Higher Prevalence of Thyroid Dysfunction in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Effects on Glycemic Control, Diabetic Complications and Comorbidities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
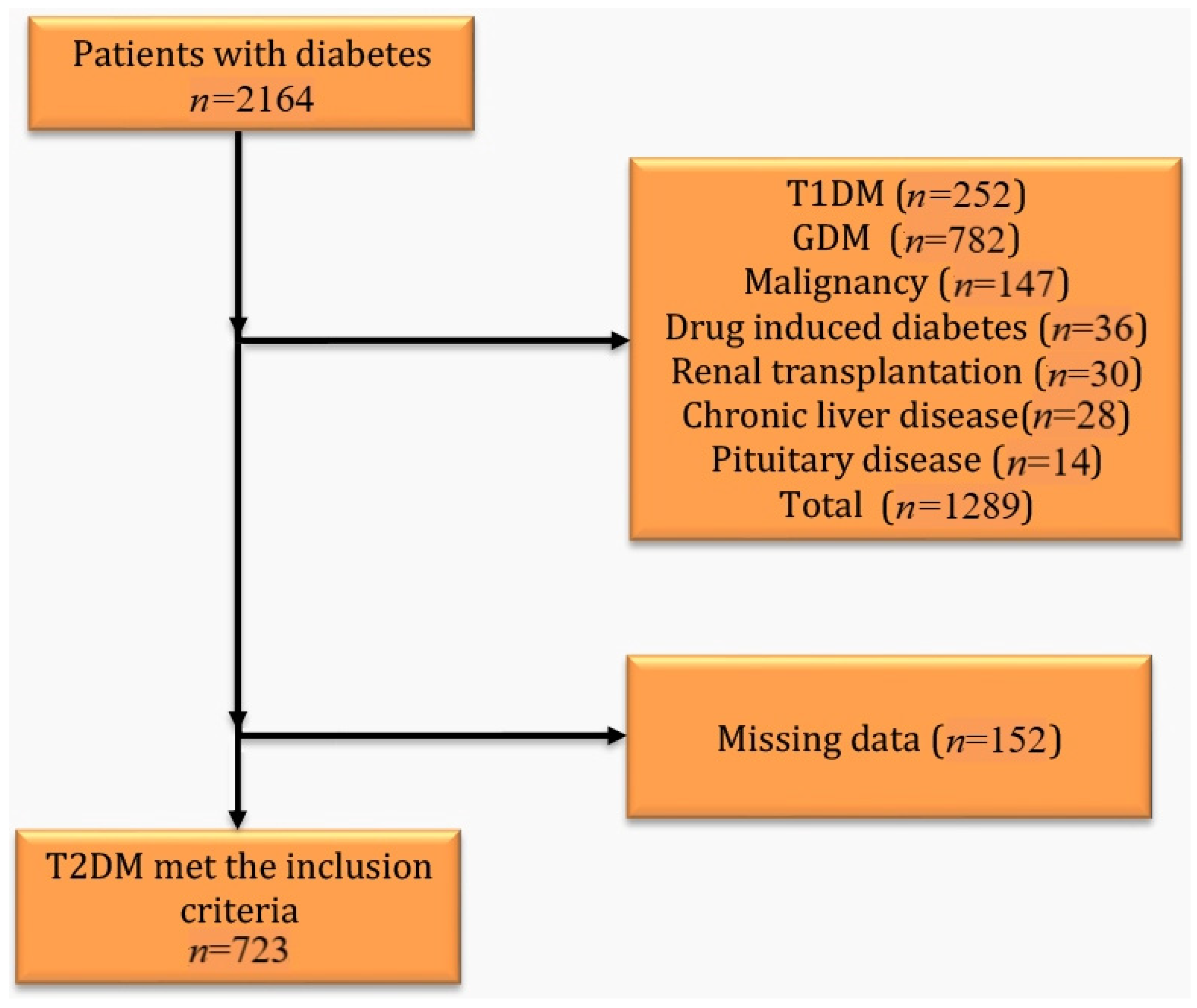
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Demographic and Clinical Variables
2.3. Measures
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Elmenshawi, I.; Alotaibi, S.; Alazmi, A.; Alazmi, A.; Alruwaili, F.; Alazmi, N.; Alazmi, Z. Prevalence of thyroid dysfunction in diabetic patients. J. Diabetes Metab. Disord. Control 2017, 4, 55–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogbonna, S.U.; Ezeani, I.U. Risk factors of thyroid dysfunction in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalra, S.; Aggarwal, S.; Khandelwal, D. Thyroid dysfunction and type 2 diabetes mellitus: Screening strategies and implications for management. Diabetes Ther. 2019, 10, 2035–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biondi, B.; Kahaly, G.J.; Robertson, R.P. Thyroid dysfunction and diabetes mellitus: Two closely associated disorders. Endocr. Rev. 2019, 40, 789–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishi, M. Diabetes mellitus and thyroid diseases. Diabetol. Int. 2018, 9, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Hashim, M.J.; King, J.K.; Govender, R.D.; Mustafa, H.; Al Kaabi, J. Epidemiology of type 2 diabetes–global burden of disease and forecasted trends. J. Epidemiol. Glob. Health 2020, 10, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Ley, S.H.; Hu, F.B. Global aetiology and epidemiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its complications. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2018, 14, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Głowińska-Olszewska, B.; Szabłowski, M.; Panas, P.; Żoła̧dek, K.; Jamiołkowska-Sztabkowska, M.; Milewska, A.J.; Kadłubiska, A.; Polkowska, A.; Łuczyński, W.; Bossowski, A. Increasing co-occurrence of additional autoimmune disorders at diabetes Type 1 onset among children and adolescents diagnosed in years 2010–2018, Single-Center Study. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Diabetes Association. 2. Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2021. Diabetes Care 2022, 45 (Suppl. 1), S17–S38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koulouri, O.; Gurnell, M. How to interpret thyroid function tests. Clin. Med. 2013, 13, 282–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Song, F.; Bao, C.; Deng, M.; Xu, H.; Fan, M.; Paillard-Borg, S.; Xu, W.; Qi, X. The prevalence and determinants of hypothyroidism in hospitalized patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Endocrine 2017, 55, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subekti, I.; Pramono, L.A.; Dewiasty, E.; Harbuwono, D.S. Thyroid dysfunction in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients. Acta Medica Indones. 2018, 49, 314. [Google Scholar]
- Mehalingam, V.; Sahoo, J.; Bobby, Z.; Vinod, K.V. Thyroid dysfunction in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and its association with diabetic complications. J. Fam. Med. Prim. Care 2020, 9, 4277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamali, N.S.; Peris, A.; Awobajo, F.O.; Muntari, B.; Prosper, R.M.; Ali, W.R.; Muhumuza, J. Prevalence, patterns and predictors of thyroid dysfunction among adult patients with diabetes mellitus attending Fort Portal Regional Referral Hospital. Res. Sq. 2024. preprint. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogbonna, S.U.; Ezeani, I.U.; Okafor, C.I.; Chinenye, S. Association between glycemic status and thyroid dysfunction in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. Targets Ther. 2019, 12, 1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elgazar, E.H.; Esheba, N.E.; Shalaby, S.A.; Mohamed, W.F. Thyroid dysfunction prevalence and relation to glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev. 2019, 13, 2513–2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Dwairi, A.; Alfaqih, M.A.; Saadeh, R.A.; Al-Shboul, O.; Alqudah, M.; Khanfar, M.; Khassawneh, A. Lack of glycemic control in type two diabetes mellitus patients is associated with reduced serum epidermal growth factor level and increased insulin resistance. Biomed. Rep. 2024, 22, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Q.; Zhang, Q.M.; Li, C.J.; Dong, R.N.; Li, J.J.; Shi, J.Y.; Yu, D.M.; Zhang, J.Y. Association of thyroid-stimulating hormone levels with microvascular complications in type 2 diabetes patients. Med. Sci. Monit. Int. Med. J. Exp. Clin. Res. 2017, 23, 2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Talwalkar, P.; Deshmukh, V.; Bhole, M. Prevalence of hypothyroidism in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and hypertension in India: A cross-sectional observational study. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. Targets Ther. 2019, 12, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Xu, F.; Shen, J.; Liu, Y.; Bi, C.; Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Gao, Z.; Liang, L.; et al. Prevalence of thyroid dysfunction in older Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes—A multicenter cross-sectional observational study across China. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0216151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; He, X.; Xia, X.; Li, Y.; Shi, X.; Shan, Z.; Teng, W. Subclinical hypothyroidism and type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0135233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, A.; Jayakumari, C.; Jabbar, P.K.; Jayakumar, R.V.; Raizada, N.; Gopi, A.; George, G.S.; Seena, T.P. Prevalence and associations of hypothyroidism in Indian patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Thyroid Res. 2018, 2018, 5386129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.H.; Chen, H.Y.; Man, K.M.; Chen, S.J.; Chen, W.; Liu, P.L.; Chen, Y.H.; Chen, W.C. Thyroid diseases increased the risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus: A nation-wide cohort study. Medicine 2019, 98, e15631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Zeng, H.; Zhang, X.; Liu, F.; Pan, J.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, J.; Li, L.; Bao, Y.; Liu, F.; et al. A high thyroid stimulating hormone level is associated with diabetic peripheral neuropathy in type 2 diabetes patients. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2016, 115, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Clinical Variable | Mean ± SD | % (n) |
|---|---|---|
| The mean onset age of DM (year) | 47.7 ± 1.5 | - |
| The mean disease duration (year) | 10.7 ± 7.9 | - |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 31.0 ± 6.2 | - |
| Smoking exposure (packs-year) | 12.8 ± 21.8 | - |
| Family history for diabetes mellitus | - | 65.1% (471) |
| Aged over 65 years | - | 31.0% (224) |
| Complications | ||
| Nephropathy | - | 32.8% (237) |
| Retinopathy | - | 31.3% (226) |
| Neuropathy | - | 34.7% (251) |
| Diabetic foot (at any time) | - | 8.6% (62) |
| Comorbidities | ||
| Dyslipidemia | - | 63.6% (460) |
| Hypertension | - | 61.0% (441) |
| Chronic kidney disease | - | 14.1% (102) |
| Cerebrovascular event | - | 2.9% (21) |
| Coronary artery disease | - | 25.7% (186) |
| Heart failure | - | 4.3% (31) |
| Peripheral artery disease | - | 1% (7) |
| Thyroid Dysfunction | - | 21.4% (154) |
| Hyperthyroidism | - | 1.4% (10) |
| Hypothyroidism | - | 15.1% (109) |
| Subclinical hypothyroidism | - | 4.3% (31) |
| Subclinical hyperthyroidism | - | 0.6% (4) |
| Whole Group (n = 723) (Mean ± SD) | TD (−) (n = 569) (Mean ± SD) | TD (+) (n = 154) (Mean ± SD) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 58.3 ± 11.2 | 58.04 ± 11.87 | 59.37 ± 12.39 | 0.186 |
| T2DM duration | 10.7 ± 7.9 | 10.38 ± 7.82 | 11.70 ± 8.02 | 0.048 * |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 31.0 ± 6.2 | 30.67 ± 6.07 | 32.08 ± 6.33 | 0.007 * |
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 192 ± 82.8 | 195.4 ± 84.34 | 180.5 ± 75.84 | 0.063 |
| HbA1c (%) | 9.1 ± 2.4 | 9.20 ± 2.33 | 8.87 ± 2.46 | 0.081 |
| TSH (mIU/L) | 2.6 ± 3.6 | 2.01 ± 1.28 | 4.81 ± 7.51 | 0.000 |
| fT4 (pmol/L) | 16.4 ± 2.8 | 16.40 ± 2.27 | 16.62 ± 4.21 | 0.931 |
| fT3 (pmol/L) | 4.6 ± 0.9 | 4.63 ± 0.69 | 4.48 ± 1.32 | 0.000 |
| Clinical Variables | Patients | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TD (−) n (%) | TD (+) n (%) | |||
| Gender | Female Male | 233 (40.9%) 336 (59.1%) | 113 (73.4%) 41 (26.6%) | 0.000 * |
| Age | <65 year >65 year | 398 (69.9%) 171 (30.1%) | 101 (65.6%) 53 (34.4%) | 0.299 |
| Chronic kidney disease | Absent Present | 489 (85.9%) 80 (14.1%) | 132 (85.7%) 22 (14.3%) | 0.943 |
| Cerebrovascular event | Absent Present | 553 (97.2%) 16 (2.8%) | 149 (96.8%) 5 (3.2%) | 0.873 |
| Peripheral artery disease | Absent Present | 563 (98.9%) 6 (1.1%) | 153 (99.4%) 1 (0.6%) | 0.649 |
| Hypertension | Absent Present | 235 (41.3%) 334 (58.7%) | 47 (30.5%) 107 (69.5%) | 0.015 * |
| Coronary artery disease | Absent Present | 415 (72.9%) 154 (27.1%) | 122 (79.2%) 32 (20.8%) | 0.113 |
| Chronic heart failure | Absent Present | 548 (96.3%) 21 (3.7%) | 144 (93.5%) 10 (6.5%) | 0.128 |
| Dyslipidemia | Absent Present | 210 (36.9%) 359 (63.1%) | 53 (34.4%) 101 (65.6%) | 0.569 |
| Retinopathy | Absent Present | 394 (69.2%) 175 (30.8%) | 103 (66.9%) 51 (33.1%) | 0.575 |
| Nephropathy | Absent Present | 383 (67.3%) 186 (32.7%) | 103 (66.9%) 51 (33.1%) | 0.920 |
| Neuropathy | Absent Present | 381 (67.0%) 188 (33.0%) | 91 (59.1%) 63 (40.9%) | 0.043 * |
| Diabetic foot | Absent Present | 519 (91.2%) 50 (8.8%) | 142 (92.2%) 12 (7.8%) | 0.696 |
| Any complication | Absent Present | 113 (19.9%) 456 (80.1%) | 31 (20.1%) 123 (79.9%) | 0.941 |
| Any comorbidity | Absent Present | 204 (35.9%) 365 (64.1%) | 42 (27.3%) 112 (72.7%) | 0.046 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Catma, Y.; Edizer, A.; Bayramlar, O.F.; Gul, N.; Selcukbiricik, O.S.; Karsidag, K.; Uzum, A.K. Higher Prevalence of Thyroid Dysfunction in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Effects on Glycemic Control, Diabetic Complications and Comorbidities. Medicina 2025, 61, 1427. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61081427
Catma Y, Edizer A, Bayramlar OF, Gul N, Selcukbiricik OS, Karsidag K, Uzum AK. Higher Prevalence of Thyroid Dysfunction in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Effects on Glycemic Control, Diabetic Complications and Comorbidities. Medicina. 2025; 61(8):1427. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61081427
Chicago/Turabian StyleCatma, Yunus, Ahmed Edizer, Osman Faruk Bayramlar, Nurdan Gul, Ozlem Soyluk Selcukbiricik, Kubilay Karsidag, and Ayse Kubat Uzum. 2025. "Higher Prevalence of Thyroid Dysfunction in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Effects on Glycemic Control, Diabetic Complications and Comorbidities" Medicina 61, no. 8: 1427. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61081427
APA StyleCatma, Y., Edizer, A., Bayramlar, O. F., Gul, N., Selcukbiricik, O. S., Karsidag, K., & Uzum, A. K. (2025). Higher Prevalence of Thyroid Dysfunction in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Effects on Glycemic Control, Diabetic Complications and Comorbidities. Medicina, 61(8), 1427. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61081427






