Protective Effect of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles on Inner Ear Sensorineural Cells Affected by Cisplatin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Isolation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells from Mouse Bone Marrow and the Characterization of the MSC Culture
2.1.1. Isolation
2.1.2. The Assessment of MSC Markers by Flow Cytometry and Fluorescence Microscopy
2.1.3. The Differentiating Capacity of the Isolated MSCs
2.2. Isolation and Characterization of Extracellular Vesicles (EV)
2.2.1. The Protein Concentration
2.2.2. Evaluation of EV Markers Using the Dot Blot Immunobinding Assay and Western Blot
2.2.3. The Size Distribution and Concentration of the Extracellular Vesicles
2.2.4. TEM
2.3. Assessment of the Protective Effect of EVs on HEI-OC1 Cells Against Cisplatin Toxicity
2.3.1. Culture of the HEI-OC1 Cells
2.3.2. Internalization of EVs into Hair Cells In Vitro
2.3.3. Evaluation of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Production
2.3.4. Evaluation of Cell Viability with Alamar Blue
2.3.5. Evaluation of Apoptosis by the Annexin V/PI Flow-Cytometry Method
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
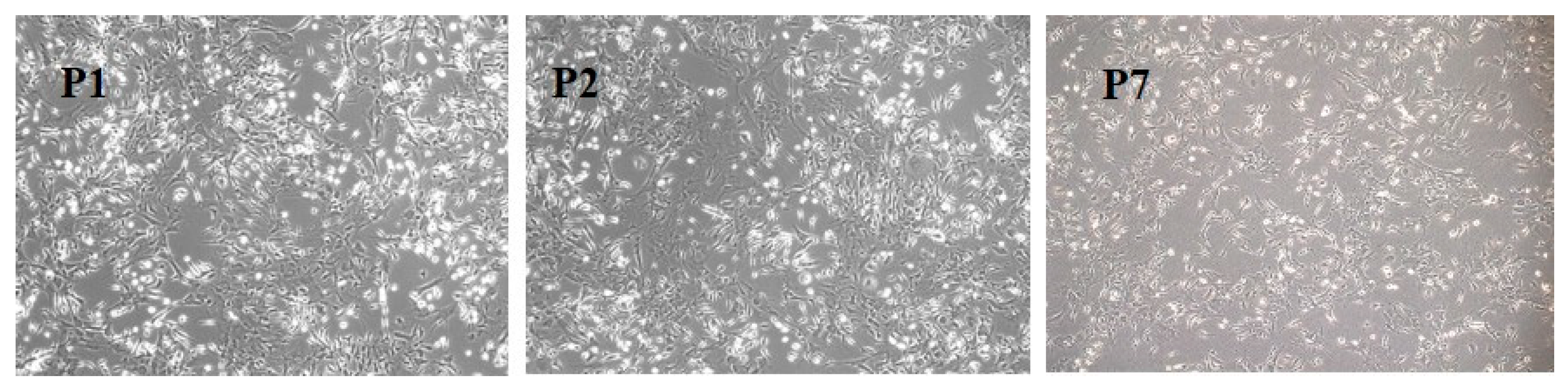
3.1. BM-MSC Culture
3.2. BM-MSC Characterization
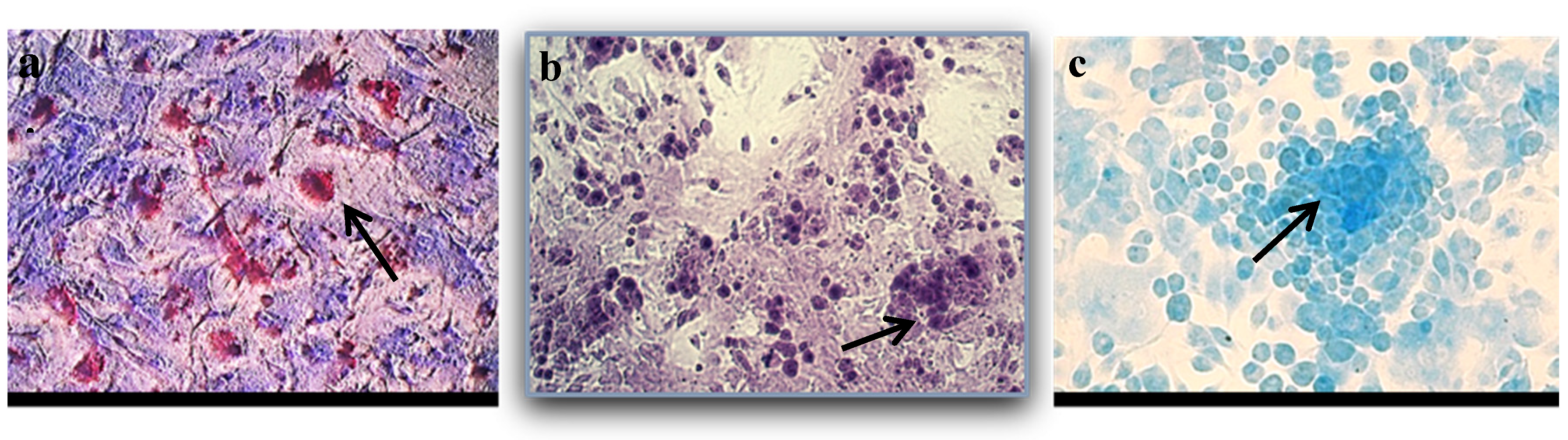
3.2.1. BM-MSC Differentiation
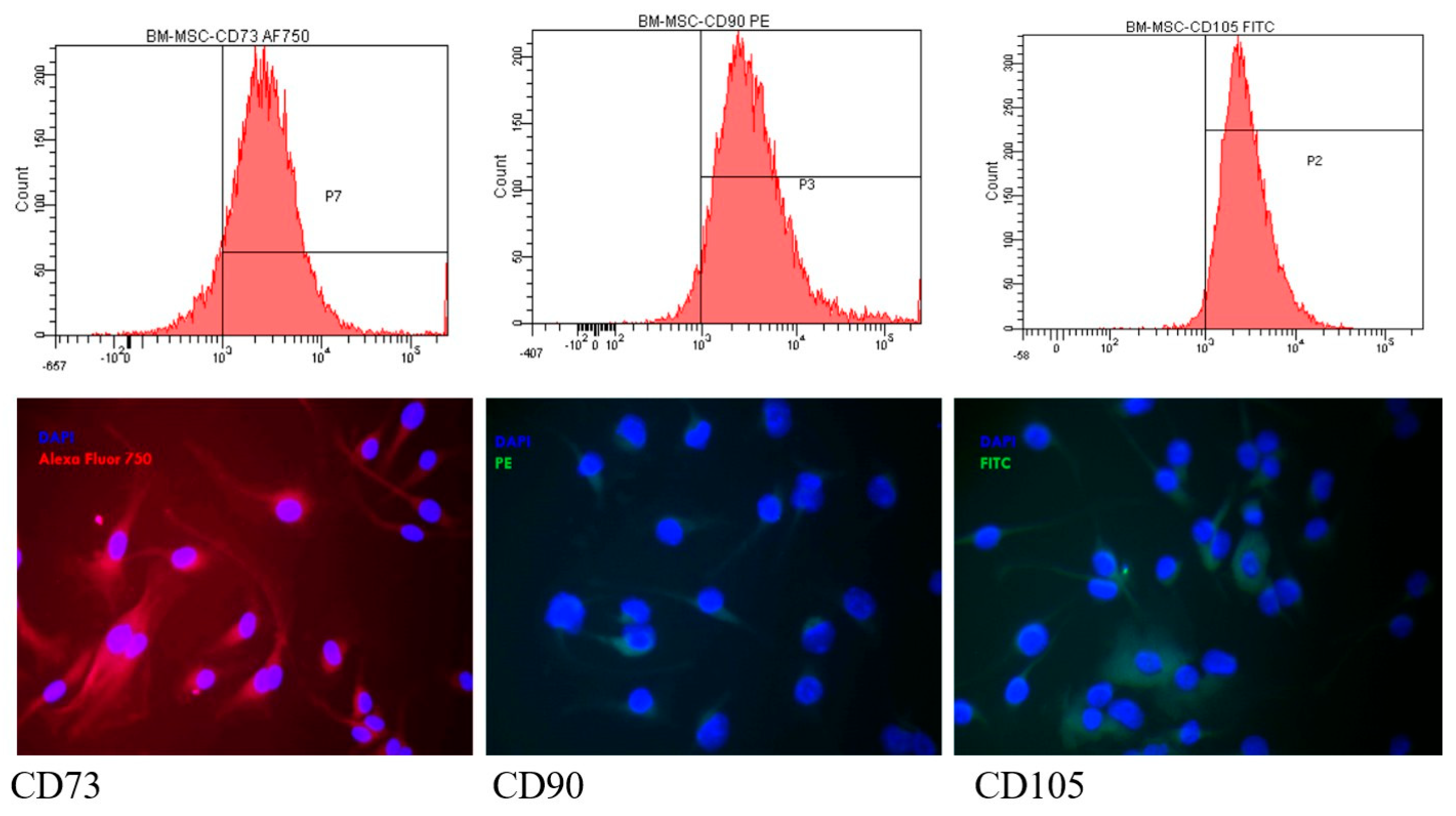
3.2.2. The Presence of MSC Markers by Flow Cytometry and Fluorescence Microscopy
3.3. Isolation and Characterization of EVs
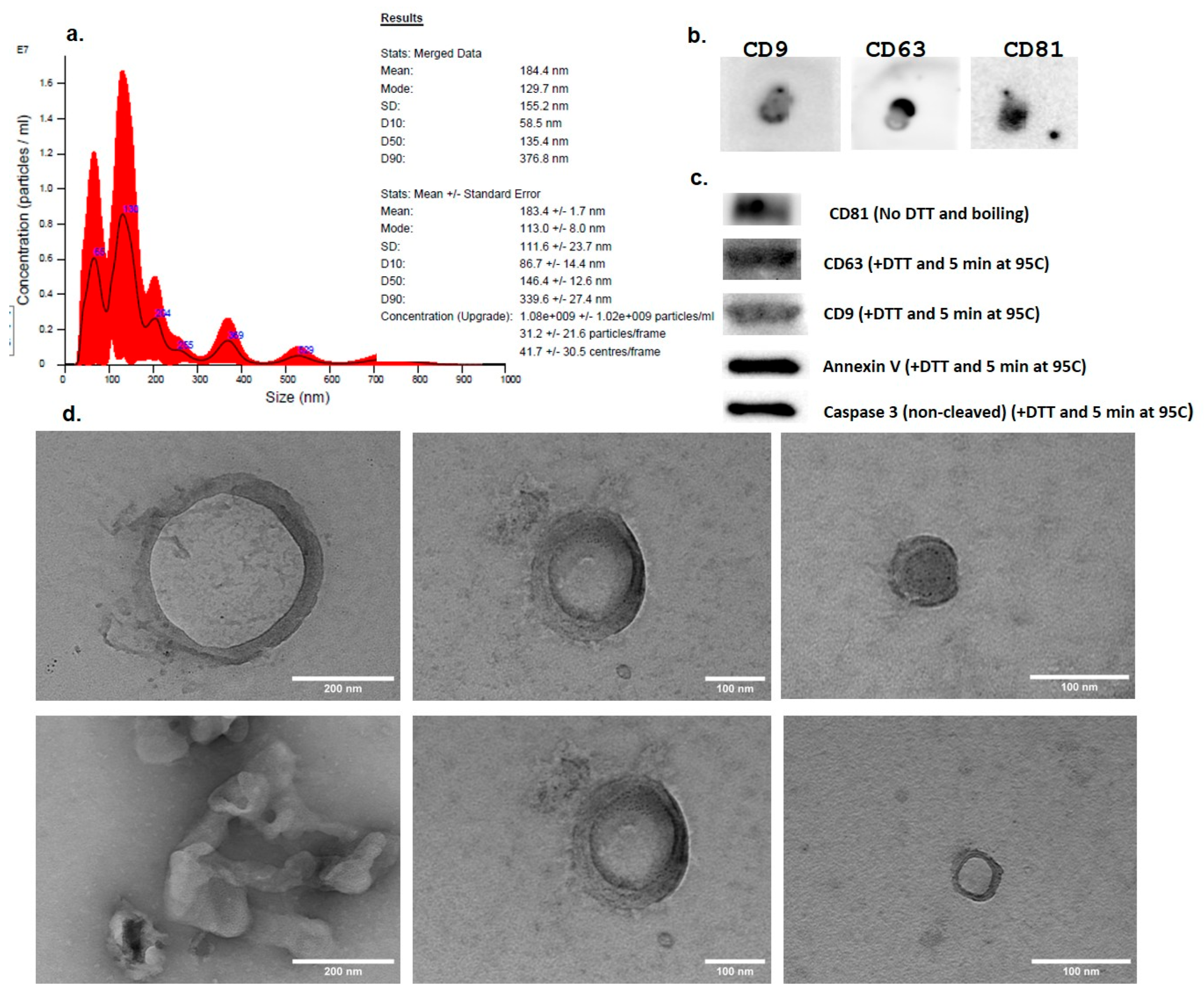
3.3.1. EV Size, Concentration, and Morphology by Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis (NTA) and TEM
3.3.2. Expression of EV Markers—Dot Blot and WB
3.4. Assessment of the Protective Effect of EVs on HEI-OC1 Cells
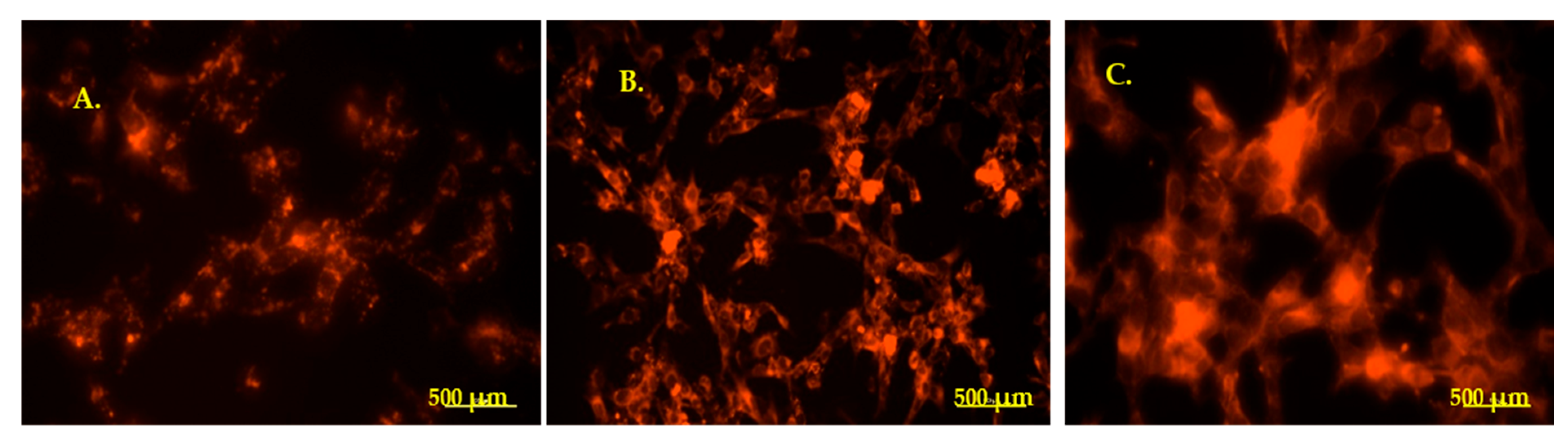
3.4.1. Internalization of PKH-Labeled EVs in HEI-OC1 Cells—Fluorescence Microscopy
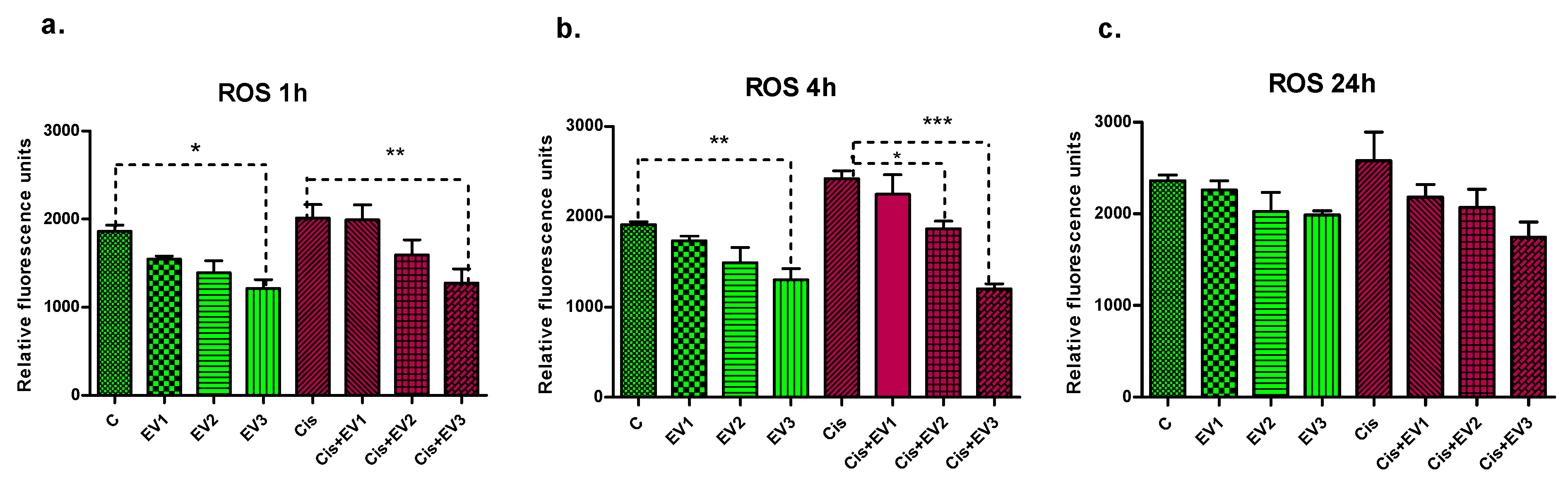
3.4.2. Assessment of ROS Generation
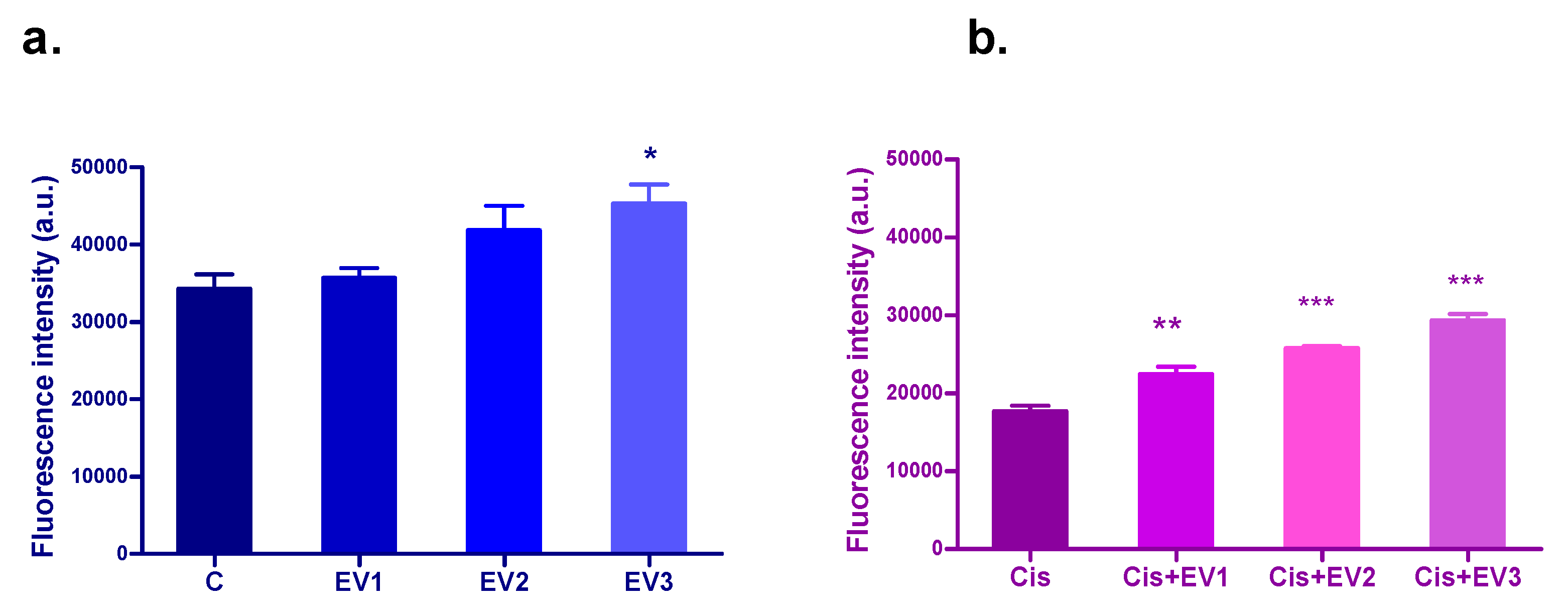
3.4.3. Evaluation of the Protection of EVs Against Cisplatin Cytotoxicity—Alamar Blue
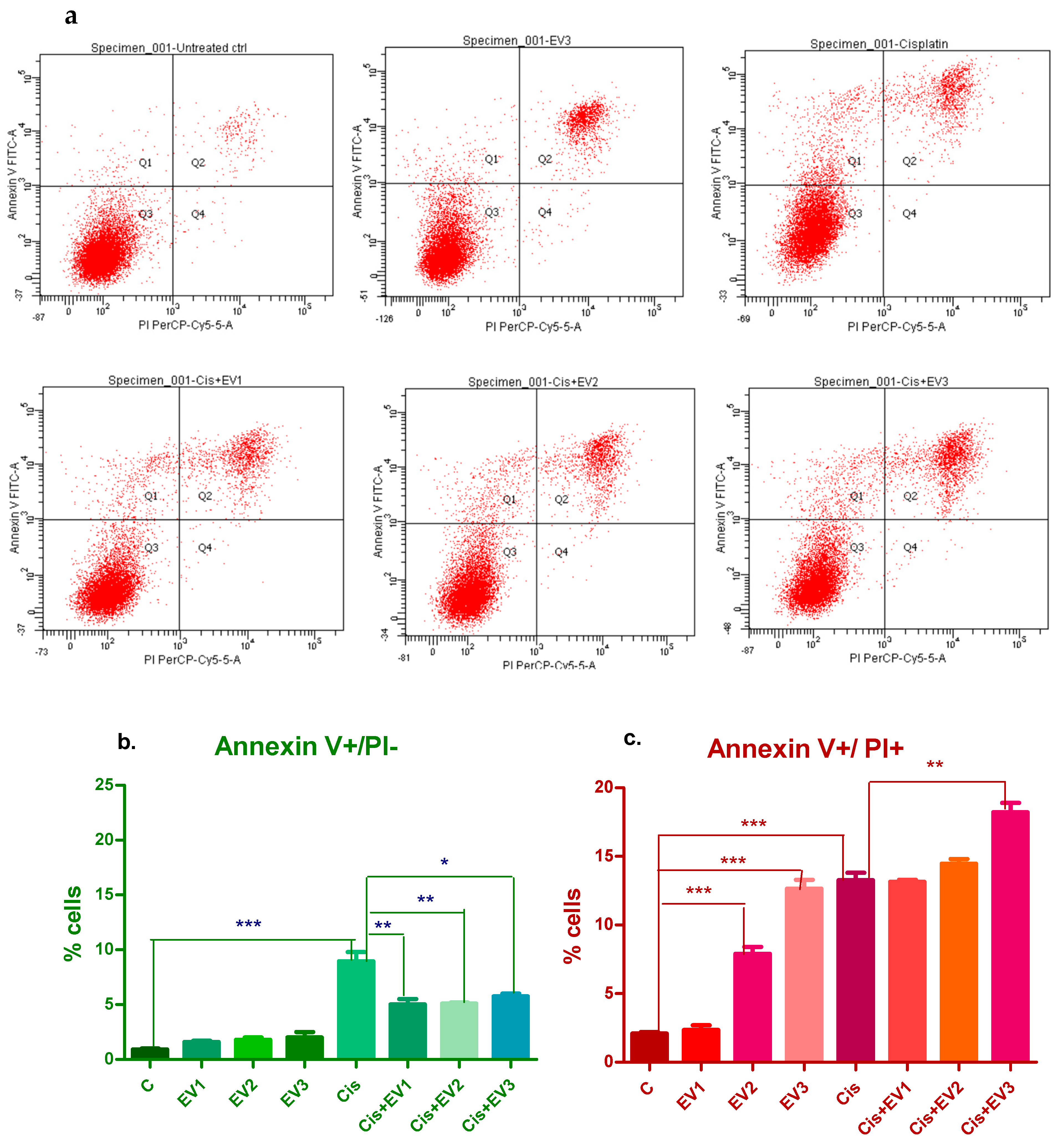
3.4.4. Evaluation of Apoptosis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BM-MSCs | Bone-marrow mesenchymal stem cells |
| EVs | Extracellular vesicles |
| apoEVs | Apoptotic extracellular vesicles |
| SNHL | Sensorineural hearing loss |
References
- Deafness and Hearing Loss, World Health Organization. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/deafness-and-hearing-loss (accessed on 12 December 2024).
- Sarow A, Important Hearing Loss Statistics and Studies 2023, Soundly. Available online: https://www.soundly.com/blog/hearing-loss-statistics (accessed on 12 December 2024).
- Hopkins, K. Handbook of Clinical Neurology Chapter 27—Deafness in Cochlear Auditory Nerve Disorders; Michael, J., Aminoff, F.B., Dick, F.S., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; Volume 129, pp. 479–494. ISSN 0072-9752. ISBN 9780444626301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Han, B.; Zhou, X.; Huang, S.; Huang, J. Research progress on the treatment and nursing of sensorineural hearing loss. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1199946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lieu, J.E.C.; Kenna, M.; Anne, S.; Davidson, L. Hearing loss in children: A review. JAMA 2020, 324, 2195–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Q.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, W.; Yan, L.; Kong, M.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Guo, L.; Zhang, L.; et al. Stem cells as potential therapeutics for hearing loss. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1259889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, L.M.; Wang, M.Z. Overview of Extracellular Vesicles, Their Origin, Composition, Purpose, and Methods for Exosome Isolation and Analysis. Cells 2019, 8, 727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheta, M.; Taha, E.A.; Lu, Y.; Eguchi, T. Extracellular Vesicles: New Classification and Tumor Immunosuppression. Biology 2023, 12, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.I.; Park, J.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, X.; Han, Y.; Zhang, D. Recent advances in extracellular vesicles for therapeutic cargo delivery. Exp. Mol. Med. 2024, 56, 836–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, S.J.; Oshima, K.; Heller, S.; Edge, A.S. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells are progenitors in vitro for inner ear hair cells. Mol. Cell Neurosci. 2007, 34, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Jang, S.; Cho, H.H.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, K.H.; Jun, J.Y.; Park, J.S.; Jeong, H.S.; Cho, Y.B. Neural-Induced Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells Promote Cochlear Cell Regeneration in Deaf Guinea Pigs. Clin. Exp. Otorhinolaryngol. 2015, 8, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Guo, W.; Yi, H.; Ren, L.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, S.; Liu, R.; Xu, L.; Cong, T.; et al. Transplantation of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells in cochlea to repair sensorineural hearing. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2016, 8, 5235–5245. [Google Scholar]
- Kada, S.; Hamaguchi, K.; Ito, J.; Omori, K.; Nakagawa, T. Bone Marrow Stromal Cells Accelerate Hearing Recovery via Regeneration or Maintenance of Cochlear Fibrocytes in Mouse Spiral Ligaments. Anat. Rec. 2020, 303, 478–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheper, V.; Hoffmann, A.; Gepp, M.M.; Schulz, A.; Hamm, A.; Pannier, C.; Hubka, P.; Lenarz, T.; Schwieger, J. Stem Cell Based Drug Delivery for Protection of Auditory Neurons in a Guinea Pig Model of Cochlear Implantation. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, D.J.; Park, J.E.; Lee, S.H.; Eliceiri, B.P.; Choi, J.S.; Seo, Y.J. Protective effect of MSC-derived exosomes against cisplatin-induced apoptosis via heat shock protein 70 in auditory explant model. Nanomedicine 2021, 38, 102447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopalarethinam, J.; P Nair, A.; Iyer, M.; Vellingiri, B.; Subramaniam, M.D. Advantages of mesenchymal stem cell over the other stem cells. Acta Histochem. 2023, 125, 152041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perde-Schrepler, M.; Ioana, B. Mesenchymal Stem Cell- Derived Exosomes as Cell-Free Therapeutics for Sensorineural Hearing Loss. Biomol Biomed [Internet]. 2025 Mar. 6 [cited 2025 Apr. 30]. Available online: https://www.bjbms.org/ojs/index.php/bjbms/article/view/11517 (accessed on 1 May 2025).
- Perde-Schrepler, M.; Fischer-Fodor, E.; Virag, P.; Brie, I.; Cenariu, M.; Pop, C.; Valcan, A.; Gurzau, E.; Maniu, A. The expression of copper transporters associated with the ototoxicity induced by platinum-based chemotherapeutic agents. Hear. Res. 2020, 388, 107893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Du, Z.; He, L.; Liang, W.; Liu, K.; Gong, S. ROS-Induced Oxidative Damage and Mitochondrial Dysfunction Mediated by Inhibition of SIRT3 in Cultured Cochlear Cells. Neural Plast. 2022, 2022, 5567174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, R.; Cai, C.; Wu, W.; Hu, P.; Wang, Q. Exosomes derived from mouse inner ear stem cells attenuate gentamicin-induced ototoxicity in vitro through the miR-182-5p/FOXO3 axis. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2020, 14, 1149–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Kuang, H.; Wang, Y.; Bao, L.; Cao, W.; Yu, L.; Qi, M.; Wang, R.; Yang, X.; Ye, Q.; et al. MSC-derived exosomes protect auditory hair cells from neomycin-induced damage via autophagy regulation. Biol. Res. 2024, 57, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.J.; Kim, J.M.; Kim, J.; Hur, J.; Park, S.; Kim, K.; Shin, H.J.; Chwae, Y.J. Molecular mechanisms of biogenesis of apoptotic exosome-like vesicles and their roles as damage-associated molecular patterns. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E11721–E11730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Kou, X.; Zhan, T.; Wei, G.; He, F.; Mao, X.; Yang, H. Apoptotic vesicles resist oxidative damage in noise-induced hearing loss through activation of FOXO3a-SOD2 pathway. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2023, 14, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higuchi, A.; Shimmura, S.; Takeuchi, T.; Suematsu, M.; Tsubota, K. Elucidation of apoptosis induced by serum deprivation in cultured conjunctival epithelial cells. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2006, 90, 760–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, C.D.; Rimmer, M.P. Extracellular vesicles arising from apoptosis: Forms, functions, and applications. J. Pathol. 2023, 260, 592–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkin-Smith, G.K.; Tixeira, R.; Paone, S.; Mathivanan, S.; Collins, C.; Liem, M.; Goodall, K.J.; Ravichandran, K.S.; Hulett, M.D.; Poon, I.K. A novel mechanism of generating extracellular vesicles during apoptosis via a beads-on-a-string membrane structure. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Kasagi, S.; Chia, C.; Zhang, D.; Tu, E.; Wu, R.; Zanvit, P.; Goldberg, N.; Jin, W. Extracellular vesicles from apoptotic cells promote TGFbeta production in macrophages and suppress experimental colitis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Liu, S.; Qiu, X.; Yang, X.; Bao, L.; Pu, F.; Liu, X.; Li, C.; Xuan, K.; Zhou, J.; et al. Donor MSCs release apoptotic bodies to improve myocardial infarction via autophagy regulation in recipient cells. Autophagy 2020, 16, 2140–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Qiu, X.; Lv, Y.; Zheng, C.; Dong, Y.; Dou, G. Apoptotic bodies derived from mesenchymal stem cells promote cutaneous wound healing via regulating the functions of macrophages. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2020, 11, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Yang, J.; Ma, S.; Gao, X.; Wang, G.; Sun, Y.; Yu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Tian, W.; Liao, L. Functional diversity of apoptotic vesicle subpopulations from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in tissue regeneration. J. Extracell. Ves. 2024, 13, e12434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.K.; Shin, J.I.; Cho, Y.S. Protective effect of minocycline against cisplatin-induced ototoxicity. Clin. Exp. Otorhinolaryngol. 2011, 4, 77–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakarla, R.; Hur, J.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, J. Apoptotic cell-derived exosomes: Messages from dying cells. Exp. Mol. Med. 2020, 52, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Garijo, A.; Steller, H. Spreading the word: Non-autonomous effects of apoptosis during development, regeneration and disease. Development 2015, 142, 3253–3262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Sui, B.; Xiang, L.; Yan, X.; Wu, D.; Shi, S.; Hu, X. Emerging understanding of apoptosis in mediating mesenchymal stem cell therapy. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brock, C.K.; Wallin, S.T.; Ruiz, O.E.; Samms, K.M.; Mandal, A.; Sumner, E.A.; Eisenhoffe, G.T. Stem cell proliferation is induced by apoptotic bodies from dying cells during epithelial tissue maintenance. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Liao, L.; Tian, W. Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Apoptotic Cells: An Essential Link Between Death and Regeneration. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 573511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Perde-Schrepler, M.; Brie, I.; Cenariu, M.; Chira, S.; Raduly, L.; Budisan, L.; Berindan-Neagoe, I.; Stiufiuc, R.; Dindelegan, M.; Blebea, C.; et al. Protective Effect of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles on Inner Ear Sensorineural Cells Affected by Cisplatin. Medicina 2025, 61, 1042. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61061042
Perde-Schrepler M, Brie I, Cenariu M, Chira S, Raduly L, Budisan L, Berindan-Neagoe I, Stiufiuc R, Dindelegan M, Blebea C, et al. Protective Effect of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles on Inner Ear Sensorineural Cells Affected by Cisplatin. Medicina. 2025; 61(6):1042. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61061042
Chicago/Turabian StylePerde-Schrepler, Maria, Ioana Brie, Mihai Cenariu, Sergiu Chira, Lajos Raduly, Liviuta Budisan, Ioana Berindan-Neagoe, Rares Stiufiuc, Maximilian Dindelegan, Cristina Blebea, and et al. 2025. "Protective Effect of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles on Inner Ear Sensorineural Cells Affected by Cisplatin" Medicina 61, no. 6: 1042. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61061042
APA StylePerde-Schrepler, M., Brie, I., Cenariu, M., Chira, S., Raduly, L., Budisan, L., Berindan-Neagoe, I., Stiufiuc, R., Dindelegan, M., Blebea, C., Pall, E., & Maniu, A. A. (2025). Protective Effect of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles on Inner Ear Sensorineural Cells Affected by Cisplatin. Medicina, 61(6), 1042. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61061042









