The Role of [18F]FDG PET-Based Radiomics and Machine Learning for the Evaluation of Cardiac Sarcoidosis: A Narrative Literature Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Role of [18F]FDG PET-Based Radiomics and ML for the Evaluation of CS
2.1. Diagnosis
2.2. Prognosis
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Use of AI
References
- Wiefels, C.; Boczar, K.; Birnie, D.; Beanlands, R.; Chareonthaitawee, P. Quantification of metabolic activity in the evaluation of cardiac sarcoidosis. J. Nucl. Cardiol. 2025, 43, 102088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terasaki, F.; Yoshinaga, K. New guidelines for diagnosis of cardiac sarcoidosis in Japan. Ann. Nucl. Cardiol. 2017, 3, 42–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terasaki, F.; Azuma, A.; Anzai, T.; Ishizaka, N.; Ishida, Y.; Isobe, M.; Inomata, T.; Ishibashi-Ueda, H.; Eishi, Y.; Kitakaze, M.; et al. Japanese Circulation Society Joint Working Group. JCS 2016 Guideline on Diagnosis and Treatment of Cardiac Sarcoidosis—Digest Version. Circ. J. 2019, 83, 2329–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judson, M.A.; Costabel, U.; Drent, M.; Wells, A.; Maier, L.; Koth, L.; Shigemitsu, H.; Culver, D.A.; Gelfand, J.; Valeyre, D.; et al. Organ Assessment Instrument Investigators TW. The WASOG Sarcoidosis Organ Assessment Instrument: An update of a previous clinical tool. Sarcoidosis Vasc. Diffuse Lung Dis. 2014, 31, 19–27. [Google Scholar]
- Trivieri, M.G.; Spagnolo, P.; Birnie, D.; Liu, P.; Drake, W.; Kovacic, J.C.; Baughman, R.; Fayad, Z.A.; Judson, M.A. Challenges in Cardiac and Pulmonary Sarcoidosis: JACC State-of-the-Art Review. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 76, 1878–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birnie, D.H.; Nery, P.B.; Ha, A.C.; Beanlands, R.S. Cardiac sarcoidosis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2016, 68, 411–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.L.; Fong, H.K.; Birati, E.Y.; Han, Y. Cardiac Sarcoidosis. Am. J. Cardiol. 2019, 123, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannuzzi, M.C.; Rybicki, B.A.; Teirstein, A.S. Sarcoidosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 2153–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginelliová, A.; Farkaš, D.; Iannaccone, S.F.; Vyhnálková, V. Sudden unexpected death due to severe pulmonary and cardiac sarcoidosis. Forensic Sci. Med. Pathol. 2016, 12, 319–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mushari, N.A.; Soultanidis, G.; Duff, L.; Trivieri, M.G.; Fayad, Z.A.; Robson, P.M.; Tsoumpas, C. Exploring the Utility of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance Radiomic Feature Extraction for Evaluation of Cardiac Sarcoidosis. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valeyre, D.; Prasse, A.; Nunes, H.; Uzunhan, Y.; Brillet, P.Y.; Muller-Quernheim, J. Sarcoidosis. Lancet 2014, 383, 1155e67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milman, N.; Selroos, O. Pulmonary sarcoidosis in the Nordic countries 1950–1982. Epidemiology and clinical picture. Sarcoidosis 1990, 7, 50–57. [Google Scholar]
- Rybicki, B.A.; Major, M.; Popovich, J., Jr.; Maliarik, M.J.; Iannuzzi, M.C. Racial differences in sarcoidosis incidence: A 5-year study in a health maintenance organization. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1997, 145, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, R.J.; Shanbhag, A.; Marcinkiewicz, A.M.; Struble, H.; Gransar, H.; Hijazi, W.; Fujito, H.; Kransdorf, E.; Kavanagh, P.; Liang, J.X.; et al. AI-enabled CT-guided end-to-end quantification of total cardiac activity in 18FDG cardiac PET/CT for detection of cardiac sarcoidosis. J. Nucl. Cardiol. 2025, 22, 102195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehtonen, J.; Uusitalo, V.; Pöyhönen, P.; Mäyränpää, M.I.; Kupari, M. Cardiac sarcoidosis: Phenotypes, diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis. Eur. Heart J. 2023, 44, 1495–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salotti, A.; Mondini, L.; Confalonieri, P.; Salton, F.; Nalli, C.; Reccardini, N.; Torregiani, C.; Antonaglia, C.; Hughes, M.; Confalonieri, M.; et al. Cardiac sarcoidosis recurrence post-heart transplant: A critical literature and case report. Sarcoidosis Vasc. Diffuse Lung Dis. 2025, 42, 16865. [Google Scholar]
- Kouranos, V.; Sharma, R. Cardiac sarcoidosis: State-of-the-art review. Heart 2021, 107, 1591–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nappi, C.; Ponsiglione, A.; Imbriaco, M.; Cuocolo, A. 18F-FDG PET/CMR in Cardiac Sarcoidosis: A Wild Card in the Deck? J. Nucl. Cardiol. 2022, 29, 765–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazelpour, S.; Sadek, M.M.; Nery, P.B.; Beanlands, R.S.; Tzemos, N.; Toma, M.; Birnie, D.H. Corticosteroid and Immunosuppressant Therapy for Cardiac Sarcoidosis: A Systematic Review. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2021, 10, e021183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roshankar, G.; Zhang, J.Y.; Parekh, D.; Lyons, K.; Isaac, D.; Miller, R.J.H. Steroid sparing immunosuppression in man agement of cardiac sarcoidosis. Health Sci. Rev. 2022, 4, 100034. [Google Scholar]
- Soejima, K.; Yada, H. The work-up and management of patients with apparent or subclinical cardiac sarcoidosis. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2009, 20, 578e83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birnie, D.H.; Sauer, W.H.; Bogun, F.; Cooper, J.M.; Culver, D.A.; Duvernoy, C.S.; Judson, M.A.; Kron, J.; Mehta, D.; Cosedis Nielsen, J.; et al. HRS expert consensus statement on the diagnosis and management of arrhythmias associated with cardiac sarcoidosis. Heart Rhythm. 2014, 11, 1305–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, M.K.; Gilotra, N.A.; Harrington, C.; Rao, S.; Dunn, J.M.; Freitag, T.B.; Halushka, M.K.; Russell, S.D. Evaluation of the role of endomyocardial biopsy in 851 patients with unexplained heart failure from 2000–2009. Circ. Heart Fail. 2013, 6, 676–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sammartino, A.M.; Falco, R.; Drera, A.; Dondi, F.; Bellini, P.; Bertagna, F.; Vizzardi, E. Vascular inflammation and cardiovascular disease: Review about the role of PET imaging. Int. J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2023, 39, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dondi, F.; Albano, D.; Bellini, P.; Volpi, G.; Giubbini, R.; Bertagna, F. 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose PET and PET/computed tomography for the evaluation of immunoglobulin G4-related disease: A systematic review. Nucl. Med. Commun. 2022, 43, 638–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sammartino, A.M.; Bonfioli, G.B.; Dondi, F.; Riccardi, M.; Bertagna, F.; Metra, M.; Vizzardi, E. Contemporary Role of Positron Emission Tomography (PET) in Endocarditis: A Narrative Review. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 4124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dondi, F.; Albano, D.; Ferrarini, G.; Camoni, L.; Bellini, P.; Treglia, G.; Bertagna, F. Role of splenic and bone marrow uptake at 18 F-FDG PET/CT for the assessment of large vessels vasculitis and the influence of glucocorticoids therapy on their values. J. Med. Imaging Radiat. Oncol. 2023, 67, 717–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crouser, E.D.; Maier, L.A.; Wilson, K.C.; Bonham, C.A.; Morgenthau, A.S.; Patterson, K.C.; Abston, E.; Bernstein, R.C.; Blankstein, R.; Chen, E.S.; et al. Diagnosis and Detection of Sarcoidosis. An Official American Thoracic Society Clinical Practice Guideline. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 201, e26–e51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chareonthaitawee, P.; Beanlands, R.S.; Chen, W.; Dorbala, S.; Miller, E.J.; Murthy, V.L.; Birnie, D.H.; Chen, E.S.; Cooper, L.T.; Tung, R.H.; et al. EXPERT CONTENT REVIEWERS. Joint SNMMI-ASNC Expert Consensus Document on the Role of 18F-FDG PET/CT in Cardiac Sarcoid Detection and Therapy Monitoring. J. Nucl. Med. 2017, 58, 1341–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slart, R.H.J.A.; Glaudemans, A.W.J.M.; Lancellotti, P.; Hyafil, F.; Blankstein, R.; Schwartz, R.G.; Jaber, W.A.; Russell, R.; Gimelli, A.; Rouzet, F.; et al. Document Reading Group. A joint procedural position statement on imaging in cardiac sarcoidosis: From the Cardiovascular and Inflammation & Infection Committees of the European Association of Nuclear Medicine, the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging, and the American Society of Nuclear Cardiology. J. Nucl. Cardiol. 2018, 25, 298–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumita, S.; Yoshinaga, K.; Miyagawa, M.; Momose, M.; Kiso, K.; Kasai, T.; Naya, M. Committee for diagnosis of cardiac sarcoidosis using 18F-FDG PET, Japanese Society of Nuclear Cardiology. Recommendations for 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography imaging for diagnosis of cardiac sarcoidosis—2018 update: Japanese Society of Nuclear Cardiology recommendations. J. Nucl. Cardiol. 2019, 26, 1414–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlhac, F.; Soussan, M.; Maisonobe, J.A.; Garcia, C.A.; Vanderlinden, B.; Buvat, I. Tumor texture analysis in 18F-FDG PET: Relationships between texture parameters, histogram indices, standardized uptake values, metabolic volumes, and total lesion glycolysis. J. Nucl. Med. 2014, 55, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dondi, F.; Gatta, R.; Gazzilli, M.; Bellini, P.; Viganò, G.L.; Ferrari, C.; Pisani, A.R.; Rubini, G.; Bertagna, F. [18F]FDG PET-Based Radiomics and Machine Learning for the Assessment of Gliomas and Glioblastomas: A Systematic Review. Information 2025, 16, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, R.Y.; Coyner, A.S.; Kalpathy-Cramer, J.; Chiang, M.F.; Campbell, J.P. Introduction to Machine Learning, Neural Networks, and Deep Learning. Transl. Vis. Sci. Technol. 2020, 9, 14. [Google Scholar]
- Deo, R.C. Machine Learning in Medicine. Circulation 2015, 132, 1920–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardi, S.; Vallati, M.; Gatta, R. Artificial Intelligence-Based Management of Adult Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: Where Are We and Where Are We Going? Cancers 2024, 16, 848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bari, B.; Vallati, M.; Gatta, R.; Lestrade, L.; Manfrida, S.; Carrie, C.; Valentini, V. Development and validation of a machine learning-based predictive model to improve the prediction of inguinal status of anal cancer patients: A preliminary report. Oncotarget 2016, 8, 108509–108521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dondi, F.; Gatta, R.; Treglia, G.; Piccardo, A.; Albano, D.; Camoni, L.; Gatta, E.; Cavadini, M.; Cappelli, C.; Bertagna, F. Application of radiomics and machine learning to thyroid diseases in nuclear medicine: A systematic review. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2024, 25, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dondi, F.; Gatta, R.; Albano, D.; Bellini, P.; Camoni, L.; Treglia, G.; Bertagna, F. Role of Radiomics Features and Machine Learning for the Histological Classification of Stage I and Stage II NSCLC at [18F] FDG PET/CT: A Comparison between Two PET/CT Scanners. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 12, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dondi, F.; Pasinetti, N.; Gatta, R.; Albano, D.; Giubbini, R.; Bertagna, F. Comparison between Two Different Scanners for the Evaluation of the Role of 18F-FDG PET/CT Semiquantitative Parameters and Radiomics Features in the Prediction of Final Diagnosis of Thyroid Incidentalomas. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosny, A.; Aerts, H.J.; Mak, R.H. Handcrafted versus deep learning radiomics for prediction of cancer therapy response. Lancet Digit. Health 2019, 1, e106–e107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beuque, M.P.L.; Lobbes, M.B.I.; van Wijk, Y.; Widaatalla, Y.; Primakov, S.; Majer, M.; Balleyguier, C.; Woodruff, H.C.; Lambin, P. Combining Deep Learning and Handcrafted Radiomics for Classification of Suspicious Lesions on Contrast-enhanced Mammograms. Radiology 2023, 307, e221843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.; Yu, H.; Park, S.H.; Woo, D.; Lee, S.J.; Chong, G.O.; Han, H.S.; Kim, J.C. Comparing deep learning and handcrafted radiomics to predict chemoradiotherapy response for locally advanced cervical cancer using pretreatment MRI. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manabe, O.; Ohira, H.; Hirata, K.; Hayashi, S.; Naya, M.; Tsujino, I.; Aikawa, T.; Koyanagawa, K.; Oyama-Manabe, N.; Tomiyama, Y.; et al. Use of 18F-FDG PET/CT texture analysis to diagnose cardiac sarcoidosis. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2019, 46, 1240–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Togo, R.; Hirata, K.; Manabe, O.; Ohira, H.; Tsujino, I.; Magota, K.; Ogawa, T.; Haseyama, M.; Shiga, T. Cardiac sarcoidosis classification with deep convolutional neural network-based features using polar maps. Comput. Biol. Med. 2019, 104, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mushari, N.A.; Soultanidis, G.; Duff, L.; Trivieri, M.G.; Fayad, Z.A.; Robson, P.; Tsoumpas, C. Exploring the Utility of Radiomic Feature Extraction to Improve the Diagnostic Accuracy of Cardiac Sarcoidosis Using FDG PET. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 840261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kote, R.; Ravina, M.; Thippanahalli Ganga, R.; Singh, S.; Reddy, M.; Prasanth, P.; Kote, R. Role of Textural Analysis Parameters Derived from FDG PET/CT in Diagnosing Cardiac Sarcoidosis. World J. Nucl. Med. 2024, 23, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manabe, O.; Koyanagawa, K.; Hirata, K.; Oyama-Manabe, N.; Ohira, H.; Aikawa, T.; Furuya, S.; Naya, M.; Tsujino, I.; Tomiyama, Y. Prognostic Value of 18F-FDG PET Using Texture Analysis in Cardiac Sarcoidosis. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2020, 13, 1096–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajo, M.; Hirahara, D.; Jinguji, M.; Ojima, S.; Hirahara, M.; Tani, A.; Takumi, K.; Kamimura, K.; Ohishi, M.; Yoshiura, T. Machine learning approach using 18F-FDG-PET-radiomic features and the visibility of right ventricle 18F-FDG uptake for predicting clinical events in patients with cardiac sarcoidosis. Jpn. J. Radiol. 2024, 42, 744–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasian Ardakani, A.; Bureau, N.J.; Ciaccio, E.J.; Acharya, U.R. Interpretation of radiomics features-A pictorial review. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2022, 215, 106609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campisi, R.; Merani, M.F.; Rodríguez, M.I. Assessment of Cardiac Sarcoidosis: FDG PET and BMIPP SPECT. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2022, 24, 1873–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boczar, K.E.; Park, Y.; Wiefels, C. Can FDG-PET Imaging Identify Cardiac Sarcoidosis Disease Phenotypes? Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2024, 26, 851–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; Pak, K.; Kim, K. Diagnostic performance of F-18 FDG PET for detection of cardiac sarcoidosis; A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Nucl. Cardiol. 2020, 27, 2103–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aitken, M.; Chan, M.V.; Urzua Fresno, C.; Farrell, A.; Islam, N.; McInnes, M.D.F.; Iwanochko, M.; Balter, M.; Moayedi, Y.; Thavendiranathan, P.; et al. Diagnostic Accuracy of Cardiac MRI versus FDG PET for Cardiac Sarcoidosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Radiology 2022, 304, 566–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyagawa, M.; Tashiro, R.; Watanabe, E.; Kawaguchi, N.; Ishimura, H.; Kido, T.; Kido, T.; Kurata, A.; Mochizuki, T. Optimal Patient Preparation for Detection and Assessment of Cardiac Sarcoidosis by FDG-PET. Ann. Nucl. Cardiol. 2017, 3, 113–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadian, A.; Brogan, A.; Berman, J.; Sverdlov, A.L.; Mercier, G.; Mazzini, M. Quantitative interpretation of FDG PET/CT with myocardial perfusion imaging increases diagnostic information in the evaluation of cardiac sarcoidosis. J. Nucl. Cardiol. 2014, 21, 925–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborne, M.T.; Hulten, E.A.; Singh, A.; Waller, A.H.; Bittencourt, M.S.; Stewart, G.C. Reduction in (18)F-fluorodeoxyglucose uptake on serial cardiac positron emission tomography is associated with improved left ventricular ejection fraction in patients with cardiac sarcoidosis. J. Nucl. Cardiol. 2013, 21, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waller, A.H.; Blankstein, R. Quantifying myocardial inflammation using 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography in cardiac sarcoidosis. J. Nucl. Cardiol. 2014, 21, 940–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lip, G.Y.H.; Nieuwlaat, R.; Pisters, R.; Lane, D.A.; Crijns, H.J.G.M. Refining clinical risk stratification for predicting stroke and thromboembolism in atrial fibrillation using a novel risk factor-based approach: The euro heart survey on atrial fibrillation. Chest 2010, 137, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Mahony, C.; Jichi, F.; Pavlou, M.; Monserrat, L.; Anastasakis, A.; Rapezzi, C.; Biagini, E.; Gimeno, J.R.; Limongelli, G.; McKenna, W.J.; et al. A novel clinical risk prediction model for sudden cardiac death in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM risk-SCD). Eur. Heart J. 2014, 35, 2010–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambin, P.; Leijenaar, R.T.H.; Deist, T.M.; Peerlings, J.; de Jong, E.E.C.; van Timmeren, J.; Sanduleanu, S.; Larue, R.T.H.M.; Even, A.J.G.; Jochems, A.; et al. Radiomics: The bridge between medical imaging and personalized medicine. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 749–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwanenburg, A.; Vallières, M.; Abdalah, M.A.; Aerts, H.J.W.L.; Andrearczyk, V.; Apte, A.; Ashrafinia, S.; Bakas, S.; Beukinga, R.J.; Boellaard, R.; et al. The Image Biomarker Standardization Initiative: Standardized Quantitative Radiomics for High-Throughput Image-based Phenotyping. Radiology 2020, 295, 328–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynes-Llompart, G.; Sabatè-Llobera, A.; Linares-Tello, E.; Martì-Climent, J.; Gamez-Cenzano, C. Image quality evaluation in a modern PET system: Impact of new reconstructions methods and a radiomics approach. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, S.; Choi, H.; Paeng, J.C.; Cheon, G.J. Radiomics in Oncological PET/CT: A Methodological Overview. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2019, 53, 14–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, G.J.R.; Azad, G.; Owczarczyk, K.; Siddique, M.; Goh, V. Challenges and Promises of PET Radiomics. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2018, 102, 1083–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwanenburg, A. Radiomics in nuclear medicine: Robustness, reproducibility, standardization, and how to avoid data analysis traps and replication crisis. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2019, 46, 2638–2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovinfosse, P.; Visvikis, D.; Hustinx, R.; Hatt, M. FDG PET radiomics: A review of the methodological aspects. Clin. Transl. Imaging 2018, 6, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfaehler, E.; van Sluis, J.; Merema, B.B.J.; van Ooijen, P.; Berendsen, R.C.M.; van Velden, F.H.P.; Boellaard, R. Experimental Multicenter and Multivendor Evaluation of the Performance of PET Radiomic Features Using 3-Dimensionally Printed Phantom Inserts. J. Nucl. Med. 2020, 61, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tankyevych, O.; Tixier, F.; Antonorsi, N.; Filali Razzouki, A.; Mondon, R.; Pinto-Leite, T.; Visvikis, D.; Hatt, M.; Cheze Le Rest, C. Can alternative PET reconstruction schemes improve the prognostic value of radiomic features in non-small cell lung cancer? Methods 2021, 188, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galavis, P.E.; Hollensen, C.; Jallow, N.; Paliwal, B.; Jeraj, R. Variability of textural features in FDG PET images due to different acquisition modes and reconstruction parameters. Acta Oncol. 2010, 49, 1012–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Chu-Shern, J.L.; Loi, H.Y.; Khor, L.K.; Sinha, A.K.; Quek, S.T.; Tham, I.W.; Townsend, D. Impact of Image Reconstruction Settings on Texture Features in 18F-FDG PET. J. Nucl. Med. 2015, 56, 1667–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, P.; Barage, S.; Jha, A.K.; Choudhury, S.; Rangarajan, V. Robustness of 18F-FDG PET Radiomic Features in Lung Cancer: Impact of Advanced Reconstruction Algorithm. J. Nucl. Med. Technol. 2025, 53, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guiot, J.; Vaidyanathan, A.; Deprez, L.; Zerka, F.; Danthine, D.; Frix, A.N.; Lambin, P.; Bottari, F.; Tsoutzidis, N.; Miraglio, B.; et al. A review in radiomics: Making personalized medicine a reality via routine imaging. Med. Res. Rev. 2022, 42, 426–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheze Le Rest, C.; Hustinx, R. Are radiomics ready for clinical prime-time in PET/CT imaging? Q. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2019, 63, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piñeiro-Fiel, M.; Moscoso, A.; Pubul, V.; Ruibal, Á.; Silva-Rodríguez, J.; Aguiar, P. A Systematic Review of PET Textural Analysis and Radiomics in Cancer. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
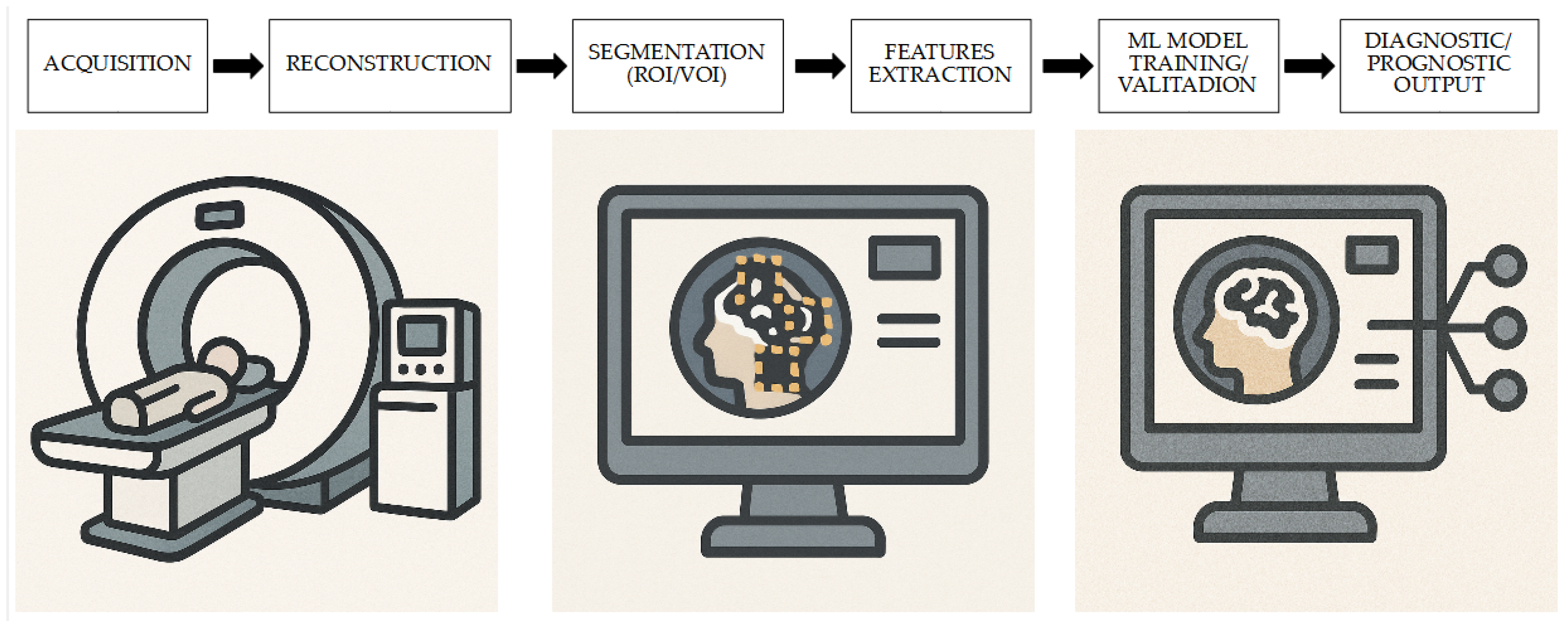
| First Author | N. Ref. | Year | Country | Study Design | N. Pts. | CS Pts. (%) | Setting |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Manabe O | [44] | 2018 | Japan | Retrospective | 89 | 37 (42) | Diagnosis |
| Togo R | [45] | 2019 | Japan | Retrospective | 85 | 33 (39) | Diagnosis |
| Manabe O | [48] | 2020 | Japan | Retrospective | 62 | 62 (100) | Prognosis |
| Mushari NA | [46] | 2022 | UK, USA, Netherlands | Retrospective | 69 | 40 (58) | Diagnosis |
| Kote R | [47] | 2024 | India | Retrospective | 67 | 17 (25) | Diagnosis |
| Nakajo M | [49] | 2024 | Japan | Retrospective | 47 | 47 (100) | Prognosis |
| First Author | N. Ref. | Device | Number of Scanners | Scanner Type | Reconstruction Protocol | Reported Activity (MBq) | Cardiac Uptake Suppression |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Manabe O | [44] | PET/CT | 1 | Siemens Biograph 64 TruePoint TrueV | PSF | 4.5/kg | LCD |
| Togo R | [45] | PET/CT | 1 | Siemens Biograph 64 TruePoint TrueV | PSF | 4.5/kg | LCD |
| Manabe O | [48] | PET/CT | 1 | Siemens Biograph 64 TruePoint TrueV | PSF | 4.5/kg | LCD, unfractionated heparin |
| Mushari NA | [46] | PET/CMR | 1 | Siemens BiographTM mMR | OSEM | 5/kg | LCD |
| Kote R | [47] | PET/CT | 1 | GE Discovery MI-DR | ns | ns | LCD |
| Nakajo M | [49] | PET/CT | 2 | GE Discovery 600M, GE Discovery MI | OSEM, PSF | 223 ± 30 | LCD |
| First Author | Ref. | Performance Validation Methods | ML Models | Class Balancing | Main Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Manabe O | [44] | Train/test | Logistic regression | 42/58 | Some textural features showed high diagnostic value for CS diagnosis. |
| Togo R | [45] | Cross-fold | Deep convolutional neural network | 33/52 | Radiomics features may be more effective than conventional semiquantitative features for CS diagnosis. |
| Manabe O | [48] | Train/test | Logistic regression | ns | [18F]FDG textural features may potentially provide prognostic information in CS subjects. |
| Mushari NA | [46] | Cross-fold | Random Forest, Logistic Regression, Support Vector Machine, Decision Tree, Gaussian Process Classifier, Stochastic Gradient Descent, Perceptron Classifier, Passive Aggressive Classifier, Neural Network Classifier and K-neighbors Classifier | ns | Radiomic analysis of PET data may not be a useful approach to detect CS. Conventional semiquantitative parameters show high performances. |
| Kote R | [47] | ROC | ns | ns | Textural analysis parameters could successfully differentiate CS from non-CS. |
| Nakajo M | [49] | Train/test | Decision tree, random forest, neural network, k-nearest neighbors, Naïve Bayes, logistic regression, and support vector machine | 38/9 | ML analyses using [18F]FDG PET-based radiomics features may be useful to predict adverse clinical events in CS subjects. |
| First Author | N. Ref. | Models |
|---|---|---|
| Manabe O | [44] |
|
| Togo R | [45] |
|
| Manabe O | [48] |
|
| Mushari NA | [46] |
|
| Kote R | [47] |
|
| Nakajo M | [49] |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dondi, F.; Bellini, P.; Gatta, R.; Camoni, L.; Rinaldi, R.; Viganò, G.; Cossandi, M.; Brangi, E.; Vizzardi, E.; Bertagna, F. The Role of [18F]FDG PET-Based Radiomics and Machine Learning for the Evaluation of Cardiac Sarcoidosis: A Narrative Literature Review. Medicina 2025, 61, 1526. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61091526
Dondi F, Bellini P, Gatta R, Camoni L, Rinaldi R, Viganò G, Cossandi M, Brangi E, Vizzardi E, Bertagna F. The Role of [18F]FDG PET-Based Radiomics and Machine Learning for the Evaluation of Cardiac Sarcoidosis: A Narrative Literature Review. Medicina. 2025; 61(9):1526. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61091526
Chicago/Turabian StyleDondi, Francesco, Pietro Bellini, Roberto Gatta, Luca Camoni, Roberto Rinaldi, Gianluca Viganò, Michela Cossandi, Elisa Brangi, Enrico Vizzardi, and Francesco Bertagna. 2025. "The Role of [18F]FDG PET-Based Radiomics and Machine Learning for the Evaluation of Cardiac Sarcoidosis: A Narrative Literature Review" Medicina 61, no. 9: 1526. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61091526
APA StyleDondi, F., Bellini, P., Gatta, R., Camoni, L., Rinaldi, R., Viganò, G., Cossandi, M., Brangi, E., Vizzardi, E., & Bertagna, F. (2025). The Role of [18F]FDG PET-Based Radiomics and Machine Learning for the Evaluation of Cardiac Sarcoidosis: A Narrative Literature Review. Medicina, 61(9), 1526. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61091526






