Acute Necrotizing Pancreatitis—Advances and Challenges in Management for Optimal Clinical Outcomes
Abstract
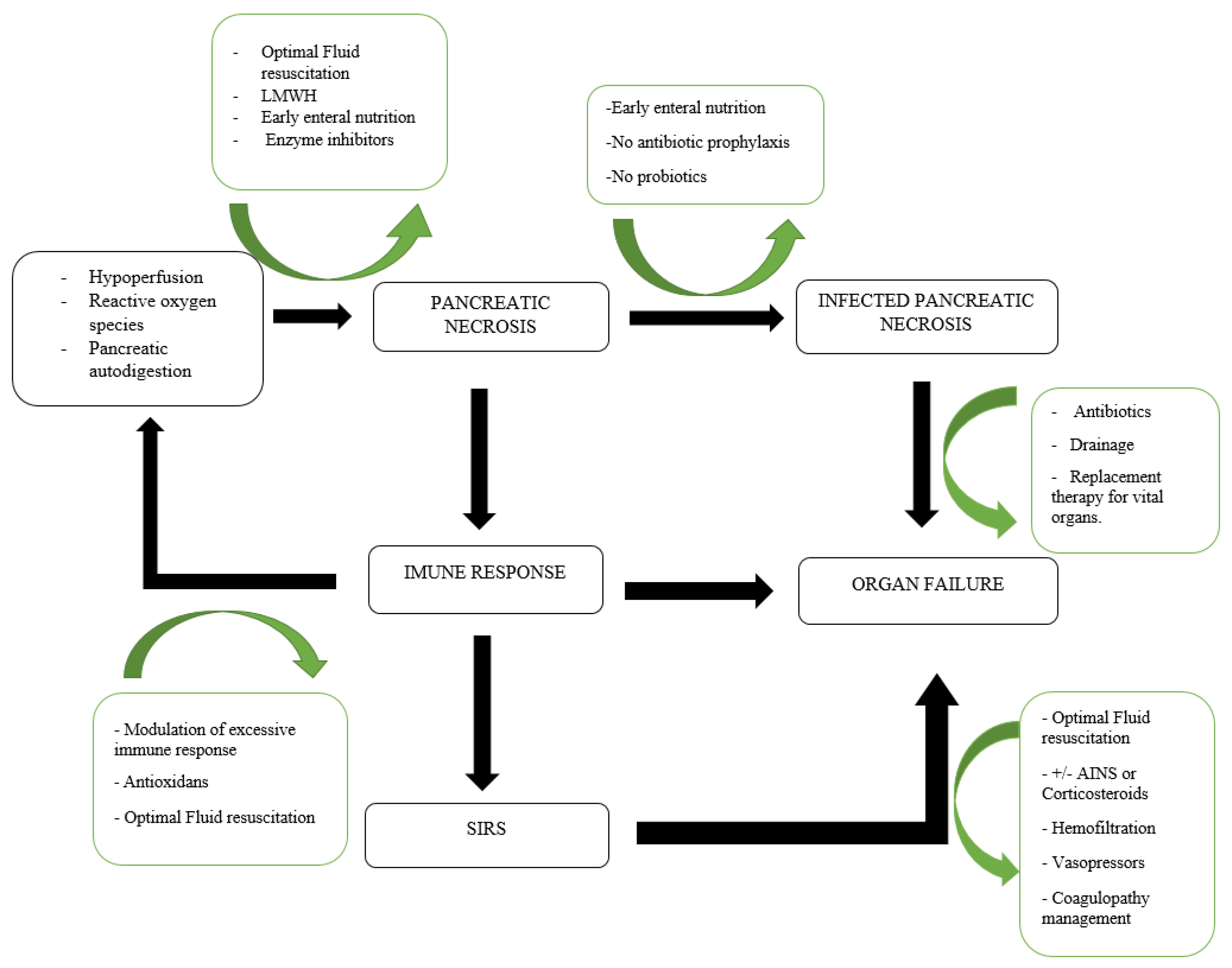
1. Introduction
2. Epidemiology
3. Prevention of Pancreatic Necrosis
3.1. Early Recognition and Prediction of Pancreatic Necrosis
3.2. Adequate Intravenous Fluid Resuscitation
3.3. Low-Molecular-Weight-Heparin
| Author, Year | I/C * | N | Male, n (%) | Age, Mean (Years) | APACHE II on Admission | Dose, T/P # | D † | Vascular Thrombosis | GI Bleeding | Need for Surgery | Organ Failure | Shock | Mortality | Length of Hospital Stay |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patil 2022 [76] | I | 70 | 37 (52.9%) | 44.2 ± 16.7 | NA | T | <8 days | 1 (1.4%) | NA | NA | 12 (17.1%) | NA | 0 (0%) | 10.9 ± 1.7 |
| C | 70 | 40 (68.6%) | 40.5 ± 15.7 | NA | 9 (12.9%) | NA | NA | 14 (20.0%) | NA | 3 (4.35%) | 11.5 ± 2.9 | |||
| Kumbha 2022 [83] | I | 50 | 42 (84%) | NA | NA | T | <8 days | NA | NA | NA | 23 (46%) | NA | 1 (2%) | NA |
| C | 50 | 41 (82%) | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 14 (28%) | NA | 1 (2%) | NA | |||
| Kröner 2021 [84] | I | 5776 | 3089 (53.5%) | 65.52 ± 16.91 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1361 (23.6%) | 239 (4.8) | 141 (2.4%) | 5.0 ± 39.1 |
| C | 5776 | 3068 (53.1%) | 65.22 ± 16.59 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1495 (25.9%) | 279 (4.8) | 188 (3.3%) | 4.0 ± 30.6 | |||
| Vadlamudi 2021 [85] | I | 290 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 (0.3%) | 1 (0.3%) | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| C | 99 | NA | NA | NA | 0 | 0 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | |||
| Zhou 2020 [86] | I | 169 | 88 (52.1%) | 42.6 ± 5.05 | 9.0 ± 1.01 | T | NA | 36 (21.3%) | 25 (14.8%) | NA | 40 (23.6%) | 37 (21.9) | 22 (1.2%) | 30 ± 6.33 |
| C | 104 | 65 (62.5%) | 42.5 ± 2.33 | 9 ± 0.6 | 48 (46.1%) | 20 (19.2%) | NA | 37 (35.5%) | 33 (31.7) | 23 (22.1%) | 38 ± 6.91 | |||
| Tozlu 2018 [24] | I | 50 | 22 (44%) | 51 ± 16 | NA | T | <8 days | 1 (2%) | NA | NA | 6 (12%) | NA | 0 (0%) | 7.8 ± 3.4 |
| C | 50 | 24 (48%) | 52 ± 20 | NA | 7 (14%) | NA | NA | 21 (42%) | NA | 5 (10%) | 11.8 ± 12.5 | |||
| Du JD 2014 [87] | I | 68 | 35 (51.5%) | 50.9 ± 0.25 | 9.27 ± 0.14 | P | 8–14 days | NA | NA | 2 (2.9%) | 4 (5.9%) | NA | 1 (1.5%) | 18.15 ± 2.35 |
| C | 66 | 34 (51.5%) | 50.5 ± 1.0 | 9.18 ± 0.03 | NA | NA | 5 (7.6%) | 10 (15.1%) | NA | 5 (7.6%) | 23.25 ± 4.15 | |||
| Lu 2009 [75] | I | 135 | 84 (62.2%) | 56 ± 11 | 11.5 ± 3.6 | P | <8 days | 0 | 8 (5.9%) | 6 (4.4%) | 19 (14.1%) | 9 (6.6) | 14 (10.4%) | 30 ± 8 |
| C | 130 | 72 (55.4%) | 54 ± 10.8 | 5.4 ± 3.4 | 1 (0.7%) | 9 (6.9%) | 15 (11.5%) | 34 (26.1%) | 7 (5.4) | 40 (30.6%) | 46 ± 11 |
3.4. Epidural Anesthesia
4. Prophylaxis of Infection of Pancreatic Necrosis
4.1. Nutrition
4.2. Antibiotics
5. Pancreatic Necrosis Treatment
5.1. Antibiotics
5.2. Interventional Treatment
5.2.1. Indications and Optimal Timing for Intervention
5.2.2. Minimally Invasive Approaches
Percutaneous Drainage
Endoscopic Interventions
Minimally Invasive Surgery
5.2.3. Open Surgery
5.2.4. Surgical Management of Complications
Abdominal Compartment Syndrome
Hemorrhage
Disconnected Pancreatic Duct Syndrome
Colonic and Enteric Fistula
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Leonard-Murali, S.; Lezotte, J.; Kalu, R.; Blyden, D.J.; Patton, J.H.; Johnson, J.L.; Gupta, A.H. Necrotizing pancreatitis: A review for the acute care surgeon. Am. J. Surg. 2021, 221, 927–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekimoto, M.; Takada, T.; Kawarada, Y.; Hirata, K.; Mayumi, T.; Yoshida, M.; Hirota, M.; Kimura, Y.; Takeda, K.; Isaji, S.; et al. JPN Guidelines for the management of acute pancreatitis: Epidemiology, etiology, natural history, and outcome predictors in acute pancreatitis. J. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Surg. 2006, 13, 10–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Huang, X.; Jin, Y.; Qiu, M.; Ambe, P.C.; Basharat, Z.; Hong, W. The role of mitochondrial damage-associated molecular patterns in acute pancreatitis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 175, 116690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Guo, H.; Li, F.; Cao, Y.; Zhao, L.; Chen, H. Identification of Key Biomarkers Associated with Immunogenic Cell Death and Their Regulatory Mechanisms in Severe Acute Pancreatitis Based on WGCNA and Machine Learning. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, P.J.; Papachristou, G.I.; Speake, C.; Lacy-Hulbert, A. Immune markers of severe acute pancreatitis. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2024, 40, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Li, A.; Xia, Q.; Liu, X.; Tian, B.; Mai, G.; Huang, Z.; Chen, G.; Tang, W.; Jin, X.; et al. The role of organ failure and infection in necrotizing pancreatitis: A prospective study. Ann. Surg. 2014, 259, 1201–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werge, M.; Novovic, S.; Schmidt, P.N.; Gluud, L.L. Infection increases mortality in necrotizing pancreatitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Pancreatology 2016, 16, 698–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Jin, S.; Pan, J.; Lin, Q.; Yang, S.; Ambe, P.C.; Basharat, Z.; Zimmer, V.; Wang, W.; Hong, W. Damage associated molecular patterns and neutrophil extracellular traps in acute pancreatitis. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 927193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakker, O.J.; van Santvoort, H.; Besselink, M.G.; Boermeester, M.A.; van Eijck, C.; Dejong, K.; van Goor, H.; Hofker, S.; Ahmed Ali, U.; Gooszen, H.G.; et al. Extrapancreatic necrosis without pancreatic parenchymal necrosis: A separate entity in necrotising pancreatitis? Gut 2013, 62, 1475–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, S.S.; Sharma, V.; Sharma, R.K.; Chhabra, P.; Gupta, R.; Bhasin, D.K. Clinical significance of presence and extent of extrapancreatic necrosis in acute pancreatitis. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 30, 794–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banks, P.A.; Freeman, M.L. Practice Parameters Committee of the American College of, G. Practice guidelines in acute pancreatitis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 101, 2379–2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, P.K.; Madan, K.; Pande, G.K.; Khanna, S.; Sathyanarayan, G.; Bohidar, N.P.; Tandon, R.K. Association of extent and infection of pancreatic necrosis with organ failure and death in acute necrotizing pancreatitis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2005, 3, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beger, H.G.; Rau, B.M. Severe acute pancreatitis: Clinical course and management. World J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 13, 5043–5051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lankisch, P.G.; Pflichthofer, D.; Lehnick, D. No strict correlation between necrosis and organ failure in acute pancreatitis. Pancreas 2000, 20, 319–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mole, D.J.; McClymont, K.L.; Lau, S.; Mills, R.; Stamp-Vincent, C.; Garden, O.J.; Parks, R.W. Discrepancy between the extent of pancreatic necrosis and multiple organ failure score in severe acute pancreatitis. World J. Surg. 2009, 33, 2427–2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, P.K.; Singh, V.P. Organ Failure Due to Systemic Injury in Acute Pancreatitis. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 2008–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsey, M.L.; Heald, B.; Gokun, Y.; Baker, J.; Groce, J.R.; Han, S.; Hart, P.A.; Krishna, S.G.; Lara, L.F.; Lee, P.J.; et al. Germline multigene panel testing in acute and chronic pancreatitis. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0307076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smeets, X.; Knoester, I.; Grooteman, K.V.; Singh, V.K.; Banks, P.A.; Papachristou, G.I.; Duarte-Rojo, A.; Robles-Diaz, G.; Kievit, W.; Besselink, M.G.H.; et al. The association between obesity and outcomes in acute pancreatitis: An individual patient data meta-analysis. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 31, 316–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotan, R.; Peto, K.; Deak, A.; Szentkereszty, Z.; Nemeth, N. Hemorheological and Microcirculatory Relations of Acute Pancreatitis. Metabolites 2022, 13, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Dobschuetz, E.; Pahernik, S.; Hoffmann, T.; Kiefmann, R.; Heckel, K.; Messmer, K.; Mueller-Hoecker, J.; Dellian, M. Dynamic intravital fluorescence microscopy--a novel method for the assessment of microvascular permeability in acute pancreatitis. Microvasc. Res. 2004, 67, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.P.; Li, Z.J.; Zhang, J. Inflammatory mediators and microcirculatory disturbance in acute pancreatitis. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Dis. Int. 2009, 8, 351–357. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.G.; Chen, Y.D. Influencing factors of pancreatic microcirculatory impairment in acute panceatitis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2002, 8, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.U.; Johannes, R.S.; Conwell, D.L.; Banks, P.A. Early hemoconcentration predicts increased mortality only among transferred patients with acute pancreatitis. Pancreatology 2009, 9, 639–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tozlu, M.; Kayar, Y.; Ince, A.T.; Baysal, B.; Senturk, H. Low molecular weight heparin treatment of acute moderate and severe pancreatitis: A randomized, controlled, open-label study. Turk. J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 30, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garber, A.; Frakes, C.; Arora, Z.; Chahal, P. Mechanisms and Management of Acute Pancreatitis. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2018, 2018, 6218798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenner, S.; Vege, S.S.; Sheth, S.G.; Sauer, B.; Yang, A.; Conwell, D.L.; Yadlapati, R.H.; Gardner, T.B. American College of Gastroenterology Guidelines: Management of Acute Pancreatitis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2024, 119, 419–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cammarata, F.; Rovati, L.; Fontana, P.; Gambitta, P.; Armellino, A.; Aseni, P. Endoscopic Ultrasound to Identify the Actual Cause of Idiopathic Acute Pancreatitis: A Systematic Review. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazza, S.; Elvo, B.; Conti, C.B.; Drago, A.; Verga, M.C.; Soro, S.; Silvestri, A.; Cereatti, F.; Grassia, R. Endoscopic ultrasound diagnostic gain over computed tomography and magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography in defining etiology of idiopathic acute pancreatitis. World J. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2022, 14, 376–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valverde-Lopez, F.; Ortega-Suazo, E.J.; Wilcox, C.M.; Fernandez-Cano, M.C.; Martinez-Cara, J.G.; Redondo-Cerezo, E. Endoscopic ultrasound as a diagnostic and predictive tool in idiopathic acute pancreatitis. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2020, 33, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, Y.; Li, W.Q. Effectiveness of contrast-enhanced ultrasound for the diagnosis of acute pancreatitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Dig. Liver Dis. 2017, 49, 623–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, S.S.; Bhasin, D.K.; Reddy, Y.R.; Sharma, V.; Rao, C.; Sharma, R.K.; Gupta, R. Morphological features of fluid collections on endoscopic ultrasound in acute necrotizing pancreatitis: Do they change over time? Ann. Gastroenterol. 2014, 27, 258–261. [Google Scholar]
- Golea, A.; Badea, R.; Socaciu, M.; Diaconu, B.; Iacob, D. Quantitative analysis of tissue perfusion using contrast-enhanced transabdominal ultrasound (CEUS) in the evaluation of the severity of acute pancreatitis. Med. Ultrason. 2010, 12, 198–204. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Q.; Zhong, Y.; Wen, X.R.; Huang, Z.W.; Fan, Y.T.; Xia, Q.; Luo, Y. Can contrast-enhanced ultrasound evaluate the severity of acute pancreatitis? Dig. Dis. Sci. 2011, 56, 1578–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kryvoruchko, I.A.; Boyko, V.V.; Sartelli, M.; Ivanova, Y.V.; Yevtushenko, D.O.; Honcharov, A.S. Pancreatic Necrosis Infection as a Determinant of Multiple Organ Failure and Mortality in Acute Pancreatitis. Pathogens 2023, 12, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.M.; Hua, T.R.; Zhang, Y.L.; Chen, G.R.; Song, K.; Pendharkar, S.; Wu, D.; Windsor, J.A. Prognostic significance of organ failure and infected pancreatic necrosis in acute pancreatitis: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Dig. Dis. 2023, 24, 648–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; He, J.; Hu, X.; Xu, S.F.; Su, W.; Luo, J.F.; Wang, Q.F.; Guo, F. Acute necrotising pancreatitis: Measurements of necrosis volume and mean CT attenuation help early prediction of organ failure and need for intervention. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 7705–7714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dancu, G.M.; Popescu, A.; Sirli, R.; Danila, M.; Bende, F.; Tarta, C.; Sporea, I. The BISAP score, NLR, CRP, or BUN: Which marker best predicts the outcome of acute pancreatitis? Medicine 2021, 100, e28121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valverde-Lopez, F.; Matas-Cobos, A.M.; Alegria-Motte, C.; Jimenez-Rosales, R.; Ubeda-Munoz, M.; Redondo-Cerezo, E. BISAP, RANSON, lactate and others biomarkers in prediction of severe acute pancreatitis in a European cohort. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 32, 1649–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Yang, H.X.; Ma, C.E. The Value of BISAP Score for Predicting Mortality and Severity in Acute Pancreatitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0130412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papachristou, G.I.; Muddana, V.; Yadav, D.; O’Connell, M.; Sanders, M.K.; Slivka, A.; Whitcomb, D.C. Comparison of BISAP, Ranson’s, APACHE-II, and CTSI scores in predicting organ failure, complications, and mortality in acute pancreatitis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 105, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwong, W.T.; Ondrejkova, A.; Vege, S.S. Predictors and outcomes of moderately severe acute pancreatitis—Evidence to reclassify. Pancreatology 2016, 16, 940–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, A.K.; Meher, S.; Prakash, S.; Tiwary, S.K.; Singh, U.; Srivastava, A.; Dixit, V.K. Comparison of Ranson, Glasgow, MOSS, SIRS, BISAP, APACHE-II, CTSI Scores, IL-6, CRP, and Procalcitonin in Predicting Severity, Organ Failure, Pancreatic Necrosis, and Mortality in Acute Pancreatitis. HPB Surg. 2013, 2013, 367581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregoric, P.; Sijacki, A.; Stankovic, S.; Radenkovic, D.; Ivancevic, N.; Karamarkovic, A.; Popovic, N.; Karadzic, B.; Stijak, L.; Stefanovic, B.; et al. SIRS score on admission and initial concentration of IL-6 as severe acute pancreatitis outcome predictors. Hepatogastroenterology 2010, 57, 349–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harshit Kumar, A.; Singh Griwan, M. A comparison of APACHE II, BISAP, Ranson’s score and modified CTSI in predicting the severity of acute pancreatitis based on the 2012 revised Atlanta Classification. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2018, 6, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, J.; Shu, W.; He, W.; Zhu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Zeng, H.; Liu, P.; Xia, L.; Lu, N. Serum Creatinine Level and APACHE-II Score within 24 h of Admission Are Effective for Predicting Persistent Organ Failure in Acute Pancreatitis. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2019, 2019, 8201096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Liu, J.; Xing, Y.; Du, L.; Chen, J.; Liu, X.; Hao, J. Comparison of BISAP, Ranson, MCTSI, and APACHE II in Predicting Severity and Prognoses of Hyperlipidemic Acute Pancreatitis in Chinese Patients. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2016, 2016, 1834256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, M.; Fan, Y.; Pan, P.; Tan, Y. Blood Urea Nitrogen as a Prognostic Marker in Severe Acute Pancreatitis. Dis. Markers 2022, 2022, 7785497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozerlat, I. Pancreas: Blood urea nitrogen levels predict mortality risk in acute pancreatitis. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 8, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.U.; Johannes, R.S.; Sun, X.; Conwell, D.L.; Banks, P.A. Early changes in blood urea nitrogen predict mortality in acute pancreatitis. Gastroenterology 2009, 137, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sefoglu, O.F.; Yaka, E.; Pekdemir, M.; Yilmaz, S.; Ozturan, I.U.; Dogan, N.O. Comparison of Bedside Index for Severity in Acute Pancreatitis and Emergency Department SpO(2), Age and Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome Scores in Predicting Severe Acute Pancreatitis in Patients with Acute Pancreatitis in the Emergency Department. J. Emerg. Med. 2024, 67, e10–e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Wu, L.; Wang, Y.; Fang, M.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, X. Predictive value of the Ranson and BISAP scoring systems for the severity and prognosis of acute pancreatitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0302046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, F.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, J.; Ge, Z.; Gu, L. Clinical value of BISAP score combined with CRP and NLR in evaluating the severity of acute pancreatitis. Medicine 2023, 102, e35934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.X.; Chen, S.T.; Zhao, Y.T.; Feng, Y.P.; Chen, J.Y.; Li, Z.S.; Du, Y.Q. Nomogram for the prediction of infected pancreatic necrosis in moderately severe and severe acute pancreatitis. J. Dig. Dis. 2024, 25, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumnicka, P.; Maduzia, D.; Ceranowicz, P.; Olszanecki, R.; Drozdz, R.; Kusnierz-Cabala, B. The Interplay between Inflammation, Coagulation and Endothelial Injury in the Early Phase of Acute Pancreatitis: Clinical Implications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Zhou, X.; Sun, X.; Fu, C.; Li, G.; Dong, X.; Kong, X.; Su, X.; Du, Y. Serum Exosomal miR-216a Contributes to Acute Pancreatitis-Associated Acute Lung Injury by Enhancing Endothelial cell Vascular Permeability via Downregulating LAMC1. Pancreas 2025, 54, e537–e546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitcomb, D.C.; Muddana, V.; Langmead, C.J.; Houghton, F.D., Jr.; Guenther, A.; Eagon, P.K.; Mayerle, J.; Aghdassi, A.A.; Weiss, F.U.; Evans, A.; et al. Angiopoietin-2, a regulator of vascular permeability in inflammation, is associated with persistent organ failure in patients with acute pancreatitis from the United States and Germany. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 105, 2287–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takada, T.; Isaji, S.; Mayumi, T.; Yoshida, M.; Takeyama, Y.; Itoi, T.; Sano, K.; Iizawa, Y.; Masamune, A.; Hirota, M.; et al. JPN clinical practice guidelines 2021 with easy-to-understand explanations for the management of acute pancreatitis. J. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Sci. 2022, 29, 1057–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, U.; Anwar, H.; Scribani, M. Ringer’s lactate versus normal saline in acute pancreatitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Dig. Dis. 2018, 19, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de-Madaria, E.; Herrera-Marante, I.; Gonzalez-Camacho, V.; Bonjoch, L.; Quesada-Vazquez, N.; Almenta-Saavedra, I.; Miralles-Macia, C.; Acevedo-Piedra, N.G.; Roger-Ibanez, M.; Sanchez-Marin, C.; et al. Fluid resuscitation with lactated Ringer’s solution vs. normal saline in acute pancreatitis: A triple-blind, randomized, controlled trial. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2018, 6, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, T.; Jiang, K.; Deng, L.; Guo, J.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Shi, N.; Zhang, X.; Lin, Z.; Asrani, V.; et al. Response and outcome from fluid resuscitation in acute pancreatitis: A prospective cohort study. HPB 2018, 20, 1082–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipinski, M.; Rydzewska-Rosolowska, A.; Rydzewski, A.; Rydzewska, G. Fluid. resuscitation in acute pancreatitis: Normal saline or lactated Ringer’s solution? World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 9367–9372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, P.J.; Culp, S.; Kamal, A.; Paragomi, P.; Pothoulakis, I.; Talukdar, R.; Kochhar, R.; Goenka, M.K.; Gulla, A.; Gonzales, J.; et al. Lactated Ringers Use in the First 24 Hours of Hospitalization Is Associated With Improved Outcomes in 999 Patients with Acute Pancreatitis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2023, 118, 2258–2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Working Group IAP/APA Acute Pancreatitis Guidelines. IAP/APA evidence-based guidelines for the management of acute pancreatitis. Pancreatology 2013, 13, e1–e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Italian Association for the Study of the Pancreas; Pezzilli, R.; Zerbi, A.; Campra, D.; Capurso, G.; Golfieri, R.; Arcidiacono, P.G.; Billi, P.; Butturini, G.; Calculli, L.; et al. Consensus guidelines on severe acute pancreatitis. Dig. Liver Dis. 2015, 47, 532–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoe, M.; Takada, T.; Mayumi, T.; Yoshida, M.; Isaji, S.; Wada, K.; Itoi, T.; Sata, N.; Gabata, T.; Igarashi, H.; et al. Japanese guidelines for the management of acute pancreatitis: Japanese Guidelines 2015. J. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Sci. 2015, 22, 405–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de-Madaria, E.; Buxbaum, J.L.; Maisonneuve, P.; Garcia Garcia de Paredes, A.; Zapater, P.; Guilabert, L.; Vaillo-Rocamora, A.; Rodriguez-Gandia, M.A.; Donate-Ortega, J.; Lozada-Hernandez, E.E.; et al. Aggressive or Moderate Fluid Resuscitation in Acute Pancreatitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 989–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehsan, M.; Ahmad, A.B.; Javed, H.; Zahid, A.; Aamir, H.S.; Cheema, H.A.; Ayyan, M.; Mustafa, B.; Shahid, A.; Ilyas, M.A.; et al. Aggressive Versus Moderate Fluid Replacement for Acute Pancreatitis: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JGH Open 2024, 8, e70073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocskay, K.; Matrai, P.; Hegyi, P.; Parniczky, A. Lactated Ringer’s Solution Reduces Severity, Mortality, Systemic and Local Complications in Acute Pancreatitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Kang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Pu, F.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, W.Q.; Yang, H.J.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, S.K. Lactated Ringer’s solution versus saline fluid resuscitation for reducing progression to moderate-to-severe acute pancreatitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Surg. 2025, 111, 3467–3480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antkowiak, R.; Bialecki, J.; Chabowski, M.; Domoslawski, P. Treatment of Microcirculatory Disturbances in Acute Pancreatitis: Where Are We Now? Pancreas 2022, 51, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellio, G.; Fattori, S.; Sozzi, A.; Cimino, M.M.; Kurihara, H. Telling Ghost Stories Around a Bonfire-A Literature Review of Acute Bleeding Secondary to Pancreatitis. Medicina 2025, 61, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhou, J.; Li, G.; Tong, Z.; Dong, J.; Pan, Y.; Ke, L.; Li, W.; Li, J. Early Spontaneous Abdominal Bleeding is associated with Poor Outcome in Moderate to Severe Acute Pancreatitis Patients: A Propensity Matched Study. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Yao, Q.; Fu, Y.; Xu, X.; Chen, S.; Ke, H.; Hu, Y.; Xiong, H.; He, W.; Zhu, Y.; et al. The severity and infection of acute pancreatitis may increase the risk of bleeding in patients undergoing EUS-guided drainage and endoscopic necrosectomy: A large retrospective cohort. Surg. Endosc. 2023, 37, 6246–6254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Li, L.; Li, J.; Huang, X.; Le, Y.; Ke, H.; Wu, Y.; Shu, X.; Liu, Z.; Xia, L.; et al. Risk factors for bleeding in patients with acute necrotizing pancreatitis undergoing endoscopic necrosectomy. HPB 2021, 23, 1856–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.S.; Qiu, F.; Li, J.Q.; Fan, Q.Q.; Zhou, R.G.; Ai, Y.H.; Zhang, K.C.; Li, Y.X. Low molecular weight heparin in the treatment of severe acute pancreatitis: A multiple centre prospective clinical study. Asian J. Surg. 2009, 32, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, B.; Meena, L.N.; Sharma, D.C.; Agarwal, G.; Dadhich, Y.; Gupta, G. Impact of low-molecular-weight heparin in the treatment of moderately severe and severe acute pancreatitis; a randomized, single blind, phase 3 control trial. Int. J. Surg. 2022, 101, 106621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shashirekha, C.A.; Gondesi, K.; Yarremsetty, V.; Prasad, K.; Yerramsetty, S.V. Efficacy of Low-Molecular-Weight Heparin in the Treatment of Severe Acute Pancreatitis: A Comparative Study at a Tertiary Health Center. Cureus 2024, 16, e65736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Choe, J.W.; Cheon, Y.K.; Choi, M.; Jung, M.K.; Jang, D.K.; Jo, J.H.; Lee, J.M.; Kim, E.J.; Han, S.Y.; et al. Revised Clinical Practice Guidelines of the Korean Pancreatobiliary Association for Acute Pancreatitis. Gut Liver 2023, 17, 34–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leppaniemi, A.; Tolonen, M.; Tarasconi, A.; Segovia-Lohse, H.; Gamberini, E.; Kirkpatrick, A.W.; Ball, C.G.; Parry, N.; Sartelli, M.; Wolbrink, D.; et al. 2019 WSES guidelines for the management of severe acute pancreatitis. World J. Emerg. Surg. 2019, 14, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podda, M.; Murzi, V.; Marongiu, P.; Di Martino, M.; De Simone, B.; Jayant, K.; Ortenzi, M.; Coccolini, F.; Sartelli, M.; Catena, F.; et al. Effectiveness and safety of low molecular weight heparin in the management of acute pancreatitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. World J. Emerg. Surg. 2024, 19, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patoni, C.; Bunduc, S.; Frim, L.; Veres, D.S.; Dembrovszky, F.; Elias, A.J.; Palinkas, D.; Hegyi, P.; Eross, B.M.; Hegyi, P.J. Low molecular weight heparin decreases mortality and major complication rates in moderately severe and severe acute pancreatitis-a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1241301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Q.; Li, G.J.; Tang, L.; Guo, Y.; Wen, L.Z.; Wang, B.; Chen, D.F.; Liu, K.J. The efficacy of low molecular weight heparin in severe acute pancreatitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Dig. Dis. 2019, 20, 512–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumbha, R.; Bathena, S.; Anand, H.B.M.; Amavasya, V.V. Study of role of low molecular weight heparin in conjunction with conventional therapy in severe acute pancreatitis. Asian J. Med. Sci. 2022, 13, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroner, P.T.; Wallace, M.B.; Raimondo, M.; Antwi, S.O.; Ma, Y.; Li, Z.; Ji, B.; Bi, Y. Systemic anticoagulation is associated with decreased mortality and morbidity in acute pancreatitis. Pancreatology 2021, 21, 1428–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadlamudi, R.S.; Matli, V.V.K.; Thoguluva Chandrasekar, V.; Kalakonda, A.; Rawlins, S.R. Chemoprophylaxis to Prevent Deep Venous Thrombosis in Patients Hospitalized for Pancreatitis: Beneficial or Harmful? Cureus 2021, 13, e19645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zhang, H.; Mao, W.; Ke, L.; Li, G.; Ye, B.; Zhang, J.; Lin, J.; Gao, L.; Tong, Z.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Early Systemic Anticoagulation for Preventing Splanchnic Thrombosis in Acute Necrotizing Pancreatitis. Pancreas 2020, 49, 1220–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.D.; Zheng, X.; Huang, Z.Q.; Cai, S.W.; Tan, J.W.; Li, Z.L.; Yao, Y.M.; Jiao, H.B.; Yin, H.N.; Zhu, Z.M. Effects of intensive insulin therapy combined with low molecular weight heparin anticoagulant therapy on severe pancreatitis. Exp. Ther. Med. 2014, 8, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Windisch, O.; Heidegger, C.P.; Giraud, R.; Morel, P.; Buhler, L. Thoracic epidural analgesia: A new approach for the treatment of acute pancreatitis? Crit. Care 2016, 20, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachmann, K.A.; Trepte, C.J.; Tomkotter, L.; Hinsch, A.; Stork, J.; Bergmann, W.; Heidelmann, L.; Strate, T.; Goetz, A.E.; Reuter, D.A.; et al. Effects of thoracic epidural anesthesia on survival and microcirculation in severe acute pancreatitis: A randomized experimental trial. Crit. Care 2013, 17, R281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirag, A.; Pastor, C.M.; Morel, P.; Jean-Christophe, C.; Sielenkamper, A.W.; Guvener, N.; Mai, G.; Berney, T.; Frossard, J.L.; Buhler, L.H. Epidural anaesthesia restores pancreatic microcirculation and decreases the severity of acute pancreatitis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 12, 915–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadowski, S.M.; Andres, A.; Morel, P.; Schiffer, E.; Frossard, J.L.; Platon, A.; Poletti, P.A.; Buhler, L. Epidural anesthesia improves pancreatic perfusion and decreases the severity of acute pancreatitis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 12448–12456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabaudon, M.; Genevrier, A.; Jaber, S.; Windisch, O.; Bulyez, S.; Laterre, P.F.; Escudier, E.; Sossou, A.; Guerci, P.; Bertrand, P.M.; et al. Thoracic epidural analgesia in intensive care unit patients with acute pancreatitis: The EPIPAN multicenter randomized controlled trial. Crit. Care 2023, 27, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moazzami, B.; Mohammadpour, Z.; Zabala, Z.E.; Chawla, S. The Effect of Epidural Analgesia on In-Hospital Outcomes in Patients with Acute Pancreatitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials. Pancreas 2024, 54, e369–e377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Keefe, S.J.; McClave, S.A. Feeding the injured pancreas. Gastroenterology 2005, 129, 1129–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Minnen, L.P.; Blom, M.; Timmerman, H.M.; Visser, M.R.; Gooszen, H.G.; Akkermans, L.M. The use of animal models to study bacterial translocation during acute pancreatitis. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2007, 11, 682–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Huang, L.; Luo, M.; Xia, X. Bacterial translocation in acute pancreatitis. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 45, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritz, S.; Hackert, T.; Hartwig, W.; Rossmanith, F.; Strobel, O.; Schneider, L.; Will-Schweiger, K.; Kommerell, M.; Buchler, M.W.; Werner, J. Bacterial translocation and infected pancreatic necrosis in acute necrotizing pancreatitis derives from small bowel rather than from colon. Am. J. Surg. 2010, 200, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, A.E.; Codner, P.A. Acute Pancreatitis: Exploring Nutrition Implications. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2020, 35, 807–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegazi, R.A.; DeWitt, T. Enteral nutrition and immune modulation of acute pancreatitis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 16101–16105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nammour, T.; Lee, A.A.; McNabb-Baltar, J.; Banks, P.A.; Jin, D.X. A Shift Toward Early Oral Feeding in Acute Pancreatitis. Pancreas 2024, 53, e164–e167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Targarona Modena, J.; Barreda Cevasco, L.; Arroyo Basto, C.; Orellana Vicuna, A.; Portanova Ramirez, M. Total enteral nutrition as prophylactic therapy for pancreatic necrosis infection in severe acute pancreatitis. Pancreatology 2006, 6, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrov, M.S.; Kukosh, M.V.; Emelyanov, N.V. A randomized controlled trial of enteral versus parenteral feeding in patients with predicted severe acute pancreatitis shows a significant reduction in mortality and in infected pancreatic complications with total enteral nutrition. Dig. Surg. 2006, 23, 336–344; discussion 344–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Li, L.; Sun, W. Efficacy comparisons of enteral nutrition and parenteral nutrition in patients with severe acute pancreatitis: A meta-analysis from randomized controlled trials. Biosci. Rep. 2018, 38, BSR20181515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakker, O.J.; van Brunschot, S.; Farre, A.; Johnson, C.D.; Kalfarentzos, F.; Louie, B.E.; Olah, A.; O’Keefe, S.J.; Petrov, M.S.; Powell, J.J.; et al. Timing of enteral nutrition in acute pancreatitis: Meta-analysis of individuals using a single-arm of randomised trials. Pancreatology 2014, 14, 340–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakker, O.J.; van Brunschot, S.; van Santvoort, H.C.; Besselink, M.G.; Bollen, T.L.; Boermeester, M.A.; Dejong, C.H.; van Goor, H.; Bosscha, K.; Ahmed Ali, U.; et al. Early versus on-demand nasoenteric tube feeding in acute pancreatitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 1983–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Shi, H.; Chen, Q.; Su, B.; Dong, X.; Shi, H.; Xu, S. Comparative safety assessment of nasogastric versus nasojejunal feeding initiated within 48 hours post-admission versus unrestricted timing in moderate or severe acute pancreatitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Gastroenterol. 2024, 24, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Yin, H.; Zhang, R.; Ye, X.; Wei, J. Nasogastric Nutrition versus Nasojejunal Nutrition in Patients with Severe Acute Pancreatitis: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2016, 2016, 6430632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.S.; Fu, H.Q.; Xiao, Y.M.; Liu, J.C. Nasogastric or nasojejunal feeding in predicted severe acute pancreatitis: A meta-analysis. Crit. Care 2013, 17, R118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClave, S.A.; Martindale, R.G. What is the role of parenteral nutrition in the management of the patient with severe acute pancreatitis? Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2025, 40, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Dai, W.; Shen, J.; Zhang, M.; Shi, Y.; Jiang, K.; Guo, L. Assessment of Prophylactic Carbapenem Antibiotics Administration for Severe Acute Pancreatitis: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Digestion 2022, 103, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.S.; Shelat, V.G. The Ongoing Debate on the Use of Prophylactic Antibiotics in Acute Pancreatitis-Is There a Conclusion? A Comprehensive Narrative Review. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poropat, G.; Goricanec, K.; Lackovic, A.; Kresovic, A.; Loncaric, A.; Marusic, M. Systematic Review with Trial Sequential Analysis of Prophylactic Antibiotics for Acute Pancreatitis. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moka, P.; Goswami, P.; Kapil, A.; Xess, I.; Sreenivas, V.; Saraya, A. Impact of Antibiotic-Resistant Bacterial and Fungal Infections in Outcome of Acute Pancreatitis. Pancreas 2018, 47, 489–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, L.; Rhodes, A.; Alhazzani, W.; Antonelli, M.; Coopersmith, C.M.; French, C.; Machado, F.R.; McIntyre, L.; Ostermann, M.; Prescott, H.C.; et al. Surviving Sepsis Campaign: International Guidelines for Management of Sepsis and Septic Shock 2021. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 49, e1063–e1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, C.; Ingaldi, C.; Alberici, L.; Marasco, G.; Pagano, N.; Mosconi, C.; Migliori, M.; Serra, C.; Davidovich, I.; Sermonesi, G.; et al. Adherence to Guidelines Influenced the Mortality, Hospital Stay, and Health Care System Costs in Patients with Acute Pancreatitis. Pancreas 2022, 51, 943–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohy-Ud-Din, N.; Deyl, I.; Umar, S.; Abdul-Baki, H.; Morrissey, S. Quality Gaps in Management of Acute Pancreatitis: A Tertiary Care Center Experience. Pancreas 2021, 50, 544–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrie, J.; Jamdar, S.; Smith, N.; McPherson, S.J.; Siriwardena, A.K.; O’Reilly, D.A. Mis-use of antibiotics in acute pancreatitis: Insights from the United Kingdom’s National Confidential Enquiry into patient outcome and death (NCEPOD) survey of acute pancreatitis. Pancreatology 2018, 18, 721–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poropat, G.; Radovan, A.; Peric, M.; Mikolasevic, I.; Giljaca, V.; Hauser, G.; Milic, S.; Stimac, D. Prevention of Infectious Complications in Acute Pancreatitis: Results of a Single-Center, Randomized, Controlled Trial. Pancreas 2019, 48, 1056–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Barrasa, A.; Borobia, F.G.; Pallares, R.; Jorba, R.; Poves, I.; Busquets, J.; Fabregat, J. A double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of ciprofloxacin prophylaxis in patients with acute necrotizing pancreatitis. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2009, 13, 768–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, P.; Deng, L.H.; Zhang, Z.D.; Yang, X.N.; Wan, M.H.; Song, B.; Xia, Q. Effect of antibiotic prophylaxis on acute necrotizing pancreatitis: Results of a randomized controlled trial. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2009, 24, 736–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellinger, E.P.; Tellado, J.M.; Soto, N.E.; Ashley, S.W.; Barie, P.S.; Dugernier, T.; Imrie, C.W.; Johnson, C.D.; Knaebel, H.P.; Laterre, P.F.; et al. Early antibiotic treatment for severe acute necrotizing pancreatitis: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Ann. Surg. 2007, 245, 674–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rokke, O.; Harbitz, T.B.; Liljedal, J.; Pettersen, T.; Fetvedt, T.; Heen, L.O.; Skreden, K.; Viste, A. Early treatment of severe pancreatitis with imipenem: A prospective randomized clinical trial. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 42, 771–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isenmann, R.; Runzi, M.; Kron, M.; Kahl, S.; Kraus, D.; Jung, N.; Maier, L.; Malfertheiner, P.; Goebell, H.; Beger, H.G.; et al. Prophylactic antibiotic treatment in patients with predicted severe acute pancreatitis: A placebo-controlled, double-blind trial. Gastroenterology 2004, 126, 997–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nordback, I.; Sand, J.; Saaristo, R.; Paajanen, H. Early treatment with antibiotics reduces the need for surgery in acute necrotizing pancreatitis--a single-center randomized study. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2001, 5, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, B.K.; Bhandohal, J.S.; Kalha, I.; Fox, K.; Jean, B. Relevance of Procalcitonin Levels as a Marker of Severity and Predictor of Mortality, Initiation and Duration of Antibiotics in Patients Admitted with Acute Pancreatitis: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Clin. Exp. Gastroenterol. 2024, 17, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parniczky, A.; Lantos, T.; Toth, E.M.; Szakacs, Z.; Godi, S.; Hagendorn, R.; Illes, D.; Koncz, B.; Marta, K.; Miko, A.; et al. Antibiotic therapy in acute pancreatitis: From global overuse to evidence based recommendations. Pancreatology 2019, 19, 488–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siriwardena, A.K.; Jegatheeswaran, S.; Mason, J.M.; PROCAP investigators. A procalcitonin-based algorithm to guide antibiotic use in patients with acute pancreatitis (PROCAP): A single-centre, patient-blinded, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 7, 913–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Li, J.; Liu, B.; Hong, X.; Luo, T.; Ye, J.; Yu, Y.; Peng, X.; Gou, S.; Tang, H.; et al. Metagenomic next-generation sequencing, instead of procalcitonin, could guide antibiotic usage in patients with febrile acute necrotizing pancreatitis: A multicenter, prospective cohort study. Int. J. Surg. 2024, 110, 2721–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, T.H.; DiMaio, C.J.; Wang, A.Y.; Morgan, K.A. American Gastroenterological Association Clinical Practice Update: Management of Pancreatic Necrosis. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 67–75.e61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Yin, S.; Jin, K.; Nie, W.; Wang, L.; Cheng, L. Effectiveness and safety of probiotics on patients with severe acute pancreatitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine 2023, 102, e36454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paramythiotis, D.; Karlafti, E.; Tsavdaris, D.; Giakoustidis, A.; Panidis, S.; Ioannidis, A.; Prassopoulos, P.; Michalopoulos, A. When to Intervene in Acute Necrotizing Pancreatitis: A Narrative Review of the Optimal Timing for Intervention Strategies. Medicina 2024, 60, 1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Grinsven, J.; van Santvoort, H.C.; Boermeester, M.A.; Dejong, C.H.; van Eijck, C.H.; Fockens, P.; Besselink, M.G.; Dutch Pancreatitis Study Group. Timing of catheter drainage in infected necrotizing pancreatitis. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 13, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banks, P.A.; Bollen, T.L.; Dervenis, C.; Gooszen, H.G.; Johnson, C.D.; Sarr, M.G.; Tsiotos, G.G.; Vege, S.S.; Acute Pancreatitis Classification Working Group. Classification of acute pancreatitis—2012: Revision of the Atlanta classification and definitions by international consensus. Gut 2013, 62, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isenmann, R.; Rau, B.; Beger, H.G. Early severe acute pancreatitis: Characteristics of a new subgroup. Pancreas 2001, 22, 274–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassi, C.; Falconi, M.; Sartori, N.; Bonora, A.; Caldiron, E.; Butturini, G.; Salvia, R.; Pederzoli, P. The role of surgery in the major early complications of severe acute pancreatitis. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 1997, 9, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mowery, N.T.; Bruns, B.R.; MacNew, H.G.; Agarwal, S.; Enniss, T.M.; Khan, M.; Guo, W.A.; Cannon, J.W.; Lissauer, M.E.; Duane, T.M.; et al. Surgical management of pancreatic necrosis: A practice management guideline from the Eastern Association for the Surgery of Trauma. J. Trauma. Acute Care Surg. 2017, 83, 316–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mier, J.; Leon, E.L.; Castillo, A.; Robledo, F.; Blanco, R. Early versus late necrosectomy in severe necrotizing pancreatitis. Am. J. Surg. 1997, 173, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakai, Y.; Shiomi, H.; Hamada, T.; Ota, S.; Takenaka, M.; Iwashita, T.; Sato, T.; Saito, T.; Masuda, A.; Matsubara, S.; et al. Early versus delayed interventions for necrotizing pancreatitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. DEN Open 2023, 3, e171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prinz, R.A.; Olen, R. Endoscopic evaluation of infected pancreatic necrosis. Surg. Laparosc. Endosc. 1991, 1, 195–197. [Google Scholar]
- Baron, T.H.; Thaggard, W.G.; Morgan, D.E.; Stanley, R.J. Endoscopic therapy for organized pancreatic necrosis. Gastroenterology 1996, 111, 755–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shonnard, K.M.; McCarter, D.L.; Lyon, R.D. Percutaneous debridement of infected pancreatic necrosis with nitinol snares. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 1997, 8, 279–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echenique, A.M.; Sleeman, D.; Yrizarry, J.; Scagnelli, T.; Guerra, J.J., Jr.; Casillas, V.J.; Huson, H.; Russell, E. Percutaneous catheter-directed debridement of infected pancreatic necrosis: Results in 20 patients. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 1998, 9, 565–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvath, K.D.; Kao, L.S.; Ali, A.; Wherry, K.L.; Pellegrini, C.A.; Sinanan, M.N. Laparoscopic assisted percutaneous drainage of infected pancreatic necrosis. Surg. Endosc. 2001, 15, 677–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Santvoort, H.C.; Besselink, M.G.; Horvath, K.D.; Sinanan, M.N.; Bollen, T.L.; van Ramshorst, B.; Gooszen, H.G.; Dutch Acute Pancreatis Study Group. Videoscopic assisted retroperitoneal debridement in infected necrotizing pancreatitis. HPB 2007, 9, 156–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Grinsven, J.; van Brunschot, S.; Bakker, O.J.; Bollen, T.L.; Boermeester, M.A.; Bruno, M.J.; Dejong, C.H.; Dijkgraaf, M.G.; van Eijck, C.H.; Fockens, P.; et al. Diagnostic strategy and timing of intervention in infected necrotizing pancreatitis: An international expert survey and case vignette study. HPB 2016, 18, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Li, A.; Xia, Q.; Lu, H.; Ke, N.; Du, X.; Zhang, Z.; Hu, W. Timing of intervention in necrotizing pancreatitis. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2014, 18, 1770–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, S.; Walklin, R.; Wewelwala, C.; Berry, R.; Devonshire, D.; Croagh, D. Interventional management of necrotizing pancreatitis: An Australian experience. ANZ J. Surg. 2017, 87, E85–E89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallick, B.; Dhaka, N.; Gupta, P.; Gulati, A.; Malik, S.; Sinha, S.K.; Yadav, T.D.; Gupta, V.; Kochhar, R. An audit of percutaneous drainage for acute necrotic collections and walled off necrosis in patients with acute pancreatitis. Pancreatology 2018, 18, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chantarojanasiri, T.; Yamamoto, N.; Nakai, Y.; Saito, T.; Saito, K.; Hakuta, R.; Ishigaki, K.; Takeda, T.; Uchino, R.; Takahara, N.; et al. Comparison of early and delayed EUS-guided drainage of pancreatic fluid collection. Endosc. Int. Open 2018, 6, E1398–E1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trikudanathan, G.; Tawfik, P.; Amateau, S.K.; Munigala, S.; Arain, M.; Attam, R.; Beilman, G.; Flanagan, S.; Freeman, M.L.; Mallery, S. Early (<4 Weeks) Versus Standard (>/=4 Weeks) Endoscopically Centered Step-Up Interventions for Necrotizing Pancreatitis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 113, 1550–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oblizajek, N.; Takahashi, N.; Agayeva, S.; Bazerbachi, F.; Chandrasekhara, V.; Levy, M.; Storm, A.; Baron, T.; Chari, S.; Gleeson, F.C.; et al. Outcomes of early endoscopic intervention for pancreatic necrotic collections: A matched case-control study. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2020, 91, 1303–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganaie, K.H.; Choh, N.A.; Parry, A.H.; Shaheen, F.A.; Robbani, I.; Gojwari, T.A.; Singh, M.; Shah, O.J. The effectiveness of image-guided percutaneous catheter drainage in the management of acute pancreatitis-associated pancreatic collections. Pol. J. Radiol. 2021, 86, e359–e365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.; Bansal, A.; Samanta, J.; Mandavdhare, H.; Sharma, V.; Gupta, V.; Yadav, T.D.; Dutta, U.; Kochhar, R.; Singh Sandhu, M. Larger bore percutaneous catheter in necrotic pancreatic fluid collection is associated with better outcomes. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 3439–3446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Chandran, S.; Chin, J.; Karim, S.; Mangira, D.; Nasr, M.; Ermerak, G.; Trinh, A.; Kia, C.Y.H.; Mules, T.; et al. Drainage of pancreatic fluid collections using a lumen-apposing metal stent with an electrocautery-enhanced delivery system. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 36, 3395–3401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, S.S.; Sharma, R.; Kishore, K.; Dhalaria, L.; Gupta, R. Safety and Efficacy of Early (<4 Weeks of Illness) Endoscopic Transmural Drainage of Post-acute Pancreatic Necrosis Predominantly Located in the Body of the Pancreas. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2021, 25, 2328–2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boxhoorn, L.; van Dijk, S.M.; van Grinsven, J.; Verdonk, R.C.; Boermeester, M.A.; Bollen, T.L.; Bouwense, S.A.W.; Bruno, M.J.; Cappendijk, V.C.; Dejong, C.H.C.; et al. Immediate versus Postponed Intervention for Infected Necrotizing Pancreatitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 1372–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagielski, M.; Piatkowski, J.; Jackowski, M. Early endoscopic treatment of symptomatic pancreatic necrotic collections. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Cao, F.; Zheng, Z.; Ding, Y.; Qu, Y.; Mei, W.; Guo, Y.; Feng, Y.L.; Li, F. How to Identify the Indications for Early Intervention in Acute Necrotizing Pancreatitis Patients: A Long-Term Follow-Up Study. Front. Surg. 2022, 9, 842016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Gao, L.; Mao, W.J.; Yang, J.; Zhou, J.; Tong, Z.H.; Ke, L.; Li, W.Q. Early versus delayed intervention in necrotizing acute pancreatitis complicated by persistent organ failure. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Dis. Int. 2022, 21, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, H.; Farook, S.; Bendale, C.U.; Gupta, P.; Singh, A.K.; Shah, J.; Samanta, J.; Mandavdhare, H.; Sharma, V.; Sinha, S.K.; et al. Early vs. late percutaneous catheter drainage of acute necrotic collections in patients with necrotizing pancreatitis. Abdom. Radiol. 2023, 48, 2415–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, H.; Inayat, F.; Jahagirdar, V.; Jaber, F.; Afzal, A.; Patel, P.; Tahir, H.; Anwar, M.S.; Rehman, A.U.; Sarfraz, M.; et al. Early versus delayed necrosectomy in pancreatic necrosis: A population-based cohort study on readmission, healthcare utilization, and in-hospital mortality. World J. Methodol. 2024, 14, 91810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Veldhuisen, C.L.; Sissingh, N.J.; Boxhoorn, L.; van Dijk, S.M.; van Grinsven, J.; Verdonk, R.C.; Boermeester, M.A.; Bouwense, S.A.W.; Bruno, M.J.; Cappendijk, V.C.; et al. Long-Term Outcome of Immediate Versus Postponed Intervention in Patients With Infected Necrotizing Pancreatitis (POINTER): Multicenter Randomized Trial. Ann. Surg. 2024, 279, 671–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bugiantella, W.; Rondelli, F.; Boni, M.; Stella, P.; Polistena, A.; Sanguinetti, A.; Avenia, N. Necrotizing pancreatitis: A review of the interventions. Int. J. Surg. 2016, 28 (Suppl. 1), S163–S171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Baal, M.C.; van Santvoort, H.C.; Bollen, T.L.; Bakker, O.J.; Besselink, M.G.; Gooszen, H.G.; Dutch Pancreatitis Study Group. Systematic review of percutaneous catheter drainage as primary treatment for necrotizing pancreatitis. Br. J. Surg. 2011, 98, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wronski, M.; Cebulski, W.; Karkocha, D.; Slodkowski, M.; Wysocki, L.; Jankowski, M.; Krasnodebski, I.W. Ultrasound-guided percutaneous drainage of infected pancreatic necrosis. Surg. Endosc. 2013, 27, 2841–2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baudin, G.; Chassang, M.; Gelsi, E.; Novellas, S.; Bernardin, G.; Hebuterne, X.; Chevallier, P. CT-guided percutaneous catheter drainage of acute infectious necrotizing pancreatitis: Assessment of effectiveness and safety. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2012, 199, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortele, K.J.; Girshman, J.; Szejnfeld, D.; Ashley, S.W.; Erturk, S.M.; Banks, P.A.; Silverman, S.G. CT-guided percutaneous catheter drainage of acute necrotizing pancreatitis: Clinical experience and observations in patients with sterile and infected necrosis. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2009, 192, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerem, E.; Ozkan, H.; Agayev, R.M. Catheter-Related Complications of Percutaneous Drainage in Step-up Approach for Management of Pancreatic Necrosis. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2020, 24, 1904–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.; Koshi, S.; Samanta, J.; Mandavdhare, H.; Sharma, V.; Sinha, S.K.; Dutta, U.; Kochhar, R. Kissing catheter technique for percutaneous catheter drainage of necrotic pancreatic collections in acute pancreatitis. Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 20, 2311–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Song, J.; Ke, H.J.; Lv, N.H.; Zhu, Y.; Zeng, H.; Zhu, Y.; Xia, L.; He, W.H.; Li, J.; et al. Double-catheter lavage combined with percutaneous flexible endoscopic debridement for infected pancreatic necrosis failed to percutaneous catheter drainage. BMC Gastroenterol. 2017, 17, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohli, P.; Gupta, V.; Kochhar, R.; Yadav, T.D.; Sinha, S.K.; Lal, A. Lavage through percutaneous catheter drains in severe acute pancreatitis: Does it help? A randomized control trial. Pancreatology 2019, 19, 929–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werge, M.; Novovic, S.; Roug, S.; Knudsen, J.D.; Feldager, E.; Gluud, L.L.; Schmidt, P.N. Evaluation of local instillation of antibiotics in infected walled-off pancreatic necrosis. Pancreatology 2018, 18, 642–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhargava, V.; Gupta, R.; Vaswani, P.; Jha, B.; Rana, S.S.; Gorsi, U.; Kang, M.; Gupta, R. Streptokinase irrigation through a percutaneous catheter helps decrease the need for necrosectomy and reduces mortality in necrotizing pancreatitis as part of a step-up approach. Surgery 2021, 170, 1532–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, R.; Kulkarni, A.; Babu, R.; Shenvi, S.; Gupta, R.; Sharma, G.; Kang, M.; Gorsi, U.; Rana, S.S. Complications of Percutaneous Drainage in Step-Up Approach for Management of Pancreatic Necrosis: Experience of 10 Years from a Tertiary Care Center. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2020, 24, 598–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhusudhan, K.S.; Gopi, S.; Singh, A.N.; Agarwal, L.; Gunjan, D.; Srivastava, D.N.; Garg, P.K. Immediate and Long-Term Outcomes of Percutaneous Radiological Interventions for Hemorrhagic Complications in Acute and Chronic Pancreatitis. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2021, 32, 1591–1600.e1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoi, Y.; Kikuyama, M.; Kurokami, T.; Sato, T. Early dual drainage combining transpapillary endotherapy and percutaneous catheter drainage in patients with pancreatic fistula associated with severe acute pancreatitis. Pancreatology 2016, 16, 497–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorsandi, M.; Beatson, K.; Dougherty, S.; Zealley, I.; Kulli, C. Interventional radiology in acute pancreatitis: Friend or foe? JOP 2012, 13, 91–93. [Google Scholar]
- Seifert, H.; Wehrmann, T.; Schmitt, T.; Zeuzem, S.; Caspary, W.F. Retroperitoneal endoscopic debridement for infected peripancreatic necrosis. Lancet 2000, 356, 653–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papachristou, G.I.; Takahashi, N.; Chahal, P.; Sarr, M.G.; Baron, T.H. Peroral endoscopic drainage/debridement of walled-off pancreatic necrosis. Ann. Surg. 2007, 245, 943–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, T.H. Endoscopic drainage of pancreatic fluid collections and pancreatic necrosis. Gastrointest. Endosc. Clin. N. Am. 2003, 13, 743–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Kahaleh, M.; Khan, Z.; Tyberg, A.; Solanki, S.; Haq, K.F.; Sofi, A.; Lee, W.M.; Ismail, M.K.; Tombazzi, C.; et al. Time for a Changing of Guard: From Minimally Invasive Surgery to Endoscopic Drainage for Management of Pancreatic Walled-off Necrosis. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2019, 53, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramai, D.; Morgan, A.D.; Gkolfakis, P.; Facciorusso, A.; Chandan, S.; Papaefthymiou, A.; Morris, J.; Arvanitakis, M.; Adler, D.G. Endoscopic management of pancreatic walled-off necrosis. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2023, 36, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boxhoorn, L.; Fockens, P.; Besselink, M.G.; Bruno, M.J.; van Hooft, J.E.; Verdonk, R.C.; Voermans, R.P.; Dutch Pancreatitis Study Group. Endoscopic Management of Infected Necrotizing Pancreatitis: An Evidence-Based Approach. Curr. Treat. Options Gastroenterol. 2018, 16, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, M.L.; Werner, J.; van Santvoort, H.C.; Baron, T.H.; Besselink, M.G.; Windsor, J.A.; Horvath, K.D.; vanSonnenberg, E.; Bollen, T.L.; Vege, S.S.; et al. Interventions for necrotizing pancreatitis: Summary of a multidisciplinary consensus conference. Pancreas 2012, 41, 1176–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varadarajulu, S.; Christein, J.D.; Tamhane, A.; Drelichman, E.R.; Wilcox, C.M. Prospective randomized trial comparing EUS and EGD for transmural drainage of pancreatic pseudocysts (with videos). Gastrointest. Endosc. 2008, 68, 1102–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, T.B.; Chahal, P.; Papachristou, G.I.; Vege, S.S.; Petersen, B.T.; Gostout, C.J.; Topazian, M.D.; Takahashi, N.; Sarr, M.G.; Baron, T.H. A comparison of direct endoscopic necrosectomy with transmural endoscopic drainage for the treatment of walled-off pancreatic necrosis. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2009, 69, 1085–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angadi, S.; Mahapatra, S.J.; Sethia, R.; Elhence, A.; Krishna, A.; Gunjan, D.; Prajapati, O.P.; Kumar, S.; Bansal, V.K.; Garg, P.K. Endoscopic transmural drainage tailored to quantity of necrotic debris versus laparoscopic transmural internal drainage for walled-off necrosis in acute pancreatitis: A randomized controlled trial. Pancreatology 2021, 21, 1291–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, P.K.; Meena, D.; Babu, D.; Padhan, R.K.; Dhingra, R.; Krishna, A.; Kumar, S.; Misra, M.C.; Bansal, V.K. Endoscopic versus laparoscopic drainage of pseudocyst and walled-off necrosis following acute pancreatitis: A randomized trial. Surg. Endosc. 2020, 34, 1157–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Siddiqui, A.; Singh, G.; Redstone, E.; Weinstein, J.; Mitchell, D.G. Pancreatic Walled-Off Necrosis: Cross-Sectional Imaging Depiction of Debris Predicts the Success of Endoscopic Drainage Using Lumen-Apposing Metal Stents. Dig. Dis. 2024, 42, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jong, D.M.; Stassen, P.M.C.; Schoots, I.G.; Verdonk, R.C.; Bruno, M.J.; Voermans, R.P.; de Jonge, P.J.F. Impact of long-term transmural plastic stents on recurrence after endoscopic treatment of walled-off pancreatic necrosis. Endoscopy 2024, 56, 676–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, Y.; Sohail, M.U.; Ibrahim, Z.S.; Batool, R.M.; Ansari, I.; Ahmed, S.Z.; Saad, M.; Aisha, E.; Waqas, S.A.; Sohail, M.O.; et al. Efficacy of Metal Stents Versus Plastic Stents for Treatment of Walled-Off Pancreatic Necrosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JGH Open 2025, 9, e70109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valente, R.; Zarantonello, L.; Del Chiaro, M.; Vujasinovic, M.; Baldaque-Silva, F.; Scandavini, C.M.; Rangelova, E.; Vespasiano, F.; Anzillotti, G.; Lohr, J.M.; et al. Lumen apposing metal stents vs. double pigtail plastic stents for the drainage of pancreatic walled-off necrosis. Minerva Gastroenterol. 2024, 70, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, V.; Gupta, Y.K.; Gupta, A.; Kumar, Y.; Khubber, M.; Sood, A.; Sehgal, T.; Mehta, P.; Vuthaluru, A.R.; Goyal, M.K. Efficacy and Safety of Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS)-Guided Lumen-Apposing Metal Stents (LAMS) as a Primary Treatment for Walled-Off Pancreatic Necrosis. Cureus 2025, 17, e78177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, I.; Shinn, B.; Mitsuhashi, S.; Boortalary, T.; Bashir, M.; Kowalski, T.; Loren, D.; Kumar, A.; Schlachterman, A.; Chiang, A. Prediction and management of bleeding during endoscopic necrosectomy for pancreatic walled-off necrosis: Results of a large retrospective cohort at a tertiary referral center. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2022, 95, 482–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biedermann, J.; Zeissig, S.; Bruckner, S.; Hampe, J. EUS-guided stent removal in buried lumen-apposing metal stent syndrome: A case series. VideoGIE 2020, 5, 37–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuda, I.; Takahashi, K. Endoscopic management of walled-off pancreatic necrosis. Dig. Endosc. 2021, 33, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, T.B.; Coelho-Prabhu, N.; Gordon, S.R.; Gelrud, A.; Maple, J.T.; Papachristou, G.I.; Freeman, M.L.; Topazian, M.D.; Attam, R.; Mackenzie, T.A.; et al. Direct endoscopic necrosectomy for the treatment of walled-off pancreatic necrosis: Results from a multicenter U.S. series. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2011, 73, 718–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakai, Y.; Matsubara, S.; Mukai, T.; Hamada, T.; Sasaki, T.; Ishiwatari, H.; Hijioka, S.; Shiomi, H.; Takenaka, M.; Iwashita, T.; et al. Drainage for fluid collections post pancreatic surgery and acute pancreatitis: Similar but different? Clin. Endosc. 2024, 57, 735–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Saftoiu, A.; Vilmann, P.; Fusaroli, P.; Giovannini, M.; Mishra, G.; Rana, S.S.; Ho, S.; Poley, J.W.; Ang, T.L.; et al. A multi-institutional consensus on how to perform endoscopic ultrasound-guided peri-pancreatic fluid collection drainage and endoscopic necrosectomy. Endosc. Ultrasound 2017, 6, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangiafico, S.; Bertani, H.; Pigo, F.; Russo, S.; Lupo, M.; Cocca, S.; Grande, G.; Germani, U.; Manta, R.; Conigliaro, R. A New Step-Up Dual Endoscopic Approach for Large-Size Infected Pancreatic Necrosis: Percutaneous Endoscopic Necrosectomy Followed by Transluminal Endoscopic Drainage/Necrosectomy. Surg. Laparosc. Endosc. Percutan. Technol. 2024, 34, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, H.; Vermani, S.; Gupta, P.; Farook, S.; Kumar, A.; Johnson, J.; Shah, J.; Singh, A.; Jearth, V.; Samanta, J.; et al. Impact of the Timing of Percutaneous Catheter Drainage following Endoscopic Drainage on Outcomes in Acute Necrotizing Pancreatitis. Indian. J. Radiol. Imaging 2024, 34, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, S.S.; Verma, S.; Kang, M.; Gorsi, U.; Sharma, R.; Gupta, R. Comparison of endoscopic versus percutaneous drainage of symptomatic pancreatic necrosis in the early (<4 weeks) phase of illness. Endosc. Ultrasound 2020, 9, 402–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, S.; Walklin, R.; Ackermann, T.; Lo, S.W.; Shilton, H.; Pilgrim, C.; Evans, P.; Burnes, J.; Croagh, D. Comparison of endoscopic and percutaneous drainage of symptomatic necrotic collections in acute necrotizing pancreatitis. Asian J. Endosc. Surg. 2019, 12, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sylla, P.; Kirman, I.; Whelan, R.L. Immunological advantages of advanced laparoscopy. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2005, 85, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobi, C.A.; Zieren, H.U.; Sabat, R.; Lorenz, W.; Halle, F.E.; Muller, J.M. Comparison of local and systemic inflammation after laparotomy or laparoscopy in the rat sepsis model. Langenbecks Arch. Chir. 1997, 382, S9–S13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, C.R.; McKay, C.J.; Imrie, C.W. Percutaneous necrosectomy and sinus tract endoscopy in the management of infected pancreatic necrosis: An initial experience. Ann. Surg. 2000, 232, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelat, V.G.; Diddapur, R.K. Minimally invasive retroperitoneal pancreatic necrosectomy in necrotising pancreatitis. Singap. Med. J. 2007, 48, e220–e223. [Google Scholar]
- Bucher, P.; Pugin, F.; Morel, P. Minimally invasive necrosectomy for infected necrotizing pancreatitis. Pancreas 2008, 36, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loveday, B.P.; Mittal, A.; Phillips, A.; Windsor, J.A. Minimally invasive management of pancreatic abscess, pseudocyst, and necrosis: A systematic review of current guidelines. World J. Surg. 2008, 32, 2383–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Santvoort, H.C.; Besselink, M.G.; Bakker, O.J.; Hofker, H.S.; Boermeester, M.A.; Dejong, C.H.; van Goor, H.; Schaapherder, A.F.; van Eijck, C.H.; Bollen, T.L.; et al. A step-up approach or open necrosectomy for necrotizing pancreatitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 1491–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eng, N.L.; Fitzgerald, C.A.; Fisher, J.G.; Small, W.C.; Willingham, F.F.; Galloway, J.R.; Kooby, D.A.; Haack, C.I. Laparoscopic-Assisted Pancreatic Necrosectomy: Technique and Initial Outcomes. Am. Surg. 2023, 89, 4459–4468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurer, L.R.; Fagenholz, P.J. Contemporary Surgical Management of Pancreatic Necrosis. JAMA Surg. 2023, 158, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.B.; Sun, B. Comparison between video-assisted retroperitoneal debridement and small incision pancreatic necrosectomy in infected pancreatic necrosis. ANZ J. Surg. 2020, 90, 2020–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Chen, W.; Chen, J.; Chen, D.; Zhang, K.; Cai, J.; Peng, H.; Huang, C.; Zeng, G.; Ma, M.; et al. Indocyanine Green-Guided Intraoperative Imaging to Facilitate Video-Assisted Retroperitoneal Debridement for Treating Acute Necrotizing Pancreatitis. J. Vis. Exp. 2022, 8, e63236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassi, C.; Butturini, G.; Falconi, M.; Salvia, R.; Frigerio, I.; Pederzoli, P. Outcome of open necrosectomy in acute pancreatitis. Pancreatology 2003, 3, 128–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connor, S.; Alexakis, N.; Raraty, M.G.; Ghaneh, P.; Evans, J.; Hughes, M.; Garvey, C.J.; Sutton, R.; Neoptolemos, J.P. Early and late complications after pancreatic necrosectomy. Surgery 2005, 137, 499–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingham, T.P.; Shamamian, P. Management and spectrum of complications in patients undergoing surgical debridement for pancreatic necrosis. Am. Surg. 2008, 74, 1050–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howard, J.M. Delayed debridement and external drainage of massive pancreatic or peripancreatic necrosis. Surg. Gynecol. Obstet. 1989, 168, 25–29. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, C.D. Timing of intervention in acute pancreatitis. Postgrad. Med. J. 1993, 69, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, J.; Uhl, W.; Hartwig, W.; Hackert, T.; Muller, C.; Strobel, O.; Buchler, M.W. Modern phase-specific management of acute pancreatitis. Dig. Dis. 2003, 21, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollemans, R.A.; Bakker, O.J.; Boermeester, M.A.; Bollen, T.L.; Bosscha, K.; Bruno, M.J.; Buskens, E.; Dejong, C.H.; van Duijvendijk, P.; van Eijck, C.H.; et al. Superiority of Step-up Approach vs. Open Necrosectomy in Long-term Follow-up of Patients with Necrotizing Pancreatitis. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 1016–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Brunschot, S.; Hollemans, R.A.; Bakker, O.J.; Besselink, M.G.; Baron, T.H.; Beger, H.G.; Boermeester, M.A.; Bollen, T.L.; Bruno, M.J.; Carter, R.; et al. Minimally invasive and endoscopic versus open necrosectomy for necrotising pancreatitis: A pooled analysis of individual data for 1980 patients. Gut 2018, 67, 697–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomatos, I.P.; Halloran, C.M.; Ghaneh, P.; Raraty, M.G.; Polydoros, F.; Evans, J.C.; Smart, H.L.; Yagati-Satchidanand, R.; Garry, J.M.; Whelan, P.A.; et al. Outcomes From Minimal Access Retroperitoneal and Open Pancreatic Necrosectomy in 394 Patients with Necrotizing Pancreatitis. Ann. Surg. 2016, 263, 992–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, M.; Cole, J.; Dove, J.; Blansfield, J.; Shabahang, M.; Wild, J.; Widom, K.; Torres, D.; Factor, M. Outcomes of Endoscopic and Surgical Pancreatic Necrosectomy: A Single Institution Experience. Am. Surg. 2019, 85, 1017–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luckhurst, C.M.; El Hechi, M.; Elsharkawy, A.E.; Eid, A.I.; Maurer, L.R.; Kaafarani, H.M.; Thabet, A.; Forcione, D.G.; Fernandez-Del Castillo, C.; Lillemoe, K.D.; et al. Improved Mortality in Necrotizing Pancreatitis with a Multidisciplinary Minimally Invasive Step-Up Approach: Comparison with a Modern Open Necrosectomy Cohort. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2020, 230, 873–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ning, C.; Sun, Z.; Shen, D.; Lin, C.; Li, J.; Wei, Q.; Chen, L.; Huang, G. Is Contemporary Open Pancreatic Necrosectomy Still Useful in the Minimally Invasive Era? Surgery 2024, 175, 1394–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarnescu, N.O.; Dumitrascu, I.; Zarnescu, E.C.; Costea, R. Abdominal Compartment Syndrome in Acute Pancreatitis: A Narrative Review. Diagnostics 2022, 13, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sgaramella, L.I.; Gurrado, A.; Pasculli, A.; Prete, F.P.; Catena, F.; Testini, M. Open necrosectomy is feasible as a last resort in selected cases with infected pancreatic necrosis: A case series and systematic literature review. World J. Emerg. Surg. 2020, 15, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, J.; Hartwig, W.; Hackert, T.; Buchler, M.W. Surgery in the treatment of acute pancreatitis--open pancreatic necrosectomy. Scand. J. Surg. 2005, 94, 130–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, E.D.; Bradley, E.L., 3rd. “Marsupialization” in the treatment of pancreatic abscess. Surgery 1981, 89, 252–256. [Google Scholar]
- Margulies, A.G.; Akin, H.E. Marsupialization of the pancreas for infected pancreatic necrosis. Am. Surg. 1997, 63, 261–265. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Warshaw, A.L.; Jin, G.L. Improved survival in 45 patients with pancreatic abscess. Ann. Surg. 1985, 202, 408–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beger, H.G.; Buchler, M.; Bittner, R.; Block, S.; Nevalainen, T.; Roscher, R. Necrosectomy and postoperative local lavage in necrotizing pancreatitis. Br. J. Surg. 1988, 75, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beger, H.G.; Buchler, M.; Bittner, R.; Oettinger, W.; Block, S.; Nevalainen, T. Necrosectomy and postoperative local lavage in patients with necrotizing pancreatitis: Results of a prospective clinical trial. World J. Surg. 1988, 12, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsiotos, G.G.; Luque-de Leon, E.; Soreide, J.A.; Bannon, M.P.; Zietlow, S.P.; Baerga-Varela, Y.; Sarr, M.G. Management of necrotizing pancreatitis by repeated operative necrosectomy using a zipper technique. Am. J. Surg. 1998, 175, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radenkovic, D.V.; Bajec, D.D.; Tsiotos, G.G.; Karamarkovic, A.R.; Milic, N.M.; Stefanovic, B.D.; Bumbasirevic, V.; Gregoric, P.M.; Masulovic, D.; Milicevic, M.M. Planned staged reoperative necrosectomy using an abdominal zipper in the treatment of necrotizing pancreatitis. Surg. Today 2005, 35, 833–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mentula, P.; Leppaniemi, A. Position paper: Timely interventions in severe acute pancreatitis are crucial for survival. World J. Emerg. Surg. 2014, 9, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leppaniemi, A.; Hienonen, P.; Mentula, P.; Kemppainen, E. Subcutaneous linea alba fasciotomy, does it really work? Am. Surg. 2011, 77, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheatham, M.L.; Fowler, J.; Pappas, P. Subcutaneous linea alba fasciotomy: A less morbid treatment for abdominal compartment syndrome. Am. Surg. 2008, 74, 746–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valverde-Lopez, F.; Han, S.; Coughlin, S.; Thiruvengadam, N.; Moreau, C.; Akshintala, V.S.; Lee, P.J.; Collaborative Alliance for Pancreatic Education and Research. Outcomes of Endoscopic Management of Sterile Walled-Off Pancreatic Necrosis: A Systematic Review. Pancreas 2021, 50, 1357–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, R.P.; Mourad, M.M.; Pall, G.; Fisher, S.G.; Bramhall, S.R. Pancreatitis: Preventing catastrophic haemorrhage. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 5460–5468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, V.; Krishna, P.; Kochhar, R.; Yadav, T.D.; Bargav, V.; Bhalla, A.; Kalra, N.; Wig, J.D. Hemorrhage complicating the course of severe acute pancreatitis. Ann. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Surg. 2020, 24, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sathyanathan, B.P.; Vennimalai, S. Disconnected Pancreatic Duct Syndrome-An Often-Overlooked Complication of Acute Necrotizing Pancreatitis. Indian. J. Radiol. Imaging 2023, 33, 281–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, S.S.; Sharma, R.; Kang, M.; Gupta, R. Natural course of low output external pancreatic fistula in patients with disconnected pancreatic duct syndrome following acute necrotising pancreatitis. Pancreatology 2020, 20, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelaez-Luna, M.; Vege, S.S.; Petersen, B.T.; Chari, S.T.; Clain, J.E.; Levy, M.J.; Pearson, R.K.; Topazian, M.D.; Farnell, M.B.; Kendrick, M.L.; et al. Disconnected pancreatic duct syndrome in severe acute pancreatitis: Clinical and imaging characteristics and outcomes in a cohort of 31 cases. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2008, 68, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearson, E.G.; Scaife, C.L.; Mulvihill, S.J.; Glasgow, R.E. Roux-en-Y drainage of a pancreatic fistula for disconnected pancreatic duct syndrome after acute necrotizing pancreatitis. HPB 2012, 14, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Zhang, J.Z.; Gao, K.; Zhou, J.; Li, G.; Li, B.Q.; Ye, B.; Ke, L.; Tong, Z.H.; Li, W.Q. Management of colonic fistulas in patients with infected pancreatic necrosis being treated with a step-up approach. HPB 2020, 22, 1738–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| System/Biomarker | Cut-Off | Sensitivity | Specificity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Systemic Inflammatory Response System (SIRS) [41,42,43] | >2 points | 55% | 88% |
| APACHE score [44,45,46] | ≥8 points | 93.3% | 85.7% |
| Blood Urea Nitrogen [47,48,49] | ≥25 mg/dL | 95.7% | 97.4% |
| Bedside Index of Acute Pancreatitis (BISAP) [50,51,52] | ≥2 points | 73.5% | 82.4% |
| Author, Year | Intervention/Control | N | Age, Years | Female, N (%) | Antibiotic | Duration of Administration | Infected Pancreatic Necrosis | Non Pancreatic Infection | Positive Blood Culture | Fungal Infection | Need for Surgery | Mortality, N (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Poropat 2019 [118] | Intervention | 49 | 74 | 41% | Imipenem | 7–21 days | 3. (6.12%) | 10 (20.40%) | 1 (2.04%) | 1 (2.04%) | 0 | 7 (14.28%) |
| Control | 49 | 74 | 45% | Placebo | 2 (4.08%) | 10 (20.40%) | 1 (2.04%) | 2 (4.08%) | 0 | 8 (16.32%) | ||
| Garrcia-Barrasa 2009 [119] | Intervention | 22 | 59.5 | 36% | Ciprofloxacin | 10 days | 8 (36.36%) | 6 (27.27%) | 3 (13.63%) | NA | 11 (50%) | 4 (18.18%) |
| Control | 19 | 67 | 21% | None | 8 (42.10%) | 8 (42.10%) | 2 (10.52%) | NA | 8 (42.10%) | 2 (10.52%) | ||
| Xue 2009 [120] | Intervention | 29 | 48.4 ± 15.1 | 52% | Imipenem-cilastatin | 7–14 days | 8 (27.58%) | 18 (62.06%) | 6 (20.68%) | NA | 8 (27.58%) | 3 (10.34%) |
| Control | 27 | 47.5 ± 12.3 | 48% | None | 10 (37.03%) | 15 (55.55%) | 7 (25.92%) | NA | 9 (33.33%) | 4 (14.81%) | ||
| Dellinger 2007 [121] | Intervention | 50 | NA | 36% | Meropenem | 7–21 days | 9 (18%) | 16 (32%) | NA | 2 (4%) | 13 (26%) | 10 (20%) |
| Control | 50 | NA | 24% | Placebo | 6 (12%) | 24 (48%) | NA | 1 (2%) | 10 (20%) | 9 (18%) | ||
| Rokke 2007 [122] | Intervention | 36 | 60 | 36% | Imipenem | 5–7 days | 3 (8.33%) | 3 (8.33%) | NA | 0 | 3 (8.33%) | 3 (8.33%) |
| Control | 37 | 57 | 30% | None | 7 (12.28%) | 12 (32.43%) | NA | 3 (8.10%) | 3 (8.10%) | 4 (8.10%) | ||
| Isenmann 2004 [123] | Intervention | 58 | 47.9 | 26% | Ciprofloxacin + Metronidazole | 21 days | 7 (12.06%) | 13 (22.41%) | NA | 2 (3.44%) | 10 (1.72%) | 3 (5.17%) |
| Control | 56 | 45.6 | 21% | Placebo | 5 (8.92%) | 13 (23.21%) | NA | 1 (1.78%) | 6 (10.71%) | 4 (7.14%) | ||
| Nordback 2001 [124] | Intervention | 25 | 47.7 | 8% | Imipenem cilastatin | 14 days | 1 (4%) | 4 (16%) | NA | 1 (4%) | 2 (8%) | 2 (8%) |
| Control | 33 | 46.7 | 15% | None | 6 (18.18%) | 1 (3.03%) | NA | 0 | 5 (15.15%) | 5 (15.15%) |
| 1. Infected pancreatic necrosis unresponsive to conservative management exhibiting increasing systemic sepsis, hemodynamic instability or organ failure. |
| 2. Sterile pancreatic necrosis with the extent of necrosis of more than 50% of the pancreatic parenchyma, rapid deterioration, or persistent organ failure. |
| 3. Failure of conservative management regarding symptoms (abdominal pain, vomiting, or other symptoms) or fluid collections. |
| 4. Complications associated with acute necrotizing pancreatitis (abdominal compartment syndrome, pseudoaneurysm, bleeding, disconnected pancreatic duct syndrome, perforation, obstruction, or fistula). |
| Name of Study | Group | Number of Patients | Endoscopic | Percutaneous | Surgical | Organ Failure | Length of Hospital Stay | Mortality |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guo 2014 [146] | Early | 136 | 0 | 22 | 114 | 61 | NA | 21% |
| Delayed | 27 | 0 | 15 | 72 | 21 | NA | 10% | |
| Woo 2017 [147] | Early | 7 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 0% |
| Delayed | 23 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 17% | |
| Mallick 2018 [148] | Early | 258 | 0 | 258 | 0 | 98 | NA | 19% |
| Delayed | 117 | 0 | 117 | 0 | 19 | NA | 14% | |
| Chanatarojanasiri 2018 [149] | Early | 12 | 12 | 0 | 0 | NA | 27.5 days | 8.33% |
| Delayed | 23 | 23 | 0 | 0 | NA | 31 days | 7.70% | |
| Trikudanathan 2018 [150] | Early | 76 | 49 | 24 | 5 | NA | 37 days | 13.20% |
| Delayed | 117 | 95 | 21 | 7 | NA | 26 days | 4.30% | |
| Oblizajek 2020 [151] | Early | 19 | 19 | 0 | 0 | NA | 26 days | 19.00% |
| Delayed | 19 | 19 | 0 | 0 | NA | 6 days | 5.00% | |
| Ganaie 2021 [152] | Early | 24 | 0 | 24 | 0 | NA | NA | NA |
| Delayed | 16 | 0 | 16 | 0 | NA | NA | NA | |
| Gupta 2021 [153] | Early | 90 | 0 | 90 | 0 | NA | NA | NA |
| Delayed | 54 | 0 | 54 | 0 | NA | NA | NA | |
| Khan 2021 [154] | Early | 16 | 16 | 0 | 0 | NA | NA | 5.23% |
| Delayed | 172 | 172 | 0 | 0 | NA | NA | 18.75% | |
| Rana 2021 [155] | Early | 34 | 34 | 0 | 0 | 15 | NA | 5.70% |
| Delayed | 136 | 136 | 0 | 0 | 0 | NA | 0.00% | |
| Boxhoorn 2021 [156] | Early | 55 | NA | NA | NA | 13 | 59 days | 13% |
| Delayed | 49 | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 51 days | 10% | |
| Jagielski 2022 [157] | Early | 25 | 25 | 0 | 0 | NA | NA | 4% |
| Delayed | 46 | 46 | 0 | 0 | NA | NA | 4% | |
| Lu 2022 [158] | Early | 43 | 0 | 43 | 0 | 19 | 40.28 (median) | 14% |
| Delayed | 55 | 0 | 55 | 0 | 10 | 47.76 (median) | 11% | |
| Zhang 2022 [159] | Early | 100 | 0 | 100 | NA | 57 | 43 days | 35% |
| Delayed | 31 | 0 | 31 | NA | 14 | 40 days | 32.30% | |
| Bhatia 2023 [160] | Early | 74 | 0 | 74 | 0 | 0 | 28 days | 24.30% |
| Delayed | 74 | 0 | 74 | 0 | 0 | 29.4 days | 18.90% | |
| Ali 2024 [161] | Early | 349 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 6.0 (median) | 1.10% |
| Delayed | 375 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 16.0 (median) | 4.30% |
| Indications | Advantages | Disadvantages | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Endoscopic management |
|
|
|
| Percutaneous management |
|
|
|
| Surgical management |
|
|
|
| First Author, Year, Type of Study | Number of Patients | Median Age | Male n (%) | APACHE | Time of Intervention (Median) | Organ Failure | Bleeding | Perforation of a Visceral Organ | Pancreatic Fistula | Death n (%) | Long Term Complications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| van Santvoort 2010 (PANTER), prospective [210] | |||||||||||
| OPN | 45 | 57.4 | 33 (72%) | 15 | NA | 18 | 10 | 10 | 17 | 7 (16%) | 43 |
| Minimally invasive step-up approach | 43 | 57.6 | 31 (73%) | 14 | 5 | 7 | 6 | 12 | 8 (19%) | 13 | |
| Gomatos 2016, retrospective [223] | |||||||||||
| OPN | 120 | 58.5 | 86 (71.7%) | 8 | 24 days | 56 | NA | NA | NA | 28 (23.3%) | NA |
| MARPN | 274 | 59 | 172 (62.8%) | 8 | 29.5 days | 42 | 42 (15.3%) | ||||
| van Brunschot 2018, retrospective [222] | |||||||||||
| OPN | 47 | 60 | 29 (61.7%) | 10 | 41 days | 7 | 10 | 8 | 13 | 6 (12.7%) | 14 |
| Endoscopy | 51 | 63 | 34 (66.6%) | 9 | 39.5 days | 9 | 11 | 4 | 2 | 9 (17.6%) | 16 |
| Martinez 2019, retrospective [224] | |||||||||||
| OPN | 34 | 55.9 | 24 (70.6%) | 10.5 days | 16 | NA | NA | NA | 7 (20.6%) | 10 | |
| Endoscopy | 22 | 53.3 | 16 (72.7%) | 38 days | 2 | 0 | 15 | ||||
| Luckhurst 2020, retrospective [225] | |||||||||||
| OPN | 88 | 56 | 64 (73%) | 9 | 42 days | NA | 8 | NA | 61 | 8 (9%) | 35 |
| Minimally invasive step-up approach | 91 | 54 | 62 (68%) | 10 | 36 days | 17 | 59 | 2 (2%) | 42 | ||
| Ning 2024, prospective [226] | |||||||||||
| OPN | 75 | 48 | 56 (74.6%) | NA | 32 | 26 | 25 | 33 | 27 (36%) | NA | |
| Minimally invasive step-up approach | 245 | 48 | 178 (72.7%) | 76 | 42 | 21 | 107 | 47 (19.2%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dumitrascu, I.; Zarnescu, N.O.; Zarnescu, E.C.; Pahomeanu, M.R.; Constantinescu, A.; Minca, D.G.; Costea, R.V. Acute Necrotizing Pancreatitis—Advances and Challenges in Management for Optimal Clinical Outcomes. Medicina 2025, 61, 1186. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61071186
Dumitrascu I, Zarnescu NO, Zarnescu EC, Pahomeanu MR, Constantinescu A, Minca DG, Costea RV. Acute Necrotizing Pancreatitis—Advances and Challenges in Management for Optimal Clinical Outcomes. Medicina. 2025; 61(7):1186. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61071186
Chicago/Turabian StyleDumitrascu, Ioana, Narcis Octavian Zarnescu, Eugenia Claudia Zarnescu, Mihai Radu Pahomeanu, Alexandru Constantinescu, Dana Galieta Minca, and Radu Virgil Costea. 2025. "Acute Necrotizing Pancreatitis—Advances and Challenges in Management for Optimal Clinical Outcomes" Medicina 61, no. 7: 1186. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61071186
APA StyleDumitrascu, I., Zarnescu, N. O., Zarnescu, E. C., Pahomeanu, M. R., Constantinescu, A., Minca, D. G., & Costea, R. V. (2025). Acute Necrotizing Pancreatitis—Advances and Challenges in Management for Optimal Clinical Outcomes. Medicina, 61(7), 1186. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61071186







