Abstract
Background and Objectives: Postoperative delirium (PODil) is a cognitive condition characterized by sudden fluctuations in consciousness and orientation after surgery. PODil following total knee arthroplasty (TKA) is associated with prolonged hospital stays and increased morbidity. Therefore, prevention of PODil is particularly important. Life’s Simple 7 score, published by the American Heart Association, is a new measure of cardiovascular health (CVH). Better CVH is associated with a lower risk of cognitive impairment. Hence, this study aimed to determine whether Life’s Simple 7 score is associated with PODil following TKA. Materials and Methods: This retrospective study included 973 patients who underwent TKA between January 2015 and January 2020. Patients were divided into two groups (group I: delirium group, n = 60; group II: non-delirium group, n = 913). Demographic data, use of analgesics, surgical factors, underlying diseases, laboratory results, and Life’s Simple 7 score were evaluated. Results: Significant differences were observed between the two groups for Parkinson’s disease, intraoperative hypotension, preoperative duloxetine administration, and Life’s Simple 7 score. In the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis, the optimal cut-off value for Life’s Simple 7 score was determined to be 8 at the maximal Youden index, with an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.82, a sensitivity of 0.92, and a specificity of 0.58. Conclusions: Lower Life’s Simple 7 score is an independent risk factor for the incidence of PODil after TKA. Given its ease of measurement, Life’s Simple 7 score may be a useful measure for predicting PODil and will aid in preoperative risk assessment and post-operative patient management.
1. Introduction
Total knee arthroplasty (TKA) is one of the most effective and successful surgeries for treating degenerative osteoarthritis of the knee [1,2,3]. However, several complications can occur after TKA, including postoperative delirium (PODil). The reported prevalence of PODil after TKA ranges from 0.54% to 18.4% [4,5,6,7]. PODil is a cognitive disorder characterized by sudden fluctuations in consciousness and orientation (i.e., inaccurate perception of date, place, and person) after surgery [8]. It is a serious condition that can have adverse clinical and economic outcomes, including an extended hospital stay, increased medical expenses, delayed recovery of normal function, and increased morbidity and mortality [9,10]. Therefore, identifying pre-existing risk factors for PODil is a crucial aspect of perioperative care.
The etiology of PODil is multifactorial, with various precipitating and predisposing factors such as advanced age, male sex, polypharmacy, low levels of hemoglobin or hematocrit, electrolyte imbalances, infection, cardiovascular disease (CVD), and preoperative cognitive impairment [11,12,13,14,15]. However, predicting the occurrence of PODil remains challenging [16], and despite its clinical significance, no reliable tool is currently available for its prediction. Therefore, there is a need for a reliable method to assess the risk of PODil.
Life’s Simple 7 score, a new index for evaluating cardiovascular health (CVH), was published by the American Heart Association in 2010 to determine the metrics needed to monitor and improve CVH status [17]. It comprises seven components: smoking, healthy diet score, body mass index (BMI), physical activity, blood pressure, fasting glucose, and total cholesterol (Table 1) [17]. For each component, a score of 0–2 is assigned according to each criterion, and the scores are summed. A score of 0–6 is considered as low, 7–8 is considered as the middle range, and 9–14 is considered as high, thereby suggesting the standard for CVH [18]. A higher Life’s Simple 7 score corresponds to better CVH, which is associated with a lower incidence of CVD [19,20,21] and CVD is an important factor that increases complications and mortality after TKA. [22] CVH also plays an important role in brain health [23], and better CVH is associated with a lower risk of cognitive impairment [18]. Therefore, a low Life’s Simple 7 score relates to a high risk of CVD and cognitive impairment. However, to the best of our knowledge, no previous studies have evaluated the association between Life’s Simple 7 score and PODil.

Table 1.
Components of Life’s Simple 7 Score [18].
Therefore, in this retrospective study, we aimed to determine whether Life’s Simple 7 score is associated with PODil after TKA and identify the additional risk factors for PODil after TKA. We hypothesized that patients with a lower Life’s Simple 7 score would have a higher incidence of PODil.
2. Materials and Methods
This retrospective study was approved by the Institutional Review Board (IRB) of our institution (CNUH 2021-09-060). We enrolled 1061 patients who underwent TKA performed by two senior surgeons at our institute between January 2015 and January 2020. Patients who met the following criteria were excluded: To control for variables such as operative time, intraoperative blood loss, and postoperative pain, patients who underwent simultaneous bilateral TKA (n = 28), revision TKA (n = 53), had multiple trauma (n = 5), or had metastatic malignant tumors (n = 2). Finally, 973 of the 1061 eligible patients were included in this study.
To diagnose PODil, we consulted psychiatric specialists at our institution when patients exhibited symptoms such as disturbances in attention and awareness or cognitive impairment (e.g., memory deficits, disorientation, language difficulties, or perceptual disturbances) during hospitalization [24]. The psychiatric specialists assessed the patients and diagnosed delirium if their symptoms met the diagnostic criteria for delirium outlined in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition. Based on these diagnoses, patients were categorized into two groups: the delirium group (Group I, n = 60) and the non-delirium group (Group II, n = 913) (Figure 1). In this study, psychiatric consultations were conducted between the day of surgery and 10 days postoperatively, with an average consultation occurring at 2.83 days postoperatively.
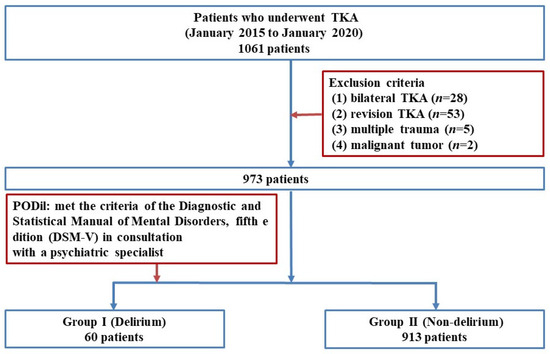
Figure 1.
Flow diagram illustrating patient selection. TKA: Total knee arthroplasty; PODil: Postoperative delirium; DSM: Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders.
Patients diagnosed with PODil were managed, when necessary, with antipsychotic medications prescribed by a psychiatrist, as well as correction of electrolyte imbalances and anemia. Environmental modifications included placement in a private room with reduced noise levels and allowing close family members to stay for supportive care.
The following data were evaluated through a review of electronic medical records: demographic data (age at TKA, sex, height, and body weight); alcohol history (number of drinks per week); American Society of Anesthesiologists grade [25]; Charlson comorbidity index (CCI) [26]; underlying diseases, including hypertension (HTN), arrhythmia, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, asthma, diabetes mellitus (DM), history of cerebral infarction, myocardial infarction, renal disease, liver disease, solid tumors, dementia, Parkinson’s disease, and insomnia; use of analgesics (preoperative duloxetine administration, preoperative gabapentin or pregabalin administration, preoperative and postoperative opioid administration, and postoperative patient-controlled analgesia [fentanyl + ramosetron]); surgical factors (type of anesthesia [general anesthesia, spinal anesthesia], operation time [measured from the start of incision to the end of skin closure, minutes], intraoperative hypotension [defined as systolic blood pressure < 90 mmHg for at least 10 min [27]], intraoperative hypothermia [defined as body temperature < 36 °C during surgery [28]], and postoperative transfusion.
Preoperative laboratory data, including the levels of hemoglobin, hematocrit, albumin, sodium (Na), potassium (K), chloride (Cl), calcium (Ca), phosphate (P), blood urea nitrogen (BUN), and creatinine (Cr), were evaluated. Life’s Simple 7 score was assessed by a researcher who was not involved in the surgery.
Statistical Analysis
Statistical analyses were conducted using SPSS version 26 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). Univariate analysis was performed to identify significant differences between the groups, with statistical significance set at p < 0.05. The Chi-square test and Fisher’s exact test were used to analyze correlations between categorical variables and PODil. The t-test was used for continuous variables. Univariate and multivariate logistic regression analyses were performed to identify risk factors for PODil. Odds ratios (OR) and 95% confidence intervals (CI) were calculated to assess relative risks. The area under the curve (AUC) of receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was used to evaluate the accuracy of Life’s Simple 7 score in predicting the incidence of PODil, and the Youden index was used to determine the optimal cut-off value.
3. Results
The incidence of PODil after TKA was 6.2% (60/973). Table 2 outlines several differences in demographic data and patient characteristics between the two groups. Age at TKA, sex (male), CCI, HTN, DM, renal disease, solid tumors, Parkinson’s disease, and insomnia among underlying diseases were found to be significant factors related with PODil. Additionally preoperative duloxetine administration, type of anesthesia, intraoperative hypotension, and intraoperative hypothermia were identified as significant factors.

Table 2.
Comparison of demographic data and characteristics of patients with/without postoperative delirium.
Among the preoperative laboratory test results, BUN and Cr levels were significantly higher in group I. The Life’s Simple 7 score was significantly higher in group II (p < 0.001).
However, multivariate logistic regression analysis showed significant differences in age at TKA, Parkinson’s disease, preoperative duloxetine administration, intraoperative hypotension, and Life’s Simple 7 scores (Table 3).

Table 3.
Multivariable logistic regression analysis of the risk factors for delirium.
Among them, the largest OR was obtained for age at TKA (OR, 1.074), followed by Life’s Simple 7 score (OR, 0.446), intraoperative hypotension (OR, 0.194), preoperative duloxetine administration (OR, 0.171) and Parkinson’s disease (OR, 0.126) (Table 3).
In the ROC curve analysis, The Life’s Simple 7 Score cut-off values were determined to be 8 at maximal Youden index, associated with AUC of ROC curve of 0.82 (95% CI 0.78–0.87), a sensitivity of 0.92, and a specificity of 0.58 (Figure 2).
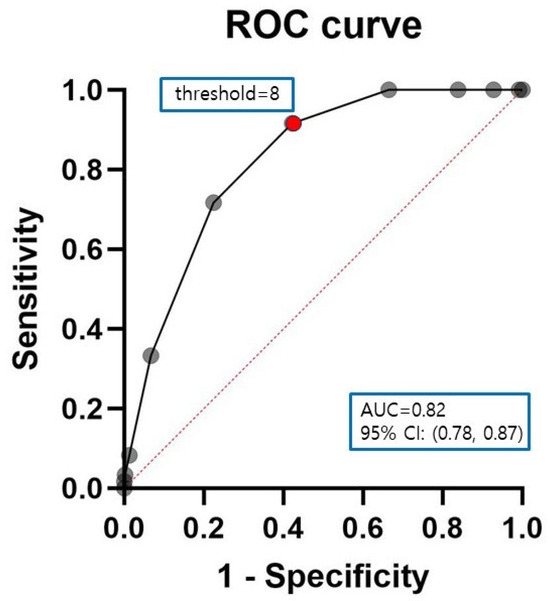
Figure 2.
Receiver-operating characteristic (ROC) curves for Life’s Simple 7 score. The area under the curve, cut-off value, Youden’s index, sensitivity, and specificity of Life’s Simple 7 score were 0.82 (0.78–0.87), 8, 0.50, 0.92, and 0.58, respectively (p < 0.0001). Black solid line: ROC curve, red dotted line: reference line, black dot: Life’s Simple 7 score, red dot: cut-off value.
4. Discussion
In this study, we determined whether Life’s Simple 7 score is associated with PODil after TKA and identified the additional risk factors for PODil after TKA.
Our findings showed that the incidence of PODil after TKA was 6.2% (60/973), which differs from previous studies by Wang et al. (18.5%, 49/265) [4], Kim et al. (6.0%, 19/318) [5], and Huang et al. (0.6%, 6/1016) [7]. These differences may be due to the subjective nature of the diagnostic criteria for delirium. When a patient exhibits mild symptoms, the diagnosis of delirium may vary depending on the psychiatrist evaluating the patient. Moreover, the differences in results may be attributed to differences in the population pool between studies.
The risk factors for PODil after TKA include advanced age, high body weight, male sex, preoperative dementia and cerebrovascular disease, prolonged hospitalization, delayed ambulation, chronic opioid use, low preoperative hemoglobin level, low preoperative protein level, high postoperative BUN level, and intraoperative hypotension [4,5,6,7].
In the present study, age at TKA, Life’s Simple 7 score, intraoperative hypotension, preoperative duloxetine administration, and Parkinson’s disease were identified as independent risk factors for PODil following TKA.
The factor with the highest OR obtained in this study was the patients’ age at the time of TKA. In older patients, age-related declines in brain function lead to anatomical changes such as decreased synapses in neurons and altered neurotransmitters levels, resulting in memory and concentration difficulties that can contribute to delirium symptoms [4].
In this study, intraoperative hypotension and underlying Parkinson’s disease were also risk factors for PODil after TKA. However, previous studies have reported mixed results regarding these associations. According to Papadopoulos et al. [29], hypotension is associated with decreased cerebral blood flow, and inadequate cerebral oxygenation may cause delirium. However, Hirsch et al. [30] reported that hypotension is not significantly associated with PODil. Preoperative duloxetine administration was associated with increased PODil. Although no studies have shown that duloxetine has a direct effect on the development of delirium, according to Goldstein [31], patients receiving a serotonin reuptake inhibitor have reported mental status changes such as delirium. Parkinson’s disease has also been suggested as a risk factor for PODil in some studies [32,33], but not in others [34]. However, Parkinson’s disease is associated with increased risks of medical and surgical complications [35,36], which suggests that it may also contribute to PODil.
In accordance with our hypothesis, Life’s Simple 7 score was identified as a risk factor for PODil after TKA, with the second highest OR. Life’s Simple 7 score, which can predict CVH, is an independent risk factor for PODil after TKA. However, among the components constituting it, the relationship between the occurrence of PODil and some components is controversial. According to Bjoro et al. [37], a higher BMI, which results in a low Life’s Simple 7 score, is known to be a risk factor for delirium. Zakriya et al. [14] reported that hypertension, DM, and smoking, which lead to low Life’s Simple 7 scores, are unrelated to the occurrence of delirium. Although some of the Life’s Simple 7 score components are unrelated to PODil, Life’s Simple 7 score is an index that evaluates CVH by scoring each component. Based on the results of several previous studies, there is a consensus that CVD increases the incidence of PODil [14,34,38], which is consistent with the results of our study. Additionally, we determined that a Life’s Simple 7 score of 8 was the optimal cut-off value for predicting PODil. The accuracy of this cut-off value was validated using ROC curve analysis, yielding an AUC of 0.82.
Based on our results, Life’s Simple 7 score can be evaluated as an independent risk factor for PODil after TKA. Due to its simplicity of measurement, we expect Life’s Simple 7 score to make an important contribution to the prediction of PODil and greatly aid in preoperative risk assessment and post-operative patient management.
The limitations of this study are as follows: As this was a retrospective study, we were unaware of any missing medical records. Second, since the patient group included in this study was distributed over a period of almost 6 years (2015–2020), three different psychiatrists diagnosed the patients with PODil over the course of the study. Third, a sex bias may exist because most patients who underwent TKA were female (male, 135; female, 831). However, we found that sex was not a factor associated with PODil after TKA. Fourth, the preoperative state of cognitive dysfunction was not baselined before the surgery. While most patients were alert preoperatively, further research is needed to examine the correlation between preoperative cognitive status and the incidence of PODil. Additionally, this study included only a limited set of chronic conditions and medication histories. Future investigations should incorporate a broader preoperative baseline assessment, including cognitive function and chronic disorders, to enhance our understanding of PODil risk factors.
5. Conclusions
Lower Life’s Simple 7 score is an independent risk factor for the incidence of PODil after TKA. Due to its simplicity of measurement, Life’s Simple 7 score may be a useful measure for predicting PODil and will aid in preoperative risk assessment and post-operative patient management. Other risk factors for PODil after TKA include age at TKA, Parkinson’s disease, intraoperative hypotension, and preoperative duloxetine administration.
Author Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Conceptualization, Y.-B.J. and Y.-M.K.; methodology, W.-Y.L.; formal analysis, J.-Y.P.; data curation, Y.-C.P. and C.-S.L.; writing—original draft preparation, J.-Y.P.; writing—review and editing, Y.-B.J.; project administration, J.-Y.P.; funding acquisition, Y.-B.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by a research fund of Chungnam National University Hospital.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was approved by Chungnam National University Hospital Institutional Review Board (CNUH 2021-09-060, 13 October 2021).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was waived due to the study’s retrospective design.
Data Availability Statement
The data generated and/or analyzed in this study are included within this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| TKA | Total knee arthroplasty |
| PODil | Postoperative delirium |
| CVD | Cardiovascular disease |
| CVH | Cardiovascular health |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| IRB | Institutional Review Board |
| CCI | Charlson comorbidity index |
| HTN | Hypertension |
| DM | Diabetes mellitus |
| BUN | Blood urea nitrogen |
| OR | Odds ratio |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| AUC | Area under the curve |
| ROC | Receiver operating characteristic |
References
- Abd Razak, H.R.B.; Yung, W.Y.A. Postoperative delirium in patients undergoing total joint arthroplasty: A systematic review. J. Arthroplast. 2015, 30, 1414–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, K.; Kim, K.H.; Ko, S.; Jo, C.; Han, H.-S.; Lee, M.C. Total knee arthroplasty: Is it safe? A single-center study of 4124 patients in South Korea. Clin. Orthop. Surg. 2023, 15, 935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirschbaum, S.; Kakzhad, T.; Granrath, F.; Jasina, A.; Oronowicz, J.; Perka, C.; Kopf, S.; Gwinner, C.; Pumberger, M. Significant increase in quantity and quality of knee arthroplasty related research in KSSTA over the past 15 years. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2022, 30, 1239–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Seok, S.; Kim, S.; Kim, K.; Lee, S.; Lee, K. The risk factors of postoperative delirium after total knee arthroplasty. J. Knee Surg. 2017, 30, 600–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.-W.; Kim, N.; Kim, J.; Kim, K.-M.; Lee, S. Risk factors for postoperative delirium following total knee arthroplasty in elderly patients. Anesth. Pain Med. 2018, 13, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, K.S.; Lee, J.K.; Park, J.S.; Choi, C.H. Risk factors of delirium in patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2015, 60, 443–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Bin Abd Razak, H.R.; Yeo, S.J. Incidence of postoperative delirium in patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty-an Asian perspective. Ann. Transl. Med. 2017, 5, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyer, C.B.; Ashton, C.M.; Teasdale, T.A. Postoperative delirium: A review of 80 primary data-collection studies. Arch. Intern. Med. 1995, 155, 461–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schor, J.D.; Levkoff, S.E.; Lipsitz, L.A.; Reilly, C.H.; Cleary, P.D.; Rowe, J.W.; Evans, D.A. Risk factors for delirium in hospitalized elderly. JAMA 1992, 267, 827–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, R.I.; Cameron, D.J.; Fahs, M.C. A prospective study of delirium and prolonged hospital stay: Exploratory study. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 1988, 45, 937–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holroyd-Leduc, J.M.; Khandwala, F.; Sink, K.M. How can delirium best be prevented and managed in older patients in hospital? CMAJ 2010, 182, 465–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansaloni, L.; Catena, F.; Chattat, R.; Fortuna, D.; Franceschi, C.; Mascitti, P.; Melotti, R. Risk factors and incidence of postoperative delirium in elderly patients after elective and emergency surgery. J. Br. Surg. 2010, 97, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, J.M. Postoperative delirium: Are there modifiable risk factors? Eur. J. Anaesthesiol./EJA 2010, 27, 403–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakriya, K.J.; Christmas, C.; Wenz, J.F.S.; Franckowiak, S.; Anderson, R.; Sieber, F.E. Preoperative Factors Associated with Postoperative Change in Confusion Assessment Method Score in Hip Fracture Patients. Anesth. Analg. 2002, 94, 1628–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankowski, C.J.; Trenerry, M.R.; Cook, D.J.; Buenvenida, S.L.; Stevens, S.R.; Schroeder, D.R.; Warner, D.O. Cognitive and functional predictors and sequelae of postoperative delirium in elderly patients undergoing elective joint arthroplasty. Anesth. Analg. 2011, 112, 1186–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deo, H.; West, G.; Butcher, C.; Lewis, P. The prevalence of cognitive dysfunction after conventional and computer-assisted total knee replacement. Knee 2011, 18, 117–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd-Jones, D.M.; Hong, Y.; Labarthe, D.; Mozaffarian, D.; Appel, L.J.; Van Horn, L.; Greenlund, K.; Daniels, S.; Nichol, G.; Tomaselli, G.F. Defining and setting national goals for cardiovascular health promotion and disease reduction: The American Heart Association’s strategic Impact Goal through 2020 and beyond. Circulation 2010, 121, 586–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thacker, E.L.; Gillett, S.R.; Wadley, V.G.; Unverzagt, F.W.; Judd, S.E.; McClure, L.A.; Howard, V.J.; Cushman, M. The American Heart Association Life's Simple 7 and Incident Cognitive Impairment: The RE asons for Geographic And Racial Differences in Stroke (REGARDS) Study. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2014, 3, e000635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulshreshtha, A.; Vaccarino, V.; Judd, S.E.; Howard, V.J.; McClellan, W.M.; Muntner, P.; Hong, Y.; Safford, M.M.; Goyal, A.; Cushman, M. Life’s Simple 7 and risk of incident stroke: The reasons for geographic and racial differences in stroke study. Stroke 2013, 44, 1909–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Rundek, T.; Wright, C.B.; Anwar, Z.; Elkind, M.S.; Sacco, R.L. Ideal cardiovascular health predicts lower risks of myocardial infarction, stroke, and vascular death across whites, blacks, and hispanics: The northern Manhattan study. Circulation 2012, 125, 2975–2984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folsom, A.R.; Yatsuya, H.; Nettleton, J.A.; Lutsey, P.L.; Cushman, M.; Rosamond, W.D.; Investigators, A.S. Community prevalence of ideal cardiovascular health, by the American Heart Association definition, and relationship with cardiovascular disease incidence. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2011, 57, 1690–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okpara, S.; Lee, T.; Pathare, N.; Ghali, A.; Momtaz, D.; Ihekweazu, U. Cardiovascular Disease in Total Knee Arthroplasty: An Analysis of Hospital Outcomes, Complications, and Mortality. Clin. Orthop. Surg. 2024, 16, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sacco, R.L. Achieving ideal cardiovascular and brain health: Opportunity amid crisis: Presidential Address at the American Heart Association 2010 Scientific Sessions. Circulation 2011, 123, 2653–2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamis, D.; Rooney, S.; Meagher, D.; Mulligan, O.; McCarthy, G. A comparison of delirium diagnosis in elderly medical inpatients using the CAM, DRS-R98, DSM-IV and DSM-5 criteria. Int. Psychogeriatr. 2015, 27, 883–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daabiss, M. American Society of Anaesthesiologists physical status classification. Indian J. Anaesth. 2011, 55, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundararajan, V.; Henderson, T.; Perry, C.; Muggivan, A.; Quan, H.; Ghali, W.A. New ICD-10 version of the Charlson comorbidity index predicted in-hospital mortality. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2004, 57, 1288–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czajka, S.; Putowski, Z.; Krzych, Ł.J. Intraoperative hypotension and its organ-related consequences in hypertensive subjects undergoing abdominal surgery: A cohort study. Blood Press. 2021, 30, 348–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasai, T.; Hirose, M.; Yaegashi, K.; Matsukawa, T.; Takamata, A.; Tanaka, Y. Preoperative risk factors of intraoperative hypothermia in major surgery under general anesthesia. Anesth. Analg. 2002, 95, 1381–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulos, G.; Karanikolas, M.; Liarmakopoulou, A.; Papathanakos, G.; Korre, M.; Beris, A. Cerebral oximetry and cognitive dysfunction in elderly patients undergoing surgery for hip fractures: A prospective observational study. Open Orthop. J. 2012, 6, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, J.; DePalma, G.; Tsai, T.; Sands, L.; Leung, J. Impact of intraoperative hypotension and blood pressure fluctuations on early postoperative delirium after non-cardiac surgery. Br. J. Anaesth. 2015, 115, 418–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, D.J. Duloxetine in the treatment of major depressive disorder. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2007, 3, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, J.M.; Sodhi, N.; Dalton, S.E.; Khlopas, A.; Newman, R.P.; Higuera, C.A.; Mont, M.A. Does Parkinson disease increase the risk of perioperative complications after total hip arthroplasty? A nationwide database study. J. Arthroplast. 2018, 33, S162–S166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edlund, A.; Lundström, M.; Brännström, B.; Bucht, G.; Gustafson, Y. Delirium before and after operation for femoral neck fracture. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2001, 49, 1335–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gustafson, Y.; Berggren, D.; Brännström, B.; Bucht, G.; Norberg, A.; Hansson, L.I.; Winblad, B. Acute confusional states in elderly patients treated for femoral neck fracture. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 1988, 36, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.-R.; Yoon, T.-H.; Lee, S.H. The effect of Parkinson’s disease on total knee arthroplasty: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Knee Surg. Relat. Res. 2023, 35, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, J.M.; Sodhi, N.; Wilhelm, A.B.; Khlopas, A.; Klika, A.K.; Naziri, Q.; Kryzak, T.J.; Higuera, C.A.; Mont, M.A. Parkinson’s disease increases the risk of perioperative complications after total knee arthroplasty: A nationwide database study. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2019, 27, 2189–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjoro, K.L.K. Pain Treatment: A Risk Factor for Delirium in Older Adults with Hip Fracture. Ph.D. Thesis, The University of Iowa, Iowa City, IA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Morrison, R.S.; Magaziner, J.; Gilbert, M.; Koval, K.J.; McLaughlin, M.A.; Orosz, G.; Strauss, E.; Siu, A.L. Relationship between pain and opioid analgesics on the development of delirium following hip fracture. J. Gerontol. Ser. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2003, 58, M76–M81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).