Interpersonal Violence-Related Facial Fractures: 12-Year Trends and Surgical Outcomes in a Southern European Level-I Trauma Centre
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Sample
2.2. Variables and Data Collection Methods
2.3. International Classification of Diseases-10 Coding of Injuries
- •
- S02.3 Fracture of orbital floor;
- •
- S02.4 Fracture of malar and maxillary bones (zygomaticomaxillary complex, Le Fort);
- •
- S02.6 Fracture of mandible (angle, condyle, symphysis, body, parasymphysis);
- •
- S02.71 Multiple fractures involving skull and facial bones;
- •
- S02.8 Other specified fractures of skull and facial bones (frontal-sinus fractures).
- •
- S01.4 Open wound of cheek and temporomandibular area;
- •
- S01.5 Open wound of lips and oral cavity.
2.4. Facial Injury Severity Score (FISS)
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
Trends in Facial Trauma
4. Discussion
Study Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yamamoto, K.; Matsusue, Y.; Horita, S.; Murakami, K.; Sugiura, T.; Kirita, T. Maxillofacial Fractures Associated with Interpersonal Violence. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2019, 30, e312–e315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Businger, A.P.; Krebs, J.; Schaller, B.; Zimmermann, H.; Exadaktylos, A.K. Cranio-maxillofacial injuries in victims of interpersonal violence. Swiss Med. Wkly. 2012, 142, w13687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Hassani, A.; Ahmad, K.; El-Menyar, A.; Abutaka, A.; Mekkodathil, A.; Peralta, R.; Al Khalil, M.; Al-Thani, H. Prevalence and patterns of maxillofacial trauma: A retrospective descriptive study. Eur. J. Trauma Emerg. Surg. 2022, 48, 2513–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, T.U.; Rahat, S.; Khan, Z.A.; Shahid, L.; Banouri, S.S.; Muhammad, N. Etiology and pattern of maxillofacial trauma. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0275515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalathil, L.S.M.; Mangalath, U.; Roshni, A.; Aslam, S.; Thomas, T.; Nair, R.B. Study of Patterns of Maxillofacial Injuries. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2021, 13, S1019–S1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diab, J.; Moore, M.H. Patterns and characteristics of maxillofacial fractures in women. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2022, 27, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveen Shankar, A.; Naveen Shankar, V.; Hegde, N.; Sharma; Prasad, R. The pattern of the maxillofacial fractures—A multicentre retrospective study. J. Cranio-Maxillofac. Surg. 2012, 40, 675–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laverick, S.; Siddappa, P.; Jones, D.C. Patterns of emergency maxillofacial referrals and provision of services. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2009, 47, 99–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, M.C.; Batista, A.M.; de Oliveira Ferreira, F.; Ramos-Jorge, M.L.; Marques, L.S. Pattern of oral–maxillofacial trauma stemming from interpersonal physical violence and determinant factors. Dent. Traumatol. 2014, 30, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yari, A.; Fasih, P.; Bagheri, A.; Aryanezhad, S.S.; Sani, M.K. Prevalence and pattern of maxillofacial injuries associated with domestic violence: A retrospective study at a major trauma center. Dent. Traumatol. 2024, 40, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchant, A.D.; Gray, S.; Ludwig, D.C.; Dillon, J. What Is the Effect of COVID-19 Social Distancing on Oral and Maxillofacial Trauma Related to Domestic Violence? J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2021, 79, e1–e2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, L.G.; Barbosa, K.G.N.; de Paula Silva, C.J.; Alencar, G.P.; D’avila, S.; Ferreira, E.F.E.; Ferreira, R.C. Trends of maxillofacial injuries resulting from physical violence in Brazil. Dent. Traumatol. 2020, 36, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyes, H.; Fan, K. Maxillofacial injuries associated with domestic violence: Experience at a major trauma centre. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2020, 58, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boffano, P.; Roccia, F.; Zavattero, E.; Dediol, E.; Uglešić, V.; Kovačič, Ž.; Vesnaver, A.; Konstantinović, V.S.; Petrović, M.; Stephens, J.; et al. European Maxillofacial Trauma (EURMAT) project: A multicentre and prospective study. J. Cranio-Maxillofac. Surg. 2015, 43, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boffano, P.; Roccia, F.; Zavattero, E.; Dediol, E.; Uglešić, V.; Kovačič, Ž.; Vesnaver, A.; Konstantinović, V.S.; Petrović, M.; Stephens, J.; et al. Assault-related maxillofacial injuries: The results from the European Maxillofacial Trauma (EURMAT) multicenter and prospective collaboration. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2015, 119, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roccia, F.; Savoini, M.; Ramieri, G.; Zavattero, E. An analysis of 711 victims of interpersonal violence to the face, Turin, Italy. J. Cranio-Maxillofac. Surg. 2016, 44, 1025–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojino, A.; Roccia, F.; Carlaw, K.; Aquilina, P.; Rae, E.; Laverick, S.; Romeo, I.; Iocca, O.; Copelli, C.; Sobrero, F.; et al. A multicentric prospective analysis of maxillofacial trauma in the elderly population. Dent. Traumatol. 2022, 38, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romeo, I.; Sobrero, F.; Roccia, F.; Dolan, S.; Laverick, S.; Carlaw, K.; Aquilina, P.; Bojino, A.; Ramieri, G.; Duran-Valles, F.; et al. A multicentric, prospective study on oral and maxillofacial trauma in the female population around the world. Dent. Traumatol. 2022, 38, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roccia, F.; Iocca, O.; Sobrero, F.; Rae, E.; Laverick, S.; Carlaw, K.; Aquilina, P.; Bojino, A.; Romeo, I.; Duran-Valles, F.; et al. World Oral and Maxillofacial Trauma (WORMAT) project: A multicenter prospective analysis of epidemiology and patterns of maxillofacial trauma around the world. J. Stomatol. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2022, 123, e849–e857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krug, E.G.; Mercy, J.A.; Dahlberg, L.L.; Zwi, A.B. The world report on violence and health. Lancet 2002, 360, 1083–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.X.; Donnelly, P.D.; Cohen, L.; Garg, S. Violence, health, and the 2030 agenda: Merging evidence and implementation. J. Public Health Policy 2016, 37, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Preventing Injuries and Violence: An Overview; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Prante, F.J.; Bramucci, A.; Truger, A. Decades of Tight Fiscal Policy Have Left the Health Care System in Italy Ill-Prepared to Fight the COVID-19 Outbreak. Intereconomics 2020, 55, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chisari, G.; Lega, F. Impact of austerity programs: Evidence from the Italian national health service. Health Serv. Manag. Res. 2023, 36, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Audigé, L.; Cornelius, C.-P.; Kunz, C.; Buitrago-Téllez, C.H.; Prein, J. The Comprehensive AOCMF Classification System: Classification and Documentation within AOCOIAC Software. Craniomaxillofacial Trauma Reconstr. 2014, 7, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neff, A.; Cornelius, C.-P.; Rasse, M.; Torre, D.D.; Audigé, L. The Comprehensive AOCMF Classification System: Condylar Process Fractures—Level 3 Tutorial. Craniomaxillofacial Trauma Reconstr. 2014, 7, 44–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buitrago-Téllez, C.H.; Cornelius, C.-P.; Prein, J.; Kunz, C.; di Ieva, A.; Audigé, L. The Comprehensive AOCMF Classification System: Radiological Issues and Systematic Approach. Craniomaxillofacial Trauma Reconstr. 2014, 7, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noffze, M.J.; Tubbs, R.S. René Le Fort 1869–1951. Clin. Anat. 2011, 24, 278–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, B.J.; Turco, L.M. Le Fort Fractures: A Collective Review. Bull. Emerg. Trauma 2017, 5, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steindel, S.J. International classification of diseases, 10th edition, clinical modification and procedure coding system: Descriptive overview of the next generation HIPAA code sets. J. Am. Med. Inform. Assoc. 2010, 17, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalik, W.; Toppich, J.; Łuksza, A.; Bargiel, J.; Gąsiorowski, K.; Marecik, T.; Szczurowski, P.; Wyszyńska-Pawelec, G.; Gontarz, M. Exploring the correlation of epidemiological and clinical factors with facial injury severity scores in maxillofacial trauma: A comprehensive analysis. Front. Oral Health 2025, 6, 1532133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Wu, J.; Yang, C.; Zhang, C.; Xu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S. Classifying and standardizing panfacial trauma according to anatomic categories and Facial Injury Severity Scale: A 10-year retrospective study. BMC Oral Health 2021, 21, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, S.C.; Dierks, E.J.; Kademani, D.; Holmgren, E.; Bell, R.B.; Hommer, L.; Potter, B.E. Application of a facial injury severity scale in craniomaxillofacial trauma. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2006, 64, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consorti, G.; Paglianiti, M.; Monarchi, G.; De Tomaso, S.; Cirignaco, G.; Gasperoni, M.; Frosolini, A.; Cascino, F.; Gilli, M.; Vellone, V.; et al. New test for systematic skills enhancement and improvement in maxillofacial surgery training: Multicentre pilot study. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2024, 62, 716–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanala, S.; Gudipalli, S.; Perumalla, P.; Jagalanki, K.; Polamarasetty, P.V.; Guntaka, S.; Gudala, A.; Boyapati, R. Aetiology, prevalence, fracture site and management of maxillofacial trauma. Ann. R. Coll. Surg. Engl. 2021, 103, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, K.S.; Forrest, W.; Greenlees, I.; Rhind, D.; Jowett, S.; Pinsky, I.; Espelt, A.; Bosque-Prous, M.; Sonderlund, A.L.; Vergani, M.; et al. Alcohol consumption, masculinity, and alcohol-related violence and anti-social behaviour in sportspeople. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2018, 21, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacLean, S.; Demant, J.; Room, R. Who or what do young adults hold responsible for men’s drunken violence? Int. J. Drug Policy 2020, 81, 102520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatzittofis, A.; Savard, J.; Arver, S.; Öberg, K.G.; Hallberg, J.; Nordström, P.; Jokinen, J. Interpersonal violence, early life adversity, and suicidal behavior in hypersexual men. J. Behav. Addict. 2017, 6, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Embleton, L.; Diaz, A. Interpersonal Violence Among Adolescents: Have Young Men Been Left Behind? J. Adolesc. Health 2024, 74, 216–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.-Y.; Tsai, H.-Y.; Yong, C.-Y.; Ohiro, Y.; Chang, Y.C.; Teng, N.C. A 10-year retrospective study on mandibular fractures in Northern Taiwan. J. Dent. Sci. 2023, 18, 1330–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gualtieri, M.; Pisapia, F.; Fadda, M.T.; Priore, P.; Valentini, V. Mandibular Fractures Epidemiology and Treatment Plans in the Center of Italy: A Retrospective Study. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2021, 32, e346–e349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alyahya, A.; Bin Ahmed, A.; Nusair, Y.; Ababtain, R.; Alhussain, A.; Alshafei, A. Mandibular condylar fracture: A systematic review of systematic reviews and a proposed algorithm for management. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2020, 58, 625–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirignaco, G.; Monarchi, G.; Catarzi, L.; Paglianiti, M.G.; Betti, E.; Committeri, U.; Bianchi, A.; Balercia, P.; Consorti, G. Airway Management in Complex Maxillofacial Trauma: Evaluating the Role of Submental Intubation as a Viable Alternative to Tracheostomy. Craniomaxillofac. Trauma Reconstr. 2025, 18, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seifert, L.B.; Mainka, T.; Herrera-Vizcaino, C.; Verboket, R.; Sader, R. Orbital floor fractures: Epidemiology and outcomes of 1594 reconstructions. Eur. J. Trauma Emerg. Surg. 2022, 48, 1427–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consorti, G.; Cirignaco, G.; Monarchi, G.; Catarzi, L.; Paglianiti, M.; Betti, E.; Committeri, U.; Togni, L.; Mascitti, M.; Balercia, P.; et al. The Role of Professional Oral Hygiene in Enhancing Outcomes of Maxillofacial Trauma Surgery. J. Stomatol. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2025; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, M. Facial injuries: Triage and applying damage control principles. Trauma 2017, 19, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spallaccia, F.; Vellone, V.; Colangeli, W.; De Tomaso, S. Maxillofacial Fractures in the Province of Terni (Umbria, Italy) in the Last 11 Years: Impact of COVID-19 Pandemic. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2022, 33, e853–e858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonavolontà, P.; Dell’aversana Orabona, G.; Abbate, V.; Vaira, L.A.; Lo Faro, C.; Petrocelli, M.; Attanasi, F.; De Riu, G.; Iaconetta, G.; Califano, L. The epidemiological analysis of maxillofacial fractures in Italy: The experience of a single tertiary center with 1720 patients. J. Cranio-Maxillofac. Surg. 2017, 45, 1319–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrocelli, M.; Ruggiero, F.; Allegri, D.; Cutrupi, S.; Baietti, A.M.; Salzano, G.; Maglitto, F.; Manfuso, A.; Copelli, C.; Barca, I.; et al. Changes in hospital admissions for facial fractures during and after COVID 19 pandemic: National multicentric epidemiological analysis on 2938 patients. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2023, 28, 753–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giovannetti, F.; Lupi, E.; Di Giorgio, D.; Scarsella, S.; Oliva, A.; Di Fabio, D.; Prata, P.; Petricca, G.; Valentini, V. Impact of COVID19 on Maxillofacial Fractures in the Province of L’Aquila, Abruzzo, Italy. Review of 296 Patients Treated with Statistical Comparison of the Two-Year Pre-COVID-19 and COVID-19. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2022, 33, 1182–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Famà, F.; Lo Giudice, R.; Di Vita, G.; Tribst, J.P.M.; Lo Giudice, G.; Sindoni, A. COVID-19 and the Impact on the Cranio-Oro-Facial Trauma Care in Italy: An Epidemiological Retrospective Cohort Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 7066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrocelli, M.; Ruggiero, F.; Feraboli, L.; Allegri, D.; Cutrupi, S.; Baietti, A.M.; Salzano, G.; Prucher, G.; Maremonti, P.; Vaira, L.A. The Evolution of the Epidemiology of Facial Fractures Before, During and After the COVID-19 Pandemic. J. Maxillofac. Oral Surg. 2025, 24, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- York, B.; Sent-Doux, K.; Heo, J.; Barnett, M.; Marsh, R.W.; Mackinnon, C.A.; Tan, S.T. Interpersonal violence and maxillofacial fractures. Ann. Maxillofac. Surg. 2019, 9, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cipriano, P.F.; Blanchard, K.A.; Rosa, W.E. Preventing Violence to Achieve Peaceful and Inclusive Societies. Am. J. Nurs. 2021, 121, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubron, K.; Verbist, M.; Shaheen, E.; Dormaar, T.J.; Jacobs, R.; Politis, C. Incidence, Aetiology, and Associated Fracture Patterns of Infraorbital Nerve Injuries Following Zygomaticomaxillary Complex Fractures: A Retrospective Analysis of 272 Patients. Craniomaxillofac. Trauma Reconstr. 2022, 15, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K. Global Trends in Maxillofacial Fractures. Craniomaxillofacial Trauma Reconstr. 2012, 5, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, L.Ø.; Ipsen, E.Ø.; Felding, U.A.; von Buchwald, C.; Steinmetz, J. Sequelae of Major Trauma Patients with Maxillofacial Fractures. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2021, 130, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boljevic, T.; Pelicic, D.; Terzic, Z.; Bojic, M. Complications in patients with facial bone fractures before and after conservative and surgical treatment, their comparison and correlation with different factors. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2023, 27, 11073–11081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wusiman, P.; Maimaitituerxun, B.; Saimaiti, A.; Moming, A. Epidemiology and Pattern of Oral and Maxillofacial Trauma. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2020, 31, e517–e520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| N = 224 | |
|---|---|
| Gender—n (%) | |
| Female/Male | 13/211 (5.8/94.2) |
| Age | |
| Mean ± SD | 29.1 ± 10.5 |
| Median (Q1–Q3) | 26.0 (22.0–34.0) |
| Fracture Site—n (%) | |
| Association of multiple fractures | 32 (14.3) |
| Zygomaticomaxillary complex | 41 (18.3) |
| Mandible | 94 (42.0) |
| Maxilla | 1 (0.4) |
| Nose | 31 (13.8) |
| NOE | 6 (2.7) |
| Orbital Region | 56 (25.0) |
| Frontal sinus | 7 (3.1) |
| Face wounds—n (%) | |
| Yes | 20 (8.9) |
| No | 204 (91.1) |
| FISS | |
| Mean ± SD | 2.1 ± 1.6 |
| Median (Q1–Q3) | 2 (1–3) |
| Timing of surgery—n (%) | |
| <24 h | 13 (5.8) |
| 24–72 h | 100 (44.6) |
| >72 h | 111 (49.6) |
| Day of hospitalization | |
| Mean ± SD | 4.1 ± 1.6 |
| Median (Q1–Q3) | 4.0 (3.0–5.0) |
| Type of treatment—n (%) | |
| ORIF | 174 (77.7) |
| ORIF and monitoring | 5 (2.2) |
| ORIF and closed treatment | 17 (7.6) |
| ORIF, closed treatment, and monitoring | 15 (6.7) |
| Monitoring | 0 (0.0) |
| Closed treatment | 13 (5.8) |
| N (%) | |
|---|---|
| Fracture of Mandible | |
| N | 101 |
| Angle of the mandible | 41 (40.6) |
| Condyle | 3 (3.0) |
| Body of the mandible | 2 (2.0) |
| Dentoalveolar | 8 (8.0) |
| Symphysis | 1 (1.0) |
| Angle and condyle | 1 (1.0) |
| Angle and body | 6 (6.0) |
| Angle and symphysis | 9 (9.0) |
| Angle and parasymphysis | 9 (7.0) |
| Condyle and body | 12 (11.9) |
| Condyle and symphysis | 1 (1.0) |
| Condyle and parasymphysis | 7 (7.0) |
| Body and parasymphysis | 1 (1.0) |
| Fracture of orbital region | |
| N | 85 |
| Orbital floor | 53 (62.4) |
| Medial wall of the orbit | 2 (2.4) |
| Roof of the orbit | 1 (1.2) |
| Orbital floor and lateral wall | 7 (8.2) |
| Orbital floor and medial wall of the orbit | 22 (25.9) |
| Fracture of frontal sinus | |
| N | 7 |
| Anterior and back part | 2 (28.6) |
| Frontal wall | 5 (71.4) |
| Fracture of maxilla | |
| N | 5 |
| LE FORT I | 4 (80.0) |
| LE FORT II | 1 (20.0) |
| Fracture Site | Face Wounds, n (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Yes | No | p-Value | |
| Multiple associated fractures | 3 (15.0) | 29 (14.2) | 0.005 |
| Zygomaticomaxillary complex | 2 (10.0) | 39 (19.1) | |
| Mandible | 15 (75.0) | 79 (38.7) | |
| Maxilla | 0 (0.0) | 1 (0.5) | |
| Orbital region | 0 (0.0) | 56 (27.5) | |
| FISS Score | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|
| Gender | ||
| Female | 1.0 (1.0–1.0) | 0.005 * |
| Male | 2.0 (1.0–3.0) | |
| Age | ||
| ≤34 years | 2.0 (1.0–2.5) | 0.035 * |
| >34 years | 2.0 (1.0–4.0) | |
| Fracture Site | ||
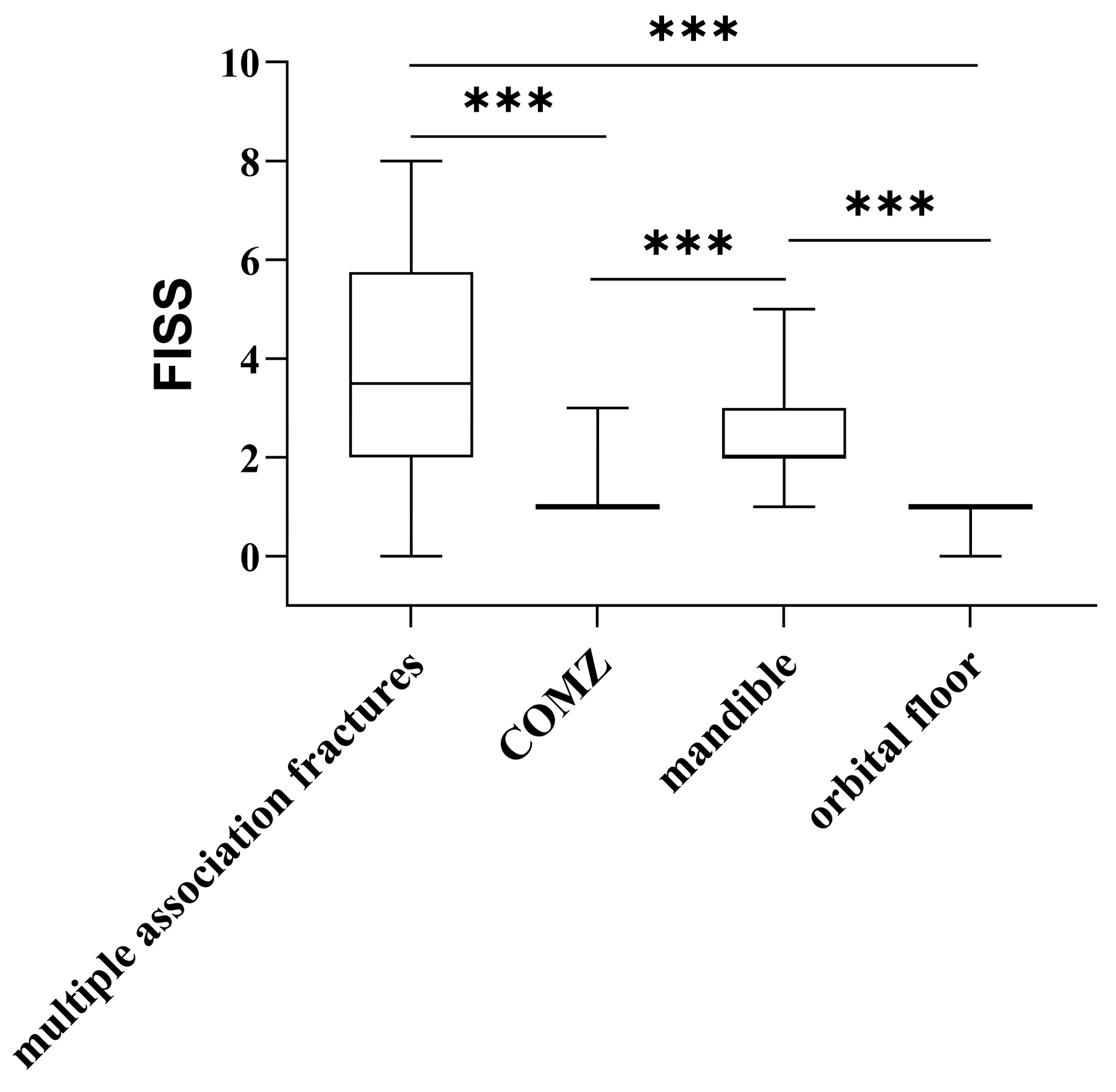
| Association | 3.5 (2.0–5.8) | <0.001 + |
| Zygomaticomaxillary complex | 1.0 (1.0–1.0) | |
| Mandible | 2.0 (2.0–3.0) | |
| Maxilla | 2.0 (2.0–2.0) | |
| Orbital region | 1.0 (1.0–1.0) | |
| Face wounds | ||
| Yes | 2.5 (2.0–4.0) | <0.001 * |
| No | 1.5 (1.0–2.75) | |
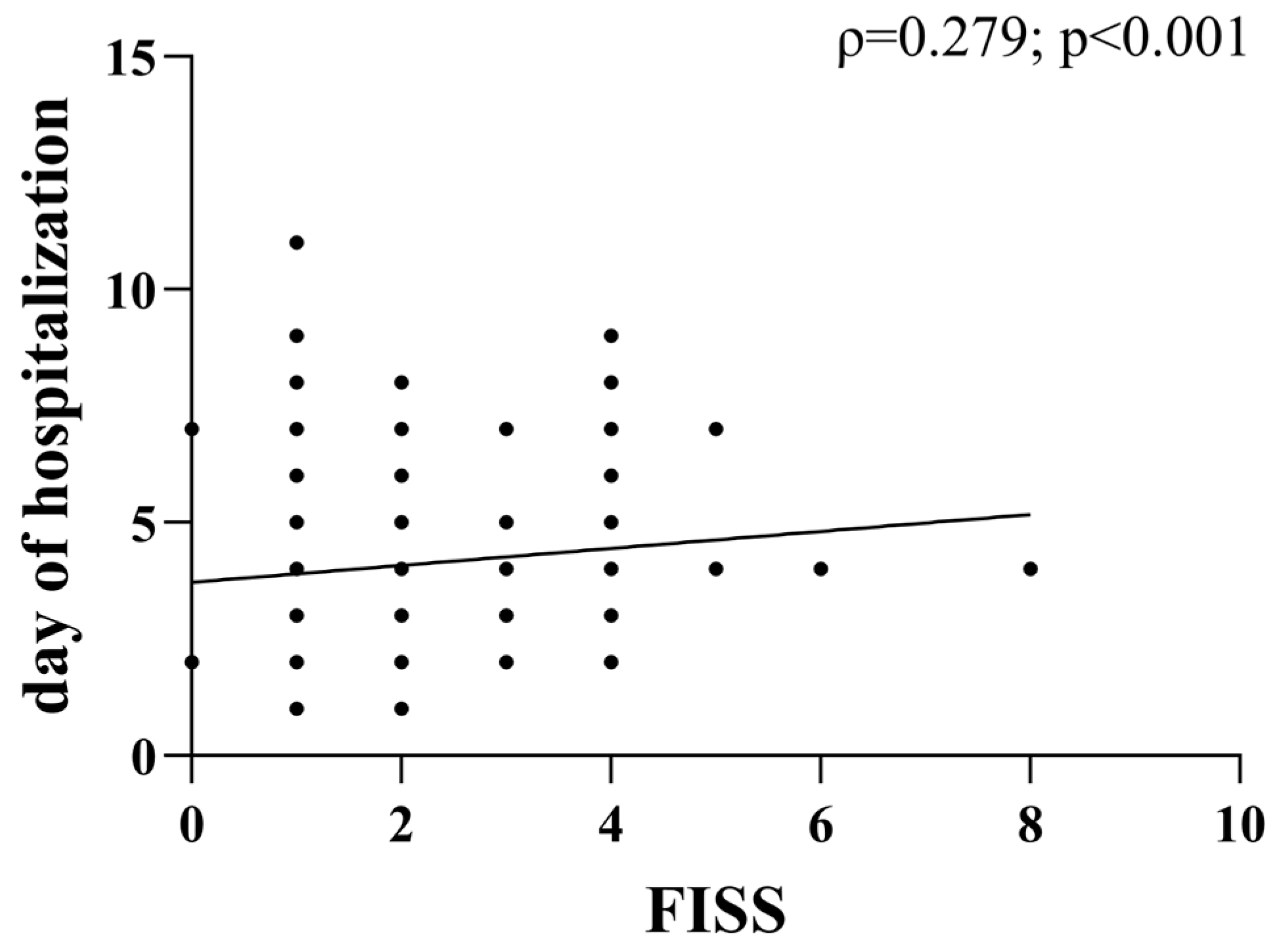
| Timing of surgery | ||
| <24 h | 2.0 (1.0–2.5) | 0.675 |
| 24–72 h | 1.0 (1.0–3.0) | |
| >72 h | 2.0 (1.0–3.0) | |
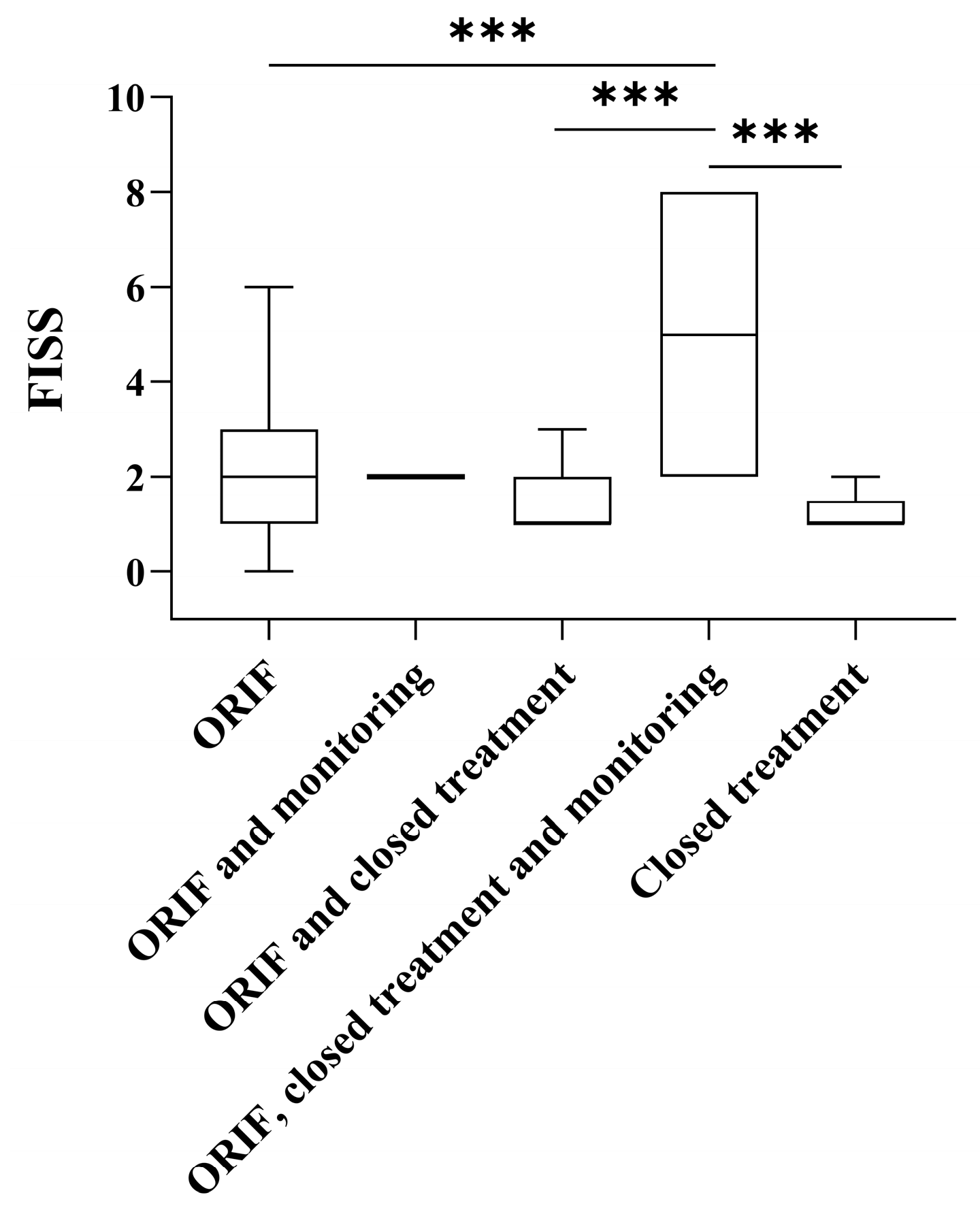
| Type of treatment | ||
| ORIF | 2.0 (1.0–3.0) | <0.001 + |
| ORIF and monitoring | 2.0 (2.0–2.0) | |
| ORIF and closed treatment | 1.0 (1.0–2.0) | |
| ORIF, closed treatment and monitoring | 5.0 (2.0–8.0) | |
| Closed treatment | 1.0 (1.0–1.5) |
| Univariate | Multivariate | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | n | OR | 95% CI | p-Value | n | OR | 95% CI | p-Value |
| Sex | ||||||||
| F vs. M | 224 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.999 | 224 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.999 |
| Age | ||||||||
| >34 vs. ≤34 years | 224 | 1.7 | 0.8–3.2 | 0.143 | 224 | 1.3 | 0.6–2.6 | 0.568 |
| Type of fracture | ||||||||
| Single vs. Multiple | 224 | 0.2 | 0.1–0.5 | <0.001 | 224 | 0.3 | 0.1–0.6 | <0.001 |
| Face wounds | ||||||||
| Yes vs. No | 224 | 3.0 | 1.2–7.6 | 0.021 | 224 | 3.1 | 1.2–8.1 | 0.024 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cirignaco, G.; Catarzi, L.; Monarchi, G.; Committeri, U.; Frosolini, A.; Togni, L.; Mascitti, M.; Balercia, P.; Santarelli, A.; Consorti, G. Interpersonal Violence-Related Facial Fractures: 12-Year Trends and Surgical Outcomes in a Southern European Level-I Trauma Centre. Medicina 2025, 61, 1443. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61081443
Cirignaco G, Catarzi L, Monarchi G, Committeri U, Frosolini A, Togni L, Mascitti M, Balercia P, Santarelli A, Consorti G. Interpersonal Violence-Related Facial Fractures: 12-Year Trends and Surgical Outcomes in a Southern European Level-I Trauma Centre. Medicina. 2025; 61(8):1443. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61081443
Chicago/Turabian StyleCirignaco, Giulio, Lisa Catarzi, Gabriele Monarchi, Umberto Committeri, Andrea Frosolini, Lucrezia Togni, Marco Mascitti, Paolo Balercia, Andrea Santarelli, and Giuseppe Consorti. 2025. "Interpersonal Violence-Related Facial Fractures: 12-Year Trends and Surgical Outcomes in a Southern European Level-I Trauma Centre" Medicina 61, no. 8: 1443. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61081443
APA StyleCirignaco, G., Catarzi, L., Monarchi, G., Committeri, U., Frosolini, A., Togni, L., Mascitti, M., Balercia, P., Santarelli, A., & Consorti, G. (2025). Interpersonal Violence-Related Facial Fractures: 12-Year Trends and Surgical Outcomes in a Southern European Level-I Trauma Centre. Medicina, 61(8), 1443. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61081443











