Abstract
Two new quinone sesquiterpenes named myrothecols G and H (1 and 2), a pair of C-1′ diastereomers of 13-hydroxyl penicilliumin A, were isolated from the mycelia solid cultures of Myrothecium sp. SC0265. Their structures, including the absolute configurations, were established on the basis of the spectroscopic data combining with the theoretical conformational analysis. The cytotoxic activities of 1 and 2 were tested against a panel of human tumor cell lines.
1. Introduction
In recent years, secondary metabolites obtained from marine-derived fungi have gained considerable attention, as many of them are structurally unique and possess interesting biological properties [1]. Their structures have been successfully elucidated mainly by modern NMR techniques, and determination of the stereochemical relationships within every new molecule is generally one of the crucial points in structural determination. The configuration elucidation of natural products is of premiere importance because it provides essential information for both total synthesis and molecular mode of actions [2]. For example, quinine, originally isolated from the bark of cinchona trees, has been used for the treatment of malaria for centuries [3]. Quinidine, a stereoisomer of quinine, on the other hand, is used as a class Ι antiarrthythmic agent by prolonging the cardiac action potential [4].
Penicilliumin A is a novel quinone-linked drimane sesquiterpene [5,6] produced by Penicillium sp. F00120 isolated from deep sea sediment sample [7], the absolute configuration of which has not been assigned yet. Our recent investigation on the secondary metabolites of Myrothecium sp. SC0265 led to the isolation of two new meroterpenoids, named myrothecols G (1) and H (2), which are structurally related to penicilliumin A (Figure 1). Herein, we presented the stereochemical assignment of the two new compounds by the detailed analysis of their spectroscopic data, especially 2D NMR spectra, combining with the theoretical conformational analysis.
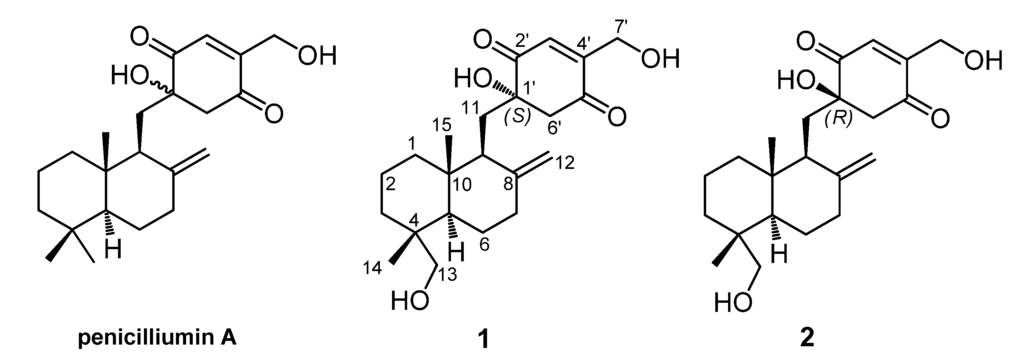
Figure 1.
Penicilliumin A and two analogues (1 and 2) from Myrothecium sp. SC0265.
Figure 1.
Penicilliumin A and two analogues (1 and 2) from Myrothecium sp. SC0265.
2. Results and Discussion
Our previous investigation on the secondary metabolites of Myrothecium sp. SC0265 led to the isolation of a series of myrothecols, displayed potent cytotoxic and antibacterial activities [8]. This motivated us to search for minor components, and reinvestigation of this fungus yielded two new penicilliumin A analogues (1 and 2) via an NMR-guided fractionation process.
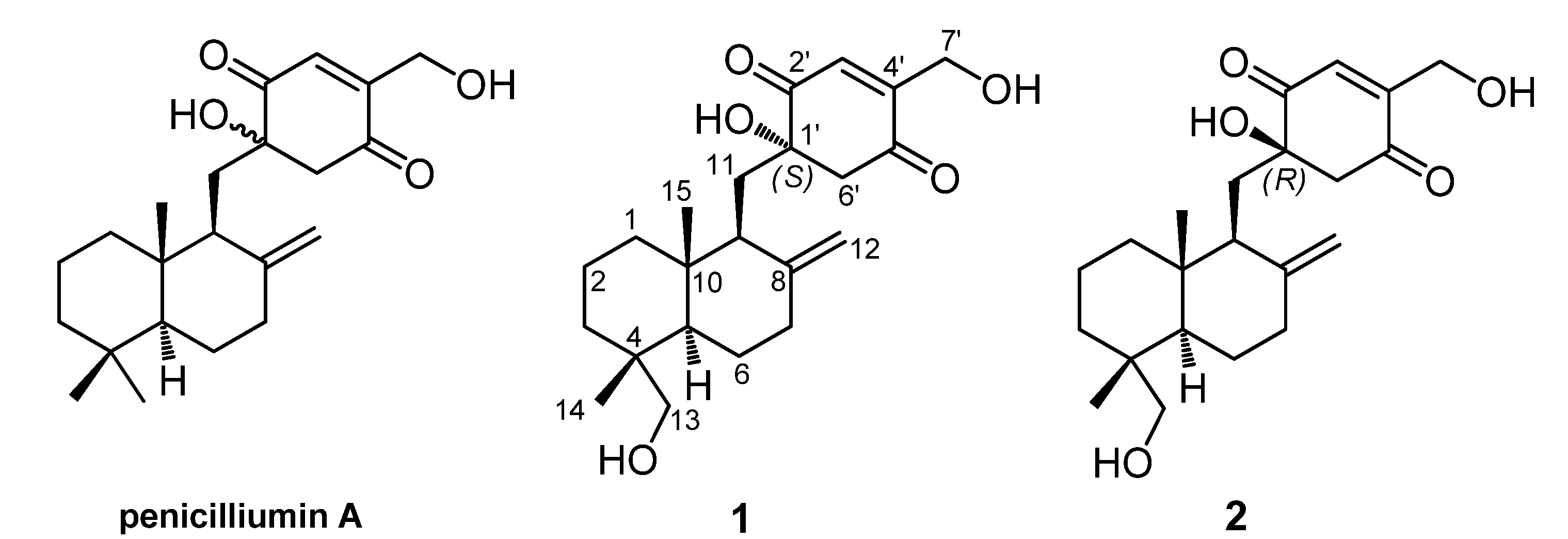
Compound 1 was obtained as yellow viscous oil and its HRESIMS spectrum showed a peak at m/z 399.2145 [M + Na]+ (calcd for C22H32NaO5, 399.2142) corresponding to the molecular formula C22H32O5 (seven unsaturations). 1H and 13C NMR spectra in combination with the HSQC analysis (Table 1) revealed the presence of two methyl groups, nine sp3 methylenes (two were oxygen-bearing), two sp3 methines, three sp3 quaternary carbons (one was oxygen-bearing), four olefinic carbons (one was terminally double-protonated) and two carbonyl carbons. In the 1H–1H COSY spectrum (Figure 2), three spin systems were confirmed: from C-1 to C-3; from C-5 to C-7; and from C-9 to C-11, as shown in Figure 2. The remaining degrees of unsaturation except two carbonyl groups and two olefinic bonds revealed the presence of three rings in 1. Only twenty-nine hydrogens directly connected to the carbon atoms in the HSQC spectrum indicated the existence of three hydroxyl groups, corresponding to the three oxygenated groups. HMBC correlations (Figure 2) from H3-14 to C-3, C-4, C-5 and C-13, and from H2-13 to C-3, C-4, C-5 and C-14, and from H-5 to C-10 and C-15, and H3-15 to C-1, C-5 and C-10 established a cyclohexane ring with a methyl group (Me-14) and an oxygenated methylene (δC 71.6, CH2OH-13) substituted at C-4, and a methyl group (Me-15) at C-10. Combining with the HMBC correlations from H-5 to C-6, and from H-9 to C-5, C-10 and C-15, and from H2-11 to C-8 and C-10, and H2-12 to C-7, C-8 and C-9, a drimane sesquiterpene skeleton was identified. A p-quinone moiety with a hydroxyl group at C-1ʹ (δC 78.1) and an oxygenated methylene (δC 58.7, CH2OH-7ʹ) at C-4ʹ, was established based on the HMBC correlations from H-3ʹ to C-1ʹ, C-5ʹ and C-7ʹ, and from H2-6ʹ to C-1ʹ, C-2ʹ and C-5ʹ, and H2-7ʹ to C-3ʹ and C-4ʹ. The p-quinone moiety was attached to the sesquiterpene ring at C-11 on account of the HMBC correlations from H-9 to C-1ʹ, and from H2-11 to C-1ʹ and C-6ʹ. These spectroscopic features indicated that 1 was a p-quinone-linked drimane sesquiterpene (Figure 1), similar to penicilliumin A, except for an additional hydroxyl group at C-13 in 1.
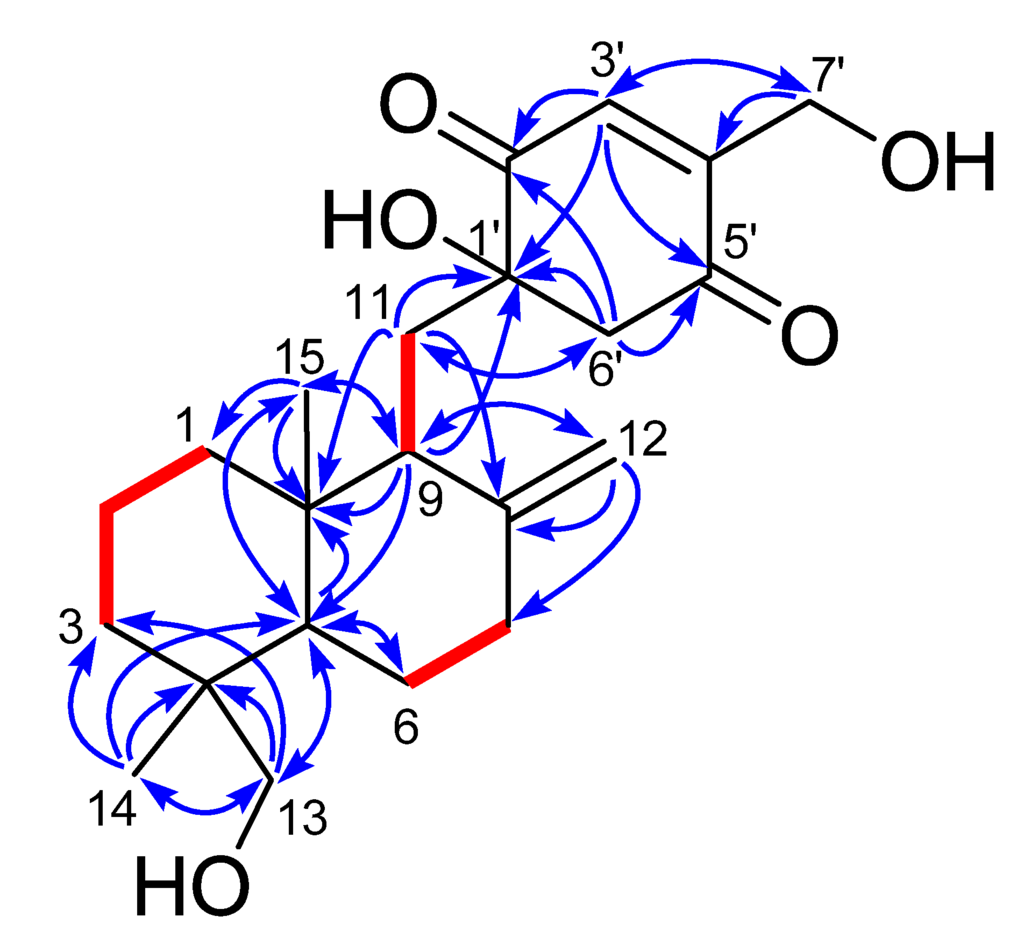
Figure 2.
1H–1H COSY (bold lines) and key HMBC correlations (arrows) of 1 and 2.
Figure 2.
1H–1H COSY (bold lines) and key HMBC correlations (arrows) of 1 and 2.
The other co-isolated quinone sesquiterpene, named myrothecol H (2) had the same molecular formula (C22H32O5) as 1, which was determined from HRESIMS data. Analysis of 1D NMR (Table 1), HSQC, 1H–1H COSY and HMBC spectra (Figure 2) of 2 revealed that 2 and 1 had the same planar structure. The main difference between 1 and 2 was the inconsistent 13C NMR data of C-11 (δC 32.5 in 1; 35.5 in 2) and C-6′ (δC 51.8 in 1; 55.0 in 2), suggested that 2 and 1 were a pair of epimers differing at the stereochemistry of C-1′.
The assignment of the relative configurations of the drimane sesquiterpene units in 1 and 2 were straightforward because of the observation of NOE correlations (NOEs) of H-5/H-9, H-5/H-13a (α-orientation) and H3-15/H-11a (β-orientation) in both of the NOESY spectra of 1 and 2. The absolute configurations of the units in both compounds could be assigned to be the same as those of previously obtained myrothecols from the same strain by comparison with their NMR data and the biosynthesis consideration [8]. However, the sesquiterpene unit and the p-quinone moiety in 1 and 2 were connected by two single bonds (C-9–C-11 and C-11–C-1′), and the two compounds should exist as an equilibrium of multiple rotamers of the two bonds. Thus, the assignment of the configurational relationship between the sesquiterpene unit and the p-quinone moiety become a critical matter for the stereochemical assignment of the two compounds.
The NOEs of H-11a/H3-15, H-11b/H-1β, H-12a/H-7β and H-11a/H-12b observed in both of the NOESY spectra of 1 and 2, and the J9,11a value (7.3 Hz in 1, 8.6 Hz in 2) indicated that H-9 was nearly in an anti relationship with H-11a and in a gauche relationship with H-11b, thus C-9–C-11 bond was relatively fixed, and the flexibilities of 1 and 2 were mainly due to the rotation of C-11–C-1′ bond.

Table 1.
NMR data (600/150 MHz, pyridine-d5) of compounds 1 and 2.
| 1 | 2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Position | δC, type | δH, mult. (J in Hz) | δC, type | δH, mult. (J in Hz) |
| 1α | 38.9, CH2 | 1.31–1.36 m | 38.9, CH2 | 1.47 dt (13.0, 3.0) |
| 1β | 1.76 br d (12.9) | 1.76–1.83 overlapped | ||
| 2α | 19.5, CH2 | 1.40–1.44 m | 19.6, CH2 | 1.52–1.57 m |
| 2β | 1.57 qt (13.4, 3.0) | 1.61 qt (13.3. 3.0) | ||
| 3α | 36.3, CH2 | 1.83 m | 36.5, CH2 | 1.79 overlapped |
| 3β | 1.38 br d (12.3) | 1.40 dt (12.8, 3.1) | ||
| 4 | 39.3, C | 38.9, C | ||
| 5 | 49.2, CH | 1.91 dd (12.9, 2.6) | 49.2, CH2 | 1.76–1.83 overlapped |
| 6α | 24.9, CH2 | 1.81–1.86 overlapped | 25.1, CH2 | 1.76–1.83 overlapped |
| 6β | 1.27–1.31 overlapped | 1.26 qd (12.3, 4.1) | ||
| 7α | 38.8, CH2 | 2.04 td (12.9, 4.5) | 38.8, CH2 | 2.02 td (12.5 5.0) |
| 7β | 2.34 dt (12.6, 3.0) | 2.23–2.28 overlapped | ||
| 8 | 150.5, C | 149.7, C | ||
| 9 | 51.5, CH | 2.43 br d (7.0) | 51.2, CH | 2.48 br d (8.5) |
| 10 | 40.9, C | 40.6, C | ||
| 11a | 32.5, CH2 | 2.25 dd (15.1, 7.3) | 35.5, CH2 | 2.27 dd (14.7, 8.7) |
| 11b | 2.24 br d (15.1) | 2.21 br d (14.7) | ||
| 12a | 108.3, CH2 | 4.94 br s | 107.5, CH2 | 4.81 br s |
| 12b | 4.71 br s | 4.64 br s | ||
| 13a | 71.6, CH2 | 3.62 d (10.7) | 71.7, CH2 | 3.54 d (10.6) |
| 13b | 3.29 d (10.7) | 3.27 d (10.6) | ||
| 14 | 18.4, CH3 | 0.79 s | 18.2, CH3 | 0.78 s |
| 15 | 15.9, CH3 | 0.72 s | 16.0, CH3 | 0.69 s |
| 1ʹ | 78.1, C | 78.8, C | ||
| 2ʹ | 202.2, C | 201.8, C | ||
| 3ʹ | 134.5, CH | 7.49 t (2.0) | 135.4, CH | 7.49 t (2.0) |
| 4ʹ | 154.9, C | 153.7, C | ||
| 5ʹ | 197.7, C | 197.9, C | ||
| 6ʹα | 51.8, CH2 | 3.24 d (16.3) | 55.0, CH2 | 3.41 d (15.7) |
| 6ʹβ | 3.32 d (16.3) | 3.47 d (15.7) | ||
| 7ʹa | 58.7, CH2 | 4.94 dd (18.6, 2.1) | 58.8, CH2 | 5.01 dd (18.4, 2.1) |
| 7′b | 4.86 dd (18.6, 2.1) | 4.85 dd (18.4, 2.1) | ||
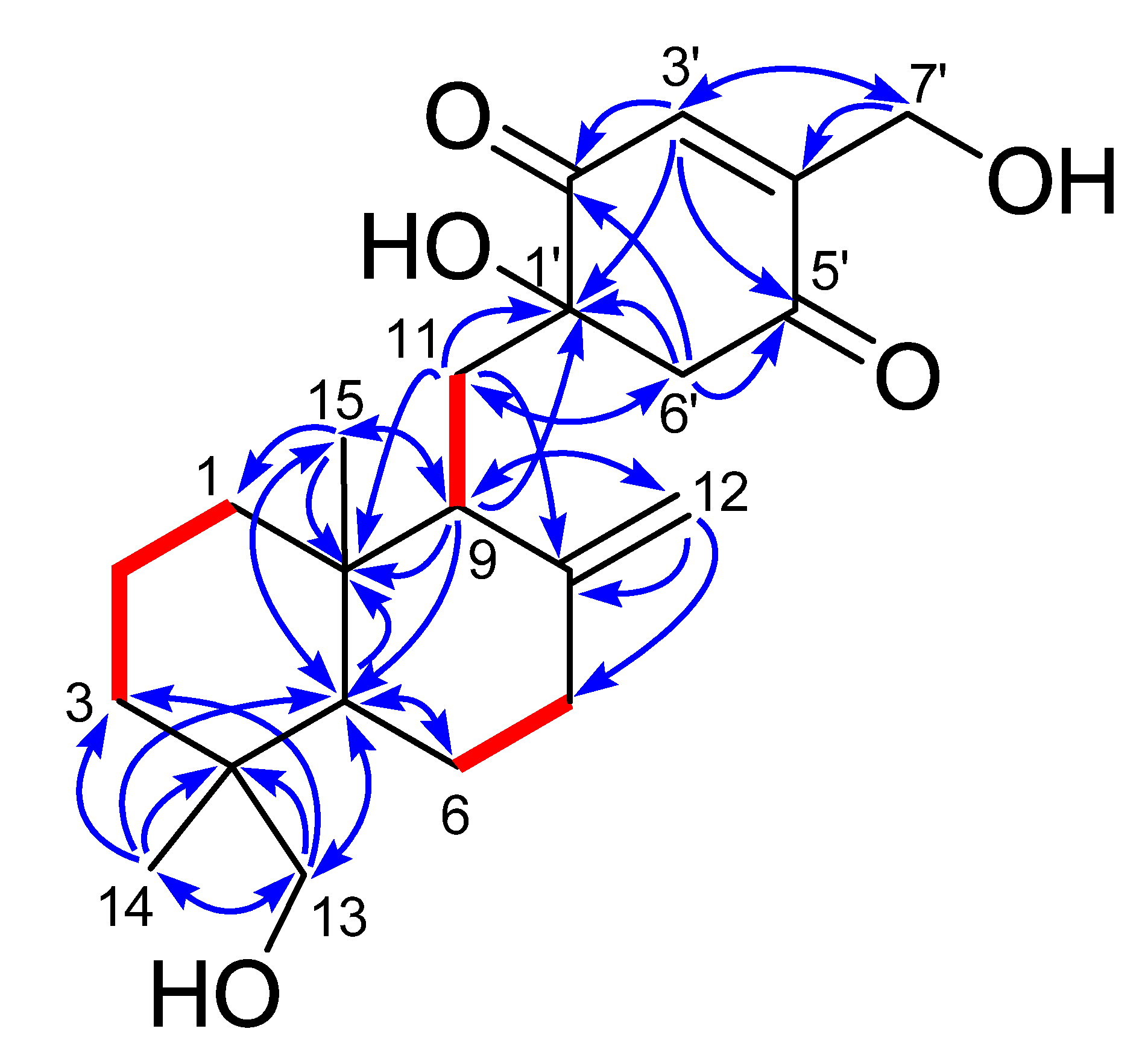
In order to find out the dominant low-energy conformers of 1 and 2, 1′S- and 1′R-isomers were built and subjected to theoretical conformational analysis as previously described [8]. As a result (Table S1), 1′S-isomer afforded three groups of low-energy conformers (1a, 1b and 1c), of which the group 1a, represented by the global energy minimum 1a1 (Figure 3) accounted for 52.6% equilibrium population of the compound in MeOH solution according to Boltzmann statistics and the group 1b, as represented by the second lowest energy minimum 1b1, accounted for 44.8% equilibrium population, whereas, 1′R-isomer gave two groups of low-energy conformers (2a and 2b) with the group 2a (accounting for 86.8% equilibrium population) being dominant minima. The NOE correlation of H-6ʹβ/H-11a observed in the NOESY spectrum of 1 was corresponding with both of the conformers 1a1 and 1b1, whereas the NOEs of H-6ʹβ/H-9 and H-6ʹβ/H-12b were distinctive of the conformer 1b1 (Figure 3). The situation in the NOESY spectrum of compound 2, was that the NOE correlation of H-6ʹα/H-11b was clearly existed while the NOEs of H-6ʹα with H-12a and H-11a were absent, which was characteristic of the energy minima 2a as shown for conformer 2a1 in Figure 3. Thus, 1 and 2 were assigned to have 1′S and 1′R configurations, respectively.
Considering that the main difference between 1 and 2 was the 13C NMR chemical shifts of C-11 and C-6′, the consistent 13C NMR data of C-11 (δC 34.7 in penicilliumin A; 35.5 in 2) and C-6′ (δC 53.0 in penicilliumin A; 55.0 in 2) suggested that the absolute configuration of penicilliumin A was the same as that of myrothecol H, although the NMR data of myrothecols G and H, and penicilliumin A were recorded in different deuterated solvents.
Since penicilliumin A showed cytotoxic activity against tumor cells [7], compounds 1 and 2 were evaluated for in vitro cytotoxicity against human lung adenocarcinoma A549, human hepatoma HepG2, and human cervical carcinoma HeLa cell lines by MTT method. Compounds 1 and 2 displayed weak cytotoxicity against the tested cell lines above. The IC50 values were presented in Table 2.
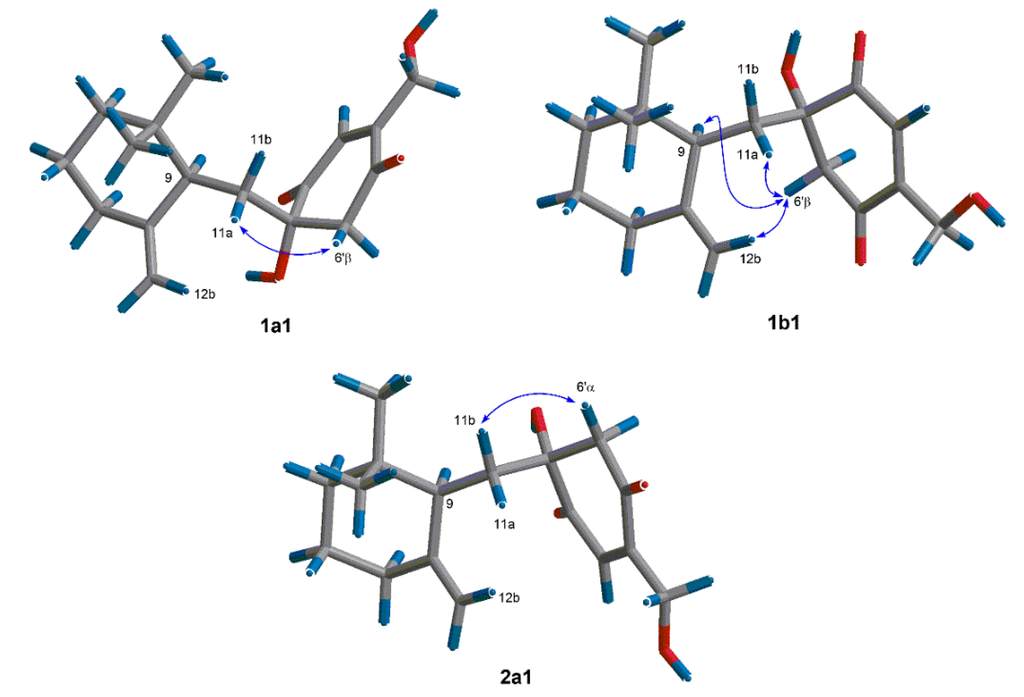
Figure 3.
Dominant low-energy conformers (1a1, 1b1 and 2a1) and key NOE correlations (curves) of 1 and 2.
Figure 3.
Dominant low-energy conformers (1a1, 1b1 and 2a1) and key NOE correlations (curves) of 1 and 2.
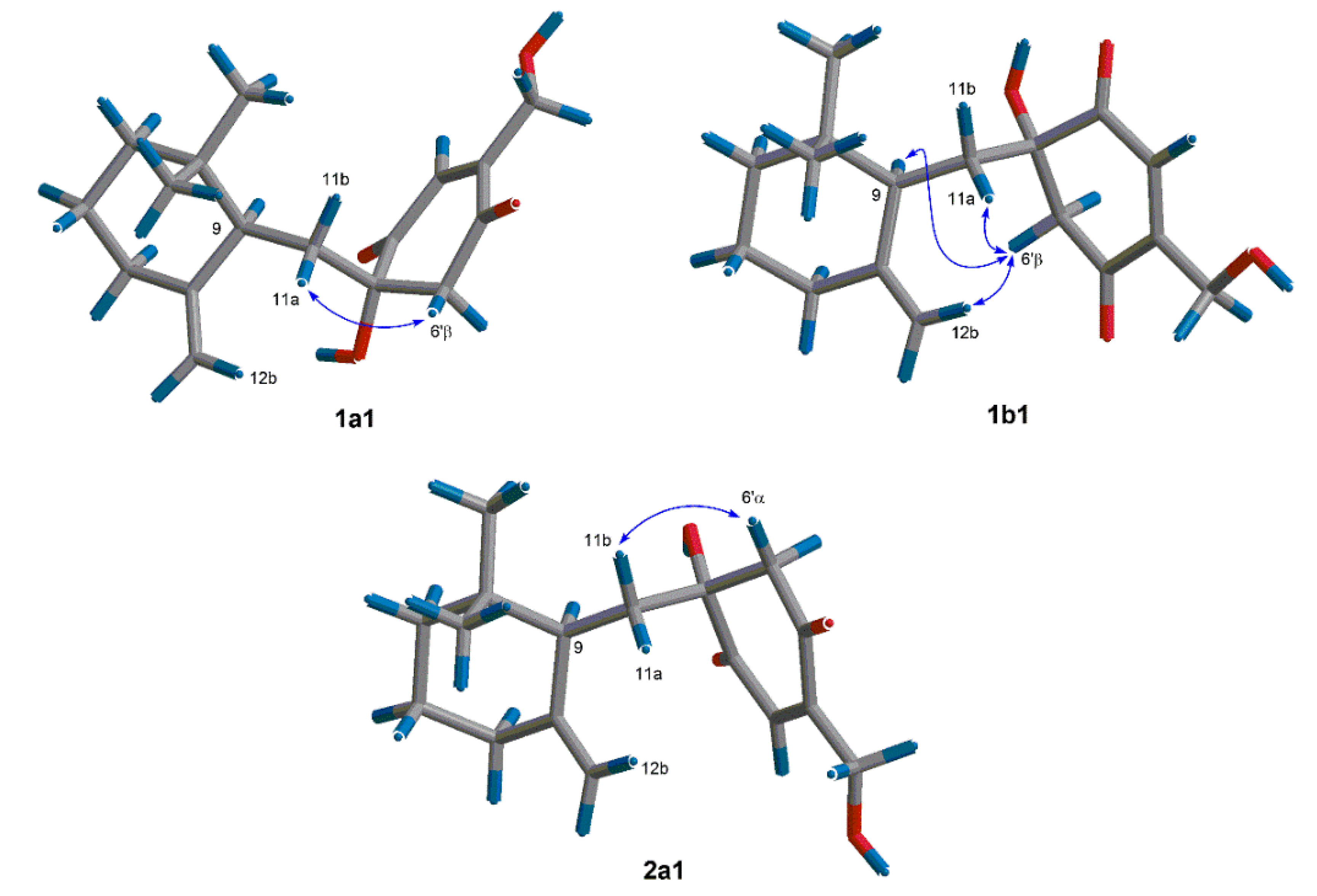

Table 2.
Cytotoxicity (IC50, μM) a of compounds 1 and 2.
| Cell Lines | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| A549 | HeLa | HepG2 | |
| 1 | 46.7 ± 0.8 | 15.9 ± 0.8 | 31.9 ± 0.9 |
| 2 | 40.2 ± 1.5 | 28.7 ± 0.8 | 25.7 ± 1.6 |
| Adriamycin b | 0.69 ± 0.06 | 0.47 ± 0.05 | 1.22 ± 0.02 |
a Values represent means ± SD based on three individual experiments; b Positive control.
3. Experimental Section
3.1. General
Optical rotations were measured on a Perkin EImer 343 spectropolarimeter. UV measurements were conducted with a Perkin EImer Lambda 650 UV/VIS spectrometer. 1H NMR (600 MHz), 13C NMR (150 MHz), and 2D NMR spectra were recorded on a Bruker AV-600 instrument in pyridine-d5 with TMS as an internal reference. HRESIMS data were obtained on a Bruker Bio TOF IIIQ mass spectrometer in positive-ion mode. Preparative HPLC was performed by an HPLC system equipped with a Shimadzu LC-6AD pump and a Shimadzu RID-10A refractive index detector (Shimadzu Corporation, Kyoto, Japan) using a YMC-pack ODS-A C18 column (5 µm, 250 × 20 mm). For column chromatography, silica gel 60 (100–200 mesh, Qingdao Marine Chemical Ltd., Qingdao, China), Chromatoxex℘ ODS (C18, MB100 40~75 µm) were used. Thiazolyl Blue Tetrazolium Bromide (MTT) regent for cytotoxicity was purchased from Aladdin℘, Shanghai Jingchun Biochemical & Technologies Inc., shanghai, China. The cytotoxicity assay was determined with a Genois microplate reader (Tecan Group, Männedorf, Zürich, Switzerland).
3.2. Fungal Material and Fermentation
The producing fungus, Myrothecium sp. SC0265, was isolated from a forest leaf litter sample collected at the district of rare and endangered tree species in the Dinghu Mountain Biosphere Reserve, Guangdong, China, in March 2003. It was authenticated by its morphological characteristics and ITS DNA sequence data (Genbank accession number KM086710) by Prof. Tai-hui Li, Guangdong Institute of Microbiology, Guangzhou, China. Fermentation of the fungus was performed as previously described [8].
3.3. Extraction and Isolation
The mycelia culture was extracted with 95% EtOH, and the resultant extract was sequentially partitioned with petroleum ether, EtOAc, and n-BuOH. The EtOAc-soluble extract (28 g) was separated by silica gel CC and eluted with CHCl3–MeOH mixtures of increasing polarity (98:2–70:30) to afford eight primary fractions (F1–F8). Fraction F3, obtained on elution with CHCl3–MeOH (95:5), was then subjected to ODS CC using decreasing polar aqueous MeOH (40%–90%) to obtain seven fractions (F3-a–F3-g). Fraction F3-d, obtained from elution with 60% MeOH, was further separated by preparative HPLC (5 mL/min) using 60% MeOH to obtain 1 (29.0 mg, tR = 17.9 min) and 2 (71.2 mg, tR = 19.5 min).
Compound 1: yellow viscous oil;
+15 (c 0.20, MeOH); UV (MeOH) λmax (log ε) 202 (4.0), 238 (3.7); 1H and 13C NMR data, see Table 1; HRESIMS m/z 399.2145 [M + Na]+ (calcd for C22H32NaO5, 399.2142).
Compound 2: yellow viscous oil;
+44 (c 0.93, MeOH); UV (MeOH) λmax (log ε) 210 (4.0), 238 (3.8); 1H and 13C NMR data, see Table 1; HRESIMS m/z 399.2144 [M + Na]+ (calcd for C22H32NaO5, 399.2142).
3.4. Theoretical Conformational Analysis Method
Molecular Merck force field (MMFF) calculations and DFT calculations were performed with Spartan’14 software package (Wavefunction Inc., Irvine, CA, USA) [9], using default grids and convergence criteria. MMFF conformational searches were performed using Monte Carlo search method. The low-energy conformers within a 10 kcal/mol energy window were optimized using DFT method at the B3LYP/6-31G (d,p) level. Frequency calculations were run at the same level to estimate free energies at 298.15 K. Solvent effects were taken into account by using polarizable continuum model (PCM). In a preliminary set of calculations with compounds 1 and 2, the truncated structure (the fragment from C-2 to C-4, including the methyl and hydroxymethyl groups attached at C-4, was removed from the intact structure and an H atom was added to C-1 and C-5) provided similar relative energies with the intact structure, and the SVP basis set gave consistent results with the TZVP one.
3.4. Cytotoxicity Assay
Human lung adenocarcinoma A549, human hepatoma HepG2, and human cervical carcinoma HeLa cell lines were obtained from Kunming Institute of Zoology, Chinese Academy of Sciences (Kunming, China). The cytotoxicity assay was conducted by MTT method [10].
4. Conclusions
In the case of quinone-drimane sesquiterpenes such as penicilliumin A, and myrothecols G and H (1 and 2), the p-quinone moiety and the drimane sesquiterpene unit were linked by two single bonds, which made the stereochemistry elucidation difficult because of the flexibility. The MMFF conformational search followed by geometry optimization using DFT method at B3LYP/6-31G (d,p) level on 1 and 2, indicated that they existed the dominant low-energy conformers, which were flexible in a certain range and revealed their tracks by NOE correlations and the specific coupling constants. Thus, the stereochemistry of myrothecols G and H (1 and 2) were identified by the detailed analysis of relevant NOE correlations and the coupling constants, combining with the theoretical conformational analysis. The absolute configuration of penicilliumin A was suggested to be the same as that of myrothecol H by the comparison with their 13C NMR data of C-11 and C-6′.
Supplementary Files
Supplementary File 1Acknowledgments
We thank Tai-Hui Li, Guangdong Institute of Microbiology, for microbiological authentication, and Ai-Jun Sun and Yun Zhang, South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, for recording the HRESIMS data. This work was supported by an NSFC grant (no. 81172942).
Author Contributions
Ying Fu was responsible for the fermentation, isolation and partial structure elucidation work. Ping Wu performed the cytotoxicity assay. Jinghua Xue carried out the isolation and the storage of the fungus. Xiaoyi Wei conducted the theoretical conformation analysis. Ying Fu, Hanxiang Li and Xiaoyi Wei wrote the paper, which was revised and approved by all the authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Hu, G.P.; Yuan, J.; Sun, L.; She, Z.G.; Wu, J.H.; Lan, X.J.; Zhu, X.Z.; Liu, Y.C.; Chen, S.P. Statistical research on marine natural products based on data obtained between 1985 and 2008. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 514–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, G.Q.; Zhang, J.G.; Cheng, J.F. Overview of chirality and chiral drugs. In Chiral Drugs: Chemistry and Biological Action, 1st ed.; Lin, G.Q., You, Q.D., Cheng, J.F., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 14–18. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, M.R. Plants against malaria. Part 1: Cinchona or the Peruvian bark. J. R. Coll. Physicians Edinb. 2002, 32, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Williams, E.M.V. The mode of action of quinidine on isolated rabbit atria interpreted from intracellular potential records. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1958, 13, 276–287. [Google Scholar]
- Fraga, B.M. Natural sesquiterpenoids. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2012, 30, 1229–1230. [Google Scholar]
- Marcos, I.S.; Conde, A.; Moro, R.F.; Basabe, P.; Diez, D.; Urones, J.G. Quinone/hydroquinone sesquiterpenes. Mini Rev. Org. Chem. 2010, 7, 230–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.P.; Zhou, X.F.; Wang, F.Z.; Liu, K.S.; Yang, B.; Yang, X.W.; Peng, Y.; Liu, J.; Ren, Z.; Liu, Y.H. A new cytotoxic sesquiterpene quinone produced by Penicillium sp. F00120 isolated from a deep sea sediment sample. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Wu, P.; Xue, J.H.; Wei, X.Y. Cytotoxic and antibacterial quinone sesquiterpenes from a Myrothecium Fungus. J. Nat. Prod. 2014, 77, 1791–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Mennucci, B.; Petersson, G.A.; et al. Gaussian 09, revision C.01; Gaussian: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2010.
- Shi, J.F.; Wu, P.; Jiang, Z.H.; Wei, X.Y. Synthesis and tumor cell growth inhibitory activity of biotinylated annonaceous acetogenins. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 71, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
