Fetuin-A Can Assess the Severity of Alcohol-Related Liver Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Assessment of Disease Severity in Patients with ALD
2.4. Serum Fetuin-A Measurement
2.5. Statistical Analysis
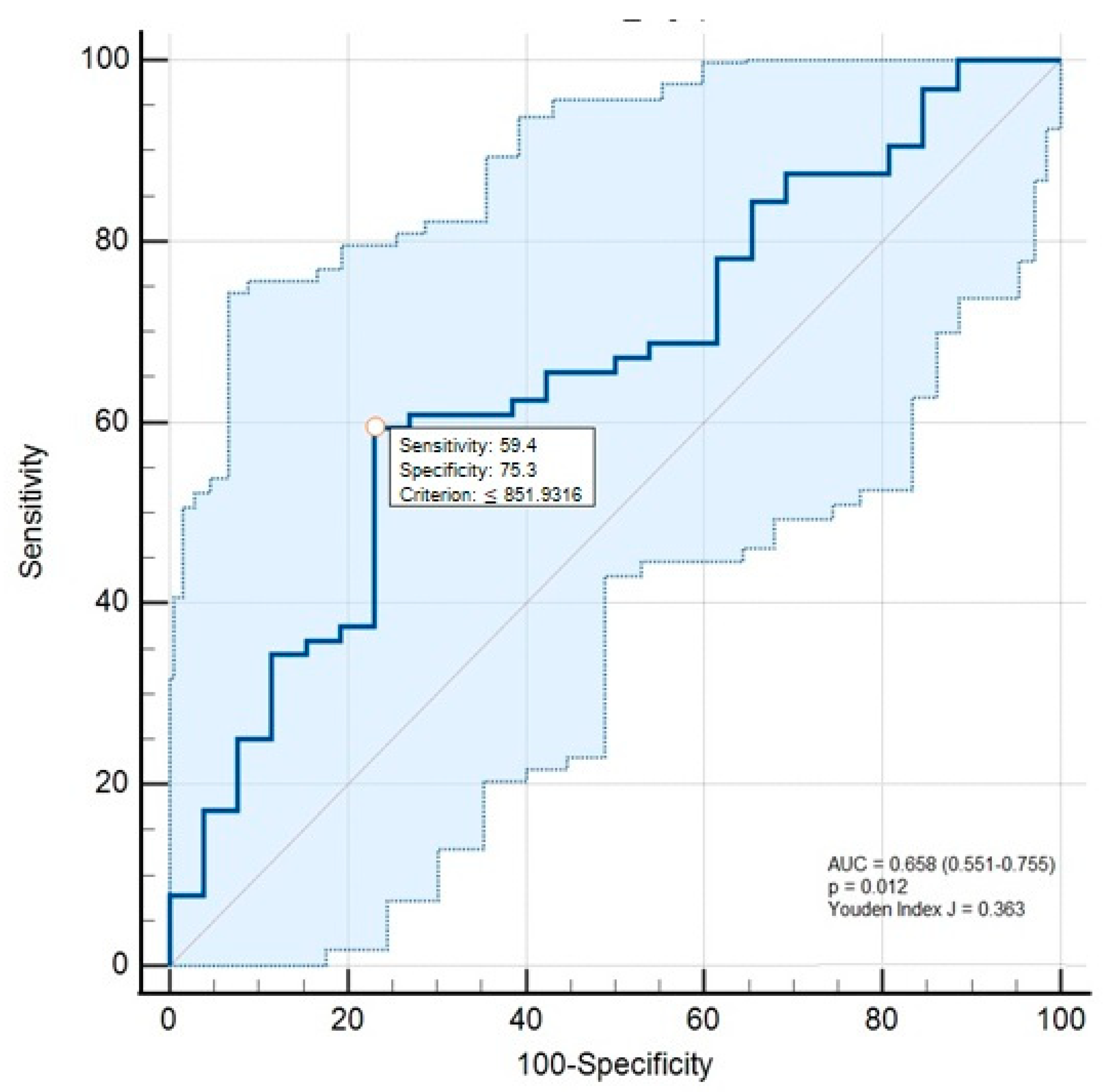
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kirpich, I.A.; Warner, D.R.; Feng, W.; Joshi-Barve, S.; McClain, C.J.; Seth, D.; Zhong, W.; Zhou, Z.; Osna, N.A.; Kharbanda, K.K. Mechanisms, biomarkers and targets for therapy in alcohol-associated liver injury: From Genetics to nutrition: Summary of the ISBRA 2018 symposium. Alcohol 2020, 83, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackowiak, B.; Fu, Y.; Maccioni, L.; Gao, B. Alcohol-associated liver disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2024, 134, e176345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramaniyan, V.; Chakravarthi, S.; Jegasothy, R.; Seng, W.Y.; Fuloria, N.K.; Fuloria, S.; Hazarika, I.; Das, A. Alcohol-associated liver disease: A review on its pathophysiology, diagnosis and drug therapy. Toxicol. Rep. 2021, 8, 376–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, Y.; Xu, C.; Lin, J.; Li, Y. Role of Hepatokines in Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. J. Transl. Int. Med. 2019, 7, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dogru, T.; Genc, H.; Tapan, S.; Aslan, F.; Ercin, C.N.; Ors, F.; Kara, M.; Sertoglu, E.; Karslioglu, Y.; Bagci, S.; et al. Plasma fetuin-A is associated with endothelial dysfunction and subclinical atherosclerosis in subjects with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin. Endocrinol. 2013, 78, 712–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahnen-Dechent, W.; Schinke, T.; Trindl, A.; Müller-Esterl, W.; Sablitzky, F.; Kaiser, S.; Blessing, M. Cloning and targeted deletion of the mouse fetuin gene. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 31496–31503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etienne, Q.; Lebrun, V.; Komuta, M.; Navez, B.; Thissen, J.P.; Leclercq, I.A.; Lanthier, N. Fetuin-A in Activated Liver Macrophages Is a Key Feature of Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis. Metabolites 2022, 12, 625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalabay, L.; Szalay, F.; Nemesánszky, E.; Telegdy, L.; Jakab, L.; Romics, L. Decreased serum alfa2-HS-glycoprotein concentration in patients with primary biliary cirrhosis. J. Hepatol. 1997, 26, 1426–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalabay, L.; Jakab, L.; Prohászka, Z.; Füst, G.; Benkö, Z.; Telegdy, L.; Lörincz, Z.; Závodszky, P.; Arnaud, P.; Fekete, B. Human fetuin/alpha2HS-glycoprotein level as a novel indicator of liver cell function and short-term mortality in patients with liver cirrhosis and liver cancer. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2002, 14, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalabay, L.; Prohászka, Z.; Füst, G.; Benkõ Zs, T.L.; Szalay, F.; Tóth, K.; Gráf, L.; Jakab, L.; Pozsonyi, T.; Arnaud, P.; et al. Human fetuin/α2HS-glycoprotein levels in sera of patients with liver disease. In Liver Cirrhosis: New Research; Chen, T.M., Ed.; Nova Science: New York, NY, USA, 2005; pp. 63–75. [Google Scholar]
- Kalabay, L.; Nemesánszky, E.; Csepregi, A.; Pusztay, M.; Dávid, K.; Horváth, G.; Ibrányi, E.; Telegdy, L.; Pár, A.; Bíró, A.; et al. Paradoxical alteration of acute-phase protein levels in patients with chronic hepatitis C treated with IFN-alpha2b. Int. Immunol. 2004, 16, 51–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ix, J.H.; Biggs, M.L.; Mukamal, K.J.; Kizer, J.R.; Zieman, S.J.; Siscovick, D.S.; Mozzaffarian, D.; Jensen, M.K.; Nelson, L.; Ruderman, N.; et al. Association of fetuin-a with incident diabetes mellitus in community-living older adults: The cardiovascular health study. Circulation 2012, 125, 2316–2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Icer, M.A.; Yıldıran, H. Effects of fetuin-A with diverse functions and multiple mechanisms on human health. Clin. Biochem. 2021, 88, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ley, S.H.; Sun, Q.; Jimenez, M.C.; Rexrode, K.M.; Manson, J.E.; Jensen, M.K.; Rimm, E.B.; Hu, F.B. Association between alcohol consumption and plasma fetuin-A and its contribution to incident type 2 diabetes in women. Diabetologia 2014, 57, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kalabay, L.; Gráf, L.; Vörös, K.; Jakab, L.; Benko, Z.; Telegdy, L.; Fekete, B.; Prohászka, Z.; Füst, G. Human serum fetuin A/alpha2HS-glycoprotein level is associated with long-term survival in patients with alcoholic liver cirrhosis, comparison with the Child-Pugh and MELD scores. BMC Gastroenterol. 2007, 7, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Prystupa, A.; Dąbrowska, A.; Sak, J.J.; Tarach, J.; Toruń-Jurkowska, A.; Lachowska-Kotowska, P.; Dzida, G. Concentrations of fetuin-A, osteoprotegerin and α-Klotho in patients with alcoholic liver cirrhosis. Exp. Ther. Med. 2016, 12, 3464–3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Crabb, D.W.; Bataller, R.; Chalasani, N.P.; Kamath, P.S.; Lucey, M.; Mathurin, P.; McClain, C.; McCullough, A.; Mitchell, M.C.; Morgan, T.R.; et al. Standard Definitions and Common Data Elements for Clinical Trials in Patients With Alcoholic Hepatitis: Recommendation From the NIAAA Alcoholic Hepatitis Consortia. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 785–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- First, M.B. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, 5th edition, and clinical utility. J. Nerv. Ment. Dis. 2013, 201, 727–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallet-Pichard, A.; Mallet, V.; Nalpas, B.; Verkarre, V.; Nalpas, A.; Dhalluin-Venier, V.; Fontaine, H.; Pol, S. FIB-4: An inexpensive and accurate marker of fibrosis in HCV infection. comparison with liver biopsy and fibrotest. Hepatology 2007, 46, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddrey, W.C.; Boitnott, J.K.; Bedine, M.S.; Weber, F.L., Jr.; Mezey, E.; White, R.I., Jr. Corticosteroid therapy of alcoholic hepatitis. Gastroenterology 1978, 75, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leise, M.D.; Kim, W.R.; Kremers, W.K.; Larson, J.J.; Benson, J.T.; Therneau, T.M. A revised model for end-stage liver disease optimizes prediction of mortality among patients awaiting liver transplantation. Gastroenterology 2011, 140, 1952–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pugh, R.N.; Murray-Lyon, I.M.; Dawson, J.L.; Pietroni, M.C.; Williams, R. Transection of the oesophagus for bleeding oesophageal varices. Br. J. Surg. 1973, 60, 646–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Cantero, J.; Martin-Rodriguez, J.L.; Gonzalez-Cantero, A.; Arrebola, J.P.; Gonzalez-Calvin, J.L. Insulin resistance in lean and overweight non-diabetic Caucasian adults: Study of its relationship with liver triglyceride content, waist circumference and BMI. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0192663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jezequel, M.; Seta, N.S.; Corbic, M.M.; Feger, J.M.; Durand, G.M. Modifications of concanavalin A patterns of alpha 1-acid glycoprotein and alpha 2-HS glycoprotein in alcoholic liver disease. Clin. Chim. Acta 1988, 176, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cholongitas, E.; Papatheodoridis, G.V.; Vangeli, M.; Terreni, N.; Patch, D.; Burroughs, A.K. Systematic review: The model for end-stage liver disease--should it replace Child-Pugh’s classification for assessing prognosis in cirrhosis? Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2005, 22, 1079–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, B.; Yun, J.M.; Park, S.; Shin, D.W.; Lee, T.H.; Yang, H.K.; Ahn, E.; Lee, H.; Park, J.H.; Cho, B. Prediction of future hepatocellular carcinoma incidence in moderate to heavy alcohol drinkers with the FIB-4 liver fibrosis index. Cancer 2015, 121, 3818–3825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Alcohol-Associated Steatotic Liver Group (n = 22) | Alcohol-Associated Hepatitis Group (n = 15) | Alcohol-Associated Cirrhosis Group (n = 27) | Healthy Control Group (n = 26) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male, n (%) | 22 (100) c | 14 (93.33) | 25 (92.59) | 21 (77.78) c | <0.001 3,* |
| Age (years), mean ± SD | 48.41 ± 9.54 e | 47.07 ± 8.84 d | 60.3 ± 7.51 d,e | 55.26 ± 11.5 | <0.001 1,* |
| Duration of alcohol intake (years), median (IQR) | 25.5 ± 12.18 | 24.13 ± 10.2 d | 36.59 ± 12.79 d | - | <0.001 2,* |
| BMI (kg/m2), mean ± SD | 28.48 ± 2.58 e | 30.8 ± 4.07 b,d | 28.9 ± 3.73 d,e | 26.01 ± 3.72 b | <0.001 1,* |
| Presence of hepatic steatosis, n (%) | 22 (100) e | 14 (93.3) d | 4 (14.8) d,e | - | <0.001 3,* |
| Presence of ascites, n (%) | - | 6 (40) d | 12 (44.44) d,e | - | <0.001 3,* |
| Presence of esophageal and/or gastric varices, n (%) | 0 (0) e,f | 3 (20) d,f | 16 (59.3) d,e | <0.001 3,* | |
| Fibrosis-4 index, median (IQR) | 1.23 (0.89) e,f | 6.46 (5.06) b,d,f | 5.38 (3.56) a,d,e | 1.13 (0.46) a,b | <0.001 2,* |
| MELD-Na score, median (IQR) | - | 16.2 ± 6.56 | 14.71 ± 7.42 | - | 0.401 2 |
| MDF, median (IQR) | - | 14.90 (17.2) | - | - | - |
| Child–Pugh class, n (%) A B C | - | - | 10 (37.04) 8 (29.63) 9 (33.33) | - | N/A |
| Child–Pugh score, median (IQR) | - | - | 7.96 (5) | - | N/A |
| Bilirubin (mg/dl), median (IQR) | 0.67 (0.44) e,f | 4.49 (2.11) b,d,f | 2.36 (2.1) a,d,e | 0.73 (0.61) a,b | <0.001 2,* |
| Albumin (mg/dl), median (IQR) | 4.30 (0.65) c,f | 3.85 (0.90) b,d,f | 3.16 (1.80) a,d | 4.62 (0.65) a,b,c | <0.001 2,* |
| CRP (mg/L), median (IQR) | 4.95 (10.36) c,f | 13.27 (24.32) b,f | 7.08 (18.62) a | 1.38 (2.64) a,b,c | <0.001 2,* |
| Serum fetuin-A (mg/L), median(IQR) | 1484.61 (858.16) e,f | 906.75 (383.95) d,f | 670.72 (412.36) a,d,e | 1553.95 (692.8) a | <0.001 2,* |
| Serum Fetuin-A (mg/L) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | Median (IQR) | p | |||
| Alcohol-associated hepatitis (n = 15) | Hepatic steatosis | Absent | 1 | 637 (N/A) | N/A |
| Present | 14 | 826.58 (365.97) | |||
| Ascites | Absent | 9 | 822.06 (379.36) | 0.724 1 | |
| Present | 6 | 824.5 (384.21) | |||
| Esophagus and/or gastric varices | Absent | 12 | 885.48 (393.26) | 0.386 1 | |
| Present | 3 | 700.41 (N/A) | |||
| Alcohol-associated cirrhosis (n = 27) | Hepatic steatosis | Absent | 23 | 698.11 (383.50) | 0.733 1 |
| Present | 4 | 767.29 (669.50) | |||
| Ascites | Absent | 15 | 700.71 (349.1) | 0.143 1 | |
| Present | 12 | 498.25 (510.24) | |||
| Esophagus and/or gastric varices | Absent | 11 | 812.95 (536.33) | 0.026 1 | |
| Present | 16 | 603.35 (393.2) | |||
| Child–Pugh Classification | A a | 10 | 844.71 (412.31) | 0.002 2,* | |
| B b | 8 | 740.52 (293.8) | |||
| C a,b | 9 | 356.82 (325.21) | |||
| Serum Fetuin-A | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CRP | Child–Pugh Score | MELD-Na | MDF | Fibrosis-4 Score | ||
| Alcohol-associated steatotic liver (n = 22) | rho | −0.121 | - | - | - | 0.193 |
| p | 0.590 | - | - | - | 0.389 | |
| Alcohol-associated hepatitis (n = 15) | rho | 0.021 | - | −0.621 * | −0.399 | 0.042 |
| p | 0.940 | - | 0.013 * | 0.141 | 0.881 | |
| Alcohol-associated cirrhosis (n = 27) | rho | −0.569 * | −0.671 * | −0.742 * | - | −0.330 |
| p | 0.002 * | <0.001 * | <0.001 * | - | 0.092 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Salmanoğlu, M.; Küçük, İ.; Baş, S. Fetuin-A Can Assess the Severity of Alcohol-Related Liver Disease. Medicina 2025, 61, 1147. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61071147
Salmanoğlu M, Küçük İ, Baş S. Fetuin-A Can Assess the Severity of Alcohol-Related Liver Disease. Medicina. 2025; 61(7):1147. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61071147
Chicago/Turabian StyleSalmanoğlu, Musa, İrfan Küçük, and Süleyman Baş. 2025. "Fetuin-A Can Assess the Severity of Alcohol-Related Liver Disease" Medicina 61, no. 7: 1147. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61071147
APA StyleSalmanoğlu, M., Küçük, İ., & Baş, S. (2025). Fetuin-A Can Assess the Severity of Alcohol-Related Liver Disease. Medicina, 61(7), 1147. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61071147






