Asprosin and Neuregulin 4 in Obesity in Children
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Method
2.1. Collection of Samples
2.2. Determination of Asprosin and Neuregulin 4 Levels by Elisa Method
2.3. Statistical Analysis
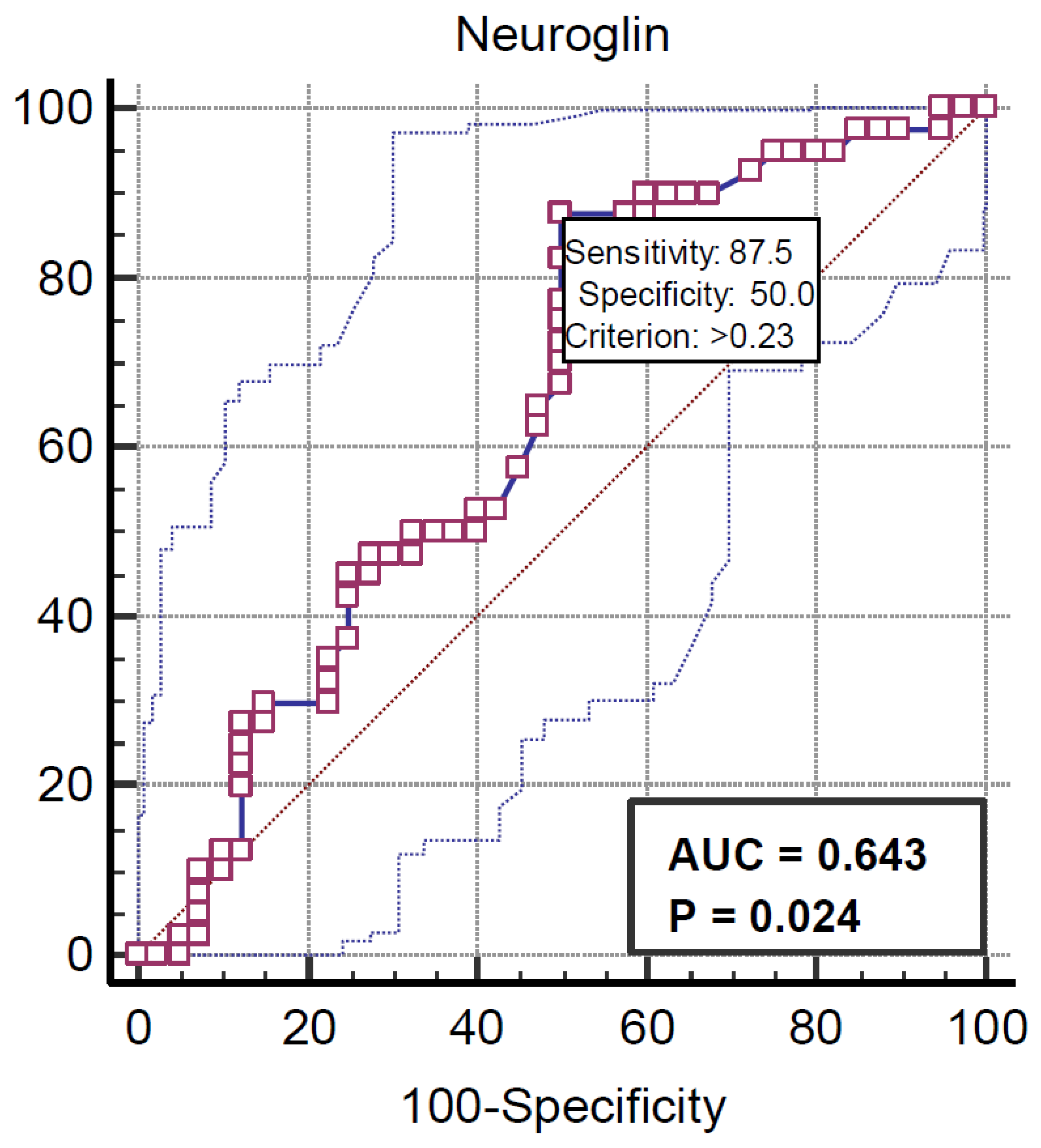
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lin, X.; Li, H. Obesity: Epidemiology, pathophysiology, and therapeutics. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 706978. [Google Scholar]
- Çamurdan, M.O. Epidemiology of obesity. In Türkiye Clinics Pediatric Endocrinology Special Topics-Obesity 2020; Türkiye Clinics Publishing House: Ankara, Türkiye, 2020; pp. 10–13. [Google Scholar]
- Lo, J.C.; Chandra, M.; Sinaiko, A.; Daniels, S.R.; Prineas, R.J.; Maring, B.; Greenspan, L.C. Severe obesity in children: Prevalence, persistence and relation to hypertension. Int. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. 2014, 2014, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Ang, Y.N.; Wee, B.S.; Poh, B.K.; Ismail, M.N. Multifactorial influences of childhood obesity. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2013, 2, 10–22. [Google Scholar]
- Romere, C.; Duerrschmid, C.; Bournat, J.; Constable, P.; Jain, M.; Xia, F.; Saha, P.K.; Del Solar, M.; Zhu, B.; York, B.; et al. Asprosin, a Fasting-Induced Glucogenic Protein Hormone. Cell 2016, 165, 566–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Li, X.; Liao, M.; Shen, R.; Zhang, L.; Hu, H.; Wu, J.; Wang, X.; Qu, H.; Guo, S.; Long, M.; et al. Plasma Asprosin Levels Are Associated with Glucose Metabolism, Lipid, and Sex Hormone Profiles in Females with Metabolic-Related Diseases. Mediat. Inflamm. 2018, 2018, 7375294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Duerrschmid, C.; He, Y.; Wang, C.; Li, C.; Bournat, J.C.; Romere, C.; Saha, P.K.; Lee, M.E.; Phillips, K.J.; Chopra, A.R.; et al. Asprosin is a centrally acting orexigenic hormone. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 1444–1453. [Google Scholar]
- Long, W.; Xie, X.; Du, C.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhan, D.; Li, Z.; Ning, Q.; Luo, X. Decreased Circulating Levels of Asprosin in Obese Children. Horm. Res. Paediatr. 2019, 91, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Qu, H.; Xiong, X.; Qiu, Y.; Liao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Zheng, H. Plasma Asprosin Concentrations Are Increased in Individuals with Glucose Dysregulation and Correlated with Insulin Resistance and First-Phase Insulin Secretion. Mediat. Inflamm. 2018, 2018, 9471583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Alan, M.; Gurlek, B.; Yilmaz, A.; Aksit, M.; Aslanipour, B.; Gulhan, I.; Mehmet, C.; Taner, C.E. Asprosin: A novel peptide hormone related to insulin resistance in women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Gynecol. Endocrinol. 2019, 35, 220–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harari, D.; Tzahar, E.; Romano, J.; Shelly, M.; Pierce, J.H.; Andrews, G.C.; Yarden, Y. Neuregulin-4: A novel growth factor that acts through the ErbB-4 receptor tyrosine kinase. Oncogene 1999, 18, 2681–2689. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, M. Neuregulin 4 as a novel adipokine in energy metabolism. Front. Physiol. 2023, 13, 1106380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Tutunchi, H.; Ostadrahimi, A.; Hosseinzadeh-Attar, M.; Miryan, M.; Mobasseri, M.; Ebrahimi-Mameghani, M. A systematic review of the association of neuregulin 4, a brown fat-enriched secreted factor, with obesity and related metabolic disturbances. Obese. Rev. 2020, 21, e12952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neyzi, O.; Günöz, H.; Furman, A.; Bundak, R.; Gökçay, G.; Darendeliler, F.; Baş, F. Body weight, height, head circumference and body mass index reference values in Turkish children. J. Child Health Dis. 2008, 51, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obesity: Preventing and managing the global epidemic. Report of a WHO consultation. World Health Organ. Tech. Rep. Ser. 2000, 894, 1–253. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Kelly, A.S. Review of Childhood Obesity: From Epidemiology, Etiology, and Comorbidities to Clinical Assessment and Treatment. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2017, 92, 251–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.-Y.; Lin, T.-A.; Liu, K.-H.; Liao, C.-H.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Wu, V.C.-C.; Wen, M.-S.; Yeh, T.-S. Serum asprosin levels and bariatric surgery outcomes in obese adults. Int. J. Obes. 2019, 43, 1019–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ugur, K.; Aydin, S. Saliva and Blood Asprosin Hormone Concentration Associated with Obesity. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2019, 2019, 2521096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yuan, M.; Li, W.; Zhu, Y.; Yu, B.; Wu, J. Asprosin: A novel player in metabolic diseases. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nugroho, D.B.; Ikeda, K.; Kajimoto, K.; Hirata, K.I.; Emoto, N. Activation of neuregulin-4 in adipocytes improves metabolic health by enhancing adipose tissue angiogenesis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 504, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Gao, M.; Liu, D. Preventing High Fat Diet-induced Obesity and Improving Insulin Sensitivity Through Neuregulin 4 Gene Transfer. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wang, R.; Yang, F.; Qing, L.; Huang, R.; Liu, Q.; Li, X. Decreased serum neuregulin 4 levels associated with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in children with obesity. Clin. Obes. 2019, 9, e12289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, S.; Hu, Y. Effects of serum irisin, neuregulin 4, and weight management on obese adolescent girls with polycystic ovary syndrome. Biosci. Rep. 2021, 41, BSR20211658. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez, C.; Latorre, J.; Ortega, F.; Arnoriaga-Rodríguez, M.; Lluch, A.; Oliveras-Cañellas, N.; Díaz-Sáez, F.; Aragonés, J.; Camps, M.; Gumà, A.; et al. Serum neuregulin 4 is negatively correlated with insulin sensitivity in human sand impairs mitochondrial respiration in HepG2 cells. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 950791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
| Variables | Group | N | Mean | Sd | t | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asprosin | Female Male | 45 35 | 18,669 0.8366 | 120,775 0.196 | 0.872 | 0.08 |
| Nrg4 | Female Male | 45 35 | 1033 1694 | 1876 6139 | −0.689 | 0.246 |
| Groups | Test Statistics | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Obese | Control | Test Value | p Value | |
| Gender, n (%) Male Female | 21 (60.0) 19 (42.2) | 14 (40.0) 26(57.8) | χ2 = 2.489 | 0.115 |
| Age (years) M (min–max) | 11 (6–18) | 9 (3–16) | z = 2.745 | 0.006 |
| Height (cm) M (min–max) | 149.5 (124.0–170.0) | 138.5 (106.0–182.0) | z = 2.291 | 0.022 |
| Weight (kg) M (min–max) | 64.65 (13.02–110.0) | 32.75 (15–65) | z = 5.692 | <0.001 |
| Body Mass Index (kg/m2) M (min–max) | 27.27 (25.04–47.78) | 17.96 (12.63–27.69) | z = 7.477 | <0.001 |
| HDL (mg/dL) M (min–max) | 44 (33–78) | 50 (30–81) | z = 2.426 | 0.015 |
| LDL (mg/dL) M (min–max) | 91 (58–302) | 79 (38–151) | z = 1.734 | 0.083 |
| Cholesterol (mg/dL) M (min–max) | 158.5 (113–369) | 154 (97–219) | z = 0.742 | 0.458 |
| Triglyceride (mg/dL) M (min–max) | 96.50 (48–236) | 70 (37–277) | z = 2.649 | 0.008 |
| VLDL (mg/dL) | 21.5 (9–47) | 15.3 (7–55) | z = 1.231 | 0.162 |
| Glucose (mg/dL) ± sd | 96.75 ± 8.79 | 93.55 ± 9.64 | t = 1.531 | 0.130 |
| ALT (U/L) M (min–max) | 19.5 (5–65) | 15 (7–161.0) | z = 2.814 | 0.005 |
| AST (U/L) M (min–max) | 26 (14–52) | 30 (13–209) | z = 2.382 | 0.017 |
| Insulin M (min–max) | 12 (3–24) | 6 (2–32) | z = 4.050 | <0.001 |
| Asprosin (ng/mL) M (min–max) | 0.78 (0.46–1.23) | 0.82 (0.55–2.65) | z = 0.760 | 0.447 |
| Neuregulin 4 (ng/mL) M (min–max) | 0.45 (0.04–5.24) | 0.28(0.02–36.74) | z = 2.194 | 0.028 |
| HOMA-IR M (min–max) | 3.10 (0.70–6.10) | 1.30 (0.40–6.90) | z = 3.801 | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dulkadir, R.; Turna Saltoglu, G.; Gunes, A. Asprosin and Neuregulin 4 in Obesity in Children. Medicina 2025, 61, 723. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61040723
Dulkadir R, Turna Saltoglu G, Gunes A. Asprosin and Neuregulin 4 in Obesity in Children. Medicina. 2025; 61(4):723. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61040723
Chicago/Turabian StyleDulkadir, Ramazan, Gamze Turna Saltoglu, and Ali Gunes. 2025. "Asprosin and Neuregulin 4 in Obesity in Children" Medicina 61, no. 4: 723. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61040723
APA StyleDulkadir, R., Turna Saltoglu, G., & Gunes, A. (2025). Asprosin and Neuregulin 4 in Obesity in Children. Medicina, 61(4), 723. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61040723






