Gut Feelings: Linking Dysbiosis to Depression—A Narrative Literature Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
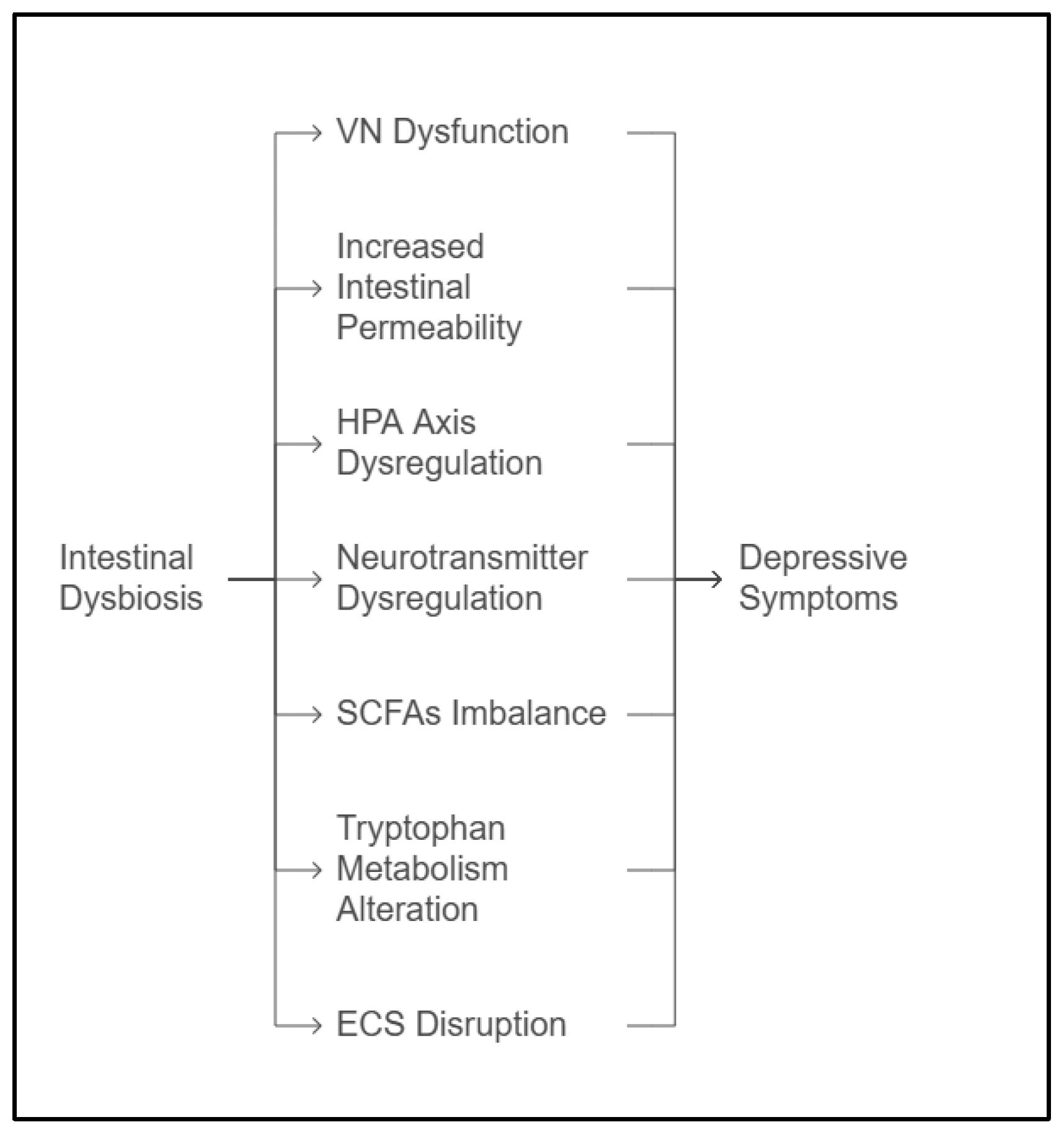
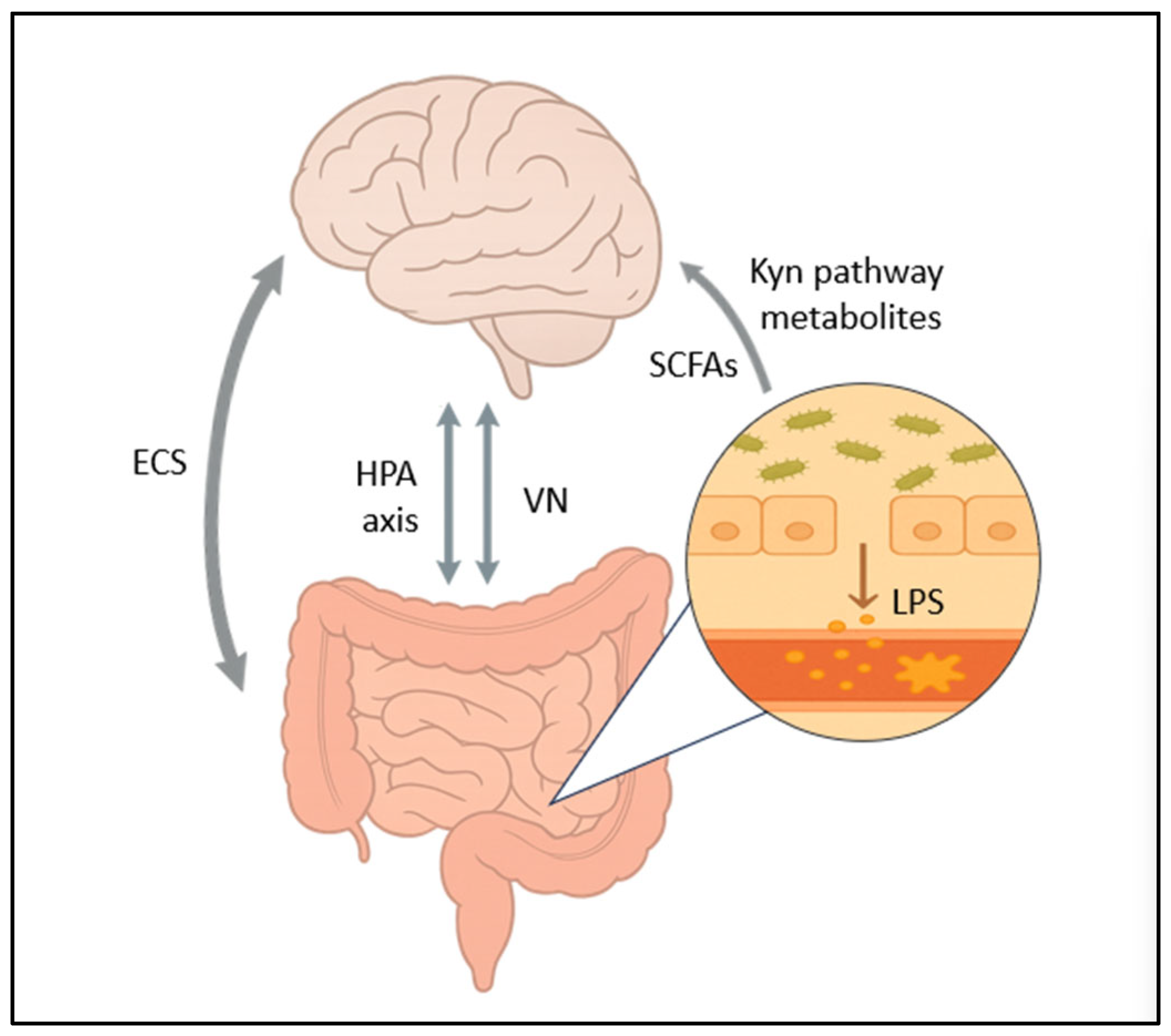
3. Mechanisms Linking Dysbiosis to Depression
3.1. The Vagus Nerve
3.2. HPA Axis Dysregulation
3.3. Short-Chain Fatty Acids
3.4. Neurotransmitter Dysregulation
3.4.1. Serotonin
3.4.2. GABA
3.5. Altered Tryptophan Metabolism
3.6. Increased Intestinal Permeability
3.7. The Endocannabinoid System
4. Potential Therapeutic Strategies Targeting Gut Dysbiosis in Depression
4.1. Probiotics and Prebiotics
4.2. FMT
5. Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th ed.; American Psychiatric Association: Arlington, VA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Arias-de la Torre, J.; Vilagut, G.; Ronaldson, A.; Bakolis, I.; Dregan, A.; Martín, V.; Martinez-Alés, G.; Molina, A.J.; Serrano-Blanco, A.; Valderas, J.M.; et al. Prevalence and variability of depressive symptoms in Europe: Update using representative data from the second and third waves of the European Health Interview Survey (EHIS-2 and EHIS-3). Lancet Public Health 2023, 8, e889–e898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akil, H.; Gordon, J.; Hen, R.; Javitch, J.; Mayberg, H.; McEwen, B.; Meaney, M.J.; Nestler, E.J. Treatment resistant depression: A multi-scale, systems biology approach. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2018, 84, 272–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Evans-Lacko, S.; Aguilar-Gaxiola, S.; Al-Hamzawi, A.; Alonso, J.; Benjet, C.; Bruffaerts, R.; Chiu, W.T. Socio-economic variations in the mental health treatment gap for people with anxiety, mood, and substance use disorders: Results from the WHO World Mental Health (WMH) surveys. Psychol. Med. 2018, 48, 1560–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. The Microbiome-Gut-Brain Axis in Health and Disease. Gastroenterol. Clin. N. Am. 2017, 46, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonaz, B.; Bazin, T.; Pellissier, S. The Vagus Nerve at the Interface of the Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Foster, J.A.; Rinaman, L.; Cryan, J.F. Stress & the gut-brain axis: Regulation by the microbiome. Neurobiol. Stress. 2017, 7, 124–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sonali, S.; Ray, B.; Ahmed Tousif, H.; Rathipriya, A.G.; Sunanda, T.; Mahalakshmi, A.M.; Rungratanawanich, W.; Essa, M.M.; Qoronfleh, M.W.; Chidambaram, S.B.; et al. Mechanistic Insights into the Link between Gut Dysbiosis and Major Depression: An Extensive Review. Cells 2022, 11, 1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Thursby, E.; Juge, N. Introduction to the human gut microbiota. Biochem. J. 2017, 474, 1823–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bäckhed, F.; Ding, H.; Wang, T.; Hooper, L.V.; Koh, G.Y.; Nagy, A.; Semenkovich, C.F.; Gordon, J.I. The gut microbiota as an environmental factor that regulates fat storage. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 15718–15723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprinz, H.; Kundel, D.W.; Dammin, G.J.; Horowitz, R.E.; Schneider, H. Formal SBThe response of the germfree guinea pig to oral bacterial challenge with Escherichia coli and Shigella flexneri. Am. J. Pathol. 1961, 39, 681–695. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hsiao, E.Y.; McBride, S.W.; Hsien, S.; Sharon, G.; Hyde, E.R.; McCue, T.; Codelli, J.A.; Chow, J.; Reisman, S.E.; Petrosino, J.F.; et al. Microbiota Modulate Behavioral and Physiological Abnormalities Associated with Neurodevelopmental Disorders. Cell 2013, 155, 1451–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Muñoz, M.E.; Arrieta, M.C.; Ramer-Tait, A.E.; Walter, J. A critical assessment of the “sterile womb” and “in utero colonization” hypotheses: Implications for research on the pioneer infant microbiome. Microbiome 2017, 5, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Almeida, C.; Oliveira, R.; Soares, R.; Barata, P. Influence of gut microbiota dysbiosis on brain function: A systematic review. Porto Biomed. J. 2020, 5, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lloyd-Price, J.; Mahurkar, A.; Rahnavard, G.; Crabtree, J.; Orvis, J.; Hall, A.B.; Brady, A.; Creasy, H.H.; McCracken, C.; Giglio, M.G.; et al. Strains, functions and dynamics in the expanded Human Microbiome Project. Nature 2017, 550, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frederix, M.; Downie, A.J. Quorum sensing: Regulating the regulators. Adv. Microb. Physiol. 2011, 58, 23–80. [Google Scholar]
- Sender, R.; Fuchs, S.; Milo, R. Revised Estimates for the Number of Human and Bacteria Cells in the Body. PLoS Biol. 2016, 14, e1002533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Diakite, A.; Dubourg, G.; Raoult, D. Updating the repertoire of cultured bacteria from the human being. Microb. Pathog. 2021, 150, 104698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donaldson, G.P.; Lee, S.M.; Mazmanian, S.K. Gut biogeography of the bacterial microbiota. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 14, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ley, R.E.; Hamady, M.; Lozupone, C.; Turnbaugh, P.J.; Ramey, R.R.; Bircher, J.S.; Gordon, J.I. Evolution of Mammals and Their Gut Microbes. Science 2008, 320, 1647–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tannock, G.W.; Savage, D.C. Influences of dietary and environmental stress on microbial populations in the murine gastrointestinal tract. Infect. Immun. 1974, 9, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wang, H.; Zhang, H.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, J.; Zhao, L.; Wang, D.; Pu, J.; Ji, P.; et al. Toward a Deeper Understanding of Gut Microbiome in Depression: The Promise of Clinical Applicability. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, e2203707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Cheung, S.G.; Goldenthal, A.R.; Uhlemann, A.C.; Mann, J.J.; Miller, J.M.; Sublette, M.E. Systematic Review of Gut Microbiota and Major Depression. Front. Psychiatry 2019, 10, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Siopi, E.; Galerne, M.; Rivagorda, M.; Saha, S.; Moigneu, C.; Moriceau, S.; Bigot, M.; Oury, F.; Lledo, P.M. Gut microbiota changes require vagus nerve integrity to promote depressive-like behaviors in mice. Mol. Psychiatry 2023, 28, 3002–3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Borovikova, L.V.; Ivanova, S.; Zhang, M.; Yang, H.; Botchkina, G.I.; Watkins, L.R.; Wang, H.; Abumrad, N.; Eaton, J.W.; Tracey, K.J. Vagus nerve stimulation attenuates the systemic inflammatory response to endotoxin. Nature 2000, 405, 458–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavlov, V.A.; Tracey, K.J. The vagus nerve and the inflammatory reflex--linking immunity and metabolism. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2012, 8, 743–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hwang, Y.K.; Oh, J.S. Interaction of the Vagus Nerve and Serotonin in the Gut-Brain Axis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Austelle, C.W.; O’Leary, G.H.; Thompson, S.; Gruber, E.; Kahn, A.; Manett, A.J.; Short, B.; Badran, B.W. A Comprehensive Review of Vagus Nerve Stimulation for Depression. Neuromodulation 2022, 25, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- SSchiweck, C.; Sausmekat, S.; Zhao, T.; Jacobsen, L.; Reif, A.; Thanarajah, S.E. No consistent evidence for the anti-inflammatory effect of vagus nerve stimulation in humans: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Brain Behav. Immun. 2024, 116, 237–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, B.; Marwaha, K.; Sanvictores, T.; Awosika, A.O.; Ayers, D. Physiology, Stress Reaction. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Knezevic, E.; Nenic, K.; Milanovic, V.; Knezevic, N.N. The Role of Cortisol in Chronic Stress, Neurodegenerative Diseases, and Psychological Disorders. Cells. 2023, 12, 2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mayer, E.A. The neurobiology of stress and gastrointestinal disease. Gut 2000, 47, 861–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konturek, P.C.; Brzozowski, T.; Konturek, S.J. Stress and the gut: Pathophysiology, clinical consequences, diagnostic approach and treatment options. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2011, 62, 591–599. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Wang, X.; Zou, Y.; He, Y.; Liang, C.; Li, J.; Li, P.; Zhang, J. Cold stress induces colitis-like phenotypes in mice by altering gut microbiota and metabolites. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1134246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sudo, N.; Chida, Y.; Aiba, Y.; Sonoda, J.; Oyama, N.; Yu, X.N.; Kubo, C.; Koga, Y. Postnatal microbial colonization programs the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal system for stress response in mice. J. Physiol. 2004, 558, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudzki, L.; Maes, M. The Microbiota-Gut-Immune-Glia (MGIG) Axis in Major Depression. Mol. Neurobiol. 2020, 57, 4269–4295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linninge, C.; Jönsson, P.; Bolinsson, H.; Önning, G.; Eriksson, J.; Johansson, G.; Ahrné, S. Effects of acute stress provocation on cortisol levels, zonulin and inflammatory markers in low- and high-stressed men. Biol. Psychol. 2018, 138, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Wang, N.; Han, M.; Ban, M.; Sun, T.; Xu, J. Reviewing the role of gut microbiota in the pathogenesis of depression and exploring new therapeutic options. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 1029495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Skonieczna-Żydecka, K.; Grochans, E.; Maciejewska, D.; Szkup, M.; Schneider-Matyka, D.; Jurczak, A.; Łoniewski, I.; Kaczmarczyk, M.; Marlicz, W.; Czerwińska-Rogowska, M.; et al. Faecal Short Chain Fatty Acids Profile is Changed in Polish Depressive Women. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Silva, Y.P.; Bernardi, A.; Frozza, R.L. The Role of Short-Chain Fatty Acids from Gut Microbiota in Gut-Brain Communication. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Fusco, W.; Lorenzo, M.B.; Cintoni, M.; Porcari, S.; Rinninella, E.; Kaitsas, F.; Lener, E.; Mele, M.C.; Gasbarrini, A.; Collado, M.C.; et al. Short-Chain Fatty-Acid-Producing Bacteria: Key Components of the Human Gut Microbiota. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Gong, Y.; Yang, R.; Chen, Z.; Hu, W.; Wu, Y.; Gao, M.; Xu, X.; Qin, Y.; et al. Sodium butyrate triggers a functional elongation of microglial process via Akt-small RhoGTPase activation and HDACs inhibition. Neurobiol. Dis. 2018, 111, 12–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soliman, M.L.; Puig, K.L.; Combs, C.K.; Rosenberger, T.A. Acetate reduces microglia inflammatory signaling in vitro. J. Neurochem. 2012, 123, 555–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Nankova, B.B.; Agarwal, R.; MacFabe, D.F.; La Gamma, E.F. Enteric bacterial metabolites propionic and butyric acid modulate gene expression, including CREB-dependent catecholaminergic neurotransmission, in PC12 cells—Possible relevance to autism spectrum disorders. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e103740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Wouw, M.; Boehme, M.; Lyte, J.M.; Wiley, N.; Strain, C.; O’Sullivan, O.; Clarke, G.; Stanton, C.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. Short-chain fatty acids: Microbial metabolites that alleviate stress-induced brain-gut axis alterations. J. Physiol. 2018, 596, 4923–4944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gao, M.; Wang, J.; Liu, P.; Tu, H.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, N.; Zhang, K. Gut microbiota composition in depressive disorder: A systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression. Transl. Psychiatry 2023, 13, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Simpson, C.A.; Diaz-Arteche, C.; Eliby, D.; Schwartz, O.S.; Simmons, J.G.; Cowan, C.S.M. The gut microbiota in anxiety and depression—A systematic review. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 2021, 83, 101943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braniste, V.; Al-Asmakh, M.; Kowal, C.; Anuar, F.; Abbaspour, A.; Toth, M.; Pettersson, S. The gut microbiota influences blood-brain barrier permeability in mice. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, 263ra158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suda, K.; Matsuda, K. How Microbes Affect Depression: Underlying Mechanisms via the Gut-Brain Axis and the Modulating Role of Probiotics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gershon, M.D.; Tack, J. The Serotonin Signaling System: From Basic Understanding to Drug Development for Functional GI Disorders. Gastroenterology 2007, 132, 397–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legan, T.B.; Lavoie, B.; Mawe, G.M. Direct and indirect mechanisms by which the gut microbiota influence host serotonin systems. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2022, 34, e14346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Banskota, S.; Ghia, J.E.; Khan, W.I. Serotonin in the gut: Blessing or a curse. Biochimie 2019, 161, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, M.; Tu, H.; Liu, P.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Jing, L.; Zhang, K. Association analysis of gut microbiota and efficacy of SSRIs antidepressants in patients with major depressive disorder. J. Affect. Disord. 2023, 330, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savignac, H.M.; Dinan, T.G.; Bienenstock, J.; Cryan, J.F. Ingestion of Lactobacillus strain regulates emotional behavior and central GABA receptor expression in a mouse via the vagus nerve. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 16050–16055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Otaru, N.; Ye, K.; Mujezinovic, D.; Berchtold, L.; Constancias, F.; Cornejo, F.A.; Krzystek, A.; de Wouters, T.; Braegger, C.; Lacroix, C.; et al. GABA Production by Human Intestinal Bacteroides spp.: Prevalence, Regulation, and Role in Acid Stress Tolerance. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 656895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hou, Y.; Li, J.; Ying, S. Tryptophan Metabolism and Gut Microbiota: A Novel Regulatory Axis Integrating the Microbiome, Immunity, and Cancer. Metabolites 2023, 13, 1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Alexeev, E.E.; Lanis, J.M.; Kao, D.J.; Campbell, E.L.; Kelly, C.J.; Battista, K.D.; Gerich, M.E.; Jenkins, B.R.; Walk, S.T.; Kominsky, D.J.; et al. Microbiota-Derived Indole Metabolites Promote Human and Murine Intestinal Homeostasis through Regulation of Interleukin-10 Receptor. Am. J. Pathol. 2018, 188, 1183–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.; Li, D.; Shi, Y.; Li, Q.; Guo, X.; Dong, K.; Chen, Q.; Lou, X.; Li, Z.; Li, P.; et al. Dysbiosis of the Gut Microbiota and Kynurenine (Kyn) Pathway Activity as Potential Biomarkers in Patients with Major Depressive Disorder. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhao, X.; Cao, F.; Liu, Q.; Li, X.; Xu, G.; Liu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.; Yi, S.; Xu, F.; et al. Behavioral, inflammatory and neurochemical disturbances in LPS and UCMS-induced mouse models of depression. Behav. Brain Res. 2019, 364, 494–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.; Zhou, M.; Wang, J.; Yao, J.; Yu, J.; Liu, W.; Wu, L.; Wang, J.; Gao, R. Involvement of the microbiota-gut-brain axis in chronic restraint stress: Disturbances of the kynurenine metabolic pathway in both the gut and brain. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1869501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhou, M.; Fan, Y.; Xu, L.; Yu, Z.; Wang, S.; Xu, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, L.; Liu, W.; Wu, L.; et al. Microbiome and tryptophan metabolomics analysis in adolescent depression: Roles of the gut microbiota in the regulation of tryptophan-derived neurotransmitters and behaviors in human and mice. Microbiome 2023, 11, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yin, R.; Zhang, K.; Li, Y.; Tang, Z.; Zheng, R.; Ma, Y.; Chen, Z.; Lei, N.; Xiong, L.; Guo, P.; et al. Lipopolysaccharide-induced depression-like model in mice: Meta-analysis and systematic evaluation. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1181973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Caspani, G.; Kennedy, S.; Foster, J.A.; Swann, J. Gut microbial metabolites in depression: Understanding the biochemical mechanisms. Microb. Cell 2019, 6, 454–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Meng, F.; Lowell, C.A. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced macrophage activation and signal transduction in the absence of Src-family kinases Hck, Fgr, and Lyn. J. Exp. Med. 1997, 185, 1661–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Peng, X.; Luo, Z.; He, S.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y. Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption by Lipopolysaccharide and Sepsis-Associated Encephalopathy. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 768108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Jiang, W.; Luo, Z.; Stephenson, S.; Li, H.; Di Germanio, C.; Norris, P.J.; Fuchs, D.; Zetterberg, H.; Gisslen, M.; Price, R.W. Cerebrospinal Fluid and Plasma Lipopolysaccharide Levels in Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Infection and Associations with Inflammation, Blood-Brain Barrier Permeability, and Neuronal Injury. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 223, 1612–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Maes, M.; Kubera, M.; Leunis, J.-C.; Berk, M.; Geffard, M.; Bosmans, E. In depression, bacterial translocation may drive inflammatory responses, oxidative and nitrosative stress (O&NS), and autoimmune responses directed against O&NS-damaged neoepitopes. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 2012, 127, 344–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariani, N.; Everson, J.; Pariante, C.M.; Borsini, A. Modulation of microglial activation by antidepressants. J. Psychopharmacol. 2022, 36, 131–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sarris, J.; Sinclair, J.; Karamacoska, D.; Davidson, M.; Firth, J. Medicinal cannabis for psychiatric disorders: A clinically-focused systematic review. BMC Psychiatry 2020, 20, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bright, U.; Akirav, I. Modulation of Endocannabinoid System Components in Depression: Pre-Clinical and Clinical Evidence. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Pires, L.; Gonzalez-Paramás, A.M.; Heleno, S.A.; Calhelha, R.C. Gut microbiota as an endocrine organ: Unveiling its role in human physiology and health. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 9383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakotoarivelo, V.; Mayer, T.Z.; Simard, M.; Flamand, N.; Di Marzo, V. The Impact of the CB2 Cannabinoid Receptor in Inflammatory Diseases: An Update. Molecules 2024, 29, 3381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chevalier, G.; Siopi, E.; Guenin-Macé, L.; Pascal, M.; Laval, T.; Rifflet, A.; Boneca, I.G.; Demangel, C.; Colsch, B.; Pruvost, A.; et al. Effect of gut microbiota on depressive-like behaviors in mice is mediated by the endocannabinoid system. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 6363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Minichino, A.; Jackson, M.A.; Francesconi, M.; Steves, C.J.; Menni, C.; Burnet, P.W.J.; Lennox, B.R. Endocannabinoid system mediates the association between gut-microbial diversity and anhedonia/amotivation in a general population cohort. Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 6269–6276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Pouranayatihosseinabad, M.; Bezabih, Y.; Hawrelak, J.; Peterson, G.M.; Veal, F.; Mirkazemi, C. Antibiotic use and the development of depression: A systematic review. J. Psychosom. Res. 2023, 164, 111113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radford-Smith, D.E.; Anthony, D.C. Prebiotic and Probiotic Modulation of the Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis in Depression. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lin, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, K.; Wang, J.; Kou, S.; Chen, K.; Zheng, W.; Chen, R. The effect and safety of probiotics on depression: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Eur. J. Nutr. 2023, 62, 2709–2721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, B.; Pan, Y.; Huang, Y.S.; Yi, M.; Hu, Y.; Lian, X.; Shi, H.Z.; Wang, M.; Xiang, G.; Yang, W.Y.; et al. Efficacy and safety of gut microbiome-targeted treatment in patients with depression: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Psychiatry 2025, 25, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhao, S.; Liang, S.; Tao, J.; Peng, Y.; Chen, S.; Wai, H.K.F.; Chung, F.Y.; Sin, Z.Y.; Wong, M.K.L.; Haqq, A.M.; et al. Probiotics for adults with major depressive disorder compared with antidepressants: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Nutr. Rev. 2025, 83, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messaoudi, M.; Lalonde, R.; Violle, N.; Javelot, H.; Desor, D.; Nejdi, A.; Cazaubiel, J.-M. Assessment of psychotropic-like properties of a probiotic formulation (Lactobacillus helveticus R0052 and Bifidobacterium longum R0175) in rats and human subjects. Br. J. Nutr. 2010, 105, 755–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunes, R.A.; Poluektova, E.U.; Vasileva, E.V.; Odorskaya, M.V.; Marsova, M.V.; Kovalev, G.I.; Danilenko, V.N. A multi-strain potential probiotic formulation of GABA-Producing Lactobacillus plantarum 90sk and Bifidobacterium adolescentis 150 with antidepressant effects. Probiot. Antimicrob. Prot. 2020, 12, 973–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desbonnet, L.; Garrett, L.; Clarke, G.; Bienenstock, J.; Dinan, T.G. The probiotic Bifidobacteria infantis: An assessment of potential antidepressant properties in the rat. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2008, 43, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tandon, D.; Haque, M.M.; Gote, M.; Jain, M.; Bhaduri, A.; Dubey, A.K.; Mande, S.S. A prospective randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-response relationship study to investigate efficacy of fructo-oligosaccharides (FOS) on human gut microflora. Sci Rep. 2019, 9, 5473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Barrio, C.; Arias-Sánchez, S.; Martín-Monzón, I. The gut microbiota-brain axis, psychobiotics and its influence on brain and behaviour: A systematic review. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2022, 137, 105640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruce-Keller, A.J.; Salbaum, J.M.; Luo, M.; Blanchard, E., IV; Taylor, C.M.; Welsh, D.A.; Berthoud, H.R. Obese-type gut microbiota induce neurobehavioral changes in the absence of obesity. Biol. Psychiatry 2015, 77, 607–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Li, N.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Sun, A.; Lin, Y.; Jin, Y.; Li, X. Fecal microbiota transplantation from chronic unpredictable mild stress mice donors affects anxiety-like and depression-like behavior in recipient mice via the gut microbiota-inflammation-brain axis. Stress 2019, 22, 592–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, P.; Zeng, B.; Zhou, C.; Liu, M.; Fang, Z.; Xu, X.; Zeng, L.; Chen, J.; Fan, S.; Du, X.; et al. Gut microbiome remodeling induces depressive-like behaviors through a pathway mediated by the host’s metabolism. Mol Psychiatry 2016, 21, 786–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, J.R.; Borre, Y.; O’ Brien, C.; Patterson, E.; El Aidy, S.; Deane, J.; Kennedy, P.J.; Beers, S.; Scott, K.; Moloney, G.; et al. Transferring the blues: Depression-associated gut microbiota induces neurobehavioural changes in the rat. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2016, 82, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, J.; Xie, R.; Lin, L.; Jiang, J.; Du, L.; Zeng, X.; Li, G.; Wang, C.; Qiao, Y.; Bellone, C. Fecal microbiota transplantation ameliorates gut microbiota imbalance and intestinal barrier damage in rats with stress-induced depressive-like behavior. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2021, 53, 3598–3611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doll, J.P.K.; Vázquez-Castellanos, J.F.; Schaub, A.C.; Schweinfurth, N.; Kettelhack, C.; Schneider, E.; Yamanbaeva, G.; Mählmann, L.; Brand, S.; Beglinger, C.; et al. Fecal Microbiota Transplantation (FMT) as an Adjunctive Therapy for Depression-Case Report. Front. Psychiatry 2022, 13, 815422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Green, J.E.; Berk, M.; Mohebbi, M.; Loughman, A.; McGuinness, A.J.; Castle, D.; Chatterton, M.L.; Perez, J.; Strandwitz, P.; Athan, E.; et al. Feasibility, Acceptability, and Safety of Faecal Microbiota Transplantation in the Treatment of Major Depressive Disorder: A Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial. Can. J. Psychiatry 2023, 68, 315–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Jiang, X.; Gao, X.; Ding, J.; Pang, B.; Pei, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Zhao, N.; Wang, Z.; Chen, C.; Gao, D.; et al. Fecal microbiota transplantation alleviates mild-moderate COVID-19 associated diarrhoea depression symptoms: Aprospective study of a randomized double-blind clinical trial. J. Med. Virol. 2024, 96, e29812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cold, F.; Svensson, C.K.; Petersen, A.M.; Hansen, L.H.; Helms, M. Long-Term Safety Following Faecal Microbiota Transplantation as a Treatment for Recurrent Clostridioides Difficile Infection Compared with Patients Treated with a Fixed Bacterial Mixture: Results from a Retrospective Cohort Study. Cells 2022, 11, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Filipp, Z.; Bloom, P.P.; Torres Soto, M.; Mansour, M.K.; Sater, M.R.A.; Huntley, M.H.; Turbett, S.; Chung, R.T.; Chen, Y.-B.; Hohmann, E.L. Drug-Resistant, E. Coli Bacteremia Transmitted by Fecal Microbiota Transplant. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 2043–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safety Alert Regarding Use of Fecal Microbiota for Transplantation and Risk of Serious Adverse Events Likely Due to Transmission of Pathogenic Organisms. FDA. 2020. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/vaccines-blood-biologics/safety-availability-biologics/safety-alert-regarding-use-fecal-microbiota-transplantation-and-risk-serious-adverse-events-likely (accessed on 15 July 2025).
- European Medicines Agency. Faecal Microbiota Transplantation—EU-IN Horizon Scanning Report. EMA/204935/2022. June 2022. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/report/faecal-microbiota-transplantation-eu-horizon-scanning-report_en.pdf (accessed on 15 July 2025).
- Dailey, F.E.; Turse, E.P.; Daglilar, E.; Tahan, V. The Dirty Aspects of Fecal Microbiota Transplantation: A Review of Its Adverse Effects and Complications. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2019, 49, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-W.; Kuo, C.-H.; Kuo, F.-C.; Wang, Y.-K.; Hsu, W.-H.; Yu, F.-J.; Hu, H.-M.; Hsu, P.-I.; Wang, J.-Y.; Wu, D.-C. Fecal Microbiota Transplantation: Review and Update. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2019, 118 (Suppl. S1), S23–S31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bibolar, A.C.; Nechita, V.I.; Lung, F.C.; Crecan-Suciu, B.D.; Păunescu, R.L. Gut Feelings: Linking Dysbiosis to Depression—A Narrative Literature Review. Medicina 2025, 61, 1360. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61081360
Bibolar AC, Nechita VI, Lung FC, Crecan-Suciu BD, Păunescu RL. Gut Feelings: Linking Dysbiosis to Depression—A Narrative Literature Review. Medicina. 2025; 61(8):1360. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61081360
Chicago/Turabian StyleBibolar, Anca C., Vlad I. Nechita, Florin C. Lung, Bianca D. Crecan-Suciu, and Ramona L. Păunescu. 2025. "Gut Feelings: Linking Dysbiosis to Depression—A Narrative Literature Review" Medicina 61, no. 8: 1360. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61081360
APA StyleBibolar, A. C., Nechita, V. I., Lung, F. C., Crecan-Suciu, B. D., & Păunescu, R. L. (2025). Gut Feelings: Linking Dysbiosis to Depression—A Narrative Literature Review. Medicina, 61(8), 1360. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61081360






