Revolutionizing Breast Reconstruction: The Rise of Hybrid Techniques
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
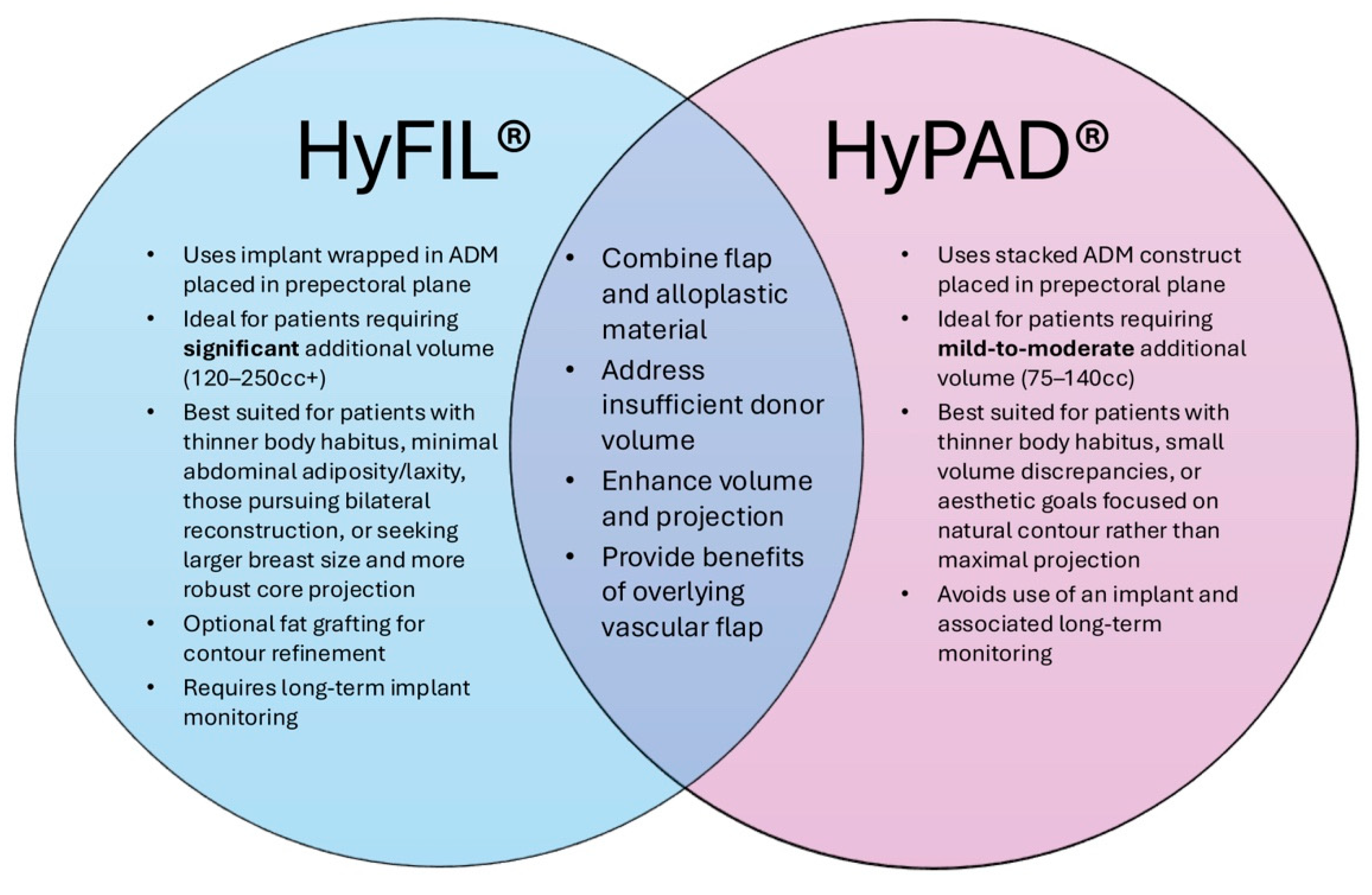
3. HyFIL®
3.1. Description of Technique
3.2. Patient Selection for HyFIL®
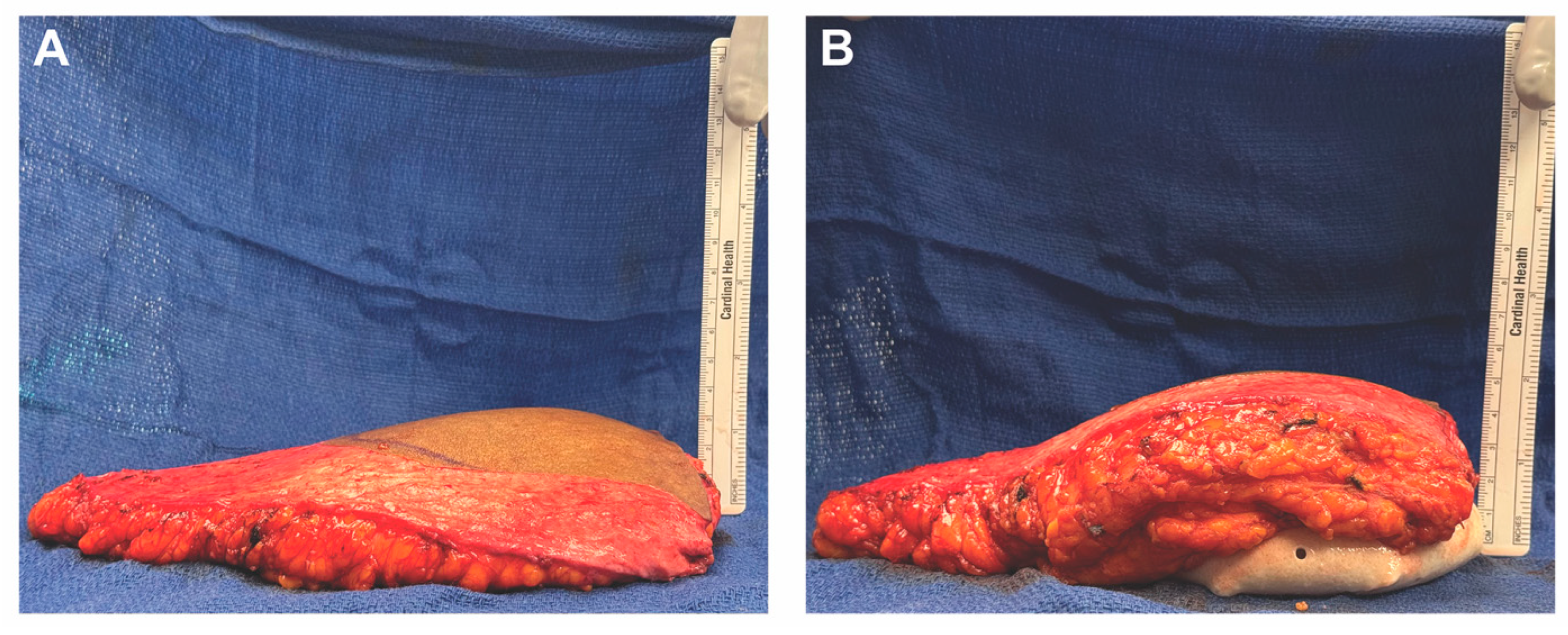
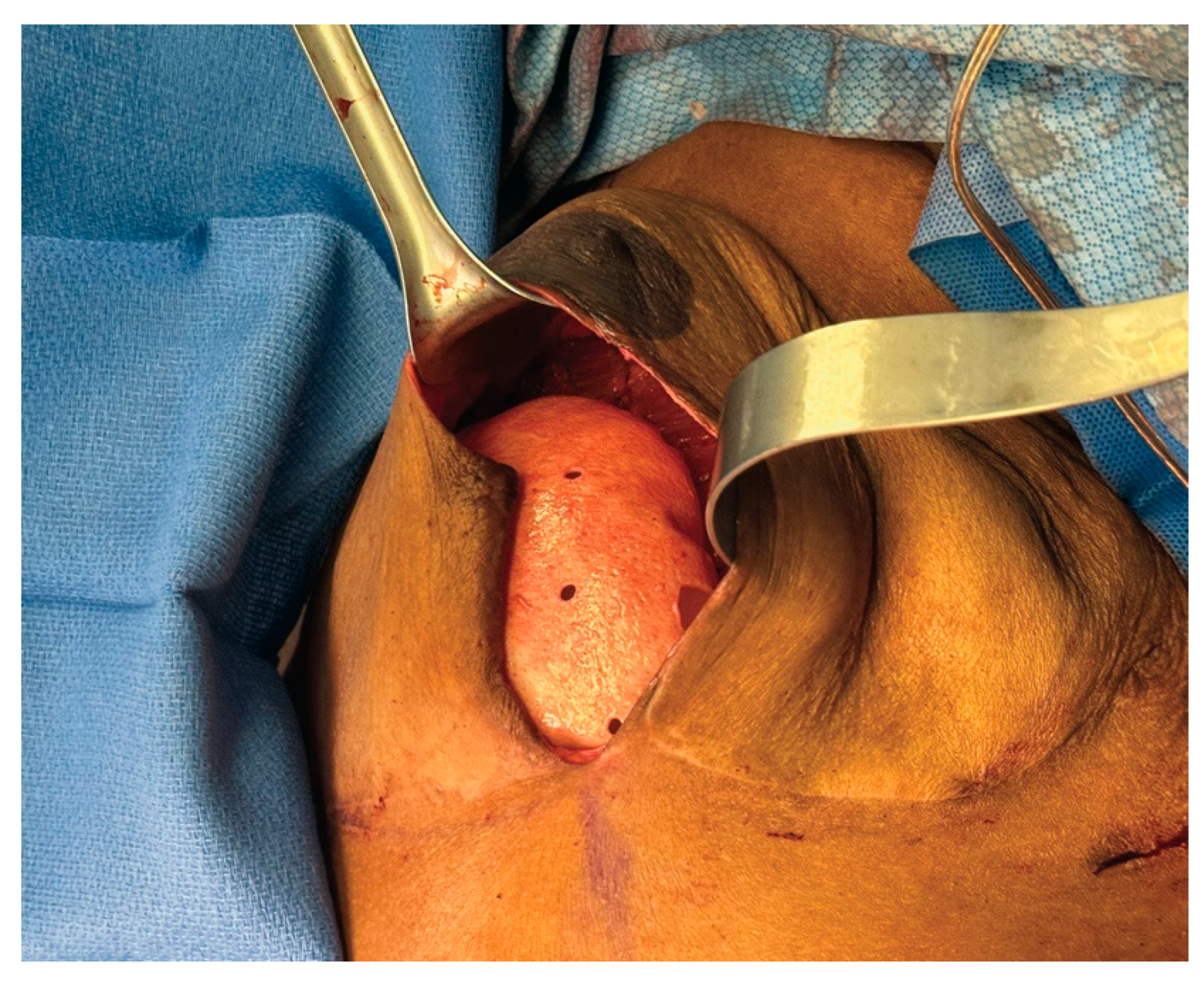
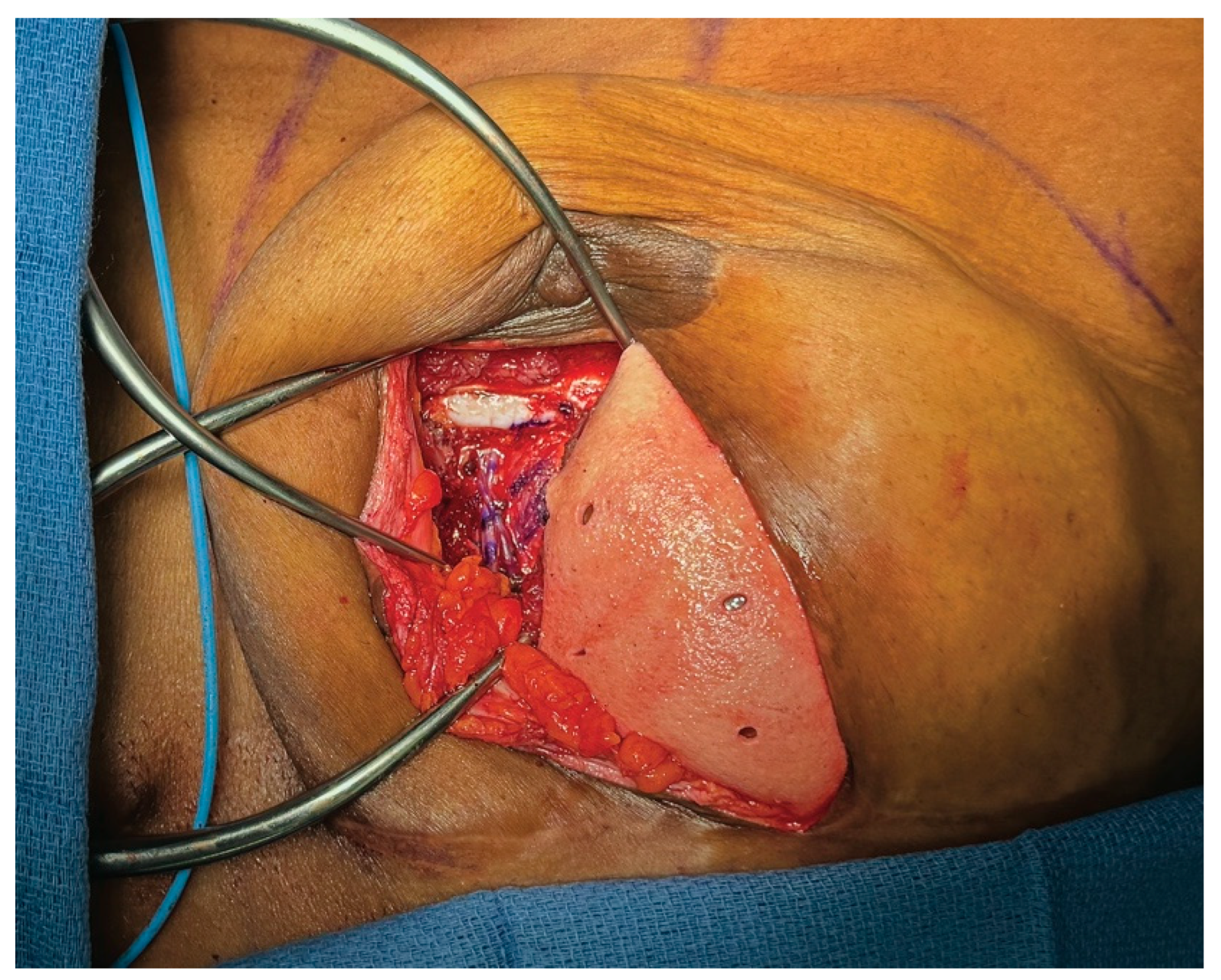
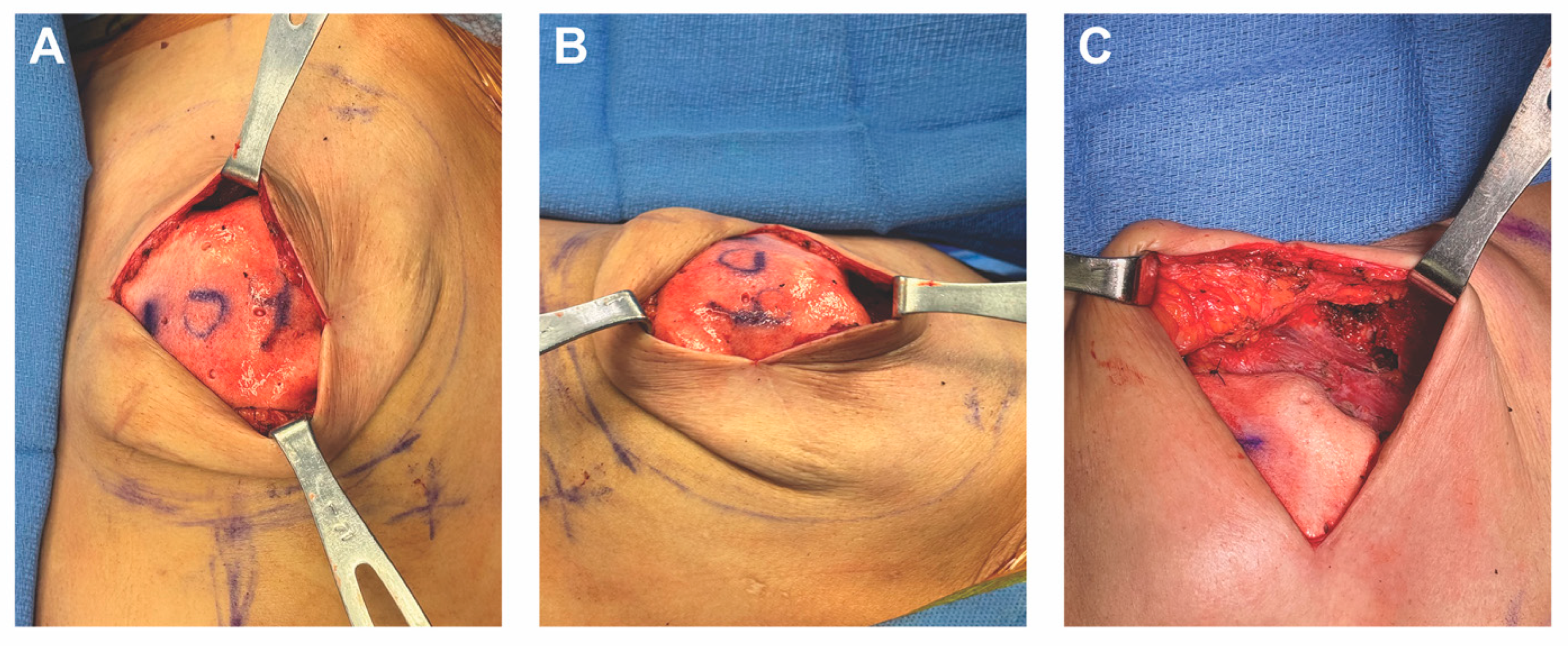
3.3. Case 1—HyFIL®
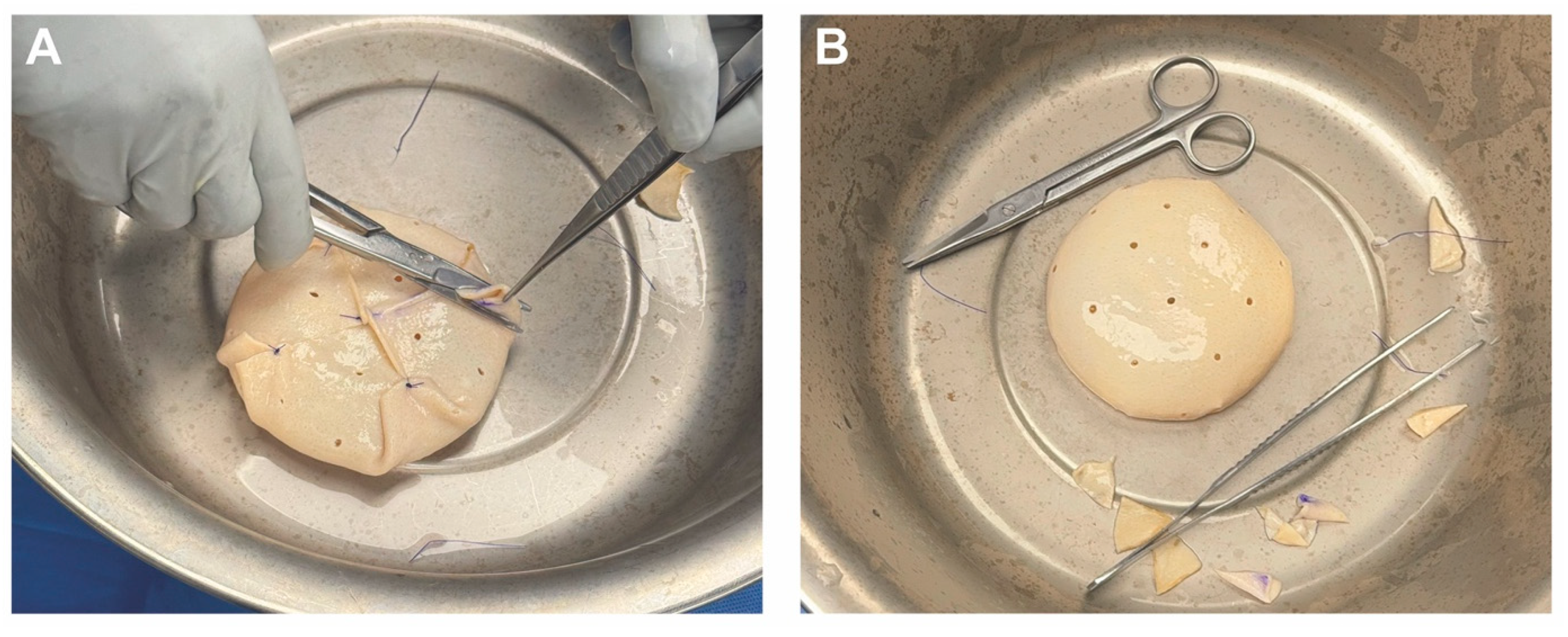
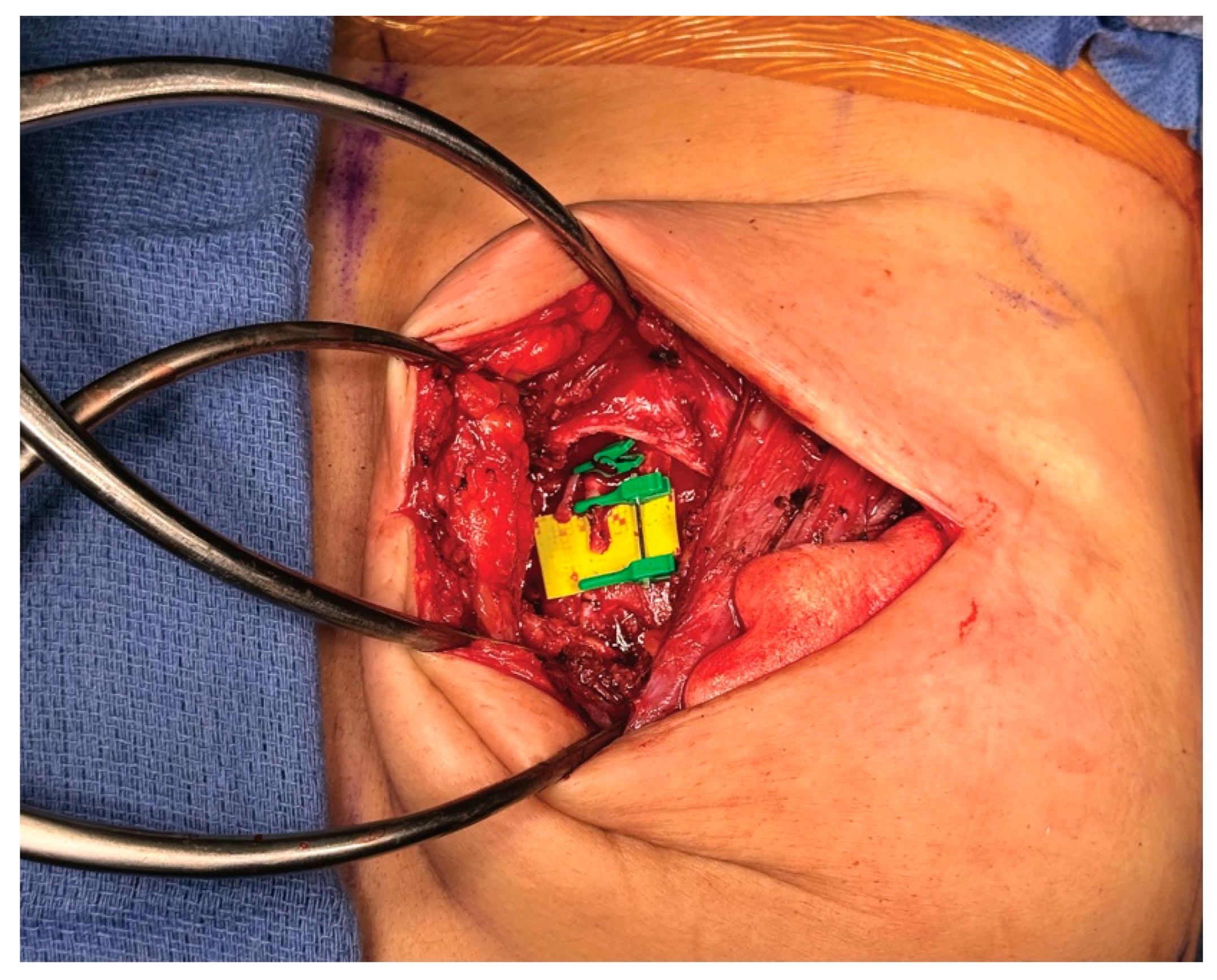
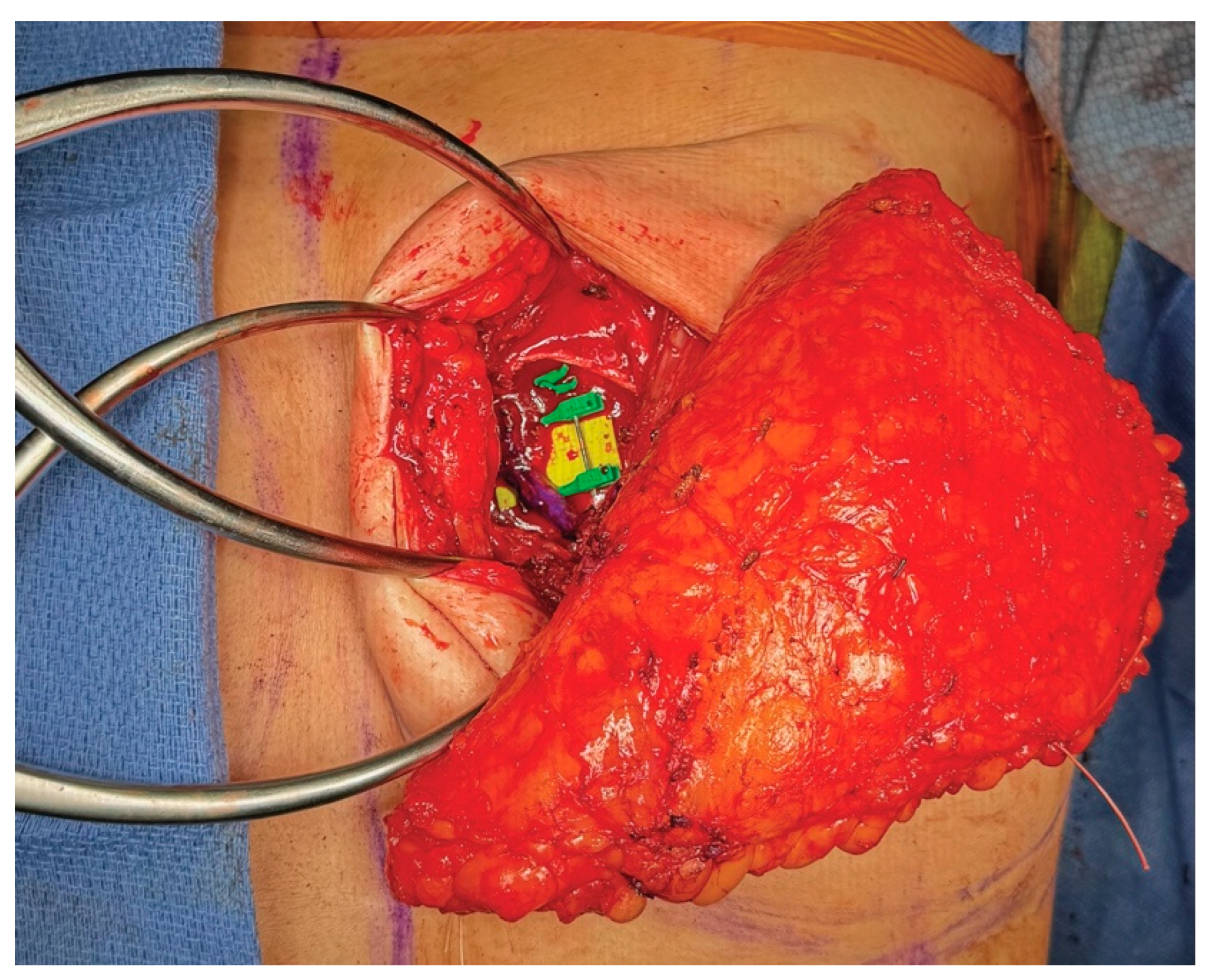
3.4. Operative Technique
4. HyPAD®
4.1. Description of Technique
4.2. Patient Selection for HyPAD®
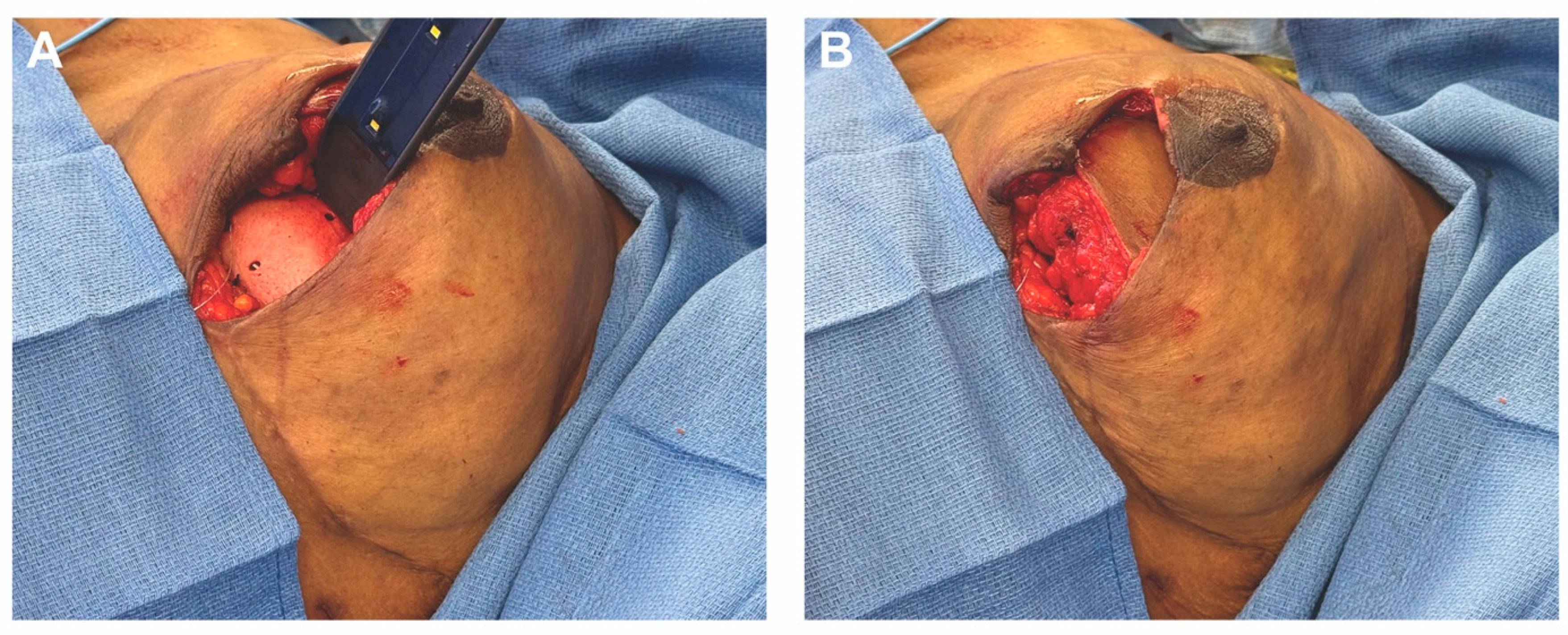
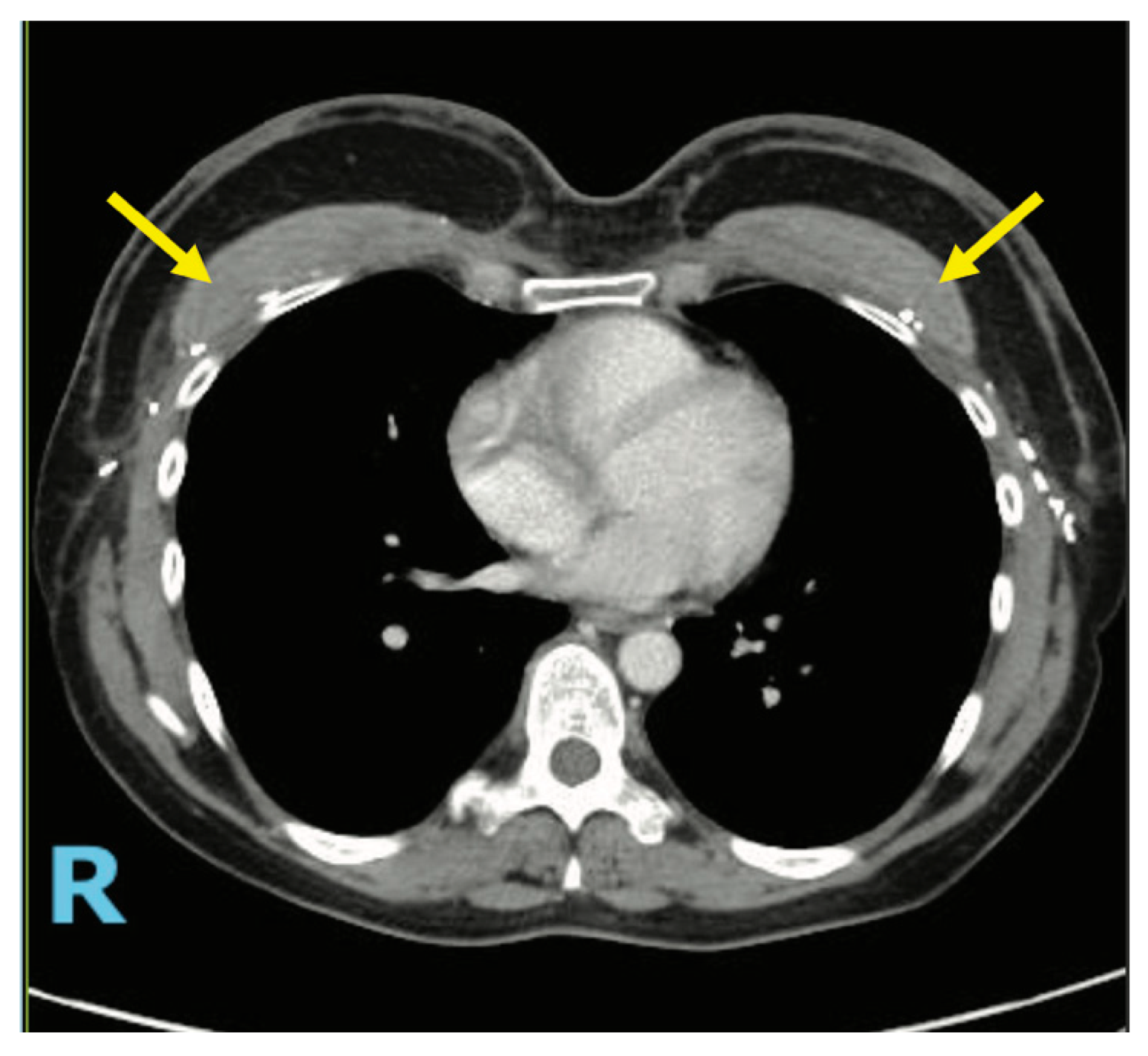
4.3. Case 2—HyPAD®
4.4. Operative Technique
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Panchal, H.; Matros, E. Current Trends in Post-Mastectomy Breast Reconstruction. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2017, 140, 7S–13S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustos, V.P.; Laikhter, E.; Manstein, S.M.; Comer, C.D.; Veeramani, A.; Shiah, E.; Xun, H.; Lin, S.J.; Lee, B.T. A national analysis of outpatient mastectomy and breast reconstruction trends from 2013 through 2019. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. 2022, 75, 2920–2929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanchwala, S.; Momeni, A. Hybrid breast reconstruction—The best of both worlds. Gland Surg. 2019, 8, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- 2023 Procedural Statistics Release. Available online: https://www.plasticsurgery.org/documents/news/statistics/2023/plastic-surgery-statistics-report-2023.pdf (accessed on 4 April 2025).
- Amro, C.; Sorenson, T.J.; Boyd, C.J.; Hemal, K.; Vernice, N.A.; Park, J.J.; Cohen, O.D.; Choi, M.; Karp, N.S. The Evolution of Implant-Based Breast Reconstruction: Innovations, Trends, and Future Directions. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 7407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobti, N.; Weitzman, R.E.; Nealon, K.P.; Jimenez, R.B.; Gfrerer, L.; Mattos, D.; Ehrlichman, R.J.; Gadd, M.; Specht, M.; Austen, W.G.; et al. Evaluation of capsular contracture following immediate prepectoral versus subpectoral direct-to-implant breast reconstruction. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colwell, A.S.; Taylor, E.M. Recent Advances in Implant-Based Breast Reconstruction. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2020, 145, 421e–432e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanna, N.; Sultan, D.L.; Minasian, R.A.; Clappier, M.; Haddock, N.T.; Chrysopoulo, M.T.; Nahabedian, M.Y.; Serletti, J.M.; Allen, R.J. Contemporary Microsurgical Breast Reconstruction: Abdominally Based Flaps. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2024, 154, 199e–214e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, A.T.; Saint-Cyr, M. Anatomic and physiological fundamentals for autologous breast reconstruction. Gland Surg. 2015, 4, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, J.P.; Wes, A.M.; Nelson, J.A.; Basta, M.; Rohrbach, J.I.; Wu, L.C.; Serletti, J.M.; Kovach, S.J. Propensity-matched, longitudinal outcomes analysis of complications and cost: Comparing abdominal free flaps and implant-based breast reconstruction. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2014, 219, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santosa, K.B.; Qi, J.; Kim, H.M.; Hamill, J.B.; Wilkins, E.G.; Pusic, A.L. Long-term Patient-Reported Outcomes in Postmastectomy Breast Reconstruction. JAMA Surg. 2018, 153, 891–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, E.I.; Soto-Miranda, M.A.; Zhang, H.; Nosrati, N.; Robb, G.L.; Chang, D.W. Comprehensive analysis of donor-site morbidity in abdominally based free flap breast reconstruction. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2013, 132, 1383–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egeberg, A.; Rasmussen, M.K.; Sørensen, J.A. Comparing the donor-site morbidity using DIEP, SIEA or MS-TRAM flaps for breast reconstructive surgery: A meta-analysis. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. 2012, 65, 1474–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa-de-Los-Monteros, A.; Frias-Frias, R.; Alvarez-Tostado-Rivera, A.; Caralampio-Castro, A.; Llanes, S.; Saldivar, A. Postoperative Abdominal Bulge and Hernia Rates in Patients Undergoing Abdominally Based Autologous Breast Reconstruction: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2021, 86, 476–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, M.; Samra, F.; Kanchwala, S.; Momeni, A. Treatment Options for Bilateral Autologous Breast Reconstruction in Patients with Inadequate Donor-Site Volume. J. Reconstr. Microsurg. 2017, 33, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kronowitz, S.J.; Robb, G.L.; Youssef, A.; Reece, G.; Chang, S.-H.; Koutz, C.A.; Ng, R.L.H.; Lipa, J.E.; Miller, M.J. Optimizing Autologous Breast Reconstruction in Thin Patients. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2003, 112, 1768–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weichman, K.; Tanna, N.; Broer, P.; Wilson, S.; Azhar, H.; Karp, N.; Choi, M.; Ahn, C.; Levine, J.; Allen, R. Microsurgical Breast Reconstruction in Thin Patients: The Impact of Low Body Mass Indices. J. Reconstr. Microsurg. 2014, 31, 020–025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weichman, K.E.; Broer, P.N.; Tanna, N.; Wilson, S.C.; Allan, A.; Levine, J.P.; Ahn, C.; Choi, M.; Karp, N.S.; Allen, R. The Role of Autologous Fat Grafting in Secondary Microsurgical Breast Reconstruction. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2013, 71, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gronovich, Y.; Winder, G.; Maisel-Lotan, A.; Lysy, I.; Sela, E.; Spiegel, G.; Carmon, M.; Hadar, T.; Elami, A.; Eizenman, N.; et al. Hybrid Prepectoral Direct-to-Implant and Autologous Fat Graft Simultaneously in Immediate Breast Reconstruction: A Single Surgeon’s Experience with 25 Breasts in 15 Consecutive Cases. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2022, 149, 386e–391e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herly, M.; Ørholt, M.; Larsen, A.; Pipper, C.B.; Bredgaard, R.; Gramkow, C.S.; Katz, A.J.; Drzewiecki, K.T.; Vester-Glowinski, P.V. Efficacy of breast reconstruction with fat grafting: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. 2018, 71, 1740–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stillaert, F.B.J.L.; Lannau, B.; Landuyt, K.V.; Blondeel, P.N. The Prepectoral, Hybrid Breast Reconstruction: The Synergy of Lipofilling and Breast Implants. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2020, 8, e2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, A.; Abu-Ghname, A.; Davis, M.J.; Winocour, S.J.; Hanson, S.E.; Chu, C.K. Fat Grafting in Breast Reconstruction. Semin. Plast. Surg. 2020, 34, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaoutzanis, C.; Xin, M.; Ballard, T.N.; Welch, K.B.; Momoh, A.O.; Kozlow, J.H.; Brown, D.L.; Cederna, P.S.; Wilkins, E.G. Autologous Fat Grafting After Breast Reconstruction in Postmastectomy Patients: Complications, Biopsy Rates, and Locoregional Cancer Recurrence Rates. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2016, 76, 270–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayo, J.L.; Allen, R.J.; Sadeghi, A. Four-flap Breast Reconstruction: Bilateral Stacked DIEP and PAP Flaps. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2015, 3, e383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haddock, N.T.; Cho, M.-J.; Teotia, S.S. Comparative Analysis of Single versus Stacked Free Flap Breast Reconstruction: A Single-Center Experience. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2019, 144, 369e–377e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stalder, M.W.; Lam, J.; Allen, R.J.; Sadeghi, A. Using the Retrograde Internal Mammary System for Stacked Perforator Flap Breast Reconstruction: 71 Breast Reconstructions in 53 Consecutive Patients. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2016, 137, 265e–277e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haddock, N.T.; Cho, M.-J.; Gassman, A.; Teotia, S.S. Stacked Profunda Artery Perforator Flap for Breast Reconstruction in Failed or Unavailable Deep Inferior Epigastric Perforator Flap. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2019, 143, 488e–494e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanna, N.; Barnett, S.L.; Robinson, E.L.; Smith, M.L. Hybrid Microsurgical Breast Reconstruction. Clin. Plast. Surg. 2023, 50, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, D.W.; Barnea, Y.; Robb, G.L. Effects of an Autologous Flap Combined with an Implant for Breast Reconstruction: An Evaluation of 1000 Consecutive Reconstructions of Previously Irradiated Breasts. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2008, 122, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roehl, K.R.; Baumann, D.P.; Chevray, P.M.; Chang, D.W. Evaluation of Outcomes in Breast Reconstructions Combining Lower Abdominal Free Flaps and Permanent Implants. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2010, 126, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figus, A.; Canu, V.; Iwuagwu, F.C.; Ramakrishnan, V. DIEP flap with implant: A further option in optimising breast reconstruction. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. 2009, 62, 1118–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Momeni, A.; Kanchwala, S. Hybrid Prepectoral Breast Reconstruction: A Surgical Approach that Combines the Benefits of Autologous and Implant-Based Reconstruction. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2018, 142, 1109–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Momeni, A.; Kanchwala, S.K. Improved pocket control in immediate microsurgical breast reconstruction with simultaneous implant placement through the use of mesh. Microsurgery 2018, 38, 450–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silverstein, M.L.; Momeni, A. Long-Term Outcomes Following Hybrid Breast Reconstruction. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2023, 154, 217e–223e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Roy, N.; Montalmant, K.E.; Shamamian, P.; Seyidova, N.; Oleru, O.; Graziano, F.; Jacobs, J.M.S.; Sbitany, H.; Henderson, P.W. Deep Inferior Epigastric Perforator Flap with Implant Placement has a Favorable Complication Profile Compared with Implant-Only or Flap-Only Reconstruction. J. Reconstr. Microsurg. 2024, a-2483-5472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atamian, E.K.; Smith, M.L. Optimizing aesthetic results in autologous breast reconstruction. Gland Surg. 2023, 12, 1110–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.C.; Lee, J.; Park, S.H.; Yoon, E.S. The Hybrid Latissimus Dorsi Flap in Immediate Breast Reconstruction: A Comparative Study With the Abdominal-Based Flap. Ann Plast Surg 2021, 86, 394–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yesantharao, P.S.; Nguyen, D.H. Hybrid breast reconstruction: A systematic review of current trends and future directions. Ann. Breast Surg. 2022, 6, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momeni, A.; Becker, A.; Torio-Padron, N.; Iblher, N.; Stark, G.B.; Bannasch, H. Nipple reconstruction: Evidence-based trials in the plastic surgical literature. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2008, 32, 18–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serletti, J.M.; Moran, S.L. The combined use of the TRAM and expanders/implants in breast reconstruction. Ann. Plast. Surg. 1998, 40, 510–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vardanian, J.A.; Clayton, L.J.; Roostaeian, J.; Shirvanian, V.; Lio, D.A.; Lipa, E.J.; Crisera, C.; Festekjian, H.J. Comparison of Implant-Based Immediate Breast Reconstruction with and without Acellular Dermal Matrix. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2011, 128, 403e–410e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, L.A.; Macadam, S.A. The Use of AlloDerm in Postmastectomy Alloplastic Breast Reconstruction: Part II. A Cost Analysis. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2011, 127, 2245–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salzberg, C.A.; Ashikari, A.Y.; Berry, C.; Hunsicker, L.M. Acellular Dermal Matrix–Assisted Direct-to-Implant Breast Reconstruction and Capsular Contracture: A 13-Year Experience. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2016, 138, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qureshi, A.A.; Broderick, K.; Funk, S.; Reaven, N.; Tenenbaum, M.M.; Myckatyn, T.M. Direct Hospital Cost of Outcome Pathways in Implant-Based Reconstruction with Acellular Dermal Matrices. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2016, 4, e831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breast Implants—Certain Labeling Recommendations to Improve Patient Communication. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents/breast-implants-certain-labeling-recommendations-improve-patient-communication (accessed on 4 April 2025).
- Chung, K.C.; Malay, S.; Shauver, M.J.; Kim, H.M. Economic analysis of screening strategies for rupture of silicone gel breast implants. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2012, 130, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walters, J.A.; Sato, E.A.; Martinez, C.A.; Hall, J.J.; Boutros, S.G. Delayed Mammoplasty with Silicone Gel Implants following DIEP Flap Breast Reconstruction. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2015, 3, e540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rothchild, E.; Smith, I.T.; Odoom, G.; Smith, M.L.; Tanna, N. Revolutionizing Breast Reconstruction: The Rise of Hybrid Techniques. Medicina 2025, 61, 1434. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61081434
Rothchild E, Smith IT, Odoom G, Smith ML, Tanna N. Revolutionizing Breast Reconstruction: The Rise of Hybrid Techniques. Medicina. 2025; 61(8):1434. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61081434
Chicago/Turabian StyleRothchild, Evan, Isabelle T. Smith, Gabrielle Odoom, Mark L. Smith, and Neil Tanna. 2025. "Revolutionizing Breast Reconstruction: The Rise of Hybrid Techniques" Medicina 61, no. 8: 1434. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61081434
APA StyleRothchild, E., Smith, I. T., Odoom, G., Smith, M. L., & Tanna, N. (2025). Revolutionizing Breast Reconstruction: The Rise of Hybrid Techniques. Medicina, 61(8), 1434. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61081434





