Neonates at Risk: Understanding the Impact of High-Risk Pregnancies on Neonatal Health
Abstract
1. Introduction
Methodology and Eligibility Criteria
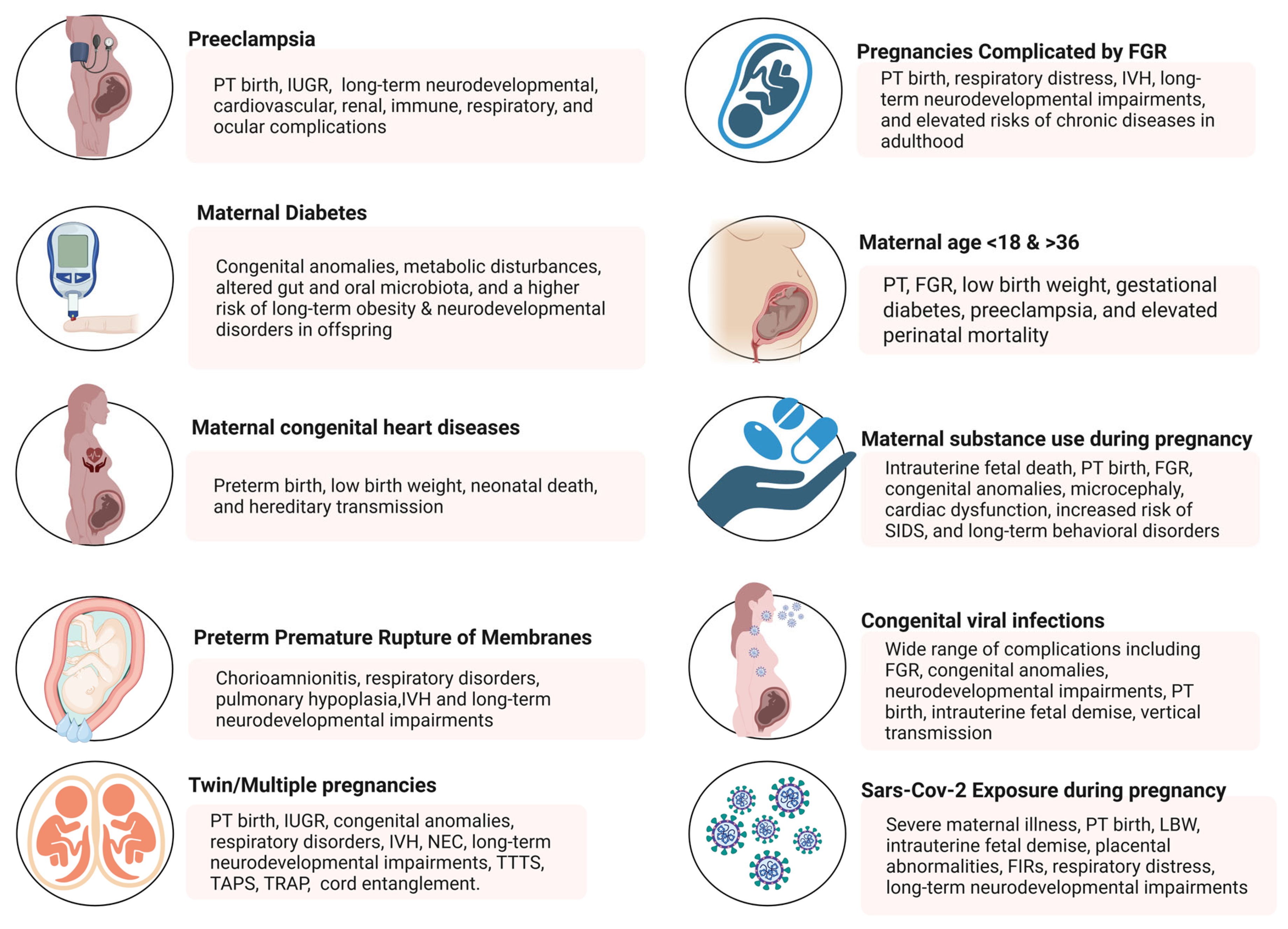
2. Risk Factors Contributing to High-Risk Pregnancies
2.1. Hypertensive Disorders During Pregnancy
2.2. Maternal Pre-Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
2.3. Congenital Heart Disease and Pregnancy (CHD)
2.4. Preterm Premature Rupture of Membranes (PPROM)
2.5. Twin and Multiple Pregnancies
2.6. Pregnancies Complicated by Fetal Growth Restriction
2.7. Maternal Age (<18 and >36 Years)
2.8. Maternal Substance Use During Pregnancy
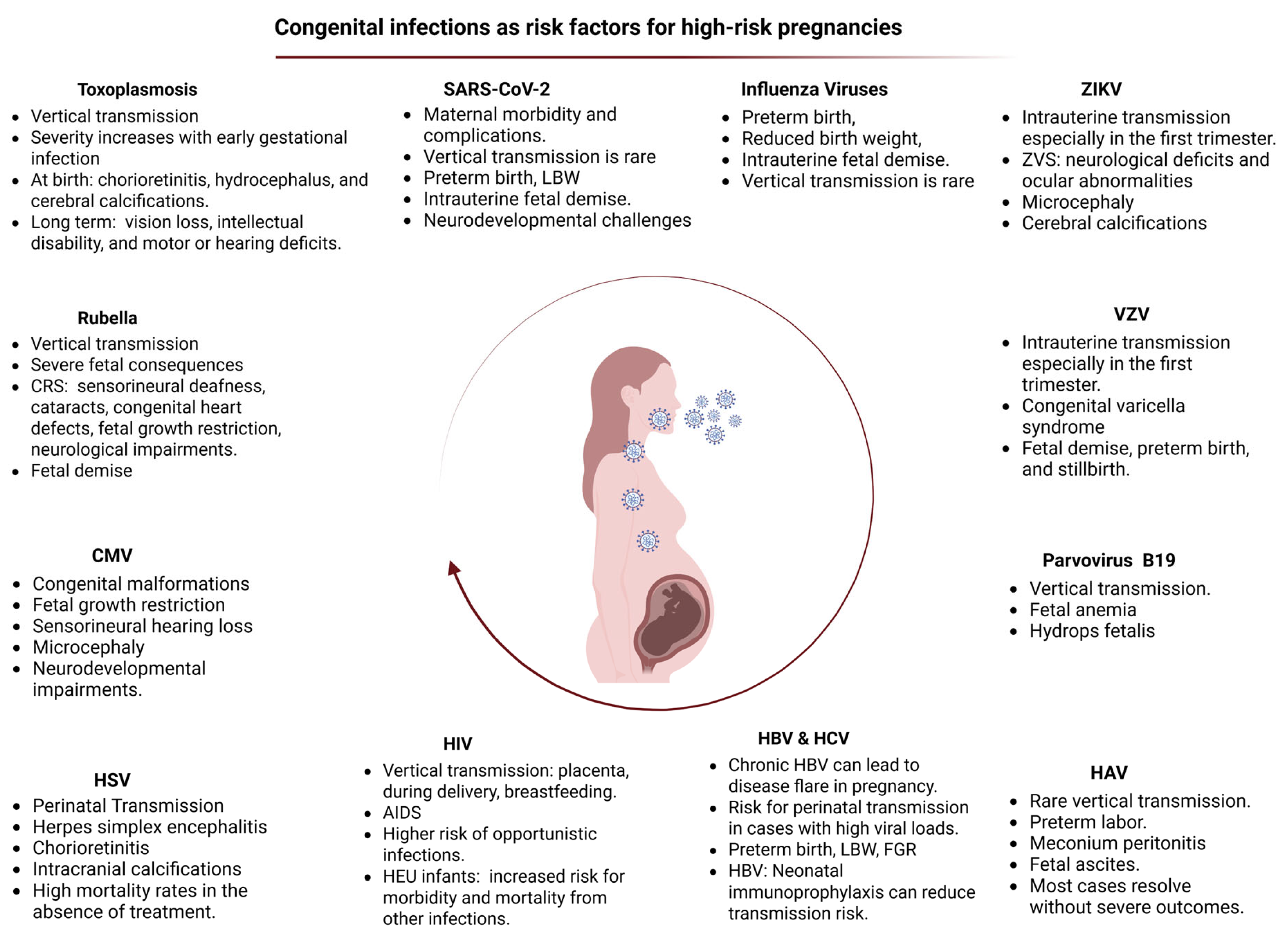
3. Congenital Viral Infections and Intrauterine Exposure to SARS-CoV-2
3.1. Cytomegalovirus (CMV)
3.2. Hepatitis Viruses
3.2.1. Hepatitis A Virus (HAV)
3.2.2. Hepatitis B Virus (HBV)
3.2.3. Hepatitis C Virus (HCV)
3.3. Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)
3.4. Toxoplasmosis
3.5. Rubella
3.6. Herpes Simplex Virus
3.7. Parvovirus
3.8. Varicella Zoster Virus (VZV)
3.9. Zika Virus (ZIKV)
3.10. Influenza Viruses
3.11. Intrauterine Exposure to SARS-CoV-2
4. Additional Risk Factors Defining a High-Risk Pregnancy and Their Neonatal Impact
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Correa-de-Araujo, R.; Yoon, S.S. Clinical Outcomes in High-Risk Pregnancies Due to Advanced Maternal Age. J. Women’s Health 2020, 30, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirzakhani, K.; Ebadi, A.; Faridhosseini, F.; Khadivzadeh, T. Well-being in high-risk pregnancy: An integrative review. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2020, 20, 526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volpe, J.J. Dysmaturation of premature brain: Importance, cellular mechanisms, and potential interventions. Pediatr. Neurol. 2019, 95, 42–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badakhsh, M.; Hastings-Tolsma, M.; Firouzkohi, M.; Amirshahi, M.; Hashemi, Z.S. The lived experience of women with a high-risk pregnancy: A phenomenology investigation. Midwifery 2020, 82, 102625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkema, L.; Chou, D.; Hogan, D.; Zhang, S.; Moller, A.B.; Gemmill, A.; Fat, D.M.; Boerma, T.; Temmerman, M.; Mathers, C.; et al. Global, regional, and national levels and trends in maternal mortality between 1990 and 2015, with scenario-based projections to 2030: A systematic analysis by the UN Maternal Mortality Estimation Inter-Agency Group. Lancet 2016, 387, 462–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, T.V.; Brunetto, S.; Ramos, J.G.; Bernardi, J.R.; Goldani, M.Z. Hypertensive disorders during pregnancy and health outcomes in the offspring: A systematic review. J. Dev. Orig. Health Dis. 2016, 7, 391–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, J.M.; Pearson, G.; Cutler, J.; Lindheimer, M. Summary of the NHLBI Working Group on Research on Hypertension During Pregnancy. Hypertension 2003, 41, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, A.L.; Suriano, K.; Aye, C.Y.; Leeson, P.; Lewandowski, A.J. The immediate and long-term impact of preeclampsia on offspring vascular and cardiac physiology in the preterm infant. Front. Pediatr. 2021, 9, 625726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poon, L.C.; Shennan, A.; Hyett, J.A.; Kapur, A.; Hadar, E.; Divakar, H.; McAuliffe, F.; da Silva Costa, F.; Von Dadelszen, P.; McIntyre, H.D. The International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics (FIGO) initiative on preeclampsia (PE): A pragmatic guide for first trimester screening and prevention. Int. J. Gynaecol. Obstet. Off. Organ Int. Fed. Gynaecol. Obstet. 2019, 145, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyselaers, W. Hemodynamic pathways of gestational hypertension and preeclampsia. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2022, 226, S988–S1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists’ Committee on Practice Bulletins—Obstetrics. ACOG Practice Bulletin No. 203: Chronic Hypertension in Pregnancy. Obstet. Gynecol. 2019, 133, e26–e50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magee, L.A.; Brown, M.A.; Hall, D.R.; Gupte, S.; Hennessy, A.; Karumanchi, S.A.; Kenny, L.C.; McCarthy, F.; Myers, J.; Poon, L.C.; et al. The 2021 International Society for the Study of Hypertension in Pregnancy classification, diagnosis & management recommendations for international practice. Pregnancy Hypertens. 2022, 27, 148–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, M.A.; Magee, L.A.; Kenny, L.C.; Karumanchi, S.A.; McCarthy, F.P.; Saito, S.; Hall, D.R.; Warren, C.E.; Adoyi, G.; Ishaku, S. The hypertensive disorders of pregnancy: ISSHP classification, diagnosis & management recommendations for international practice. Pregnancy Hypertens. 2018, 13, 291–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maher, G.M.; O’Keeffe, G.W.; Kearney, P.M.; Kenny, L.C.; Dinan, T.G.; Mattsson, M.; Khashan, A.S. Association of hypertensive disorders of pregnancy with risk of neurodevelopmental disorders in offspring: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Psychiatry 2018, 75, 809–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittara, T.; Vyrides, A.; Lamnisos, D.; Giannakou, K. Pre-eclampsia and long-term health outcomes for mother and infant: An umbrella review. BJOG Int. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2021, 128, 1421–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barron, A.; McCarthy, C.M.; O’Keeffe, G.W. Preeclampsia and neurodevelopmental outcomes: Potential pathogenic roles for inflammation and oxidative stress? Mol. Neurobiol. 2021, 58, 2734–2756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koulouraki, S.; Paschos, V.; Pervanidou, P.; Christopoulos, P.; Gerede, A.; Eleftheriades, M. Short- and Long-Term Outcomes of Preeclampsia in Offspring: Review of the Literature. Children 2023, 10, 826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajantie, E.; Eriksson, J.G.; Osmond, C.; Thornburg, K.; Barker, D.J. Pre-eclampsia is associated with increased risk of stroke in the adult offspring: The Helsinki birth cohort study. Stroke 2009, 40, 1176–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiro-Filho, E.A.; Mak, L.E.; Reynolds, J.N.; Stroman, P.W.; Smith, G.N.; Forkert, N.D.; Paolozza, A.; Rätsep, M.T.; Croy, B.A. Neurological function in children born to preeclamptic and hypertensive mothers–A systematic review. Pregnancy Hypertens. 2017, 10, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand, J.S.; Lawlor, D.A.; Larsson, H.; Montgomery, S. Association Between Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy and Neurodevelopmental Outcomes Among Offspring. JAMA Pediatr. 2021, 175, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Chen, X.; Liang, Y.; Forsell, Y.; Gissler, M.; Lavebratt, C. Association of Preeclampsia and Perinatal Complications With Offspring Neurodevelopmental and Psychiatric Disorders. JAMA Netw. Open 2022, 5, e2145719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stellwagen, D.; Malenka, R.C. Synaptic scaling mediated by glial TNF-α. Nature 2006, 440, 1054–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smyth, A.M.; Lawrie, S.M. The neuroimmunology of schizophrenia. Clin. Psychopharmacol. Neurosci. 2013, 11, 107. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Lin, J.; Zhao, H. Impacts of Maternal Preeclampsia Exposure on Offspring Neuronal Development: Recent Insights and Interventional Approaches. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 11062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Olsen, J.; Agerbo, E.; Yuan, W.; Wu, C.S.; Li, J. Maternal preeclampsia and childhood asthma in the offspring. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2015, 26, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rorman, E.; Freud, A.; Wainstock, T.; Sheiner, E. Maternal preeclampsia and long-term infectious morbidity in the offspring–A population based cohort analysis. Pregnancy Hypertens. 2020, 21, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shane, A.L.; Sánchez, P.J.; Stoll, B.J. Neonatal sepsis. Lancet 2017, 390, 1770–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazacliu, C.; Neu, J. Pathophysiology of Necrotizing Enterocolitis: An Update. Curr. Pediatr. Rev. 2019, 15, 68–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cetinkaya, M.; Ozkan, H.; Koksal, N. Maternal preeclampsia is associated with increased risk of necrotizing enterocolitis in preterm infants. Early Hum. Dev. 2012, 88, 893–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leybovitz-Haleluya, N.; Wainstock, T.; Sheiner, E. Maternal preeclampsia and the risk of pediatric gastrointestinal diseases of the offspring: A population-based cohort study. Pregnancy Hypertens. 2019, 17, 144–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gluckman, P.D.; Hanson, M.A. The developmental origins of health and disease. In Early Life Origins of Health and Disease; Wintour, E.M., Owens, J.A., Eds.; Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2006; Volume 573, pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, E.H.; Robledo, C.; Boghossian, N.; Zhang, C.; Mendola, P. Developmental Origins of Cardiovascular Disease. Curr. Epidemiol. Rep. 2014, 1, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thornburg, K.L.; Drake, R.; Valent, A.M. Maternal Hypertension Affects Heart Growth in Offspring. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2020, 9, e016538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, S.; Zhang, L.; Huang, L.; Li, Y.; Liang, Y.; Huang, M.; Huang, B.; Liang, J.; Gu, S.; Chen, J. Long-term effects of preeclampsia on metabolic and biochemical outcomes in offspring: What can be expected from a meta-analysis? Obes. Rev. 2022, 23, e13411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, A.; Hadlich, F.; Abbas, M.W.; Iqbal, M.A.; Tesfaye, D.; Bouma, G.J.; Winger, Q.A.; Ponsuksili, S. MicroRNA–mRNA networks in pregnancy complications: A comprehensive downstream analysis of potential biomarkers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luyckx, V.A.; Bertram, J.F.; Brenner, B.M.; Fall, C.; Hoy, W.E.; Ozanne, S.E.; Vikse, B.E. Effect of fetal and child health on kidney development and long-term risk of hypertension and kidney disease. Lancet 2013, 382, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Linde, D.; Konings, E.E.; Slager, M.A.; Witsenburg, M.; Helbing, W.A.; Takkenberg, J.J.; Roos-Hesselink, J.W. Birth prevalence of congenital heart disease worldwide: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2011, 58, 2241–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idkowiak, J.; Lavery, G.G.; Dhir, V.; Barrett, T.G.; Stewart, P.M.; Krone, N.; Arlt, W. Premature adrenarche: Novel lessons from early onset androgen excess. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2011, 165, 189–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogland, B.; Nilsen, S.T.; Forman, M.R.; Vatten, L.J. Pubertal development in daughters of women with pre-eclampsia. Arch. Dis. Child. 2011, 96, 740–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsnes, I.V.; Janszky, I.; Åsvold, B.O.; Økland, I.; Forman, M.R.; Vatten, L.J. Maternal Preeclampsia and Androgens in the Offspring around Puberty: A Follow-Up Study. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0167714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagliaferro, T.; Jain, D.; Vanbuskirk, S.; Bancalari, E.; Claure, N. Maternal preeclampsia and respiratory outcomes in extremely premature infants. Pediatr. Res. 2019, 85, 693–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, N.; Chaput, K.; Alshaikh, B.; Yusuf, K. Preeclampsia and the Risk of Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia in Preterm Infants Less Than 32 Weeks’ Gestation. Am. J. Perinatol. 2017, 34, 585–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matyas, M.; Hasmasanu, M.; Silaghi, C.N.; Samasca, G.; Lupan, I.; Orsolya, K.; Zaharie, G. Early Preeclampsia Effect on Preterm Newborns Outcome. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thébaud, B.; Abman, S.H. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia: Where have all the vessels gone? Roles of angiogenic growth factors in chronic lung disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2007, 175, 978–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, C.D.; Abman, S.H. Impaired pulmonary vascular development in bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Neonatology 2015, 107, 344–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahum Sacks, K.; Friger, M.; Shoham-Vardi, I.; Sergienko, R.; Landau, D.; Sheiner, E. In utero exposure to pre-eclampsia as an independent risk factor for long-term respiratory disease. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2020, 55, 723–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzakhani, H.; Carey, V.J.; McElrath, T.F.; Qiu, W.; Hollis, B.W.; O’Connor, G.T.; Zeiger, R.S.; Bacharier, L.; Litonjua, A.A.; Weiss, S.T. Impact of preeclampsia on the relationship between maternal asthma and offspring asthma. An observation from the VDAART clinical trial. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 199, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lykke, J.A.; Langhoff-Roos, J.; Sibai, B.M.; Funai, E.F.; Triche, E.W.; Paidas, M.J. Hypertensive pregnancy disorders and subsequent cardiovascular morbidity and type 2 diabetes mellitus in the mother. Hypertension 2009, 53, 944–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.H.; Lee, H.S. Hypertension and diabetes mellitus as risk factors for asthma in Korean adults: The Sixth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Int. Health 2020, 12, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simcock, D.E.; Kanabar, V.; Clarke, G.W.; Mahn, K.; Karner, C.; O’Connor, B.J.; Lee, T.H.; Hirst, S.J. Induction of angiogenesis by airway smooth muscle from patients with asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2008, 178, 460–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.X.; Varraso, R.; Dumas, O.; Stuart, J.J.; Florio, A.; Wang, L.; Rich-Edwards, J.W.; Camargo, C.A., Jr.; Chavarro, J.E. Hypertensive disorders of pregnancy and risk of asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: A prospective cohort study. Lancet Reg. Health Am. 2023, 23, 100540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kedar Sade, E.; Wainstock, T.; Tsumi, E.; Sheiner, E. Prenatal exposure to preeclampsia and long-term ophthalmic morbidity of the offspring. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tal, R. The role of hypoxia and hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha in preeclampsia pathogenesis. Biol. Reprod. 2012, 87, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gluckman, P.D.; Hanson, M.A.; Cooper, C.; Thornburg, K.L. Effect of in utero and early-life conditions on adult health and disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakim, J.; Senterman, M.K.; Hakim, A.M. Preeclampsia is a biomarker for vascular disease in both mother and child: The need for a medical alert system. Int. J. Pediatr. 2013, 2013, 953150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shulman, J.P.; Weng, C.; Wilkes, J.; Greene, T.; Hartnett, M.E. Association of Maternal Preeclampsia With Infant Risk of Premature Birth and Retinopathy of Prematurity. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2017, 135, 947–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCance, D.R. Pregnancy and diabetes. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 25, 945–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, M.; Shah, P.S.; Rusconi, F.; Reichman, B.; Modi, N.; Kusuda, S.; Lehtonen, L.; Håkansson, S.; Yang, J.; Isayama, T.; et al. Association of Maternal Diabetes With Neonatal Outcomes of Very Preterm and Very Low-Birth-Weight Infants: An International Cohort Study. JAMA Pediatr. 2018, 172, 867–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Shan, C.; Shi, Z. Role of the Gut Microbiota in the Increased Infant Body Mass Index Induced by Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. mSystems 2022, 7, e00465-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogurtsova, K.; Guariguata, L.; Barengo, N.C.; Ruiz, P.L.-D.; Sacre, J.W.; Karuranga, S.; Sun, H.; Boyko, E.J.; Magliano, D.J. IDF diabetes Atlas: Global estimates of undiagnosed diabetes in adults for 2021. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2022, 183, 109118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rueangdetnarong, H.; Sekararithi, R.; Jaiwongkam, T.; Kumfu, S.; Chattipakorn, N.; Tongsong, T.; Jatavan, P. Comparisons of the oxidative stress biomarkers levels in gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) and non-GDM among Thai population: Cohort study. Endocr. Connect. 2018, 7, 681–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganapathy, A.; Holla, R.; Darshan, B.; Kumar, N.; Kulkarni, V.; Unnikrishnan, B.; Thapar, R.; Mithra, P.; Kumar, A. Determinants of gestational diabetes mellitus: A hospital-based case–control study in coastal South India. Int. J. Diabetes Dev. Ctries. 2021, 41, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Janzen, C.; Zhu, Y.; Seamans, M.; Fei, Z.; Nianogo, R.; Chen, L. Prevalence of maternal hyperglycemic subtypes by race/ethnicity and associations between these subtypes with adverse pregnancy outcomes: Findings from a large retrospective multi-ethnic cohort in the United States. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2024, 209, 111576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thanawala, U.; Divakar, H.; Jain, R.; Agarwal, M.M. Negotiating gestational diabetes mellitus in India: A national approach. Medicina 2021, 57, 942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaminathan, G.; Swaminathan, A.; Corsi, D.J. Prevalence of gestational diabetes in India by individual socioeconomic, demographic, and clinical factors. JAMA Netw. Open 2020, 3, e2025074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moses, R.G.; Wong, V.C.; Lambert, K.; Morris, G.J.; San Gil, F. Seasonal changes in the prevalence of gestational diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 2016, 39, 1218–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokou, R.; Moschari, E.; Palioura, A.E.; Palioura, A.-P.; Mpakosi, A.; Adamakidou, T.; Vlachou, E.; Theodoraki, M.; Iacovidou, N.; Tsartsalis, A.N. The Impact of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus (GDM) on the Development and Composition of the Neonatal Gut Microbiota: A Systematic Review. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mpakosi, A.; Sokou, R.; Theodoraki, M.; Kaliouli-Antonopoulou, C. Neonatal Gut Mycobiome: Immunity, Diversity of Fungal Strains, and Individual and Non-Individual Factors. Life 2024, 14, 902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Liu, E.; Qiao, Y.; Katzmarzyk, P.T.; Chaput, J.P.; Fogelholm, M.; Johnson, W.D.; Kuriyan, R.; Kurpad, A.; Lambert, E.V.; et al. Maternal gestational diabetes and childhood obesity at age 9–11: Results of a multinational study. Diabetologia 2016, 59, 2339–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mpakosi, A.; Sokou, R.; Theodoraki, M.; Iacovidou, N.; Cholevas, V.; Kaliouli-Antonopoulou, C. Deciphering the Role of Maternal Microchimerism in Offspring Autoimmunity: A Narrative Review. Medicina 2024, 60, 1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grewal, J.; Siu, S.C.; d’Souza, R.; Lee, T.; Singer, J.; Rychel, V.; Kiess, M.; Sermer, M.; Silversides, C.K. Cardiac Risk Score to Predict Small for Gestational Age Infants in Pregnant Women With Heart Disease. Can. J. Cardiol. 2021, 37, 1915–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, M.; Nie, Y.; Shao, R.; Duan, S.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, M.; Xing, Z.; Sun, Q.; Liu, X.; Xu, W. Diversified gut microbiota in newborns of mothers with gestational diabetes mellitus. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0205695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Z.; Wu, J.; Xiao, B.; Xiao, S.; Li, H.; Wu, K. The Initial Oral Microbiota of Neonates Among Subjects With Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Front. Pediatr. 2019, 7, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crusell, M.K.W.; Hansen, T.H.; Nielsen, T.; Allin, K.H.; Rühlemann, M.C.; Damm, P.; Vestergaard, H.; Rørbye, C.; Jørgensen, N.R.; Christiansen, O.B.; et al. Comparative Studies of the Gut Microbiota in the Offspring of Mothers With and Without Gestational Diabetes. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 536282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Ning, X.; Rui, B.; Wang, Y.; Lei, Z.; Yu, D.; Liu, F.; Deng, Y.; Yuan, J.; Li, W.; et al. Alterations of milk oligosaccharides in mothers with gestational diabetes mellitus impede colonization of beneficial bacteria and development of RORγt+ Treg cell-mediated immune tolerance in neonates. Gut Microbes 2023, 15, 2256749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, W.; Luo, C.; Huang, J.; Li, C.; Liu, Z.; Liu, F. Gestational diabetes mellitus and adverse pregnancy outcomes: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ 2022, 377, e067946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, W.; Luo, C.; Zhou, J.; Liang, X.; Wen, J.; Huang, J.; Zeng, Y.; Wu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Liu, Z.; et al. Association between maternal diabetes and neurodevelopmental outcomes in children: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 202 observational studies comprising 56·1 million pregnancies. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2025, 13, 494–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lammers, A.E.; Diller, G.P.; Lober, R.; Möllers, M.; Schmidt, R.; Radke, R.M.; De-Torres-Alba, F.; Kaleschke, G.; Marschall, U.; Bauer, U.M.; et al. Maternal and neonatal complications in women with congenital heart disease: A nationwide analysis. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 4252–4260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardee, I.; Wright, L.; McCracken, C.; Lawson, E.; Oster, M.E. Maternal and Neonatal Outcomes of Pregnancies in Women With Congenital Heart Disease: A Meta-Analysis. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2021, 10, e017834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhiman, S.; Sharma, A.; Gupta, A.; Vatsa, R.; Bharti, J.; Kulshrestha, V.; Yadav, S.; Dadhwal, V.; Malhotra, N. Fetomaternal outcomes in pregnant women with congenital heart disease: A comparative analysis from an apex institute. Obstet. Gynecol. Sci. 2024, 67, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, B.T.; Baer, R.J.; Chambers, C.D.; Peyvandi, S.; Jelliffe-Pawlowski, L.L.; Steurer, M.A. What drives outcomes in infants of mothers with congenital heart disease? A mediation analysis. J. Perinatol. Off. J. Calif. Perinat. Assoc. 2024, 44, 366–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Campos, B.A.; Grewal, J.; Kiess, M.; Siu, S.C.; Pfaller, B.; Sermer, M.; Mason, J.; Silversides, C.K.; Haberer, K. Adverse fetal/neonatal and obstetric outcomes in pregnancies with both maternal and fetal heart disease. J. Perinatol. 2024, 44, 1424–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wald, R.M.; Silversides, C.K.; Kingdom, J.; Toi, A.; Lau, C.S.; Mason, J.; Colman, J.M.; Sermer, M.; Siu, S.C. Maternal Cardiac Output and Fetal Doppler Predict Adverse Neonatal Outcomes in Pregnant Women With Heart Disease. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2015, 4, e002414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gronningsaeter, L.; Langesaeter, E.; Sørbye, I.K.; Quattrone, A.; Almaas, V.M.; Skulstad, H.; Estensen, M.E. High prevalence of pre-eclampsia in women with coarctation of the aorta. Eur. Heart J. Open 2023, 3, oead072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramlakhan, K.P.; Malhamé, I.; Marelli, A.; Rutz, T.; Goland, S.; Franx, A.; Sliwa, K.; Elkayam, U.; Johnson, M.R.; Hall, R.; et al. Hypertensive disorders of pregnant women with heart disease: The ESC EORP ROPAC Registry. Eur. Heart J. 2022, 43, 3749–3761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, H.K.; Splitt, M.; Sharland, G.K.; Simpson, J.M. Patterns of recurrence of congenital heart disease: An analysis of 6,640 consecutive pregnancies evaluated by detailed fetal echocardiography. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2003, 42, 923–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, A.; Ferrer, Q.; Sánchez, O.; Ribera, I.; Arévalo, S.; Alomar, O.; Mendoza, M.; Cabero, L.; Carrerras, E.; Llurba, E. Placenta-related complications in women carrying a foetus with congenital heart disease. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2016, 29, 3271–3275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nora, J.J.; Nora, A.H. Maternal transmission of congenital heart diseases: New recurrence risk figures and the questions of cytoplasmic inheritance and vulnerability to teratogens. Am. J. Cardiol. 1987, 59, 459–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Øyen, N.; Boyd, H.A.; Carstensen, L.; Søndergaard, L.; Wohlfahrt, J.; Melbye, M. Risk of Congenital Heart Defects in Offspring of Affected Mothers and Fathers. Circ. Genom. Precis. Med. 2022, 15, e003533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodwall, K.; Leirgul, E.; Greve, G.; Vollset, S.E.; Holmstrøm, H.; Tell, G.S.; Øyen, N. Possible Common Aetiology behind Maternal Preeclampsia and Congenital Heart Defects in the Child: A Cardiovascular Diseases in Norway Project Study. Paediatr. Perinat. Epidemiol. 2016, 30, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, H.A.; Basit, S.; Behrens, I.; Leirgul, E.; Bundgaard, H.; Wohlfahrt, J.; Melbye, M.; Øyen, N. Association Between Fetal Congenital Heart Defects and Maternal Risk of Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy in the Same Pregnancy and Across Pregnancies. Circulation 2017, 136, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steurer, M.A.; Peyvandi, S.; Baer, R.J.; Oltman, S.P.; Chambers, C.D.; Norton, M.E.; Ryckman, K.K.; Moon-Grady, A.J.; Keller, R.L.; Shiboski, S.C.; et al. Impaired Fetal Environment and Gestational Age: What Is Driving Mortality in Neonates With Critical Congenital Heart Disease? J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2019, 8, e013194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linehan, L.A.; Walsh, J.; Morris, A.; Kenny, L.; O’Donoghue, K.; Dempsey, E.; Russell, N. Neonatal and maternal outcomes following midtrimester preterm premature rupture of the membranes: A retrospective cohort study. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2016, 16, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorrenti, S.; Di Mascio, D.; Khalil, A.; D’Antonio, F.; Rizzo, G.; Zullo, F.; D’Alberti, E.; D’Ambrosio, V.; Mappa, I.; Muzii, L.; et al. Outcome of prelabor rupture of membranes before or at the limit of viability: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. MFM 2024, 6, 101370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, J.A.; Park, M.M. Trends in twin and triplet births: 1980-97. In National Vital Statistics Reports: From the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Health Statistics, National Vital Statistics System; National Center for Health Statistics: Hyattsville, MD, USA, 1999; Volume 47, pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Joyce, A.; Martin, M.P.H.; Hamilton, B.E.; Michelle, J.K.; Osterman, M.H.S.; Driscoll, A.K. Births: Final Data for 2019’. In National Vital Statistics Reports: From the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Health Statistics, National Vital Statistics System; National Center for Health Statistics: Hyattsville, MD, USA, 2021; Volume 70, pp. 1–51. [Google Scholar]
- Mandy, G.T. Neonatal Complications, Outcome, and Management of Multiple Births. Available online: https://www.uptodate.com/contents/neonatal-complications-outcome-and-management-of-multiple-births (accessed on 16 May 2025).
- Bodeau-Livinec, F.; Zeitlin, J.; Blondel, B.; Arnaud, C.; Fresson, J.; Burguet, A.; Subtil, D.; Marret, S.; Rozé, J.C.; Marchand-Martin, L.; et al. Do very preterm twins and singletons differ in their neurodevelopment at 5 years of age? Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2013, 98, F480–F487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalikkot Thekkeveedu, R.; Dankhara, N.; Desai, J.; Klar, A.L.; Patel, J. Outcomes of multiple gestation births compared to singleton: Analysis of multicenter KID database. Matern. Health Neonatol. Perinatol. 2021, 7, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farmer, N.; Hillier, M.; Kilby, M.D.; Hodgetts-Morton, V.; Morris, R.K. Outcomes in intervention and management of multiple pregnancies trials: A systematic review. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2021, 261, 178–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, M.; Bhattacharya, S. Epidemiology of multiple pregnancy and the effect of assisted conception. Semin. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2010, 15, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Xu, Q.; Qian, J.; Liu, D.; Zhang, B.; Chen, X.; Zheng, M. Pregnancy outcomes of monochorionic diamniotic and dichorionic diamniotic twin pregnancies conceived by assisted reproductive technology and conceived naturally: A study based on chorionic comparison. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2024, 24, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giouleka, S.; Tsakiridis, I.; Mamopoulos, A.; Kalogiannidis, I.; Athanasiadis, A.; Dagklis, T. Fetal Growth Restriction: A Comprehensive Review of Major Guidelines. Obstet. Gynecol. Surv. 2023, 78, 690–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanney, M.; Marlow, N. Paediatric consequences of fetal growth restriction. Semin. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2004, 9, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dall’Asta, A.; Stampalija, T.; Mecacci, F.; Ramirez Zegarra, R.; Sorrentino, S.; Minopoli, M.; Ottaviani, C.; Fantasia, I.; Barbieri, M.; Lisi, F.; et al. Incidence, clinical features and perinatal outcome in anomalous fetuses with late-onset growth restriction: Cohort study. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. Off. J. Int. Soc. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2022, 60, 632–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, T.-Y.; Li, D.-Z. Perinatal outcome of late-onset fetal growth restriction: Etiology matters. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2022, 60, 707–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sacchi, C.; Marino, C.; Nosarti, C.; Vieno, A.; Visentin, S.; Simonelli, A. Association of Intrauterine Growth Restriction and Small for Gestational Age Status With Childhood Cognitive Outcomes: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Pediatr. 2020, 174, 772–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akseer, N.; Keats, E.C.; Thurairajah, P.; Cousens, S.; Bétran, A.P.; Oaks, B.M.; Osrin, D.; Piwoz, E.; Gomo, E.; Ahmed, F.; et al. Characteristics and birth outcomes of pregnant adolescents compared to older women: An analysis of individual level data from 140,000 mothers from 20 RCTs. eClinicalMedicine 2022, 45, 101309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marvin-Dowle, K.; Soltani, H. A comparison of neonatal outcomes between adolescent and adult mothers in developed countries: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. X 2020, 6, 100109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekari, M.; Shirzadfardjahromi, M.; Ranjbar, A.; Mehrnoush, V.; Darsareh, F.; Roozbeh, N. Advanced maternal age and adverse obstetrical and neonatal outcomes of singleton pregnancies. Gynecol. Obstet. Clin. Med. 2022, 2, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-N.; Choi, D.-W.; Kim, D.S.; Park, E.-C.; Kwon, J.-Y. Maternal age and risk of early neonatal mortality: A national cohort study. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blomberg, M.; Birch Tyrberg, R.; Kjølhede, P. Impact of maternal age on obstetric and neonatal outcome with emphasis on primiparous adolescents and older women: A Swedish Medical Birth Register Study. BMJ Open 2014, 4, e005840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irner, T.B.; Teasdale, T.W.; Nielsen, T.; Vedal, S.; Olofsson, M. Substance use during pregnancy and postnatal outcomes. J. Addict. Dis. 2012, 31, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, E.J.; Graham, D.L.; Money, K.M.; Stanwood, G.D. Developmental Consequences of Fetal Exposure to Drugs: What We Know and What We Still Must Learn. Neuropsychopharmacology 2015, 40, 61–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louw, K.A. Substance use in pregnancy: The medical challenge. Obstet. Med. 2018, 11, 54–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragsdale, A.S.; Al-Hammadi, N.; Loux, T.M.; Bass, S.; Keller, J.M.; Chavan, N.R. Perinatal substance use disorder: Examining the impact on adverse pregnancy outcomes. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. X 2024, 22, 100308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, G.; Blasina, F.; Rodríguez Rey, M.; Anesetti, G.; Sapiro, R.; Chavarría, L.; Cardozo, R.; Rey, G.; Sobrevia, L.; Nicolson, G.L. Pathophysiological and molecular considerations of viral and bacterial infections during maternal-fetal and –neonatal interactions of SARS-CoV-2, Zika, and Mycoplasma infectious diseases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Mol. Basis Dis. 2022, 1868, 166285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Beloushi, M.; Saleh, H.; Ahmed, B.; Konje, J.C. Congenital and Perinatal Viral Infections: Consequences for the Mother and Fetus. Viruses 2024, 16, 1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Saadaoui, M.; Al Khodor, S. Infections and Pregnancy: Effects on Maternal and Child Health. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 873253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enders, G.; Daiminger, A.; Bäder, U.; Exler, S.; Enders, M.J.J.o.C.V. Intrauterine transmission and clinical outcome of 248 pregnancies with primary cytomegalovirus infection in relation to gestational age. J. Clin. Virol. 2011, 52, 244–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boppana, S.B.; Rivera, L.B.; Fowler, K.B.; Mach, M.; Britt, W.J. Intrauterine transmission of cytomegalovirus to infants of women with preconceptional immunity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 344, 1366–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhry, S.A.; Koren, G. Hepatitis A infection during pregnancy. Can. Fam. Physician Med. Fam. Can. 2015, 61, 963–964. [Google Scholar]
- Motte, A.; Blanc, J.; Minodier, P. Acute hepatitis A in a pregnant woman at delivery. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2009, 13, e49–e51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elinav, E.; Ben–Dov, I.Z.; Shapira, Y.; Daudi, N.; Adler, R.; Shouval, D.; Ackerman, Z.J.G. Acute hepatitis A infection in pregnancy is associated with high rates of gestational complications and preterm labor. Gastroenterology 2006, 130, 1129–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirilert, S.; Tongsong, T. Hepatitis B Virus Infection in Pregnancy: Immunological Response, Natural Course and Pregnancy Outcomes. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dionne-Odom, J.; Cozzi, G.D.; Franco, R.A.; Njei, B.; Tita, A.T.N. Treatment and prevention of viral hepatitis in pregnancy. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2022, 226, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.-S. Prevention of Peripartum Hepatitis B Transmission. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1497. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shen, G.F.; Ge, C.H.; Shen, W.; Liu, Y.H.; Huang, X.Y. Association between hepatitis C infection during pregnancy with maternal and neonatal outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2023, 27, 3475–3488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Shabrawi, M.H.F.; Kamal, N.M.; Mogahed, E.A.; Elhusseini, M.A.; Aljabri, M.F. Perinatal transmission of hepatitis C virus: An update. Arch. Med. Sci. 2020, 16, 1360–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chudnovets, A.; Liu, J.; Narasimhan, H.; Liu, Y.; Burd, I. Role of Inflammation in Virus Pathogenesis during Pregnancy. J. Virol. 2020, 95, 10–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.; Silveira, L.; Crotteau, M.; Garth, K.; Canniff, J.; Fetters, K.B.; Lazarus, S.; Capraro, S.; Weinberg, A. Congenital Co-infections Among HIV-Exposed Infants Born to Mothers on Antiretroviral Treatment in the United States. Front. Pediatr. 2022, 10, 894627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donadono, V.; Saccone, G.; Sarno, L.; Esposito, G.; Mazzarelli, L.L.; Sirico, A.; Guida, M.; Martinelli, P.; Zullo, F.; Maruotti, G.M. Association between lymphadenopathy after toxoplasmosis seroconversion in pregnancy and risk of congenital infection. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Eur. Soc. Clin. Microbiol. 2022, 41, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallon, M.; Peyron, F. Congenital Toxoplasmosis: A Plea for a Neglected Disease. Pathogens 2018, 7, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyron, F.; Lobry, J.R.; Musset, K.; Ferrandiz, J.; Gomez-Marin, J.E.; Petersen, E.; Meroni, V.; Rausher, B.; Mercier, C.; Picot, S.; et al. Serotyping of Toxoplasma gondii in chronically infected pregnant women: Predominance of type II in Europe and types I and III in Colombia (South America). Microbes Infect. 2006, 8, 2333–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shwab, E.K.; Zhu, X.Q.; Majumdar, D.; Pena, H.F.; Gennari, S.M.; Dubey, J.P.; Su, C. Geographical patterns of Toxoplasma gondii genetic diversity revealed by multilocus PCR-RFLP genotyping. Parasitology 2014, 141, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bollani, L.; Auriti, C.; Achille, C.; Garofoli, F.; De Rose, D.U.; Meroni, V.; Salvatori, G.; Tzialla, C. Congenital Toxoplasmosis: The State of the Art. Front. Pediatr. 2022, 10, 894573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.; Dubey, J.P.; Su, C.; Ajioka, J.W.; Rosenthal, B.M.; Sibley, L.D. Genetic analyses of atypical Toxoplasma gondii strains reveal a fourth clonal lineage in North America. Int. J. Parasitol. 2011, 41, 645–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabilloud, M.; Wallon, M.; Peyron, F. In utero and at birth diagnosis of congenital toxoplasmosis: Use of likelihood ratios for clinical management. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2010, 29, 421–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, D.; Wallon, M.; Peyron, F.; Petersen, E.; Peckham, C.; Gilbert, R. Mother-to-child transmission of toxoplasmosis: Risk estimates for clinical counselling. Lancet 1999, 353, 1829–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moodley, A.; Payton, K.S.E. The Term Newborn: Congenital Infections. Clin. Perinatol. 2021, 48, 485–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallon, M.; Peyron, F. Effect of Antenatal Treatment on the Severity of Congenital Toxoplasmosis. Clin. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Infect. Dis. Soc. Am. 2016, 62, 811–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyron, F.; L’Ollivier, C.; Mandelbrot, L.; Wallon, M.; Piarroux, R.; Kieffer, F.; Hadjadj, E.; Paris, L.; Garcia-Meric, P. Maternal and Congenital Toxoplasmosis: Diagnosis and Treatment Recommendations of a French Multidisciplinary Working Group. Pathogens 2019, 8, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salari, N.; Rahimi, A.; Zarei, H.; Abdolmaleki, A.; Rasoulpoor, S.; Shohaimi, S.; Mohammadi, M. Global seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii in pregnant women: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2025, 25, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyron, F.; Mc Leod, R.; Ajzenberg, D.; Contopoulos-Ioannidis, D.; Kieffer, F.; Mandelbrot, L.; Sibley, L.D.; Pelloux, H.; Villena, I.; Wallon, M.; et al. Congenital Toxoplasmosis in France and the United States: One Parasite, Two Diverging Approaches. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0005222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prusa, A.R.; Kasper, D.C.; Pollak, A.; Gleiss, A.; Waldhoer, T.; Hayde, M. The Austrian Toxoplasmosis Register, 1992–2008. Clin. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Infect. Dis. Soc. Am. 2015, 60, e4–e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldonado, Y.A.; Read, J.S. Diagnosis, Treatment, and Prevention of Congenital Toxoplasmosis in the United States. Pediatrics 2017, 139, e20163860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torgerson, P.R.; Mastroiacovo, P. The global burden of congenital toxoplasmosis: A systematic review. Bull. World Health Organ. 2013, 91, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, P.V.; de Toledo, D.N.M.; de Souza, D.M.S.; Menezes, T.P.; Perucci, L.O.; Silva, Z.M.; Teixeira, D.C.; Vieira, E.W.R.; de Andrade-Neto, V.F.; Guimarães, N.S.; et al. The imbalance in the relationship between inflammatory and regulatory cytokines during gestational toxoplasmosis can be harmful to fetuses: A systematic review. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1074760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltrami, S.; Rizzo, S.; Schiuma, G.; Speltri, G.; Di Luca, D.; Rizzo, R.; Bortolotti, D. Gestational Viral Infections: Role of Host Immune System. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammad, W.A.B.; Konje, J.C. Herpes simplex virus infection in pregnancy—An update. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2021, 259, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dittmer, F.P.; Guimarães, C.M.; Peixoto, A.B.; Pontes, K.F.M.; Bonasoni, M.P.; Tonni, G.; Araujo Júnior, E. Parvovirus B19 Infection and Pregnancy: Review of the Current Knowledge. J. Pers. Med. 2024, 14, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindenburg, I.T.; Van Kamp, I.L. Intrauterine blood transfusion: Current indications and associated risks. Fetal Diagn. Ther. 2014, 36, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auriti, C.; De Rose, D.U.; Santisi, A.; Martini, L.; Piersigilli, F.; Bersani, I.; Ronchetti, M.P.; Caforio, L. Pregnancy and viral infections: Mechanisms of fetal damage, diagnosis and prevention of neonatal adverse outcomes from cytomegalovirus to SARS-CoV-2 and Zika virus. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2021, 1867, 166198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanthakumar, M.P.; Sood, A.; Ahmed, M.; Gupta, J. Varicella Zoster in pregnancy. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2021, 258, 283–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darmuzey, M.; Touret, F.; Slowikowski, E.; Gladwyn-Ng, I.; Ahuja, K.; Sanchez-Felipe, L.; de Lamballerie, X.; Verfaillie, C.; Marques, P.E.; Neyts, J.; et al. Epidemic Zika virus strains from the Asian lineage induce an attenuated fetal brain pathogenicity. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 10870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabata, T.; Petitt, M.; Puerta-Guardo, H.; Michlmayr, D.; Wang, C.; Fang-Hoover, J.; Harris, E.; Pereira, L. Zika Virus Targets Different Primary Human Placental Cells, Suggesting Two Routes for Vertical Transmission. Cell Host Microbe 2016, 20, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcelin, G.; Aldridge, J.R.; Duan, S.; Ghoneim, H.E.; Rehg, J.; Marjuki, H.; Boon, A.C.; McCullers, J.A.; Webby, R.J. Fatal outcome of pandemic H1N1 2009 influenza virus infection is associated with immunopathology and impaired lung repair, not enhanced viral burden, in pregnant mice. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 11208–11219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wastnedge, E.A.N.; Reynolds, R.M.; van Boeckel, S.R.; Stock, S.J.; Denison, F.C.; Maybin, J.A.; Critchley, H.O.D. Pregnancy and COVID-19. Physiol. Rev. 2021, 101, 303–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivanti, A.J.; Vauloup-Fellous, C.; Prevot, S.; Zupan, V.; Suffee, C.; Do Cao, J.; Benachi, A.; De Luca, D. Transplacental transmission of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, M.; Bunch, K.; Vousden, N.; Morris, E.; Simpson, N.; Gale, C.; O’Brien, P.; Quigley, M.; Brocklehurst, P.; Kurinczuk, J.J. Characteristics and outcomes of pregnant women admitted to hospital with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection in UK: National population based cohort study. BMJ 2020, 369, m2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allotey, J.; Chatterjee, S.; Kew, T.; Gaetano, A.; Stallings, E.; Fernández-García, S.; Yap, M.; Sheikh, J.; Lawson, H.; Coomar, D.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 positivity in offspring and timing of mother-to-child transmission: Living systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ 2022, 376, e067696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Mei, H.; Zheng, T.; Fu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Buka, S.; Yao, X.; Tang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Qiu, L.; et al. Pregnant women with COVID-19 and risk of adverse birth outcomes and maternal-fetal vertical transmission: A population-based cohort study in Wuhan, China. BMC Med. 2020, 18, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gale, C.; Quigley, M.A.; Placzek, A.; Knight, M.; Ladhani, S.; Draper, E.S.; Sharkey, D.; Doherty, C.; Mactier, H.; Kurinczuk, J.J. Characteristics and outcomes of neonatal SARS-CoV-2 infection in the UK: A prospective national cohort study using active surveillance. Lancet Child Adolesc. Health 2021, 5, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullins, E.; Hudak, M.L.; Banerjee, J.; Getzlaff, T.; Townson, J.; Barnette, K.; Playle, R.; Perry, A.; Bourne, T.; Lees, C.C.; et al. Pregnancy and neonatal outcomes of COVID-19: Coreporting of common outcomes from PAN-COVID and AAP-SONPM registries. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2021, 57, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papapanou, M.P.M.; Petta, A.; Routsi, E.; Farmaki, M.; Vlahos, N.; Siristatidis, C. Maternal and Neonatal Characteristics and Outcomes of COVID-19 in Pregnancy: An Overview of Systematic Reviews. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanes, E.D.; Mithal, L.B.; Otero, S.; Azad, H.A.; Miller, E.S.; Goldstein, J.A. Placental Pathology in COVID-19. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2020, 154, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patberg, E.T.; Adams, T.; Rekawek, P.; Vahanian, S.A.; Akerman, M.; Hernandez, A.; Rapkiewicz, A.V.; Ragolia, L.; Sicuranza, G.; Chavez, M.R.; et al. Coronavirus disease 2019 infection and placental histopathology in women delivering at term. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2021, 224, 382.e1–382.e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baergen, R.N.; Heller, D.S. Placental Pathology in Covid-19 Positive Mothers: Preliminary Findings. Pediatr. Dev. Pathol. Off. J. Soc. Pediatr. Pathol. Paediatr. Pathol. Soc. 2020, 23, 177–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulvey, J.J.; Magro, C.M.; Ma, L.X.; Nuovo, G.J.; Baergen, R.N. Analysis of complement deposition and viral RNA in placentas of COVID-19 patients. Ann. Diagn. Pathol. 2020, 46, 151530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linehan, L.; O’Donoghue, K.; Dineen, S.; White, J.; Higgins, J.R.; Fitzgerald, B. SARS-CoV-2 placentitis: An uncommon complication of maternal COVID-19. Placenta 2021, 104, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, D.A.; Baldewijns, M.; Benachi, A.; Bugatti, M.; Collins, R.R.J.; De Luca, D.; Facchetti, F.; Linn, R.L.; Marcelis, L.; Morotti, D.; et al. Chronic Histiocytic Intervillositis With Trophoblast Necrosis Is a Risk Factor Associated With Placental Infection From Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) and Intrauterine Maternal-Fetal Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) Transmission in Live-Born and Stillborn Infants. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2020, 145, 517–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redline, R.W.; Ravishankar, S.; Bagby, C.; Saab, S.; Zarei, S. Diffuse and Localized SARS-CoV-2 Placentitis: Prevalence and Pathogenesis of an Uncommon Complication of COVID-19 Infection During Pregnancy. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2022, 46, 1036–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, D.A.; Mulkey, S.B.; Roberts, D.J. SARS-CoV-2 placentitis, stillbirth, and maternal COVID-19 vaccination: Clinical–pathologic correlations. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2023, 228, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, C.A.; O’Reilly, D.P.; Edebiri, O.; Weiss, L.; Cullivan, S.; El-Khuffash, A.; Doyle, E.; Donnelly, J.C.; Malone, F.D.; Ferguson, W.; et al. Haematological parameters and coagulation in umbilical cord blood following COVID-19 infection in pregnancy. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2021, 266, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humberg, A.; Fortmann, I.; Siller, B.; Kopp, M.V.; Herting, E.; Göpel, W.; Härtel, C.; German Neonatal Network, German Center for Lung Research and Priming Immunity at the beginning of life (PRIMAL) Consortium. Preterm birth and sustained inflammation: Consequences for the neonate. Semin. Immunopathol. 2020, 42, 451–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Flores, V.; Romero, R.; Xu, Y.; Theis, K.R.; Arenas-Hernandez, M.; Miller, D.; Peyvandipour, A.; Bhatti, G.; Galaz, J.; Gershater, M.; et al. Maternal-fetal immune responses in pregnant women infected with SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taglauer, E.S.; Dhole, Y.; Boateng, J.; Snyder-Cappione, J.; Parker, S.E.; Clarke, K.; Juttukonda, L.; Devera, J.; Hunnewell, J.; Barnett, E.; et al. Evaluation of maternal-infant dyad inflammatory cytokines in pregnancies affected by maternal SARS-CoV-2 infection in early and late gestation. J. Perinatol. Off. J. Calif. Perinat. Assoc. 2022, 42, 1319–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, G.S.M.A.; de Souza, R.C.; de Oliveira Azevedo, V.M.G.; Guimarães, N.S.; Pires, L.G.; Lemos, S.M.A.; Alves, C.R.L. Effects of intrauterine exposure to SARS-CoV-2 on infants’ development: A rapid review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2023, 182, 2041–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayesa-Arriola, R.; Castro Quintas, Á.; Ortiz-García de la Foz, V.; Miguel Corredera, M.; San Martín González, N.; Murillo-García, N.; Neergaard, K.; Fañanás Saura, L.; de las Cuevas-Terán, I. Exploring the impact of COVID-19 on newborn neurodevelopment: A pilot study. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 2983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edlow, A.G.; Castro, V.M.; Shook, L.L.; Kaimal, A.J.; Perlis, R.H. Neurodevelopmental Outcomes at 1 Year in Infants of Mothers Who Tested Positive for SARS-CoV-2 During Pregnancy. JAMA Netw. Open 2022, 5, e2215787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, O.M.; Azamor, T.; Cambou, M.C.; Fuller, T.L.; Kerin, T.; Paiola, S.G.; Cranston, J.S.; Mok, T.; Rao, R.; Chen, W.; et al. Respiratory distress in SARS-CoV-2 exposed uninfected neonates followed in the COVID Outcomes in Mother-Infant Pairs (COMP) Study. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mor, G.; Aldo, P.; Alvero, A.B. The unique immunological and microbial aspects of pregnancy. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 469–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammoud, M.S.; Raghupathy, R.; Barakat, N.; Eltomi, H.; Elsori, D. Cytokine profiles at birth and the risk of developing severe respiratory distress and chronic lung disease. J. Res. Med. Sci. Off. J. Isfahan Univ. Med. Sci. 2017, 22, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrantsidis, D.M.; van de Wouw, M.; Hall, E.R.M.; Kuret, V.; Rioux, C.; Conrad, M.L.; Mesa, C.; Harris, A.; Lebel, C.; Tomfohr-Madsen, L.; et al. Neurodevelopment in the First 2 Years of Life Following Prenatal Exposure to Maternal SARS-CoV-2 Infection. JAMA Netw. Open 2024, 7, e2443697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturrock, S.; Ali, S.; Gale, C.; Battersby, C.; Le Doare, K. Neonatal outcomes and indirect consequences following maternal SARS-CoV-2 infection in pregnancy: A systematic review. BMJ Open 2023, 13, e063052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox Bauer, C.M.; Bernhard, K.A.; Greer, D.M.; Merrill, D.C. Maternal and neonatal outcomes in obese women who lose weight during pregnancy. J. Perinatol. Off. J. Calif. Perinat. Assoc. 2016, 36, 278–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurnaz, D.; Karaçam, Z. The effect of methods used in the management of maternal obesity on pregnancy and birth outcomes: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Int. J. Obes. 2025, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolin, C.D.; Kominiarek, M.A. Pregnancy in Women with Obesity. Obstet. Gynecol. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 45, 217–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haseler, E.; Melhem, N.; Sinha, M.D. Renal disease in pregnancy: Fetal, neonatal and long-term outcomes. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2019, 57, 60–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hildebrand, A.M.; Liu, K.; Shariff, S.Z.; Ray, J.G.; Sontrop, J.M.; Clark, W.F.; Hladunewich, M.A.; Garg, A.X. Characteristics and outcomes of AKI treated with dialysis during pregnancy and the postpartum period. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 26, 3085–3091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ma, X.; Zheng, J.; Liu, X.; Yan, T. Pregnancy outcomes in patients with acute kidney injury during pregnancy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2017, 17, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munkhaugen, J.; Lydersen, S.; Romundstad, P.R.; Widerøe, T.-E.; Vikse, B.E.; Hallan, S. Kidney function and future risk for adverse pregnancy outcomes: A population-based study from HUNT II, Norway. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2009, 24, 3744–3750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.; Davison, J. Chronic kidney disease in pregnancy. BMJ 2008, 336, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benatar, S.; Cross-Barnet, C.; Johnston, E.; Hill, I. Prenatal Depression: Assessment and Outcomes among Medicaid Participants. J. Behav. Health Serv. Res. 2020, 47, 409–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagberg, K.W.; Robijn, A.L.; Jick, S. Maternal depression and antidepressant use during pregnancy and the risk of autism spectrum disorder in offspring. Clin. Epidemiol. 2018, 10, 1599–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahan, N.; Went, T.R.; Sultan, W.; Sapkota, A.; Khurshid, H.; Qureshi, I.A.; Alfonso, M. Untreated Depression During Pregnancy and Its Effect on Pregnancy Outcomes: A Systematic Review. Cureus 2021, 13, e17251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreoli, L.; Andersen, J.; Avcin, T.; Chambers, C.D.; Fazzi, E.M.; Marlow, N.; Wulffraat, N.M.; Tincani, A. The outcomes of children born to mothers with autoimmune rheumatic diseases. Lancet Rheumatol. 2024, 6, e573–e586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sammaritano, L.R.; Bermas, B.L.; Chakravarty, E.E.; Chambers, C.; Clowse, M.E.; Lockshin, M.D.; Marder, W.; Guyatt, G.; Branch, D.W.; Buyon, J. 2020 American College of Rheumatology guideline for the management of reproductive health in rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020, 72, 529–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Steenwinkel, F.D.; Hokken-Koelega, A.C.; de Ridder, M.A.; Hazes, J.M.; Dolhain, R.J. Rheumatoid arthritis during pregnancy and postnatal catch-up growth in the offspring. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014, 66, 1705–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mofors, J.; Eliasson, H.; Ambrosi, A.; Salomonsson, S.; Skog, A.; Fored, M.; Ekbom, A.; Bergman, G.; Sonesson, S.-E.; Wahren-Herlenius, M. Comorbidity and long-term outcome in patients with congenital heart block and their siblings exposed to Ro/SSA autoantibodies in utero. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 78, 696–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohebalizadeh, M.; Babapour, G.; Maleki Aghdam, M.; Mohammadi, T.; Jafari, R.; Shafiei-Irannejad, V. Role of maternal immune factors in neuroimmunology of brain development. Mol. Neurobiol. 2024, 61, 9993–10005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, W.; Norrbäck, M.; Levine, S.Z.; Rivera, N.; Buxbaum, J.D.; Zhu, H.; Yip, B.; Reichenberg, A.; Askling, J.; Sandin, S. Maternal rheumatoid arthritis and risk of autism in the offspring. Psychol. Med. 2023, 53, 7300–7308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokou, R.; Parastatidou, S.; Iliodromiti, Z.; Lampropoulou, K.; Vrachnis, D.; Boutsikou, T.; Konstantinidi, A.; Iacovidou, N. Knowledge gaps and current evidence regarding breastfeeding issues in mothers with chronic diseases. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, V.M.; Davies, M.J. Diet during pregnancy, neonatal outcomes and later health. Reprod. Fertil. Dev. 2005, 17, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, X.; Mackean, P.P.; Cape, G.A.; Johnson, J.W.; Ou, X. Maternal Nutrition during Pregnancy and Offspring Brain Development: Insights from Neuroimaging. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quezada-Pinedo, H.G.; Cassel, F.; Duijts, L.; Muckenthaler, M.U.; Gassmann, M.; Jaddoe, V.W.V.; Reiss, I.K.M.; Vermeulen, M.J. Maternal Iron Status in Pregnancy and Child Health Outcomes after Birth: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christian, P.; Mullany, L.C.; Hurley, K.M.; Katz, J.; Black, R.E. Nutrition and maternal, neonatal, and child health. Semin. Perinatol. 2015, 39, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crispi, F.; Miranda, J.; Gratacós, E. Long-term cardiovascular consequences of fetal growth restriction: Biology, clinical implications, and opportunities for prevention of adult disease. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2018, 218, S869–S879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thulstrup, A.M.; Bonde, J.P. Maternal occupational exposure and risk of specific birth defects. Occup. Med. 2006, 56, 532–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinder, N.; Prins, J.R.; Bergman, J.E.H.; Smidt, N.; Kromhout, H.; Boezen, H.M.; de Walle, H.E.K. Congenital anomalies in the offspring of occupationally exposed mothers: A systematic review and meta-analysis of studies using expert assessment for occupational exposures. Hum. Reprod. 2019, 34, 903–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haggerty, D.K.; Upson, K.; Pacyga, D.C.; Franko, J.E.; Braun, J.M.; Strakovsky, R.S. REPRODUCTIVE TOXICOLOGY: Pregnancy exposure to endocrine disrupting chemicals: Implications for women’s health. Reproduction 2021, 162, F169–F180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, R.A.; Abar, B.; Elman, L.N.; Walsh, K.M.; Hurst, J.H.; Cohen, J.L. Identifying associations between genetic conditions in offspring and pregnancy health complications. Reprod. Female Child Health 2024, 3, e80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardy, A.H.; Chetty, S.P.; Norton, M.E. Maternal genetic disorders and fetal development. Prenat. Diagn. 2020, 40, 1056–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastrolia, S.A.; Baumfeld, Y.; Hershkovitz, R.; Yohay, D.; Trojano, G.; Weintraub, A.Y. Independent association between uterine malformations and cervical insufficiency: A retrospective population-based cohort study. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2018, 297, 919–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.-A.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, Y.-H. Reproductive, Obstetric and Neonatal Outcomes in Women with Congenital Uterine Anomalies: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 4797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilarski, N.; Bhogal, G.; Hamer, J.; Man, R.; Morris, R.K.; Hodgetts-Morton, V. Interventions for women with premature cervical dilatation and exposed fetal membranes to prevent pregnancy loss and preterm birth—A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2024, 300, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tellum, T.; Bracco, B.; De Braud, L.V.; Knez, J.; Ashton-Barnett, R.; Amin, T.; Chaggar, P.; Jurkovic, D. Reproductive outcome in 326 women with unicornuate uterus. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2023, 61, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murvai, V.-R.; Galiș, R.; Macrea, C.-M.; Tărău-Copos, A.-F.; Goman, M.D.; Ghitea, T.C.; Huniadi, A. The Impact of Thrombophilia on Maternal and Neonatal Outcomes: A Multisystem Analysis of Clinical, Hematological, and Metabolic Parameters. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 3665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, B.-C.; Yang, H.-Y.; Su, J.-Y.; Deng, L. Analysis of pregnancy and neonatal outcomes in 100 pregnant women with Rh-negative blood type. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2024, 24, 815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahr, T.M.; Tweddell, S.M.; Zalla, J.M.; Dizon-Townson, D.; Ohls, R.K.; Henry, E.; Ilstrup, S.J.; Kelley, W.E.; Ling, C.Y.; Lindgren, P.C.; et al. Neonatal and Obstetrical Outcomes of Pregnancies Complicated by Alloimmunization. Pediatrics 2024, 153, e2023064604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granese, R.; Calagna, G.; Alibrandi, A.; Martinelli, C.; Romeo, P.; Filomia, R.; Ferraro, M.I.; Piccione, E.; Ercoli, A.; Saitta, C. Maternal and Neonatal Outcomes in Intrahepatic Cholestasis of Pregnancy. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouwers, L.; Koster, M.P.; Page-Christiaens, G.C.; Kemperman, H.; Boon, J.; Evers, I.M.; Bogte, A.; Oudijk, M.A. Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy: Maternal and fetal outcomes associated with elevated bile acid levels. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2015, 212, 100.e101–100.e107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Tang, M.; Jiang, F.; Jia, Y.; Chin, R.K.H.; Liang, W.; Cheng, H. Intrahepatic Cholestasis of Pregnancy and Associated Adverse Maternal and Fetal Outcomes: A Retrospective Case-Control Study. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2021, 2021, 6641023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazarpour, S.; Ramezani Tehrani, F.; Simbar, M.; Azizi, F. Thyroid dysfunction and pregnancy outcomes. Iran. J. Reprod. Med. 2015, 13, 387–396. [Google Scholar]
- Vamja, R.M.Y.; Patel, M.; Vala, V.; Ramachandran, A.; Surati, B.; Nagda, J. Impact of maternal thyroid dysfunction on fetal and maternal outcomes in pregnancy: A prospective cohort study. Clin. Diabetes Endocrinol. 2024, 10, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hizkiyahu, R.; Badeghiesh, A.; Baghlaf, H.; Dahan, M.H. Associations between hypothyroidism and adverse obstetric and neonatal outcomes: A study of a population database including over 184,000 women with hypothyroidism. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. Off. J. Eur. Assoc. Perinat. Med. Fed. Asia Ocean. Perinat. Soc. Int. Soc. Perinat. Obs. 2023, 36, 2278027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nam, J.Y.; Oh, S.S.; Park, E.C. The Association Between Adequate Prenatal Care and Severe Maternal Morbidity Among Teenage Pregnancies: A Population-Based Cohort Study. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 782143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirshberg, A.; Srinivas, S.K. Epidemiology of maternal morbidity and mortality. Semin. Perinatol. 2017, 41, 332–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, J.Y.; Cho, E.; Park, E.C. Do severe maternal morbidity and adequate prenatal care affect the delivery cost? A nationwide cohort study for 11 years with follow up. BJOG Int. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2019, 126, 1623–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Bekai, E.; Beaini, C.E.; Kalout, K.; Safieddine, O.; Semaan, S.; Sahyoun, F.; Ghadieh, H.E.; Azar, S.; Kanaan, A.; Harb, F. The Hidden Impact of Gestational Diabetes: Unveiling Offspring Complications and Long-Term Effects. Life 2025, 15, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, A.; Potdar, J. Maternal Mental Health During Pregnancy: A Critical Review. Cureus 2022, 14, e30656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Wambua, S.; Lee, S.I.; Okoth, K.; Wang, Z.; Fayaz, F.F.A.; Eastwood, K.-A.; Nelson-Piercy, C.; Reynolds, J.A.; Nirantharakumar, K.; et al. Autoimmune diseases and adverse pregnancy outcomes: An umbrella review. BMC Med. 2024, 22, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, S.; Vora, N.L. Maternal Genetic Disorders in Pregnancy. Obstet. Gynecol. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 45, 249–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsammani, M.A.; Jafer, A.M.; Khieri, S.A.; Ali, A.O.; Shaaeldin, M.A. Effect of Grand Multiparity on Pregnancy Outcomes in Women Under 35 Years of Age: A Comparative Study. Med. Arch. 2019, 73, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, D.; Sun, F.; Han, S.; Lu, L.; Sun, Y.; Song, Q. Adverse outcomes in subsequent pregnancies in women with history of recurrent spontaneous abortion: A meta-analysis. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Res. 2024, 50, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buicu, C.F.; Mitranovici, M.I.; Dumitrascu Biris, D.; Craina, M.; Bernad, E.S. Birth Outcomes in Pregnancies with Uterine Malformations: A Single-Center Retrospective Study. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholls-Dempsey, L.; Badeghiesh, A.; Baghlaf, H.; Dahan, M.H. How does high socioeconomic status affect maternal and neonatal pregnancy outcomes? A population-based study among American women. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. X 2023, 20, 100248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekechi, C. Fear of using medicines in pregnancy risks the lives of women and children. Br. J. Hosp. Med. 2022, 83, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, A.L.; Ahmadzia, H.; Ashcroft, R.; Bucci-Rechtweg, C.; Spencer, R.N.; Thornton, S. Improving Development of Drug Treatments for Pregnant Women and the Fetus. Ther. Innov. Regul. Sci. 2022, 56, 976–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCloskey, L.; Bernstein, J.; The Bridging The Chasm, C.; Amutah-Onukagha, N.; Anthony, J.; Barger, M.; Belanoff, C.; Bennett, T.; Bird, C.E.; Bolds, D.; et al. Bridging the Chasm between Pregnancy and Health over the Life Course: A National Agenda for Research and Action. Women’s Health Issues Off. Publ. Jacobs Inst. Women’s Health 2021, 31, 204–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vedam, S.; Stoll, K.; Taiwo, T.K.; Rubashkin, N.; Cheyney, M.; Strauss, N.; McLemore, M.; Cadena, M.; Nethery, E.; Rushton, E.; et al. The Giving Voice to Mothers study: Inequity and mistreatment during pregnancy and childbirth in the United States. Reprod. Health 2019, 16, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manuck, T.A.; Rice, M.M.; Bailit, J.L.; Grobman, W.A.; Reddy, U.M.; Wapner, R.J.; Thorp, J.M.; Caritis, S.N.; Prasad, M.; Tita, A.T.; et al. Preterm neonatal morbidity and mortality by gestational age: A contemporary cohort. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2016, 215, 103.e1–103.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Maternal Disease/Risk Factor | Pregnancy Complications and Neonatal Outcomes | References | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metabolic disease | Obesity/Severe weight loss | Pregnancy | Increases risk of gestational diabetes, preeclampsia, dystocia, and cesarean delivery. | [186,187,188] |
| Offspring | Macrosomia or fetal growth restriction (FGR), shoulder dystocia, neonatal hypoglycemia, increased neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) admissions. | |||
| Renal disease | Chronic kidney disease, acute kidney injury | Pregnancy | Linked with hypertension, preeclampsia. | [189,190,191,192,193] |
| Offspring | Preterm birth, low birth weight, FGR, increased perinatal mortality. | |||
| Mental Health | History of depression/anxiety | Pregnancy | Elevated risk of postpartum depression. | [194,195,196] |
| Offspring | Preterm birth, low Apgar score impaired maternal-infant bonding, and increases long-term cognitive/behavioral issues | |||
| Immunologic Disorders | Antiphospholipid syndrome, autoimmune rheumatic diseases, systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), inflammatory bowel disorders | Pregnancy | High risk for miscarriage, stillbirth, preeclampsia, and maternal thrombosis. | [197,198,199,200,201,202,203] |
| Offspring | FGR, preterm birth, increased neonatal susceptibility to infections, suboptimal vaccine responses, potential organ toxicity, congenital malformations neonatal lupus, congenital heart block, and adverse long-term outcomes such as metabolic and cardiovascular diseases as well as neurodevelopmental impairments and autism spectrum disorder. | |||
| Nutritional status | Inadequate maternal nutrition, maternal under- and over-nutrition | Pregnancy | Placental insufficiency, and metabolic dysregulation preeclampsia, anemia, increased maternal mortality | [204,205,206,207,208] |
| Offspring | FGR, preterm birth, small for gestational age (SGA), low birth weight, neural tube defects, increased neonatal susceptibility to infections, neonatal hypothermia, elevated risk of neonatal death, and long-term health complications, including obesity, type 2 diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and cognitive impairments. | |||
| Environmental/Occupational | Exposure to chemicals, heavy labor | Pregnancy | Risk of embryotoxicity, miscarriage, preterm delivery, and impaired placental oxygenation. | [209,210,211] |
| Offspring | Congenital anomalies, prematurity and low birth weight | |||
| Genetic | Hereditary diseases/family history | Pregnancy | Increased risk for, miscarriage and perinatal loss and preterm birth, risk of maternal HELLP syndrome or acute fatty liver of pregnancy | [212,213] |
| Offspring | Preterm birth, congenital anomalies and inherited disorders in the fetus. | |||
| Obstetric History | Uterine anomalies, cervical insufficiency, previous preterm labor, miscarriages, stillbirth, uterine surgery | Pregnancy | Associated with cervical insufficiency, cord prolapse, uterine rupture, placenta accreta, and intrapartum hemorrhage and placenta previa, miscarriage, preterm labor, abnormal fetal presentation. Raises the likelihood of complications in subsequent deliveries (e.g., dystocia). | [214,215,216,217] |
| Offspring | Birth injuries, prematurity, perinatal asphyxia, congenital abnormality. | |||
| Hematologic | Anemia, Thrombophilia, Rh isoimmunization, | Pregnancy | Preeclampsia, placental abruption, coagulation abnormalities, increased risk of thrombosis, preterm delivery. | [218,219,220] |
| Offspring | Hemolytic disease of the newborn, neonatal anemia, FGR, fetal loss, fetal anemia, edema, thrombosis-related neonatal complications, neonatal jaundice, increased NICU admissions | |||
| Liver/Biliary | Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy | Pregnancy | Increased risk of stillbirth, preterm labor, post-partum hemorrhage, and emergency caesarean section risk | [221,222,223] |
| Offspring | Stillbirth, meconium-stained amniotic fluid, respiratory distress, NICU admission, perinatal death | |||
| Thyroid dysfunction | hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism and thyroid autoimmune disorders | Pregnancy | Pregnancy induced hypertension thyroid crisis, preeclampsia, preterm labor, miscarriage, postpartum hemorrhage | [224,225,226] |
| Offspring | Congenital anomalies (cardiac, neural tube), macrosomia, preterm birth, hypoglycemia, neurodevelopmental delays | |||
| Social Factors | Low socioeconomic status Inadequate prenatal follow-up (<3 visits) | Pregnancy | Linked to higher maternal morbidity and mortality, inadequate prenatal care, malnutrition. | [227,228,229] |
| Offspring | Increases the risk of undetected complications, low birth weight, prematurity, neonatal infection, hypothermia, increased risk of perinatal and neonatal mortality | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sokou, R.; Lianou, A.; Lampridou, M.; Panagiotounakou, P.; Kafalidis, G.; Paliatsiou, S.; Volaki, P.; Tsantes, A.G.; Boutsikou, T.; Iliodromiti, Z.; et al. Neonates at Risk: Understanding the Impact of High-Risk Pregnancies on Neonatal Health. Medicina 2025, 61, 1077. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61061077
Sokou R, Lianou A, Lampridou M, Panagiotounakou P, Kafalidis G, Paliatsiou S, Volaki P, Tsantes AG, Boutsikou T, Iliodromiti Z, et al. Neonates at Risk: Understanding the Impact of High-Risk Pregnancies on Neonatal Health. Medicina. 2025; 61(6):1077. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61061077
Chicago/Turabian StyleSokou, Rozeta, Alexandra Lianou, Maria Lampridou, Polytimi Panagiotounakou, Georgios Kafalidis, Styliani Paliatsiou, Paraskevi Volaki, Andreas G. Tsantes, Theodora Boutsikou, Zoi Iliodromiti, and et al. 2025. "Neonates at Risk: Understanding the Impact of High-Risk Pregnancies on Neonatal Health" Medicina 61, no. 6: 1077. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61061077
APA StyleSokou, R., Lianou, A., Lampridou, M., Panagiotounakou, P., Kafalidis, G., Paliatsiou, S., Volaki, P., Tsantes, A. G., Boutsikou, T., Iliodromiti, Z., & Iacovidou, N. (2025). Neonates at Risk: Understanding the Impact of High-Risk Pregnancies on Neonatal Health. Medicina, 61(6), 1077. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61061077










