Association of Inflammatory and Metabolic Markers with Mortality in Patients with Postoperative Femur Fractures in the Intensive Care Unit
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Study Population
2.2. Laboratory Parameters
- Pan-Immune-Inflammation Value (PIV): [(Neutrophil × Platelet)/Lymphocyte].
- CRP-to-albumin ratio (CAR): CRP/Albumin.
- CRP-to-lymphocyte ratio (CLR): CRP/Lymphocyte.
- Platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR): Platelet/Lymphocyte.
- Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR): Neutrophil/Lymphocyte.
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Limitations of the Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Halvachizadeh, S.; Martin, D.P.; Pfeifer, R.; Jukema, G.N.; Gueorguiev, B.; Pape, H.C.; Berk, T. Which non-infection related risk factors are associated with impaired proximal femur fracture healing in patients under the age of 70 years? BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2023, 24, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, N.; Hafner, T.; Pishnamaz, M.; Hildebrand, F.; Kobbe, P. Patient-specific risk factors for adverse outcomes following geriatric proximal femur fractures. Eur. J. Trauma Emerg. Surg. 2022, 48, 753–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbosa, T.A.; Souza, A.M.F.; Leme, F.C.O.; Grassi, L.D.V.; Cintra, F.B.; Lima, R.M.E.; Gumieiro, D.N.; Lima, L. Perioperative complications and mortality in elderly patients following surgery for femoral fracture: Prospective observational study. Braz. J. Anesthesiol. 2019, 69, 569–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merchan-Galvis, A.M.; Munoz-Garcia, D.A.; Solano, F.; Velasquez, J.C.; Sotelo, N.F.; Molina, D.A.; Caicedo, J.P.; Concha, J.M.; Calvache, J.A.; Martinez-Zapata, M.J. Delayed surgery and health related quality of life in patients with proximal femoral fracture. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 11131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cirik, M.Ö.; Yenibertiz, D. What are the prognostic factors affecting 30-day mortality in geriatric patients with respiratory failure in the Intensive Care Unit? Pak. J. Med. Sci. 2020, 37, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Song, C.; Zhang, J. Elevated serum albumin-to-creatinine ratio as a protective factor on clinical outcomes among critically ill patients with sepsis: A retrospective study. Front. Med. 2024, 11, 1436533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tie, X.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, T.; Zhou, R.; Li, J.; Su, J.; Yin, W. Associations between serum albumin level trajectories and clinical outcomes in sepsis patients in ICU: Insights from longitudinal group trajectory modeling. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1433544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skouras, A.Z.; Antonakis-Karamintzas, D.; Tsolakis, C.; Tsantes, A.E.; Kourlaba, G.; Zafeiris, I.; Soucacos, F.; Papagiannis, G.; Triantafyllou, A.; Houhoula, D.; et al. Pre- and Postoperative Exercise Effectiveness in Mobility, Hemostatic Balance, and Prognostic Biomarkers in Hip Fracture Patients: A Study Protocol for a Randomized Controlled Trial. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tschon, M.; Contartese, D.; Pagani, S.; Borsari, V.; Fini, M. Gender and Sex Are Key Determinants in Osteoarthritis Not Only Confounding Variables. A Systematic Review of Clinical Data. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, D.E.; Yoon, H.J.; Nam, S.B.; Song, S.W.; Lee, G.; Ham, S.Y. Preoperative Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio, Platelet to Lymphocyte Ratio, and Mean Platelet Volume as Predictors of 1-Year Mortality in Patients Undergoing an Open Repair of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms: A Retrospective Study. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 5410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsabani, M.H.; Alenezi, F.K.; Alotaibi, B.A.; Alotaibi, A.A.; Olayan, L.H.; Aljurais, S.F.; Alarfaj, N.; Alkhurbush, D.; Almuhaisen, G.; Alkhmies, L.; et al. Ratios of Neutrophils and Platelets to Lymphocytes as Predictors of Postoperative Intensive Care Unit Admission and Length of Stay in Bariatric Surgery Patients: A Retrospective Study. Medicina 2024, 60, 753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sefil, F.; Ulutas, K.T.; Dokuyucu, R.; Sumbul, A.T.; Yengil, E.; Yagiz, A.E.; Yula, E.; Ustun, I.; Gokce, C. Investigation of neutrophil lymphocyte ratio and blood glucose regulation in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Int. Med. Res. 2014, 42, 581–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Tu, C.; Liu, G.; Peng, W.; Zhang, J.; Ge, Y.; Tan, Z.; Bei, M.; Gao, F.; Tian, M.; et al. Association between admission inflammatory indicators and 3-year mortality risk in geriatric patients after hip fracture surgery: A retrospective cohort study. Front. Surg. 2024, 11, 1440990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niccolai, F.; Parchi, P.D.; Vigorito, A.; Pasqualetti, G.; Monzani, F.; Lisanti, M. The correlation between preoperative levels of albumin and tlc and mortality in patients with femoral neck fracture. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2016, 30, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yamada, Y.; Kotani, T.; Kishida, S.; Ogata, Y.; Okuwaki, S.; Ohyama, S.; Iwata, S.; Iijima, Y.; Ise, S.; Sakuma, T.; et al. Factors influencing the achievement of early surgery in proximal femoral fractures under a Japanese incentive policy. J. Orthop. Sci. 2024, 8, 2652–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilgin, M.; Akkaya, E.; Dokuyucu, R. Inflammatory and Metabolic Predictors of Mortality in Pulmonary Thromboembolism: A Focus on the Triglyceride–Glucose Index and Pan-Immune Inflammation Value. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 6008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilgin, M.; Akkaya, E.; Dokuyucu, R. The Role of Triglyceride/HDL Ratio, Triglyceride–Glucose Index, and Pan-Immune-Inflammation Value in the Differential Diagnosis of Acute Coronary Syndrome and Predicting Mortality. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 4832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinerua-Gonsalvez, J.F.; Ruiz Rebollo, M.L.; Zambrano-Infantino, R.D.C.; Rizzo-Rodriguez, M.A.; Fernandez-Salazar, L. Value of CRP/albumin ratio as a prognostic marker of acute pancreatitis: A retrospective study. Rev. Esp. Enferm. Dig. 2023, 115, 707–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntalouka, M.P.; Brotis, A.; Mermiri, M.; Pagonis, A.; Chatzis, A.; Bareka, M.; Kotsi, P.; Pantazopoulos, I.; Gourgoulianis, K.; Arnaoutoglou, E.M. Predicting the Outcome of Patients with Severe COVID-19 with Simple Inflammatory Biomarkers: The Utility of Novel Combined Scores-Results from a European Tertiary/Referral Centre. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, R.; Hu, L.; Ling, Y.; Hou, Y.; Fang, H.; Zhang, H.; Liang, S.; He, Z.; Fang, M.; Li, J.; et al. C-reactive protein concentration as a risk predictor of mortality in intensive care unit: A multicenter, prospective, observational study. BMC Anesthesiol. 2020, 20, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segmen, F.; Aydemir, S.; Kucuk, O.; Dokuyucu, R. The Roles of Vitamin D Levels, Gla-Rich Protein (GRP) and Matrix Gla Protein (MGP), and Inflammatory Markers in Predicting Mortality in Intensive Care Patients: A New Biomarker Link? Metabolites 2024, 14, 620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Guo, Y.; Tong, G.; He, Y.; Zhang, R.; Liu, Q. Combined nutritional status and activities of daily living disability is associated with one-year mortality after hip fracture surgery for geriatric patients: A retrospective cohort study. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2024, 36, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Xie, J.-W.; Liu, L.; Wang, D.; Huang, Z.-Y.; Zhou, Z.-K. Combination of CRP with NLR is a sensitive tool for screening fixation-related infection in patients undergoing conversion total hip arthroplasty after failed internal fixation for femoral neck fracture. Bone Jt. J. 2021, 103-B, 1534–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Liang, H.; Zheng, H.; Li, S.; Liu, H.; Ge, X. CONUT can be a predictor of postoperative complications after laparoscopic-assisted radical gastrectomy for elderly gastric cancer patients. Medicine 2023, 102, e35424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vyhnanek, F.; Ocadlik, M.; Drienko, M.; Gurlich, R. Trauma Care on Geriatric Population in Trauma Centre Faculty Hospital Kralovske Vinohrady in Prague. Cas. Lek. Cesk 2020, 159, 17–21. [Google Scholar]
- Widyastuti, Y.; Zaki, W.A.; Widodo, U.; Jufan, A.Y.; Pratomo, B.Y. Predictive accuracy of the APACHE IV scores on mortality and prolonged stay in the intensive care unit of Dr Sardjito Hospital. Med. J. Malays. 2022, 77, 53–58. [Google Scholar]
- Cakin, O.; Karaveli, A.; Yuce Aktepe, M.; Gumus, A.; Yildirim, O.E. Comparison of Inflammatory Marker Scoring Systems and Conventional Inflammatory Markers in Patients over 65 Years of Age Admitted to the Intensive Care Unit: A Multicenter, Retrospective, Cohort Study. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 4011–4017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimoda, M.; Udo, R.; Imasato, R.; Oshiro, Y.; Suzuki, S. What are the risk factors of conversion from total cholecystectomy to bailout surgery? Surg. Endosc. 2021, 35, 2206–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.B.; Xu, Y.H.; He, Y.; Lin, X.H.; Suo, Z.; Shu, H.; Zhang, H. Association between admission pan-immune-inflammation value and short-term mortality in septic patients: A retrospective cohort study. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 15205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.W.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.P.; Yin, X.S. Association between a four-parameter inflammatory index and all-cause mortality in critical ill patients with non-traumatic subarachnoid hemorrhage: A retrospective analysis of the MIMIC-IV database (2012–2019). Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1235266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darden, D.B.; Brakenridge, S.C.; Efron, P.A.; Ghita, G.L.; Fenner, B.P.; Kelly, L.S.; Mohr, A.M.; Moldawer, L.L.; Moore, F.A. Biomarker Evidence of the Persistent Inflammation, Immunosuppression and Catabolism Syndrome (PICS) in Chronic Critical Illness (CCI) After Surgical Sepsis. Ann. Surg. 2021, 274, 664–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.S.; Min, H.S.; Moon, J.Y.; Lim, D.; Kim, Y.; Ko, E.; Kim, Y.S.; Kim, J.; Lee, J.; Sung, H.K. Patient and hospital characteristics predict prolonged emergency department length of stay and in-hospital mortality: A nationwide analysis in Korea. BMC Emerg. Med. 2022, 22, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Patients (N = 121) Mean ± SD/Frequency (%) | |
|---|---|
| Age | 76.3 ± 9.6 years |
| Gender | Male: 58 (47.9%); female: 63 (52.1%) |
| Diabetes, n (%) | 60 (49.6%) |
| Hypertension, n (%) | 82 (67.8%) |
| CAD, n (%) | 35 (28.9%) |
| Heart failure, n (%) | 24 (19.8%) |
| CKD, n (%) | 17 (14.0%) |
| COPD, n (%) | 7 (5.8%) |
| Malignancy, n (%) | 8 (6.6%) |
| WBC (×103/µL) | 11.2 ± 3.5 |
| RDW (%) | 15.5 ± 2.0 |
| Platelet (Plt) (×103/µL) | 230 ± 50 |
| Neutrophil (×103/µL) | 7.0 ± 2.2 |
| MPV (fL) | 9.5 ± 1.0 |
| Monocyte (×103/µL) | 0.7 ± 0.2 |
| Lymphocyte (×103/µL) | 1.5 ± 0.6 |
| Ca++ (mg/dL) | 9.0 ± 0.5 |
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 120 ± 30 |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 3.5 ± 0.5 |
| BUN (mmol/L) | 15 ± 5 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 1.1 ± 0.3 |
| Troponin (U/L) | 0.05 ± 0.02 |
| D-dimer (mg/L) | 1.5 ± 0.5 |
| CRP (mg/L) | 50 ± 20 |
| Procalcitonin (ng/L) | 0.5 ± 0.3 |
| CCI | 4.5 ± 1.5 |
| APACHE II score | 18 ± 5 |
| PIV | 406.50 ± 102.50 |
| CAR | 1.5 ± 0.5 |
| CLR | 5.5 ± 2.3 |
| PLR | 180 ± 45 |
| NLR | 4.5 ± 1.8 |
| ICU Stay (days) | 8.2 ± 5.6 |
| ICU Mortality | 24 (20%) |
| Parameters | Survivor (N = 97) Mean ± SD, Frequency (%) | Mortality (N = 24) Mean ± SD, Frequency (%) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Diabetes, n (%) | 48 (49.5%) | 12 (50%) | 0.88 |
| Hypertension, n (%) | 68 (70.1%) | 14 (58.3%) | 0.22 |
| CAD, n (%) | 32 (33%) | 8 (33.3%) | 0.95 |
| Heart failure, n (%) | 18 (18.5%) | 6 (25%) | 0.42 |
| CKD, n (%) | 15 (15.5%) | 5 (20.8%) | 0.55 |
| COPD, n (%) | 5 (5.1%) | 2 (8.3%) | 0.52 |
| Malignancy, n (%) | 6 (6.2%) | 2 (8.3%) | 0.72 |
| WBC (×103/µL) | 10.8 ± 3.2 | 12.2 ± 3.7 | 0.03 * |
| RDW (%) | 15.2 ± 1.9 | 16.3 ± 2.1 | 0.04 * |
| Platelet (Plt) (×103/µL) | 235 ± 45 | 220 ± 38 | 0.07 |
| Neutrophil (×103/µL) | 6.8 ± 2.0 | 7.5 ± 2.5 | 0.08 |
| MPV (fL) | 9.4 ± 0.9 | 9.8 ± 1.1 | 0.15 |
| Monocyte (×103/µL) | 0.65 ± 0.15 | 0.73 ± 0.18 | 0.12 |
| Lymphocyte (×103/µL) | 1.6 ± 0.6 | 1.3 ± 0.5 | 0.04 * |
| Ca++ (mg/dL) | 9.1 ± 0.4 | 8.8 ± 0.5 | 0.02 * |
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 118 ± 27 | 130 ± 35 | 0.09 |
| Albumin (g/dL) (ALB) | 3.7 ± 0.4 | 3.2 ± 0.6 | 0.001 ** |
| BUN (mmol/L) | 14.8 ± 4.8 | 17.5 ± 6.5 | 0.05 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 1.0 ± 0.25 | 1.2 ± 0.4 | 0.02 * |
| Troponin (U/L) | 0.04 ± 0.02 | 0.08 ± 0.03 | 0.01 * |
| D-dimer (mg/L) | 1.4 ± 0.6 | 2.1 ± 0.9 | 0.001 ** |
| CRP (mg/L) | 48 ± 19 | 70 ± 28 | 0.02 * |
| Procalcitonin (ng/L) | 0.4 ± 0.2 | 0.7 ± 0.3 | 0.03 * |
| CCI | 4.2 ± 1.4 | 5.6 ± 1.2 | 0.04 * |
| APACHE II score | 14 ± 4 | 26 ± 2 | 0.001 ** |
| PIV | 350 ± 120 | 470 ± 140 | 0.03 * |
| CAR | 1.4 ± 0.6 | 2.1 ± 0.8 | 0.02 * |
| CLR | 4.8 ± 1.8 | 6.5 ± 2.3 | 0.04 * |
| PLR | 170 ± 50 | 200 ± 45 | 0.04 * |
| NLR | 4.2 ± 1.5 | 5.6 ± 2.1 | 0.02 * |
| Hospital stay (days) | 7.5 ± 4.3 | 11.5 ± 5.1 | 0.001 ** |
| Parameters | Hospital Stay (Days) r Value, p Value | Mortality r Value, p Value |
|---|---|---|
| WBC (×103/µL) | r = 0.32, p = 0.01 | r = 0.35, p = 0.01 |
| RDW (%) | r = 0.45, p = 0.002 | r = 0.47, p = 0.001 |
| Platelet (Plt) (×103/µL) | r = −0.24, p = 0.03 | r = −0.20, p = 0.06 |
| Neutrophil (×103/µL) | r = 0.38, p = 0.003 | r = 0.41, p = 0.002 |
| MPV (fL) | r = 0.28, p = 0.02 | r = 0.33, p = 0.01 |
| Monocyte (×103/µL) | r = 0.22, p = 0.05 | r = 0.20, p = 0.07 |
| Lymphocyte (×103/µL) | r = −0.30, p = 0.01 | r = −0.35, p = 0.01 |
| Ca++ (mg/dL) | r = −0.27, p = 0.03 | r = −0.32, p = 0.01 |
| Glucose (mg/dL) | r = 0.33, p = 0.01 | r = 0.37, p = 0.01 |
| Albumin (g/dL) (ALB) | r = −0.48, p < 0.001 | r = -0.52, p < 0.001 |
| BUN (mmol/L) | r = 0.39, p = 0.002 | r = 0.42, p = 0.001 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | r = 0.36, p = 0.01 | r = 0.39, p = 0.01 |
| Troponin (U/L) | r = 0.42, p = 0.001 | r = 0.47, p < 0.001 |
| D-dimer (mg/L) | r = 0.40, p = 0.002 | r = 0.46, p = 0.001 |
| CRP (mg/L) | r = 0.49, p < 0.001 | r = 0.53, p < 0.001 |
| Procalcitonin (ng/L) | r = 0.46, p = 0.001 | r = 0.50, p < 0.001 |
| CCI | r = 0.50, p < 0.001 | r = 0.55, p < 0.001 |
| APACHE II score | r = 0.54, p < 0.001 | r = 0.60, p < 0.001 |
| PIV | r = 0.41, p = 0.002 | r = 0.48, p = 0.001 |
| CAR | r = 0.45, p = 0.001 | r = 0.51, p < 0.001 |
| CLR | r = 0.42, p = 0.001 | r = 0.48, p = 0.001 |
| PLR | r = 0.30, p = 0.02 | r = 0.35, p = 0.01 |
| NLR | r = 0.48, p < 0.001 | r = 0.53, p < 0.001 |
| Parameters | B | St. Error | Beta | t | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WBC (×103/µL) | 0.25 | 0.12 | 0.20 | 2.08 | 0.04 * |
| RDW (%) | 0.35 | 0.10 | 0.30 | 3.50 | 0.001 ** |
| Platelet (Plt) (×103/µL) | −0.18 | 0.09 | −0.15 | −2.00 | 0.05 * |
| Neutrophil (×103/µL) | 0.28 | 0.11 | 0.22 | 2.45 | 0.02 * |
| MPV (fL) | 0.20 | 0.10 | 0.18 | 2.00 | 0.05 * |
| Monocyte (×103/µL) | 0.12 | 0.08 | 0.10 | 1.50 | 0.14 |
| Lymphocyte (×103/µL) | −0.25 | 0.09 | −0.20 | −2.78 | 0.01 ** |
| Ca++ (mg/dL) | −0.22 | 0.08 | −0.25 | −2.75 | 0.01 ** |
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 0.15 | 0.09 | 0.14 | 1.67 | 0.09 |
| Albumin (g/dL) | −0.40 | 0.12 | −0.35 | −3.33 | 0.001 ** |
| BUN (mmol/L) | 0.30 | 0.11 | 0.25 | 2.73 | 0.01 ** |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.20 | 0.10 | 0.18 | 2.00 | 0.05 * |
| Troponin (U/L) | 0.35 | 0.12 | 0.30 | 2.92 | 0.01 ** |
| D-dimer (mg/L) | 0.45 | 0.13 | 0.40 | 3.46 | 0.001 ** |
| CRP (mg/L) | 0.50 | 0.15 | 0.45 | 3.33 | 0.001 ** |
| Procalcitonin (ng/L) | 0.30 | 0.11 | 0.25 | 2.73 | 0.01 ** |
| CCI | 0.55 | 0.14 | 0.50 | 3.93 | <0.001 ** |
| APACHE II score | 0.60 | 0.15 | 0.55 | 4.00 | <0.001 ** |
| PIV | 0.55 | 0.13 | 0.50 | 4.23 | <0.001 ** |
| CAR | 0.50 | 0.12 | 0.45 | 4.17 | <0.001 ** |
| CLR | 0.48 | 0.11 | 0.44 | 4.10 | <0.001 ** |
| PLR | 0.35 | 0.10 | 0.30 | 3.50 | 0.001 ** |
| NLR | 0.50 | 0.13 | 0.45 | 3.85 | <0.001 ** |
| Hospital stay (days) | 0.55 | 0.14 | 0.50 | 3.93 | <0.001 ** |
| ICU Mortality | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Odds Ratio | 95% CI | p Value | |
| Diabetes | −1.10 | 0.85–1.40 | 0.22 |
| Hypertension | −1.15 | 0.90–1.35 | 0.18 |
| RDW | +1.30 | 1.12–1.48 | 0.002 ** |
| Albumin | −2.20 | 1.60–3.00 | <0.001 ** |
| Troponin | +1.45 | 1.20–1.70 | <0.001 ** |
| D-dimer | +1.40 | 1.15–1.65 | 0.001 ** |
| CRP | +1.50 | 1.35–1.75 | <0.001 ** |
| Procalcitonin | +1.35 | 1.15–1.55 | 0.002 ** |
| CCI | +1.25 | 1.10–1.40 | <0.001 ** |
| APACHE II score | +1.80 | 1.50–2.00 | <0.001 ** |
| PIV | +1.80 | 1.50–2.20 | <0.001 ** |
| CAR | +1.75 | 1.45–2.15 | <0.001 ** |
| CLR | +1.70 | 1.45–2.00 | <0.001 ** |
| PLR | +1.40 | 1.10–1.70 | 0.01 * |
| NLR | +1.80 | 1.55–2.15 | <0.001 ** |
| Hospital stay (days) | +1.55 | 1.30–1.80 | <0.001 ** |
| Cut-Off | Sensitivity | Specificity | AUC (95% CI) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
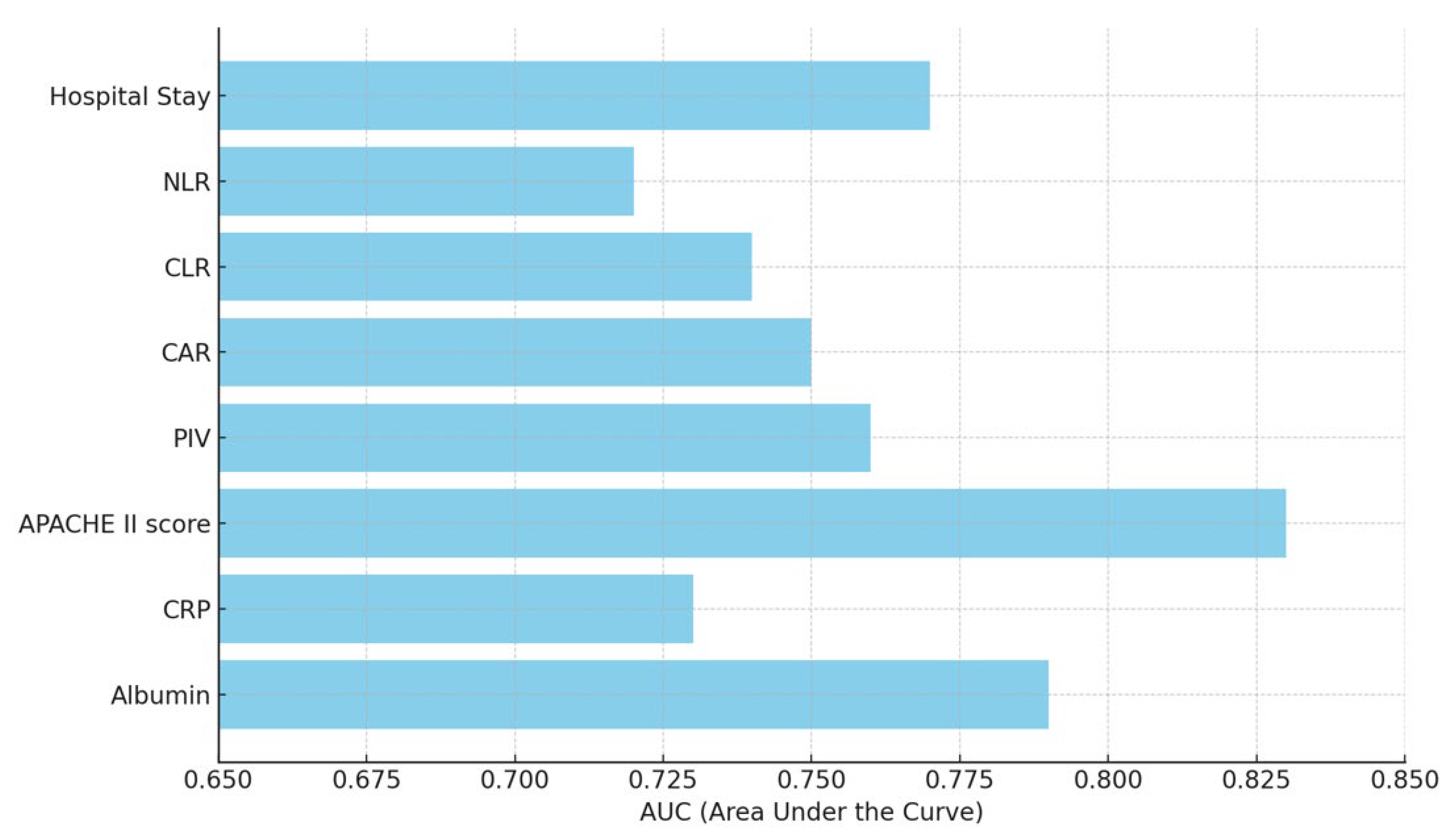
| Albumin | <2.5 g/dL | 75% | 78% | 0.79 (0.72–0.85) | <0.001 ** |
| CRP | >62.8 mg/L | 52% | 77% | 0.73 (0.65–0.81) | 0.001 ** |
| APACHE II score | >23 | 76% | 84% | 0.83 (0.75–0.88) | <0.001 ** |
| PIV | >450 | 70% | 72% | 0.76 (0.68–0.82) | <0.001 ** |
| CAR | >2.94 | 66% | 73% | 0.75 (0.68–0.80) | <0.001 ** |
| CLR | >14.0 | 64% | 71% | 0.74 (0.67–0.79) | <0.001 ** |
| NLR | >10.0 | 60% | 70% | 0.72 (0.65–0.77) | <0.001 ** |
| Hospital stay | >10 days | 74% | 75% | 0.77 (0.69–0.82) | <0.001 ** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kilinc, M.; Çelik, E.; Demir, I.; Aydemir, S.; Akelma, H. Association of Inflammatory and Metabolic Markers with Mortality in Patients with Postoperative Femur Fractures in the Intensive Care Unit. Medicina 2025, 61, 538. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61030538
Kilinc M, Çelik E, Demir I, Aydemir S, Akelma H. Association of Inflammatory and Metabolic Markers with Mortality in Patients with Postoperative Femur Fractures in the Intensive Care Unit. Medicina. 2025; 61(3):538. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61030538
Chicago/Turabian StyleKilinc, Metin, Enes Çelik, Ibrahim Demir, Semih Aydemir, and Hakan Akelma. 2025. "Association of Inflammatory and Metabolic Markers with Mortality in Patients with Postoperative Femur Fractures in the Intensive Care Unit" Medicina 61, no. 3: 538. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61030538
APA StyleKilinc, M., Çelik, E., Demir, I., Aydemir, S., & Akelma, H. (2025). Association of Inflammatory and Metabolic Markers with Mortality in Patients with Postoperative Femur Fractures in the Intensive Care Unit. Medicina, 61(3), 538. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61030538







