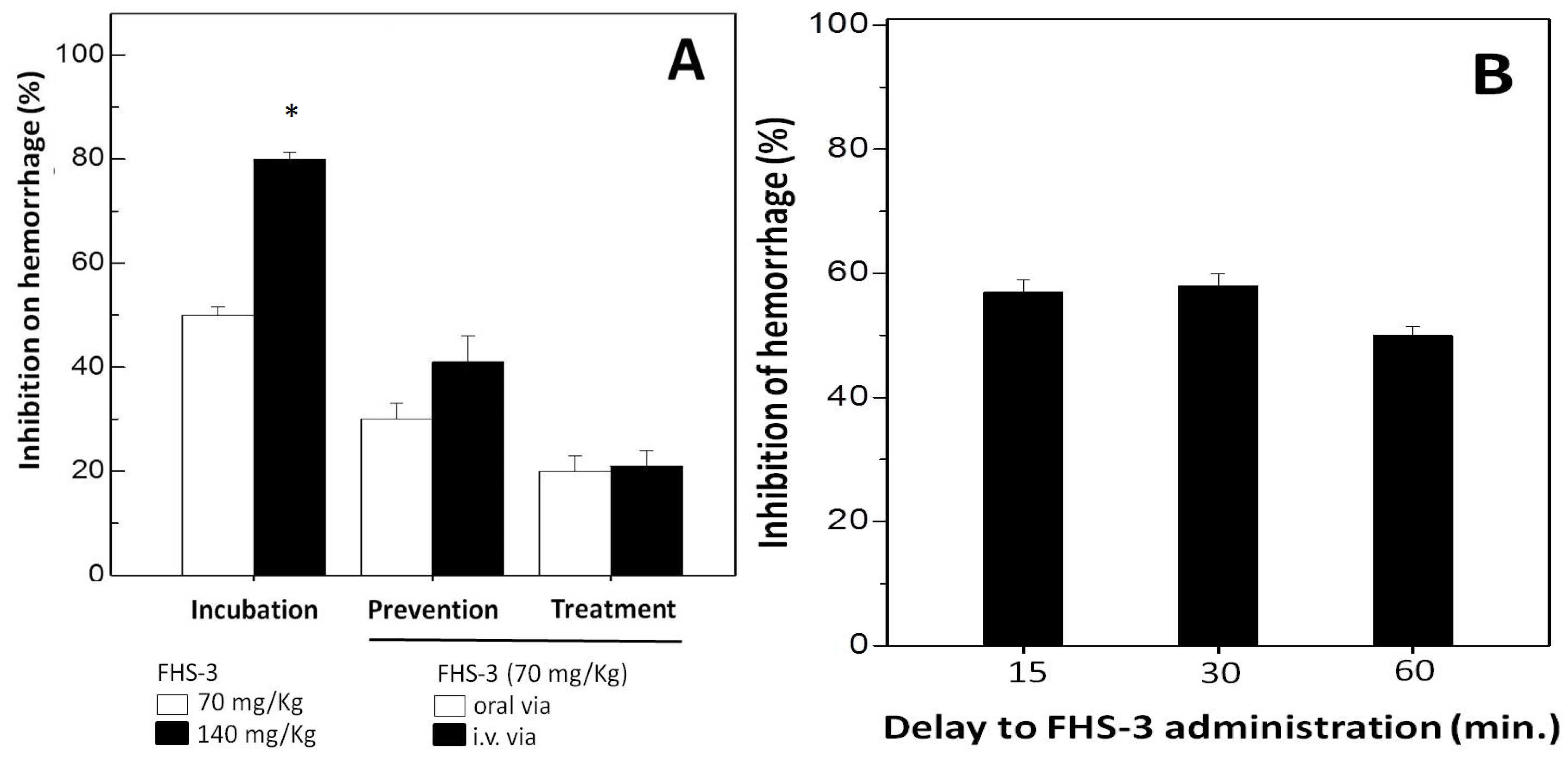
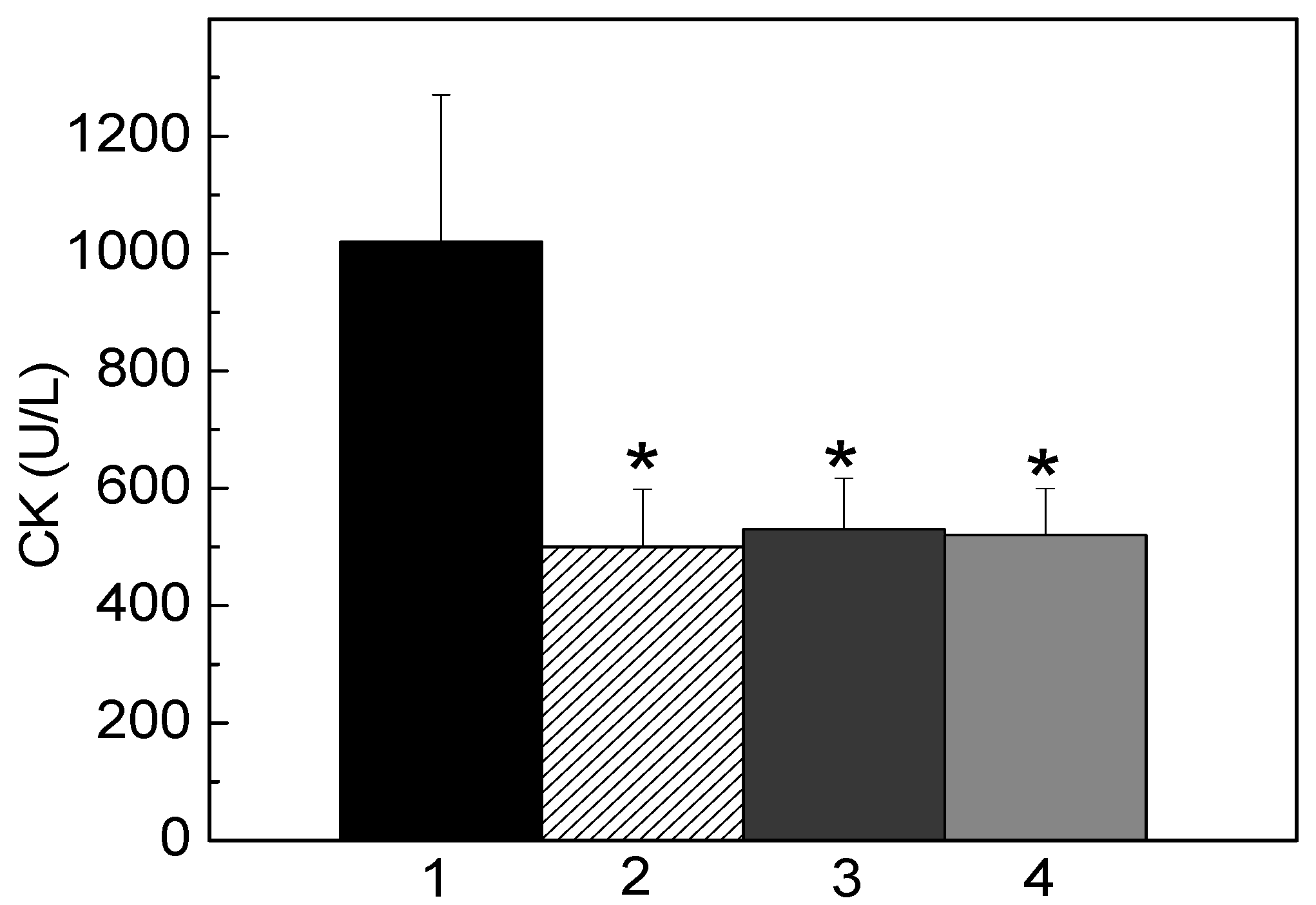
2.3. Neutralization of Hemorrhage and Myotoxicity
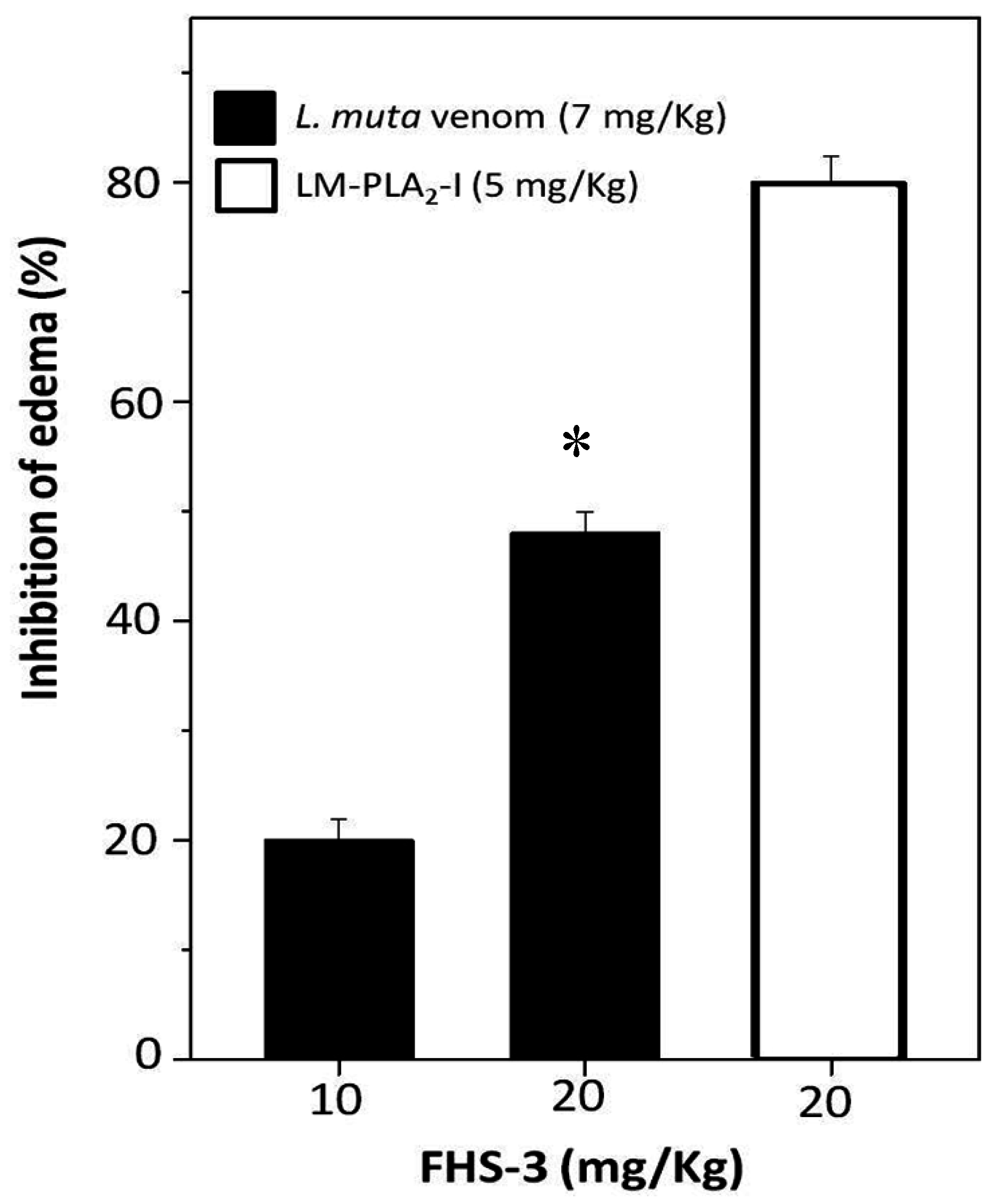
2.4. Neutralization of Edema
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Venom and Animals
3.2. Algal Collection and Isolation of the Sulfated Galactan FHS-3
3.3. Antihemolytic Activity
3.4. Antiproteolytic Activity
3.5. Anticoagulant Activity
3.6. Antihemorrhagic Activity
3.7. Antiedematogenic Activity
3.8. Antimyotoxic Activity
3.9. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gutiérrez, J.M.; León, G.; Burnouf, T. Antivenoms for the treatment of snakebite envenomings: The road ahead. Biologicals 2011, 39, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutiérrez, J.M.; Fan, H.W.; Silvera, C.L.M.; Ângulo, Y. Stability, distribution and use of antivenoms for snakebite envenomation in Latin America: Report of a workshop. Toxicon 2009, 53, 625–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasturiratne, A.; Wickremasinghe, A.R.; de Silva, N.; Gunawardena, N.K.; Pathmeswaran, A.; Premaratna, R.; Savioli, L.; Lalloo, D.G.; de Silva, H.J. The global burden of snakebite: A literature analysis and modelling based on regional estimates of envenoming and deaths. PLoS Med. 2008, 5, e218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chippaux, J.P. Snake-bites: Appraisal of the global situation. World Health Organ. 1998, 76, 515–524. [Google Scholar]
- Calvete, J.J.; Sanz, L.; Ângulo, Y.; Lomonte, B.; Gutiérrez, J.M. Venoms, venomics, antivenomics. FEBS Lett. 2009, 583, 1736–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenfeld, G. Symptomatology, pathology and treatment of snake bites in South America. In Venomous Animals and Their Venoms; Bucherl, W., Buckley, E.E., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1971; pp. 345–384. [Google Scholar]
- Jorge, M.T.; Sano-Martins, I.S.; Tomy, S.G.; Castro, S.C.B.; Ferrari, R.A.; Ribeiro, L.A.; Warrel, D.A. Snake bite by the bushmaster (Lachesis muta) in Brazil: Case report and review of the literature. Toxicon 1997, 35, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, D.L.; Haad, J.J.S. A review of venom toxinology and epidemiology of envenoming of the bushmaster (Lachesis) with report of a fatal bite. Bull. Chic. Herp. Soc. 1998, 33, 113–123. [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez, E.F.; Freitas, T.V.; Ferreira-Alves, D.; Velarde, D.T.; Diniz, M.R.; Diniz, C.R. Biological activities of venoms from South American snakes. Toxicon 1992, 30, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz, L.; Escolano, J.; Ferretti, M.; Biscoglio, M.; Rivera, E.; Crescenti, E.J.; Ângulo, Y.; Lomonte, B.; Gutierrez, J.M.; Calvete, J.J. Snake venomics of the South and Central American bushmasters. Comparison of the toxic composition of Lachesis muta gathered from proteomic versus transcriptomic analysis. J. Proteom. 2008, 71, 46–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, E.F. Mutalysins. In Handbook of Proteolytic Enzymes; Rawlings, N.D., Salvensen, G.S., Eds.; Oxford Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2013; pp. 1067–1070. [Google Scholar]
- Magalhaes, A.; Ferreira, N.R.; Richardson, M.; Gontijo, S.; Yarleque, A.; Bloc, C.; Sanchez, E.F. Coagulant thrombin-like enzymes from the venoms of Brazilian and Peruvian bushmaster (Lachesis muta muta) snakes. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 2003, 136, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, E.F.; Felicori, L.F.; Chavez-Olortegui, C.; Magalhaes, H.B.; Hermogenes, A.L.; Diniz, M.V.; Junqueira de Azevedo, I.L.M.; Magalhaes, A.; Richardson, M. Biochemical characterization and molecular cloning of a plasminogen activator proteinase (LV-PA) from bushmaster snake venom. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2006, 1760, 1762–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinberg, M.L.; Felicori, L.F.; Bello, C.; Magalhães, H.P.; Almeida, A.P.; Sanchez, E.F. Biochemical properties of a bushmaster snake venom serine proteinase (LV-Ka) and its king releasing activity evaluated in mesenteric arterial rings. J. Pharm. Sci. 2004, 96, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuly, A.L.; Machado, O.L.; Alves, E.W.; Carlini, C.R. Mechanism of inhibitory action on platelet activation of a phospholipase A2 isolated from Lachesis muta (Bushmaster) snake venom. Thromb. Haemost. 1997, 78, 1372–1380. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fuly, A.L.; De Miranda, A.L.; Zingali, R.B.; Guimarães, J.A. Purification and characterization of a phospholipase A2 isoenzyme isolated from Lachesis muta snake venom. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2002, 63, 1589–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Silva, H.A.; Pathmeswaran, A.; Ranasinha, C.D.; Jayamanne, S.; Samarakoon, S.B.; Hittharage, A.; Kalupahana, R.; Ratnatilaka, G.A.; Uluwatthage, W.; Aronson, J.K. Low-dose adrenaline, promethazine, and hydrocortisone in the prevention of acute adverse reactions to antivenom following snakebite: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. PLoS Med. 2011, 8, e1000435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aneiros, A.; Garateix, A. Bioactive peptides from marine sources: Pharmacological properties and isolation procedures. J. Chromatogr. B 2004, 803, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwak, J.Y. Fucoidan as a marine anticancer agent in preclinical development. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 851–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.K.; Li, Y.X. Medicinal benefits of sulfated polysaccharides from sea vegetables. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2011, 64, 391–402. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Guerra Dore, C.M.; Faustino Alves, M.G.; Santos, N.D.; Cruz, A.K.; Câmara, R.B.; Castro, A.J.; Guimarães Alves, L.; Nader, H.B.; Leite, E.L. Antiangiogenic activity and direct antitumor effect from a sulfated polysaccharide isolated from seaweed. Microvasc. Res. 2013, 88, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pomin, V.H. Fucanomics and Galactanomics: Marine Distribution, Medicinal Impact, Conceptions, and Challenges. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 793–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guangling, J.; Guangli, Y.; Junzeng, Z.; Stephen, E. Chemical structures and bioactivities of sulfated polysaccharides from marine algae. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 196–223. [Google Scholar]
- Angulo, Y.; Lomonte, B. Inhibitory effect of fucoidan on the activities of crotaline snake venom myotoxic phospholipases A2. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2003, 66, 1993–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azofeifa, K.; Angulo, Y.; Lomonte, B. Ability of fucoidan to prevent muscle necrosis induced by snake venom myotoxins: Comparison of high-and low-molecular weight fractions. Toxicon 2008, 51, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usov, A.I. Polysaccharides of the red algae. Adv. Carbohydr. Chem. Biochem. 2011, 65, 115–217. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Damonte, E.B.; Matulewicz, M.C.; Cerezo, A.S. Sulfated seaweed polysaccharides as antiviral agents. Curr. Med. Chem. 2004, 11, 2399–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lordan, S.; Ross, R.P.; Stanton, C. Marine bioactives as functional food ingredients: Potential to reduce the incidence of chronic diseases. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 1056–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araújo, C.A.; Noseda, M.D.; Cipriani, T.R.; Gonçalves, A.G.; Duarte, M.E.R.; Ducatti, D.R.B. Selective sulfation of carrageenans and the influence of sulfate regiochemistry on anticoagulant properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 91, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardoso, M.A.; Noseda, M.D.; Fujii, M.T.; Zibetti, R.G.M.; Duarte, M.E.R. Sulfated xylomannans isolated from red seaweeds Chondrophycus papillosus and C. flagelliferus (Ceramiales) from Brazil. Carbohydr. Res. 2007, 342, 2766–2775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, L.G.; Noseda, M.D.; Gonçalves, A.G.; Ducatti, D.R.B.; Fujii, M.T.; Duarte, M.E.R. Chemical structure of the complex pyruvylated and sulfated agaran from the red seaweed Palisada flagellifera (Ceramiales, Rhodophyta). Carbohydr. Res. 2012, 347, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leon, G.; Valverde, J.M.; Rojas, G.; Lomonte, B.; Gutierrez, J.M. Comparative study on the ability of IgG and Fab sheep antivenoms to neutralize local hemorrhage, edema and myonecrosis induced by Bothrops asper (terciopelo) snake venom. Toxicon 2000, 38, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mors, W.B.; Nascimento, M.C.; Pereira, B.M.; Pereira, N.A. Plant natural products active against snake-bite the molecular approach. Phytochemistry 2000, 55, 627–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, A.M.; Ticli, F.K.; Marcussi, S.; Lourenço, M.V.; Januário, A.H.; Sampaio, S.V.; Giglio, J.R.; Lomonte, B.; Pereira, P.S. Medicinal plants with inhibitory properties against snake venoms. Curr. Med. Chem. 2005, 12, 2625–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domingos, T.F.; Vallim, M.A.; Cavalcanti, D.N.; Sanchez, E.F.; Teixeira, V.L.; Fuly, A.L. Effect of diterpenes isolated of the marine alga Canistrocarpus cervicornis against some toxic effects of the venom of the Bothrops jararaca snake. Molecules 2015, 18, 3515–3526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monteiro-Machado, M.; Tomaz, M.A.; Fonseca, R.J.; Strauch, M.A.; Cons, B.L.; Borges, P.A.; Patrão-Neto, F.C.; Tavares-Henriques, M.S.; Teixeira-Cruz, J.M.; Calil-Elias, S.; et al. Occurrence of sulfated fucose branches in fucosylated chondroitin sulfate are essential for the polysaccharide effect preventing muscle damage induced by toxins and crude venom from Bothrops jararacussu snake. Toxicon 2015, 98, 20–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duarte, M.E.R.; Cauduro, J.P.; Noseda, D.G.; Noseda, M.D.; Gonçalves, A.G.; Pujol, C.A.; Damonte, E.B.; Cerezo, A.S. The structure of the agaran sulfate from Acanthophora spicifera (Rhodomelaceae, Ceramiales) and its antiviral activity. Relation between structure and antiviral activity in agarans. Carbohydr. Res. 2004, 339, 335–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciancia, M.; Quintana, I.; Cerezo, A.S. Overview of anticoagulant activity of sulfated polysaccharides from seaweeds in relation to their structures, focusing on those of green seaweeds. Curr. Med. Chem. 2010, 17, 2503–2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pomin, V.H.; Mourão, P.A. Specific sulfation and glycosylation—A structural combination for the anticoagulation of marine carbohydrates. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2014, 6, 33–55. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, M.S.; Melo, F.R.; Mourão, P.A.S. Is there a correlation between structure and anticoagulant action of sulfated galactans and sulfated fucans. Glycobiology 2002, 12, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berling, I.; Isbister, G.K. Hematologic Effects and Complications of Snake Envenoming. Transfus. Med. Rev. 2015, 29, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, T.; Camargo, E.A.; Ribela, M.T.; Damico, D.C.; Marangoni, S.; Antunes, E.; De Nucci, G.; Landucci, E.C. Inflammatory oedema induced by Lachesis muta muta (Surucucu) venom and LmTX-I in the rat paw and dorsal skin. Toxicon 2009, 53, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markland, F.S.; Swenson, S. Snake venom metalloproteinases. Toxicon 2013, 62, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lomonte, B.; Moreno, E.; Tarkowski, A.; Hanson, L.A.; Maccarana, M. Neutralizing interaction between heparins and myotoxin II, a lysine 49 phospholipase A2 from Bothrops asper snake venom. Identification of a heparin-binding and cytolytic toxin region by the use of synthetic peptides and molecular modeling. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 29867–29873. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lomonte, B.; Tarkowski, A.; Hanson, L.A. Broad cytolytic specificity of myotoxin II, a lysine-49 phospholipase A2 of Bothrops asper snake venom. Toxicon 1994, 32, 1359–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, E.S.; Guimaraes, J.A.; Prado, J.L. Purification and characterization of a sulfhydryl-dependent protease from Rhodnius prolixus midgut. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1978, 188, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, H.S.; Ikezawa, H.; Murata, R. Studies on the quantitative method for determination of hemorrhagic activity of Habu snake venom. Jpn. J. Med. Sci. Biol. 1960, 13, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamakawa, M.; Nozani, M.; Hokama, Z. Toxins: Animal, Plant and Microbial; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1976; pp. 97–120. [Google Scholar]
- Melo, P.A.; Ownby, C.L. Ability of wedelolactone, heparin, and para-bromophenacyl bromide to antagonize the myotoxic effects of two crotaline venoms and their PLA2 myotoxins. Toxicon 1999, 37, 199–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, P.A.; Suarez-Kurtz, G. Release of sarcoplasmic enzymes from skeletal muscle by Bothrops jararacussu venom: Antagonism by heparin and by the serum of South American marsupials. Toxicon 1988, 26, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Da Silva, A.C.R.; Ferreira, L.G.; Duarte, M.E.R.; Noseda, M.D.; Sanchez, E.F.; Fuly, A.L. Sulfated Galactan from Palisada flagellifera Inhibits Toxic Effects of Lachesis muta Snake Venom. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 3761-3775. https://doi.org/10.3390/md13063761
Da Silva ACR, Ferreira LG, Duarte MER, Noseda MD, Sanchez EF, Fuly AL. Sulfated Galactan from Palisada flagellifera Inhibits Toxic Effects of Lachesis muta Snake Venom. Marine Drugs. 2015; 13(6):3761-3775. https://doi.org/10.3390/md13063761
Chicago/Turabian StyleDa Silva, Ana Cláudia Rodrigues, Luciana Garcia Ferreira, Maria Eugênia Rabello Duarte, Miguel Daniel Noseda, Eladio Flores Sanchez, and André Lopes Fuly. 2015. "Sulfated Galactan from Palisada flagellifera Inhibits Toxic Effects of Lachesis muta Snake Venom" Marine Drugs 13, no. 6: 3761-3775. https://doi.org/10.3390/md13063761
APA StyleDa Silva, A. C. R., Ferreira, L. G., Duarte, M. E. R., Noseda, M. D., Sanchez, E. F., & Fuly, A. L. (2015). Sulfated Galactan from Palisada flagellifera Inhibits Toxic Effects of Lachesis muta Snake Venom. Marine Drugs, 13(6), 3761-3775. https://doi.org/10.3390/md13063761




