Association Between Uric Acid to HDL-C Ratio and Liver Transaminase Abnormalities: Insights from a Large-Scale General Population Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
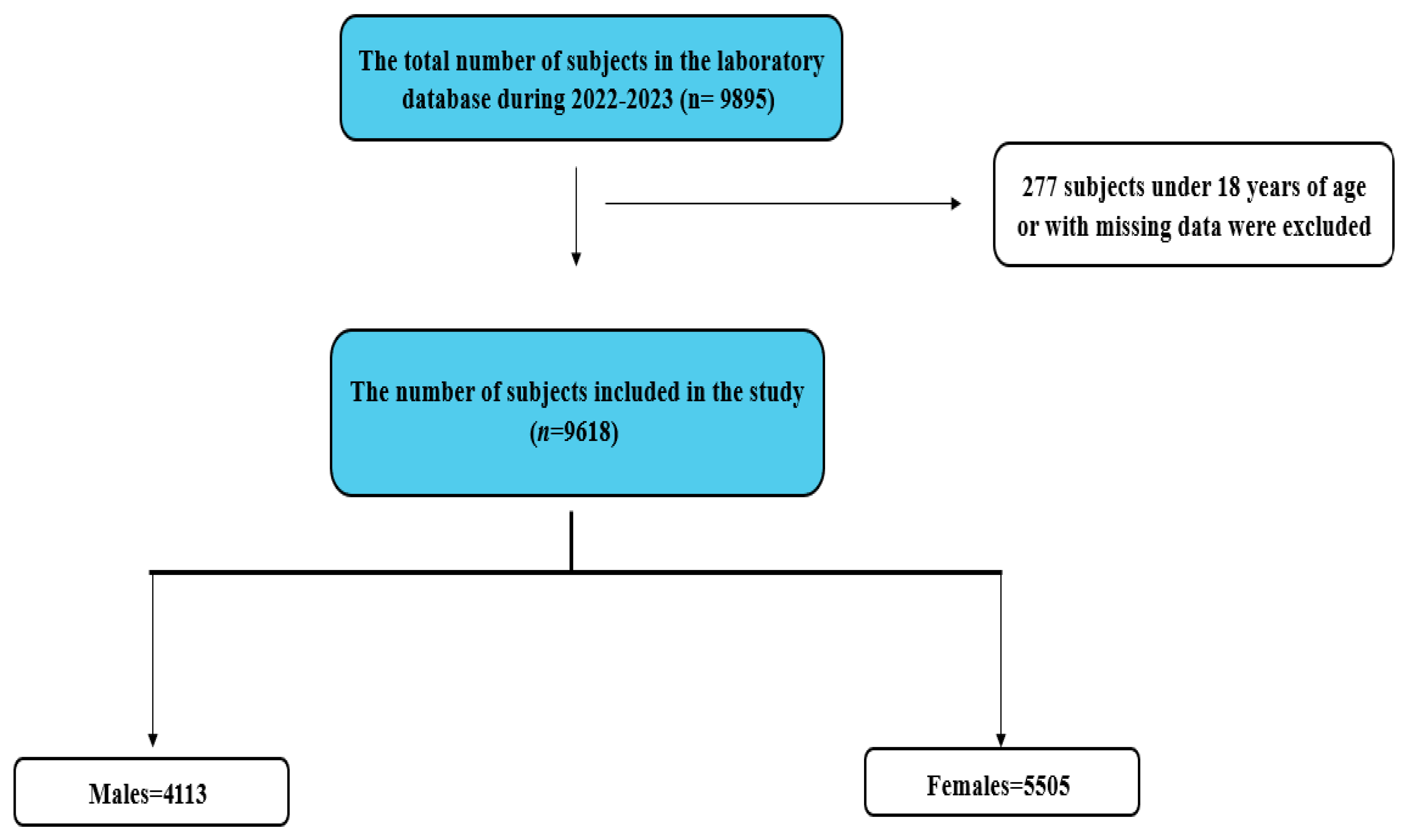
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection and Study Design
2.2. Statistics
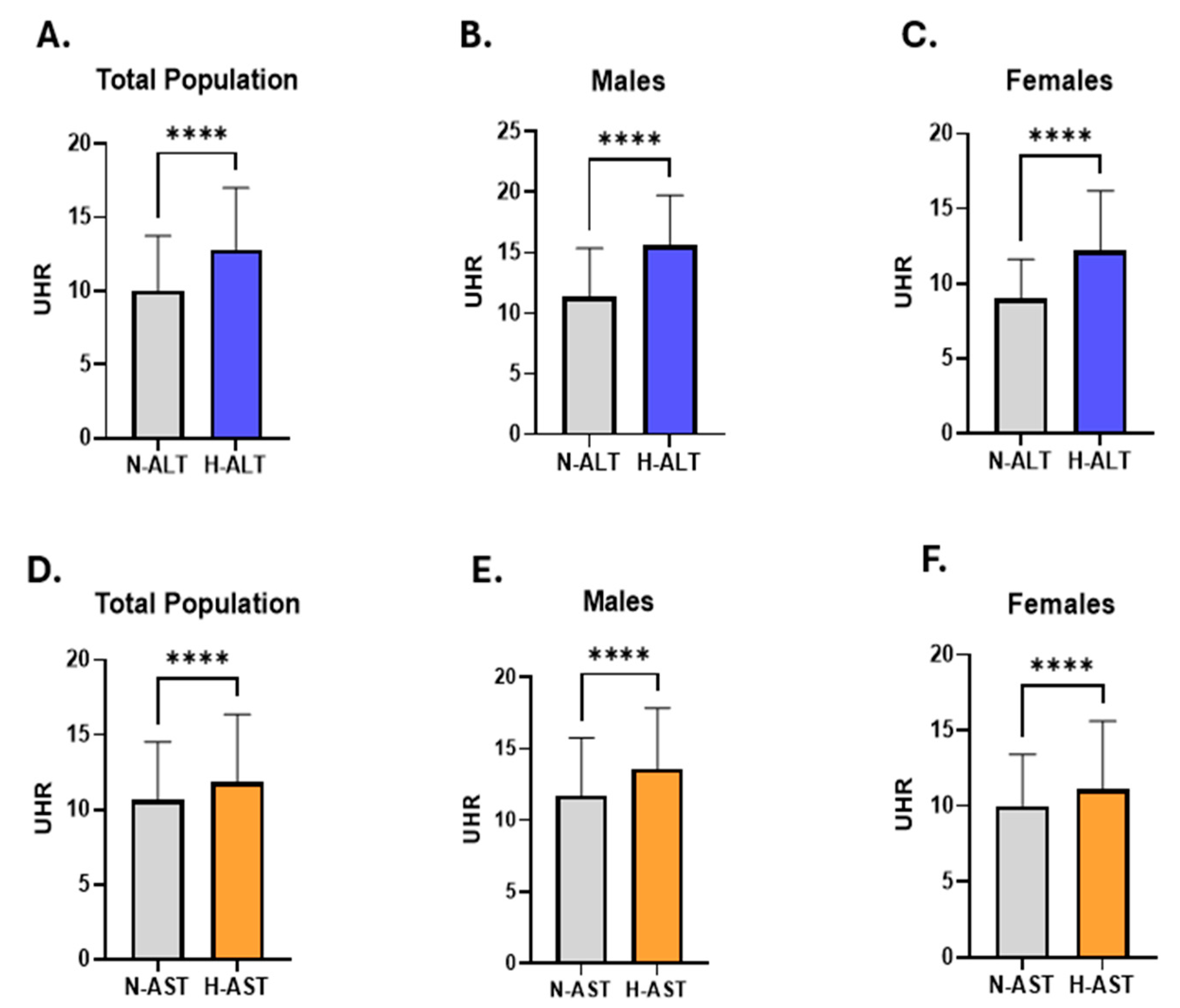
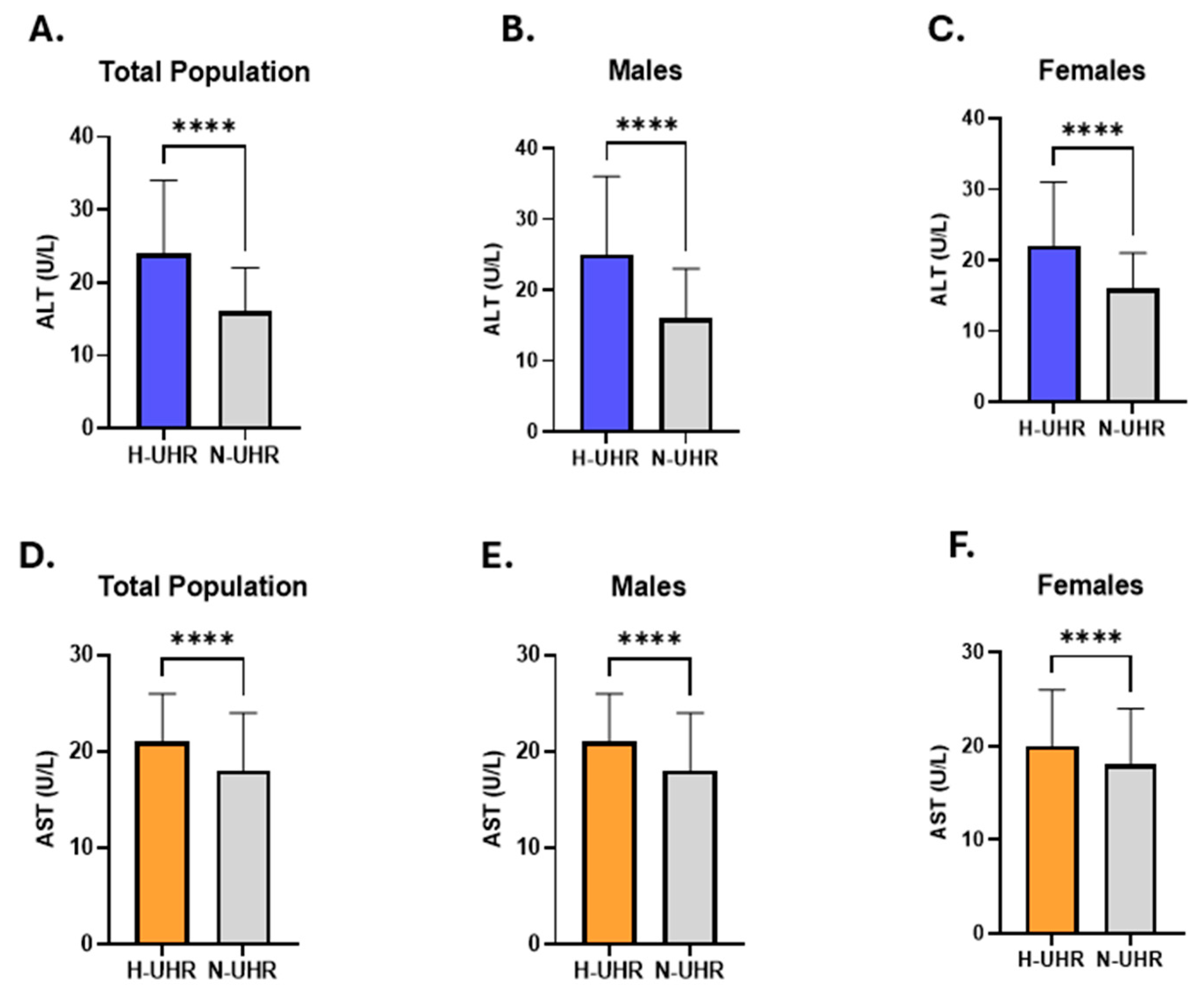
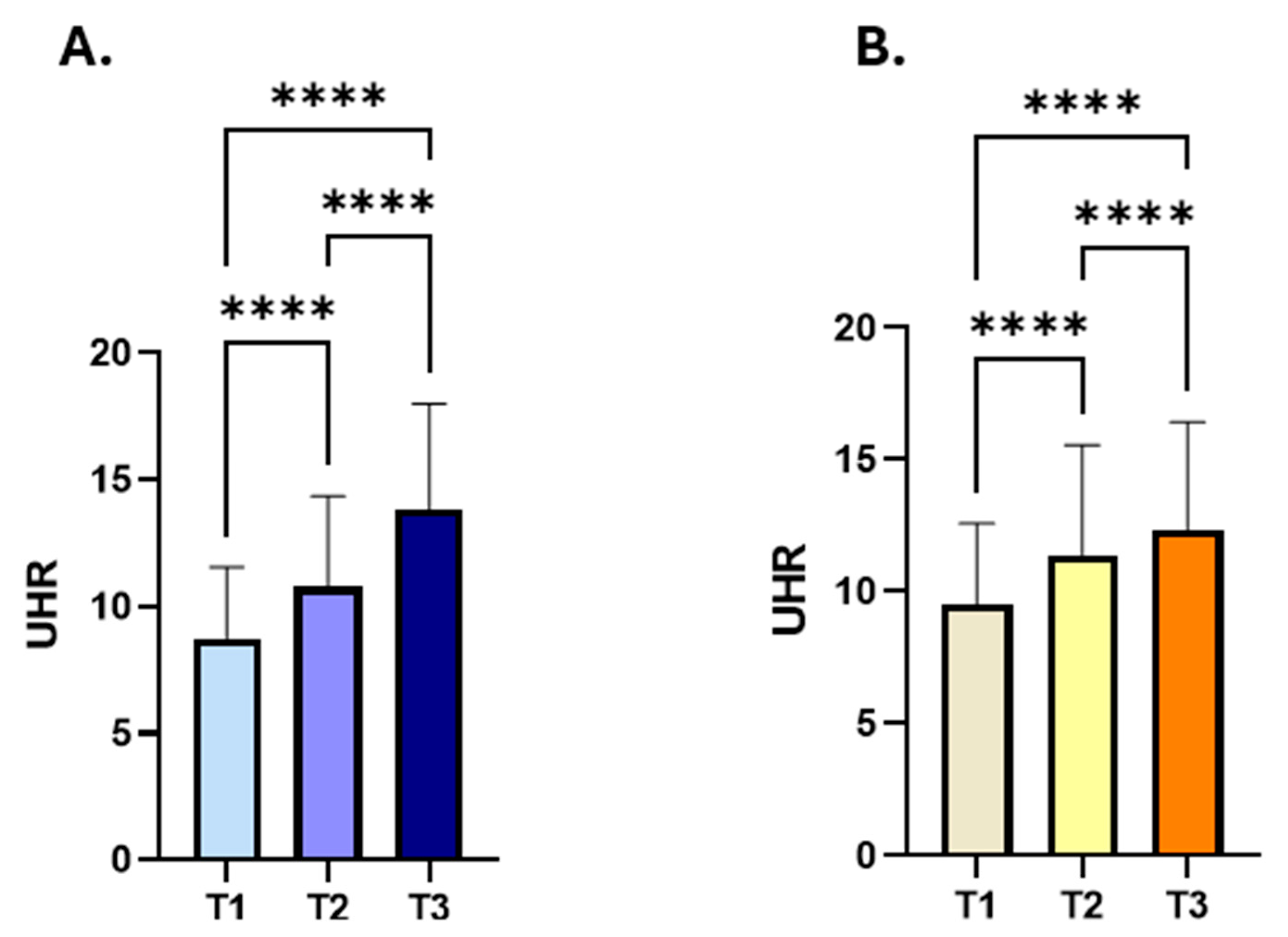
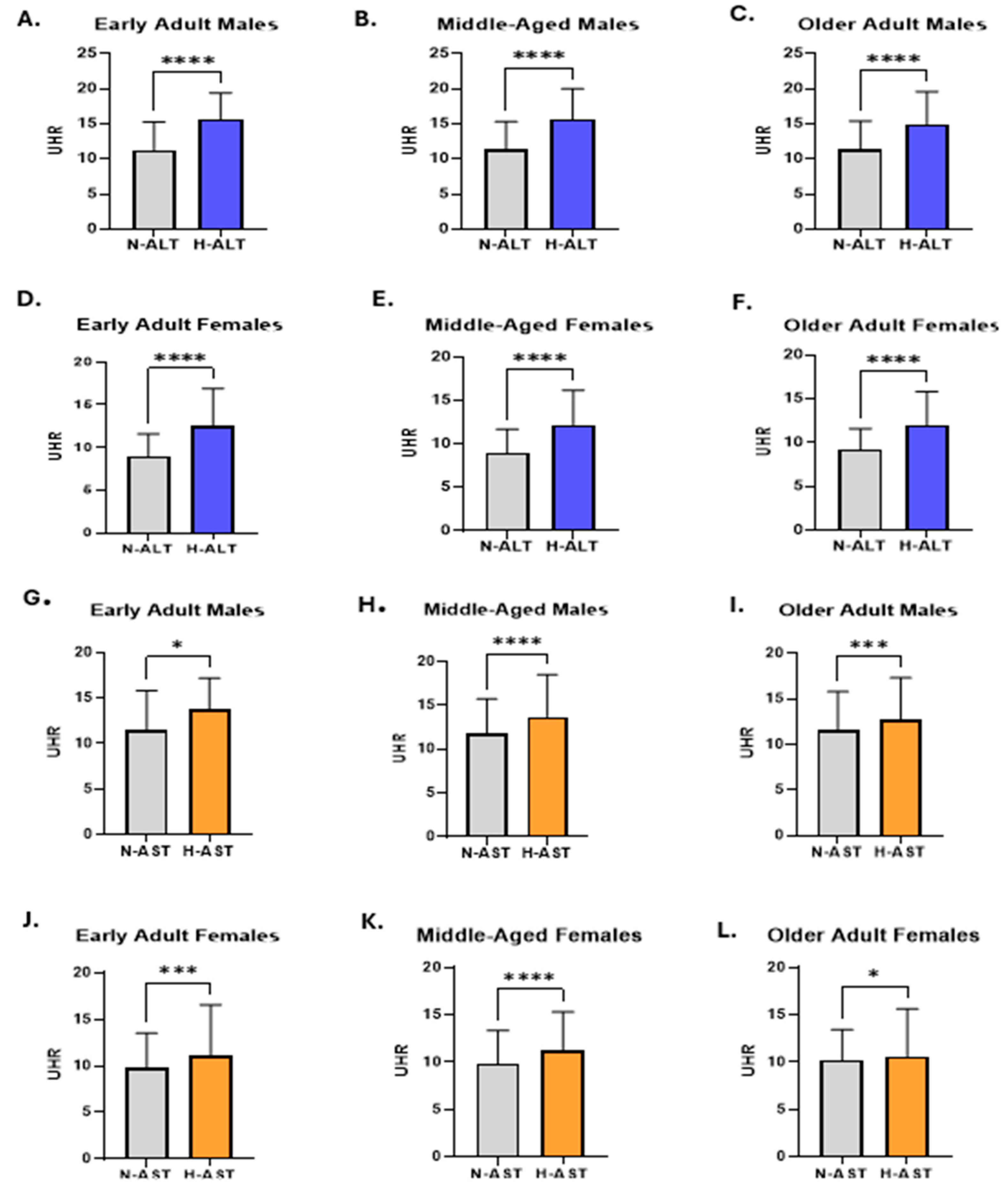
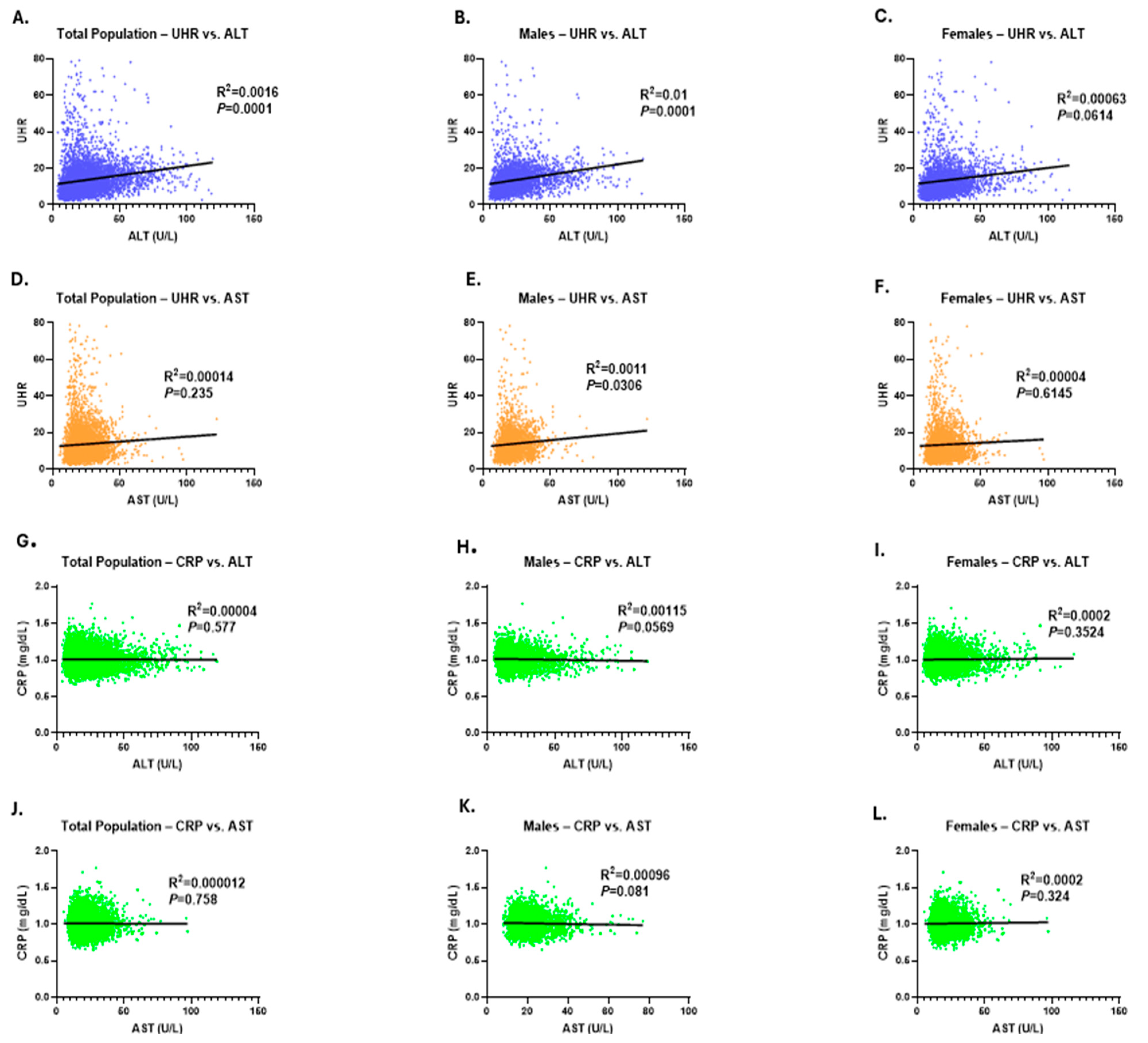
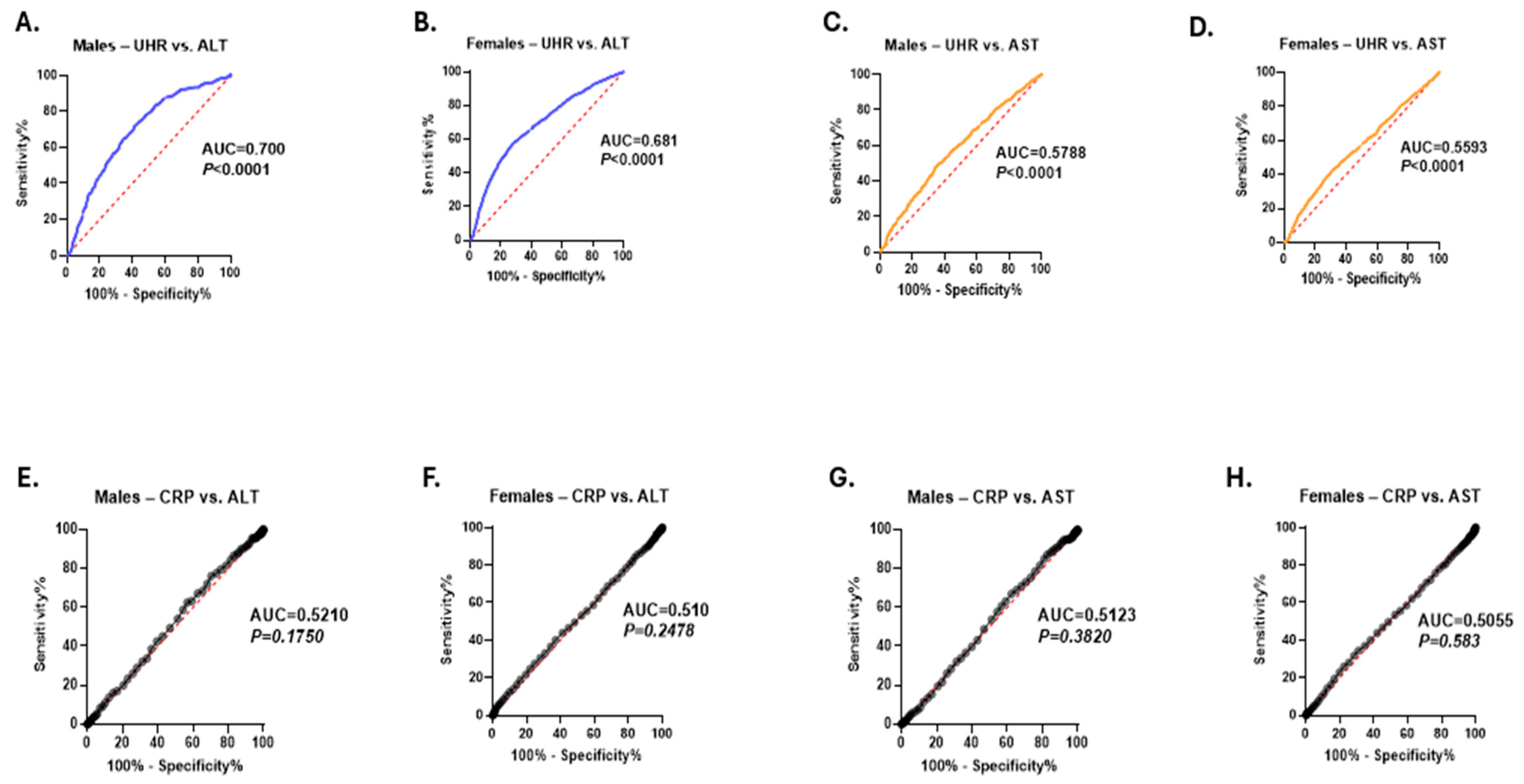
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Trefts, E.; Gannon, M.; Wasserman, D.H. The Liver. Curr. Biol. 2017, 27, R1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iluz-Freundlich, D.; Zhang, M.; Uhanova, J.; Minuk, G.Y. The Relative Expression of Hepatocellular and Cholestatic Liver Enzymes in Adult Patients with Liver Disease. Ann. Hepatol. 2020, 19, 204–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sookoian, S.; Pirola, C.J. Liver Enzymes, Metabolomics and Genome-Wide Association Studies: From Systems Biology to the Personalized Medicine. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 711–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, K.; Zhong, S.; Xie, K.; Yu, D.; Yang, R.; Gong, D.W. Hepatic ALT Isoenzymes Are Elevated in Gluconeogenic Conditions Including Diabetes and Suppressed by Insulin at the Protein Level. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2015, 31, 562–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, N.H.; Jang, H.C.; Sung, H.C.; Kim, H.R.; Hong, K.L.; Chan, J.C.N.; Lim, S. Abnormal Liver Function Test Predicts Type 2 Diabetes: A Community-Based Prospective Study. Diabetes Care 2007, 30, 2566–2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, S.; Islam, S.; Haque, T.; Kathak, R.R.; Ali, N. Association between Serum Liver Enzymes and Hypertension: A Cross-Sectional Study in Bangladeshi Adults. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2020, 20, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndrepepa, G. Aspartate Aminotransferase and Cardiovascular Disease—A Narrative Review. J. Lab. Precis. Med. 2021, 6, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattar, N.; Forrest, E.; Preiss, D. Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Br. Med. J. 2014, 349, g4596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochiai, H.; Shirasawa, T.; Yoshimoto, T.; Nagahama, S.; Watanabe, A.; Sakamoto, K.; Kokaze, A. Elevated Alanine Aminotransferase and Low Aspartate Aminotransferase/Alanine Aminotransferase Ratio Are Associated with Chronic Kidney Disease among Middle-Aged Women: A Cross-Sectional Study. BMC Nephrol. 2020, 21, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noroozi Karimabad, M.; Khalili, P.; Ayoobi, F.; Esmaeili-Nadimi, A.; La Vecchia, C.; Jamali, Z. Serum Liver Enzymes and Diabetes from the Rafsanjan Cohort Study. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2022, 22, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanley, A.J.G.; Williams, K.; Festa, A.; Wagenknecht, L.E.; D’Agostino, R.B.; Kempf, J.; Zinman, B.; Haffner, S.M. Elevations in Markers of Liver Injury and Risk of Type 2 DiabetesThe Insulin Resistance Atherosclerosis Study. Diabetes 2004, 53, 2623–2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moffatt, B.A.; Ashihara, H. Purine and Pyrimidine Nucleotide Synthesis and Metabolism. Arab. Book/Am. Soc. Plant Biol. 2002, 1, e0018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xie, L.; Song, X.; Wang, J.; Li, X.; Lin, Z.; Su, T.; Liang, B.; Huang, D. Purine-Induced IFN-γ Promotes Uric Acid Production by Upregulating Xanthine Oxidoreductase Expression. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 773001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, A.; Kaze, A.D.; McMullan, C.J.; Isakova, T.; Waikar, S.S. Uric Acid and the Risks of Kidney Failure and Death in Individuals With CKD. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2018, 71, 362–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, T.; Rahman, S.; Islam, S.; Molla, N.H.; Ali, N. Assessment of the Relationship between Serum Uric Acid and Glucose Levels in Healthy, Prediabetic and Diabetic Individuals. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2019, 11, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gout and Hyperuricemia-PubMed. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21229813/ (accessed on 7 November 2023).
- Kontush, A.; De Faria, E.C.; Chantepie, S.; Chapman, M.J. A Normotriglyceridemic, Low HDL-Cholesterol Phenotype Is Characterised by Elevated Oxidative Stress and HDL Particles with Attenuated Antioxidative Activity. Atherosclerosis 2005, 182, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, K.M.; Wonnerth, A.; Huber, K.; Wojta, J. Cardiovascular Disease Risk Reduction by Raising HDL Cholesterol—Current Therapies and Future Opportunities. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 167, 1177–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, G.; Feng, L.; Zhao, Y. Association between Ratio of γ-Glutamyl Transpeptidase to High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol and Prevalence of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Metabolic Syndrome: A Cross-Sectional Study. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nam, K.H.; Chang, T.I.; Joo, Y.S.; Kim, J.; Lee, S.; Lee, C.; Yun, H.R.; Park, J.T.; Yoo, T.H.; Sung, S.A.; et al. Association Between Serum High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Levels and Progression of Chronic Kidney Disease: Results From the KNOW-CKD. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2019, 8, e011162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Femlak, M.; Gluba-Brzózka, A.; Ciałkowska-Rysz, A.; Rysz, J. The Role and Function of HDL in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus and the Related Cardiovascular Risk. Lipids Health Dis. 2017, 16, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drew, B.G.; Rye, K.A.; Duffy, S.J.; Barter, P.; Kingwell, B.A. The Emerging Role of HDL in Glucose Metabolism. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2012, 8, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hausenloy, D.J.; Yellon, D.M. Targeting Residual Cardiovascular Risk: Raising High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Levels. Heart 2008, 94, 706–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Tao, L.; Cao, K.; Wang, Z.; Chen, D.; Guo, J.; Zhu, H.; Yang, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; et al. Association of High-Density Lipoprotein with Development of Metabolic Syndrome Components: A Five-Year Follow-up in Adults. BMC Public Health 2015, 15, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aktas, G.; Khalid, A.; Kurtkulagi, O.; Duman, T.T.; Bilgin, S.; Kahveci, G.; Atak Tel, B.M.; Sincer, I.; Gunes, Y. Poorly Controlled Hypertension Is Associated with Elevated Serum Uric Acid to HDL-Cholesterol Ratio: A Cross-Sectional Cohort Study. Postgrad. Med. 2022, 134, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, B.; Jung, D.H.; Lee, Y.J. Predictive Value of Serum Uric Acid to HDL Cholesterol Ratio for Incident Ischemic Heart Disease in Non-Diabetic Koreans. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xuan, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, B.; Xia, F.; Zhang, K.; Li, Q.; Wang, N.; Lu, Y. Association Between Uric Acid to HDL Cholesterol Ratio and Diabetic Complications in Men and Postmenopausal Women. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2023, 16, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtkulagi, O.; Meryem, B.; Tel, A.; Kahveci, G.; Bilgin, S.; Taslamacioglu Duman, T.; Ertürk, A.; Balci, B.; Aktas, G. Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis Is Associated with Elevated Serum Uric Acid to High Density Lipoprotein-Cholesterol Ratio. Rom. J. Intern. Med. 2021, 59, 403–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borai, A.; Ichihara, K.; Al Masaud, A.; Tamimi, W.; Bahijri, S.; Armbuster, D.; Bawazeer, A.; Nawajha, M.; Otaibi, N.; Khalil, H.; et al. Establishment of Reference Intervals of Clinical Chemistry Analytes for the Adult Population in Saudi Arabia: A Study Conducted as a Part of the IFCC Global Study on Reference Values. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2016, 54, 843–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinboboye, O.; Williams, J.S.; Garacci, E.; Egede, L.E. The Relationship between C-Reactive Protein and Mortality in Adults with Diabetes: Influences of Demographic Characteristics, Lifestyle Behaviors, and Medications. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2022, 32, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poustchi, H.; George, J.; Esmaili, S.; Esna-Ashari, F.; Ardalan, G.; Sepanlou, S.G.; Alavian, S.M. Gender Differences in Healthy Ranges for Serum Alanine Aminotransferase Levels in Adolescence. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e21178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, X.; Ban, B.; Zhang, M. Association between the Uric Acid to High Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Ratio and Alanine Transaminase in Chinese Short Stature Children and Adolescents: A Cross-Sectional Study. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1063534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosekli, M.A.; Kurtkulagi, O.; Kahveci, G.; Duman, T.T.; Meryem, B.; Tel, A.; Bilgin, S.; Demirkol, M.E.; Aktas, G. The Association between Serum Uric Acid to High Density Lipoprotein-Cholesterol Ratio and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: The Abund Study. Rev. Assoc. Med. Bras. 2021, 67, 549–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, Y.; Qin, Z.; Wang, P.; Zou, F. Serum Uric Acid to High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Ratio Predicts All-Cause Mortality in Adults with Metabolic Dysfunction Associated Steatotic Liver Disease. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 11278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Huang, K.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Z.; Wu, Y.; Chu, J.; Kong, W.; Qian, G. Association of Serum Uric Acid-to-High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Ratio with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in American Adults: A Population-Based Analysis. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1164096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, A.; Handral, M.S. Predictive Ability of Serum Uric Acid Levels in Assessing the Severity of Chronic Liver Disease. Int. J. Sci. Study 2023, 71, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y.; Wang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Tan, A.; Gao, Y.; Liang, Z.; Shi, D.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, H.; et al. Serum Uric Acid and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Non-Diabetic Chinese Men. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e67152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzali, A.; Weiss, N.S.; Boyko, E.J.; Ioannou, G.N. Association between Serum Uric Acid Level and Chronic Liver Disease in the United States. Hepatology 2010, 52, 578–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, F.; Li, J.; Chen, C.; Zhang, K.; Cao, L.; Wang, X.; Ma, J.; Feng, S.; Li, W.D. Higher Serum Uric Acid Level Predicts Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A 4-Year Prospective Cohort Study. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, C.F.; Yu, K.H.; Luo, S.F.; Chiu, C.T.; Ko, Y.S.; Hwang, J.S.; Tseng, W.Y.; Chang, H.C.; Chen, H.W.; See, L.C. Gout and Risk of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2010, 39, 466–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandra, S.; Lesmana, C.R.A.; Purnamasari, D.; Kurniawan, J.; Gani, R.A. Hyperuricemia as an Independent Risk Factor for Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Progression Evaluated Using Controlled Attenuation Parameter-Transient Elastography: Lesson Learnt from Tertiary Referral Center. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2019, 13, 424–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanaspa, M.A.; Sanchez-Lozada, L.G.; Choi, Y.J.; Cicerchi, C.; Kanbay, M.; Roncal-Jimenez, C.A.; Ishimoto, T.; Li, N.; Marek, G.; Duranay, M.; et al. Uric Acid Induces Hepatic Steatosis by Generation of Mitochondrial Oxidative Stress: POTENTIAL ROLE IN FRUCTOSE-DEPENDENT AND -INDEPENDENT FATTY LIVER*. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 40732–40744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, P.; George, J.; Dillon, J.F.; Clare, K. Determining the Role for Uric Acid in Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis Development and the Utility of Urate Metabolites in Diagnosis: An Opinion Review. World J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 26, 1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, R.; Aggarwal, S.; Kumar, R.; Sharma, G. Association of Atherosclerosis with Dyslipidemia and Co-Morbid Conditions: A Descriptive Study. J. Nat. Sci. Biol. Med. 2015, 6, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedayatnia, M.; Asadi, Z.; Zare-Feyzabadi, R.; Yaghooti-Khorasani, M.; Ghazizadeh, H.; Ghaffarian-Zirak, R.; Nosrati-Tirkani, A.; Mohammadi-Bajgiran, M.; Rohban, M.; Sadabadi, F.; et al. Dyslipidemia and Cardiovascular Disease Risk among the MASHAD Study Population. Lipids Health Dis. 2020, 19, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordero, A.; Moreno-Arribas, J.; Bertomeu-González, V.; Agudo, P.; Miralles, B.; Masiá, M.D.; López-Palop, R.; Bertomeu-Martínez, V. Low Levels of High-Density Lipoproteins Cholesterol Are Independently Associated with Acute Coronary Heart Disease in Patients Hospitalized for Chest Pain. Rev. Española De Cardiol. 2012, 65, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.G.; Mukamal, K.; Tapper, E.; Robson, S.C.; Tsugawa, Y. Low LDL-C and High HDL-C Levels Are Associated with Elevated Serum Transaminases amongst Adults in the United States: A Cross-Sectional Study. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e85366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trojak, A.; Waluś-Miarka, M.; Woźniakiewicz, E.; Małecki, M.T.; Idzior-Waluś, B. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Is Associated with Low HDL Cholesterol and Coronary Angioplasty in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Med. Sci. Monit. 2013, 19, 1167–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Trieb, M.; Rainer, F.; Stadlbauer, V.; Douschan, P.; Horvath, A.; Binder, L.; Trakaki, A.; Knuplez, E.; Scharnagl, H.; Stojakovic, T.; et al. HDL-Related Biomarkers Are Robust Predictors of Survival in Patients with Chronic Liver Failure. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parthasarathy, S.; Raghavamenon, A.; Garelnabi, M.O.; Santanam, N. Oxidized Low-Density Lipoprotein. Methods Mol. Biol. 2010, 610, 403–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brites, F.; Martin, M.; Guillas, I.; Kontush, A. Antioxidative Activity of High-Density Lipoprotein (HDL): Mechanistic Insights into Potential Clinical Benefit. BBA Clin. 2017, 8, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Ridi, R.; Tallima, H. Physiological Functions and Pathogenic Potential of Uric Acid: A Review. J. Adv. Res. 2017, 8, 487–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lala, V.; Zubair, M.; Minter, D.A. Liver Function Tests; StatPearls: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Giannini, E.G.; Testa, R.; Savarino, V. Liver Enzyme Alteration: A Guide for Clinicians. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 2005, 172, 367–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Zheng, R.D.; Xu, S.H.; Fan, Y.F.; Sun, H.P.; Liu, C. Association between Sex Hormone and Blood Uric Acid in Male Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2017, 2017, 4375253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.; Luo, Q.; Chen, J.; Chen, Z.; Aydemir, H.A.; Chen, P.; Tang, J.; Luo, F.; Fang, Z. Association between the Uric Acid-to-HDL-Cholesterol Ratio (UHR) and the Risk of Cardiovascular Disease and Dyslipidemia: A Population-Based Study. Lipids Health Dis. 2025, 24, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smilowitz, N.R.; Kunichoff, D.; Garshick, M.; Shah, B.; Pillinger, M.; Hochman, J.S.; Berger, J.S. C-Reactive Protein and Clinical Outcomes in Patients with COVID-19. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 2270–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaptoge, S.; Di Angelantonio, E.; Lowe, G.; Pepys, M.B.; Thompson, S.G.; Collins, R.; Danesh, J.; Tipping, R.W.; Ford, C.E.; Pressel, S.L.; et al. C-Reactive Protein Concentration and Risk of Coronary Heart Disease, Stroke, and Mortality: An Individual Participant Meta-Analysis. Lancet 2010, 375, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atono, Y.; Sata, M.; Tanikawa, K. Kinetics of C-Reactive Protein in Acute Viral Hepatitis. Gastroenterol. Jpn. 1989, 24, 655–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Gender | Number of Subjects (%) | Median UHR (IQR) |
|---|---|---|
| Total population | 9618 | 10.83 (7.920–14.91) |
| Male subjects | 42.76% | 11.96 (8.50–16.14) |
| Early Adults | 5.88% | 12.02 (8.495–15.99) |
| Middle-Aged Adults | 22.65% | 12.04 (8.360–16.17) |
| Older Adults | 14.22% | 10.83 (7.920–14.91) |
| Female subjects | 57.24% | 10.20 (7.620–13.85) |
| Early Adults | 10.55% | 10.20 (7.780–13.90) |
| Middle-Aged Adults | 33.24% | 10.19 (7.50–13.83) |
| Older Adults | 13.44% | 10.23 (7.73–13.86) |
| Parameter | N-ALT Group | H-ALT Group | N-AST Group | H-AST Group |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Both gender | ||||
| H-UHR | 41.57% | 62.32% | 46.63% | 54.71% |
| N-UHR | 58.43% | 37.68% | 53.37% | 45.29% |
| Males | ||||
| H-UHR | 51.90% | 80.82% | 54.15% | 64.31% |
| N-UHR | 48.10% | 19.18% | 45.85% | 35.69% |
| Females | ||||
| H-UHR | 28.97% | 58.33% | 40.35% | 50.04% |
| N-UHR | 71.03% | 41.67% | 59.65% | 49.96% |
| Score | 95% CI | Z Statistic | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PR | |||||
| Both genders | 1.49 | 1.44–1.55 | 20.009 | <0.001 | |
| Males | 1.55 | 1.47–1.63 | 16.915 | <0.001 | |
| Females | 2.01 | 1.88–2.14 | 20.937 | <0.001 | |
| OR | |||||
| ALT | Both genders | 2.32 | 2.12–2.53 | 18.913 | <0.001 |
| Males | 3.9 | 3.13–4.87 | 12.096 | <0.001 | |
| Females | 3.43 | 3.06–3.83 | 21.613 | <0.001 | |
| PR | |||||
| Both genders | 1.17 | 1.12–1.22 | 6.807 | <0.001 | |
| Males | 1.18 | 1.11–1.26 | 5.268 | <0.001 | |
| Females | 1.24 | 1.16–1.32 | 6.555 | <0.001 | |
| AST | OR | ||||
| Both genders | 1.38 | 1.25–1.52 | 6.505 | <0.001 | |
| Males | 1.52 | 1.28–1.80 | 4.846 | <0.001 | |
| Females | 1.48 | 1.31–1.67 | 6.294 | <0.001 |
| Variable | Estimate (β) | 95% CI | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | −0.0338 | −0.1103 to 0.0428 | 0.3868 |
| Gender | 0.1875 | −1.321 to 1.696 | 0.8075 |
| ALT | 0.1304 | 0.0654 to 0.1954 | <0.001 |
| AST | −0.0823 | −0.1953 to 0.0308 | 0.1537 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Almuqrin, A.M.; Muqri, M.H.; Basudan, A.M.; Alshuweishi, Y. Association Between Uric Acid to HDL-C Ratio and Liver Transaminase Abnormalities: Insights from a Large-Scale General Population Study. Medicina 2025, 61, 1417. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61081417
Almuqrin AM, Muqri MH, Basudan AM, Alshuweishi Y. Association Between Uric Acid to HDL-C Ratio and Liver Transaminase Abnormalities: Insights from a Large-Scale General Population Study. Medicina. 2025; 61(8):1417. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61081417
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlmuqrin, Abdulaziz M., Mousa H. Muqri, Ahmed M. Basudan, and Yazeed Alshuweishi. 2025. "Association Between Uric Acid to HDL-C Ratio and Liver Transaminase Abnormalities: Insights from a Large-Scale General Population Study" Medicina 61, no. 8: 1417. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61081417
APA StyleAlmuqrin, A. M., Muqri, M. H., Basudan, A. M., & Alshuweishi, Y. (2025). Association Between Uric Acid to HDL-C Ratio and Liver Transaminase Abnormalities: Insights from a Large-Scale General Population Study. Medicina, 61(8), 1417. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61081417






