The Diagnostic and Prognostic Value of Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte and Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratios in Urosepsis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Clinical Implications
4.2. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AUC | Area Under the Curve |
| CBC | Complete Blood Count |
| CI | Confidence Interval |
| COPD | Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease |
| CRP | C-Reactive Protein |
| CT | Computed Tomography |
| ECLIA | Electro-Chemiluminescence Immunoassay |
| GCS | Glasgow Coma Scale |
| HR | Heart Rate |
| ICU | Intensive Care Unit |
| IQR | Interquartile Range |
| LYM | Lymphocytes |
| MAP | Mean Arterial Pressure |
| NEU | Neutrophils |
| NEWS | National Early Warning Score |
| NLR | Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio |
| PCT | Procalcitonin |
| PLR | Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratio |
| PLT | Platelets |
| ROC | Receiver Operating Characteristic |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
| SE | Standard Error |
| SIRS | Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome |
| SOFA | Sequential Organ Failure Assessment |
| UTI | Urinary Tract Infection |
| WBC | White Blood Cell Count |
References
- Karamouzos, V.; Paraskevas, T.; Mulita, F.; Karteri, S.; Oikonomou, E.; Ntoulias, N.; Pantzaris, N.D.; Bourganou, V.; Velissaris, D. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and platelet-to-lymphocyte percentage ratio as predictors of in-hospital mortality in sepsis: An observational cohort study. Mater. Sociomed. 2022, 34, 33–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Peng, W.; Zheng, X. The prognostic value of the combined neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and neutrophil-to-platelet ratio (NPR) in sepsis. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 15075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppola, A.; Costantino, S.; Ciccozzi, M.; Angeletti, S. Diagnostic accuracy and prognostic value of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratios in septic patients outside the intensive care unit. Medicina 2021, 57, 811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Mivefroshan, A.; Yaghoobpoor, S.; Khanzadeh, S.; Siri, G.; Rahmani, F.; Aleseidi, S. Prognostic value of platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio in sepsis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Biomed. Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 9056363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, M.; Deutschman, C.S.; Seymour, C.W.; Shankar-Hari, M.; Annane, D.; Bauer, M.; Bellomo, R.; Bernard, G.R.; Chiche, J.-D.; Coopersmith, C.M.; et al. The third international consensus definitions for sepsis and septic shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA 2016, 315, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.S.; Kim, N.Y.; Na, S.H.; Youn, Y.H.; Shin, C.S. Reference values of neutrophil–lymphocyte ratio, lymphocyte–monocyte ratio, platelet–lymphocyte ratio, and mean platelet volume in healthy adults in South Korea. Medicine 2018, 97, e11138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mireștean, C.C.; Stan, M.C.; Iancu, R.I.; Iancu, D.P.T.; Bădulescu, F. The prognostic value of platelet–lymphocyte ratio, neutrophil–lymphocyte ratio, and monocyte–lymphocyte ratio in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC)—A retrospective single-center study and a literature review. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 3396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thombare, D.; Bhalerao, A.; Dixit, P.; Joshi, S.; Dapkekar, P. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio in antenatal women with pre-eclampsia: A case–control study. Cureus 2023, 15, e40338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagenlehner, F.M.; Pilatz, A.; Weidner, W. Urosepsis—From the view of the urologist. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2011, 38, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Roberts, D.; Wood, K.E.; Light, B.; Parrillo, J.E.; Sharma, S.; Suppes, R.; Feinstein, D.; Zanotti, S.; Taiberg, L.; et al. Duration of hypotension before initiation of effective antimicrobial therapy is the critical determinant of survival in human septic shock. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 34, 1589–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, T.A.; Johnson, J.R. Medical and economic impact of extraintestinal infections due to Escherichia coli: Focus on urosepsis an increasingly important endemic problem. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2003, 5, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellinger, R.P.; Schorr, C.A.; Levy, M.M. A users’ guide to the 2016 surviving sepsis guidelines. Intensive Care Med. 2017, 43, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagenlehner, F.; Wullt, B.; Ballarini, S.; Zingg, D.; Naber, K.G. Social and economic burden of recurrent urinary tract infections and quality of life: A patient web-based study (GESPRIT). Expert Rev. Pharmacoecon. Outcomes Res. 2018, 18, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonkat, G.; Bartoletti, R.; Bruyere, F.; Cai, T.; Geerlings, S.; Köves, B.; Pilatz, A.; Medina-Polo, J.; Schneidewind, L.; Schubert, S.; et al. EAU Guidelines on Urological Infections; EAU Annual Congress: Milan, Italy, 2023; ISBN 978-94-92671-19-6. [Google Scholar]
- Bonkat, G.; Wagenlehner, F.; Cai, T.; Geerlings, S.; Medina-Polo, J.; Köves, B.; Pilatz, A.; Schneidewind, L.; Schubert, S.; Veeratterapillay, R.; et al. Classification of urinary tract infections in 2025: Moving beyond uncomplicated and complicated. Eur. Urol. Open Sci. 2025, 75, 44–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragoescu, A.N.; Pădureanu, V.; Stănculescu, A.D.; Chiutu, L.; Pădureanu, R.; Andrei, M.; Radu, M.A.; Mitroi, G.; Dragoescu, P.O. The role of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) in urosepsis-associated delirium. Cureus 2024, 16, e62110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salciccioli, J.D.; Marshall, D.C.; Pimentel, M.A.; Santos, M.D.; Pollard, T.; Celi, L.A.; Shalhoub, J. The association between the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and mortality in critical illness: An observational cohort study. Crit. Care 2015, 19, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forget, P.; Khalifa, C.; Defour, J.P.; Latinne, D.; Van Pel, M.C.; De Kock, M. What is the normal value of the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio? BMC Res. Notes 2017, 10, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djordjevic, D.; Rondovic, G.; Surbatovic, M.; Stanojevic, I.; Udovicic, I.; Andjelic, T.; Zeba, S.; Milosavljevic, S.; Stankovic, N.; Abazovic, D.; et al. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, monocyte-to-lymphocyte ratio, platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio, and mean platelet volume-to-platelet count ratio as biomarkers in critically ill and injured patients: Which ratio to choose to predict outcome and nature of bacteremia? Mediat. Inflamm. 2018, 2018, 3758068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, R.; Gupta, M.; Sharma, M.; Jash, D.; Jain, N.; Sinha, N.; Chaudhry, A.; Chaudhry, D. Diagnostic and prognostic role of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in early and late phase of sepsis. Indian J. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 22, 660–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kriplani, A.; Pandit, S.; Chawla, A.; de la Rosette, J.J.M.C.H.; Laguna, P.; Reddy, S.J.; Somani, B.K. Neutrophil–lymphocyte ratio (NLR), platelet–lymphocyte ratio (PLR) and lymphocyte–monocyte ratio (LMR) in predicting SIRS and sepsis after percutaneous nephrolithotomy. Urolithiasis 2022, 50, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Zhang, D.; Jin, T.; Lu, T.; Zhou, F. Progress in the study of biomarkers for early prediction of systemic inflammatory response syndrome after percutaneous nephrolithotomy. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1142346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guliciuc, M.; Porav-Hodade, D.; Chibelean, B.C.; Voidazan, S.T.; Ghirca, V.M.; Maier, A.C.; Marinescu, M.; Firescu, D. The role of biomarkers and scores in describing urosepsis. Medicina 2023, 59, 597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Li, X.; Zhao, J.; Wang, X.; Ma, L. Analysis and modelling of the predictive value of PCT, PLR and NLR for ureteric sepsis after ureteral stone surgery: A retrospective cohort study. Arch. Esp. Urol. 2024, 77, 498–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villanueva-Congote, J.; Hinojosa-Gonzalez, D.; Segall, M.; Eisner, B.H. The relationship between neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio, platelet/neutrophil ratio, and risk of urosepsis in patients with ureteral stones and suspected urinary tract infection. World J. Urol. 2024, 42, 596–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Zhang, Q.; Duan, M.; Xu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J. Predictive value of the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in the prognosis and risk of death for adult sepsis patients: A meta-analysis. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1336456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.M.; Satici, M.O.; Eroglu, S.E. Unraveling the clinical significance and prognostic value of NLR, PLR, SII, SIRI, and DNI: An extensive literature review. Turk. J. Emerg. Med. 2024, 24, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schupp, T.; Weidner, K.; Rusnak, J.; Jawhar, S.; Forner, J.; Dulatahu, F.; Brück, L.M.; Dudda, J.; Hoffmann, U.; Abba, M.L.; et al. The neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as diagnostic and prognostic tool in sepsis and septic shock. Clin. Lab. 2023, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, C.D.; Parajuli, A.; Gale, H.J.; Bulteel, N.S.; Schuetz, P.; de Jager, C.P.C.; Loonen, A.J.M.; Merekoulias, G.I. The utility of peripheral blood leucocyte ratios as biomarkers in infectious diseases: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Infect. 2019, 78, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Huang, X.; Zhang, W. Platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio as a prognostic predictor of mortality for sepsis: Interaction effect with disease severity—A retrospective study. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e022896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Abdou, A.A.A.; Al-Daher, N.A. Study of the platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio as a prognostic indicator in patients with infections. Front. Health Inform. 2024, 13, 8920–8930. [Google Scholar]
- Malah, M.; Abusaba, M.A.; Said-Gebaly, A.; El Baradey, G.F.; Youse, N.K. Comparison between platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio, procalcitonin serum level, and SOFA score for outcome prediction in patients with sepsis. Egypt. J. Anaesth. 2024, 40, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Liu, Y.; Yang, C.; Li, X. Review of the predictive value of biomarkers in sepsis mortality. Emerg. Med. Int. 2024, 2024, 2715606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Poll, T.; Shankar-Hari, M.; Wiersinga, W.J. The immunology of sepsis. Immunity 2021, 54, 2450–2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Parameter | Total (n = 223) | Urosepsis (n = 159) | Septic Shock (n = 64) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 63.9 ± 13.0 | 63.4 ± 13.9 | 65.1 ±10.3 | 0.156 * |
| Sex (M/F) | 141/82 | 102/57 | 39/25 | 0.652 # |
| SOFA score | 6 [4–8] | 5 [4–7] | 8 [6–10] | <0.001 ^ |
| NEWS | 6 [5–8] | 5 [5–7] | 9 [7–10] | <0.001 ^ |
| GCS | 12 [11–14] | 13 [12–14] | 11 [10–12] | <0.001 ^ |
| MAP (mmHg) | 74.2 ± 9.6 | 78.3 ± 7.7 | 64.1 ± 5.3 | <0.001 * |
| HR (beats/min) | 86 ± 19 | 81 ± 12 | 98 ± 27 | <0.001 * |
| RR (breaths/min) | 23 ± 7 | 22 ± 6 | 27 ± 8 | <0.001 * |
| WBC (×103/mm3) | 16 [14–19] | 16 [13–19] | 16 [14–18] | 0.562 ^ |
| NEU (×103/mm3) | 13 [11–16] | 13 [11–16] | 13 [11–16] | 0.423 ^ |
| LYM (×103/mm3) | 1.2 [0.8–1.6] | 1.3 [0.8–1.5] | 1.0 [0.6–1.8] | 0.496 ^ |
| PLT (×103/mm3) | 203 [160–275] | 216 [162–277] | 195 [156–237] | 0.112 ^ |
| Lactate (mmol/L) | 1.3 [1.0–1.9] | 1.2 [1.0–1.7] | 1.9 [1.3–3.9] | <0.001 ^ |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 1.4 [1.0–2.3] | 1.2 [1.0–2.2] | 2.0 [1.4–2.3] | <0.05 ^ |
| Bilirubin (mg/dL) | 1.5 [1.1–2.2] | 1.3 [1.1–2.1] | 2.2 [1.3–2.8] | <0.05 ^ |
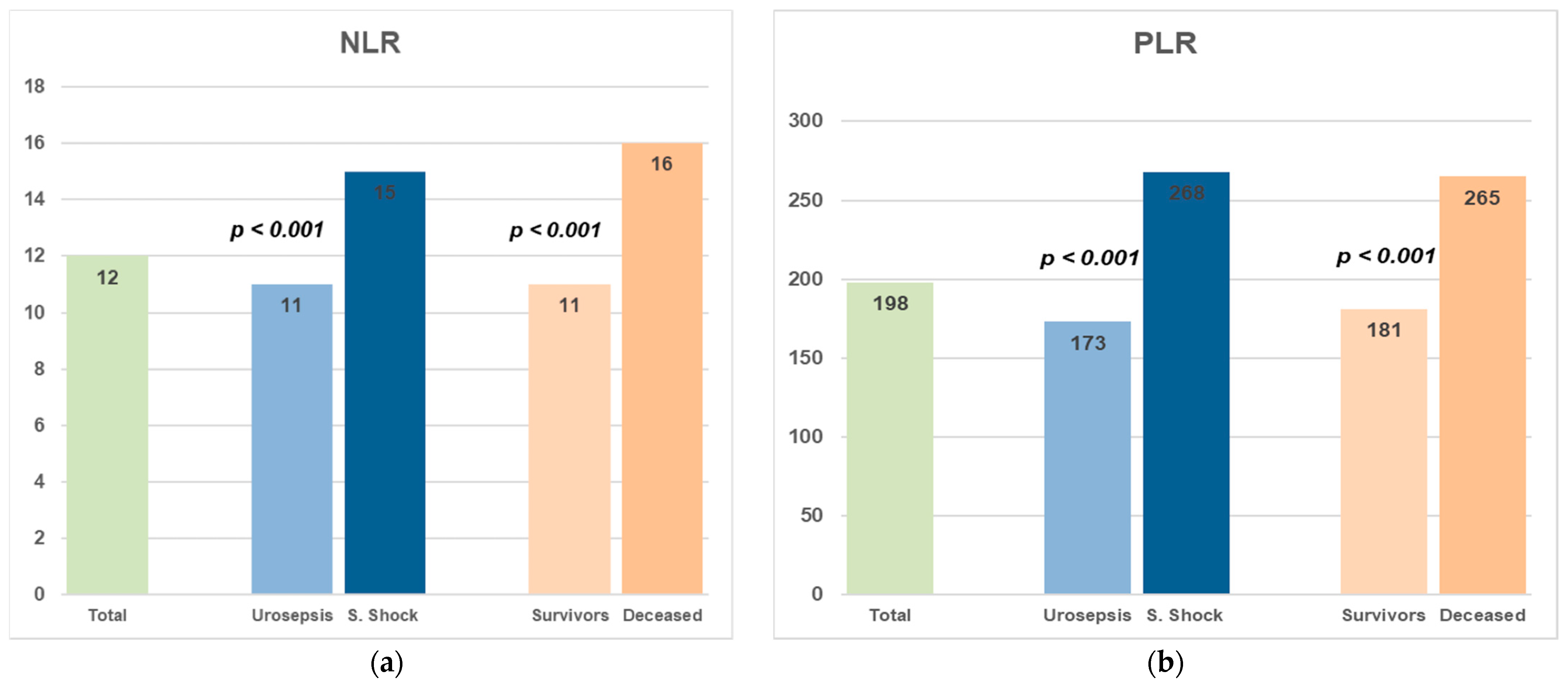
| NLR | 12 [9–15] | 11 [8–13] | 15 [13–20] | <0.001 ^ |
| PLR | 198 [144–277] | 173 [133–243] | 268 [207–329] | <0.001 ^ |
| C-Reactive Protein (mg/L) | 121 [96–143] | 116 [94–135] | 131 [101–150] | 0.413 ^ |
| Procalcitonin (ng/mL) | 11.8 [9.1–14.6] | 11.4 [8.5–13.5] | 13.5 [11.5–19.2] | <0.001 ^ |
| Comorbidity | Total (n = 223) | Urosepsis (n = 159) | Septic Shock (n = 64) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diabetes mellitus | 72 | 46 | 26 | 0.312 |
| Chronic kidney disease | 56 | 36 | 20 | 0.221 |
| Ischemic heart disease | 48 | 31 | 17 | 0.415 |
| Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease | 34 | 22 | 12 | 0.540 |
| Chronic liver disease | 12 | 7 | 5 | 0.284 |
| Dementia | 10 | 6 | 4 | 0.442 |
| Cerebrovascular disease | 18 | 13 | 5 | 0.622 |
| Malignancy (prior or active) | 29 | 18 | 11 | 0.187 |
| Parameter | Total (n = 223) | Survivors (n = 180) | Deceased (n = 43) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 63.9 ± 13.0 | 64.1 ± 13.2 | 62.8 ± 12.1 | 0.253 * |
| Sex (M/F) | 141/82 | 119/61 | 22/21 | 0.652 # |
| SOFA score | 6 [4–8] | 6 [4–8] | 7 [6–9] | <0.01 ^ |
| NEWS | 6 [5–8] | 6 [5–7] | 7 [6–10] | <0.001 ^ |
| GCS | 12 [11–14] | 13 [11–14] | 12 [10–13] | <0.05 ^ |
| MAP (mmHg) | 74.2 ± 9.6 | 75.1 ± 9.1 | 70.3 ± 10.7 | <0.01 * |
| HR (beats/min) | 86 ± 19 | 86 ± 17 | 88 ± 28 | 0.325 * |
| RR (breaths/min) | 23 ± 7 | 23 ± 6 | 26 ± 9 | <0.05 * |
| WBC (×103/mm3) | 16 [14–19] | 16 [13–18] | 17 [14–22] | <0.05 ^ |
| NEU (×103/mm3) | 13 [11–16] | 13 [11–15] | 15 [11–17] | <0.05 ^ |
| LYM (×103/mm3) | 1.2 [0.8–1.6] | 1.1 [0.6–1.4] | 1.2 [0.7–1.6] | 0.231 ^ |
| PLT (×103/mm3) | 203 [160–275] | 208 [164–275] | 195 [155–266] | 0.453 ^ |
| Lactate (mmol/L) | 1.3 [1.0–1.9] | 1.3 [1.0–1.9] | 1.4 [1.2–2.4] | 0.373 ^ |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 1.4 [1.0–2.3] | 1.3 [1.0–2.5] | 1.4 [1.1–2.0] | 0.610 ^ |
| Bilirubin (mg/dL) | 1.5 [1.1–2.2] | 1.8 [1.1–2.3] | 1.2 [1.0–2.2] | <0.05 ^ |
| NLR | 12 [9–15] | 11 [8–14] | 16 [13–22] | <0.001 ^ |
| PLR | 198 [144–277] | 181 [137–265] | 265 [197–347] | <0.001 ^ |
| C-Reactive Protein (mg/L) | 121 [96–143] | 120 [96–140] | 126 [95–151] | 0.342 ^ |
| Procalcitonin (ng/mL) | 11.8 [9.1–14.6] | 11.7 [8.8–14.3] | 12.6 [10.6–18.4] | <0.05 ^ |
| Urosepsis vs. Septic Shock | Survivors vs. Deceased | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | AUC | SE | 95% CI | AUC | SE | 95% CI |
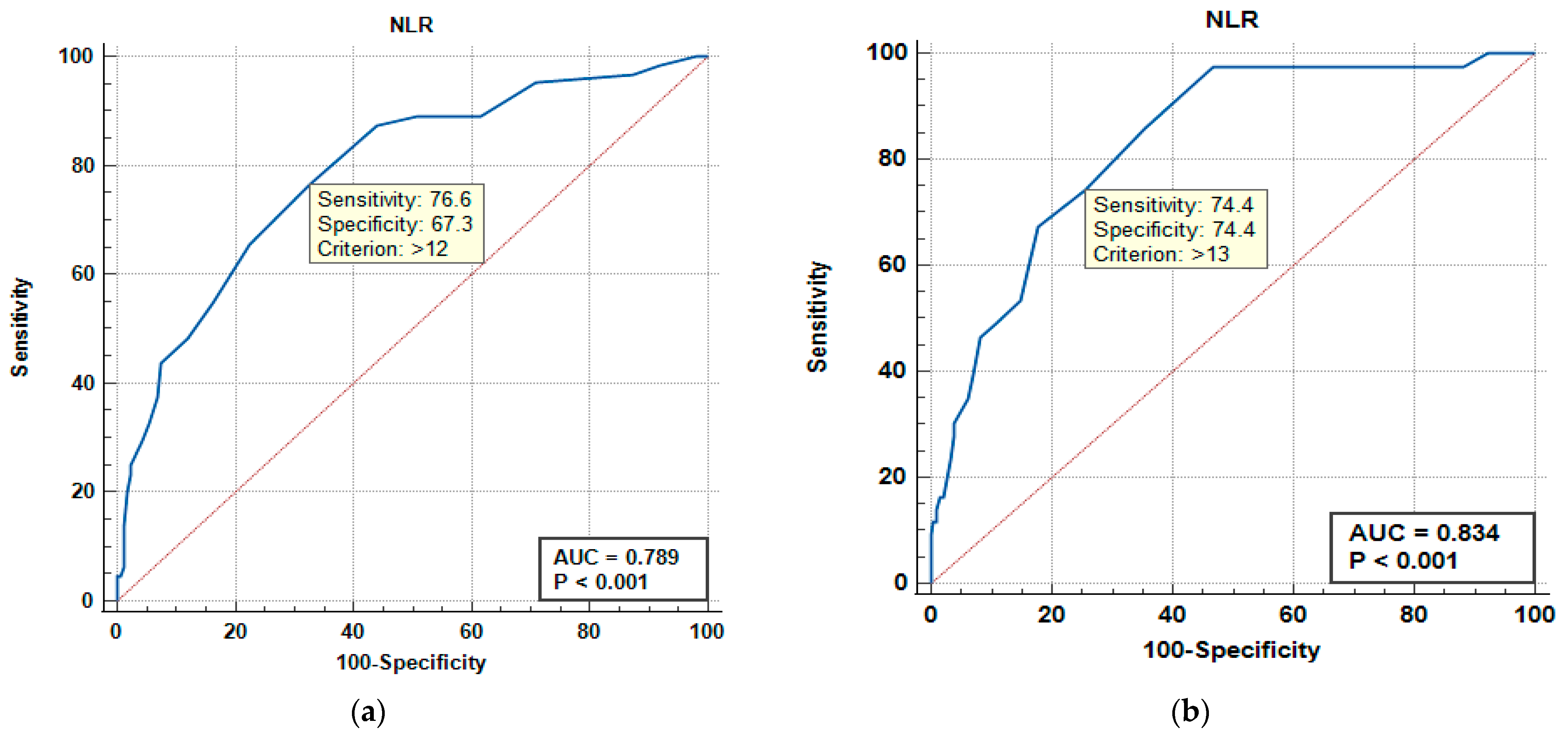
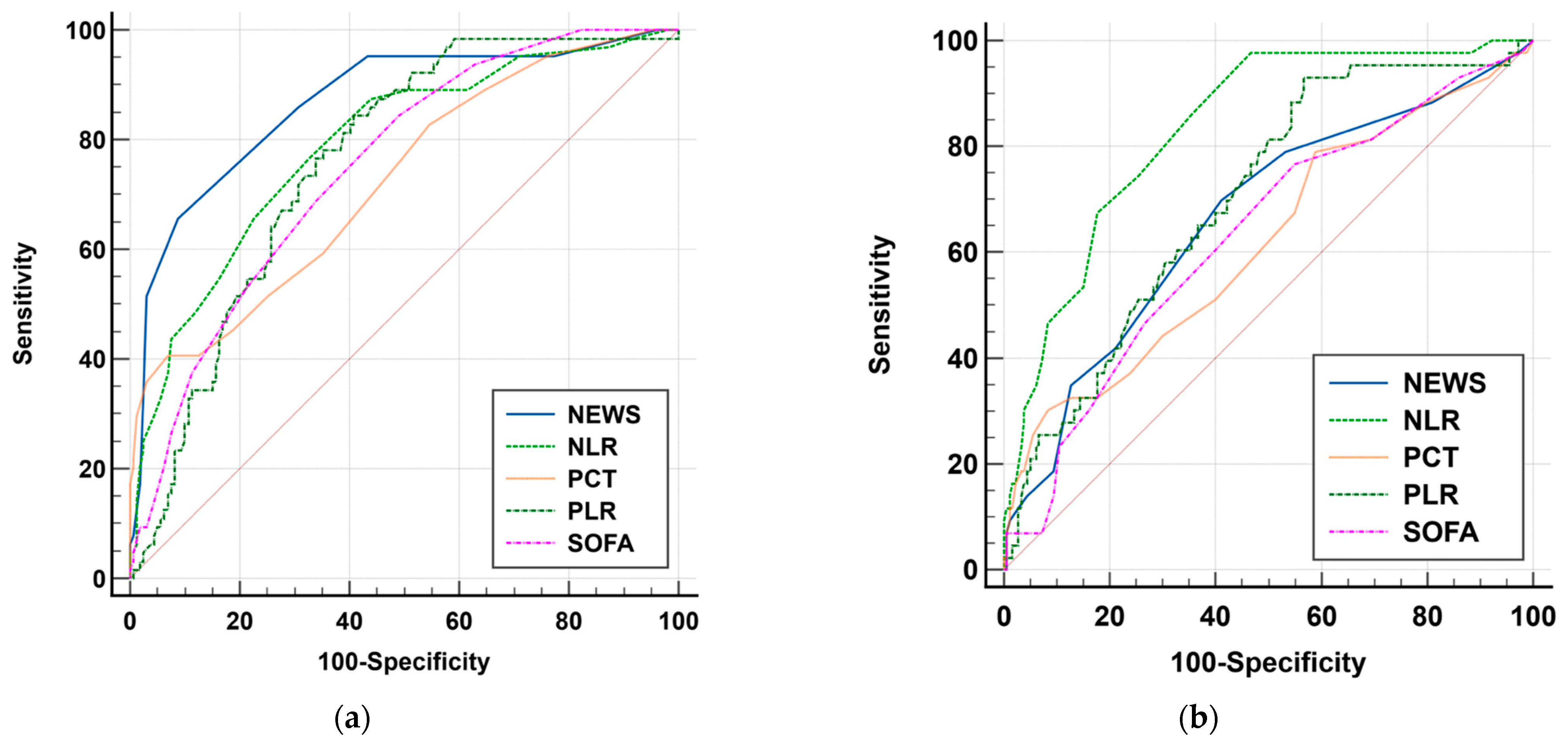
| NEWS | 0.866 | 0.0281 | 0.814 to 0.908 | 0.666 | 0.0473 | 0.600 to 0.727 |
| SOFA | 0.748 | 0.0337 | 0.686 to 0.804 | 0.631 | 0.0475 | 0.564 to 0.695 |
| PCT | 0.723 | 0.0381 | 0.660 to 0.781 | 0.618 | 0.0504 | 0.551 to 0.682 |
| PLR | 0.759 | 0.0328 | 0.698 to 0.814 | 0.700 | 0.0423 | 0.636 to 0.760 |
| NLR | 0.789 | 0.0340 | 0.730 to 0.841 | 0.834 | 0.0317 | 0.778 to 0.880 |
| Urosepsis (n = 223) | Severity—Sepsis Shock | Outcome—Death | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | Adjusted OR | 95% CI | p | Adjusted OR | 95% CI | p |
| NLR | 1.24 | 1.15–1.35 | <0.001 | 1.26 | 1.16–1.37 | <0.001 |
| PLR | 1.06 | 1.01–1.19 | 0.043 | 1.09 | 1.03–1.25 | 0.027 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 0.38 | 0.16–0.92 | 0.032 | 1.54 | 0.63–3.77 | 0.348 |
| Chronic kidney disease | 3.39 | 1.48–7.74 | 0.004 | 0.83 | 0.33–2.10 | 0.701 |
| Ischemic heart disease | 0.27 | 0.09–0.82 | 0.021 | 1.09 | 0.34–3.52 | 0.884 |
| COPD | 0.72 | 0.26–2.00 | 0.525 | 1.10 | 0.34–3.52 | 0.871 |
| Chronic liver disease | 0.49 | 0.09–2.66 | 0.407 | 4.25 | 0.90–20.07 | 0.068 |
| Dementia | 0.27 | 0.06–1.17 | 0.080 | 4.32 | 1.31–14.21 | 0.016 |
| Cerebrovascular disease | 0.74 | 0.12–4.74 | 0.752 | 2.02 | 0.39–10.56 | 0.406 |
| Malignancy (prior/active) | 0.55 | 0.16–1.98 | 0.363 | 2.09 | 0.52–8.37 | 0.300 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Drăgoescu, P.O.; Grigorescu, B.L.; Stănculescu, A.D.; Pănuș, A.; Florescu, N.D.; Cara, M.; Andrei, M.; Radu, M.; Mitroi, G.; Drăgoescu, A.N. The Diagnostic and Prognostic Value of Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte and Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratios in Urosepsis. Medicina 2025, 61, 1713. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61091713
Drăgoescu PO, Grigorescu BL, Stănculescu AD, Pănuș A, Florescu ND, Cara M, Andrei M, Radu M, Mitroi G, Drăgoescu AN. The Diagnostic and Prognostic Value of Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte and Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratios in Urosepsis. Medicina. 2025; 61(9):1713. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61091713
Chicago/Turabian StyleDrăgoescu, Petru Octavian, Bianca Liana Grigorescu, Andreea Doriana Stănculescu, Andrei Pănuș, Nicolae Dan Florescu, Monica Cara, Maria Andrei, Mihai Radu, George Mitroi, and Alice Nicoleta Drăgoescu. 2025. "The Diagnostic and Prognostic Value of Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte and Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratios in Urosepsis" Medicina 61, no. 9: 1713. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61091713
APA StyleDrăgoescu, P. O., Grigorescu, B. L., Stănculescu, A. D., Pănuș, A., Florescu, N. D., Cara, M., Andrei, M., Radu, M., Mitroi, G., & Drăgoescu, A. N. (2025). The Diagnostic and Prognostic Value of Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte and Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratios in Urosepsis. Medicina, 61(9), 1713. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61091713






