Liquid Biopsy as a Diagnostic and Monitoring Tool in Glioblastoma
Abstract
1. Introduction
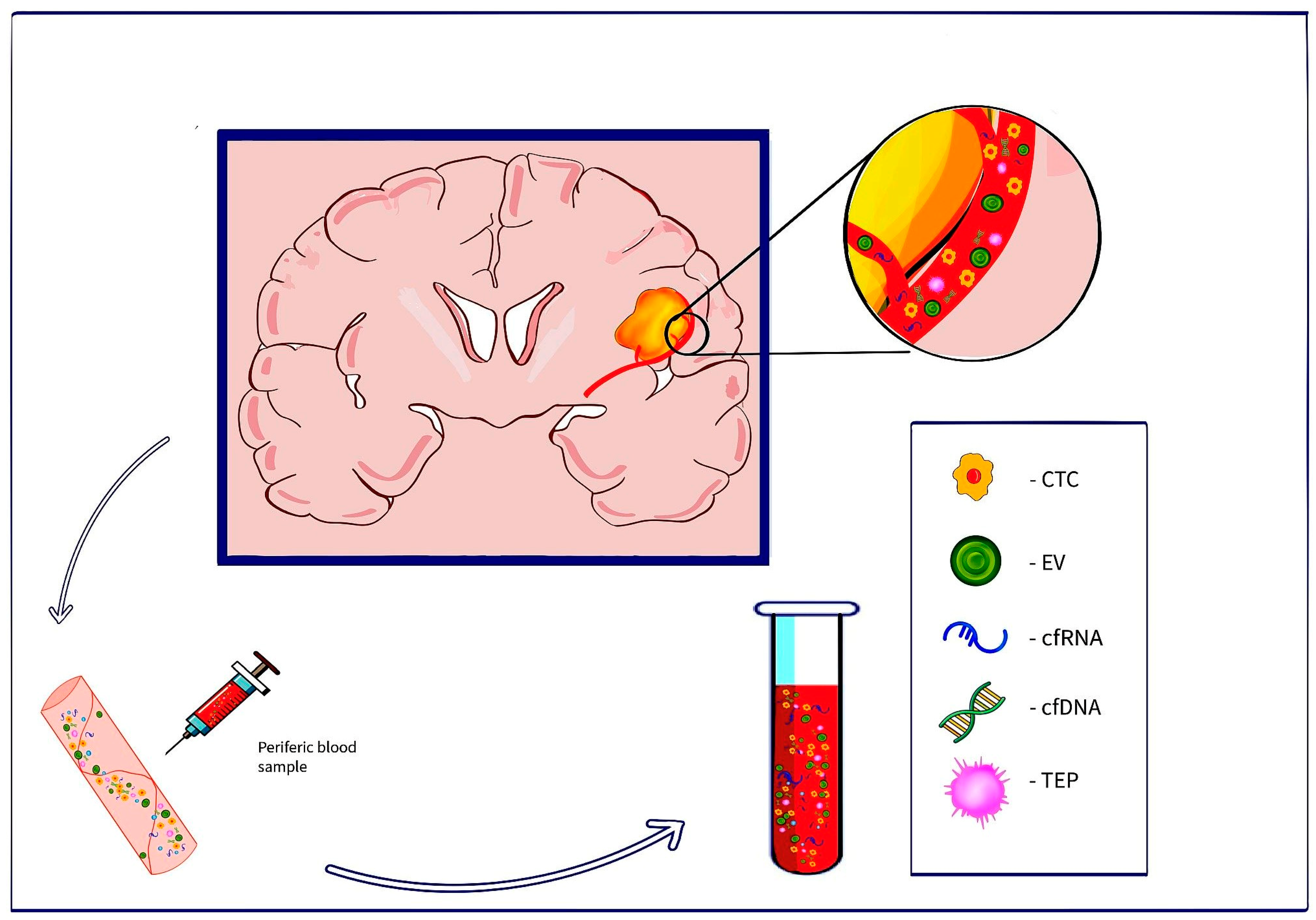
2. Liquid Biopsy
2.1. Cell-Free Nucleic Acids (cfNAs)
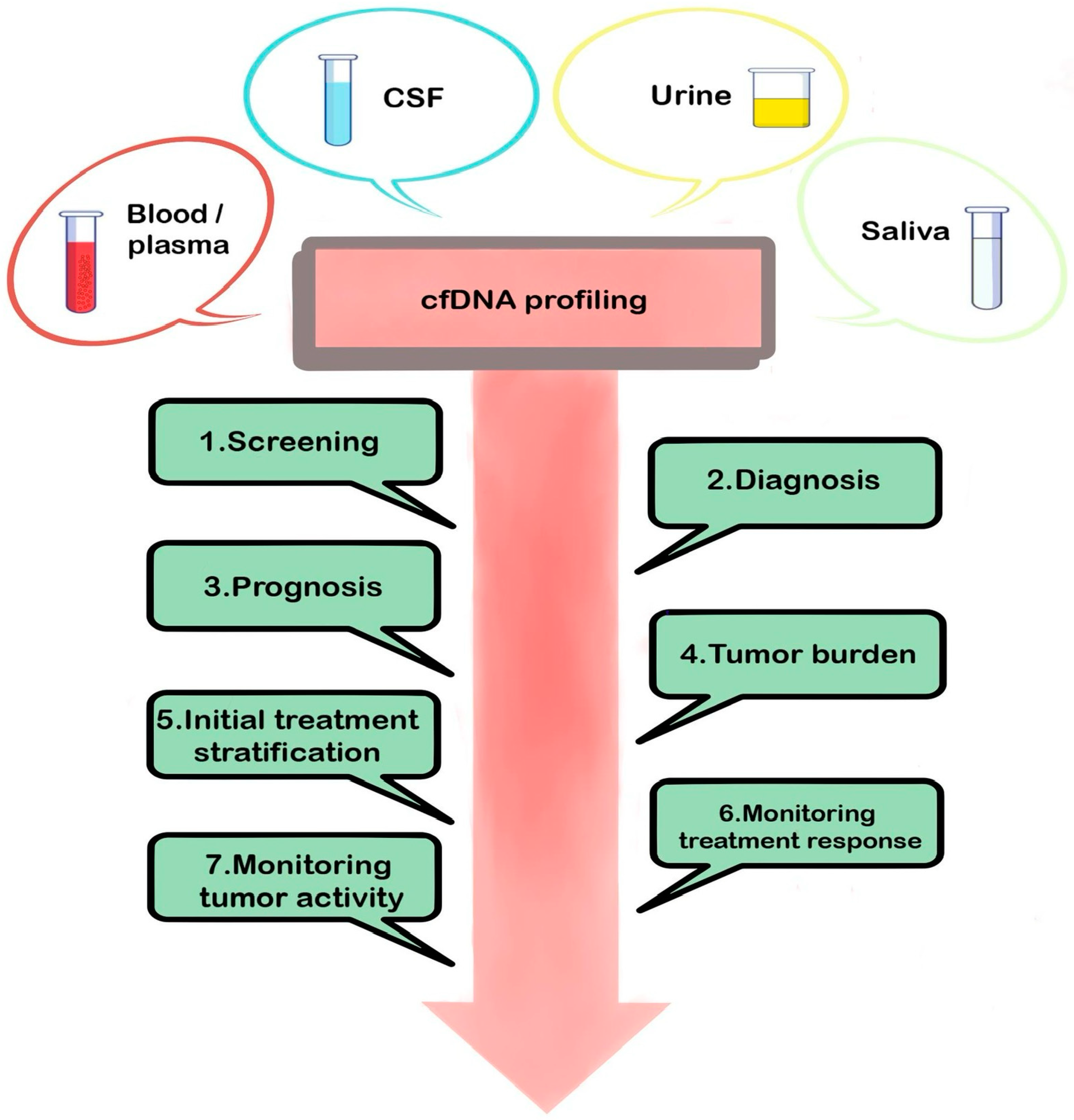
2.1.1. Cell-Free DNA (cfDNA)
2.1.2. Cell-Free RNA (cfRNA)
2.2. Extracellular Vesicles
2.2.1. Exosomes
2.2.2. Microvesicles
2.3. CTCs—Circulating Tumor Cells
2.4. TEPs
3. Future Directions
4. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- King, J.L.; Benhabbour, S.R. Glioblastoma Multiforme—A Look at the Past and a Glance at the Future. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Zhou, W.; Tan, Y.; Tian, D.; Zhong, C. 5-Hydroxymethylcytosines in circulating cell-free DNA reveal a diagnostic biomarker for glioma. Heliyon 2022, 8, e11022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohgaki, H.; Kleihues, P. Genetic Pathways to Primary and Secondary Glioblastoma. Am. J. Pathol. 2007, 170, 1445–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrom, Q.T.; Cioffi, G.; Waite, K.; Kruchko, C.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S. CBTRUS Statistical Report: Primary Brain and Other Central Nervous System Tumors Diagnosed in the United States in 2014–2018. Neuro-Oncology 2021, 23, iii1–iii105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldape, K.; Zadeh, G.; Mansouri, S.; Reifenberger, G.; von Deimling, A. Glioblastoma: Pathology, molecular mechanisms and markers. Acta Neuropathol. 2015, 129, 829–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, K.; Tachibana, O.; Sato, K.; Yonekawa, Y.; Kleihues, P.; Ohgaki, H. Overexpression of the EGF Receptor and p53 Mutations are Mutually Exclusive in the Evolution of Primary and Secondary Glioblastomas. Brain Pathol. 1996, 6, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Wesseling, P.; Brat, D.J.; Cree, I.A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Hawkins, C.; Ng, H.K.; Pfister, S.M.; Reifenberger, G.; et al. The 2021 WHO Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: A summary. Neuro-Oncology 2021, 23, 1231–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuss, D.E.; Mamatjan, Y.; Schrimpf, D.; Capper, D.; Hovestadt, V.; Kratz, A.; Sahm, F.; Koelsche, C.; Korshunov, A.; Olar, A.; et al. IDH mutant diffuse and anaplastic astrocytomas have similar age at presentation and little difference in survival: A grading problem for WHO. Acta Neuropathol. 2015, 129, 867–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslan, K.; Turco, V.; Blobner, J.; Sonner, J.K.; Liuzzi, A.R.; Nunez, N.G.; de Feo, D.; Kickingereder, P.; Fischer, M.; Green, E.; et al. Heterogeneity of response to immune checkpoint blockade in hypermutated experimental gliomas. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammirati, M.; Chotai, S.; Newton, H.; Lamki, T.; Wei, L.; Grecula, J. Hypofractionated intensity modulated radiotherapy with temozolomide in newly diagnosed glioblastoma multiforme. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2014, 21, 633–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannas, J.P.; Lightner, D.D.; DeFrates, S.R.; Pittman, T.; Villano, J.L. Long-term treatment with temozolomide in malignant glioma. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2014, 21, 121–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Ma, Y.; Wu, Z.; Xie, R.; Zeng, F.; Cai, H.; Lui, S.; Song, B.; Chen, L.; Wu, M. Advanced Imaging Techniques for Differentiating Pseudoprogression and Tumor Recurrence After Immunotherapy for Glioblastoma. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 790674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, C.M.; Toms, S.A. The Role of Circulating MicroRNA in Glioblastoma Liquid Biopsy. World Neurosurg. 2020, 138, 425–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, J.D.; Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Thoburn, C.; Afsari, B.; Danilova, L.; Douville, C.; Javed, A.A.; Wong, F.; Mattox, A.; et al. Detection and localization of surgically resectable cancers with a multi-analyte blood test. Science 2018, 359, 926–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Zhao, H. Next-generation sequencing in liquid biopsy: Cancer screening and early detection. Hum. Genom. 2019, 13, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perakis, S.; Speicher, M.R. Emerging concepts in liquid biopsies. BMC Med. 2017, 15, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skouras, P.; Markouli, M.; Kalamatianos, T.; Stranjalis, G.; Korkolopoulou, P.; Piperi, C. Advances on Liquid Biopsy Analysis for Glioma Diagnosis. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurma, K.; Eslami-S, Z.; Alix-Panabières, C.; Cayrefourcq, L. Liquid biopsy: Paving a new avenue for cancer research. Cell Adhes. Migr. 2024, 18, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirahata, T.; ul Quraish, R.; Quraish, A.U.; ul Quraish, S.; Naz, M.; Razzaq, M.A. Liquid Biopsy: A Distinctive Approach to the Diagnosis and Prognosis of Cancer. Cancer Inform. 2022, 21, 11769351221076062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corcoran, R.B.; Chabner, B.A. Application of Cell-free DNA Analysis to Cancer Treatment. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 1754–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantel, K.; Alix-Panabières, C. Circulating tumour cells in cancer patients: Challenges and perspectives. Trends Mol. Med. 2010, 16, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pantel, K.; Alix-Panabières, C. Liquid biopsy and minimal residual disease—latest advances and implications for cure. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 16, 409–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauman, M.M.J.; Bouchal, S.M.; Monie, D.D.; Aibaidula, A.; Singh, R.; Parney, I.F. Strategies, considerations, and recent advancements in the development of liquid biopsy for glioblastoma: A step towards individualized medicine in glioblastoma. Neurosurg. Focus 2022, 53, E14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jelski, W.; Mroczko, B. Molecular and Circulating Biomarkers of Brain Tumors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westphal, M.; Lamszus, K. Circulating biomarkers for gliomas. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2015, 11, 556–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lone, S.N.; Nisar, S.; Masoodi, T.; Singh, M.; Rizwan, A.; Hashem, S.; El-Rifai, W.; Bedognetti, D.; Batra, S.K.; Haris, M.; et al. Liquid biopsy: A step closer to transform diagnosis, prognosis and future of cancer treatments. Mol. Cancer 2022, 21, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.; Nguyen, H.; Drummond, K.; Morokoff, A. Circulating Biomarkers for Glioma: A Review. Neurosurgery 2021, 88, E221–E230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandel, P.; Metais, P. Nuclear Acids in Human Blood Plasma. C R Seances. Soc. Biol. Fil. 1948, 142, 241–243. [Google Scholar]
- Saenz-Antoñanzas, A.; Auzmendi-Iriarte, J.; Carrasco-Garcia, E.; Moreno-Cugnon, L.; Ruiz, I.; Villanua, J.; Egaña, L.; Otaegui, D.; Samprón, N.; Matheu, A. Liquid biopsy in glioblastoma: Opportunities, applications and challenges. Cancers 2019, 11, 950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontanilles, M.; Sanson, M.; Touat, M. Liquid biopsy in neuro-oncology: Are we finally there? Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, 1472–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller Bark, J.; Kulasinghe, A.; Chua, B.; Day, B.W.; Punyadeera, C. Circulating biomarkers in patients with glioblastoma. Br. J. Cancer 2020, 122, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palande, V.; Siegal, T.; Detroja, R.; Gorohovski, A.; Glass, R.; Flueh, C.; Kanner, A.A.; Laviv, Y.; Har-Nof, S.; Levy-Barda, A.; et al. Detection of gene mutations and gene–gene fusions in circulating cell-free DNA of glioblastoma patients: An avenue for clinically relevant diagnostic analysis. Mol. Oncol. 2022, 16, 2098–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Bonner, E.R.; Wierzbicki, K.; Panditharatna, E.; Huang, T.; Lulla, R.; Mueller, S.; Koschmann, C.; Nazarian, J.; Saratsis, A.M. Standardization of the liquid biopsy for pediatric diffuse midline glioma using ddPCR. Sci Rep. 2021, 11, 5098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasmita, A.O.; Wong, Y.P.; Ling, A.P.K. Biomarkers and therapeutic advances in glioblastoma multiforme. Asia. Pac. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 14, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagley, S.J.; Till, J.; Abdalla, A.; Sangha, H.K.; Yee, S.S.; Freedman, J.; Black, T.A.; Hussain, J.; Binder, Z.A.; Brem, S.; et al. Clinical Utility of Plasma Cell-Free DNA in Adult Patients with Newly Diagnosed Glioblastoma: A Pilot Prospective Study. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 397–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettegowda, C.; Sausen, M.; Leary, R.J.; Kinde, I.; Wang, Y.; Agrawal, N.; Bartlett, B.R.; Wang, H.; Luber, B.; Alani, R.M.; et al. Detection of Circulating Tumor DNA in Early- and Late-Stage Human Malignancies. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leon, S.A.; Shapiro, B.; Sklaroff, D.M.; Yaros, M.J. Free DNA in the serum of cancer patients and the effect of therapy. Cancer Res. 1977, 37, 646–650. [Google Scholar]
- Aarthy, R.; Mani, S.; Velusami, S.; Sundarsingh, S.; Rajkumar, T. Role of Circulating Cell-Free DNA in Cancers. Mol. Diagn. Ther. 2015, 19, 339–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diehl, F.; Schmidt, K.; Choti, M.A.; Romans, K.; Goodman, S.; Li, M.; Thornton, K.; Agrawal, N.; Sokoll, L.; Szabo, S.A.; et al. Circulating mutant DNA to assess tumor dynamics. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 985–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroun, M.; Anker, P.; Maurice, P.; Lyautey, J.; Lederrey, C.; Beljanski, M. Neoplastic Characteristics of the DNA Found in the Plasma of Cancer Patients. Oncology 1989, 46, 318–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.C.; Yee, S.S.; Troxel, A.B.; Savitch, S.L.; Fan, R.; Balli, D.; Lieberman, D.B.; Morrissette, J.D.; Evans, T.L.; Bauml, J.; et al. Detection of Therapeutically Targetable Driver Resistance Mutations in Lung Cancer Patients by Next-Generation Sequencing of Cell-Free Circulating Tumor DNA. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 5772–5782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, A.M.; Bratman, S.V.; To, J.; Wynne, J.F.; Eclov, N.C.W.; Modlin, L.A.; Liu, C.L.; Neal, J.W.; Wakelee, H.A.; Merritt, R.E.; et al. An ultrasensitive method for quantitating circulating tumor DNA with broad patient coverage. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 548–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz, L.A., Jr.; Williams, R.T.; Wu, J.; Kinde, I.; Hecht, J.R.; Berlin, J.; Allen, B.; Bozic, I.; Reiter, J.G.; Nowak, M.A.; et al. The molecular evolution of acquired resistance to targeted EGFR blockade in colorectal cancers. Nature 2012, 486, 537–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, C.; Thompson, J.C.; Black, T.A.; Katz, S.I.; Fan, R.; Yee, S.S.; Chien, A.L.; Evans, T.L.; Bauml, J.M.; Alley, E.W.; et al. Clinical Implications of Plasma-Based Genotyping with the Delivery of Personalized Therapy in Metastatic Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2019, 5, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacher, A.G.; Paweletz, C.; Dahlberg, S.E.; Alden, R.S.; O’Connell, A.; Feeney, N.; Mach, S.L.; Jänne, P.A.; Oxnard, G.R. Prospective Validation of Rapid Plasma Genotyping for the Detection of EGFR and KRAS Mutations in Advanced Lung Cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2016, 2, 1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.K.; Harrell, M.I.; Oza, A.M.; Oaknin, A.; Ray-Coquard, I.; Tinker, A.V.; Helman, E.; Radke, M.R.; Say, C.; Vo, L.-T.; et al. BRCA Reversion Mutations in Circulating Tumor DNA Predict Primary and Acquired Resistance to the PARP Inhibitor Rucaparib in High-Grade Ovarian Carcinoma. Cancer Discov. 2019, 9, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, A.D.; Werner, L.; Francini, E.; Wei, X.X.; Ha, G.; Freeman, S.S.; Rhoades, J.; Reed, S.C.; Gydush, G.; Rotem, D.; et al. Tumor fraction in cell-free DNA as a biomarker in prostate cancer. JCI Insight 2018, 3, e122109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, T.; Zhang, Q.; Li, X.; Su, W.; Li, G.; Ma, T.; Gao, S.; Lou, J.; Que, R.; Zheng, L.; et al. Monitoring Tumor Burden in Response to FOLFIRINOX Chemotherapy Via Profiling Circulating Cell-Free DNA in Pancreatic Cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2019, 18, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valpione, S.; Gremel, G.; Mundra, P.; Middlehurst, P.; Galvani, E.; Girotti, M.R.; Lee, R.J.; Garner, G.; Dhomen, N.; Lorigan, P.C.; et al. Plasma total cell-free DNA (cfDNA) is a surrogate biomarker for tumour burden and a prognostic biomarker for survival in metastatic melanoma patients. Eur. J. Cancer 2018, 88, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangadhar, T.C.; Savitch, S.L.; Yee, S.S.; Xu, W.; Huang, A.C.; Harmon, S.; Lieberman, D.B.; Soucier, D.; Fan, R.; Black, T.A.; et al. Feasibility of monitoring advanced melanoma patients using cell-free DNA from plasma. Pigment. Cell Melanoma Res. 2018, 31, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, K.C.; Verhaak, R.G.W. Serum cell-free DNA epigenetic biomarkers aid glioma diagnostics and monitoring. Neuro-oncology 2021, 23, 1423–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aran, V.; de Melo Junior, J.O.; Pilotto Heming, C.; Zeitune, D.J.; Moura Neto, V.; Niemeyer Filho, P. Unveiling the impact of corticosteroid therapy on liquid biopsy-detected cell-free DNA levels in meningioma and glioblastoma patients. J. Liq. Biopsy. 2024, 5, 100149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Springer, S.; Zhang, M.; McMahon, K.W.; Kinde, I.; Dobbyn, L.; Ptak, J.; Brem, H.; Chaichana, K.; Gallia, G.L.; et al. Detection of tumor-derived DNA in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with primary tumors of the brain and spinal cord. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 9704–9709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyun, K.-A.; Gwak, H.; Lee, J.; Kwak, B.; Jung, H.-I. Salivary Exosome and Cell-Free DNA for Cancer Detection. Micromachines 2018, 9, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, W.; Mei, C.; Nan, X.; Hui, L. Evaluation and comparison of in vitro degradation kinetics of DNA in serum, urine and saliva: A qualitative study. Gene 2016, 590, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.Y.; Lee, E.-J.; Yoon, H.; Lee, D.H.; Kim, K.H. Comparison of Four Commercial Kits for Isolation of Urinary Cell-Free DNA and Sample Storage Conditions. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabavizadeh, S.A.; Ware, J.B.; Guiry, S.; Nasrallah, M.P.; Mays, J.J.; Till, J.E.; Hussain, J.; Abdalla, A.; Yee, S.S.; Binder, Z.A.; et al. Imaging and histopathologic correlates of plasma cell-free DNA concentration and circulating tumor DNA in adult patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma. Neuro-Oncol. Adv. 2020, 2, vdaa016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccioni, D.E.; Achrol, A.S.; Kiedrowski, L.A.; Banks, K.C.; Boucher, N.; Barkhoudarian, G.; Kelly, D.F.; Juarez, T.; Lanman, R.B.; Raymond, V.M.; et al. Analysis of cell-free circulating tumor DNA in 419 patients with glioblastoma and other primary brain tumors. CNS Oncol. 2019, 8, CNS34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zill, O.A.; Banks, K.C.; Fairclough, S.R.; Mortimer, S.A.; Vowles, J.V.; Mokhtari, R.; Gandara, D.R.; Mack, P.C.; Odegaard, J.I.; Nagy, R.J.; et al. The Landscape of Actionable Genomic Alterations in Cell-Free Circulating Tumor DNA from 21,807 Advanced Cancer Patients. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 3528–3538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwaederle, M.; Husain, H.; Fanta, P.T.; Piccioni, D.E.; Kesari, S.; Schwab, R.B.; Banks, K.C.; Lanman, R.B.; Talasaz, A.; Parker, B.A.; et al. Detection rate of actionable mutations in diverse cancers using a biopsy-free (blood) circulating tumor cell DNA assay. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 9707–9717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomei, S.; Volontè, A.; Ravindran, S.; Mazzoleni, S.; Wang, E.; Galli, R.; Maccalli, C. MicroRNA Expression Profile Distinguishes Glioblastoma Stem Cells from Differentiated Tumor Cells. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontanilles, M.; Marguet, F.; Beaussire, L.; Magne, N.; Pépin, L.-F.; Alexandru, C.; Tennevet, I.; Hanzen, C.; Langlois, O.; Jardin, F.; et al. Cell-free DNA and circulating TERT promoter mutation for disease monitoring in newly-diagnosed glioblastoma. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2020, 8, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagley, S.J.; Till, J.; Abdalla, A.; Sangha, H.K.; Yee, S.S.; Freedman, J.; Black, T.A.; Hussain, J.; Binder, Z.A.; Brem, S.; et al. Association of plasma cell-free DNA with survival in patients with IDH wild-type glioblastoma. Neuro-Oncol. Adv. 2021, 3, vdab011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouliere, F.; Smith, C.G.; Heider, K.; Su, J.; van der Pol, Y.; Thompson, M.; Morris, J.; Wan, J.C.M.; Chandrananda, D.; Hadfield, J.; et al. Fragmentation patterns and personalized sequencing of cell-free DNA in urine and plasma of glioma patients. EMBO Mol. Med. 2021, 13, e12881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontanilles, M.; Marguet, F.; Bohers, É.; Viailly, P.-J.; Dubois, S.; Bertrand, P.; Camus, V.; Mareschal, S.; Ruminy, P.; Maingonnat, C.; et al. Non-invasive detection of somatic mutations using next-generation sequencing in primary central nervous system lymphoma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 48157–48168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebs, S.; Eder, T.; Klauschen, F.; Schütte, M.; Yaspo, M.-L.; Keilholz, U.; Tinhofer, I.; Kidess-Sigal, E.; Braunholz, D. Applicability of liquid biopsies to represent the mutational profile of tumor tissue from different cancer entities. Oncogene 2021, 40, 5204–5212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karczewski, K.J.; Snyder, M.P. Integrative omics for health and disease. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2018, 19, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamai, S.; Ichinose, T.; Nakada, M. Liquid biomarkers in glioma. Brain Tumor Pathol. 2023, 40, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustos, M.A.; Rahimzadeh, N.; Ryu, S.; Gross, R.; Tran, L.T.; Renteria-Lopez, V.M.; Ramos, R.I.; Eisenberg, A.; Hothi, P.; Kesari, S.; et al. Cell-free plasma microRNAs that identify patients with glioblastoma. Lab. Investig. 2022, 102, 711–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopkova, A.; Sana, J.; Machackova, T.; Vecera, M.; Radova, L.; Trachtova, K.; Vybihal, V.; Smrcka, M.; Kazda, T.; Slaby, O.; et al. Cerebrospinal Fluid MicroRNA Signatures as Diagnostic Biomarkers in Brain Tumors. Cancers 2019, 11, 1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derrien, T.; Johnson, R.; Bussotti, G.; Tanzer, A.; Djebali, S.; Tilgner, H.; Guernec, G.; Martin, D.; Merkel, A.; Knowles, D.G.; et al. The GENCODE v7 catalog of human long noncoding RNAs: Analysis of their gene structure, evolution, and expression. Genome Res. 2012, 22, 1775–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senhaji, N.; Squalli Houssaini, A.; Lamrabet, S.; Louati, S.; Bennis, S. Molecular and Circulating Biomarkers in Patients with Glioblastoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, F.; Cui, Y.; Jiang, H.; Sui, D.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Zhao, J.; Lin, S. Circulating tumor cell is a common property of brain glioma and promotes the monitoring system. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 71330–71340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ita, M.I.; Wang, J.H.; Toulouse, A.; Lim, C.; Fanning, N.; O’Sullivan, M.; Nolan, Y.; Kaar, G.F.; Redmond, H.P. The utility of plasma circulating cell-free messenger RNA as a biomarker of glioma: A pilot study. Acta Neurochir. 2022, 164, 723–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Quintero, B. Cell-free microRNAs in blood and other body fluids, as cancer biomarkers. Cell Prolif. 2016, 49, 281–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swellam, M.; Ezz El Arab, L.; Al-Posttany, A.S.; Said, S.B. Clinical impact of circulating oncogenic MiRNA-221 and MiRNA-222 in glioblastoma multiform. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2019, 144, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makowska, M.; Smolarz, B.; Romanowicz, H. microRNAs (miRNAs) in Glioblastoma Multiforme (GBM)—Recent Literature Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Li, P.; Li, A.; Jiang, W.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Xie, K. Plasma specific miRNAs as predictive biomarkers for diagnosis and prognosis of glioma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 31, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rynkeviciene, R.; Simiene, J.; Strainiene, E.; Stankevicius, V.; Usinskiene, J.; Miseikyte Kaubriene, E.; Meskinyte, I.; Cicenas, J.; Suziedelis, K. Non-Coding RNAs in Glioma. Cancers. 2018, 11, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zan, X.-Y.; Li, L. Construction of lncRNA-mediated ceRNA network to reveal clinically relevant lncRNA biomarkers in glioblastomas. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 17, 4369–4374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Hodges, T.R.; Song, R.; Gong, Y.; Calin, G.A.; Heimberger, A.B.; Zhao, H. Serum HOTAIR and GAS5 levels as predictors of survival in patients with glioblastoma. Mol. Carcinog. 2018, 57, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahir, B.K.; Ozer, H.; Engelhard, H.H.; Lakka, S.S. MicroRNAs in glioblastoma pathogenesis and therapy: A comprehensive review. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2017, 120, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.-X.; Han, L.; Bao, Z.-S.; Wang, Y.-Y.; Chen, L.-Y.; Yan, W.; Yu, S.-Z.; Pu, P.-Y.; Liu, N.; You, Y.-P.; et al. HOTAIR, a cell cycle–associated long noncoding RNA and a strong predictor of survival, is preferentially expressed in classical and mesenchymal glioma. Neuro-Oncology 2013, 15, 1595–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, S.K.; Pastori, C.; Penas, C.; Komotar, R.J.; Ivan, M.E.; Wahlestedt, C.; Ayad, N.G. Serum long noncoding RNA HOTAIR as a novel diagnostic and prognostic biomarker in glioblastoma multiforme. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokorná, M.; Černá, M.; Boussios, S.; Ovsepian, S.V.; O’Leary, V.B. lncRNA Biomarkers of Glioblastoma Multiforme. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordonnier, M.; Chanteloup, G.; Isambert, N.; Seigneuric, R.; Fumoleau, P.; Garrido, C.; Gobbo, J. Exosomes in cancer theranostic: Diamonds in the rough. Cell Adh. Migr. 2017, 11, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cilibrasi, C.; Simon, T.; Vintu, M.; Tolias, C.; Samuels, M.; Mazarakis, N.K.; Eravci, M.; Stewart, N.; Critchley, G.; Giamas, G. Definition of an Inflammatory Biomarker Signature in Plasma-Derived Extracellular Vesicles of Glioblastoma Patients. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahand, J.S.; Vandchali, N.R.; Darabi, H.; Doroudian, M.; Banafshe, H.R.; Moghoofei, M.; Babaei, F.; Salmaninejad, A.; Mirzaei, H. Exosomal MicroRNAs: Novel Players in Cervical Cancer. Epigenomics 2020, 12, 1651–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azhdari, M.H.; Goodarzi, N.; Doroudian, M.; MacLoughlin, R. Molecular Insight into the Therapeutic Effects of Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes in Respiratory Diseases and the Potential for Pulmonary Delivery. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudi, K.; Ezrin, A.; Hadjipanayis, C. Small extracellular vesicles as tumor biomarkers for glioblastoma. Mol. Asp. Med. 2015, 45, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, A.; Kumari Singh, D.; Panda, S.; Shiras, A. Extracellular Vesicles as Modulators of Tumor Microenvironment and Disease Progression in Glioma. Front. Oncol. 2017, 7, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tkach, M.; Théry, C. Communication by Extracellular Vesicles: Where We Are and Where We Need to Go. Cell 2016, 164, 1226–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yáñez-Mó, M.; Siljander, P.R.-M.; Andreu, Z.; Bedina Zavec, A.; Borràs, F.E.; Buzas, E.I.; Buzas, K.; Casal, E.; Cappello, F.; Carvalho, J. Biological properties of extracellular vesicles and their physiological functions. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2015, 4, 27066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanjani, N.A.; Esmaelizad, N.; Zanganeh, S.; Gharavi, A.T.; Heidarizadeh, P.; Radfar, M.; Omidi, F.; MacLoughlin, R.; Doroudian, M. Emerging role of exosomes as biomarkers in cancer treatment and diagnosis. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2022, 169, 103565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharavi, A.T.; Hanjani, N.A.; Movahed, E.; Doroudian, M. The role of macrophage subtypes and exosomes in immunomodulation. Cell Mol. Biol. Lett. 2022, 27, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Bene, M.; Osti, D.; Faletti, S.; Beznoussenko, G.V.; DiMeco, F.; Pelicci, G. Extracellular vesicles: The key for precision medicine in glioblastoma. Neuro-Oncology 2022, 24, 184–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doroudian, M.; Zanganeh, S.; Abbasgholinejad, E.; Donnelly, S.C. Nanomedicine in Lung Cancer Immunotherapy. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1144653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tataranu, L.G.; Turliuc, S.; Kamel, A.; Rizea, R.E.; Dricu, A.; Staicu, G.-A.; Baloi, S.C.; Rodriguez, S.M.B.; Manole, A.I.M. Glioblastoma Tumor Microenvironment: An Important Modulator for Tumoral Progression and Therapy Resistance. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2024, 46, 9881–9894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soung, Y.; Ford, S.; Zhang, V.; Chung, J. Exosomes in Cancer Diagnostics. Cancers. 2017, 9, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitehead, C.A.; Kaye, A.H.; Drummond, K.J.; Widodo, S.S.; Mantamadiotis, T.; Vella, L.J.; Stylli, S.S. Extracellular vesicles and their role in glioblastoma. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2020, 57, 227–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, C.J.; Lustig, R.A.; Yang, X.-Y.; Jenkins, W.T.; Wolf, R.L.; Martinez-Lage, M.; Desai, A.; Williams, D.; Evans, S.M. Microvesicles as a Biomarker for Tumor Progression versus Treatment Effect in Radiation/Temozolomide-Treated Glioblastoma Patients. Transl. Oncol. 2014, 7, 752–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, S.M.; Putt, M.; Yang, X.-Y.; Lustig, R.A.; Martinez-Lage, M.; Williams, D.; Desai, A.; Wolf, R.; Brem, S.; Koch, C.J. Initial evidence that blood-borne microvesicles are biomarkers for recurrence and survival in newly diagnosed glioblastoma patients. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2016, 127, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osti, D.; Del Bene, M.; Rappa, G.; Santos, M.; Matafora, V.; Richichi, C.; Faletti, S.; Beznoussenko, G.V.; Mironov, A.; Bachi, A. Clinical Significance of Extracellular Vesicles in Plasma from Glioblastoma Patients. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 266–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galindo-Hernandez, O.; Villegas-Comonfort, S.; Candanedo, F.; González-Vázquez, M.-C.; Chavez-Ocaña, S.; Jimenez-Villanueva, X.; Sierra-Martinez, M.; Salazar, E.P. Elevated Concentration of Microvesicles Isolated from Peripheral Blood in Breast Cancer Patients. Arch. Med. Res. 2013, 44, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Döring, K.; Malinova, V.; Bettag, C.; Rohde, V.; Schulz, M.; Menck, K.; Bleckmann, A.; Binder, C.; Büntzel, J. The Diagnostic Potential of Extracellular Vesicles Derived from the Blood Plasma of Glioblastoma Patients. In Vivo 2024, 38, 2735–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosas-Alonso, R.; Colmenarejo-Fernández, J.; Pernía, O.; Burdiel, M.; Rodríguez-Antolín, C.; Losantos-García, I.; Rubio, T.; Moreno-Velasco, R.; Esteban-Rodríguez, I.; Martínez-Marín, V.; et al. Evaluation of the clinical use of MGMT methylation in extracellular vesicle-based liquid biopsy as a tool for glioblastoma patient management. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 11398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, B.-T.; Johnstone, R.M. Fate of the transferrin receptor during maturation of sheep reticulocytes in vitro: Selective externalization of the receptor. Cell 1983, 33, 967–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Meng, J.; Zhu, L.; Peng, Y. Exosomal noncoding RNAs in Glioma: Biological functions and potential clinical applications. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heydari, R.; Koohi, F.; Rasouli, M.; Rezaei, K.; Abbasgholinejad, E.; Bekeschus, S.; Doroudian, M. Exosomes as Rheumatoid Arthritis Diagnostic Biomarkers and Therapeutic Agents. Vaccines 2023, 11, 687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Su, Y.; Zhong, S.; Cong, L.; Liu, B.; Yang, J.; Tao, Y.; He, Z.; Chen, C.; Jiang, Y. Exosomes: Key players in cancer and potential therapeutic strategy. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Zhang, H.; Mao, J.; Cao, H.; Tao, Y.; Zhao, G.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, N.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, J.; et al. Exosome-based nanoimmunotherapy targeting TAMs, a promising strategy for glioma. Cell Death Dis. 2023, 14, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Shan, S.; Xia, B.; Zhang, L.; Liang, X. Brain-Targeted Exosomes-Based Drug Delivery System to Overcome the Treatment Bottleneck of Brainstem Glioma. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2302378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaidya, M.; Sugaya, K. DNA Associated with Circulating Exosomes as a Biomarker for Glioma. Genes 2020, 11, 1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Pillai, P.P. Current insights on extracellular vesicle-mediated glioblastoma progression: Implications in drug resistance and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Gen. Subj. 2022, 1866, 130065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cumba Garcia, L.M.; Bouchal, S.M.; Bauman, M.M.J.; Parney, I.F. Advancements and Technical Considerations for Extracellular Vesicle Isolation and Biomarker Identification in Glioblastoma. Neurosurgery 2023, 93, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatami, S.H.; Karami, N.; Taheri-Anganeh, M.; Taghvimi, S.; Tondro, G.; Khorsand, M.; Soltani Fard, E.; Sedighimehr, N.; Kazemi, M.; Rahimi Jaberi, K.; et al. Exosomes: Promising Delivery Tools for Overcoming Blood-Brain Barrier and Glioblastoma Therapy. Mol. Neurobiol. 2023, 60, 4659–4678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Wei, B.; Peng, C.; Wang, L.; Li, C. Identification of serum exosomal miR-98–5p, miR-183–5p, miR-323–3p and miR-19b-3p as potential biomarkers for glioblastoma patients and investigation of their mechanisms. Curr. Res. Transl. Med. 2022, 70, 103315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Wang, F.; Wang, K.; Zhong, Y.; Wei, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, H. Engineered Exosomes: A Promising Drug Delivery Strategy for Brain Diseases. Curr. Med. Chem. 2022, 29, 3111–3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, D.; Ye, Z.; Xu, J. Engineering Extracellular Vesicles as Delivery Systems in Therapeutic Applications. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, 2300552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kar, R.; Dhar, R.; Mukherjee, S.; Nag, S.; Gorai, S.; Mukerjee, N.; Mukherjee, D.; Vatsa, R.; Chandrakanth Jadhav, M.; Ghosh, A.; et al. Exosome-Based Smart Drug Delivery Tool for Cancer Theranostics. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2023, 9, 577–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, X.; Xiao, Y.-T.; Wu, T.; Yao, M.; Du, L.; Ren, S.; Wang, J. Microvesicles and chemokines in tumor microenvironment: Mediators of intercellular communications in tumor progression. Mol. Cancer. 2019, 18, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rackles, E.; Lopez, P.H.; Falcon-Perez, J.M. Extracellular vesicles as source for the identification of minimally invasive molecular signatures in glioblastoma. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2022, 87, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menck, K.; Sivaloganathan, S.; Bleckmann, A.; Binder, C. Microvesicles in Cancer: Small Size, Large Potential. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simionescu, N.; Nemecz, M.; Petrovici, A.-R.; Nechifor, I.S.; Buga, R.-C.; Dabija, M.G.; Eva, L.; Georgescu, A. Microvesicles and Microvesicle-Associated microRNAs Reflect Glioblastoma Regression: Microvesicle-Associated miR-625-5p Has Biomarker Potential. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baillie, J.K.; Barnett, M.W.; Upton, K.R.; Gerhardt, D.J.; Richmond, T.A.; De Sapio, F.; Brennan, P.M.; Rizzu, P.; Smith, S.; Fell, M.; et al. Somatic retrotransposition alters the genetic landscape of the human brain. Nature. 2011, 479, 534–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Zhou, M.; Xu, Y.; Gu, X.; Zou, M.; Abudushalamu, G.; Yao, Y.; Fan, X.; Wu, G. Clinical application and detection techniques of liquid biopsy in gastric cancer. Mol. Cancer 2023, 22, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Tao, L.; Qiu, J.; Xu, J.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, X.; Guan, X.; Cen, X.; Zhao, Y. Tumor biomarkers for diagnosis, prognosis and targeted therapy. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanganeh, S.; Abbasgholinejad, E.; Doroudian, M.; Esmaelizad, N.; Farjadian, F.; Benhabbour, S.R. The Current Landscape of Glioblastoma Biomarkers in Body Fluids. Cancers 2023, 15, 3804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yuan, F.; Qi, Y.; Liu, B.; Chen, Q. Circulating Tumor Cells for Glioma. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 607150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Schaijik, B.; Wickremesekera, A.C.; Mantamadiotis, T.; Kaye, A.H.; Tan, S.T.; Stylli, S.S.; Itinteang, T. Circulating tumor stem cells and glioblastoma: A review. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2019, 61, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Xu, H.; Huang, M.; Ma, W.; Saxena, D.; Lustig, R.A.; Alonso-Basanta, M.; Zhang, Z.; O’Rourke, D.M.; Zhang, L.; et al. Circulating Glioma Cells Exhibit Stem Cell-like Properties. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 6632–6642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynch, D.; Powter, B.; Po, J.W.; Cooper, A.; Garrett, C.; Koh, E.-S.; Sheridan, M.; van Gelder, J.; Darwish, B.; Mckechnie, S.; et al. Isolation of Circulating Tumor Cells from Glioblastoma Patients by Direct Immunomagnetic Targeting. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacArthur, K.M.; Kao, G.D.; Chandrasekaran, S.; Alonso-Basanta, M.; Chapman, C.; Lustig, R.A.; Wileyto, E.P.; Hahn, S.M.; Dorsey, J.F. Detection of Brain Tumor Cells in the Peripheral Blood by a Telomerase Promoter-Based Assay. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 2152–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, C.; Holtschmidt, J.; Auer, M.; Heitzer, E.; Lamszus, K.; Schulte, A.; Matschke, J.; Langer-Freitag, S.; Gasch, C.; Stoupiec, M.; et al. Hematogenous dissemination of glioblastoma multiforme. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, 247ra101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, J.P.; Nahed, B.V.; Madden, M.W.; Oliveira, S.M.; Springer, S.; Bhere, D.; Chi, A.S.; Wakimoto, H.; Rothenberg, S.M.; Sequist, L.V.; et al. Brain Tumor Cells in Circulation Are Enriched for Mesenchymal Gene Expression. Cancer Discov. 2014, 4, 1299–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirkel, G.A.; Gadellaa-van Hooijdonk, C.G.; Koudijs, M.J.; Willems, S.M.; Voest, E.E. Tumor Heterogeneity and Personalized Cancer Medicine: Are we Being Outnumbered? Future Oncol. 2014, 10, 417–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, X.; Castanares, M.; Mukherjee, A.; Lupold, S.E. Nucleic Acid Aptamers: Clinical Applications and Promising New Horizons. Curr. Med. Chem. 2011, 18, 4206–4214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kichkailo, A.S.; Narodov, A.A.; Komarova, M.A.; Zamay, T.N.; Zamay, G.S.; Kolovskaya, O.S.; Erakhtin, E.E.; Glazyrin, Y.E.; Veprintsev, D.V.; Moryachkov, R.V.; et al. Development of DNA aptamers for visualization of glial brain tumors and detection of circulating tumor cells. Mol. Ther. Nucleic. Acids 2023, 32, 267–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, S.M.B.; Kamel, A.; Ciubotaru, G.V.; Onose, G.; Sevastre, A.-S.; Sfredel, V.; Danoiu, S.; Dricu, A.; Tataranu, L.G. An Overview of EGFR Mechanisms and Their Implications in Targeted Therapies for Glioblastoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joosse, S.A.; Pantel, K. Tumor-Educated Platelets as Liquid Biopsy in Cancer Patients. Cancer Cell 2015, 28, 552–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatto, L.; Franceschi, E.; Di Nunno, V.; Tosoni, A.; Lodi, R.; Brandes, A.A. Liquid Biopsy in Glioblastoma Management: From Current Research to Future Perspectives. Oncologist 2021, 26, 865–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stratz, C.; Nührenberg, T.G.; Binder, H.; Valina, C.M.; Trenk, D.; Hochholzer, W.; Neumann, F.; Fiebich, B.L. Micro-array profiling exhibits remarkable intra-individual stability of human platelet, m.i.c.r.o.-R.N.A. Thromb. Haemost. 2012, 107, 634–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilsson, R.J.A.; Balaj, L.; Hulleman, E.; van Rijn, S.; Pegtel, D.M.; Walraven, M.; Widmark, A.; Gerritsen, W.R.; Verheul, H.M.; Vandertop, W.P.; et al. Blood platelets contain tumor-derived RNA biomarkers. Blood 2011, 118, 3680–3683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Best, M.G.; Wesseling, P.; Wurdinger, T. Tumor-Educated Platelets as a Noninvasive Biomarker Source for Cancer Detection and Progression Monitoring. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 3407–3412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sol, N.; in ‘t Veld, S.G.J.G.; Vancura, A.; Tjerkstra, M.; Leurs, C.; Rustenburg, F.; Schellen, P.; Verschueren, H.; Post, E.; Zwaan, K.; et al. Tumor-Educated Platelet RNA for the Detection and (Pseudo)progression Monitoring of Glioblastoma. Cell Rep. Med. 2020, 1, 100101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Yang, L.; Zhang, X.; Chen, R.; Chen, X.; Tang, W.; Zhang, M. Identification of Potential Biomarkers in Glioblastoma through Bioinformatic Analysis and Evaluating Their Prognostic Value. BioMed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 6581576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyhan, A.A. Circulating Liquid Biopsy Biomarkers in Glioblastoma: Advances and Challenges. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tataranu, L.G. Liquid Biopsy as a Diagnostic and Monitoring Tool in Glioblastoma. Medicina 2025, 61, 716. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61040716
Tataranu LG. Liquid Biopsy as a Diagnostic and Monitoring Tool in Glioblastoma. Medicina. 2025; 61(4):716. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61040716
Chicago/Turabian StyleTataranu, Ligia Gabriela. 2025. "Liquid Biopsy as a Diagnostic and Monitoring Tool in Glioblastoma" Medicina 61, no. 4: 716. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61040716
APA StyleTataranu, L. G. (2025). Liquid Biopsy as a Diagnostic and Monitoring Tool in Glioblastoma. Medicina, 61(4), 716. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61040716





