Curcumin as an Epigenetic Modulator: Suppression of Breast Cancer via the Hsa_circ_0001946/MiR-7-5p/Target Gene Axis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Tissue Specimens
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. Curcumin Treatment and Cell Transfection with circ_0001946 siRNA and miR-7-5p Mimic
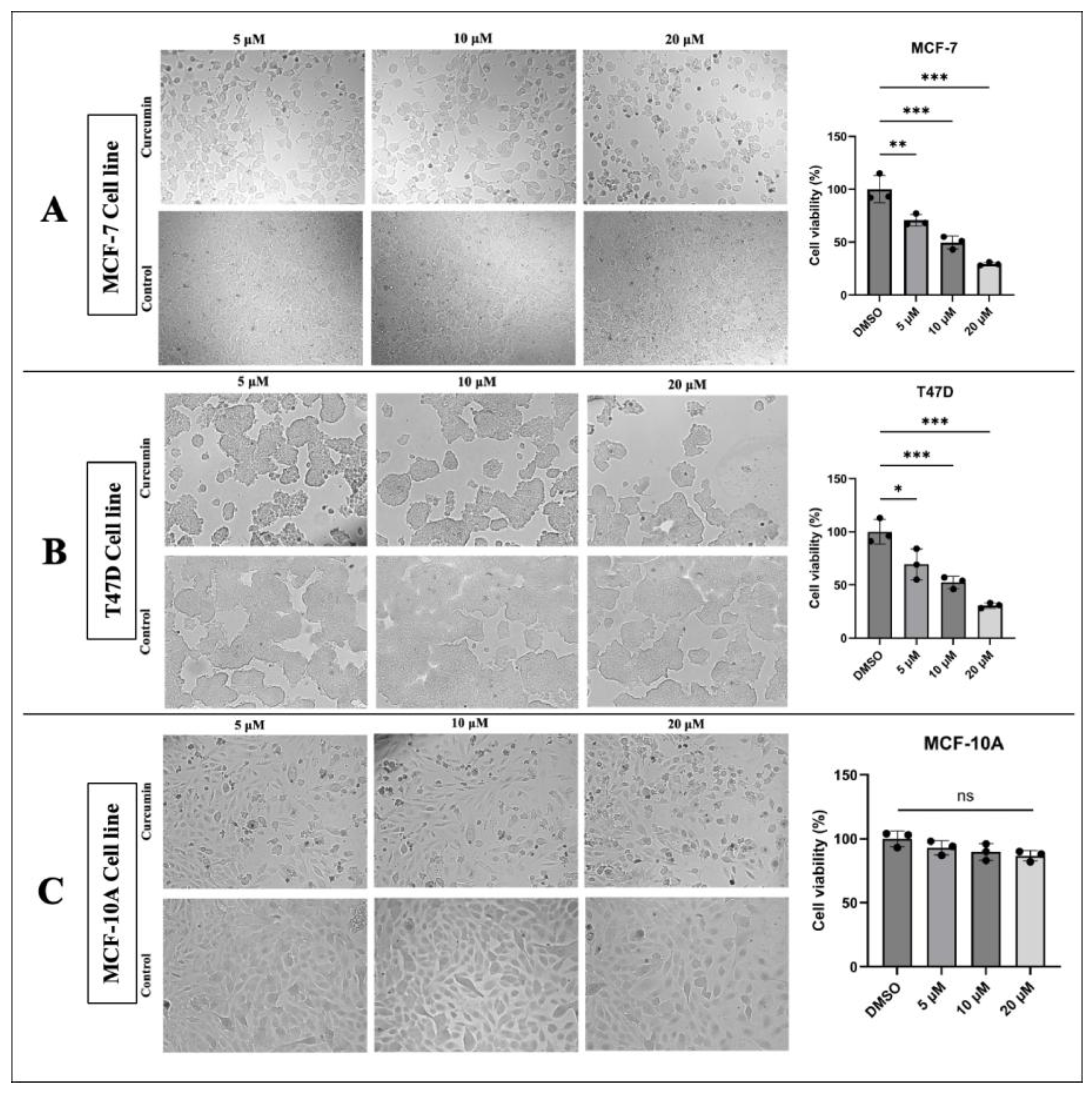
2.4. Cell Viability Detection
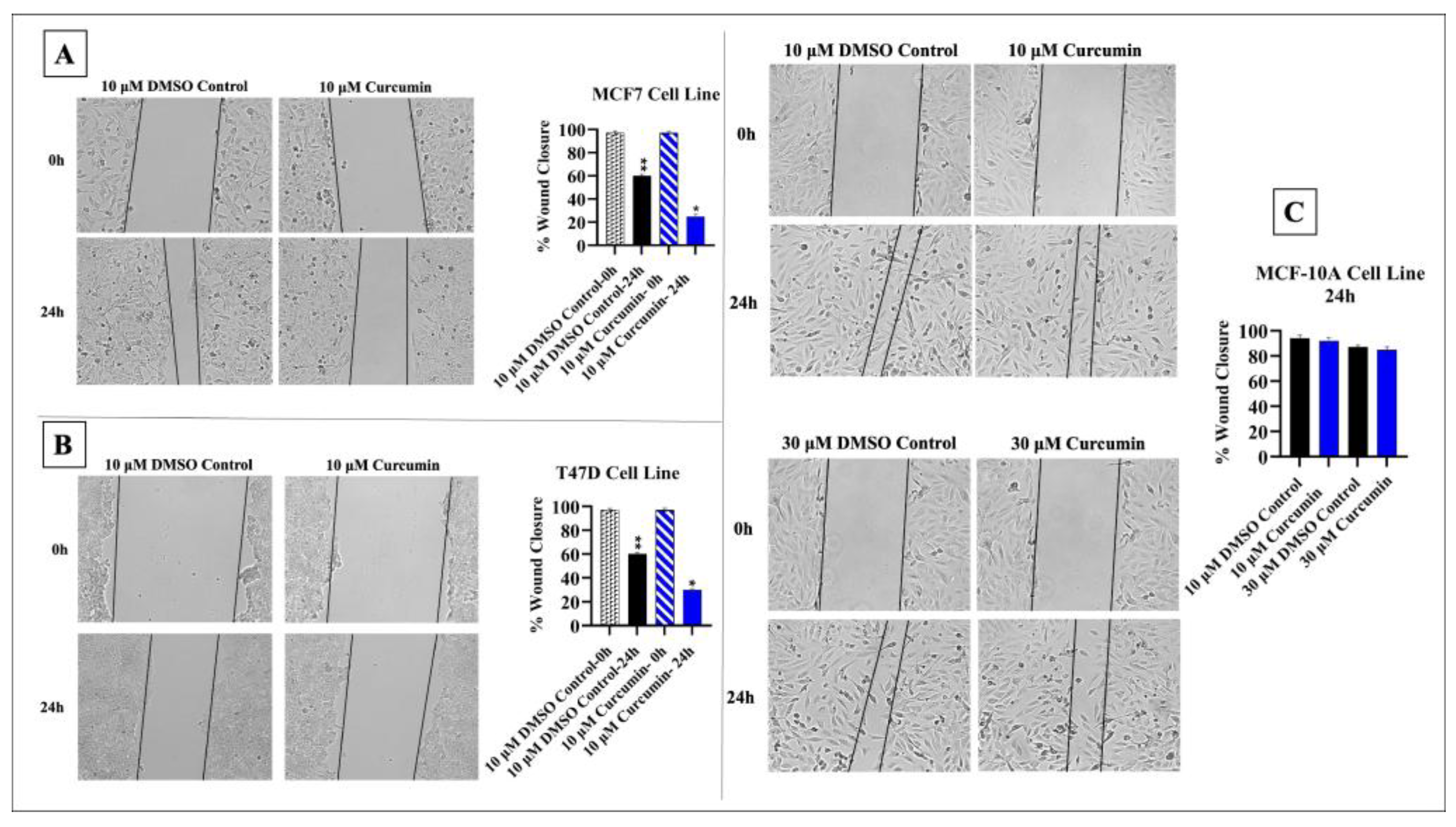
2.5. Wound Healing Assay
2.6. Cell Apoptosis Analysis
2.7. Identification of the Potential Target Genes of miR-7-5p
2.8. Relative Expression Levels Evaluated by qPCR
2.9. Western Blot Analysis
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Curcumin Inhibits the Proliferation and Migration of BC Cells
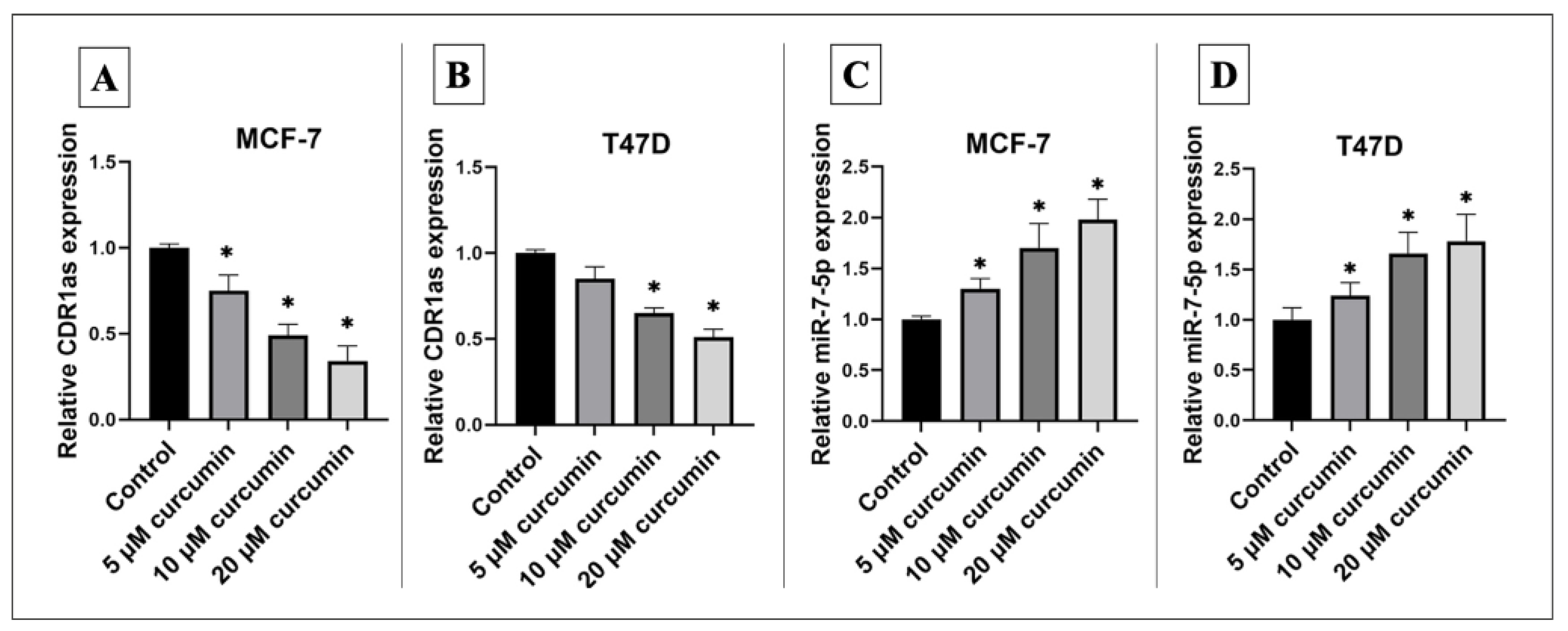
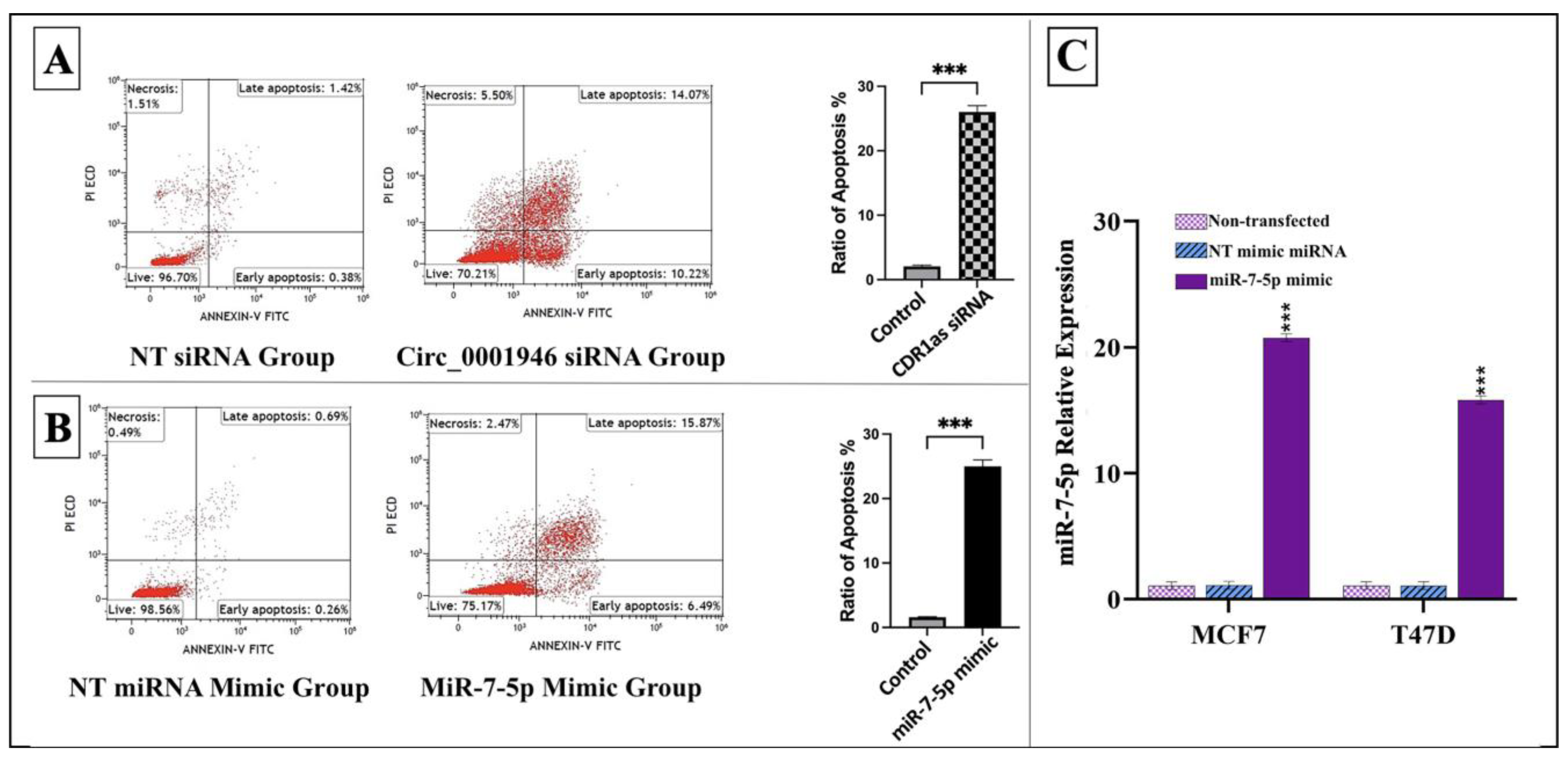
3.2. Curcumin Alters Expression of hsa_circ_0001946 and miR-7-5p in BC Cell Line
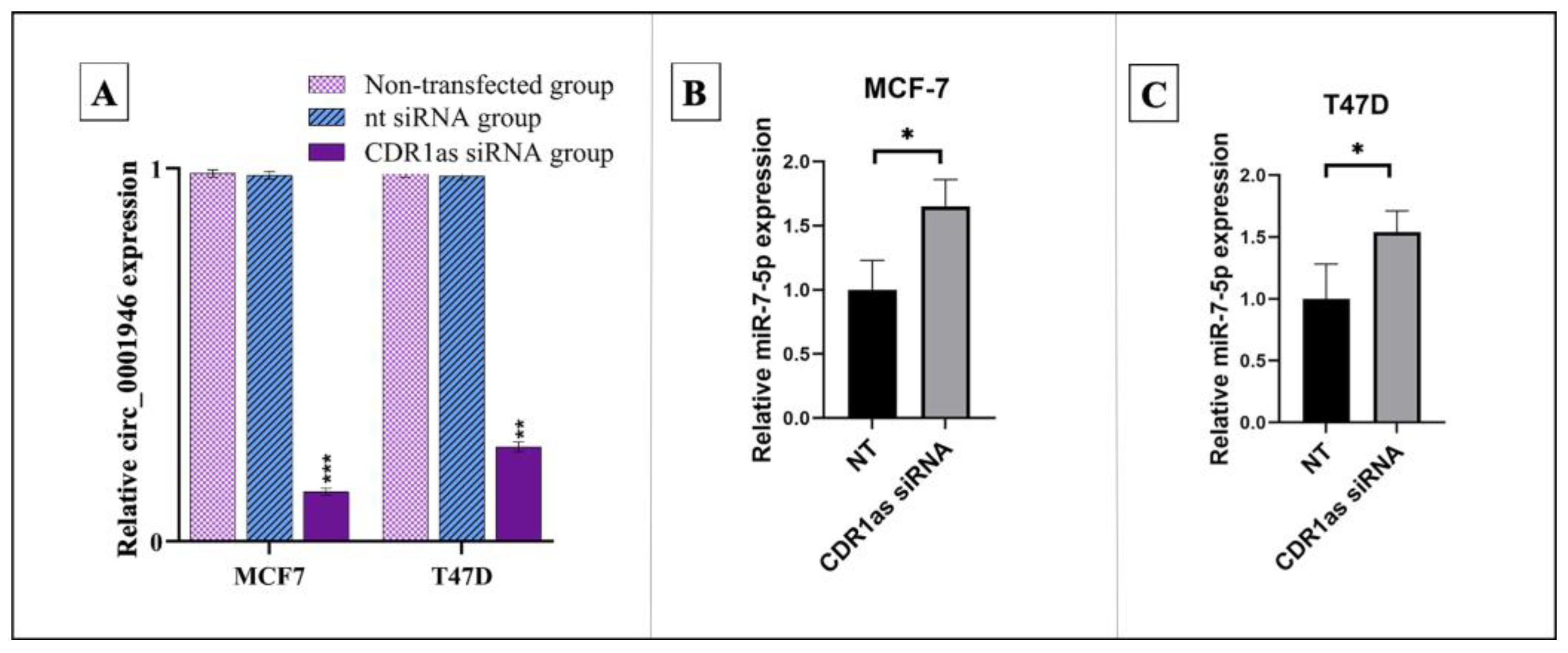
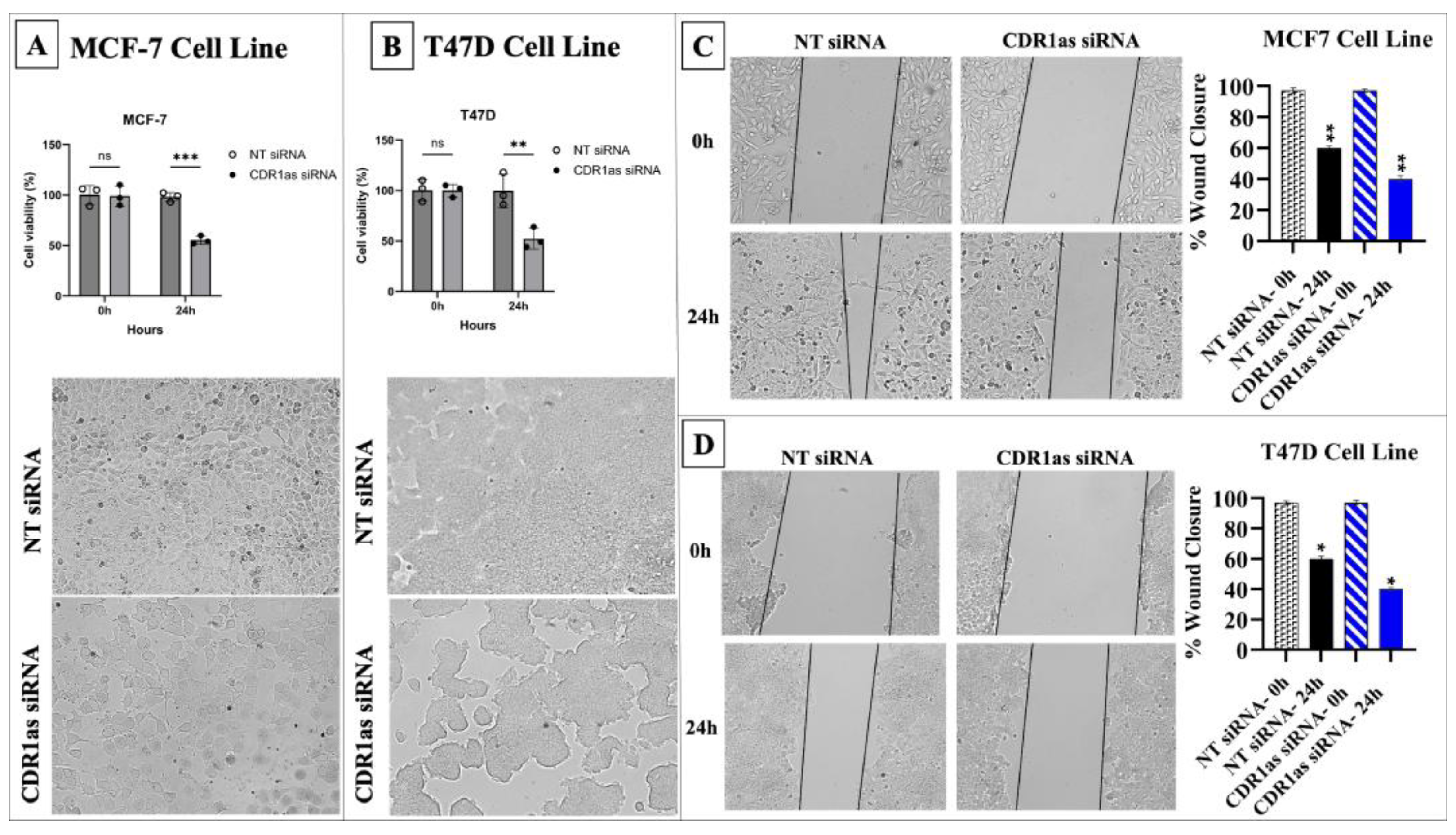
3.3. Knockdown of circ_0001946 Hindered the Viability and Migration of BC Cells by Upregulating miR-7-5p
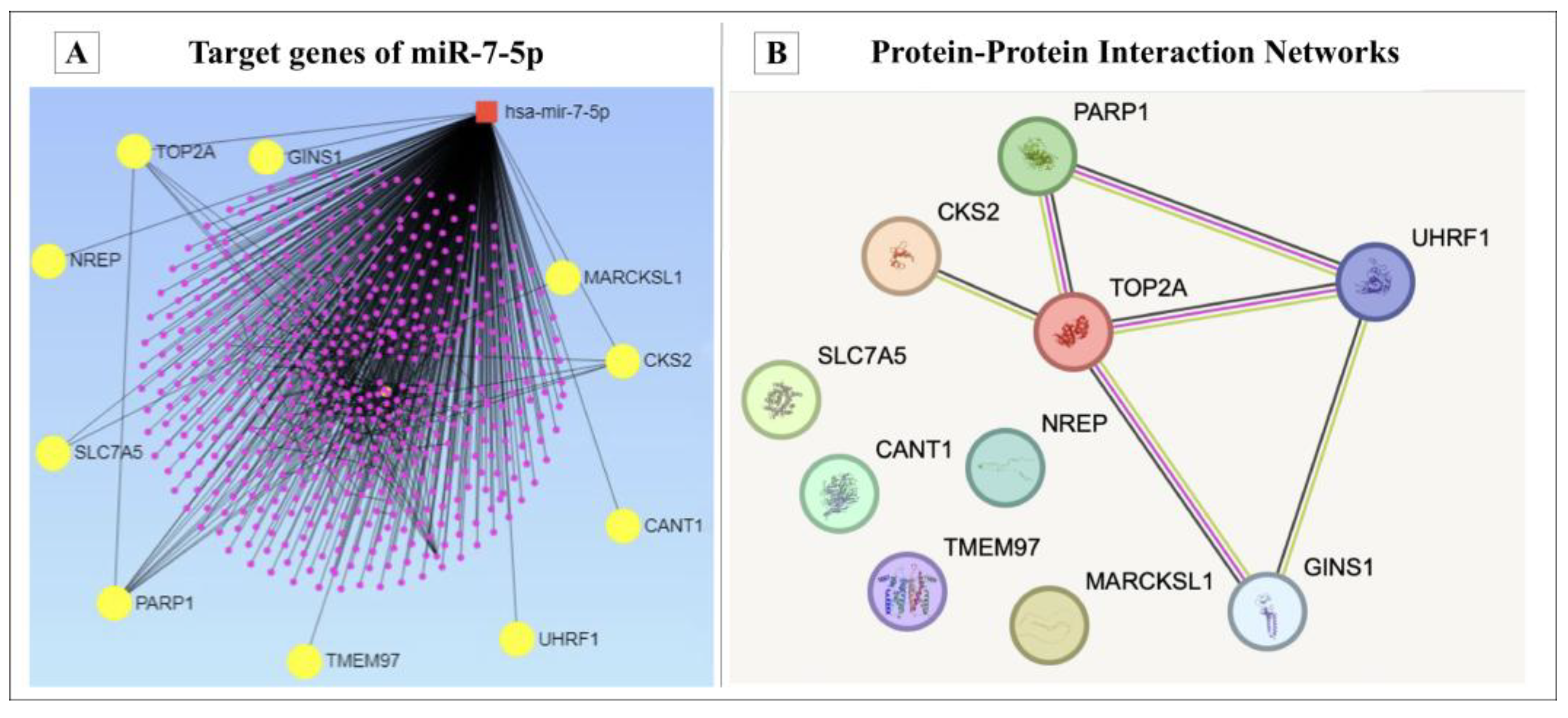
3.4. Bioinformatic Analysis of miR-7-5p Target Genes
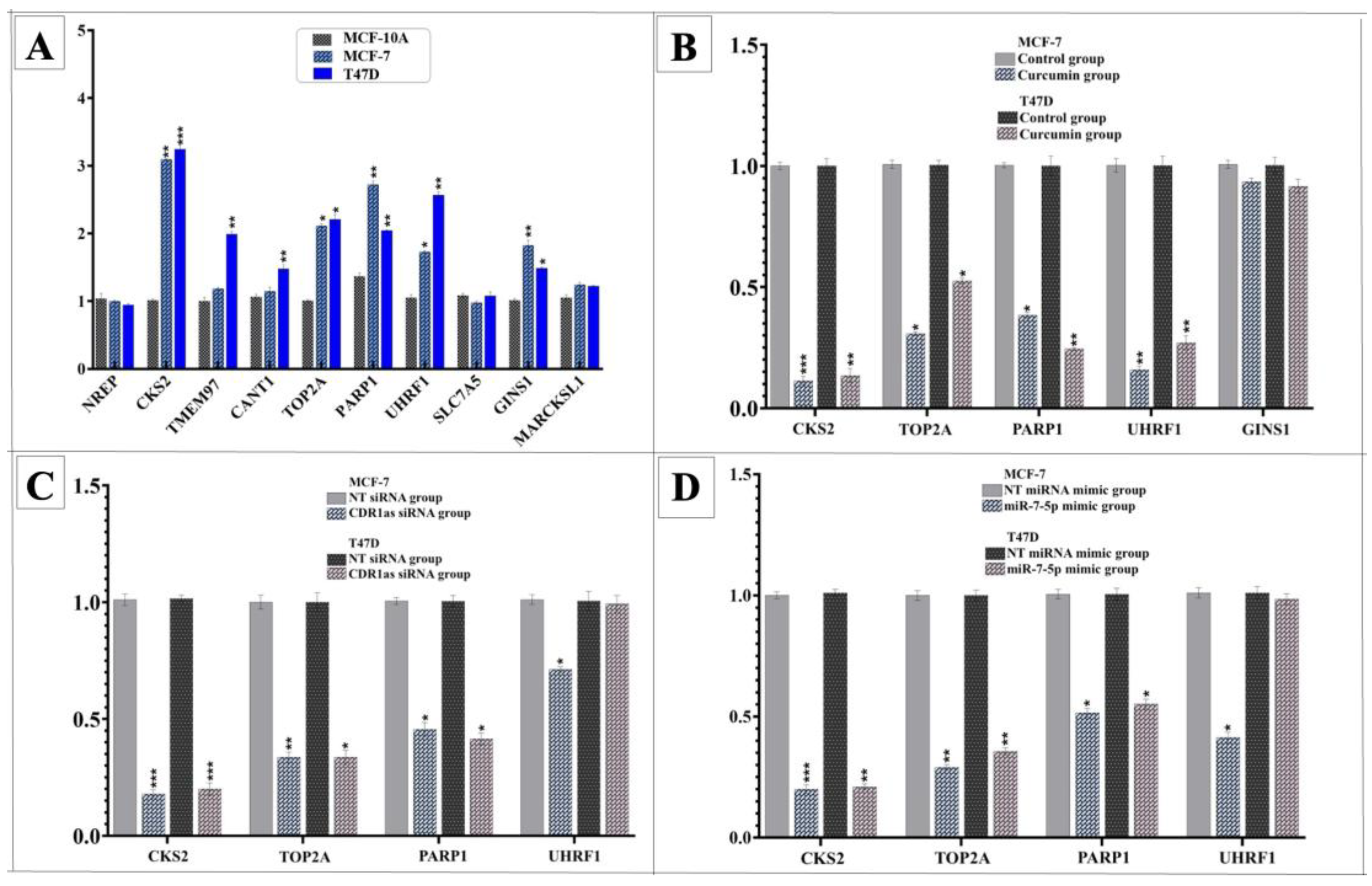
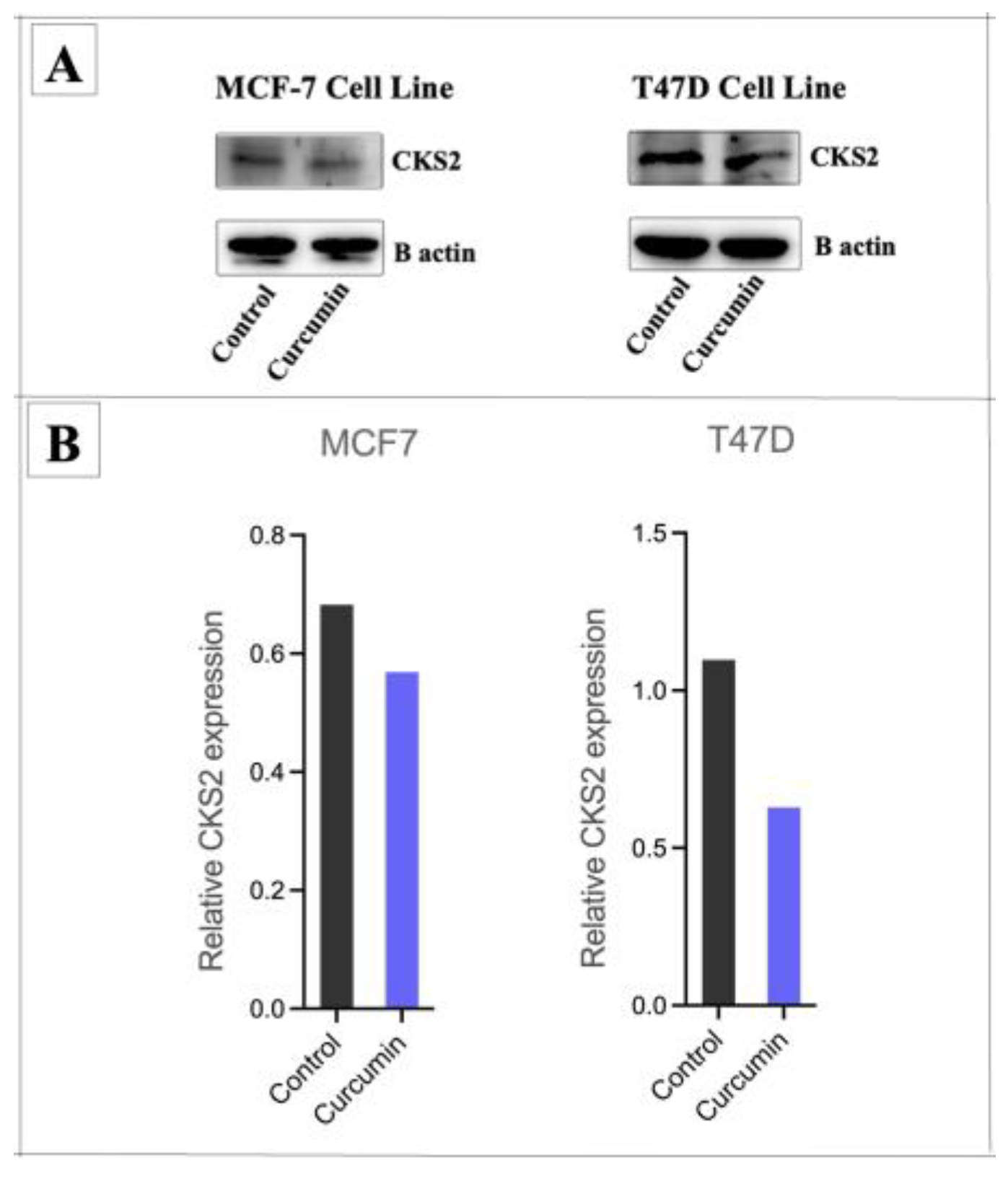
3.5. Curcumin Suppresses BC Cells by Modulating miR-7-5p Target Genes
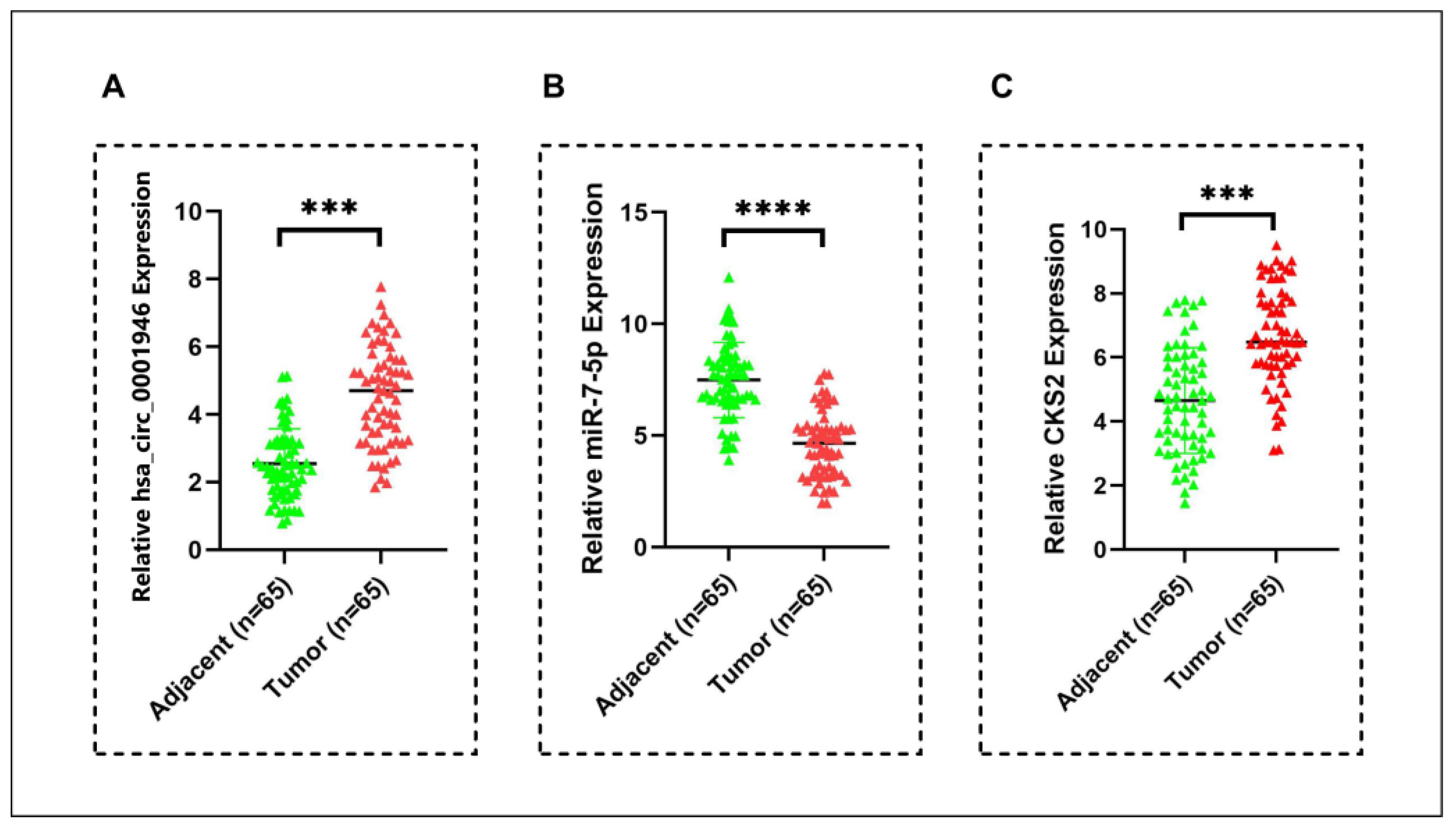
3.6. Hsa_circ_0001946/miR-7-5p/CKS2 Axis as Potential Biomarker in Breast Cancer
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BC | Breast Cancer |
| CircRNA | Circular RNA |
| MiRNA | MicroRNA |
| ncRNAs | Non-Coding RNAs |
| HG-DMEM | High-Glucose Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium |
| DMSO | Dimethyl Sulfoxide |
| NT siRNA | Non-Target siRNA Negative Control |
| NT-miRNA | Non-Target miRNA Mimic Negative Control |
| PBS | Phosphate-Buffered Saline |
| qPCR | Quantitative Real-Time PCR |
| PPI | Protein–Protein Interaction |
| IC50 | Half-Maximal Inhibitory Concentration |
| DNMT | DNA Methyltransferase |
| 5-Aza-2′-Deoxycytidine | 5-Azacytidine and Decitabine |
| CKS2 | Cyclin Kinase Subunit 2 |
References
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X. Molecular Classification of Breast Cancer: Relevance and Challenges. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2023, 147, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barone, D.; Cito, L.; Tommonaro, G.; Abate, A.A.; Penon, D.; De Prisco, R.; Penon, A.; Forte, I.M.; Benedetti, E.; Cimini, A.; et al. Antitumoral potential, antioxidant activity and carotenoid content of two Southern Italy tomato cultivars extracts: San Marzano and Corbarino. J. Cell Physiol. 2018, 233, 1266–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yallapu, M.M.; Jaggi, M.; Chauhan, S.C. Curcumin nanomedicine: A road to cancer therapeutics. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2013, 19, 1994–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yadav, N.; Parveen, S.; Banerjee, M. Potential of nano-phytochemicals in cervical cancer therapy. Clin. Chim. Acta 2020, 505, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, S.; Gupta, S.C.; Tyagi, A.K.; Aggarwal, B.B. Curcumin, a component of golden spice: From bedside to bench and back. Biotechnol. Adv. 2014, 32, 1053–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Y.; Tan, Y.; Wei, X.; Li, X.; Chen, H.; Yang, Z.; Tang, G.; Yao, X.; Mi, P.; Zheng, X. Recent Advances of Curcumin Derivatives in Breast Cancer. Chem. Biodivers. 2022, 19, e202200485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, F.C.; Anil Kumar, N.V.; Thakur, G. Developments in the anticancer activity of structurally modified curcumin: An up-to-date review. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 177, 76–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, M.; Zhai, B.T.; Fan, Y.; Sun, J.; Shi, Y.J.; Zhang, X.F.; Zou, J.B.; Wang, J.W.; Guo, D.Y. Targeted Drug Delivery Systems for Curcumin in Breast Cancer Therapy. Int. J. Nanomed. 2023, 18, 4275–4311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Liu, Y.; Sun, H.; Makabel, B.; Cui, Q.; Li, J.; Su, C.; Ashby, C.R., Jr.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, J. The targeting of non-coding RNAs by curcumin: Facts and hopes for cancer therapy (Review). Oncol. Rep. 2019, 42, 20–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kaya, M.; Abuaisha, A.; Suer, I.; Emiroglu, S.; Abanoz, F.; Palanduz, S.; Cefle, K.; Ozturk, S. Turmeric Inhibits MDA-MB-231 Cancer Cell Proliferation, Altering miR-638-5p and Its Potential Targets. Eur. J. Breast Health 2024, 20, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Suer, I.; Abuaisha, A.; Kaya, M.; Abanoz, F.; Cefle, K.; Palanduz, S.; Ozturk, S. Curcumin suppresses cell viability in breast cancer cell line by affecting the expression of miR-15a-5p. Turk. J. Biochem. 2024, 49, 656–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.; Cui, C.; Jiao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, M.; Wang, J.; Sheng, X. Circular RNA and its potential diagnostic and therapeutic values in breast cancer. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2024, 51, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Li, Q.; Wu, Z.; Xu, W.; Jiang, R. Circular RNA-mediated miRNA sponge & RNA binding protein in biological modulation of breast cancer. Noncoding RNA Res. 2024, 9, 262–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Jiang, C.; Zeng, X.; Shan, R.; Wen, W.; Li, J.; Tan, J.; Li, L.; Wan, R. The Emerging Picture of the Roles of CircRNA-CDR1as in Cancer. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 590478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Piwecka, M.; Glažar, P.; Hernandez-Miranda, L.R.; Memczak, S.; Wolf, S.A.; Rybak-Wolf, A.; Filipchyk, A.; Klironomos, F.; Cerda Jara, C.A.; Fenske, P.; et al. Loss of a mammalian circular RNA locus causes miRNA deregulation and affects brain function. Science 2017, 357, eaam8526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleaveland, B.; Shi, C.Y.; Stefano, J.; Bartel, D.P. A Network of Noncoding Regulatory RNAs Acts in the Mammalian Brain. Cell 2018, 174, 350–362.e317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yang, W.; Yang, X.; Wang, X.; Gu, J.; Zhou, D.; Wang, Y.; Yin, B.; Guo, J.; Zhou, M. Silencing CDR1as enhances the sensitivity of breast cancer cells to drug resistance by acting as a miR-7 sponge to down-regulate REGγ. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 4921–4932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yang, W.; Gu, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Feng, M.; Zhou, D.; Guo, J.; Zhou, M. Inhibition of circular RNA CDR1as increases chemosensitivity of 5-FU-resistant BC cells through up-regulating miR-7. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 3166–3177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kaya, M.; Suer, I.; Aytatli, A.; Karatas, O.F.; Palanduz, S.; Cefle, K.; Ozturk, S. CDR1as/miR-7-5p/IGF1R axis contributes to the suppression of cell viability in prostate cancer. Turk. J. Biochem. 2024, 50, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadoughi, F.; Maleki Dana, P.; Asemi, Z.; Yousefi, B. Targeting microRNAs by curcumin: Implication for cancer therapy. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 7718–7729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nirgude, S.; Desai, S.; Choudhary, B. Curcumin alters distinct molecular pathways in breast cancer subtypes revealed by integrated miRNA/mRNA expression analysis. Cancer Rep. 2022, 5, e1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Abuaisha, A.; Kaya, M.; Suer, İ.; Emiroğlu, S.; Abanoz, F.; Palanduz, Ş.; Çefle, K.; Öztürk, Ş. Effect of curcumin on breast cancer cells through miR-145-5p and its target genes. J. Istanb. Fac. Med. 2024, 87, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Fu, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Ma, M.; Wang, C. Curcumin inhibits proteasome activity in triple-negative breast cancer cells through regulating p300/miR-142-3p/PSMB5 axis. Phytomedicine 2020, 78, 153312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences, 2nd ed.; Hillsdale, N., Ed.; Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Publishers: Mahwah, NJ, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, S.; Kim, T.; Yoo, K.H.; Kang, K. The T47D cell line is an ideal experimental model to elucidate the progesterone-specific effects of a luminal A subtype of breast cancer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 486, 752–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soule, H.D.; Maloney, T.M.; Wolman, S.R.; Peterson, W.D., Jr.; Brenz, R.; McGrath, C.M.; Russo, J.; Pauley, R.J.; Jones, R.F.; Brooks, S.C. Isolation and characterization of a spontaneously immortalized human breast epithelial cell line, MCF-10. Cancer Res. 1990, 50, 6075–6086. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, B.; Ghosh, K.; Suresh, L.; Kanade, S.R. Curcumin ameliorates PRMT5-MEP50 arginine methyltransferase expression by decreasing the Sp1 and NF-YA transcription factors in the A549 and MCF-7 cells. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2019, 455, 73–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.L.; Pan, Y.Y.; Chen, O.; Luan, Y.; Xue, X.; Zhao, J.J.; Liu, L.; Jia, H.Y. Curcumin inhibits MCF-7 cells by modulating the NF-κB signaling pathway. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 5581–5584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Li, C.; Li, M.; Xue, Y. Downregulation of CircRNA CDR1as specifically triggered low-dose Diosbulbin-B induced gastric cancer cell death by regulating miR-7-5p/REGγ axis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 120, 109462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.Z.; Wen, L.; Wei, X.; Wang, Q.R.; Xu, L.W.; Zhang, H.M.; Liu, W.C. Inhibition of miR-7 promotes angiogenesis in human umbilical vein endothelial cells by upregulating VEGF via KLF4. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 36, 1569–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalındemirtaş, F.D.; Kaya, B.; Sert, E.; Şahin, O.; Kuruca, S.E.; Ülküseven, B. New oxovanadium(IV) complexes overcame drug resistance and increased in vitro cytotoxicity by an apoptotic pathway in breast cancer cells. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2022, 363, 109997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Kirsch, R.; Koutrouli, M.; Nastou, K.; Mehryary, F.; Hachilif, R.; Gable, A.L.; Fang, T.; Doncheva, N.T.; Pyysalo, S.; et al. The STRING database in 2023: Protein-protein association networks and functional enrichment analyses for any sequenced genome of interest. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D638–D646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- An, M.; Akyuz, M.; Capik, O.; Yalcin, C.; Bertram, R.; Karatas, E.A.; Karatas, O.F.; Yildirim, V. Gain of function mutation in K(ATP) channels and resulting upregulation of coupling conductance are partners in crime in the impairment of Ca2+ oscillations in pancreatic ß-cells. Math. Biosci. 2024, 374, 109224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babin, L.; Piganeau, M.; Renouf, B.; Lamribet, K.; Thirant, C.; Deriano, L.; Mercher, T.; Giovannangeli, C.; Brunet, E.C. Chromosomal Translocation Formation Is Sufficient to Produce Fusion Circular RNAs Specific to Patient Tumor Cells. iScience 2018, 5, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hua, K.; Jin, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, B.; Wu, C.; Xu, H.; Fang, L. MicroRNA-7 inhibits proliferation, migration and invasion of thyroid papillary cancer cells via targeting CKS2. Int. J. Oncol. 2016, 49, 1531–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Shi, M.; Hu, C.; Chen, B.; Li, S. MALAT1 modulated FOXP3 ubiquitination then affected GINS1 transcription and drived NSCLC proliferation. Oncogene 2021, 40, 3870–3884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brase, J.C.; Schmidt, M.; Fischbach, T.; Sültmann, H.; Bojar, H.; Koelbl, H.; Hellwig, B.; Rahnenführer, J.; Hengstler, J.G.; Gehrmann, M.C. ERBB2 and TOP2A in breast cancer: A comprehensive analysis of gene amplification, RNA levels, and protein expression and their influence on prognosis and prediction. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 2391–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.J.; Zeng, S.H.; Hu, Y.D.; Zhang, Y.H.; Li, J.P. Overexpression of NREP Promotes Migration and Invasion in Gastric Cancer Through Facilitating Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 746194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Shu, L.; Peng, Y.; Zhong, L.; Feng, X.; Qiao, L.; Yi, Y. CircZNF124 regulates cell proliferation, leucine uptake, migration and invasion by miR-199b-5p/SLC7A5 pathway in endometrial cancer. Immun. Inflamm. Dis. 2021, 9, 1291–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ulaşli, M.; Gürses, S.; Cengiz, B.; Öztuzcu, S.; Balakan, O.; Süner, A.; Gögebakan, B.; İğci, M.; Balik, A.; Arslan, A.; et al. Expression of PARP1 Gene in Breast Cancer Patients. Uluslararası Hematol.-Onkol. Derg. 2013, 23, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, G.; Sun, W.; Zou, Y.; Cai, Z.; Wang, P.; Lin, X.; Huang, J.; Jiang, L.; Ding, X.; Hu, G. RNA interference against TMEM97 inhibits cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in glioma cells. Tumour Biol. 2015, 36, 8231–8238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, C.Y.; Xiang, W.; Liu, J.B.; Jiang, G.X.; Sun, F.; Wu, J.J.; Yang, X.L.; Xin, R.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, D.D.; et al. MiR-9-1 Suppresses Cell Proliferation and Promotes Apoptosis by Targeting UHRF1 in Lung Cancer. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2021, 20, 15330338211041191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yao, Q.; Yu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, M.; Ma, J.; Wu, Y.; Zheng, Q.; Li, J. CANT1 serves as a potential prognostic factor for lung adenocarcinoma and promotes cell proliferation and invasion in vitro. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Liang, W.; Gao, R.; Yang, M.; Wang, X.; Cheng, K.; Shi, X.; He, C.; Li, Y.; Wu, Y.; Shi, L.; et al. MARCKSL1 promotes the proliferation, migration and invasion of lung adenocarcinoma cells. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 19, 2272–2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Flint, A.L.; Hansen, D.W.; Brown, L.D.; Stewart, L.E.; Ortiz, E.; Panda, S.S. Modified Curcumins as Potential Drug Candidates for Breast Cancer: An Overview. Molecules 2022, 27, 8891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Pan-On, S.; Dilokthornsakul, P.; Tiyaboonchai, W. Trends in advanced oral drug delivery system for curcumin: A systematic review. J. Control Release 2022, 348, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayo, B.; Penroz, S.; Torres, K.; Simón, L. Curcumin Administration Routes in Breast Cancer Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Belcaro, G.; Hosoi, M.; Pellegrini, L.; Appendino, G.; Ippolito, E.; Ricci, A.; Ledda, A.; Dugall, M.; Cesarone, M.R.; Maione, C.; et al. A controlled study of a lecithinized delivery system of curcumin (Meriva®) to alleviate the adverse effects of cancer treatment. Phytother. Res. 2014, 28, 444–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Hegde, M.; Parama, D.; Kunnumakkara, A.B. Curcumin: The Golden Nutraceutical on the Road to Cancer Prevention and Therapeutics. A Clinical Perspective. Crit. Rev. Oncog. 2022, 27, 33–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giordano, A.; Tommonaro, G. Curcumin and Cancer. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Saghatelyan, T.; Tananyan, A.; Janoyan, N.; Tadevosyan, A.; Petrosyan, H.; Hovhannisyan, A.; Hayrapetyan, L.; Arustamyan, M.; Arnhold, J.; Rotmann, A.R.; et al. Efficacy and safety of curcumin in combination with paclitaxel in patients with advanced, metastatic breast cancer: A comparative, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Phytomedicine 2020, 70, 153218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szczepanek, J.; Skorupa, M.; Jarkiewicz-Tretyn, J.; Cybulski, C.; Tretyn, A. Harnessing Epigenetics for Breast Cancer Therapy: The Role of DNA Methylation, Histone Modifications, and MicroRNA. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Nepali, K.; Liou, J.P. Recent developments in epigenetic cancer therapeutics: Clinical advancement and emerging trends. J. Biomed. Sci. 2021, 28, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kaya, M.; Abuaisha, A.; Suer, I.; Emiroglu, S.; Önder, S.; Onay Ucar, E.; Yenerel, M.N.; Palanduz, S.; Cefle, K.; Ozturk, S. Let-7b-5p sensitizes breast cancer cells to doxorubicin through Aurora Kinase B. PLoS ONE 2025, 20, e0307420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazimoradi, M.H.; Babashah, S. The role of CircRNA/miRNA/mRNA axis in breast cancer drug resistance. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 966083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Erdogan, C.; Suer, I.; Kaya, M.; Ozturk, S.; Aydin, N.; Kurt, Z. Bioinformatics analysis of the potentially functional circRNA-miRNA-mRNA network in breast cancer. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0301995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sun, S.; Fang, H. Curcumin inhibits ovarian cancer progression by regulating circ-PLEKHM3/miR-320a/SMG1 axis. J. Ovarian Res. 2021, 14, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wu, Z.; Zhao, X.; Sun, Y.; Yu, H. Curcumin suppresses colorectal cancer development with epithelial-mesenchymal transition via modulating circular RNA HN1/miR-302a-3p/PIK3R3 axis. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2022, 73, 219–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahmati, Y.; Asemani, Y.; Aghamiri, S.; Ezzatifar, F.; Najafi, S. CiRS-7/CDR1as; An oncogenic circular RNA as a potential cancer biomarker. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2021, 227, 153639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Zhu, D.; Liu, S.; Shao, M.; Liu, Y.; Li, A.; Lv, Y.; Huang, M.; Lou, D.; Fan, Q. Curcumin enhances radiosensitization of nasopharyngeal carcinoma by regulating circRNA network. Mol. Carcinog. 2020, 59, 202–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Nie, B.; Liu, L.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, M.; Mei, Y. Curcumin Prevents Brain Damage and Cognitive Dysfunction During Ischemic-reperfusion Through the Regulation of miR-7-5p. Curr. Neurovasc Res. 2019, 16, 441–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urbanowicz-Kachnowicz, I.; Baghdassarian, N.; Nakache, C.; Gracia, D.; Mekki, Y.; Bryon, P.A.; Ffrench, M. ckshs expression is linked to cell proliferation in normal and malignant human lymphoid cells. Int. J. Cancer 1999, 82, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, H.; Lin, H.; Zhang, Z. CKS2 in human cancers: Clinical roles and current perspectives (Review). Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 3, 459–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wang, J.; Xu, L.; Liu, Y.; Chen, J.; Jiang, H.; Yang, S.; Tan, H. Expression of cyclin kinase subunit 2 in human breast cancer and its prognostic significance. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2014, 7, 8593–8601. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Huang, N.; Wu, Z.; Hong, H.; Wang, X.; Yang, F.; Li, H. Overexpression of CKS2 is associated with a poor prognosis and promotes cell proliferation and invasion in breast cancer. Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 19, 4761–4769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Si, L.; Zhang, L.; Xing, S.; Fang, P.; Tian, X.; Liu, X.; Xv, X. Curcumin as a therapeutic agent in cancer therapy: Focusing on its modulatory effects on circular RNAs. Phytother. Res. 2023, 37, 3121–3134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pdq Integrative, A.; Complementary Therapies Editorial, B. Curcumin (Curcuma, Turmeric) and Cancer (PDQ®): Health Professional Version. In PDQ Cancer Information Summaries; National Cancer Institute (US): Bethesda, MD, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Tohidi, M.; Allahyari, A.; Ataei Azimi, S.; Alimi, H.; Elyasi, S.; Qoorchi Moheb Seraj, F.; Mehrad-Majd, H. The protective effect of nano curcumin supplementation on doxorubicin induced cardiotoxicity in breast cancer patients; a randomized, double-blind clinical trial. J. Oncol. Pharm. Pract. 2024, 10781552241277958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heydari, B.; Sheikhalishahi, S.; Hoseinzade, F.; Shabani, M.; Ramezani, V.; Saghafi, F. Topical Curcumin for Prevention of Radiation-Induced Dermatitis: A Pilot Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Cancer Investig. 2025, 43, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemati, S.; Mehrabinejad, F.; Elhaie, M.; Najafizade, N. Curcumin Supplementation as a Preventive Strategy Against Tamoxifen-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in ER+ Breast Cancer Patients: A Triple-Blind Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trial. J. Diet. Suppl. 2025, 22, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Gene | Primer Sequences | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| CDR1as | F 5′-ACGTCTCCAGTGTGCTGA-3′ | [19] |
| R 5′-CTTGACACAGGTGCCATC-3′ | ||
| GAPDH | F 5′-GCCATCAATGACCCCTTCAT-3′ | [35] |
| R 5′-TGACAAGCTTCCCGTTCTCA-3′ | ||
| CKS2 | F 5′-TTCGACGAACACTACGAGTACC-3′ | [36] |
| R 5′-GGACACCAAGTCTCCTCCAC-3′ | ||
| GINS1 | F 5′-AGGTCACTGGGAGGAGATGA-3′ | [37] |
| R 5′-TCGAGGTAAAAAGTGCTGGCT-3′ | ||
| TOP2A | F 5′-CATTGAAGACGCTTCGTTATGG-3′ | [38] |
| R 5′-CCAGTTGTGATGGATAAAATTAATCAG-3′ | ||
| NREP | F 5′-TTGAGCGAATGCTACCAGAG-3′ | [39] |
| R 5′-AGGCGAGGCTACGGAAAG-3′ | ||
| SLC7A5 | F 5′-TAGGAGACAGAGCCAAGCAC-3′ | [40] |
| R 5′-CACGGGAACAACAGAAACAA-3′ | ||
| PARP1 | F 5′-CCACACACAATGCGTATGACT-3′ | [41] |
| R 5′-CCACAGCAATCTTCGGTTATGA-3′ | ||
| TMEM97 | F 5′-CTCCAAAGCCAGTGGTTTC-3′ | [42] |
| R 5′-GCCAGTGGTTGTTTCCTTC-3′ | ||
| UHRF1 | F 5′-TGTCAAGGGTGGCAAGAAT-3′ | [43] |
| R 5′-GCCAGGCTCATCATCGTC-3′ | ||
| CANT1 | F 5′-GCTTCTCGTCCTTCAAGTTCATC-3′ | [44] |
| R 5′-ACGCTTCCGATCTTGGTCTC-3′ | ||
| MARCKSL1 | F 5′-CAGGCTACAGAGCCATCCACTC-3′ | [45] |
| R 5′-GCAGCTTAGAGATCACCCACCT-3′ |
| Characteristics | Number (%) |
|---|---|
| All | 65 (100.0) |
| Age, mean ± SD | 56.45 ± 11.89 |
| Age group | |
| ≤50 | 22 (33.8) |
| >50 | 43 (66.2) |
| Menopausal status | |
| Premenopausal | 20 (30.8) |
| Postmenopausal | 45 (69.2) |
| Family history of BC | |
| Yes | 16 (24.6) |
| No | 49 (75.4) |
| Smoking | |
| Yes | 13 (20.0) |
| No | 52 (80.0) |
| Alcohol consumption | |
| Yes | 3 (4.6) |
| No | 62 (95.4) |
| Characteristics | Category | Number (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Molecular subtype | Luminal A | 30 (46.2) |
| Luminal B | 35 (53.8) | |
| Histological Type | Invasive ductal carcinoma | 47 (72.3) |
| Invasive lobular carcinoma | 9 (13.8) | |
| Mixed | 5 (7.7) | |
| Other | 4 (6.2) | |
| Pathological tumor stage | I | 17 (26.2) |
| II | 46 (70.8) | |
| III | 2 (3.1) | |
| Pathological lymph node involvement | Negative | 38 (58.5) |
| Positive | 27 (41.5) | |
| Histological tumor grade | I | 4 (6.2) |
| II | 33 (50.8) | |
| III | 28 (43.1) | |
| Tumor focal status | Unifocal | 52 (80.0) |
| Multifocal | 13 (20.0) | |
| Lympho-vascular invasion | Yes | 39 (60.0) |
| No | 26 (40.0) | |
| Estrogen receptor | Negative | 0 (0.0) |
| Positive | 65 (100.0) | |
| Progesterone receptor | Negative | 6 (9.2) |
| Positive | 59 (90.8) | |
| HER2 | Negative | 59 (90.8) |
| Positive | 6 (9.2) | |
| Ki-67 expression | <20% | 27 (41.5) |
| ≥20% | 38 (58.5) | |
| Surgical treatment-Breast | Breast-conserving surgery | 53 (81.5) |
| Mastectomy | 12 (18.5) | |
| Surgical treatment-Axilla | Sentinel lymph node biopsy | 57 (87.7) |
| Axillary lymph node dissection | 8 (12.3) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abuaisha, A.; Kaya, M.; Suer, I.; Emiroglu, S.; Bayram, A.; Tukenmez, M.; Cabioglu, N.; Muslumanoglu, M.; Nazligul, E.; Papila, B.; et al. Curcumin as an Epigenetic Modulator: Suppression of Breast Cancer via the Hsa_circ_0001946/MiR-7-5p/Target Gene Axis. Medicina 2025, 61, 1600. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61091600
Abuaisha A, Kaya M, Suer I, Emiroglu S, Bayram A, Tukenmez M, Cabioglu N, Muslumanoglu M, Nazligul E, Papila B, et al. Curcumin as an Epigenetic Modulator: Suppression of Breast Cancer via the Hsa_circ_0001946/MiR-7-5p/Target Gene Axis. Medicina. 2025; 61(9):1600. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61091600
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbuaisha, Asmaa, Murat Kaya, Ilknur Suer, Selman Emiroglu, Aysel Bayram, Mustafa Tukenmez, Neslihan Cabioglu, Mahmut Muslumanoglu, Esra Nazligul, Berrin Papila, and et al. 2025. "Curcumin as an Epigenetic Modulator: Suppression of Breast Cancer via the Hsa_circ_0001946/MiR-7-5p/Target Gene Axis" Medicina 61, no. 9: 1600. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61091600
APA StyleAbuaisha, A., Kaya, M., Suer, I., Emiroglu, S., Bayram, A., Tukenmez, M., Cabioglu, N., Muslumanoglu, M., Nazligul, E., Papila, B., Aytatlı, A., Karatas, O. F., Cefle, K., Palanduz, S., & Ozturk, S. (2025). Curcumin as an Epigenetic Modulator: Suppression of Breast Cancer via the Hsa_circ_0001946/MiR-7-5p/Target Gene Axis. Medicina, 61(9), 1600. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61091600







