CBX1 as a Prognostic Biomarker and Therapeutic Target in Liver Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Insight into DNA Methylation and Non-Coding RNA Networks from Comprehensive Bioinformatics Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. mRNA Expression Analysis of CBX1 in LIHC
2.2. Protein Expression Analysis of CBX1 in LIHC via Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
2.3. Prognostic Analysis of CBX1 in LIHC
2.4. DNA Methylation and Prognostic Analysis of CBX1 in LIHC
2.5. Construction of the miRNA–lncRNA–circRNA–mRNA Network and Prognostic Analysis of CBX1of CBX1 in LIHC
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. mRNA Expression of CBX1 in LIHC
3.2. Protein Expression of CBX1 in LIHC
3.3. Prognostic Value of CBX1 Expression in LIHC
3.4. Relationship Between CBX1 Expression Level and Clinicopathological Characteristics of LIHC
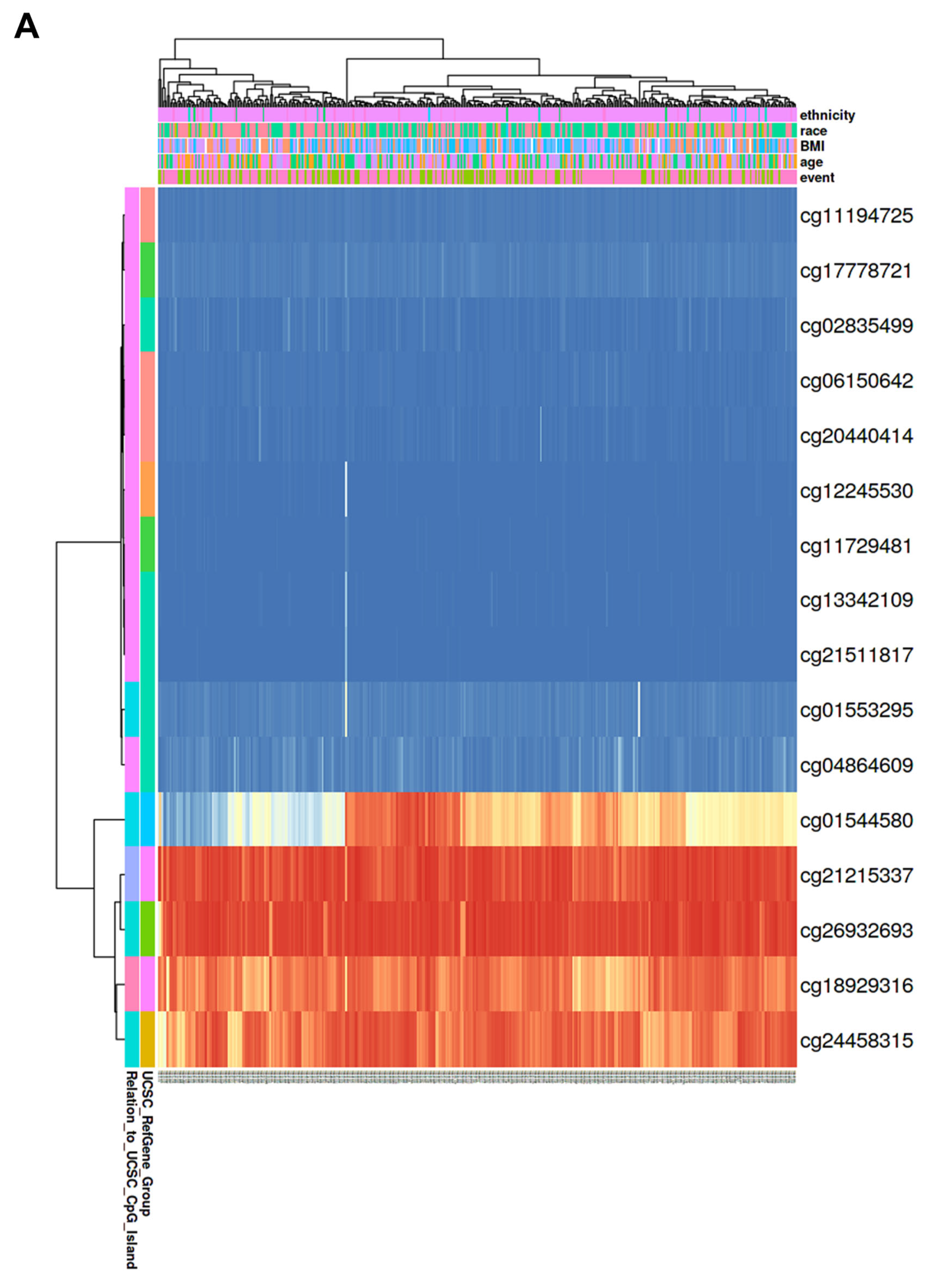
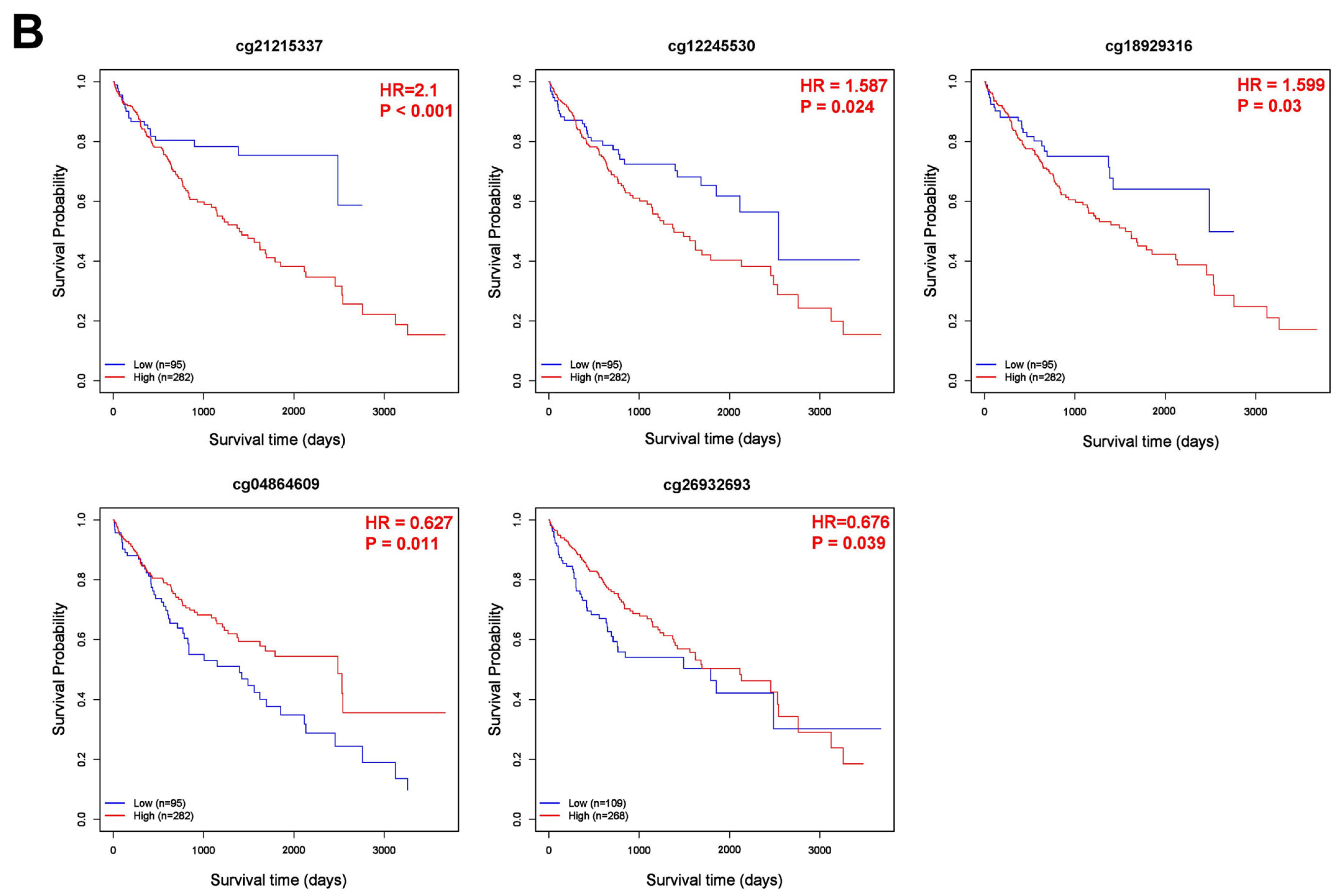
3.5. Correlation of CBX1 Expression with DNA Methylation in LIHC
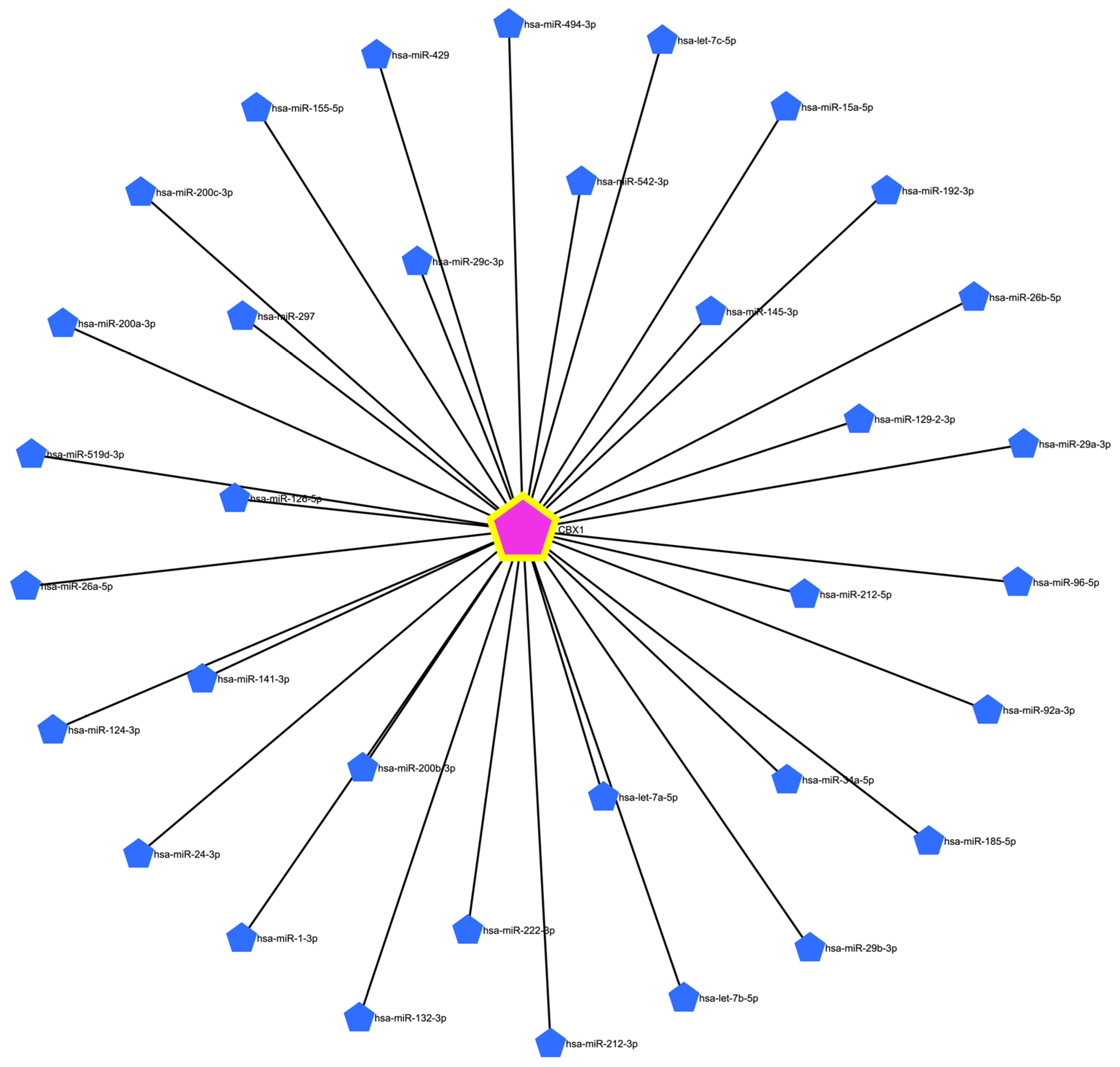
3.6. Prediction of Target miRNAs and Construction of the CBX1-Associated Co-Expression Network
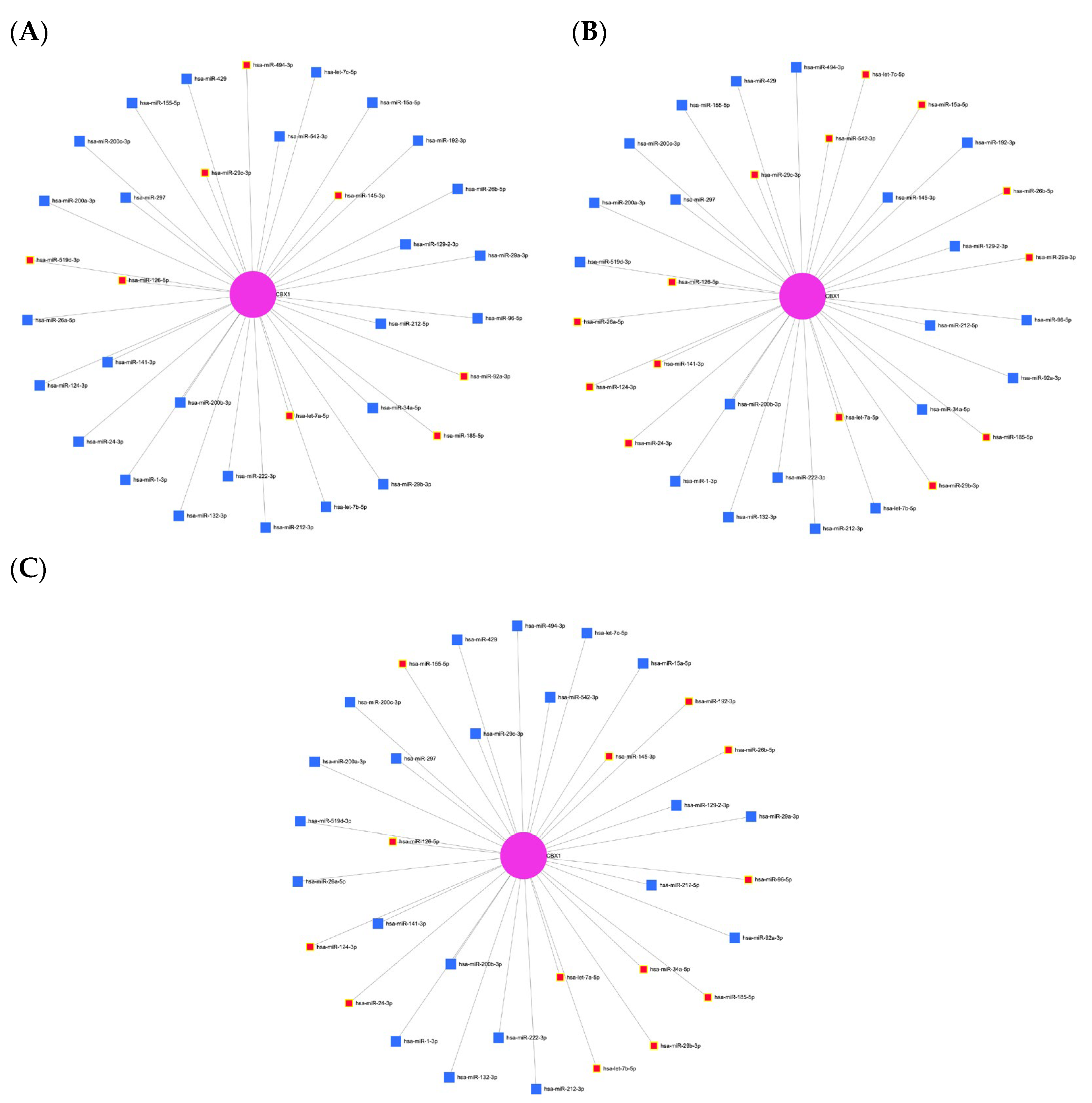
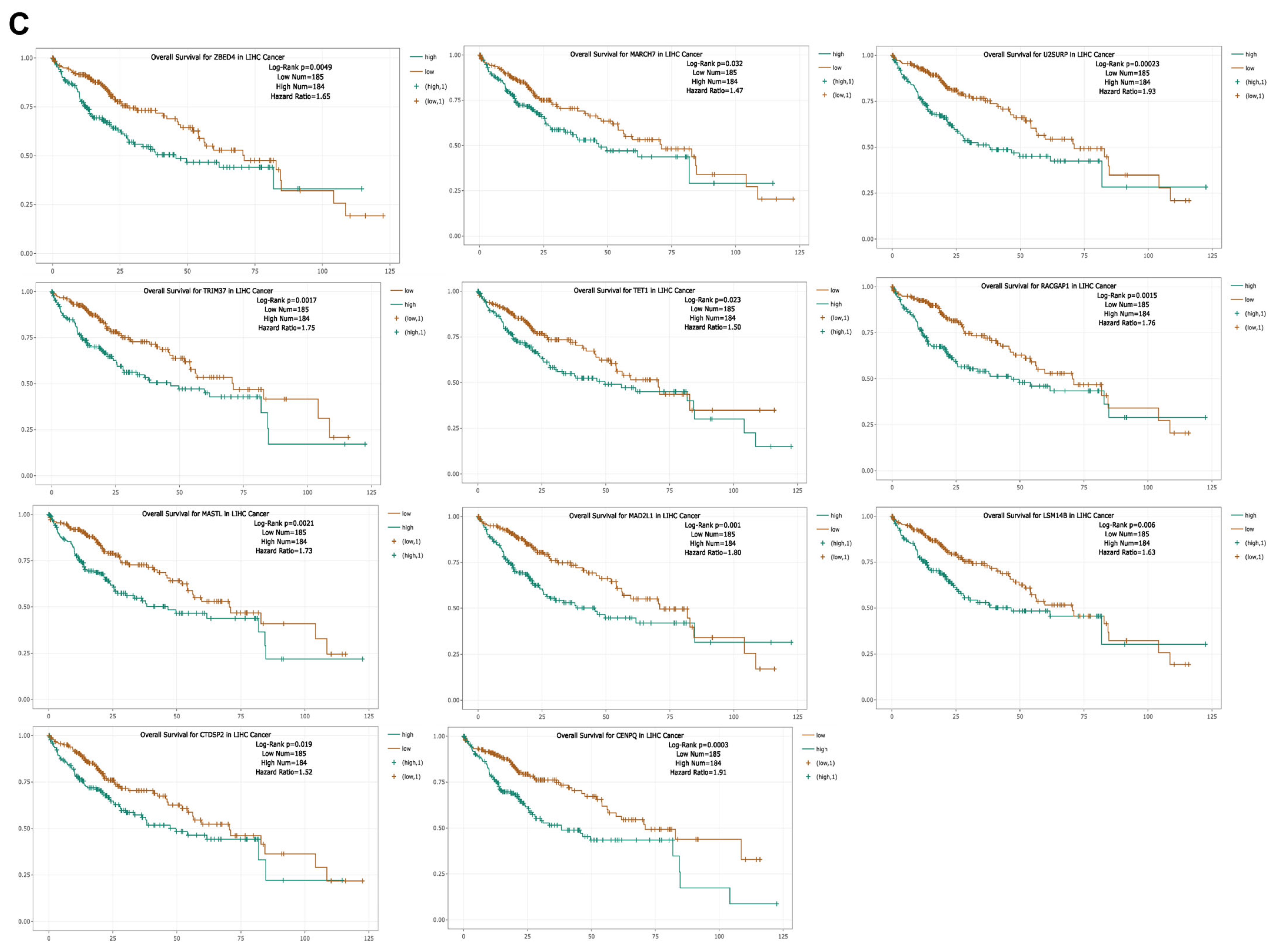
3.7. Expression and Prognostic Significance of CBX1-Associated miRNAs in LIHC
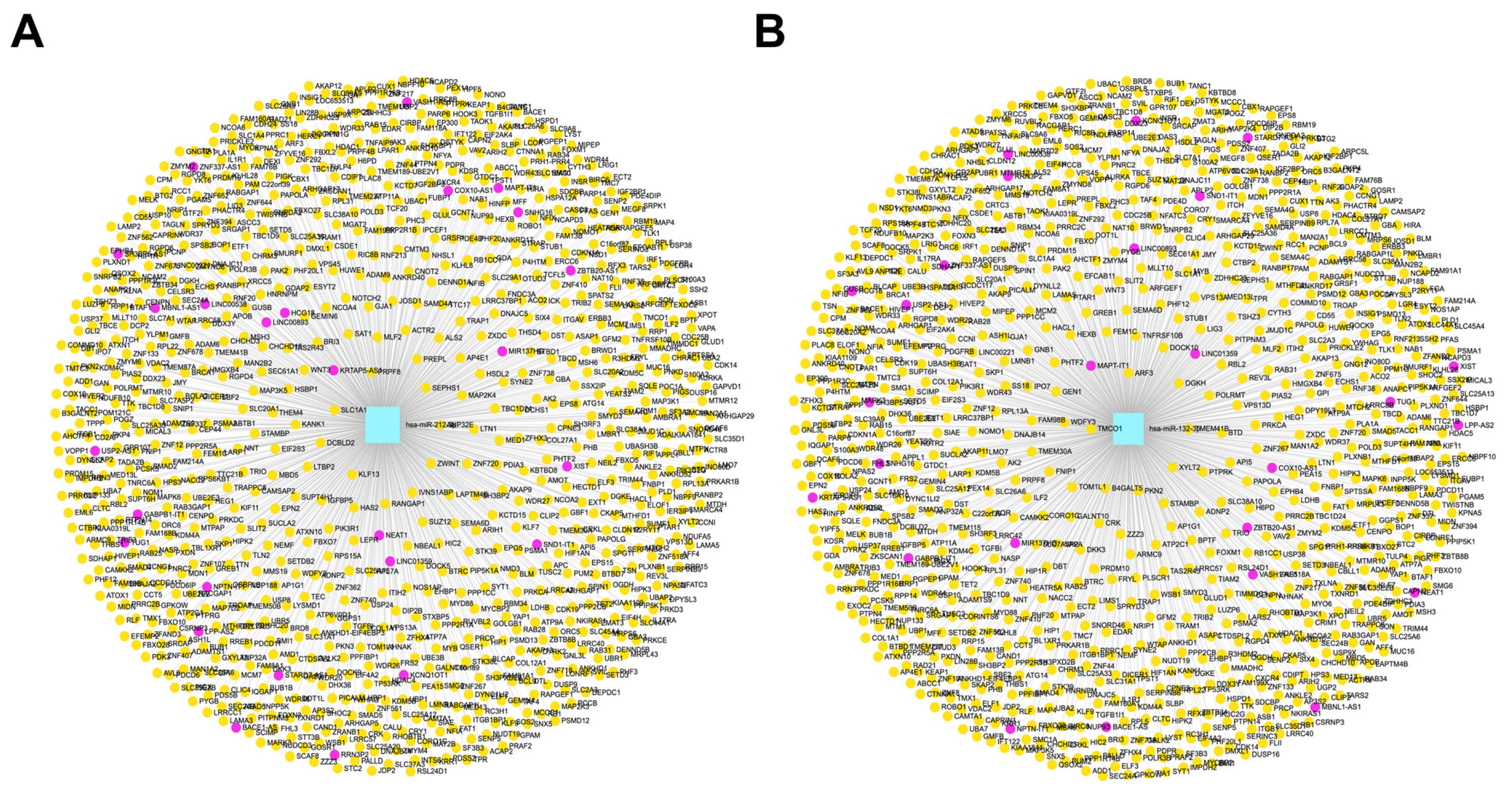
3.8. Construction of lncRNA and circRNA Networks for CBX1-Associated miRNAs in LIHC
3.9. Correlation of lncRNA Genes Associated with CBX1-Targeting miRNAs in LIHC
3.10. Correlation of Pseudogenes Associated with CBX1-Targeting miRNAs in LIHC
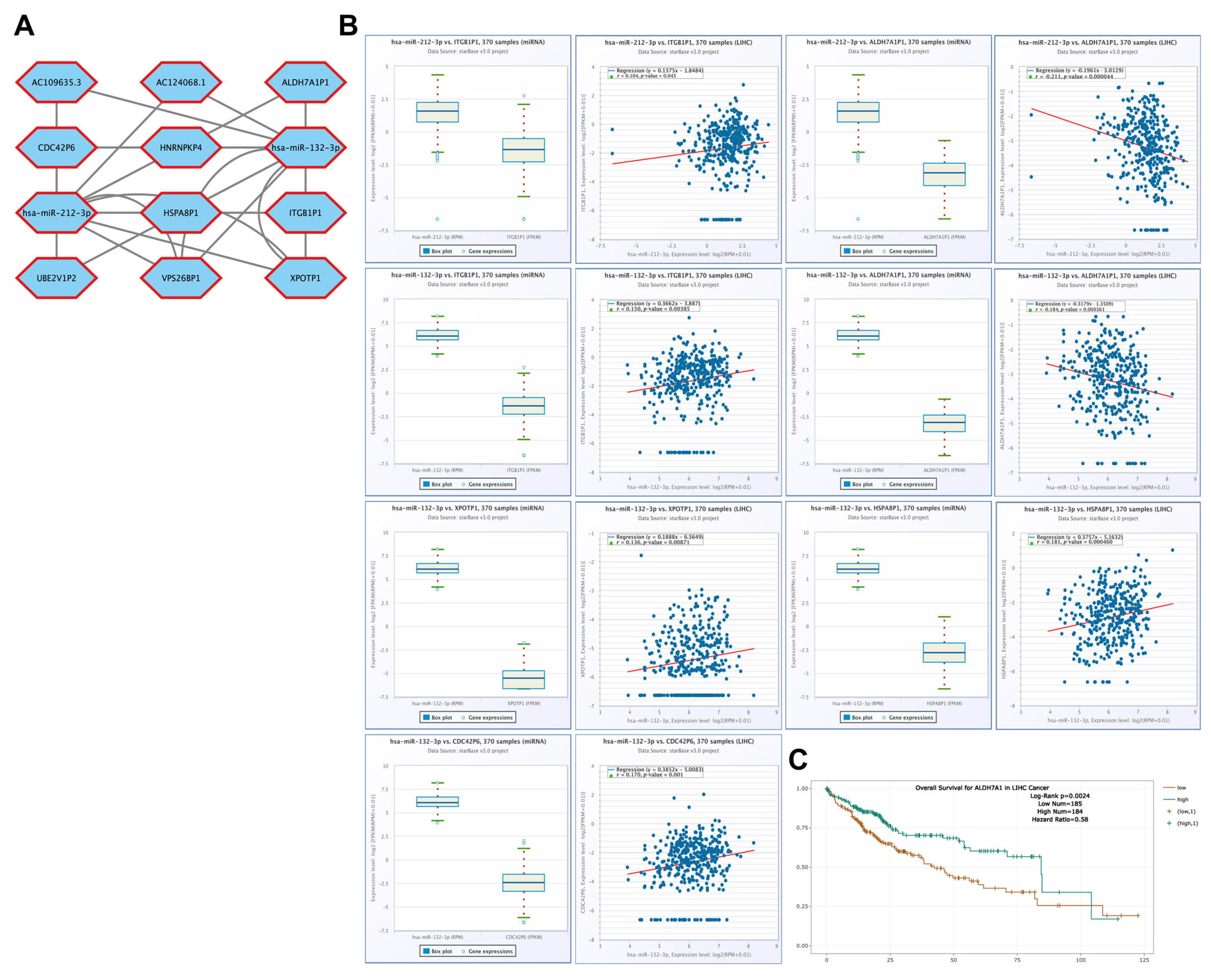
3.11. Correlation of ceRNAs Associated with CBX1 in LIHC
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aly, A.; Ronnebaum, S.; Patel, D.; Doleh, Y.; Benavente, F. Epidemiologic, humanistic and economic burden of hepatocellular carcinoma in the USA: A systematic literature review. Hepat. Oncol. 2020, 7, HEP27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujiwara, N.; Friedman, S.L.; Goossens, N.; Hoshida, Y. Risk factors and prevention of hepatocellular carcinoma in the era of precision medicine. J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, 526–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altekruse, S.F.; Henley, S.J.; Cucinelli, J.E.; McGlynn, K.A. Changing hepatocellular carcinoma incidence and liver cancer mortality rates in the United States. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 109, 542–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yıldırım, H.Ç.; Kavgaci, G.; Chalabiyev, E.; Dizdar, O. Advances in the Early Detection of Hepatobiliary Cancers. Cancers 2023, 15, 3880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, A.; Joosten, S.C.; Feng, Z.; de Ruijter, T.C.; Draht, M.X.; Melotte, V.; Smits, K.M.; Veeck, J.; Herman, J.G.; Van Neste, L.; et al. Analysis of DNA methylation in cancer: Location revisited. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irizarry, R.A.; Ladd-Acosta, C.; Wen, B.; Wu, Z.; Montano, C.; Onyango, P.; Cui, H.; Gabo, K.; Rongione, M.; Webster, M.; et al. The human colon cancer methylome shows similar hypo- and hypermethylation at conserved tissue-specific CpG island shores. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Wei, D.; Ji, Y.; Chen, L.; Yang, L.; Li, G.; Wu, L.; Hou, T.; Xie, L.; Ding, G.; et al. Integrative analysis of DNA methylation and gene expression reveals hepatocellular carcinoma-specific diagnostic biomarkers. Genome Med. 2018, 10, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Shui, L.; Jia, J.; Wu, C. Construction and Validation of Novel Diagnostic and Prognostic DNA Methylation Signatures for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.C.; Oxnard, G.R.; Klein, E.A.; Swanton, C.; Seiden, M.V.; CCGA Consortium. Sensitive and specific multi-cancer detection and localization using methylation signatures in cell-free DNA. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 745–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Tong, W.; Xie, F.; Zhu, L.; Wu, H.; Shi, R.; Wang, L.; Yang, L.; Liu, Z.; Miao, F.; et al. DNA methylation biomarkers for diagnosis of primary liver cancer and distinguishing hepatocellular carcinoma from intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Aging 2021, 13, 17592–17606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villanueva, A.; Minguez, B.; Forner, A.; Reig, M.; Llovet, J.M. Hepatocellular carcinoma: Novel molecular approaches for diagnosis, prognosis, and therapy. Annu. Rev. Med. 2010, 61, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kataoka, M.; Wang, D.Z. NonCoding RNAs Including miRNAs and lncRNAs in Cardiovascular Biology and Disease. Cells 2014, 3, 883–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, M.T.; Song, H.J.; Ding, X.Y. Long non-coding RNAs involved in metastasis of gastric cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 3724–3737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, B.; Zhang, X.; Chao, L.; Zheng, Y.; Tan, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, W. Comprehensive analysis of key genes, microRNAs and long non-coding RNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma. FEBS Open Bio. 2018, 8, 1424–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmena, L.; Poliseno, L.; Tay, Y.; Kats, L.; Pandolfi, P.P. A ceRNA hypothesis: The Rosetta Stone of a hidden RNA language? Cell 2011, 146, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Xu, W.Y.; Xiao, Y.; Jin, B.; Du, S.D.; Mao, Y.L.; Zhang, Z.T. The emerging roles of non-coding competing endogenous RNA in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Cell Int. 2020, 20, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, H.; Su, H. Long Noncoding RNAs Act as Novel Biomarkers for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Progress and Prospects. Biomed. Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 6049480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Chen, J.; Zhang, K.; Feng, B.; Wang, R.; Chen, L. Progress and Prospects of Long Noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 36, 423–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Li, S.Y.; Fang, J.H.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, J.E. Functional long non-coding RNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2021, 500, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Liu, J.B.; Deng, J.; Zou, D.Z.; Wu, J.J.; Cao, Y.H.; Yin, J.; Ma, Y.S.; Da, F.; Li, W. The role of ceRNA-mediated diagnosis and therapy in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hereditas 2021, 158, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.Q.; Zhou, S.L.; Li, J.; Zhou, Z.J.; Wang, P.C.; Xin, H.Y.; Mao, L.; Luo, C.B.; Yu, S.Y.; Huang, X.W.; et al. Circular RNA Sequencing Identifies CircASAP1 as a Key Regulator in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Metastasis. Hepatology 2020, 72, 906–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rundegren, J.; Arnold, R.R. Differentiation and interaction of secretory immunoglobulin A and a calcium-dependent parotid agglutinin for several bacterial strains. Infect. Immun. 1987, 55, 288–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Ji, L.; Liang, Y.; Wan, Z.; Zheng, W.; Song, X.; Gorshkov, K.; Sun, Q.; Lin, H.; Zheng, X.; et al. CircRNA-SORE mediates sorafenib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma by stabilizing YBX1. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, G.; Peng, X.; Tian, Y.; Fu, X.; Zhang, Y. Circular RNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma: Biogenesis, function, and pathology. Front. Genet. 2023, 14, 1106665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, P.; Fu, X.; Lin, W. Circular RNAs in renal cell carcinoma: Implications for tumorigenesis, diagnosis, and therapy. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poliseno, L. Pseudogenes: Newly discovered players in human cancer. Sci. Signal. 2012, 5, re5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poliseno, L.; Marranci, A.; Pandolfi, P.P. Pseudogenes in Human Cancer. Front. Med. 2015, 2, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kritika, C. Transforming 'Junk' DNA into Cancer Warriors: The Role of Pseudogenes in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancer Diagn. Progn. 2024, 4, 214–222. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.; Fu, J.; Zeng, Z.; Cohen, D.; Li, J.; Chen, Q.; Li, B.; Liu, X.S. TIMER2.0 for analysis of tumor-infiltrating immune cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, W509–W514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.; Cho, M.; Wang, X. OncoDB: An interactive online database for analysis of gene expression and viral infection in cancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D1334–D1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandrashekar, D.S.; Karthikeyan, S.K.; Korla, P.K.; Patel, H.; Shovon, A.R.; Athar, M.; Netto, G.J.; Qin, Z.S.; Kumar, S.; Manne, U.; et al. UALCAN: An update to the integrated cancer data analysis platform. Neoplasia 2022, 25, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fei, Q.; Zhang, X.; Wang, S.; Shu, G.; Yin, G. A pan-cancer characterization of immune-related NFIL3 identifies potential predictive biomarker. J. Cancer 2024, 15, 1271–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Li, L.; Han, G. CHST12: A potential prognostic biomarker related to the immunotherapy response in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 14, 1226547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xia, Q.; He, H.; Mao, Q.; Dong, H.; Zhu, L.; Hu, Z.; Xia, J.; Weng, Z.; et al. Pan-Cancer Analysis of PTBP1 to Identify it as a Prognostic and Immunological Biomarker. Cancer Control 2024, 31, 10732748241302865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modhukur, V.; Iljasenko, T.; Metsalu, T.; Lokk, K.; Laisk-Podar, T.; Vilo, J. MethSurv: A web tool to perform multivariable survival analysis using DNA methylation data. Epigenomics 2018, 10, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Xia, J. MicroRNA Regulatory Network Analysis Using miRNet 2.0. Methods Mol. Biol. 2023, 2594, 185–204. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.H.; Liu, S.; Zhou, H.; Qu, L.H.; Yang, J.H. starBase v2.0: Decoding miRNA-ceRNA, miRNA-ncRNA and protein-RNA interaction networks from large-scale CLIP-Seq data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D92–D97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forner, A.; Reig, M.; Bruix, J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 2018, 391, 1301–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, D.A.; Roberts, L.R.; Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. Comprehensive and Integrative Genomic Characterization of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cell 2017, 169, 1327–1341.e23. [Google Scholar]
- Rovida, E.; Di Maira, G.; Tusa, I.; Cannito, S.; Paternostro, C.; Navari, N.; Vivoli, E.; Deng, X.; Gray, N.S.; Esparís-Ogando, A.; et al. The mitogenactivated protein kinase ERK5 regulates the development and growth of hepatocellular carcinoma. Gut 2015, 64, 1454–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, M.H.; You, S.L.; Chen, C.J.; Liu, C.J.; Lai, M.W.; Wu, T.C.; Wu, S.F.; Lee, C.M.; Yang, S.S.; Chu, H.C.; et al. Long-term Effects of Hepatitis B Immunization of Infants in Preventing Liver Cancer. Gastroenterology 2016, 151, 472–480.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clavien, P.A.; Lesurtel, M.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Gores, G.J.; Langer, B.; Perrier, A.; OLT for HCC Consensus Group. Recommendations for liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma: An international consensus conference report. Lancet Oncol. 2012, 13, e11–e22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Zhou, J.K.; Peng, Y.; He, W.; Huang, C. The role of long noncoding RNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teschendorff, A.E.; Widschwendter, M. Differential variability improves the identification of cancer risk markers in DNA methylation studies profiling precursor cancer lesions. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1487–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baylin, S.B.; Jones, P.A. A decade of exploring the cancer epigenome—Biological and translational implications. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 726–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Xu, W.; Zhang, L.; Liu, T.; Jin, G.; Song, J.; Wu, J.; Wang, Y.; Chen, W.; Zhang, C.; et al. Development and validation of a CIMP-associated prognostic model for hepatocellular carcinoma. eBioMedicine 2019, 47, 128–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, L.; Gu, J.; Zhang, H.; Yuan, J.; Lian, Q.; Lv, G.; Wang, S.; Wu, Y.; Yang, Y.T.; et al. Recurrently deregulated lncRNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, W.J.; Huang, H.; Wang, T.; Zeng, W.H.; Guo, M.; Ren, C.R.; Fan, T.Y.; Liu, F.; Zeng, X. Long non-coding RNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2023, 248, 154604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Y.; Wang, D.; Wang, J.; Yu, W.; Yang, J. Long Non-Coding RNA in the Pathogenesis of Cancers. Cells 2019, 8, 1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristensen, L.S.; Andersen, M.S.; Stagsted, L.V.W.; Ebbesen, K.K.; Hansen, T.B.; Kjems, J. The biogenesis, biology and characterization of circular RNAs. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2019, 20, 675–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Mao, X.; Peng, R.; Bai, D. CircRNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma: Characteristic, functions and clinical significance. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2022, 19, 2033–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Chang, Y.; Xu, L.; Qin, L. Elevated expression of circular RNA circ_0008450 predicts dismal prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma and regulates cell proliferation, apoptosis, and invasion via sponging miR-548p. J. Cell Biochem. 2019, 120, 9487–9494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Yang, M.; Zhou, B.; Luo, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Yan, Z. CircRNA-104718 acts as competing endogenous RNA and promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression through microRNA-218-5p/TXNDC5 signaling pathway. Clin. Sci. 2019, 133, 1487–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, C.; Li, D.; Liu, H.; Sun, H.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Hu, Y. The competing endogenous circular RNA ADAMTS14 suppressed hepatocellular carcinoma progression through regulating microRNA-572/regulator of calcineurin 1. J. Cell Physiol. 2019, 234, 2460–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Yu, Y.; Huang, Z.; Kong, Y.; Hu, X.; Xiao, W.; Quan, J.; Fan, X. CircRNA-5692 inhibits the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma by sponging miR-328-5p to enhance DAB2IP expression. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooke, S.L.; Shlien, A.; Marshall, J.; Pipinikas, C.P.; Martincorena, I.; Tubio, J.M.; Li, Y.; Menzies, A.; Mudie, L.; Ramakrishna, M.; et al. Processed pseudogenes acquired somatically during cancer development. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Yuan, Y.; Zheng, S.; Yang, Y.; Li, J.; Edgerton, M.E.; Diao, L.; Xu, Y.; Verhaak, R.G.W.; Liang, H. The Pan-Cancer analysis of pseudogene expression reveals biologically and clinically relevant tumour subtypes. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Guo, Z.Y.; Zhang, R.; Xin, B.; Chen, R.; Zhao, J.; Wang, T.; Wen, W.H.; Jia, L.T.; Yao, L.B.; et al. Pseudogene OCT4-pg4 functions as a natural micro RNA sponge to regulate OCT4 expression by competing for miR-145 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Carcinogenesis 2013, 34, 1773–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Ishida, M.; Li, L.; Saito, A.; Kamiya, A.; Hamilton, J.P.; Fu, R.; Olaru, A.V.; An, F.; Popescu, I.; et al. Pseudogene INTS6P1 regulates its cognate gene INTS6 through competitive binding of miR-17-5p in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 5666–5677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Pan, C.; Wei, X.; Shi, Y.; Zheng, J.; Lin, X.; Shi, L. lncRNA KRAL reverses 5-fluorouracil resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma cells by acting as a ceRNA against miR-141. Cell Commun. Signal. 2018, 16, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, G.; Liang, M.; Liu, H.; Huang, J.; Li, P.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Jiang, X. CircRNA hsa_circRNA_104348 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression through modulating miR-187-3p/RTKN2 axis and activating Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, L.N.; Qiao, G.L.; Yu, J.; Yang, C.M.; Chen, Y.; Deng, Z.F.; Song, L.H.; Ma, L.J.; Yan, H.L. Hsa_circ_0003998 promotes epithelial to mesenchymal transition of hepatocellular carcinoma by sponging miR-143-3p and PCBP1. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 39, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Y.; Long, J.; Liu, Z.; Lin, J.; Huang, H.; Wang, D.; Yang, X.; Miao, F.; Mao, Y.; Sang, X.; et al. Comprehensive analysis of a ceRNA network reveals potential prognostic cytoplasmic lncRNAs involved in HCC progression. Cell Physiol. 2019, 234, 18837–18848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, D.; Wang, X.; Lu, G.; Ren, M.; Lu, X.; He, S. DANCR promotes HCC progression and regulates EMT by sponging miR-27a-3p via ROCK1/LIMK1/COFILIN1 pathway. Cell Prolif. 2019, 52, e12628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.G.; Wang, T.; Ding, M.; Xiang, S.H.; Shi, M.; Zhai, B. hsa_circ_0091570 acts as a ceRNA to suppress hepatocellular cancer progression by sponging hsa-miR-1307. Cancer Lett. 2019, 460, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spin, J.M.; Quertermous, T.; Tsao, P.S. Chromatin remodeling pathways in smooth muscle cell differentiation, and evidence for an integral role for p300. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e14301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

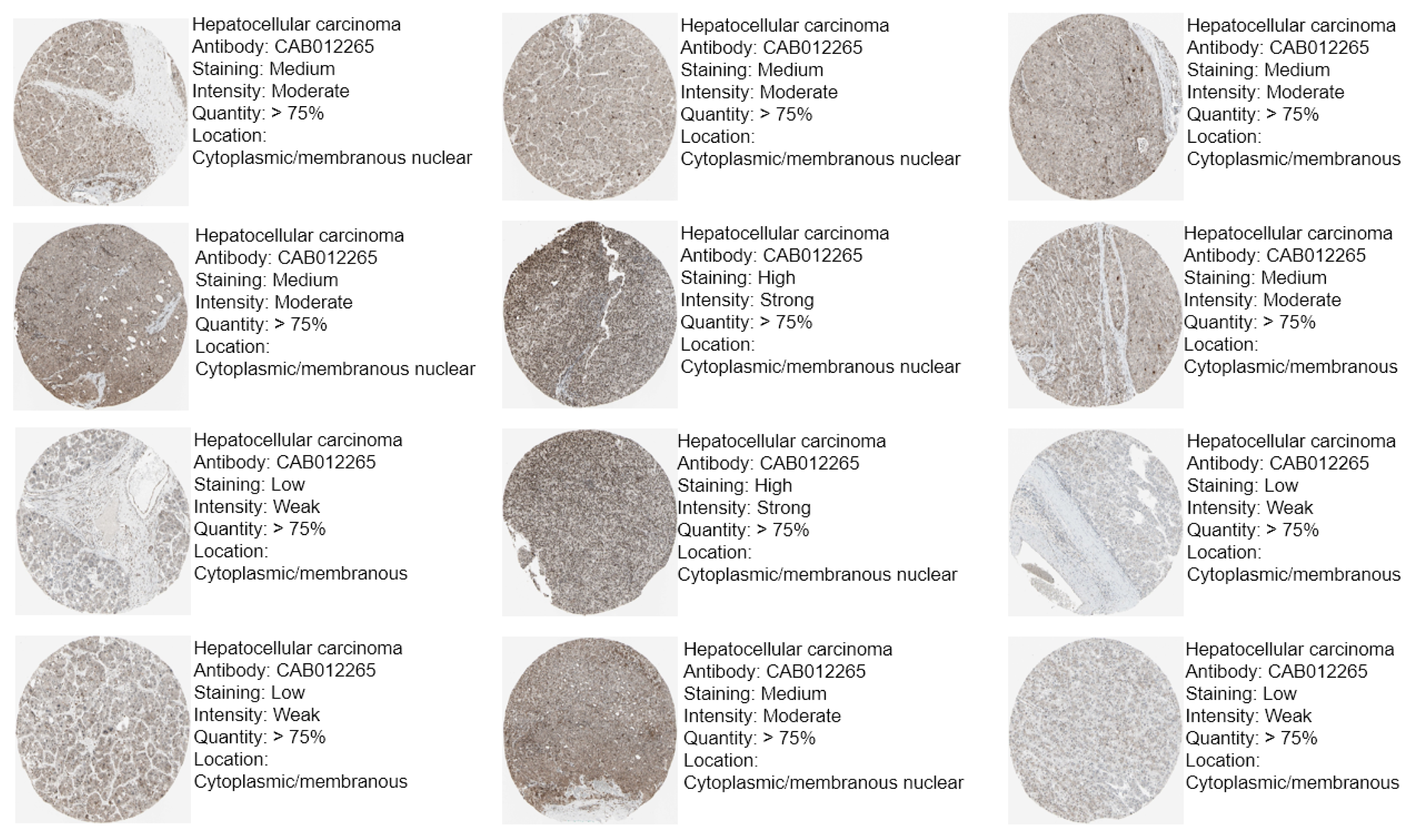
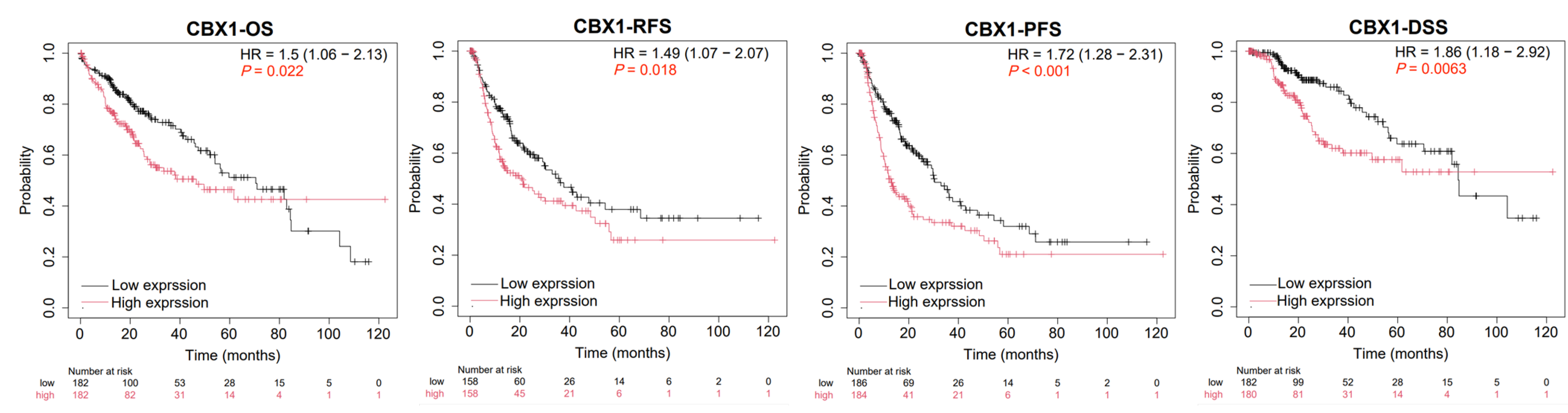






| Clinicopathological Characteristics | Overall Survival (n = 3218) | Relapse Free Survival (n = 2809) | Progression Free Survival (n = 3162) | Disease Specific Survival (n = 3189) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | Hazard Ratio | p-Value | N | Hazard Ratio | p-Value | N | Hazard Ratio | p-Value | N | Hazard Ratio | p-Value | |
| SEX | ||||||||||||
| Male | 246 | 1.5 (0.96–2.35) | 0.07 | 210 | 1.48 (1–2.21) | 0.051 | 249 | 1.79 (1.25–2.58) | 0.0014 | 244 | 1.76 (0.99–3.14) | 0.05 |
| Female | 118 | 1.51 (0.84–2.71) | 0.17 | 106 | 1.84 (1.01–3.37) | 0.044 | 121 | 1.71 (1.02–2.87) | 0.04 | 118 | 2.21 (1.02–4.8) | 0.04 |
| STAGE | ||||||||||||
| I | 170 | 1.33 (0.72–2.44) | 0.36 | 153 | 1.39 (0.81–2.4) | 0.23 | 171 | 1.49 (0.91–2.46) | 0.11 | 168 | 1.66 (0.68–4.06) | 0.27 |
| I+II | 253 | 1.18 (0.73–1.9) | 0.49 | 228 | 1.42 (0.94–2.17) | 0.097 | 256 | 1.44 (0.98–2.1) | 0.062 | 251 | 1.73 (0.86–3.48) | 0.12 |
| II | 83 | 1.33 (0.6–2.92) | 0.48 | 75 | 1.1 (0.57–2.11) | 0.78 | 85 | 1.31 (0.73–2.36) | 0.36 | 83 | 1.34 (0.45–4) | 0.6 |
| II+III | 166 | 1.45 (0.9–2.32) | 0.12 | 145 | 1.26 (0.81–1.97) | 0.3 | 170 | 1.38 (0.93–2.06) | 0.11 | 166 | 1.43 (0.79–2.6) | 0.24 |
| III | 83 | 1.54 (0.85–2.78) | 0.15 | 70 | 1.35 (0.73–2.49) | 0.33 | 85 | 1.32 (0.76–2.28) | 0.32 | 83 | 1.71 (0.84–3.48) | 0.13 |
| III+IV | 87 | 1.26 (0.71–2.23) | 0.42 | 70 | 1.35 (0.73–2.49) | 0.33 | 90 | 1.36 (0.8–2.31) | 0.26 | 87 | 1.47 (0.74–2.92) | 0.27 |
| IV | 4 | - | - | 0 | - | - | 5 | - | - | 3 | - | - |
| GRADE | ||||||||||||
| I | 55 | 2.34 (0.89–6.15) | 0.079 | 45 | 0.89(0.33–2.41) | 0.82 | 55 | 2.07 (0.93–4.61) | 0.071 | 55 | 2.66 (0.77–9.25) | 0.11 |
| II | 174 | 1.99 (1.17–3.36) | 0.0094 | 149 | 1.84 (1.12–3.01) | 0.014 | 177 | 2.38 (1.52–3.72) | 0.000097 | 171 | 2.92 (1.44–5.89) | 0.0018 |
| III | 118 | 1.23 (0.68–2.25) | 0.49 | 107 | 1.53 (0.89–2.62) | 0.12 | 121 | 1.41 (0.86–2.32) | 0.18 | 119 | 1.08 (0.51–2.31) | 0.84 |
| IV | 12 | - | - | 11 | - | - | 12 | - | - | 12 | - | - |
| AJCC_T | ||||||||||||
| I | 180 | 1.31 (0.73–2.34) | 0.36 | 160 | 1.58 (0.93–2.69) | 0.09 | 181 | 1.55 (0.95–2.52) | 0.075 | 178 | 1.59 (0.71–3.6) | 0.26 |
| II | 90 | 1.38 (0.66–2.87) | 0.39 | 80 | 1.12 (0.6–2.09) | 0.72 | 93 | 1.3 (0.75–2.24) | 0.35 | 91 | 1.4 (0.54–3.64) | 0.49 |
| III | 78 | 1.53 (0.83–2.81) | 0.17 | 67 | 1.2 (0.64–2.26) | 0.57 | 80 | 1.36 (0.77–2.4) | 0.29 | 77 | 1.56 (0.75–3.25) | 0.23 |
| IV | 13 | - | - | 6 | - | - | 13 | - | - | 13 | - | - |
| Vascular invasion | ||||||||||||
| None | 203 | 1.27 (0.76–2.13) | 0.35 | 175 | 1.15 (0.71–1.86) | 0.57 | 205 | 1.42 (0.91–2.22) | 0.12 | 201 | 1.52 (0.74–3.09) | 0.25 |
| Micro | 90 | 1.24 (0.57–2.67) | 0.59 | 82 | 1.2 (0.64–2.25) | 0.57 | 92 | 1.59 (0.9–2.81) | 0.11 | 90 | 0.9 (0.3–2.68) | 0.85 |
| Macro | 16 | - | - | 14 | - | - | 16 | - | - | 14 | - | - |
| RACE | ||||||||||||
| White | 181 | 1.57 (0.99–2.48) | 0.055 | 147 | 1.46 (0.93–2.3) | 0.1 | 184 | 1.85 (1.24–2.76) | 0.0021 | 179 | 2.05 (1.15–3.64) | 0.013 |
| Asian | 155 | 2.99 (1.56–5.71) | 0.00052 | 145 | 1.74 (1.04–2.89) | 0.032 | 157 | 1.97 (1.22–3.18) | 0.0047 | 154 | 3.56 (1.49–8.54) | 0.0024 |
| Alcohol consumption | ||||||||||||
| Yes | 115 | 1.91 (1.01–3.62) | 0.043 | 99 | 2.26 (1.24–4.13) | 0.0063 | 117 | 2.65 (1.55–4.54) | 0.00023 | 117 | 2.29 (1.1–4.76) | 0.023 |
| None | 202 | 1.4 (0.88–2.24) | 0.15 | 183 | 1.26 (0.81–1.96) | 0.31 | 205 | 1.44 (0.97–2.16) | 0.071 | 199 | 1.76 (0.94–3.31) | 0.075 |
| Sorafenib treatment | ||||||||||||
| Treated | 29 | 1.42 (0.44–4.63) | 0.56 | 22 | 3.34 (1.12–9.96) | 0.023 | 30 | 1.77 (0.78–3.98) | 0.16 | 30 | 1.62 (0.5–5.24) | 0.42 |
| Hepatitis virus | ||||||||||||
| Yes | 150 | 0.82 (0.43–1.56) | 0.54 | 99 | 2.26 (1.24–4.13) | 0.0063 | 117 | 2.65 (1.55–4.54) | 0.00023 | 151 | 1.1 (0.49–2.5) | 0.81 |
| None | 167 | 2.79 (1.68–4.62) | 0.000037 | 183 | 1.26 (0.81–1.96) | 0.31 | 205 | 1.44 (0.97–2.16) | 0.071 | 165 | 4.22 (2.17–8.23) | 0.0000057 |
| Probe | Chr | Position | Average of Cancer Sample | Average of Normal Sample | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cg24458315 | chr17 | 48,071,045 | 0.84 | 0.88 | p < 0.001 |
| cg26932693 | chr17 | 48,075,087 | 0.92 | 0.94 | 0.0012 |
| cg21215337 | chr17 | 48,098,755 | 0.91 | 0.93 | p < 0.001 |
| cg18929316 | chr17 | 48,099,486 | 0.82 | 0.86 | p < 0.001 |
| cg06150642 | chr17 | 48,100,857 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.0025 |
| cg20440414 | chr17 | 48,100,984 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.46 |
| cg11194725 | chr17 | 48,100,998 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.014 |
| cg12245530 | chr17 | 48,101,256 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.076 |
| cg11729481 | chr17 | 48,101,375 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.96 |
| cg17778721 | chr17 | 48,101,383 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.59 |
| cg04864609 | chr17 | 48,101,553 | 0.05 | 0.04 | p < 0.001 |
| cg02835499 | chr17 | 48,101,556 | 0.03 | 0.02 | p < 0.001 |
| cg21511817 | chr17 | 48,101,565 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.0076 |
| cg13342109 | chr17 | 48,101,569 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.72 |
| cg01553295 | chr17 | 48,101,633 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.86 |
| cg01544580 | chr17 | 48,102,907 | 0.59 | 0.6 | 0.54 |
| Gene | miRNA | |
|---|---|---|
| CBX1 | hsa-let-7a-5p | hsa-miR-132-3p |
| hsa-let-7b-5p | hsa-miR-141-3p | |
| hsa-let-7c-5p | hsa-miR-126-5p | |
| hsa-miR-15a-5p | hsa-miR-185-5p | |
| hsa-miR-24-3p | hsa-miR-200c-3p | |
| hsa-miR-26a-5p | hsa-miR-155-5p | |
| hsa-miR-26b-5p | hsa-miR-29c-3p | |
| hsa-miR-29a-3p | hsa-miR-200a-3p | |
| hsa-miR-92a-3p | hsa-miR-429 | |
| hsa-miR-96-5p | hsa-miR-494-3p | |
| hsa-miR-29b-3p | hsa-miR-519d-3p | |
| hsa-miR-34a-5p | hsa-miR-542-3p | |
| hsa-miR-212-3p | hsa-miR-297 | |
| hsa-miR-222-3p | hsa-miR-192-3p | |
| hsa-miR-200b-3p | hsa-miR-145-3p | |
| hsa-miR-1-3p | hsa-miR-129-2-3p | |
| hsa-miR-124-3p | hsa-miR-212-5p | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, H.-R.; Kim, J. CBX1 as a Prognostic Biomarker and Therapeutic Target in Liver Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Insight into DNA Methylation and Non-Coding RNA Networks from Comprehensive Bioinformatics Analysis. Medicina 2025, 61, 983. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61060983
Kim H-R, Kim J. CBX1 as a Prognostic Biomarker and Therapeutic Target in Liver Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Insight into DNA Methylation and Non-Coding RNA Networks from Comprehensive Bioinformatics Analysis. Medicina. 2025; 61(6):983. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61060983
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Hye-Ran, and Jongwan Kim. 2025. "CBX1 as a Prognostic Biomarker and Therapeutic Target in Liver Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Insight into DNA Methylation and Non-Coding RNA Networks from Comprehensive Bioinformatics Analysis" Medicina 61, no. 6: 983. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61060983
APA StyleKim, H.-R., & Kim, J. (2025). CBX1 as a Prognostic Biomarker and Therapeutic Target in Liver Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Insight into DNA Methylation and Non-Coding RNA Networks from Comprehensive Bioinformatics Analysis. Medicina, 61(6), 983. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61060983





