Prevalence and Fall Risk of Sarcopenia Based on the 2023 Korean Working Group on Sarcopenia Criteria
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Measurement Methods and Criteria According to the KWGS Guidelines
2.2.1. Muscle Mass
2.2.2. Muscle Strength
2.2.3. Physical Performance
2.3. Fall Incidents in a Year
2.4. Covariates
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Main Findings
4.2. Clinical Implications
4.3. Limitation, Strengths and Suggestions for Future Studies
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Sayer, A.A. Sarcopenia. Lancet 2019, 393, 2636–2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santilli, V.; Bernetti, A.; Mangone, M.; Paoloni, M. Clinical definition of sarcopenia. Clin. Cases Miner. Bone Metab. 2014, 11, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muscaritoli, M.; Anker, S.D.; Argilés, J.; Aversa, Z.; Bauer, J.; Biolo, G.; Boirie, Y.; Bosaeus, I.; Cederholm, T.; Costelli, P. Consensus definition of sarcopenia, cachexia and pre-cachexia: Joint document elaborated by Special Interest Groups (SIG)“cachexia-anorexia in chronic wasting diseases” and “nutrition in geriatrics”. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 29, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morley, J. Sarcopenia: Diagnosis and treatment. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2008, 12, 452–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallengren, O.; Bosaeus, I.; Frändin, K.; Lissner, L.; Falk Erhag, H.; Wetterberg, H.; Sterner, T.R.; Rydén, L.; Rothenberg, E.; Skoog, I. Comparison of the 2010 and 2019 diagnostic criteria for sarcopenia by the European Working Group on Sarcopenia in Older People (EWGSOP) in two cohorts of Swedish older adults. BMC Geriatr. 2021, 21, 600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Baeyens, J.P.; Bauer, J.M.; Boirie, Y.; Cederholm, T.; Landi, F.; Martin, F.C.; Michel, J.-P.; Rolland, Y.; Schneider, S.M. Sarcopenia: European consensus on definition and diagnosis: Report of the European Working Group on Sarcopenia in Older People. Age Ageing 2010, 39, 412–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.-K.; Woo, J.; Assantachai, P.; Auyeung, T.-W.; Chou, M.-Y.; Iijima, K.; Jang, H.C.; Kang, L.; Kim, M.; Kim, S. Asian Working Group for Sarcopenia: 2019 consensus update on sarcopenia diagnosis and treatment. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2020, 21, 300–307.e302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, J.Y.; Jung, H.-W.; Kim, K.M.; Kim, M.; Park, C.Y.; Lee, K.-P.; Lee, S.Y.; Jang, I.-Y.; Jeon, O.H.; Lim, J.-Y. Korean Working Group on Sarcopenia guideline: Expert consensus on sarcopenia screening and diagnosis by the Korean Society of Sarcopenia, the Korean Society for Bone and Mineral Research, and the Korean Geriatrics Society. Ann. Geriatr. Med. Res. 2023, 27, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dionyssiotis, Y. Analyzing the problem of falls among older people. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2012, 5, 805–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganz, D.A.; Bao, Y.; Shekelle, P.G.; Rubenstein, L.Z. Will my patient fall? JAMA 2007, 297, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, S.S.; Reijnierse, E.M.; Pham, V.K.; Trappenburg, M.C.; Lim, W.K.; Meskers, C.G.; Maier, A.B. Sarcopenia and its association with falls and fractures in older adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2019, 10, 485–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Hao, Q.; Ge, M.; Dong, B. Association of sarcopenia and fractures in community-dwelling older adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. Osteoporos. Int. 2018, 29, 1253–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malmstrom, T.K.; Miller, D.K.; Simonsick, E.M.; Ferrucci, L.; Morley, J.E. SARC-F: A symptom score to predict persons with sarcopenia at risk for poor functional outcomes. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2016, 7, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malmstrom, T.K.; Morley, J.E. SARC-F: A simple questionnaire to rapidly diagnose sarcopenia. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2013, 14, 531–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, C.W.; Lee, S.; Kim, J.; Chon, D.; Kim, S.; Kim, C.-O.; Kim, M.K.; Cho, B.; Choi, K.M.; Roh, E. Korean frailty and aging cohort study (KFACS): Cohort profile. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e035573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezzotti, P.; Scalmana, S.; Mastromattei, A.; Di Lallo, D.; Group, P.A.W. The accuracy of the MMSE in detecting cognitive impairment when administered by general practitioners: A prospective observational study. BMC Fam. Pract. 2008, 9, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Hu, K.; Yan, C.; Zhao, B.; Mei, F.; Chen, F.; Zhao, L.; Shang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Ma, B. Associated factors of sarcopenia in community-dwelling older adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Won, C.W. Sarcopenia in Korean community-dwelling adults aged 70 years and older: Application of screening and diagnostic tools from the Asian Working Group for Sarcopenia 2019 update. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2020, 21, 752–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choo, Y.J.; Chang, M.C. Prevalence of sarcopenia among the elderly in Korea: A meta-analysis. J. Prev. Med. Public Health 2021, 54, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Ha, Y.-C.; Kim, D.-Y.; Yoo, J.-I. Recent Update on the Prevalence of Sarcopenia in Koreans: Findings from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. J. Bone Metab. 2024, 31, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spira, D.; Norman, K.; Nikolov, J.; Demuth, I.; Steinhagen-Thiessen, E.; Eckardt, R. Prevalence and definition of sarcopenia in community dwelling older people. Z. Für Gerontol. Und Geriatr. 2016, 49, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doherty, T.J. The influence of aging and sex on skeletal muscle mass and strength. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2001, 4, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersson, B.; Nordin, E.; Ramnemark, A.; Lundin-Olsson, L. Neither Timed Up and Go test nor Short Physical Performance Battery predict future falls among independent adults aged≥ 75 years living in the community. J. Frailty Sarcopenia Falls 2020, 5, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyrdalen, I.L.; Thingstad, P.; Sandvik, L.; Ormstad, H. Associations between gait speed and well-known fall risk factors among community-dwelling older adults. Physiother. Res. Int. 2019, 24, e1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freiberger, E.; Fabbietti, P.; Corsonello, A.; Lattanzio, F.; Sieber, C.; Tap, L.; Mattace-Raso, F.; Ärnlöv, J.; Carlsson, A.C.; Roller-Wirnsberger, R. Short physical performance battery is not associated with falls and injurious falls in older persons: Longitudinal data of the SCOPE project. Eur. Geriatr. Med. 2024, 15, 831–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Studenski, S.; Perera, S.; Patel, K.; Rosano, C.; Faulkner, K.; Inzitari, M.; Brach, J.; Chandler, J.; Cawthon, P.; Connor, E.B. Gait speed and survival in older adults. JAMA 2011, 305, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verghese, J.; Holtzer, R.; Lipton, R.B.; Wang, C. Quantitative gait markers and incident fall risk in older adults. J. Gerontol. Ser. A Biomed. Sci. Med. Sci. 2009, 64, 896–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narici, M.V.; Maffulli, N. Sarcopenia: Characteristics, mechanisms and functional significance. Br. Med. Bull. 2010, 95, 139–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, L.; Ding, Y.; Leung, B.; Ismail, N.; Yeo, A.; Yew, S.; Tay, K.; Tan, C.; Chong, M. Sex-specific differences in risk factors for sarcopenia amongst community-dwelling older adults. Age 2015, 37, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Cheng, K.Y.-K.; Tong, X.; Cheung, W.-H.; Chow, S.K.-H.; Law, S.W.; Wong, R.M.Y. The role of obesity in sarcopenia and the optimal body composition to prevent against sarcopenia and obesity. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1077255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.-H.; Hwang, A.-C.; Liu, L.-K.; Peng, L.-N.; Chen, L.-K. Sex differences of sarcopenia in Asian populations: The implications in diagnosis and management. J. Clin. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2016, 7, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaap, L.A.; Van Schoor, N.M.; Lips, P.; Visser, M. Associations of sarcopenia definitions, and their components, with the incidence of recurrent falling and fractures: The longitudinal aging study Amsterdam. J. Gerontol. Ser. A 2018, 73, 1199–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, A.; Ma, Y.; Zhou, X.; Guo, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X. Association between sarcopenia and levels of growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor-1 in the elderly. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2020, 21, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirchengast, S.; Huber, J. Gender and age differences in lean soft tissue mass and sarcopenia among healthy elderly. Anthropol. Anz. 2009, 67, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jong, J.C.; Attema, B.J.; van der Hoek, M.D.; Verschuren, L.; Caspers, M.P.; Kleemann, R.; van der Leij, F.R.; van den Hoek, A.M.; Nieuwenhuizen, A.G.; Keijer, J. Sex differences in skeletal muscle-aging trajectory: Same processes, but with a different ranking. Geroscience 2023, 45, 2367–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haizlip, K.; Harrison, B.; Leinwand, L. Sex-based differences in skeletal muscle kinetics and fiber-type composition. Physiology 2015, 30, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagotto, V.; Silveira, E.A. Methods, diagnostic criteria, cutoff points, and prevalence of sarcopenia among older people. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 231312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.-H.; Do, J.G.; Lee, Y.-T.; Yoon, K.J. Sex difference in cutoff and prevalence of sarcopenia among 300,090 Urban Korean population: Association with metabolic syndrome. Medicina 2022, 58, 1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sialino, L.D.; Schaap, L.A.; van Oostrom, S.H.; Picavet, H.S.J.; Twisk, J.W.; Verschuren, W.M.; Visser, M.; Wijnhoven, H.A. The sex difference in gait speed among older adults: How do sociodemographic, lifestyle, social and health determinants contribute? BMC Geriatr. 2021, 21, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinoshita, K.; Satake, S.; Matsui, Y.; Arai, H. Association between sarcopenia and fall risk according to the muscle mass adjustment method in Japanese older outpatients. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2021, 25, 762–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Studenski, S.A.; Peters, K.W.; Alley, D.E.; Cawthon, P.M.; McLean, R.R.; Harris, T.B.; Ferrucci, L.; Guralnik, J.M.; Fragala, M.S.; Kenny, A.M. The FNIH sarcopenia project: Rationale, study description, conference recommendations, and final estimates. J. Gerontol. Ser. A Biomed. Sci. Med. Sci. 2014, 69, 547–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
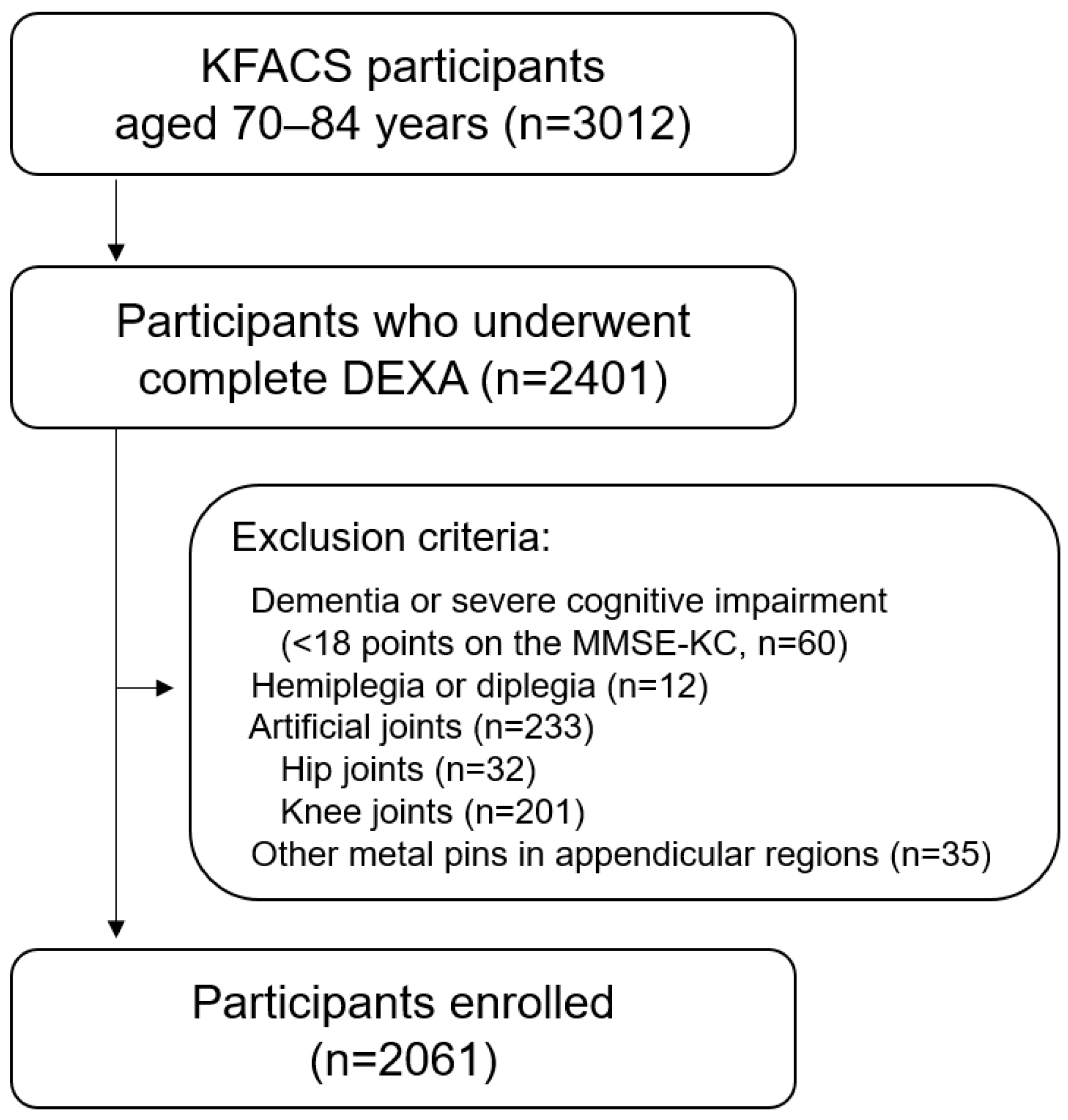
| Variables | Overall (n = 2061) | Men (n = 1040) | Women (n = 1021) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 75.87 ± 3.92 | 76.35 ± 3.93 | 75.36 ± 3.86 |
| Height, cm | 158.56 ± 8.43 | 164.97 ± 5.58 | 152.03 ± 5.21 |
| Weight, kg | 61.01 ± 9.32 | 65.21 ± 8.95 | 56.72 ± 7.58 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 24.22 ± 2.86 | 23.94 ± 2.86 | 24.52 ± 2.80 |
| MMSE-KC | 26.08 ± 2.71 | 26.51 ± 2.86 | 25.65 ± 2.88 |
| Hypertension, n (%) | 1145 (55.6%) | 551 (53.0%) | 594 (56.2%) |
| Dyslipidemia, n (%) | 674 (32.7%) | 251 (24.1%) | 423 (41.4%) |
| Cardiovascular diseases, n (%) | 92 (4.5%) | 59 (5.7%) | 33 (3.2%) |
| Osteoarthritis, n (%) | 407 (19.7%) | 111 (10.7%) | 296 (29.0%) |
| Rheumatoid arthritis, n (%) | 40 (1.9%) | 9 (0.9%) | 31 (3.0%) |
| Osteoporosis, n (%) | 271 (13.1%) | 29 (2.8%) | 242 (23.7%) |
| Asthma, n (%) | 65 (3.2%) | 24 (2.3%) | 41 (4.0%) |
| COPD, n (%) | 26 (1.3%) | 21 (2.0%) | 5 (0.5%) |
| Diabetes mellitus, n (%) | 459 (22.3%) | 259 (24.9%) | 200 (19.6%) |
| Kidney disease, n (%) | 31 (1.5%) | 21 (2.0%) | 10 (1.0%) |
| Cancer, n (%) | 72 (3.5%) | 50 (4.8%) | 22 (2.2%) |
| Number of prescription medications | 3.36 ± 2.83 | 3.50 ± 3.00 | 3.21 ± 2.64 |
| Number of over-the-counter medications | 0.90 ± 1.23 | 0.71 ± 1.08 | 1.10 ± 1.33 |
| Fall in a year, n (%) | 391 (19.0%) | 158 (15.2%) | 233 (22.8%) |
| Two or more falls in a year, n (%) | 132 (6.4%) | 55 (5.3%) | 77 (7.5%) |
| Three or more falls in a year, n (%) | 70 (3.4%) | 27 (2.6%) | 43 (4.2%) |
| Four or more falls in a year, n (%) | 41 (2.0%) | 15 (1.4%) | 26 (2.5%) |
| Fractures related to falls, n (%) | 57 (2.8%) | 25 (2.4%) | 32 (3.1%) |
| Variables | Overall (n = 2061) | Men (n = 1040) | Women (n = 1021) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SARC-F score | 1.02 ± 1.43 | 0.62 ± 1.09 | 1.43 ± 1.61 | <0.01 ** |
| CC, cm | 33.75 ± 2.83 | 34.62 ± 2.70 | 32.87 ± 2.69 | <0.01 ** |
| ASM, kg | 16.35 ± 3.68 | 19.19 ± 2.70 | 13.47 ± 1.84 | <0.01 ** |
| Adjusted ASM, kg/m2 | 6.44 ± 0.99 | 7.04 ± 0.86 | 5.82 ± 0.71 | <0.01 ** |
| HGS, kg | 26.88 ± 7.43 | 32.41 ± 5.74 | 21.25 ± 3.88 | <0.01 ** |
| Gait speed, m/s | 1.13 ± 0.25 | 1.17 ± 0.26 | 1.09 ± 0.23 | <0.01 ** |
| CST, s | 11.16 ± 3.63 | 10.50 ± 3.00 | 11.83 ± 4.07 | <0.01 ** |
| SPPB | 10.07 ± 1.85 | 10.42 ± 1.66 | 9.72 ± 1.96 | <0.01 ** |
| TUG, s | 10.22 ± 2.42 | 10.03 ± 2.24 | 10.41 ± 2.57 | <0.01 ** |
| Variables | Overall (n = 2061) | Men (n = 1040) | Women (n = 1021) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sarcopenia, n (%) | ||||
| MM + MS or PP † | 562 (27.3%) | 342 (32.9%) | 220 (21.5%) | <0.01 ** |
| MM + MS | 215 (10.4%) | 151 (14.5%) | 64 (6.3%) | <0.01 ** |
| MM + PP † | 521 (25.3%) | 312 (30.0%) | 209 (20.5%) | <0.01 ** |
| MM + SPPB | 273 (13.2%) | 149 (14.3%) | 124 (12.1%) | 0.14 * |
| MM + gait speed | 242 (11.7%) | 139 (13.3%) | 104 (10.2%) | 0.03 * |
| MM + TUG | 145 (7.0%) | 88 (8.5%) | 57 (5.6%) | 0.01 * |
| MM + CST | 469 (22.8%) | 278 (26.7%) | 191 (18.7%) | <0.01 ** |
| Severe sarcopenia, n (%) | ||||
| MM + MS + PP † | 174 (8.4%) | 121 (11.6%) | 53 (5.2%) | <0.01 ** |
| MM + MS + SPPB | 118 (5.7%) | 78 (7.5%) | 40 (3.9%) | <0.01 ** |
| MM + MS + gait speed | 100 (4.9%) | 68 (6.5%) | 32 (3.1%) | 0.01 * |
| MM + MS + TUG | 72 (3.5%) | 47 (4.5%) | 25 (2.4%) | <0.01 ** |
| MM + MS + CST | 156 (7.6%) | 105 (10.1%) | 51 (5.0%) | <0.01 ** |
| Functional sarcopenia, n (%) | ||||
| MS + PP † | 160 (7.8%) | 53 (5.1%) | 107 (10.5%) | <0.01 ** |
| MS + SPPB | 98 (4.8%) | 25 (2.4%) | 73 (7.1%) | <0.01 ** |
| MS + gait speed | 89 (4.3%) | 22 (2.1%) | 67 (6.6%) | <0.01 ** |
| MS + TUG | 69 (3.3%) | 20 (1.9%) | 49 (4.8%) | <0.01 ** |
| MS + CST | 139 (6.7%) | 43 (4.1%) | 96 (9.4%) | <0.01 ** |
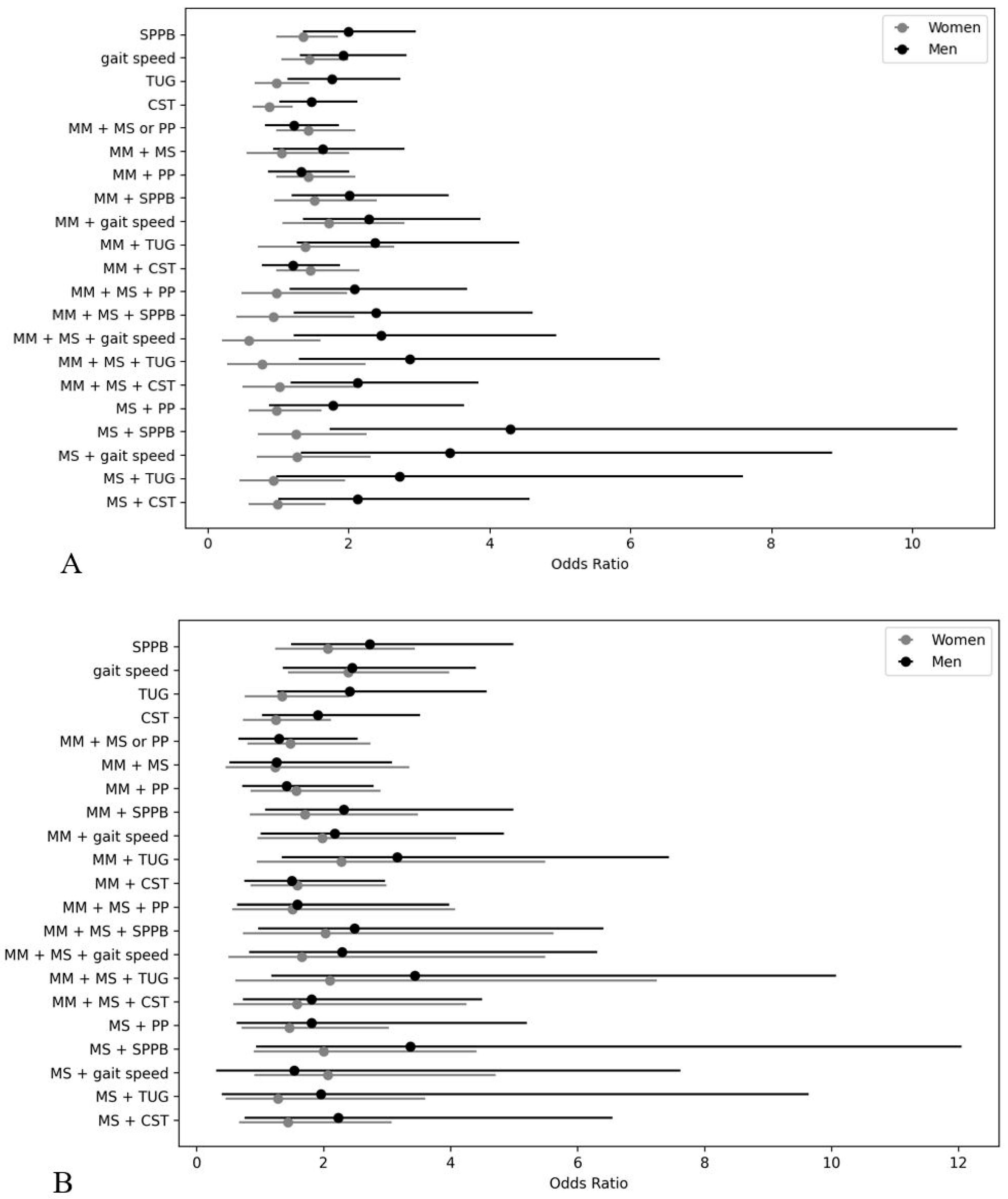
| Variables | Unadjusted Model | Fully Adjusted Model †† | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Men | Women | Men | Women | |
| OR (95% CI) | OR (95% CI) | OR (95% CI) | OR (95% CI) | |
| Physical performance | ||||
| SPPB | 2.13 (1.49–3.05) ** | 1.47 (1.10–1.98) * | 2.00 (1.36–2.96) ** | 1.35 (0.98–1.85) |
| gait speed | 2.11 (1.47–3.04) ** | 1.57 (1.16–2.12) ** | 1.92 (1.31–2.82) ** | 1.44 (1.05–1.99) * |
| TUG | 1.92 (1.27–2.91) ** | 1.11 (0.78–1.60) | 1.76 (1.14–2.73) * | 0.98 (0.67–1.44) |
| CST | 1.64 (1.16–2.32) * | 0.96 (0.71–1.31) | 1.47 (1.02–2.12) * | 0.88 (0.64–1.21) |
| Sarcopenia | ||||
| MM + MS or PP † | 1.29 (0.90–1.86) | 1.38 (0.98–1.96) | 1.23 (0.81–1.87) | 1.43 (0.97–2.09) |
| MM + MS | 1.70 (1.09–2.67) * | 1.13 (0.62–2.07) | 1.63 (0.94–2.80) | 1.05 (0.55–2.01) |
| MM + PP † | 1.42 (0.98–2.04) | 1.38 (0.97–1.97) | 1.32 (0.86–2.01) | 1.43 (0.97–2.10) |
| MM + SPPB | 1.94 (1.25–3.02) ** | 1.57 (1.03–2.40) * | 2.01 (1.20–3.42) ** | 1.51 (0.95–2.40) |
| MM + gait speed | 2.15 (1.40–3.36) ** | 1.79 (1.13–2.81) * | 2.28 (1.35–3.87) ** | 1.72 (1.06–2.80) * |
| MM + TUG | 2.24 (1.32–3.79) ** | 1.57 (0.86–2.85) | 2.37 (1.27–4.43) ** | 1.38 (0.72–2.65) |
| MM + CST | 1.32 (0.90–1.94) | 1.42 (0.98–2.04) | 1.21 (0.77–1.88) | 1.45 (0.97–2.16) |
| Severe sarcopenia | ||||
| MM + MS + PP † | 2.18 (1.37–3.47) ** | 1.08 (0.55–2.11) | 2.08 (1.17–3.68) * | 0.97 (0.48–1.98) |
| MM + MS + SPPB | 2.33 (1.35–4.04) ** | 1.07 (0.50–2.30) | 2.39 (1.23–4.62) * | 0.93 (0.41–2.08) |
| MM + MS + gait speed | 2.45 (1.38–4.36) ** | 0.68 (0.26–1.81) | 2.46 (1.22–4.95) * | 0.58 (0.21–1.60) |
| MM + MS + TUG | 2.69 (1.38–5.22) ** | 0.92 (0.34–2.50) | 2.87 (1.29–6.42) * | 0.78 (0.28–2.24) |
| MM + MS + CST | 2.30 (1.41–3.75) ** | 1.14 (0.58–2.22) | 2.13 (1.18–3.85) * | 1.02 (0.50–2.09) |
| Functional sarcopenia | ||||
| MS + PP † | 1.85 (0.93–3.66) | 1.13 (0.69–1.82) | 1.78 (0.87–3.64) | 0.97 (0.58–1.62) |
| MS + SPPB | 4.22 (1.84–9.69) ** | 1.49 (0.87–2.55) | 4.29 (1.73–10.64) ** | 1.26 (0.71–2.26) |
| MS + gait speed | 3.62 (1.48–8.87) ** | 1.46 (0.83–2.56) | 3.43 (1.32–8.86) * | 1.27 (0.70–2.32) |
| MS + TUG | 2.71 (1.01–7.25) * | 1.07 (0.53–2.14) | 2.72 (0.98–7.59) | 0.94 (0.45–1.95) |
| MS + CST | 2.18 (1.06–4.47) * | 1.16 (0.70–1.92) | 2.13 (1.00–4.57) | 0.99 (0.58–1.68) |
| Variables | Unadjusted Model | Fully Adjusted Model †† | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Men | Women | Men | Women | |
| OR (95% CI) | OR (95% CI) | OR (95% CI) | OR (95% CI) | |
| Physical performance | ||||
| SPPB | 2.93 (1.69–5.07) ** | 2.25 (1.41–3.61) ** | 2.73 (1.49–4.99) ** | 2.07 (1.24–3.44) ** |
| gait speed | 2.71 (1.56–4.71) ** | 2.51 (1.57–4.02) ** | 2.45 (1.36–4.40) ** | 2.39 (1.44–3.98) ** |
| TUG | 2.73 (1.50–4.98) ** | 1.48 (0.87–2.52) | 2.41 (1.27–4.57) ** | 1.35 (0.76–2.40) |
| CST | 2.15 (1.20–3.84) * | 1.38 (0.83–2.28) | 1.91(1.03–3.52) * | 1.25 (0.73–2.12) |
| Sarcopenia | ||||
| MM + MS or PP † | 1.39 (0.78–2.48) | 1.44 (0.83–2.50) | 1.30 (0.66–2.54) | 1.48 (0.80–2.74) |
| MM + MS | 1.51 (0.72–3.16) | 1.49 (0.61–3.65) | 1.26 (0.52–3.08) | 1.24 (0.46–3.35) |
| MM + PP † | 1.53 (0.86–2.73) | 1.53 (0.88–2.65) | 1.42 (0.72–2.79) | 1.57 (0.85–2.90) |
| MM + SPPB | 2.74 (1.46–5.12) ** | 1.84 (0.98–3.46) | 2.32 (1.08–4.99) * | 1.71 (0.84–3.49) |
| MM + gait speed | 2.40 (1.23–4.67) * | 2.06 (1.07–3.97) * | 2.18 (1.01–4.84) * | 1.98 (0.96–4.09) |
| MM + TUG | 3.68 (1.83–7.39) ** | 2.70 (1.25–5.86) * | 3.16 (1.34–7.44) ** | 2.28 (0.95–5.49) |
| MM + CST | 1.65 (0.92–2.96) | 1.59 (0.91–2.80) | 1.50 (0.75–2.97) | 1.59 (0.85–2.99) |
| Severe sarcopenia | ||||
| MM + MS + PP † | 1.91 (0.91–4.04) | 1.84 (0.75–4.54) | 1.59 (0.64–3.98) | 1.51 (0.56–4.07) |
| MM + MS + SPPB | 3.12 (1.46–6.9) ** | 2.55 (1.02–6.38) * | 2.49 (0.97–6.41) | 2.03 (0.73–5.62) |
| MM + MS + gait speed | 2.83 (1.24–6.47) * | 2.06 (0.69–6.13) | 2.29 (0.83–6.31) | 1.66 (0.50–5.49) |
| MM + MS + TUG | 4.36 (1.87–10.16) ** | 2.75 (0.90–8.35) | 3.44 (1.18–10.07) * | 2.10 (0.61–7.25) |
| MM + MS + CST | 2.24 (1.06–4.74) * | 1.92 (0.78–4.75) | 1.81 (0.73–4.50) | 1.58 (0.58–4.28) |
| Functional sarcopenia | ||||
| MS + PP † | 2.21 (0.82–5.98) | 1.82 (0.93–3.59) | 1.81 (0.63–5.20) | 1.46 (0.71–3.03) |
| MS + SPPB | 4.05 (1.30–12.55) * | 2.56 (1.26–5.19) ** | 3.37 (0.94–12.05) | 2.00 (0.90–4.41) |
| MS + gait speed | 2.12 (0.47–9.52) | 2.53 (1.21–5.29) * | 1.54 (0.31–7.62) | 2.07 (0.91–4.71) |
| MS + TUG | 2.36 (0.52–10.66) | 1.64 (0.62–4.34) | 1.96 (0.40–9.64) | 1.28 (0.46–3.60) |
| MS + CST | 2.80 (1.02–7.63) * | 1.87 (0.93–3.75) | 2.23 (0.76–6.55) | 1.44 (0.67–3.07) |
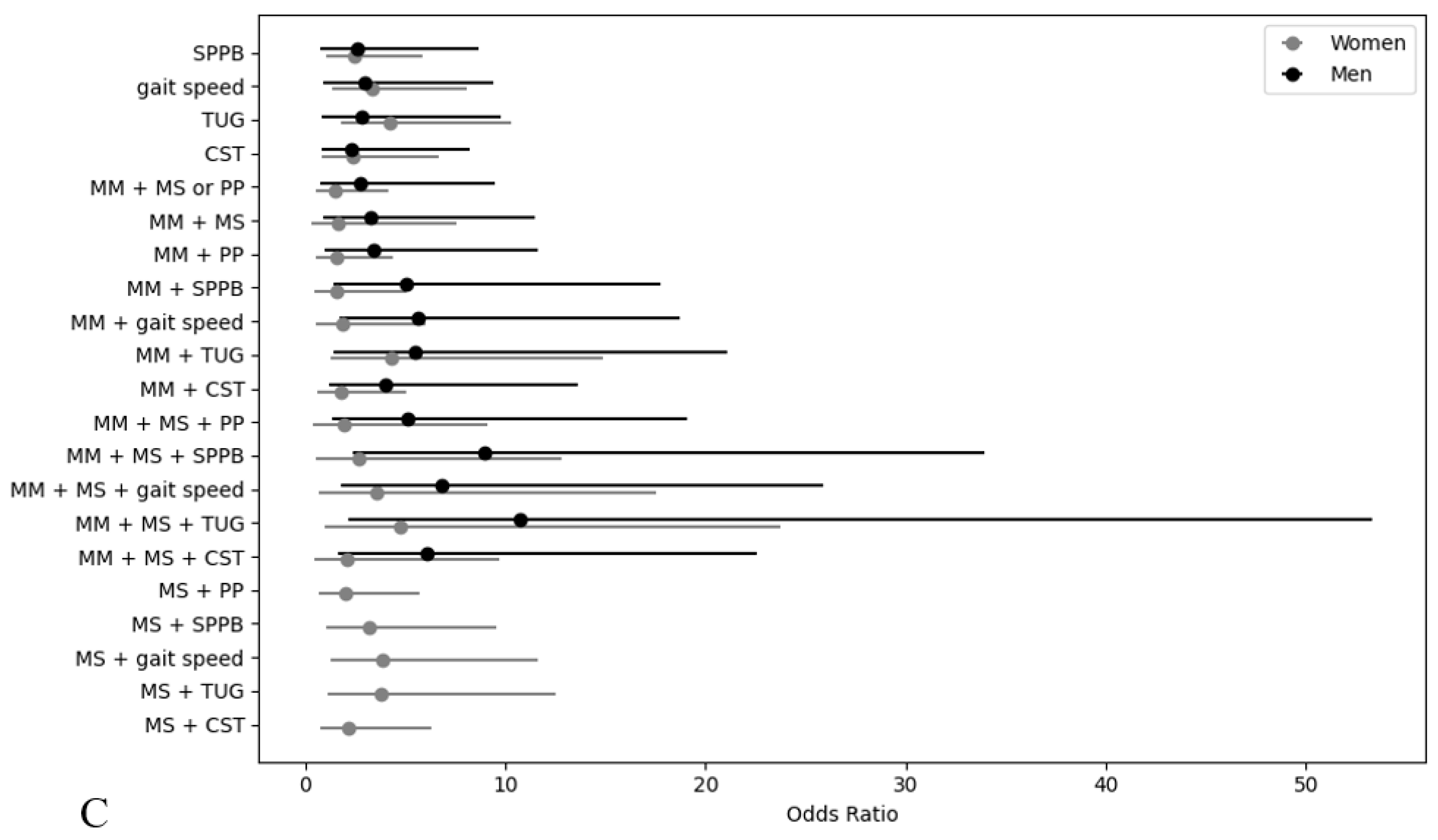
| Variables | Unadjusted Model | Fully Adjusted Model †† | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Men | Women | Men | Women | |
| OR (95% CI) | OR (95% CI) | OR (95% CI) | OR (95% CI) | |
| Physical performance | ||||
| SPPB | 3.56 (1.28–9.92) * | 2.60 (1.17–5.79) * | 2.61 (0.78–8.66) | 2.46 (1.03–5.89) * |
| gait speed | 3.84 (1.38–10.71) * | 3.21 (1.44–7.15) ** | 2.99 (0.95–9.40) | 3.35 (1.38–8.14) ** |
| TUG | 3.80 (1.33–10.82) * | 3.66 (1.66–8.03) ** | 2.87 (0.84–9.76) | 4.27 (1.77–10.33) ** |
| CST | 2.88 (0.91–9.11) | 2.45 (0.92–6.55) | 2.35 (0.87–8.21) | 2.37 (0.84–6.65) |
| Sarcopenia | ||||
| MM + MS or PP † | 4.18 (1.42–12.31) * | 1.10 (0.43–2.76) | 2.73 (0.78–9.51) | 1.51 (0.54–4.17) |
| MM + MS | 5.35 (1.91–14.99) ** | 1.25 (0.29–5.43) | 3.28 (0.94–11.47) | 1.63 (0.35–7.59) |
| MM + PP † | 4.79 (1.62–14.13) ** | 1.17 (0.46–2.95) | 3.42 (0.99–11.60) | 1.59 (0.58–4.42) |
| MM + SPPB | 7.17 (2.56–20.07) ** | 1.33 (0.45–3.91) | 5.07 (1.45–17.79) * | 1.56 (0.48–5.03) |
| MM + gait speed | 7.87 (2.81–22.06) ** | 1.63 (0.55–4.82) | 5.64 (1.71–18.69) ** | 1.87 (0.58–6.03) |
| MM + TUG | 7.67 (2.66–22.07) ** | 3.23 (1.08–9.72) * | 5.47 (1.42–21.06) * | 4.33 (1.26–14.86) * |
| MM + CST | 5.65 (1.91–16.68) ** | 1.31 (0.52–3.32) | 4.04 (1.20–13.65) * | 1.81 (0.65–5.04) |
| Severe sarcopenia | ||||
| MM + MS + PP † | 6.99 (2.49–19.64) ** | 1.54 (0.36–6.71) | 5.14 (1.38–19.09) * | 1.95 (0.42–9.10) |
| MM + MS + SPPB | 11.76 (4.15–33.35) ** | 2.10 (0.48–9.21) | 8.95 (2.36–33.92) ** | 2.70 (0.57–12.84) |
| MM + MS + gait speed | 10.36 (3.57–30.02) ** | 2.68 (0.61–11.87) | 6.86 (1.82–25.86) ** | 3.57 (0.73–17.53) |
| MM + MS + TUG | 11.70 (3.83–35.76) ** | 3.52 (0.79–15.79) | 10.76 (2.17–53.31) ** | 4.79 (0.96–23.76) |
| MM + MS + CST | 8.28 (2.94–23.31) ** | 1.61 (0.37–7.00) | 6.11 (1.66–22.53) ** | 2.08 (0.45–9.73) |
| Functional sarcopenia | ||||
| MS + PP † | — | 2.09 (0.77–5.65) | — | 2.00 (0.70–5.71) |
| MS + SPPB | — | 3.25 (1.20–8.88) * | — | 3.20 (1.07–9.57) * |
| MS + gait speed | — | 3.58 (1.31–9.82) * | — | 3.87 (1.29–11.62) * |
| MS + TUG | — | 3.84 (1.27–11.61) * | — | 3.79 (1.15–12.55) * |
| MS + CST | — | 2.37 (0.87–5.42) | — | 2.21 (0.77–6.34) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, M.; Choi, S.; Yun, D.H.; Soh, Y.; Won, C.W. Prevalence and Fall Risk of Sarcopenia Based on the 2023 Korean Working Group on Sarcopenia Criteria. Medicina 2025, 61, 1065. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61061065
Kim M, Choi S, Yun DH, Soh Y, Won CW. Prevalence and Fall Risk of Sarcopenia Based on the 2023 Korean Working Group on Sarcopenia Criteria. Medicina. 2025; 61(6):1065. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61061065
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Minjung, Seongmin Choi, Dong Hwan Yun, Yunsoo Soh, and Chang Won Won. 2025. "Prevalence and Fall Risk of Sarcopenia Based on the 2023 Korean Working Group on Sarcopenia Criteria" Medicina 61, no. 6: 1065. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61061065
APA StyleKim, M., Choi, S., Yun, D. H., Soh, Y., & Won, C. W. (2025). Prevalence and Fall Risk of Sarcopenia Based on the 2023 Korean Working Group on Sarcopenia Criteria. Medicina, 61(6), 1065. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61061065






