Assessment of the Rapid Shallow Breathing Index, Integrative Weaning Index, and Dead Space to Tidal Volume Ratio by Respiratory Failure Type in Successfully Weaned Emergency Department Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Setting
2.2. Ethical Consideration
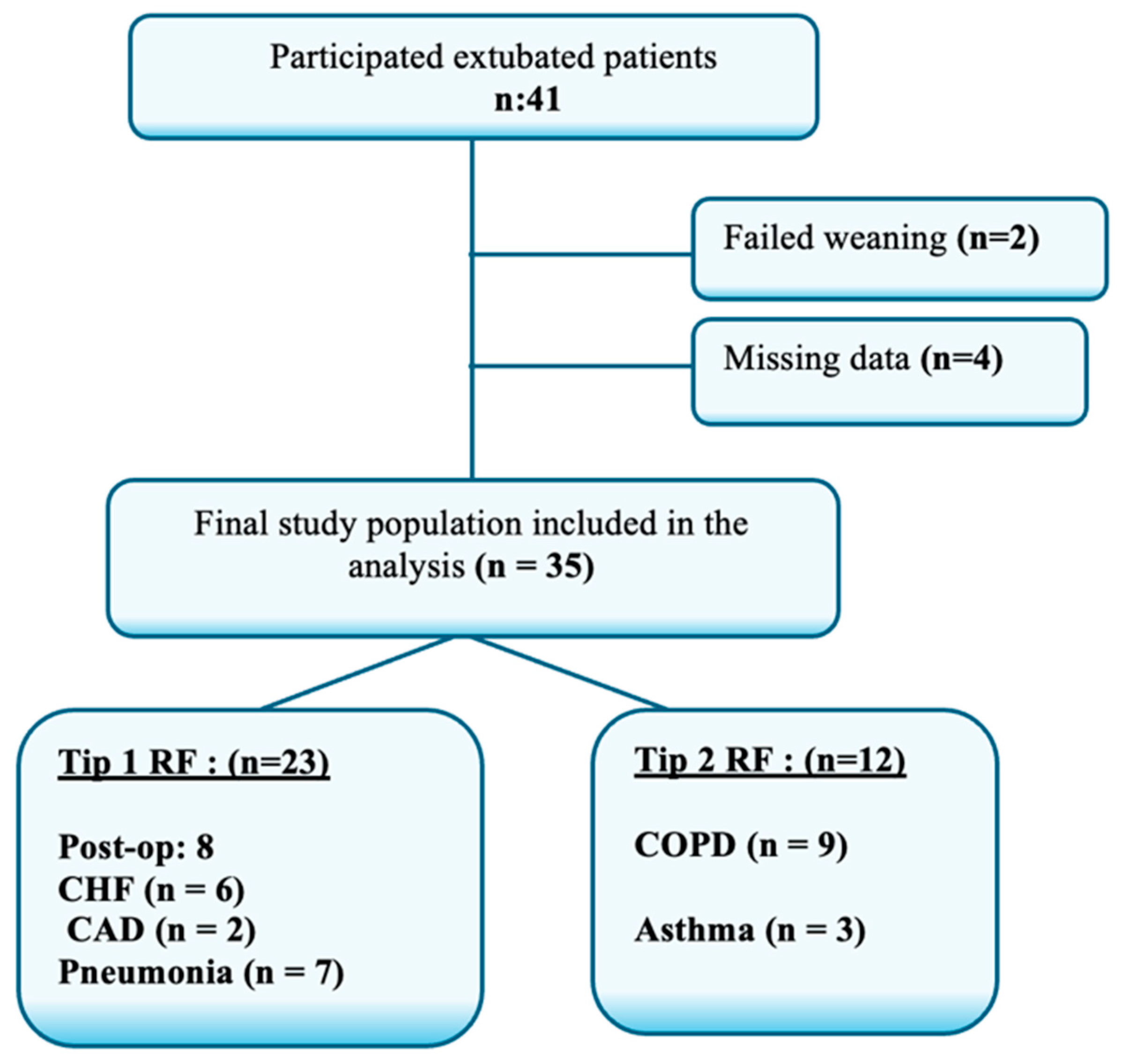
2.3. Participants and Recruitment
2.4. Data Collection
2.5. Weaning Procedure
- RSBI: Derived from respiratory rate and tidal volume and presented as a fractional value of f/VT.
- Dead Space to Tidal Volume Ratio (VD/VT): Measured as (PaCO2 − End TidalCO2)/PaCO2.
- Integrative Weaning Index (IWI): Static compliance × Oxygen saturation SaO2/RSBI.
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABG | Arterial Blood Gas |
| ARDS | Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome |
| BUN | Blood Urea Nitrogen |
| CDyn | Dynamic Compliance |
| CStat | Static Compliance |
| COPD | Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease |
| ED | Emergency Department |
| EtCO2 | End-Tidal Carbon Dioxide |
| VD/VT | Dead Space to Tidal Volume Ratio |
| FiO2 | Fraction of Inspired Oxygen |
| Hb | Hemoglobin |
| IWI | Integrative Weaning Index |
| MV | Mechanical Ventilation |
| OHS | Obesity Hypoventilation Syndrome |
| PaCO2 | Partial Arterial Carbon Dioxide Pressure |
| PaO2 | Partial Arterial Oxygen Pressure |
| PAO2 | Partial Alveolar Oxygen Pressure |
| PEEP | Positive End-Expiratory Pressure |
| Pmax | Peak Inspiratory Pressure |
| Pplato | Plateau Pressure |
| RF | Respiratory Failure |
| RR | Respiratory Rate |
| RSBI | Rapid Shallow Breathing Index |
References
- Battaglini, D.; Sottano, M.; Ball, L.; Robba, C.; Rocco, P.R.M.; Pelosi, P. Ten golden rules for individualized mechanical ventilation in acute respiratory distress syndrome. J. Intensive Med. 2021, 1, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.; Oh, D.K.; Lee, S.Y.; Park, M.H.; Lim, C.M. Korean Sepsis Alliance (KSA) investigators. Impact of the timing of invasive mechanical ventilation in patients with sepsis: A multicenter cohort study. Crit. Care 2024, 28, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parada-Gereda, H.M.; Tibaduiza, A.L.; Rico-Mendoza, A.; Molano-Franco, D.; Nieto, V.H.; Arias-Ortiz, W.A.; Perez-Terán, P.; Masclans, J.R. Effectiveness of diaphragmatic ultrasound as a predictor of successful weaning from mechanical ventilation: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit. Care 2023, 27, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shamil, P.K.; Gupta, N.K.; Ish, P.; Sen, M.K.; Kumar, R.; Chakrabarti, S.; Gupta, N. Prediction of Weaning Outcome from Mechanical Ventilation Using Diaphragmatic Rapid Shallow Breathing Index. Indian. J. Crit. Care Med. 2022, 26, 1000–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swamy, A.H.M.; Kumararadhya, G.B.; Shivaramu, D.; Challakere, G.L.; Chaitanya, K.U. Rapid Shallow Breathing Index and Ultrasonographic Diaphragmatic Parameters as Predictors of Weaning Outcome in Critically Ill Patients on Mechanical Ventilation. Ann. Afr. Med. 2025, 24, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartos, S.; Svoboda, M.; Brat, K.; Lukes, M.; Predac, A.; Homolka, P.; Olson, L.J.; Cundrle, I. Causes of ventilatory inefficiency in lung resection candidates. ERJ Open Res. 2025, 11, 00792–02024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boniatti, V.M.; Boniatti, M.M.; Andrade, C.F.; Zigiotto, C.C.; Kaminski, P.; Gomes, S.P.; Lippert, R.; Miguel, D.C.; A Felix, E. The modified integrative weaning index as a predictor of extubation failure. Respir Care 2014, 59, 1042–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakti, P.P.; Anjarwani, S. Weaning failure in mechanical ventilation: A literature review. Heart Sci. J. 2023, 4, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanayakkara, B.; McNamara, S. Pathophysiology of Chronic Hypercapnic Respiratory Failure. Sleep. Med. Clin. 2024, 19, 379–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadhan, A.R.; Betcy, B.; Aurora, R.G.; Prasenohadi, P.; Alatas, M.F. Obesity hypoventilation syndrome (Pickwickian syndrome): A literature review. Respir Sci. 2024, 5, 48–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eser, P.; Käesermann, D.; Calamai, P.; Kalberer, A.; Stütz, L.; Huber, S.; Duffin, J.; Wilhelm, M. Excess ventilation and chemosensitivity in patients with inefficient ventilation and chronic coronary syndrome or heart failure: A case-control study. Front. Physiol. 2025, 15, 1509421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura, J.C.D.S.; Gianfrancesco, L.; Souza, T.H.; Hortencio, T.D.R.; Nogueira, R.J.N. Extubation in the pediatric intensive care unit: Predictive methods. An integrative literature review. Extubação em unidade de terapia intensiva pediátrica: Métodos preditores. Uma revisão integrativa da literatura. Rev. Bras. Ter. Intensiv. 2021, 33, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racca, F.; Geraci, C.; Cremascoli, L.; Ruvolo, D.; Piccolella, F.; Romenskaya, T.; Longhitano, Y.; Martuscelli, E.; Saviano, A.; Savioli, G.; et al. Invasive Mechanical Ventilation in Traumatic Brain Injured Patients with Acute Respiratory Failure. Rev. Recent. Clin. Trials 2023, 18, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.Q.; Si, Q.; Feng, Y.P.; Guo, J.; Jiang, L.P. Research progress in pulmonary rehabilitation in patients who have been weaned off mechanical ventilation: A review article. Technol. Health Care 2024, 32, 2859–2864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonifazi, M.; Romitti, F.; Busana, M.; Palumbo, M.M.; Steinberg, I.; Gattarello, S.; Palermo, P.; Saager, L.; Meissner, K.; Quintel, M.; et al. End-tidal to arterial PCO2 ratio: A bedside meter of the overall gas exchanger performance. Intensive Care Med. Exp. 2021, 9, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maj, R.; Palermo, P.; Gattarello, S.; Brusatori, S.; D’albo, R.; Zinnato, C.; Velati, M.; Romitti, F.; Busana, M.; Wieditz, J.; et al. Ventilatory ratio, dead space, and venous admixture in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome. Br. J. Anaesth. 2023, 130, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, P.D.; Malhotra, A.; Prisk, G.K. Using pulmonary gas exchange to estimate shunt and deadspace in lung disease: Theoretical approach and practical basis. J. Appl. Physiol. 2022, 132, 1104–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trivedi, V.; Chaudhuri, D.; Jinah, R.; Piticaru, J.; Agarwal, A.; Liu, K.; McArthur, E.; Sklar, M.C.; Friedrich, J.O.; Rochwerg, B.; et al. The Usefulness of the Rapid Shallow Breathing Index in Predicting Successful Extubation: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Chest 2022, 161, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahedian-Azimi, A.; Gohari-Moghadam, K.; Rahimi-Bashar, F.; Samim, A.; Khoshfetrat, M.; Mohammadi, S.M.; de Souza, L.C.; Mahmoodpoor, A. New integrated weaning indices from mechanical ventilation: A derivation-validation observational multicenter study. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 830974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzari, S.; Romitti, F.; Busana, M.; Vassalli, F.; Bonifazi, M.; Macrí, M.M.; Giosa, L.; Collino, F.; Heise, D.; Golinski, M.; et al. End-Tidal to Arterial Pco2 Ratio as Guide to Weaning from Venovenous Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2022, 206, 973–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Chen, H.; Chang, W.; Sun, Q.; Yuan, X.; Wu, Z.; Xie, J.; Liu, L.; Yang, Y. Time-varying intensity of ventilatory inefficiency and mortality in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome. Ann. Intensive Care 2025, 15, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, M.; Pereira, S.M.; Sanders, N.; Girard, M.; Sankar, A.; Sklar, M.C. Weaning from mechanical ventilation in the operating room: A systematic review. Br. J. Anaesth. 2024, 133, 424–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiumello, D.; Fioccola, A. Recent advances in cardiorespiratory monitoring in acute respiratory distress syndrome patients. J. Intensive Care 2024, 12, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghiani, A.; Walcher, S.; Lutfi, A.; Gernhold, L.; Feige, S.F.; Neurohr, C. Mechanical power density, spontaneous breathing indexes, and weaning readiness following prolonged mechanical ventilation. Respir. Med. 2025, 237, 107943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sterr, F.; Reintke, M.; Bauernfeind, L.; Senyol, V.; Rester, C.; Metzing, S.; Palm, R. Predictors of weaning failure in ventilated intensive care patients: A systematic evidence map. Crit. Care 2024, 28, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, M.; Sengupta, S. Diaphragmatic ultrasound: A new frontier in weaning from mechanical ventilation. Indian. J. Anaesth. 2023, 67 (Suppl. 4), S205–S207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akella, P.; Voigt, L.P.; Chawla, S. To Wean or Not to Wean: A Practical Patient Focused Guide to Ventilator Weaning. J. Intensive Care Med. 2022, 37, 1417–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depta, F.; Gentile, M.A.; Kallet, R.H.; Donic, V.; Zdravkovic, M. Evaluation of time constant, dead space and compliance to determine PEEP in COVID-19 ARDS: A prospective observational study. Signa Vitae 2024, 20, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, M.-L. Combining Dynamic Hyperinflation with Dead Space Volume during Maximal Exercise in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghiasi, F.; Gohari, M.K.; Alikiaii, B.; Sadrzadeh, S.; Farajzadegan, Z. The prognostic value of rapid shallow breathing index and physiologic dead space for weaning success in intensive care unit patients under mechanical ventilation. J. Res. Med. Sci. 2019, 24, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, Y.; Guo, S.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, T.; Li, B.; Zhang, Q.; Han, Y.; Wang, X.; Hu, Z. A clinical study on the ability of the integrative weaning index to predict weaning from mechanical ventilation. Ann. Palliat. Med. 2020, 9, 3162–3169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turhan, S.; Tutan, D.; Şahiner, Y.; Kısa, A.; Özdemir, S.Ö.; Tutan, M.B.; Kayır, S.; Doğan, G. Predictive Value of Serial Rapid Shallow Breathing Index Measurements for Extubation Success in Intensive Care Unit Patients. Medicina 2024, 60, 1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwack, W.G. Evaluation of the Daily Change in PaO2/FiO2 Ratio as a Predictor of Abnormal Chest X-rays in Intensive Care Unit Patients Post Mechanical Ventilation Weaning: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Medicina 2022, 58, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhalla, A.K.; Chau, A.; Khemani, R.G.; Newth, C.J.L. The end-tidal alveolar dead space fraction for risk stratification during the first week of invasive mechanical ventilation: An observational cohort study. Crit. Care 2023, 27, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Type 1 RF (n:23) | Type 2 RF (n:12) | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (mean ± SD) | 72.57 ± 18.2 | 71.75 ± 8.7 | 0.88 * | |
| Gender | Male (%) | 16 (69.6) | 10 (83.3) | 0.37 ** |
| Female (%) | 7 (30.4) | 2 (16.7) | ||
| Heart Rate (bpm/min) | 97.52 ± 14.19 | 88.25 ± 14.34 | 0.07 * | |
| SBP (mmHg) | 122.96 ± 14.59 | 130.17 ± 21.95 | 0.25 * | |
| RR (breath/min) | 17.39 ± 2.85 | 17.00 ± 2.89 | 0.70 * | |
| Hemoglobin (gr/dL) | 11.93 ± 3.21 | 12.90 ± 2.97 | 0.39 * | |
| BUN (mg/dL) | 28.00 (21.5–37.5) | 37.00 (20.3–43.8) | 0.70 *** | |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 1.16 (0.81–1.47) | 0.97 (0.85–1.13) | 0.56 *** | |
| Type 1 RF (n:23) | Type 2 RF (n:12) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| PEEP (cmH2O) | 5.0 (5.0–5.5) | 5.00 (5.00–5.50) | 0.82 ** |
| Pmax (cmH2O) | 24.0(23.0–25.5) | 26.50 (24.50–29.30) | 0.16 ** |
| Pplato (cmH2O) | 18.9 (17.0–20.5) | 21.50 (17.00–23.00) | 0.14 ** |
| FiO2 (%) | 30.0(25.5–35.0) | 37.50 (25.50–40.00) | 0.03 ** |
| VT (mL) | 423(400–450) | 421 (425–450) | 0.76 ** |
| Cdyn (mL/cmH2O) | 22.0 ± 3.85 | 20.8 ± 3.87 | 0.39 * |
| Cstat (mL/cmH2O) | 32.5 ± 5.93 | 30.0 ± 8.17 | 0.31 * |
| Ph | 7.36 ± 0.04 | 7.38 ± 0.05 | 0.37 * |
| PaO2 (mm/Hg) | 70.1 ± 13.6 | 61.1 ± 14.2 | 0.07 * |
| PaCO2 (mm/Hg) | 40.3 ± 4.49 | 49.1 ± 9.65 | <0.001 * |
| VE (L/min) | 7.03 ± 1.02 | 7.21 ± 1.19 | 0.65 * |
| EtCO2 (mm/Hg) | 28.5 ± 6.51 | 30.6 ± 6.57 | 0.38 * |
| Weaning Indexes | Type 1 RF (n:23) | Type 2 RF (n:12) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| RSBI (bpm/L) | 40.0 (35.0–40.0) | 40.0 (35.0–40.0) | 1.00 ** |
| VD/VT | 0.29 ± 0.13 | 0.37 ± 0.04 | 0.046 * |
| PaO2/FiO2 (mmHg) | 244 ± 95.6 | 169 ± 49.6 | 0.017 * |
| IWI (bpm/mL) | 79.3 ± 32.5 | 70.8 ± 30.7 | 0.45 * |
| PaO2/PAO2 | 0.45 (0.36–0.69) | 0.33 (0.29–0.39) | 0.053 * |
| GCS | 15 (14–15) | 15 (14–15) | 0.78 ** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kaya, M.; Yildirim, H.; Halici, A.; Coskun, A.; Ulu, M.; Toprak, M.; Eksert, S. Assessment of the Rapid Shallow Breathing Index, Integrative Weaning Index, and Dead Space to Tidal Volume Ratio by Respiratory Failure Type in Successfully Weaned Emergency Department Patients. Medicina 2025, 61, 1438. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61081438
Kaya M, Yildirim H, Halici A, Coskun A, Ulu M, Toprak M, Eksert S. Assessment of the Rapid Shallow Breathing Index, Integrative Weaning Index, and Dead Space to Tidal Volume Ratio by Respiratory Failure Type in Successfully Weaned Emergency Department Patients. Medicina. 2025; 61(8):1438. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61081438
Chicago/Turabian StyleKaya, Murtaza, Harun Yildirim, Ali Halici, Abdil Coskun, Mehmed Ulu, Mehmet Toprak, and Sami Eksert. 2025. "Assessment of the Rapid Shallow Breathing Index, Integrative Weaning Index, and Dead Space to Tidal Volume Ratio by Respiratory Failure Type in Successfully Weaned Emergency Department Patients" Medicina 61, no. 8: 1438. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61081438
APA StyleKaya, M., Yildirim, H., Halici, A., Coskun, A., Ulu, M., Toprak, M., & Eksert, S. (2025). Assessment of the Rapid Shallow Breathing Index, Integrative Weaning Index, and Dead Space to Tidal Volume Ratio by Respiratory Failure Type in Successfully Weaned Emergency Department Patients. Medicina, 61(8), 1438. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61081438





