Nasal Irrigations: A 360-Degree View in Clinical Practice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Upper Respiratory Tract: Barrier and Cleansing Mechanisms
2.1. The Upper Respiratory Tract Is the Gateway for Pathogens
2.2. The Upper Respiratory Tract as the Gateway for Allergens
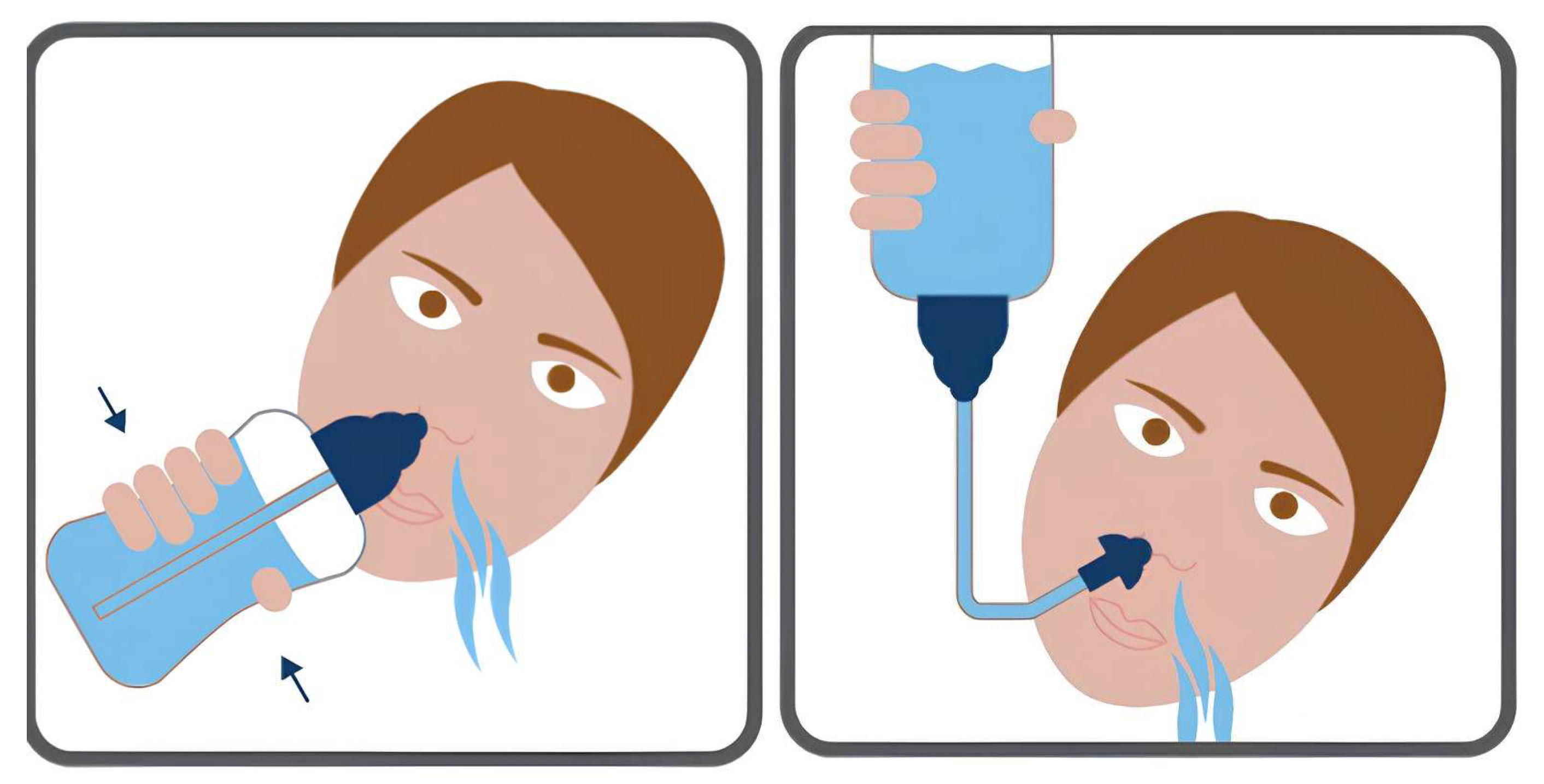
2.3. The Mechanism of Action of NI
3. Demonstrated Use of NI in Clinical Practice
3.1. Infants with Nasal Congestion
3.2. Prevention of Respiratory Infections
3.3. Recurrent Acute Respiratory Infections
3.4. Acute Sinusitis
3.5. Acute Recurrent Sinusitis
3.6. Chronic Sinusitis
3.7. Empty Nose Syndrome
3.8. Allergic Rhinitis (AR)
3.9. Gestational Rhinitis
4. Physicians’ Attitude to Nasal Lavage Prescription and Patients’ Adherence to Therapy
5. Risks Related to the Use of NI
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Math, S. Yoga Magazine: Neti-Nasal Cleaning. 1991. Available online: http://www.yogamag.net/archives/1990s/1991/9105/9105neti.html (accessed on 20 May 2025).
- Rama, S.; Ballentine, R.; Hymes, A. Science of Breath: A Practical Guide; Himalayan Institute Press: Honesdale, PA, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Wingrave, W. The nature of discharges and douches. Lancet 1902, 159, 1373–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, J.L. Nasal lavage. J. Otholaryngol. 1992, 21, 83. [Google Scholar]
- Benninger, M.S.; Holy, C.E.; Trask, D.K. Acute rhinosinusitis: Prescription patterns in a real-world setting. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2016, 154, 957–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudmik, L.; Hoy, M.; Schlosser, R.J.; Harvey, R.J.; Welch, K.C.; Lund, V.; Smith, T.L. Topical therapies in managing chronic rhinosinusitis: An evidence-based review with recommendations. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2013, 3, 281–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beswick, D.M.; Ramadan, H.; Baroody, F.M.; Hwang, P.H. Practice patterns in pediatric chronic rhinosinusitis: A survey of the American Rhinologic Society. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2016, 30, 418–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobol, S.E.; Samadi, D.S.; Kazahaya, K.; Tom, L.W. Trends in managing pediatric chronic sinusitis: Survey of the American Society of Pediatric Otolaryngology. Laryngoscope 2005, 115, 78–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sur, D.K.; Plesa, M.L. Treatment of allergic rhinitis. Am. Fam. Physician 2015, 92, 985–992. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Marchisio, P.; Picca, M.; Torretta, S.; Baggi, E.; Pasinato, A.; Bianchini, S.; Nazzari, E.; Esposito, S.; Principi, N. Nasal saline irrigation in preschool children: A survey of attitudes and prescribing habits of primary care pediatricians working in northern Italy. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2014, 40, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slapak, I.; Skoupá, J.; Strnad, P.; Horník, P. Efficacy of isotonic nasal wash (seawater) in the treatment and prevention of rhinitis in children. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2008, 134, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Principi, N.; Esposito, S. Nasal Irrigation: An Imprecisely Defined Medical Procedure. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baraniuk, J.N.; Ali, M.; Yuta, A.; Fang, S.Y.; Naranch, K. Hypertonic saline nasal provocation stimulates nociceptive nerves, substance P release, and glandular mucous exocytosis in normal humans. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1999, 160, 655–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurt, Y.; Yildirim, Y.S. Effectiveness of pediatric nasal irrigation solution with or without xylitol. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2022, 158, 111183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Gabory, L.; Kérimian, M.; Sagardoy, T.; Verdaguer, A.; Gauchez, H. Paediatric nasal irrigation: The “fencing” method. Eur. Ann. Otorhinolaryngol. Head Neck Dis. 2021, 138, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prussin, A.J., 2nd; Garcia, E.B.; Marr, L.C. Total Virus and Bacteria Concentrations in Indoor and Outdoor Air. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2015, 2, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Airborne Microbes Part 2: How Many Bacteria Do We Breathe in Each Day. Available online: https://steemit.com/steemstem/@tking77798/airborne-microbes-part-2-how-many-bacteria-do-we-breathe-in-each-day (accessed on 20 May 2025).
- Li, N.; Georas, S.; Alexis, N.; Fritz, P.; Xia, T.; Williams, M.A.; Horner, E.; Nel, A. A work group report on ultrafine particles (American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology): Why ambient ultrafine and engineered nanoparticles should receive special attention for possible adverse health outcomes in human subjects. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 138, 386–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huff, R.D.; Carlsten, C.; Hirota, J.A. An update on immunologic mechanisms in the respiratory mucosa in response to air pollutants. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 143, 1989–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Amato, G.; Cecchi, L.; Bonini, S.; Nunes, C.; Annesi-Maesano, I.; Behrendt, H.; Liccardi, G.; Popov, T.; Van Cauwenberge, P. Allergenic pollen and pollen allergy in Europe. Allergy 2007, 62, 976–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, P.; Marsh, D.G. ‘Isoallergens’ from rye grass pollen. Nature 1965, 206, 935–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsh, D.G. Allergens and the genetics of allergy. In The Antigens; Sela, M., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1975; Volume III, p. 271. [Google Scholar]
- Pfaar, O.; Bastl, K.; Berger, U.; Buters, J.; Calderon, M.A.; Clot, B.; Darsow, U.; Demoly, P.; Durham, S.R.; Galán, C.; et al. Defining pollen exposure times for clinical trials of allergen immunotherapy for pollen-induced rhinoconjunctivitis—An EAACI position paper. Allergy 2017, 72, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, J.; Steckling-Muschack, N.; Mittermeier, I.; Bergmann, K.C.; Böse-O’Reilly, S.; Buters, J.; Damialis, A.; Heigl, K.; Heinrich, J.; Kabesch, M.; et al. Threshold values of grass pollen (Poaceae) concentrations and increase in emergency department visits, hospital admissions, drug consumption and allergic symptoms in patients with allergic rhinitis: A systematic review. Aerobiologia 2021, 37, 633–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfaar, O.; Karatzas, K.; Bastl, K.; Berger, U.; Buters, J.; Darsow, U.; Demoly, P.; Durham, S.R.; Galán, C.; Gehrig, R.; et al. Pollen season is reflected on symptom load for grass and birch pollen-induced allergic rhinitis in different geographic areas—An EAACI Task Force Report. Allergy 2020, 75, 1099–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Platts-Mills, T.A.; Schuyler, A.J.; Erwin, E.A.; Commins, S.P.; Woodfolk, J.A. IgE in the diagnosis and treatment of allergic disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 137, 1662–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tovey, E.R.; Chapman, M.D.; Wells, C.W.; Platts-Mills, T.A.E. The distribution of dust mite allergen in the houses of patients with asthma. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1981, 124, 630–635. [Google Scholar]
- Tovey, E.R.; Chapman, M.D.; Platts-Mills, T.A.E. Mite faeces are a major source of house dust allergens. Nature 1981, 289, 592–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloepfer, K.M.; Gern, J.E. Virus/allergen interactions and exacerbations of asthma. Immunol. Allergy Clin. N. Am. 2010, 30, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto-Quiros, M.; Avila, L.; Platts-Mills, T.A.E.; Hunt, J.F.; Erdman, D.D.; Carper, H.; Murphy, D.D.; Odio, S.; James, H.R.; Patrie, J.T.; et al. High titers of IgE antibody to dust mite allergen and risk for wheezing among asthmatic children infected with rhinovirus. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 129, 1499–1505.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopuhaä, C.E.; Out, T.A.; Jansen, H.M.; Aalberse, R.C.; van der Zee, J.S. Allergen-induced bronchial inflammation in house dust mite-allergic patients with or without asthma. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2002, 32, 1720–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platts-Mills, T.A.E.; Woodfolk, J.A. Mite Avoidance as a Logical Treatment for Severe Asthma in Childhood. Why Not? Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 196, 119–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luczynska, C.M.; Li, Y.; Chapman, M.D.; Platts-Mills, T.A.E. Airborne concentrations and particle size distribution of allergen derived from domestic cats (Felis domesticus). Measurements using cascade impactor, liquid impinger, and a two-site monoclonal antibody assay for Fel d I. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1990, 141, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Platts-Mills, J.A.; Custis, N.J.; Woodfolk, J.A.; Platts-Mills, T.A.E. Airborne endotoxin in homes with domestic animals: Implications for cat-specific tolerance. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2005, 116, 384–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozsoylu, S. Nose drops and the common cold. Eur. J. Pediatr. 1985, 144, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karadag, A. Nasal saline for acute sinusitis. Pediatrics 2002, 109, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurtaran, H.; Karadag, A.; Catal, F.; Avci, Z. A reappraisal of nasal saline solution use in chronic sinusitis. Chest 2003, 124, 2036–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ponikau, J.U.; Sherris, D.A.; Kephart, G.M.; Kern, E.B.; Congdon, D.J.; Adolphson, C.R.; Springett, M.J.; Gleich, G.J.; Kita, H. Striking deposition of toxic eosinophil major basic protein in mucus: Implications for chronic rhinosinusitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2005, 116, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgitis, J.W. Nasal hyperthermia and simple irrigation for perennial rhinitis. Changes in inflammatory mediators. Chest 1994, 106, 1487–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boek, W.M.; Graamans, K.; Natzijl, H.; van Rijk, P.P.; Huizing, E.H. Nasal mucociliary transport: New evidence for a key role of ciliary beat frequency. Laryngoscope 2002, 112, 570–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talbot, A.R.; Herr, T.M.; Parsons, D.S. Mucociliary clearance and buffered hypertonic saline solution. Laryngoscope 1997, 107, 500–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Homer, J.J.; Dowley, A.C.; Condon, L.; El-Jassar, P.; Sood, S. The effect of hypertonicity on nasal mucociliary clearance. Clin. Otolaryngol. Allied Sci. 2000, 25, 558–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabago, D.; Zgierska, A. Saline nasal irrigation for upper respiratory conditions. Am. Fam. Physician 2009, 80, 1117–1119. [Google Scholar]
- Jantsch, J.; Schatz, V.; Friedrich, D.; Schröder, A.; Kopp, C.; Siegert, I.; Maronna, A.; Wendelborn, D.; Linz, P.; Binger, K.J.; et al. Cutaneous Na+ storage strengthens the antimicrobial barrier function of the skin and boosts macrophage-driven host defense. Cell Metab. 2015, 21, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalingam, S.; Cai, B.; Wong, J.; Twomey, M.; Chen, R.; Fu, R.M.; Boote, T.; McCaughan, H.; Griffiths, S.J.; Haas, J.G. Antiviral innate immune response in non-myeloid cells is augmented by chloride ions via an increase in intracellular hypochlorous acid levels. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalingam, S.; Graham, C.; Dove, J.; Morrice, L.; Sheikh, A. A pilot, open labelled, randomised controlled trial of hypertonic saline nasal irrigation and gargling for the common cold. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoseyov, D.; Bibi, H.; Shai, P.; Shoseyov, N.; Shazberg, G.; Hurvitz, H. Treatment with hypertonic saline versus normal saline nasal wash of pediatric chronic sinusitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1998, 101, 602–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangete, E.D.; West, D.; Blankson, C.D. Hypertonic saline solution for wound dressing. Lancet 1992, 340, 1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowthian, P.; Oke, S.; Sacoor, N.; Smith, I. Hypertonic saline solution as disinfectant. Lancet 1993, 341, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bitter, C.; Suter-Zimmermann, K.; Surber, C. Nasal drug delivery in humans. Curr. Probl. Dermatol. 2011, 40, 20–35. [Google Scholar]
- Succar, E.F.; Turner, J.H.; Chandra, R.K. Nasal saline irrigation: A clinical update. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2019, 9, S4–S8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Audag, N.; Cnockaert, P.; Reychler, G.; Poncin, W. Consensus on nasal irrigation in infants: A Delphi study. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2023, 132, 674–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wormald, P.J.; Cain, T.; Oates, L.; Hawke, L.; Wong, I. A comparative study of three methods of nasal irrigation. Laryngoscope 2004, 114, 2224–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, W.W., 3rd; Harvey, R.J.; Rudmik, L.; Hwang, P.H.; Schlosser, R.J. Distribution of topical agents to the paranasal sinuses: An evidence-based review with recommendations. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2013, 3, 691–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manes, R.P.; Tong, L.; Batra, P.S. Prospective evaluation of aerosol delivery by a powered nasal nebuliser in the cadaver model. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2011, 1, 366–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamond, I.R.; Grant, R.C.; Feldman, B.M.; Pencharz, P.B.; Ling, S.C.; Moore, A.M.; Wales, P.W. Defining consensus: A systematic review recommends methodologic criteria for reporting of Delphi studies. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2014, 67, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiber, S. Nasal irrigation with saline solution significantly improves oxygen saturation in infants with bronchiolitis. Acta Paediatr. 2016, 105, 292–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baraldi, E. Is nasal suctioning warranted before measuring O2 saturation in infants with bronchiolitis? Arch. Dis. Child. 2016, 101, 114–115. [Google Scholar]
- Wald, E.R.; Guerra, N.; Byers, C. Upper respiratory tract infections in young children: Duration and frequency of com-plications. Pediatrics 1991, 87, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Cauwenberge, P.; Watelet, J.B. Epidemiology of chronic rhinosinusitis. Thorax 2000, 55 (Suppl. 2), S20–S21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, D.R.; Harman, J.; Wald, E.R.; Kelleher, K.J. Antibiotic prescribing by primary care physicians for children with upper respiratory tract infections. Arch. Pediatr. Adolesc. Med. 2002, 156, 1114–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeffe, J.S.; Bhushan, B.; Schroeder, J.W., Jr. Nasal saline irrigation in children: A study of compliance and tolerance. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2012, 76, 409–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, A.B. The environment and disease: Association or causation? Proc. R. Soc. Med. 1965, 58, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiselev, A.B.; Chaukina, V.A. [Prophylaxis of acute respiratory infections in children’s collectives: Results of treatment with nasal and nasopharyngeal irrigation]. Vestn. Otorinolaringol. 2012, 1, 44–46. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tano, L.; Tano, K. A daily nasal spray with saline prevents symptoms of rhinitis. Acta Otolaryngol. 2004, 124, 1059–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woods, C.M.; Tan, S.; Ullah, S.; Frauenfelder, C.; Ooi, E.H.; Carney, A.S. The effect of nasal irrigation formulation on the antimicrobial activity of nasal secretions. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2015, 5, 1104–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalska, K.; Carr, D.B.; Lipkowski, A.W. Direct antimicrobial properties of substance P. Life Sci. 2002, 71, 747–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustyniak, D.; Nowak, J.; Lundy, F.T. Direct and indirect antimicrobial activities of neuropeptides and their therapeutic potential. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2012, 13, 723–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergsson, G.; Reeves, E.P.; McNally, P.; Chotirmall, S.H.; Greene, C.M.; Greally, P.; Murphy, P.; O’Neill, S.J.; McElvaney, N.G. LL-37 complexation with glycosaminoglycans in cystic fibrosis lungs inhibits antimicrobial activity, which can be restored by hypertonic saline. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 543–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrabani, S. COVID-19 infection and children: A comprehensive review. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2020, 11, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vissing, N.H.; Chawes, B.L.; Rasmussen, M.A.; Bisgaard, H. Epidemiology and risk factors of infection in early childhood. Pediatrics 2018, 141, e20170933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Linstow, M.; Holst, K.K.; Larsen, K.; Koch, A.; Andersen, P.K.; Høgh, B. Acute respiratory symptoms and general illness during the first year of life: A population-based birth cohort study. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2008, 43, 584–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trabalon, M.; Schaal, B. It takes a mouth to eat and a nose to breathe: Abnormal oral respiration affects neonates’ oral competence and systemic adaptation. Int. J. Pediatr. 2012, 2012, 207605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichichero, M.E. Recurrent and persistent otitis media. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2000, 19, 911–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabaillot, A.; Vorilhon, P.; Roca, M.; Boussageon, R.; Eschalier, B.; Pereirad, B. Saline nasal irrigation for acute upper respir-atory tract infections in infants and children: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Paediatr. Respir. Rev. 2020, 36, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Macchi, A.; Castelnuovo, P.; Terranova, P.; Digilio, E. Effects of sodium hyaluronate in children with recurrent upper respiratory tract infections: Results of a randomised controlled study. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2013, 26, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendley, J.O.; Gwaltney, J.M. Viral titers in nasal lining fluid compared to viral titers in nasal washes during experimental rhinovirus infection. J. Clin. Virol. 2004, 30, 326–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, N.F.; Klatt-Cromwell, C.; Schneider, J.S. Benefits and safety of nasal saline irrigations in a pandemic—Washing COVID-19 away. JAMA Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2020, 146, 787–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Sharma, N.; Singh, U.; Singh, T.; Mangal, D.K.; Singh, V. Nasopharyngeal wash in preventing and treating upper respiratory tract infections: Could it prevent COVID-19? Lung India 2020, 37, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyers, C.; Robison, R.; Milici, J.; Alam, S.; Quillen, D.; Goldenberg, D.; Kass, R. Lowering the transmission and spread of human coronavirus. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, D. The role of the oral cavity in SARS-CoV-2 and other viral infections. Clin. Oral Investig. 2023, 27 (Suppl. 1), 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huijghebaert, S.; Hoste, L.; Vanham, G. Essentials in saline pharmacology for nasal or respiratory hygiene in times of COVID-19. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2021, 77, 1275–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridges, J.P.; Vladar, E.K.; Huang, H.; Mason, R.J. Respiratory epithelial cell responses to SARS-CoV-2 in COVID-19. Thorax 2022, 77, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baxter, A.L.; Schwartz, K.R.; Johnson, R.W.; Kuchinski, A.-M.; Swartout, K.M.; Rao, A.S.R.S.; Gibson, R.W.; Cherian, E.; Giller, T.; Boomer, H.; et al. Rapid initiation of nasal saline irrigation to reduce severity in high-risk COVID+ outpatients. Ear Nose Throat J. 2024, 10, 30S–39S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenforde, M.W.; Kim, S.S.; Lindsell, C.J.; Billig Rose, E.; Shapiro, N.I.; Files, D.C.; Gibbs, K.W.; Erickson, H.L.; Steingrub, J.S.; Smithline, H.A.; et al. Symptom duration and risk factors for delayed return to usual health among outpatients with COVID-19 in a multistate health care systems network–United States, March-June 2020. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2020, 69, 993–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radulesco, T.; Lechien, J.R.; Saussez, S.; Hopkins, C.; Michel, J. Safety and impact of nasal lavages during viral infections such as SARS-CoV-2. Ear Nose Throat J. 2021, 100 (Suppl. 2), 188S–191S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez-García, R.; De La Cerda-Ángeles, J.C.; Cabrera-Licona, A.; Delgado-Enciso, I.; Mervitch-Sigal, N.; Paz-Michel, B.A. Nasopharyngeal and oropharyngeal rinses with neutral electrolyzed water prevent COVID-19 in front-line health professionals: A randomized, open-label, controlled trial in a general hospital in Mexico City. Biomed. Rep. 2022, 16, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hicks, L.A.; Shepard, C.W.; Britz, P.H.; Erdman, D.D.; Fischer, M.; Flannery, B.L.; Peck, A.J.; Lu, X.; Thacker, W.L.; Benson, R.F.; et al. Two outbreaks of severe respiratory disease in nursing homes associated with rhinovirus. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2006, 54, 284–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speir, R.W. Effect of several inorganic salts on the infectivity of Mengo virus. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1961, 106, 402–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.S.; Ference, E.H.; Evans, C.T.; Tan, B.K.; Kern, R.C.; Chandra, R.K. The prevalence of bacterial infection in acute rhinosinusitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Laryngoscope 2015, 125, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meltzer, E.O.; Bachert, C.; Staudinger, H. Treating acute rhinosinusitis: Comparing efficacy and safety of mometasone furoate nasal spray, amoxicillin, and placebo. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2005, 116, 1289–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabago, D.; Zgierska, A.; Mundt, M.; Barrett, B.; Bobula, J.; Maberry, R. Efficacy of daily hypertonic saline nasal irrigation among patients with sinusitis: A randomized controlled trial. J. Fam. Pract. 2002, 51, 1049–1055. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ciofalo, A.; Zambetti, G.; Altissimi, G.; Fusconi, M.; Soldo, P.; Gelardi, M.; Iannella, G.; Pasquariello, B.; Magliulo, G. Pathological and cytological changes of the nasal mucosa in acute rhinosinusitis: The role of hyaluronic acid as supportive therapy. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2017, 21, 4411–4418. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fokkens, W.J.; Lund, V.J.; Hopkins, C.; Hellings, P.W.; Kern, R.; Reitsma, S.; Toppila-Salmi, S.; Bernal-Sprekelsen, M.; Mullol, J.; Alobid, I.; et al. European Position Paper on Rhinosinusitis and Nasal Polyps 2020. Rhinology 2020, 58 (Suppl. S29), 1–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hildenbrand, T.; Weber, R.; Heubach, C.; Mösges, R. Nasal douching in acute rhinosinusitis. Laryngorhinootologie 2011, 90, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenfeld, R.M.; Piccirillo, J.F.; Chandrasekhar, S.S.; Brook, I.; Kumar, K.A.; Kramper, M.; Orlandi, R.R.; Palmer, J.N.; Patel, Z.M.; Peters, A.; et al. Clinical practice guideline (update): Adult sinusitis executive summary. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2015, 152, 598–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlandi, R.R.; Kingdom, T.T.; Hwang, P.H.; Smith, T.L.; Alt, J.A.; Baroody, F.M.; Batra, P.S.; Bernal-Sprekelsen, M.; Bhattacharyya, N.; Chandra, R.K.; et al. International consensus statement on allergy and rhinology: Rhinosinusitis. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2016, 6, S22–S209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saltagi, M.Z.; Comer, B.T.; Hughes, S.; Ting, J.Y.; Higgins, T.S. Management of recurrent acute rhinosinusitis: A systematic review. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2021, 35, 902–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, V.; Sykes, K.; Wei, J. Long-term outcome of once daily nasal irrigation for treating pediatric chronic rhinosinusitis. Laryngoscope 2014, 124, 1000–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.D.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, H.Y.; Jang, M.S.; Dhong, H.J.; Chung, S.K. Compliance and efficacy of saline irrigation in pediatric chronic rhinosinusitis. Auris Nasus Larynx 2014, 41, 46–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Conde, A.S.; Soler, Z.M. Chronic rhinosinusitis: Epidemiology and burden of disease. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2016, 30, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, P.P.; Wang, Z.C.; Schleimer, R.P.; Liu, Z. Pathophysiologic mechanisms of chronic rhinosinusitis and their roles in emerging disease endotypes. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2019, 122, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudmik, L.; Smith, T.L. Quality of life in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2011, 11, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alt, J.A.; Smith, T.L. Chronic rhinosinusitis and sleep: A contemporary review. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2013, 3, 941–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soler, Z.M.; Mace, J.; Smith, T.L. Symptom-based presentation of chronic rhinosinusitis and symptom-specific outcomes after endoscopic sinus surgery. Am. J. Rhinol. 2008, 22, 297–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinke, J.W.; Payne, S.C.; Chen, P.G.; Negri, J.; Stelow, E.B.; Borish, L. Etiology of nasal polyps in cystic fibrosis: Not a unimodal disease. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2012, 121, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.L.; Sykes, K.J.; Johnson, P.; He, J.; Mayo, M.S. Safety and efficacy of once-daily nasal irrigation for the treatment of pediatric chronic rhinosinusitis. Laryngoscope 2011, 121, 1989–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, L.Y.; Head, K.; Hopkins, C.; Philpott, C.; Glew, S.; Scadding, G.; Burton, M.J.; Schilder, A.G. Saline irrigation for chronic rhinosinusitis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016, 4, CD011995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Johansen, H.K.; Skov, M.; Buchvald, F.F.; Aanaes, K.; Hjuler, T.; Pressler, T.; Hoiby, N.; Nielsen, K.G.; von Buchwald, C. Clinical effects of sinus surgery and adjuvant therapy in cystic fibrosis patients—Can chronic lung infections be postponed? Rhinology 2013, 51, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alanin, M.C.; Johansen, H.K.; Aanaes, K.; Høiby, N.; Pressler, T.; Skov, M.; Nielsen, K.G.; von Buchwald, C. Simultaneous sinus and lung infections in patients with primary ciliary dyskinesia. Acta Otolaryngol. 2015, 135, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aanaes, K. Bacterial sinusitis can be a focus for initial lung colonisation and chronic lung infection in patients with cystic fibrosis. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2013, 12 (Suppl. 2), S1–S20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somayaji, R.; Thornton, C.S.; Acosta, N.; Smith, K.; Clark, J.; Fatovich, L.; Thakrar, M.V.; Parkins, M.D. Evaluating sinus microbiology by transplant status in persons with cystic fibrosis: A matched cohort study. OTO Open 2024, 8, e101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesold, V.V.; Wendler, O.; Gröhn, F.; Mueller, S.K. Lymphatic vessels in chronic rhinosinusitis. J. Inflamm. Res. 2024, 17, 865–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassandro, E.; Cassandro, C.; Chiarella, G.; Cavaliere, M.; Sequino, G.; Prasad, S.C.; Scarpa, A.; Iemma, M. Hyaluronan in the treatment of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal poly-posis. Indian J. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2015, 67, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelardi, M.; Guglielmi, A.V.; De Candia, N.; Maffezzoni, E.; Berardi, P.; Quaranta, N. Effect of sodium hyaluronate on mucociliary clearance after functional endoscopic sinus surgery. Eur. Ann. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 45, 103–108. [Google Scholar]
- Singhal, D.; Psaltis, A.J.; Foreman, A.; Wormald, P.J. Staphylococcus aureus biofilms: Nemesis of endoscopic sinus surgery. Laryngoscope 2011, 121, 1578–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatziri, A.; Vynios, D.H.; Panogeorgou, T.; Bouga, H.; Triantaphyllidou, I.E.; Naxakis, S.S.; Stathas, T.; Aletras, A.J.; Kourousis, C.; Mastronikolis, N.S. Presence of hyaluronidase isoforms in nasal polyps. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2013, 17, 247–252. [Google Scholar]
- Gross, C.W.; Gurucharri, M.J.; Lazar, R.H.; Long, T.E. Functional endonasal sinus surgery (FESS) in the pediatric age group. Laryngoscope 1989, 99, 272–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieser, J.D.; Derkay, C.S. Pediatric sinusitis: When do we operate? Curr. Opin. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2005, 13, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosugi, E.M.; Moussalem, G.F.; Simões, J.C.; de Souza, R.d.P.S.F.; Chen, V.G.; Neto, P.S.; Neto, J.A.M. Topical therapy with high-volume budesonide nasal irrigations in diffi-cult-to-treat chronic rhinosinusitis. Braz. J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2016, 82, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, S.M. Reasons for failure in endoscopic sinus surgery. Curr. Otorhinolaryngol. Rep. 2013, 1, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Segboer, C.; Gevorgyan, A.; Avdeeva, K.; Chusakul, S.; Kanjanaumporn, J.; Aeumjaturapat, S.; Reeskamp, L.F.; Snidvongs, K.; Fokkens, W. Intranasal corticosteroids for non-allergic rhinitis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 2019, CD010592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, T.R.; Muntz, H.R.; Gilbert, M.E.; Orlandi, R.R. Comparison of topical medication delivery systems after sinus surgery. Laryngoscope 2004, 114, 201–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnanasekaran, S.; Jayaraj, V.; Yazhini, V.B.; Selvam, M.P.; Rajendran, V. Evaluating the efficacy of nasal irrigation in postoperative functional endoscopic sinus surgery patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2024, 281, 3903–3913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thanneru, M.; Lanke, S.; Kolavali, S. The effectiveness of budesonide nasal irrigation after endoscopic sinus surgery in chronic allergic rhinosinusitis with polyps. Indian J. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2020, 72, 350–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fong, E.; Garcia, M.; Woods, C.M.; Ooi, E. Hyaluronic acid for post-sinus surgery care: Systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2017, 131, S2–S11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manji, J.; Patel, V.S.; Nayak, J.V.; Thamboo, A. Environmental Triggers Associated with Empty Nose Syndrome Symptoms: A Cross-Sectional Study. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2019, 128, 601–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modrzynski, M. Hyaluronic Acid Gel in the Treatment of Empty Nose Syndrome. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2011, 25, 103–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, R.W.; Jones, A.S.; Charters, P.; Sherman, I. The Role of Mucosal Receptors in the Nasal Sensation of Airflow. Clin. Otolaryngol. Allied Sci. 1992, 17, 383–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheithauer, M.O. Surgery of the Turbinates and “Empty Nose” Syndrome. GMS Curr. Top. Otorhinolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2010, 9, Doc03. [Google Scholar]
- Baptista, P.; Moffa, A.; Giorgi, L.; Casale, M. Randomized Clinical Trial to Evaluate the Efficacy and Tolerability of Nebulized Hyaluronic Acid and Xylitol Based Solution after Septoturbinoplasty. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermelingmeier, K.E.; Weber, R.K.; Hellmich, M.; Heubach, C.P.; Mösges, R. Nasal Irrigation as an Adjunctive Treatment in Allergic Rhinitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2012, 26, e119–e125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Head, K.; Snidvongs, K.; Glew, S.; Scadding, G.; Schilder, A.G.; Philpott, C.; Hopkins, C. Saline Irrigation for Allergic Rhinitis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 6, CD012597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.L.; Lin, H.C.; Lin, C.Y.; Hsu, T.F. Effectiveness of Hypertonic Saline Nasal Irrigation for Alleviating Allergic Rhinitis in Children: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Jin, L.; Liu, S.X.; Fan, K.; Qin, M.L.; Yu, S.Q. Role of Nasal Saline Irrigation in the Treatment of Allergic Rhinitis in Children and Adults: A Systematic Analysis. Allergol. Immunopathol. 2020, 48, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez-Cardona, N.; Sands, P.; Roberts, G.; Lucas, J.S.; Walker, W.; Salib, R.; Burgess, A.; Ismail-Koch, H. The Acceptability and Tolerability of Nasal Douching in Children with Allergic Rhinitis: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2017, 98, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchisio, P.; Varricchio, A.; Baggi, E.; Bianchini, S.; Capasso, M.E.; Torretta, S.; Capaccio, P.; Gasparini, C.; Patria, F.; Esposito, S.; et al. Hypertonic Saline Is More Effective Than Normal Saline in Seasonal Allergic Rhinitis in Children. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2012, 25, 721–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, S.A.; Psaltis, A.J.; Schlosser, R.J. Isotonic Saline Nasal Irrigation Is an Effective Adjunctive Therapy to Intranasal Corticosteroid Spray in Allergic Rhinitis. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2014, 28, 308–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, R.J.; Psaltis, A.; Schlosser, R.J.; Witterick, I.J. Current Concepts in Topical Therapy for Chronic Sinonasal Disease. J. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2010, 39, 217–231. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Naclerio, R.M.; Baroody, F.M.; Kagey-Sobotka, A.; Lichtenstein, L.M. Basophils and eosinophils in allergic rhinitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1994, 94, 1303–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Yan, W.; Zhao, X. Treatment of allergic rhinitis with normal saline nasal irrigation at different temperature. Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi 2014, 49, 109–114. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ocak, E.; Mulazimoglu, S.; Kocaoz, D.; Mirici, E.; Dagli, E.; Acar, A. Effect of adjunctive sodium hyaluronate versus surfactant nasal irrigation on mucociliary clearance in allergic rhinitis: A single-blind, randomised, controlled study. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2021, 135, 529–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demoly, P.; Piette, V.; Daures, J.P. Treatment of allergic rhinitis during pregnancy. Drugs 2003, 63, 1813–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namazy, J.A.; Schatz, M. Diagnosing rhinitis during pregnancy. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2014, 14, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park-Wyllie, L.; Mazzotta, P.; Pastuszak, A.; Moretti, M.E.; Beique, L.; Hunnisett, L.; Friesen, M.H.; Jacobson, S.; Kasapinovic, S.; Chang, D.; et al. Birth defects after maternal exposure to corticosteroids: Prospective cohort study and metaanalysis of epidemiological studies. Teratology 2000, 62, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yau, W.P.; Mitchell, A.A.; Lin, K.J.; Werler, M.M.; Hernández-Díaz, S. Use of decongestants during pregnancy and the risk of birth defects. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2013, 178, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seto, A.; Einarson, T.; Koren, G. Pregnancy outcome following first trimester exposure to antihistamines: Meta-analysis. Am. J. Perinatol. 1997, 14, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norjavaara, E.; de Verdier, M.G. Normal pregnancy outcomes in a population-based study including 2,968 pregnant women exposed to budesonide. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2003, 111, 736–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namazy, J.; Schatz, M. The treatment of allergic respiratory disease during pregnancy. J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 2016, 26, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garavello, W.; Somigliana, E.; Acaia, B.; Gaini, L.; Pignataro, L.; Gaini, R.M. Nasal lavage in pregnant women with seasonal allergic rhinitis: A randomized study. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2010, 151, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orban, N.; Maughan, E.; Bleach, N. Pregnancy-induced rhinitis. Rhinology 2013, 51, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shushan, S.; Sadan, O.; Lurie, S.; Evron, S.; Golan, A.; Roth, Y. Pregnancy-associated rhinitis. Am. J. Perinatol. 2006, 23, 431–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellegard, E.; Hellgren, M.; Toren, K.; Karlsson, T. The incidence of pregnancy rhinitis. Gynecol. Obstet. Invest. 2000, 49, 98–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellegard, E. Pregnancy rhinitis. Immunol. Allergy Clin. N. Am. 2006, 26, 119–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franklin, K.A.; Holmgren, P.A.; Jönsson, F.; Poromaa, N.; Stenlund, H.; Svanborg, E. Snoring, pregnancy-induced hypertension, and growth retardation of the fetus. Chest 2000, 117, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellegård, E.; Oscarsson, J.; Bougoussa, M.; Igout, A.; Hennen, G.; Edén, S.; Karlsson, G. Serum level of placental growth hormone is raised in pregnancy rhinitis. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 1998, 124, 439–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamano, N.; Terada, N.; Maesako, K.; Ikeda, T.; Fukuda, S.; Wakita, J.; Yamashita, T.; Konno, A. Expression of histamine receptors in nasal epithelial cells and endothelial cells–the effect of sex hormones. Int. Arch. Allergy Appl. Immunol. 1998, 115, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schatz, M.; Zeiger, R.S. Asthma and allergy in pregnancy. Clin. Perinatol. 1997, 24, 407–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franchini, M.; Caruso, C.; Perico, A.; Pacifici, R.; Monleon, T.; Garcia-Algar, O.; Rossi, S.; Pichini, S. Assessment of foetal exposure to cigarette smoke after recent implementations of smoke-free policy in Italy. Acta Paediatr. 2008, 97, 546–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, J.M.; Platts-Mills, T.A.E. Home environmental interventions for house dust mite. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2018, 6, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caparroz, F.A.; Gregorio, L.L.; Bongiovanni, G.; Izu, S.C.; Kosugi, E.M. Rhinitis and pregnancy: Literature review. Braz. J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2016, 82, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derkay, C.S. Eustachian tube and nasal function during pregnancy: A prospective study. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 1988, 99, 558–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabmurg, B. Pregnancy rhinitis and rhinitis medicamentosa. J. Am. Acad. Nurse Pract. 2002, 14, 527–530. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, K.K.; Anari, S. Medical management of rhinitis in pregnancy. Auris Nasus Larynx 2022, 49, 905–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabago, D.; Zgierska, A.; Peppard, P.; Bamber, A. The prescribing patterns of Wisconsin family physicians surrounding saline nasal irrigation for upper respiratory conditions. WMJ 2009, 108, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Khianey, R.; Oppenheimer, J. Is nasal saline irrigation all it is cracked up to be? Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2012, 109, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Year | Author | Country | Number of Subjects | Indication for NI | Study Design | Type of NI | Saline | Volume | Duration | Main Results | Adverse Events | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nasal congestion | 2016 | Schreiber et al. [57] | Italy | 133 infants (0–12 years) | Bronchiolitis with respiratory symptoms | Observational study | NI with Isotonic vs. NI with Hypertonic | Isotonic/ hypertonic | 1 mL/nostril, once day | Not reported | Improvement in SatO2 after NI with isotonic solution after 15 min (p < 0.001) | None |
| Prevention of respiratory infections | 2008 | Slapak et al. [11] | Czech Republic | 401 children (6–10 years) | Prevention and treatment of common cold | RCT | NI with sea water | Isotonic | Not reported | Not reported | Reduced recurrences, sick days, complications (Recurrent illness: 31% vs. 75%; absences 17% vs. 35%) | None reported |
| 2004 | Tano, L. et al. [65] | Sweden | 108 young adults on military service | Prevention of symptoms of common cold in a population of otherwise healthy adults | Clinical trial | Nasal spray with isotonic solution | Isotonic | Not reported | Daily spray for 10 weeks | Significant reduction in days with nasal discharge or stuffy nose (p = 0.027) | None | |
| Recurrent infections | 2013 | Macchi et al. [76] | Italy | 75 children | Recurrent respiratory infections | RCT | NI with isotonic solution vs. isotonic solution + hyaluronic acid | Isotonic | 9 mg of hyaluronic acid in 3 mL of saline OR 6 mL of saline × 2/day | 15 days/month for 3 months | Improved ciliary clearance, adenoid hypertrophy, bacterial clearance, reduced rhinitis duration (p < 0.001) | None |
| 2022 | Baxter et al. [84] | USA | 79 COVID + patients (>55 years) | Reduce hospitalization | RCT | NI saline solution + sodium bicarbonate vs. saline solution + povidone | Hypertonic | 240 mL | Twice a day for 14 days | 8-fold lower hospitalization risk; mortality 0% vs. 1.5% | 11 reports of irritations | |
| 2022 | Gutiérrez-García et al. [87] | Mexico | Healthcare workers | Prevention of COVID-19 infection | RCT | NI called neutral electrolized water (SES) | Hypertonic | 4 sprays of 0.4 mL × 3/day or 10 mL by gargling for 60 s × 3/day | 4 weeks | Decrease in COVID-19 incidence in the group that adhered to protocol with SES (1.2% vs. 18.8% of control group) | None | |
| Acute sinusitis | 2002 | Rabago et al. [92] | USA | 79 adults with acute sinusitis | Patients with a history of sinusitis | RCT | NI with hypertonic solution | Hypertonic | 1 irrigation/day | 6 months | Improvement in sinus-related quality of life (p ≤ 0.05), decreases symptoms, and decreases medication use in patients with frequent sinusitis | None |
| 2002 | Karadag. [36] | Turkey | Not reported | Acute sinusitis | Clinical trial | Drops of isotonic solution | Isotonic | 4 drops/nastril × 4/day | Until remission of symptoms | Reduction in inflammatory mediators, improvement in nasal drainage | None | |
| 2017 | Ciofalo, A. et al. [93] | Italy | 48 adults with acute sinusitis and treated with Levofloxacin and Prednisone | Acute sinusitis | RCT | NI with isotonic solution vs. NI with isotonic solution + sodium hyaluronate | isotonic | 3 mL of saline + sodium hyaluronate or 6 mL of saline, both × 2/day | 30 days | Treatment with sodium hyaluronate + saline solution brought about a significant improvement in global assessment of subjective symptoms, normalization of mucociliary transport time and reduction in neutrophil count on nasal cytology | None | |
| Acute recurrent sinusitis | 2021 | Saltagi, M.Z. et al. [98] | USA | 890 patients | Acute recurrent sinusitis | systematic Review | Isotonic solution, sometimes combined with other treatments (antibiotics, intranasal glucocorticoids, decongestants) | Isotonic | Non-standardized | Non-standardized | Positive trend in the combined use of saline irrigation and medical therapy for symptom control, quality of life, and prevention of relapses | None |
| Chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS) | 2011 | Wei, J.L. et al. [107] | USA | 40 children with CRS | Treatment of chronic rhinosinusitis | RCT | NI with isotonic solution vs. NI with isotonic solution + gentamicin | Isotonic | 1 irrigation/day (volume not reported) | 6 weeks | Improvement in quality of life, decrease in Lund–Macay score, reduced need for surgery | None |
| 2020 | Thanneru, M. et al. [125] | India | 60 patients post-FESS | Control of local inflammation in post-FESS patients with allergic rhinosinusitis with polyps. | RCT | NI with isotonic solution vs. isotonic solution + budesonide | Isotonic | 250 mL of saline OR 250 mL of saline + 2 mg of budesonide × 2/day | 10 weeks post-FESS | Improvement in quality of life, improvement in endoscopy (Lund–Kennedy score), decrease in severity of symptoms after NI with budesonide (p < 0.001) | None | |
| Empty-nose syndrome (ENS) | 2011 | Modrzyński [128] | Poland | 3 patients affected by ENS | Treatment of ENS | Pilot clinical study | Subcutaneous injections of hyaluronic acid gel | / | Not reported | Not reported | Improvement in ENS symptoms | None |
| Allergic rhinitis | 2012 | Jeffe, J. et al. [62] | USA | 61 children (<18 years) | Allergic rhinitis | Retrospective observational Study | NI with isotonic solution | Isotonic | 100 mL × nostril × 2/day | 2–4 months | Most children tolerated NI. Improvement in nasal symptoms (p < 0.001) | 12% mild AE (ear pain, cough, nausea) |
| 2012 | Marchisio et al. [137] | Italy | 220 children (5–9 years) | Allergic rhinitis | RCT | NI with isotonic solution vs. NI with hypertonic solution | Isotonic/hypertonic | 20 mL/nostril × 2/day | 4 weeks | Significant reduction in all symptoms with hypertonic solution (p < 0.0001), reduction in rhinorrhoea (p = 0.0002) and sneezing (p = 0.002) with isotonic solution | None | |
| 2014 | Nguyen, S.A [138] | USA | 40 adult patients with allergic rhinitis treated with intranasal corticosteroids | Allergic rhinitis already on intranasal corticosteroid pharmacotherapy | Prospective, non-randomized study | NI with isotonic solution | Isotonic | Low pressure, high volume × 2/day | 8 weeks | Significant (p < 0.001) reduction in mini-Rhinoconjunctivitis Quality of Life Questionnaire | None | |
| Gestational rhinitis | 2010 | Garavello et al. [150] | Switzerland | 45 pregnant women with seasonal allergic rhinitis | Allergic rhinitis in pregnant women | RCT | NI with hypertonic solution | Hypertonic | NI with hypertonic × 3/day | 6 weeks | Improvement in rhinitis symptoms (p < 0.001), reduction in the use of oral antihistamines (p < 0.001), reduction in nasal resistance measured by rhinomanometry (p = 0.006) | None |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pecoraro, L.; Di Muri, E.; Lezzi, G.; Picciolo, S.; De Musso, M.; Piazza, M.; Bosoni, M.; Indrio, F. Nasal Irrigations: A 360-Degree View in Clinical Practice. Medicina 2025, 61, 1402. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61081402
Pecoraro L, Di Muri E, Lezzi G, Picciolo S, De Musso M, Piazza M, Bosoni M, Indrio F. Nasal Irrigations: A 360-Degree View in Clinical Practice. Medicina. 2025; 61(8):1402. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61081402
Chicago/Turabian StylePecoraro, Luca, Elisabetta Di Muri, Gianluca Lezzi, Silvia Picciolo, Marta De Musso, Michele Piazza, Mariangela Bosoni, and Flavia Indrio. 2025. "Nasal Irrigations: A 360-Degree View in Clinical Practice" Medicina 61, no. 8: 1402. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61081402
APA StylePecoraro, L., Di Muri, E., Lezzi, G., Picciolo, S., De Musso, M., Piazza, M., Bosoni, M., & Indrio, F. (2025). Nasal Irrigations: A 360-Degree View in Clinical Practice. Medicina, 61(8), 1402. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61081402







