Relationship Between Dyspnoea Scales and Quality of Life in Stroke Survivors: A Retrospective Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
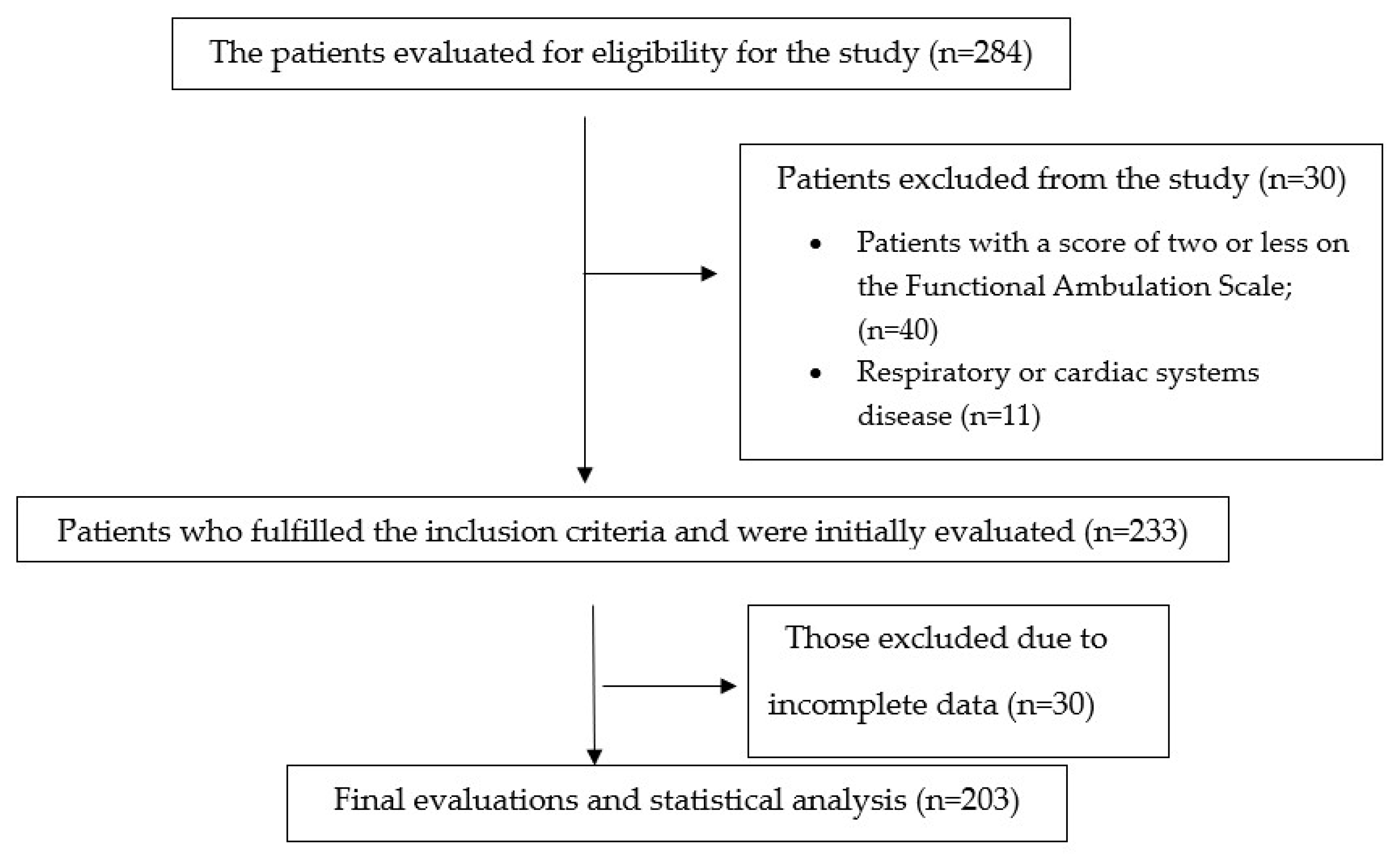
2.2. Participants
2.3. Outcome Measures
2.3.1. Demographic Characteristics
2.3.2. Rating of Dyspnoea
2.3.3. Strength of Respiratory Muscle
2.3.4. Quality of Life
2.4. Data Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Relationship Between Age and Respiratory Muscle Strength with Dyspnoea Scales
3.2. The Correlation Between Dyspnoea Scales and Quality of Life
3.3. The Correlations Among Four Dyspnoea Scales
3.4. Multiple Regression Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADL | Daily living activities |
| BDI | Baseline Dyspnoea Index |
| mMRC | Medical Research Council Dyspnoea scale |
| OCD | Oxygen Cost Diagram |
| SIS | Stroke Impact Scale |
| VAS | Visual Analogue Scale |
References
- Tsao, C.W.; Aday, A.W.; Almarzooq, Z.I.; Anderson, C.A.; Arora, P.; Avery, C.L.; Baker-Smith, C.M.; Beaton, A.Z.; Boehme, A.K.; Buxton, A.E. Heart disease and stroke statistics—2023 update: A report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2023, 147, e93–e621. [Google Scholar]
- Teixeira-Salmela, L.F.; Parreira, V.F.; Britto, R.R.; Brant, T.C.; Inácio, É.P.; Alcântara, T.O.; Carvalho, I.F. Respiratory pressures and thoracoabdominal motion in community-dwelling chronic stroke survivors. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2005, 86, 1974–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yildiz, A.; Mustafaoglu, R.; Bardak, A.N. Respiratory muscle strength in stroke: A case-control study. Rev. Assoc. Med. Bras. 2024, 70, e20240061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Almeida, I.C.L.; Clementino, A.C.C.R.; Rocha, E.H.T.; Brandão, D.C.; de Andrade, A.D. Effects of hemiplegy on pulmonary function and diaphragmatic dome displacement. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2011, 178, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drakopanagiotakis, F.; Bonelis, K.; Steiropoulos, P.; Tsiptsios, D.; Sousanidou, A.; Christidi, F.; Gkantzios, A.; Serdari, A.; Voutidou, S.; Takou, C.-M.; et al. Pulmonary Function Tests Post-Stroke. Correlation between Lung Function, Severity of Stroke, and Improvement after Respiratory Muscle Training. Neurol. Int. 2024, 16, 139–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezes, K.K.P.; Nascimento, L.R.; Alvarenga, M.T.M.; Avelino, P.R.; Teixeira-Salmela, L.F. Prevalence of dyspnea after stroke: A telephone-based survey. Braz. J. Phys. Ther. 2019, 23, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.; Lei, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, X.; Dai, W.; Xu, W.; Zhang, J.; Yu, Q.; Su, X.; Huang, Y.; et al. Shortness of breath on the day of discharge: An early alert for post-discharge complications in patients undergoing lung cancer surgery. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2024, 19, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garus, M.; Jura, M.; Guzik, M.; Zymliński, R.; Iwanek, G.; Ponikowski, P.; Biegus, J. Prognostic significance and clinical determinants of residual dyspnoea at discharge in acute heart failure: A single-centre, prospective observational study. BMJ Open 2023, 13, e075302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coccia, C.B.; Palkowski, G.H.; Schweitzer, B.; Motsohi, T.; Ntusi, N.A. Dyspnoea: Pathophysiology and a clinical approach. S. Afr. Med. J. 2016, 106, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Wang, S.; Jiang, S. The occurrence mechanism, assessment, and non-pharmacological treatment of dyspnea. Med. Rev. 2024, 4, 392–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meriggi, F. Dyspnea in Cancer Patients: A Well-Known and Neglected Symptom. Rev. Recent. Clin. Trials 2018, 13, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmutzhard, E. Central breathing disturbances. J. Neurol. Sci. 2019, 405, 9–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, G. Early and late complications of stroke. Stroke Older Pers. 2020, 231, 231–248. [Google Scholar]
- O’Donnell, D.E. Breathlessness in patients with chronic airflow limitation: Mechanisms and management. Chest 1994, 106, 904–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahler, D.A.; Weinberg, D.H.; Wells, C.K.; Feinstein, A.R. The measurement of dyspnea. Contents, interobserver agreement, and physiologic correlates of two new clinical indexes. Chest 1984, 85, 751–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bestall, J.C.; Paul, E.A.; Garrod, R.; Garnham, R.; Jones, P.W.; Wedzicha, J.A. Usefulness of the Medical Research Council (MRC) dyspnoea scale as a measure of disability in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Thorax 1999, 54, 581–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eakin, E.G.; Kaplan, R.M.; Ries, A.L. Measurement of dyspnoea in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Qual. Life Res. 1993, 2, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kara, D.; Yıldız, H. Effectiveness and frequencies of dyspnea scales in evaluating symptom of dyspnea. Gümüşhane Univ. J. Health Sci. 2013, 2, 137–149. [Google Scholar]
- Witek, T.J.; Mahler, D.A. Minimal important difference of the transition dyspnoea index in a multinational clinical trial. Eur. Respir. J. 2003, 21, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssens, J.P.; Breitenstein, E.; Rochat, T.; Fitting, J.W. Does the ‘oxygen cost diagram’ reflect changes in six minute walking distance in follow up studies? Respir. Med. 1999, 93, 810–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, C.M.; Elmes, P.C.; Fairbairn, A.S.; Wood, C.H. The significance of respiratory symptoms and the diagnosis of chronic bronchitis in a working population. Br. Med. J. 1959, 2, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, M.R.; Hankinson, J.; Brusasco, V.; Burgos, F.; Casaburi, R.; Coates, A.; Crapo, R.; Enright, P.; Van Der Grinten, C.; Gustafsson, P. Standardisation of spirometry. Eur. Respir. J. 2005, 26, 319–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, P.W.; Bode, R.K.; Lai, S.M.; Perera, S.; Glycine Antagonist in Neuroprotection Americans Investigators. Rasch analysis of a new stroke-specific outcome scale: The Stroke Impact Scale. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2003, 84, 950–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pallant, J. SPSS Survival Manual: A Step by Step Guide to Data Analysis Using IBM SPSS; Routledge: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- McConnell, A. Respiratory Muscle Training: Theory and Practice; Elsevier Health Sciences: Centro Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Parreiras de Menezes, K.K.; Nascimento, L.R.; Ada, L.; Avelino, P.R.; Polese, J.C.; Mota Alvarenga, M.T.; Barbosa, M.H.; Teixeira-Salmela, L.F. High-Intensity Respiratory Muscle Training Improves Strength and Dyspnea Poststroke: A Double-Blind Randomized Trial. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2019, 100, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, G.; Ding, S.; Yu, L.; Wang, Y.; Qiao, L.; Wu, Q.; Ni, W.; Fan, H.; Zheng, Q.; et al. Liuzijue qigong versus traditional breathing training for patients with post-stroke dysarthria complicated by abnormal respiratory control: Results of a single-center randomized controlled trial. Clin. Rehabil. 2021, 35, 999–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanania, N.A.; O’Donnell, D.E. Activity-related dyspnea in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: Physical and psychological consequences, unmet needs, and future directions. Int. J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2019, 14, 1127–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schinwelski, M.; Sitek, E.; Wąż, P.; Sławek, J. Prevalence and predictors of post-stroke spasticity and its impact on daily living and quality of life. Neurol. Neurochir. Pol. 2019, 53, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.E.; Cho, K.H. Factor Analysis Related to the Change in Activities of Daily Living Performance of Stroke Patients. BioMed Res. Int. 2023, 2023, 6147413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kose, E.; Matsumoto, A.; Yoshimura, Y. Deprescribing psychotropic medications is associated with improvements in activities of daily living in post-stroke patients. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2024, 24, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telebuh, M.; Bertić, Ž.; Grozdek Čovčić, G.; Grubišić, M.; Begic, M. Quality of life in elderly stroke patients Kvaliteta života starijih osoba nakon moždanog udara. In Proceedings of the Quality of Life in Elderly Stroke Patients, Pula, Croatia, 24 July 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Chinchai, P.; Sirisatayawong, P.; Jindakum, N. Community Integration and Quality of Life: Stroke Survivors as Recipients of Rehabilitation by Village Health Volunteers (VHVs) in Thailand. Occup. Ther. Health Care 2020, 34, 277–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrianur, F.; Era, D.P.; Hidayat, A.; Ismansyah, I.; Setiani, D. The effect of five activities daily living on improving cognitive function in ischemic stroke patients. Healthc. Low-Resour. Settings 2023, 11, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozuelo-Carrascosa, D.P.; Carmona-Torres, J.M.; Laredo-Aguilera, J.A.; Latorre-Román, P.Á.; Párraga-Montilla, J.A.; Cobo-Cuenca, A.I. Effectiveness of respiratory muscle training for pulmonary function and walking ability in patients with stroke: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menezes, K.K.P.; Nascimento, L.R.; Avelino, P.R.; Alvarenga, M.T.M.; Teixeira-Salmela, L.F. Efficacy of Interventions to Improve Respiratory Function After Stroke. Respir. Care 2018, 63, 920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldman, M.; Lucke-Wold, B.; Katz, J.; Dawoud, B.; Dagra, A. Respiratory Patterns in Neurological Injury, Pathophysiology, Ventilation Management, and Future Innovations: A Systematic Review. Explor. Res. Hypothesis Med. 2023, 8, 338–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, R.S.; Rudd, A.G.; Wolfe, C.D.; Williams, A.J. Pathophysiological and clinical aspects of breathing after stroke. Postgrad. Med. J. 2001, 77, 700–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.S.; Zhang, K.; Huang, L.; Wei, J.X.; Bi, Z.T.; Xiao, J.H.; Huang, J.; Luo, C.S.; Li, Y.D.; Zhang, J.M. The effects of respiratory muscle training on respiratory function and functional capacity in patients with early stroke: A meta-analysis. Eur. Rev. Aging Phys. Act. 2024, 21, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Guo, H.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, X. The effect of moderate and vigorous aerobic exercise training on the cognitive and walking ability among stroke patients during different periods: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0298339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahler, D.A.; Faryniarz, K.; Tornlinson, D.; Colice, G.L.; Robins, A.G.; Olmstead, E.M.; O’connor, G.T. Impactof Dyspnea and Physiologic Functionon Genera lHealth Status in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Chest 1992, 102, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhabra, S.K.; Gupta, A.K.; Khuma, M.Z. Evaluation of three scales of dyspnea in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Ann. Thorac. Med. 2009, 4, 128–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahler, D.A.; Rosiello, R.A.; Harver, A.; Lentine, T.; McGovern, J.F.; Daubenspeck, J.A. Comparison of Clinical Dyspnea Ratings and Psychophysical Measurements of Respiratory Sensation in Obstructive Airway Disease. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1987, 135, 1229–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Total (n = 203) Mean ± SD or N | Ischemic (n = 154) Mean ± SD or N | Haemorrhagic (n = 49) Mean ± SD or N | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Demographic characteristics | Sex-Female/Male | 119/84 | 93/61 | 26/23 | 0.867 a |
| Age (year) | 56.51 ± 11.78 | 56.8 ± 11.9 | 55.7 ± 11.5 | 0.945 b | |
| Height (cm) | 166.81 ± 8.19 | 167.0 ± 8.1 | 166.3 ± 8.3 | 0.876 b | |
| Weight (kg) | 76.05 ± 13.21 | 74.2 ± 13.3 | 77.8 ± 12.9 | 0.945 b | |
| BMI (kg/cm2) | 27.27 ± 4.48 | 27.3 ± 4.5 | 26.2 ± 4.4 | 0.982 b | |
| Time since stroke (day) | 388.39 ± 731.96 | 390.2 ± 720.1 | 384.5 ± 750.3 | 0.734 b | |
| Respiratory muscle strength | MIP, cmH2O | 45.83 ± 23.43 | 44.0 ± 23.5 | 47.2 ± 23.2 | 0.888 b |
| Quality of life | SIS-Strength | 59.96 ± 25.66 | 58.1 ± 25.7 | 62.4 ± 25.5 | 0.897 b |
| SIS-Memory and thinking | 81.74 ± 22.07 | 77.0 ± 22.1 | 85.8 ± 22.0 | 0.739 b | |
| SIS-Emotions | 63.55 ± 13.71 | 60.7 ± 13.8 | 66.2 ± 13.6 | 0.976 b | |
| SIS-Communication | 85.25 ± 23.21 | 82.4 ± 23.3 | 88.9 ± 23.0 | 0.981 b | |
| SIS-ADL | 53.72 ± 21.11 | 54.0 ± 21.2 | 53.1 ± 21.0 | 0.911 b | |
| SIS-Mobility | 62.43 ± 27.76 | 64.6 ± 27.8 | 58.9 ± 27.5 | 0.671 b | |
| SIS-Hand function | 38.21 ± 21.78 | 40.4 ± 21.8 | 36.7 ± 21.6 | 0.564 b | |
| SIS-Participation/role function | 49.94 ± 25.13 | 49.2 ± 25.2 | 52.3 ± 25.0 | 0.760 b | |
| SIS-Stroke Recovery | 45.99 ± 20.44 | 43.1 ± 20.5 | 48.6 ± 20.3 | 0.456 b | |
| SIS-Total | 60.09 ± 14.48 | 57.3 ± 14.5 | 62.7 ± 14.4 | 0.345 b | |
| Rating of dyspnoea | OCD | 4.35 ± 2.85 | 4.6 ± 2.8 | 4.0 ± 2.9 | 0.855 b |
| mMRC | 0.58 ± 0.97 | 0.5 ± 1.0 | 0.7 ± 0.9 | 0.733 b | |
| VAS | 0.99 ± 1.71 | 1.0 ± 1.7 | 0.9 ± 1.7 | 0.921 b | |
| BDI | 9.50 ± 2.96 | 8.6 ± 3.0 | 10.3 ± 2.9 | 0.645 b |
| OCD | mMRC | VAS | BDI | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r | p | r | p | r | p | r | p | |
| Age | −0.153 | 0.056 | 0.170 | 0.032 * | 0.191 | 0.016 * | −0.269 | <0.001 * |
| MIP, cmH2O | 0.291 | <0.001 * | −0.090 | 0.259 | −0.157 | 0.552 | 0.195 | 0.014 * |
| SIS-Strength | 0.195 | 0.028 * | −0.073 | 0.415 | −0.110 | 0.218 | 0.279 | 0.002 * |
| SIS-Memory/thinking | 0.155 | 0.083 * | −0.209 | 0.019 * | −0.198 | 0.026 * | 0.195 | 0.029 * |
| SIS-Emotions | 0.018 | 0.846 | −0.089 | 0.320 | −0.140 | 0.118 | 0.074 | 0.408 |
| SIS-Communication | 0.105 | 0.242 | −0.092 | 0.303 | −0.067 | 0.457 | 0.222 | 0.013 * |
| SIS-ADL | 0.397 | <0.001 * | −0.100 | 0.266 | −0.123 | 0.169 | 0.205 | 0.021 * |
| SIS-Mobility | 0.319 | <0.001 * | −0.082 | 0.363 | −0.107 | 0.233 | 0.101 | 0.261 |
| SIS-Hand function | 0.267 | 0.003 * | −0.157 | 0.079 | −0.178 | 0.046 * | 0.203 | 0.023 * |
| SIS-Participation/role function | 0.132 | 0.140 | −0.072 | 0.422 | −0.101 | 0.259 | 0.108 | 0.229 |
| SIS-Stroke Recovery | 0.300 | <0.001 * | −0.101 | 0.259 | −0.101 | 0.260 | 0.109 | 0.224 |
| SIS-Total | 0.248 | <0.001 * | −0.184 | 0.039 * | −0.209 | 0.019 * | 0.287 | <0.001 * |
| OCD | mMRC | VAS | BDI | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r | p | r | p | r | p | r | p | |
| OCD | - | - | −0.060 | 0.459 | −0.021 | 0.791 | 0.238 | 0.003 * |
| mMRC | −0.060 | 0.459 | - | - | 0.821 | <0.001 * | 0.290 | <0.001 * |
| VAS | −0.021 | 0.791 | 0.821 | <0.001 * | - | - | 0.300 | <0.001 * |
| BDI | 0.238 | 0.003 * | 0.290 | <0.001 * | 0.300 | <0.001 * | - | - |
| Predictor Variable | R2 | Corrected R2 | ∆R2 | ∆F | ∆P | Standardized β | t | p | Correlations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zero-Order | Partial | Part | |||||||||
| SIS total | 0.449 | 0.175 | 0.202 | 7.650 | 0.001 | ||||||
| OCD | 1.846 | 3.966 | 0.001 | 0.348 | 0.339 | 0.322 | |||||
| mMRC | 1.634 | 0.700 | 0.485 | −0.184 | 0.063 | 0.057 | |||||
| VAS | −2.040 | −1.532 | 0.128 | −0.209 | −0.138 | −0.124 | |||||
| BDI | 0.805 | 2.118 | 0.036 | 0.287 | 0.189 | 0.172 | |||||
| Age | 0.309 | 0.072 | 0.095 | 4.038 | 0.004 | ||||||
| OCD | −0.401 | −1.267 | 0.207 | −0.153 | −0.102 | −0.097 | |||||
| mMRC | −0.005 | −0.003 | 0.998 | 0.170 | 0.000 | 0.000 | |||||
| VAS | 0.845 | 0.937 | 0.350 | 0.191 | 0.076 | 0.072 | |||||
| BDI | −0.795 | −20.489 | 0.014 | −0.269 | −0.197 | −0.191 | |||||
| Duration of stroke | 0.140 | −0.013 | 0.020 | 0.600 | 0.664 | ||||||
| OCD | −29.784 | −0.911 | 0.364 | −0.075 | −0.083 | −0.082 | |||||
| mMRC | −141.143 | −0.868 | 0.387 | 0.042 | −0.079 | −0.078 | |||||
| VAS | 112.070 | 1.208 | 0.229 | 0.084 | 0.110 | 0.109 | |||||
| BDI | −3.208 | −0.121 | 0.904 | −0.041 | −0.011 | −0.011 | |||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yildiz, A.; Mustafaoglu, R.; Bardak, A.N. Relationship Between Dyspnoea Scales and Quality of Life in Stroke Survivors: A Retrospective Analysis. Medicina 2025, 61, 540. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61030540
Yildiz A, Mustafaoglu R, Bardak AN. Relationship Between Dyspnoea Scales and Quality of Life in Stroke Survivors: A Retrospective Analysis. Medicina. 2025; 61(3):540. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61030540
Chicago/Turabian StyleYildiz, Abdurrahim, Rustem Mustafaoglu, and Ayse Nur Bardak. 2025. "Relationship Between Dyspnoea Scales and Quality of Life in Stroke Survivors: A Retrospective Analysis" Medicina 61, no. 3: 540. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61030540
APA StyleYildiz, A., Mustafaoglu, R., & Bardak, A. N. (2025). Relationship Between Dyspnoea Scales and Quality of Life in Stroke Survivors: A Retrospective Analysis. Medicina, 61(3), 540. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61030540







