Comparison of Margin Quality for Intersegmental Plan Identification in Pulmonary Segmentectomy †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
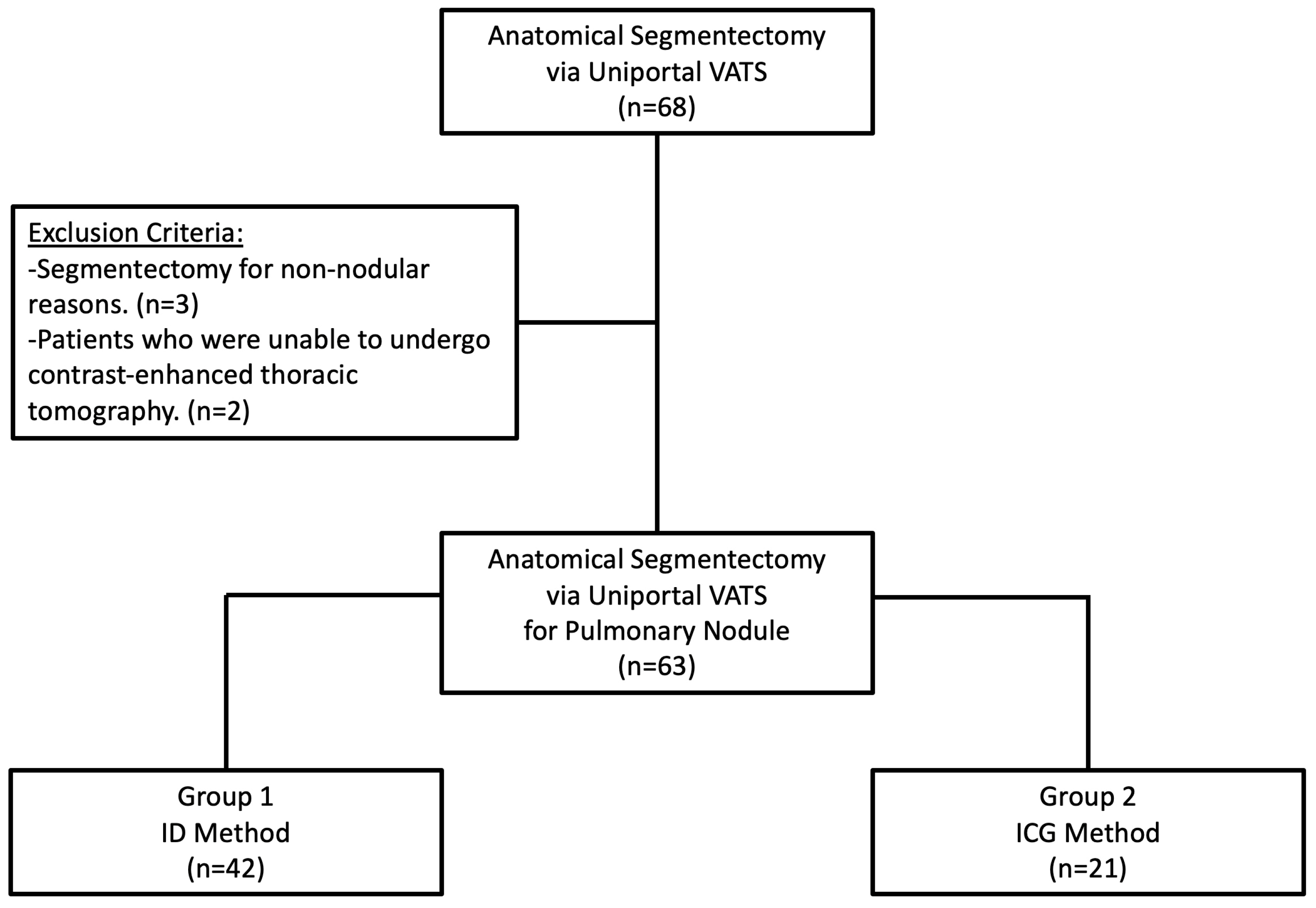
2.1. Study Design, Data Source, and Patients
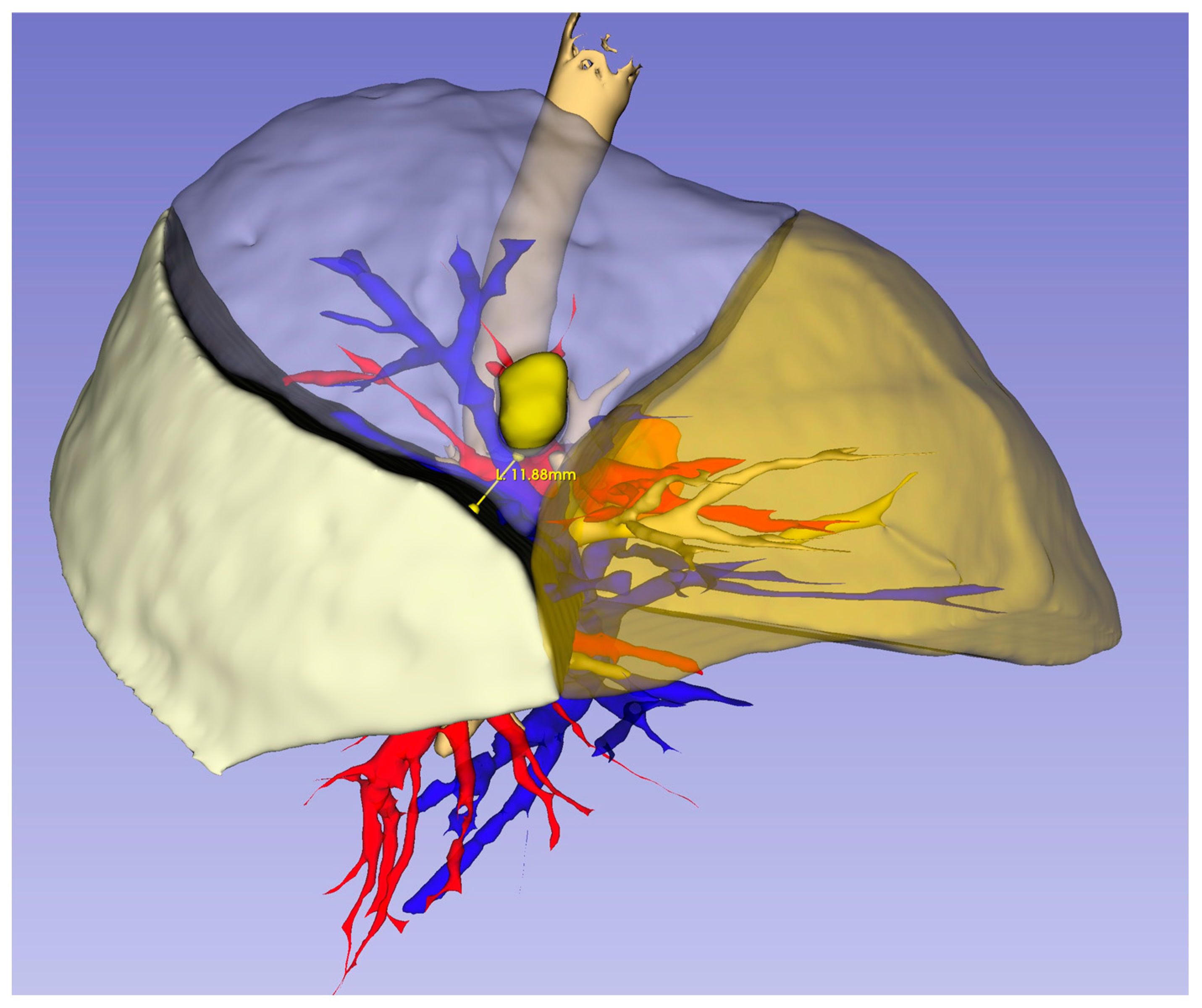
2.2. Three-Dimensional Reconstruction and Virtual Measurements
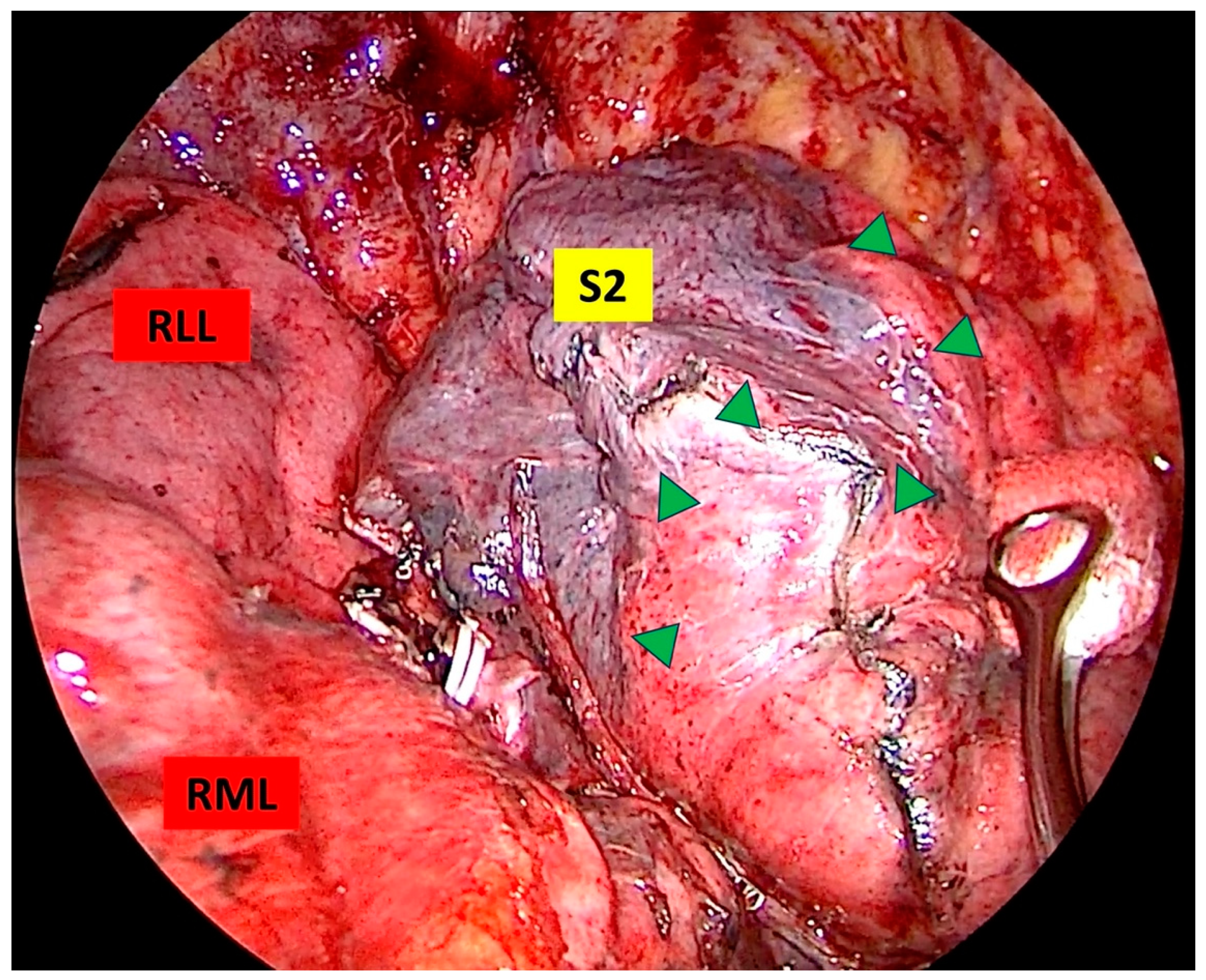
2.3. Sugical Technique
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saji, H.; Okada, M.; Tsuboi, M.; Nakajima, R.; Suzuki, K.; Aokage, K.; Aoki, T.; Okami, J.; Yoshino, I.; Ito, H.; et al. Segmentectomy versus lobectomy in small-sized peripheral non-small-cell lung cancer (JCOG0802/WJOG4607L): A multicentre, open-label, phase 3, randomised, controlled, non-inferiority trial. Lancet 2022, 399, 1607–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Petersen, R.H. Impact of Margin Distance on Locoregional Recurrence and Survival After Thoracoscopic Segmentectomy. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2025, 119, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuura, Y. Precise identification of the intersegmental plane for lung cancer segmentectomy. Transl. Cancer Res. 2023, 12, 213–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andolfi, M.; Potenza, R.; Seguin-Givelet, A.; Gossot, D. Identification of the intersegmental plane during thoracoscopic segmentectomy: State of the art. Interact. CardioVasc. Thorac. Surg. 2019, 30, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomori, H.; Okada, M. Illustrated Textbook of Anatomical Pulmonary Segmentectomy; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Oizumi, H.; Kato, H.; Endoh, M.; Inoue, T.; Watarai, H.; Sadahiro, M. Techniques to define segmental anatomy during segmentectomy. Ann. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2014, 3, 170–175. [Google Scholar]
- Tsubota, N. An improved method for distinguishing the intersegmental plane of the lung. Surg. Today 2000, 30, 963–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misaki, N.; Chang, S.S.; Gotoh, M.; Yamamoto, Y.; Satoh, K.; Yokomise, H. A novel method for determining adjacent lung segments with infrared thoracoscopy. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2009, 138, 613–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.X.; Chen, Q.; Hong, S.M.; Hong, J.J. Comparison of ICG-Guided Near-Infrared Fluorescence Imaging and Modified Inflation-Deflation Method in Identifying the Intersegmental Plane During Lung Segmentectomy of Infants. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2024, 59, 1708–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Shao, F.; Yang, R. Is the near-infrared fluorescence imaging with intravenous indocyanine green method for identifying the intersegmental plane concordant with the modified inflation-deflation method in lung segmentectomy? Thorac. Cancer 2019, 10, 2013–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yotsukura, M.; Okubo, Y.; Yoshida, Y.; Nakagawa, K.; Watanabe, S.I. Indocyanine green imaging for pulmonary segmentectomy. JTCVS Tech. 2021, 6, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onodera, K.; Suzuki, J.; Miyoshi, T.; Tane, K.; Samejima, J.; Aokage, K.; Tsuboi, M. Comparison of various lung intersegmental plane identification methods. Gen. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2023, 71, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurz, S.; Sengul, A.; Buyukkarabacak, Y.; Pirzirenli, M.G.; Temel, N.G.; Sullu, Y.; Tanrivermis Sayit, A.; Gundogdu, H.; Basoglu, A. Effect of preoperative three-dimensional modeling on uniportal video-assisted thoracoscopic bronchial sleeve resection and early postoperative outcomes. Turk Gogus Kalp Damar Cerrahisi Derg. 2024, 32, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Handa, Y.; Tsutani, Y.; Mimae, T.; Miyata, Y.; Okada, M. Complex segmentectomy in the treatment of stage IA non-small-cell lung cancer. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2020, 57, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakazawa, S.; Shimizu, K.; Mogi, A.; Kuwano, H. VATS segmentectomy: Past, present, and future. Gen. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2018, 66, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueno, H.; Setogawa, T.; Makita, A.; Ohara, Y.; Imamura, Y.; Okado, S.; Watanabe, H.; Kawasumi, Y.; Kadomatsu, Y.; Kato, T. Influencing Factors on Intersegmental Identification Adequacy in Segmentectomy with Intraoperative Indocyanine Green (ICG) Intravenous Administration. Cancers 2023, 15, 5876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libor, L.; Pécsy, B.; Szűcs, E.; Lantos, J.; Bakos, A.; Lázár, G.; Furák, J. Effect of transbronchial or intravenous administration of indocyanine green on resection margins during near-infrared-guided segmentectomy: A review. Front. Surg. 2024, 11, 1430100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bédat, B.; Gonzalez, M.; Karenovics, W. How to identify the intersegmental plane?—A narrative review. J. Vis. Surg. 2021, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldham, M.J.; Moss, O.R. Pores of Kohn: Forgotten alveolar structures and potential source of aerosols in exhaled breath. J. Breath Res. 2019, 13, 021003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamiyoshihara, M.; Kakegawa, S.; Morishita, Y. Convenient and improved method to distinguish the intersegmental plane in pulmonary segmentectomy using a butterfly needle. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2007, 83, 1913–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.; Mei, N.; Ning, Y.; Zhang, W.; Li, Y.; Jiang, L. Identifying the intersegmental plane for segmentectomy using the open insufflation technique. J. Surg. Case Rep. 2024, 2024, rjad620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Yang, R.; Cao, H. Near-infrared intraoperative imaging with indocyanine green is beneficial in video-assisted thoracoscopic segmentectomy for patients with chronic lung diseases: A retrospective single-center propensity-score matched analysis. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2020, 15, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuroda, H.; Yoshida, T.; Arimura, T.; Mizuno, T.; Sakakura, N.; Sakao, Y. Novel development of Spectra-A using indocyanine green for segmental boundary visibility in thoracoscopic segmentectomy. J. Surg. Res. 2018, 227, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funai, K.; Kawase, A.; Shimizu, K.; Sekihara, K.; Yamashita, T.; Shiiya, N. Fluorescence navigation with indocyanine green for identification of intersegmental planes using a photodynamic eye camera. J. Thorac. Dis. 2020, 12, 4817–4824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, H.; Tanaka, T.; Hayashi, T.; Yoshida, K.; Furukawa, M.; Yoshiyama, K.; Okabe, K. Influence of stapling the intersegmental planes on lung volume and function after segmentectomy. Interact. CardioVasc. Thorac. Surg. 2016, 23, 548–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, M.; Murayama, T.; Nakajima, J. Techniques of stapler-based navigational thoracoscopic segmentectomy using virtual assisted lung mapping (VAL-MAP). J. Thorac. Dis. 2016, 8 (Suppl. S9), S716–S730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Shao, F.; Yang, R. Feasibility investigation of near-infrared fluorescence imaging with intravenous indocyanine green method in uniport video-assisted thoracoscopic anatomical segmentectomy for identifying the intersegmental boundary line. Thorac. Cancer 2021, 12, 1407–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurz, S.; Sullu, Y.; Tomak, L.; Temel, N.G.; Sengul, A. Comparison of Margin Quality for Intersegmental Plan Determination in Pulmonary Segmentectomy. In Proceedings of the Sixth International Thoracic Surgery Joint Meeting, Barcelona, Spain, 20–22 November 2024; P-14. Available online: https://www.thoracicsurgery2024.org/#poster-video (accessed on 14 March 2025).

| Variables | Total (n = 63) | Group 1 (n = 42) | Group 2 (n = 21) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (year, mean ± SD) | 60.03 ± 12.63 | 60.19 ± 13.66 | 59.71 ± 10.55 | 0.73 |
| Sex [n (%)] | 0.17 | |||
| Male | 36 (57.1) | 27 (64.3) | 9 (42.9) | |
| Female | 27 (42.9) | 15 (35.7) | 12 (57.1) | |
| Nodule Size (mm, mean ± SD) | 14.71 ± 8.09 | 15.5 ± 9.19 | 13.14 ± 5.09 | 0.53 |
| Nodule Type [n (%)] | 0.63 | |||
| GGO | 14 (22.2) | 9 (21.4) | 5 (23.8) | |
| Semi-solid | 8 (12.7) | 4 (9.5) | 4 (19.0) | |
| Solid | 41 (65.1) | 29 (69.1) | 12 (57.1) | |
| Nodule Follow-up [month, median (IQR)] | 7 (13) | 6 (10) | 12 (12) | 0.05 |
| Histology [n (%)] | 0.49 | |||
| Primary | 46 (73) | 29 (69.1) | 17 (81.0) | |
| Secondary | 6 (9.5) | 4 (9.5) | 2 (9.5) | |
| Other | 11 (17.5) | 9 (21.4) | 2 (9.5) | |
| Segmentectomy Type [n (%)] | 0.15 | |||
| Simple | 21 (33.3) | 17 (40.5) | 4 (19) | |
| Complex | 42 (66.7) | 25 (59.5) | 17 (81) | |
| Segmentectomy Side [n (%)] | ||||
| Right | 38 (60.3) | 25 (59.5) | 13 (61.9) | - |
| Left | 25 (39.7) | 17 (40.5) | 8 (38.1) | |
| Upper Lobe | 38 (60.3) | 25 (59.5) | 13 (61.9) | - |
| Lower Lobe | 25 (39.7) | 17 (40.5) | 8 (38.1) | |
| Segmentectomy [n (%)] | - | |||
| S1 | 13 (20.6) | 9 (21.4) | 4 (19) | |
| S2 | 6 (9.5) | 3 (7.1) | 3 (14.3) | |
| S1+2 | 6 (9.5) | 4 (9.5) | 2 (9.5) | |
| S3 | 5 (7.9) | 4 (9.5) | 1 (4.8) | |
| S2+3 | 1 (1.6) | 0 | 1 (4.8) | |
| S1+2+3 | 4 (6.3) | 3 (7.1) | 1 (4.8) | |
| S4+5 | 3 (4.8) | 2 (4.8) | 1 (4.8) | |
| S3+4+5 | 1 (1.6) | 1 (2.4) | 0 | |
| S6 | 14 (22.2) | 12 (28.6) | 2 (9.5) | |
| S7 | 2 (3.2) | 0 | 2 (9.5) | |
| S7+8 | 1 (1.6) | 1 (2.4) | 0 | |
| S10 | 2 (3.2) | 1 (2.4) | 1 (4.8) | |
| S6+10 | 1 (1.6) | 1 (2.4) | 0 | |
| S9+10 | 3 (4.8) | 0 | 3 (14.3) | |
| S8+9+10 | 1 (1.6) | 1 (2.4) | 0 | |
| Introperative Complication [n (%)] | 0.54 | |||
| No | 61 (96.8) | 40 (95.2) | 21 (100) | |
| Yes | 2 (3.2) | 2 (4.8) | 0 | |
| Postoperative Complication [n (%) | 0.16 | |||
| No | 57 (90.5) | 36 (85.7) | 21 (100) | |
| Yes | 6 (9.5) | 6 (14.3) | 0 | |
| Chest Tube Removal [day, median (IQR)] | 2 (1) | 2 (1) | 2 (1) | 0.43 |
| Postoperative LOS [day, median (IQR)] | 3 (2) | 3 (1.3) | 3 (1) | 0.05 |
| Variables | Total (n = 63) | Group 1 (n = 42) | Group 2 (n = 21) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Virtual Margin (mm, mean ± SD) | 21.52 ± 7.07 | 21.14 ± 6.44 | 22.28 ± 8.30 | 0.92 |
| Pathological Margin (mm, mean ± SD) | 15.15 ± 9.48 | 14.14 ± 9.23 | 17.19 ± 9.87 | 0.21 |
| Margin Deviation (mm, mean ± SD) | 7.25 ± 5.16 | 8.28 ± 5.52 | 5.19 ± 3.64 | 0.04 |
| Margin Success [n (%)] | 0.05 | |||
| Yes | 46 (73) | 27 (64.3) | 19 (90.5) | |
| No | 17 (27) | 15 (35.7) | 2 (9.5) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gurz, S.; Sullu, Y.; Tomak, L.; Temel, N.G.; Sengul, A. Comparison of Margin Quality for Intersegmental Plan Identification in Pulmonary Segmentectomy. Medicina 2025, 61, 535. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61030535
Gurz S, Sullu Y, Tomak L, Temel NG, Sengul A. Comparison of Margin Quality for Intersegmental Plan Identification in Pulmonary Segmentectomy. Medicina. 2025; 61(3):535. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61030535
Chicago/Turabian StyleGurz, Selcuk, Yurdanur Sullu, Leman Tomak, Necmiye Gul Temel, and Aysen Sengul. 2025. "Comparison of Margin Quality for Intersegmental Plan Identification in Pulmonary Segmentectomy" Medicina 61, no. 3: 535. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61030535
APA StyleGurz, S., Sullu, Y., Tomak, L., Temel, N. G., & Sengul, A. (2025). Comparison of Margin Quality for Intersegmental Plan Identification in Pulmonary Segmentectomy. Medicina, 61(3), 535. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61030535






