Association Between Hearing Loss and Systemic Small-Vessel Vasculitis: Audiological Aspects Across Disease Types
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. World Report on Hearing: Executive Summary (Electronic Version); World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021; ISBN 978-92-4-002157-0. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, F.R.; Yaffe, K.; Xia, J.; Xue, Q.-L.; Harris, T.B.; Purchase-Helzner, E.; Satterfield, S.; Ayonayon, H.N.; Ferrucci, L.; Simonsick, E.M.; et al. Hearing loss and cognitive decline in older adults. JAMA Intern. Med. 2013, 173, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, F.R.; Metter, E.J.; O’bRien, R.J.; Resnick, S.M.; Zonderman, A.B.; Ferrucci, L. Hearing loss and incident dementia. Arch. Neurol. 2011, 68, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.-M.; Zhang, X.; Hoffman, H.J.; Cotch, M.F.; Themann, C.L.; Wilson, M.R. Hearing impairment associated with depression in US adults, National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2005–2010. JAMA Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2014, 140, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancini, P.; Atturo, F.; Di Mario, A.; Portanova, G.; Ralli, M.; De Virgilio, A.; de Vincentiis, M.; Greco, A. Hearing loss in autoimmune disorders: Prevalence and therapeutic options. Autoimmun. Rev. 2018, 17, 644–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralli, M.; D’Aguanno, V.; Di Stadio, A.; De Virgilio, A.; Croce, A.; Longo, L.; Greco, A.; Vincentiis, M. Audiovestibular Symptoms in Systemic Autoimmune Diseases. J. Immunol. Res. 2018, 2018, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Vambutas, A.; Pathak, S. AAO: Autoimmune and autoinflammatory (disease) in otology: What is new in immune-mediated hearing loss. Laryngoscope Investig. Otolaryngol. 2016, 1, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossini, B.A.A.; Penido, N.O.; Munhoz, M.S.L.; Bogaz, E.A.; Curi, R.S. Sudden sensorioneural hearing loss and autoimmune systemic diseases. Int. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2017, 21, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greco, A.; Marinelli, C.; Fusconi, M.; Macri, G.F.; Gallo, A.; De Virgillio, A.; Zambetti, G.; Vincentiis, M. Clinic manifestations in granulomatosis with polyangiitis. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2016, 29, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, F.; Salviz, M.; Domond, H.; Nadol, J.B. Otopathology of vasculitis in granulomatosis with polyangitis. Otol. Neurotol. 2015, 36, 1657–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsirves, G.T.; Voulgari, P.V.; Pelechas, E.; Asimakopoulos, A.; Drosos, A. Cochlear involvement in patients with systemic autoimmune rheumatic diseases: A clinical and laboratory comparative study. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2019, 276, 2419–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takagi, D.; Nakamaru, Y.; Maguchi, S. Otologic manifestations of Wegener’s granulomatosis. Laryngoscope 2002, 112, 1684–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langford, C.A. Vasculitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 125, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahne, T.; Plontke, S.K.; Keyßer, G. Vasculitis and the ear: A literature review. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2020, 32, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias-Gamarra, A.; Penaranda, E.; Espinosa, L.R. Vasculitides throughout history and their clinical treatment today. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2011, 13, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, T.H.; Paparella, M.M.; Schachern, P.A. Systemic vasculitis: A temporal bone histopathologic study. Laryngoscope 1989, 99, 600–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillevin, L.; Pagnoux, C.; Guilpain, P. Classification of systemic vasculatides. Presse Med. 2007, 36, 845–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennette, J.C.; Falk, R.J.; Bacon, P.A.; Basu, N.; Cid, M.C.; Ferrario, F.; Flores-Suarez, L.F.; Gross, W.L.; Guillevin, L.; Hagen, E.C.; et al. 2012 Revised International Chapel Hill Consensus Conference Nomenclature of Vasculitides. Arthritis Rheum. 2013, 65, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadonienė, J. Vaskulitai ir Kitos Retos Reumatinės Būklės; Vilnius University: Vilnius, Lithuania, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Suresh, E. Diagnostic approach to patients with suspected vasculitis. Postgrad. Med. J. 2006, 82, 483–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lidar, M.; Carmel, E.; Kronenberg, Y.; Langevitz, P. Hearing loss as the presenting feature of systemic vasculitis. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2007, 1107, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahne, T.; Clauß, F.; Plontke, S.K.; Keyßer, G. Prevalence of Hearing Impairment in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis, Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis (GPA, Wegener’s Granulomatosis), or Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Clin. Rheumatol. 2017, 36, 1501–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, M.U.; Pandian, V.; Masood, H.; Diaz, D.A.; Varela, V.; Dávalos-Balderas, A.J.; Parra-Cardenas, M.; Seo, P.; Francis, H.W. Spectrum of immune–mediated inner ear disease and cochlear implant results. Laryngoscope 2012, 122, 2557–2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jerger, J.F. Clinical experience with impedence audiometry. Arch. Otolaryngol. 1970, 92, 311–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kramer, S. Audiology: Science to Practice; Plural Publishing: San Diego, CA, USA, 2008; pp. 111–174. [Google Scholar]
- Vainutienė, V.; Ivaška, J.; Kardelis, V.; Ivaškienė, T.; Lesinskas, E. Speech audiometry: The development of Lithuanian bisyllabic phonemically balanced word lists for evaluation of speech recognition. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 2897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawson, G.; Peterson, M. Speech Audiometry; Plural Publishing: San Diego, CA, USA, 2011; pp. 27–45. [Google Scholar]
- Felicetti, M.; Cazzador, D.; Padoan, R. Ear, nose and throat involvement in granulomatosis with polyangiitis: How it present and how it determines disease severity and long-term outcomes. Clin. Rheumatol. 2018, 37, 1075–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galarza-Delgado, D.A.; Villegas Gonzalez, M.J.; Riega Torres, J.; Soto-Galindo, G.A.; Mendoza Flores, L.; Trevino Gonzalez, J.L. Early Hearing Loss Detection in Rheumatoid Arthritis and Primary Sjogren Syndrome Using Extended High Frequency Audiometry. Clin. Rheumatol. 2018, 37, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hervier, B.; Bordure, P.; Masseau, A.; Calais, C.; Agard, C.; Hamidou, M. Auto-immune sensorineural deafness: Physiopathology and therapeutic approach. Rev. Med. Interne 2010, 31, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildirim, A.; Surucu, G.; Dogan, S.; Karabiber, M. Relationship between disease activity and hearing impairment in patients with rheumatoid arthritis compared with controls. Clin. Rheumatol. 2016, 35, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrup, L.; Luxon, M. Immune–mediated inner–ear dis–orders in neuro–otology. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2006, 19, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruckenstein, M.J. Autoimmune inner ear disease. Curr. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2004, 12, 426–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, G.B.; Barna, B.P.; Kinney, S.E.; Calabrese, L.H.; Nalepa, N.J. Clinical diagnosis of immune inner–eardisease. Laryngoscope 1988, 98, 251–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robson, J.; Doll, H.; Suppiah, R.; Flossmann, O.; Harper, L.; Höglund, P.; Jayne, D.; Mahr, A.; Westman, K.; Luqmani, R. Damage in the anca–associated vasculitides: Long–term data from the European vasculitis study group (EUVAS) therapeutic trials. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.R.; Niparko, J.K.; Ferrucci, L. Hearing loss prevalence in the United States. Arch. Intern. Med. 2011, 171, 1851–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamasoba, T.; Lin, F.R.; Someya, S.; Kashio, A.; Sakamoto, T.; Kondo, K. Current concepts in age–related hearing loss: Epidemiology and mechanistic pathways. Hear. Res. 2013, 303, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grover, R.A.; Grover, R.S. Missed Otological Presentation of Wegener’s Granulomatosis: A Case. Indian J. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2022, 74, 492–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djeric, D.; Peric, A.; Pavlocic, B.; Folic, M.; Bontic, A.; Baralic, M.; Pavlovic, J.; Radovic, M. Otitis media with effusion as an initial manifestation of granulomatosis with polyangiitis. SAGE Open Med. Case Rep. 2021, 29, 2050313X211036006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braga, F.L.V.; de Carvalho, G.M.; Guimarães, A.C.; Scaramussa, L.; Gusmão, R.J. Otolaryngological manifestations of Wegener’s disease. Acta Otorrinolaringol. Esp. 2013, 64, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicklasson, B.; Stangeland, N. Wegener’s granulomatosis presenting as otitis media. J. Laryngol. Otol. 1982, 96, 277–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vainutienė, V.; Ivaška, J.; Dadonienė, J.; Beleškienė, V.; Ivaškienė, T.; Lesinskas, E. Audiological Manifestations in Patients with Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis. Medicina 2024, 60, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kempf, H.G. Ear involvement in Wegener’s granulomatosis. Clin. Otolaryngol. Allied Sci. 1989, 14, 451–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornton, M.A.; O’Sullivan, T.J. Otological Wegener’s granulomatosis: A diagnostic dilemma. Clin. Otolaryngol. Allied Sci. 2000, 25, 433–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safavi Naini, A.; Ghorbani, J.; Montazer Lotfe Elahi, S.; Beigomi, M. Otologic Manifestations and Progression in Patients with Wegener’s granulomatosis: A Survey in 55 Patients. Iran J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2017, 29, 327–331. [Google Scholar]
- Wali, J.P.; Wig, N.; Handa, R. Otological manifestations of Wegener’s granulomatosis. Indian J. Otol. 1998, 4, 29–36. [Google Scholar]
- Bakthavachalam, S.; Driver, M.S.; Cox, C.; Spiegel, J.H.; Grundfast, K.M.; Merkel, P.A. Hearing loss in Wegener’s granulomatosis. Otol. Neurotol. 2004, 25, 833–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seccia, V.; Fortunato, S.; Cristofani-Mencacci, L.; Dallan, I.; Casani, A.P.; Latorre, M.; Paggiaro, P.; Bs, M.L.B.; Sellari-Franceschini, S.; Baldini, C. Focus on Audiologic Impairment in Eosinophilic Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis. Laryngoscope 2016, 126, 2792–2797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciorba, A.; Corazzi, V.; Bianchini, C.; Aimoni, C.; Pelucchi, S.; Skarżyński, P.H.; Hatzopoulos, S. Autoimmune Inner Ear Disease (AIED): A Diagnostic Challenge. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2018, 32, 2058738418808680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koike, H.; Furukawa, S.; Mouri, N.; Fukami, Y.; Iijima, M.; Katsuno, M. Early ultrastructural lesions of anti–neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody– versus complement–associated vasculitis. Neuropathology 2022, 42, 420–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralli, M.; Greco, A.; Falasca, V.; Altissimi, G.; Tombolini, M.; Turchetta, R.; Fazio, S.; Vincentiis, M.; Cianfrone, G. Recovery from repeated sudden hearing loss in a patient with Takayasu’s arteritis treated with hyperbaric oxygen therapy: The first report in the literature. Case Rep. Otolaryngol. 2017, 2017, 3281984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franz, L.; Frosolini, A.; Parrino, D.; Lovato, A.; de Filippis, C.; Marioni, G. Ototoxicity of immunosuppressant drugs: A systematic review. J. Int. Adv. Otol. 2022, 18, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynard, P.; Thai–Van, H. Drug–induced hearing loss: Listening to the latest advances. Therapie 2024, 79, 283–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
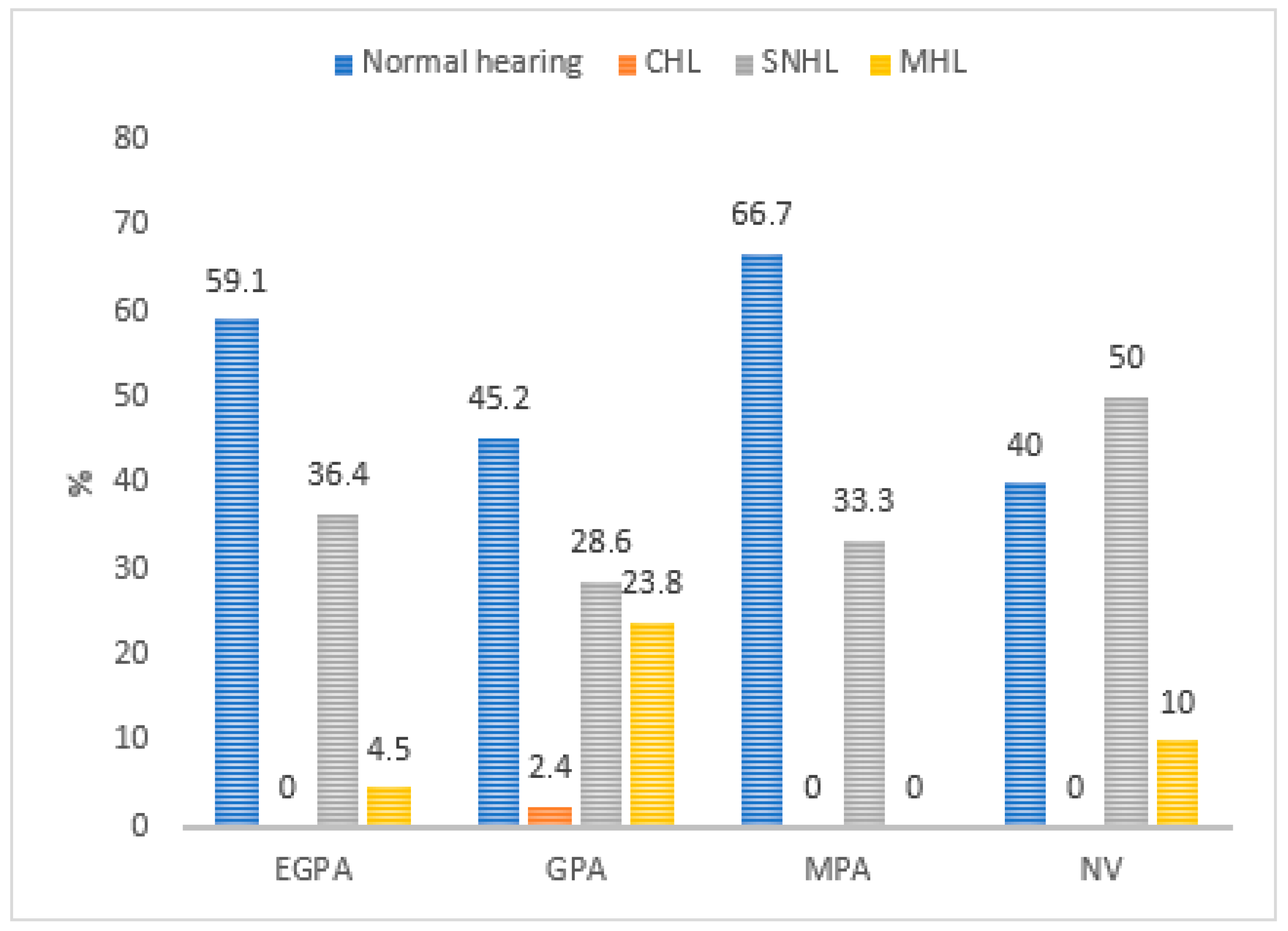
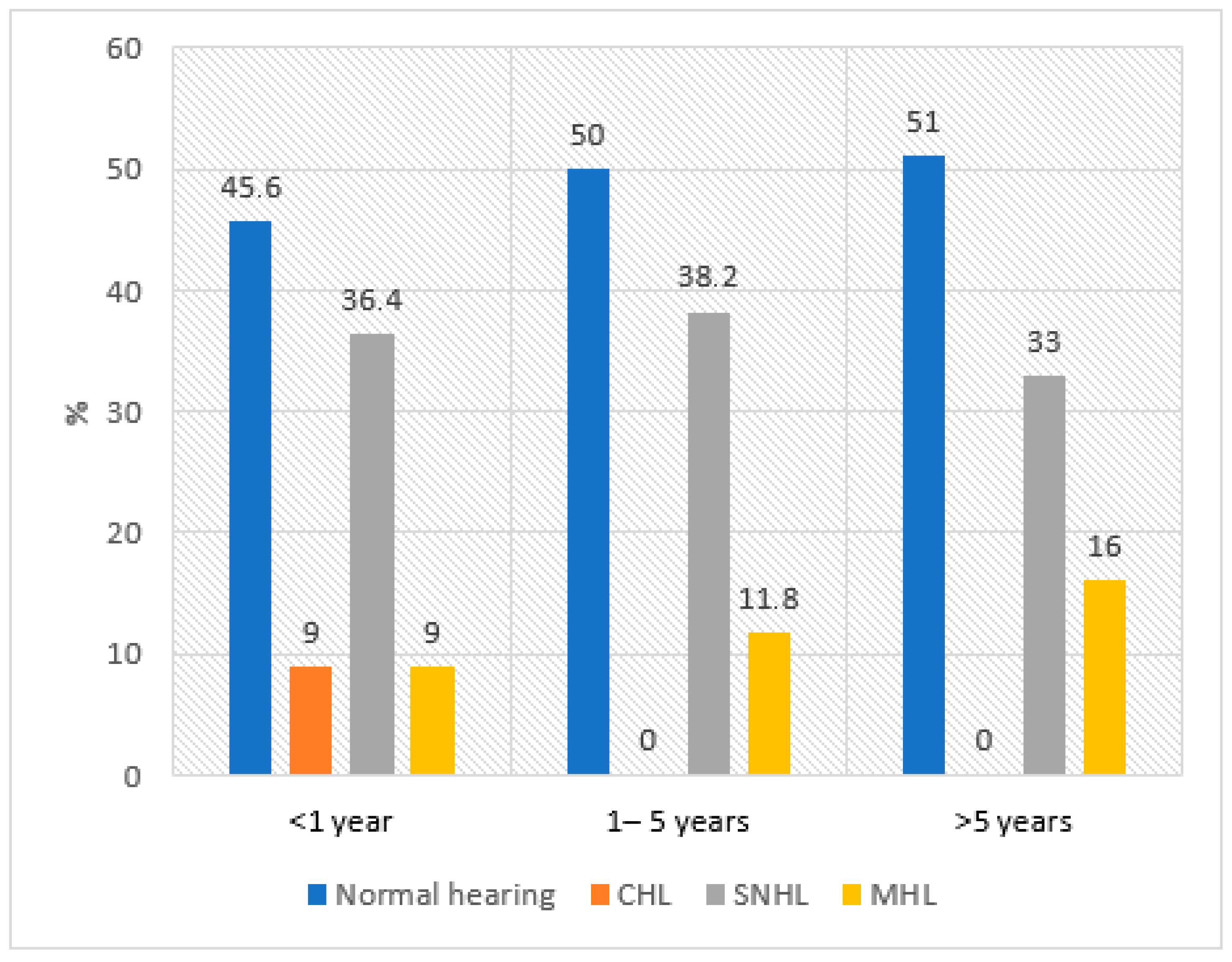
| Systemic Vasculitis (n = 40 Participants) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Age, Average ±SD | 48.9 ± 11.47 | |
| Sex | Female | 21 (52.5%) |
| Male | 19 (47.5%) | |
| Systemic vasculitis disease | Granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA) | 21 (52.5%) |
| Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (EGPA) | 11 (27.5%) | |
| Necrotizing vasculopathy (NV) | 5 (12.5%) | |
| Microscopic polyangiitis (MPA) | 3 (7.5%) | |
| Disease duration | <1 year | 11 (27.5%) |
| 1–5 years | 17 (42.5%) | |
| >5 years | 12 (30.0%) | |
| ANCA | Positive | 27 (67.5%) |
| Negative | 13 (32.5%) | |
| Medication usage (ever) | Glucocorticoids | 9 (22.5%) |
| Glucocorticoids and immunosuppressants | 20 (50.0%) | |
| Glucocorticoids, immunosuppressants and biologicals | 11 (27.5%) | |
| Organ involvement (ever) | Lung | 30 (75.0%) |
| Ear, nose, throat | 29 (72.0%) | |
| Kidney | 13 (32.5%) | |
| Nervous system | 8 (20.0%) | |
| Skin | 4 (10.0%) | |
| Musculoskeletal system | 3 (7.5%) | |
| Eye | 1 (2.5%) | |
| Otoscopy | Normal findings | 82.5% |
| Exostoses | 6.6% | |
| Retracted tympanic membrane | 3.8% | |
| Immobile tympanic membrane | 1.3% | |
| Postoperative changes in tympanic membrane | 1.3% | |
| Presence of ventilation tube | 1.3% | |
| Tympanometry | A type | 85.0% |
| B type | 11.3% | |
| C type | 0.0% | |
| Not recorded | 3.7% | |
| Pure tone audiometry | Normal hearing | 50.0% |
| Sensorineural hearing loss | 33.8% | |
| Mixed hearing loss | 13.7% | |
| Conductive hearing loss | 2.5% |
| Frequency | EGPA Group (dB) (n = 22 Ears) | GPA Group (dB) (n = 42 Ears) | MPA Group (dB) (n = 6 Ears) | NV Group (dB) (n = 10 Ears) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | p Value | |
| 125 Hz | 13.4 ±12.27 | 20.2 ± 14.27 | 5.0 ± 0.00 | 12.0 ± 5.70 | 0.055 |
| 250 Hz | 14.5 ± 14.74 | 20.5 ± 16.42 | 5.0 ± 0.00 | 10.0 ± 3.54 | 0.060 |
| 500 Hz | 15.5 ± 17.39 | 24.5 ± 19.74 | 11.7 ± 7.64 | 10.0 ± 3.54 | 0.156 |
| 1000 Hz | 15.0 ± 14.83 | 25.2 ± 21.48 | 16.7 ± 7.64 | 15.0 ± 7.91 | 0.360 |
| 2000 Hz | 20.2 ± 17.36 | 26.2 ± 21.56 | 11.7 ± 2.89 | 25.0 ± 14.58 | 0.641 |
| 4000 Hz | 29.1 ± 23.11 | 34.8 ± 24.00 | 16.7 ± 12.58 | 34.0 ± 21.62 | 0.537 |
| 8000 Hz | 35.9 ± 30.81 | 37.1 ± 30.68 | 28.3 ± 15.28 | 45.0 ± 28.28 | 0.795 |
| EGPA Group (dB) (n = 22 Ears) | GPA Group (dB) (n = 42 Ears) | MPA Group (dB) (n = 6 Ears) | NV Group (dB) (n = 10 Ears) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | p Value | |
| SDT (dB) | 21.8 ±16.92 | 31.9 ± 22.05 | 15.0 ± 13.23 | 25.0 ± 11.18 | 0.352 |
| SRT (dB) | 35.9 ± 21.66 | 42.4 ± 21.19 | 25.0 ± 13.23 | 32.0 ± 10.37 | 0.400 |
| WRS (%) | 96.0 ± 10.88 | 93.9 ± 19.22 | 100.0 ± 0.00 | 97.6 ± 3.58 | 0.524 |
| SDL (dB) | 100.5 ± 6.50 | 99.5 ± 8.05 | 106.7± 2.89 | 97.0 ± 12.55 | 0.226 |
| DR (dB) | 78.6 ± 19.51 | 67.1 ± 23.64 | 91.7 ± 10.41 | 72.0 ± 9.75 | 0.130 |
| ANCA Positive (n = 54 Ears) Mean (±SD) | ANCA Negative (n = 26 Ears) Mean (±SD) | p- Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| PTA at frequency 500–2000 Hz (dB) | 19.4 ± 16.89 | 22.7 ± 25.83 | 0.631 |
| PTA at frequency 4000–8000 Hz (dB) | 33.7 ± 24.45 | 34.2 ± 30.0) | 0.65 |
| SDT (dB) | 25.6 ± 18.19 | 26.7 ± 23.15 | 0.832 |
| SRT (dB) | 36.5 ± 17.69 | 38.1 ± 24.98 | 0.667 |
| WRS (%) | 96.7 ± 12.22 | 92.9 ± 20.96 | 0.595 |
| SDL (dB) | 100.9 ± 6.94 | 97.9 ± 9.18 | 0.199 |
| DR (dB) | 75.2 ± 19.45 | 71.2 ± 25.78 | 0.581 |
| Group 1 (n = 22 Ears) Mean (±SD) | Group 2 (n = 34 Ears) Mean (±SD) | Group 3 (n = 24 Ears) Mean (±SD) | p- Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PTA at frequency 500–2000 Hz (dB) | 22.2 ± 25.72 | 18.5 ± 16.81 | 21.6 ±19.28 | 0.944 |
| PTA at frequency 4000–8000 Hz (dB) | 36.5 ± 31.13 | 31.8 ± 23.39 | 34.3 ± 25.95 | 0.986 |
| SDT (dB) | 28.2 ± 21.80 | 25.6 ± 17.79 | 24.4 ± 21.23 | 0.567 |
| SRT (dB) | 39.3 ± 20.55 | 36.0 ± 17.05 | 36.3 ± 24.33 | 0.438 |
| WRS (%) | 89.0 ± 27.80 | 98.4 ± 2.97 | 97.3 ± 7.70 | 0.627 |
| SDL (dB) | 97.5 ± 9.85 | 100.6 ± 8.14 | 101.3 ± 4.23 | 0.568 |
| DR (dB) | 68.9 ± 23.50 | 75.0 ± 19.66 | 76.9 ± 22.64 | 0.276 |
| Group 1 (n = 18 Ears) Mean (±SD) | Group 2 (n = 40 Ears) Mean (±SD) | Group 3 (n = 22 Ears) Mean (±SD) | p- Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PTA at frequency 500–2000 Hz (dB) | 18.1 ± 26.89 | 20.1 ± 15.16 | 23.0 ± 22.34 | 0.103 |
| PTA at frequency 4000–8000 Hz (dB) | 31.9 ± 31.68) | 34.5 ± 23.22 | 34.2 ± 27.62 | 0.541 |
| SDT (dB) | 22.5 ± 22.44 | 28.4 ± 15.99 | 24.3 ± 23.82 | 0.054 |
| SRT (dB) | 33.1 ± 20.30 | 39.5 ± 18.36 | 35.7 ± 23.42 | 0.110 |
| WRS (%) | 93.6 ± 23.45 | 96.6 ± 7.44 | 95.0 ± 18.93 | 0.477 |
| SDL (dB) | 98.3 ± 9.70 | 99.3 ± 8.29 | 102.5 ± 4.01 | 0.193 |
| DR (dB) | 75.8 ± 23.34 | 70.6 ± 19.29 | 78.2 ± 24.18 | 0.133 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vainutienė, V.; Lesinskas, E.; Ivaškienė, T.; Mieliauskaitė, D.; Dadonienė, J.; Miltinienė, D.; Ivaška, J. Association Between Hearing Loss and Systemic Small-Vessel Vasculitis: Audiological Aspects Across Disease Types. Medicina 2025, 61, 1117. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61071117
Vainutienė V, Lesinskas E, Ivaškienė T, Mieliauskaitė D, Dadonienė J, Miltinienė D, Ivaška J. Association Between Hearing Loss and Systemic Small-Vessel Vasculitis: Audiological Aspects Across Disease Types. Medicina. 2025; 61(7):1117. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61071117
Chicago/Turabian StyleVainutienė, Vija, Eugenijus Lesinskas, Tatjana Ivaškienė, Diana Mieliauskaitė, Jolanta Dadonienė, Dalia Miltinienė, and Justinas Ivaška. 2025. "Association Between Hearing Loss and Systemic Small-Vessel Vasculitis: Audiological Aspects Across Disease Types" Medicina 61, no. 7: 1117. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61071117
APA StyleVainutienė, V., Lesinskas, E., Ivaškienė, T., Mieliauskaitė, D., Dadonienė, J., Miltinienė, D., & Ivaška, J. (2025). Association Between Hearing Loss and Systemic Small-Vessel Vasculitis: Audiological Aspects Across Disease Types. Medicina, 61(7), 1117. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61071117







