Comparison of Skeletal, Dental, and Soft Tissue Changes Before and After Orthodontic Treatment in Patients with Congenitally Missing Bilateral Maxillary Lateral Incisors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design, Sample Size Calculation, and Criteria
2.2. Ethical Approval and Consent
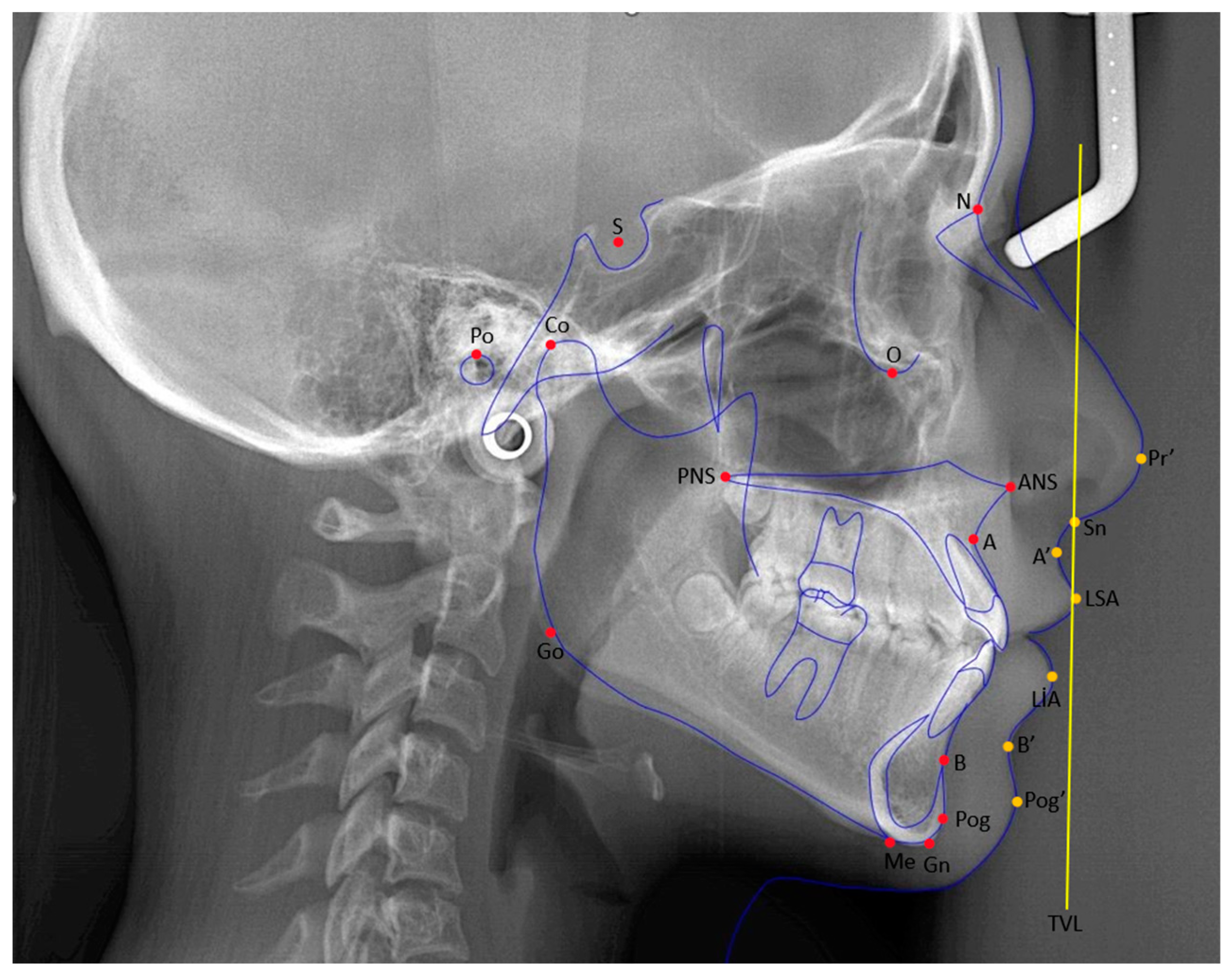
2.3. Orthodontic Interventions and Cephalometric Measurements
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Method Error
3.2. Results of Skeletal Measurements
3.3. Results of Dental Measurements
3.4. Results of Soft Tissue Measurements
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- (i)
- Ensures the planned maxillary incisor position,
- (ii)
- Eliminates the waiting period for prosthetic restoration,
- (iii)
- Provides a cost-effective solution,
- (iv)
- Avoids potential anatomical disadvantages in the alveolar bone for future implant surgery.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Meade, M.J.; Dreyer, C.W. Tooth agenesis: An overview of diagnosis, aetiology and management. Jpn. Dent. Sci. Rev. 2023, 59, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polder, B.J.; Van’t Hof, M.A.; Van der Linden, F.P.; Kuijpers-Jagtman, A.M. A meta-analysis of the prevalence of dental agenesis of permanent teeth. Community Dent. Oral Epidemiol. 2004, 32, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazanci, F.; Celikoglu, M.; Miloglu, O.; Ceylan, I.; Kamak, H. Frequency and distribution of developmental anomalies in the permanent teeth of a Turkish orthodontic patient population. J. Dent. Sci. 2011, 6, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fauzi, N.H.; Lestari, W.; Kharuddin, A.F.; Ardini, Y.D. Prevalence, pattern and distribution of non-syndromic tooth agenesis in permanent dentition among Malaysian population. Mater. Today Proc. 2019, 16, 2204–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirac, D.; Eraydin, F.; Avcilar, T.; Ulucan, K.; Guney, A.; Keshi, E.; Isbir, T. Effects of PAX9 and MSX1 gene variants to hypodontia, tooth size and the type of congenitally missing teeth. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2016, 62, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, T.; Maeda, T. Prevalence and genetic basis of tooth agenesis. Jpn. Dent. Sci. Rev. 2009, 45, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamoudi, R.; Kanavakis, G.; Oeschger, E.S.; Halazonetis, D.; Gkantidis, N. Occlusal characteristics in modern humans with tooth agenesis. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 5840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassiouny, D.S.; Afify, A.R.; Baeshen, H.A.; Birkhed, D.; Zawawi, K.H. Prevalence of maxillary lateral incisor agenesis and associated skeletal characteristics in an orthodontic patient population. Acta Odontol. Scand. 2016, 74, 456–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amm, E.W.; Antoszewska-Smith, J.; Boley, J. Canine substitution of congenitally missing maxillary lateral incisors in Class I and Class III malocclusions by using skeletal anchorage. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2019, 156, 512–521.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilgin, N.; Kaya, B. Etiology and treatment alternatives in tooth agenesis: A comprehensive review. Stomatol. Dis. Sci. 2018, 2, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Naoum, S.; Allan, Z.; Yeap, C.K.; Razza, J.M.; Murray, K.; Turlach, B.; Goonewardene, M.S. Trends in orthodontic management strategies for patients with congenitally missing lateral incisors and premolars. Angle Orthod. 2021, 91, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, D.D.; de Oliveira, B.F.; da Mata Cid Pinto, L.S.; Figueiredo, D.S.F.; Pithon, M.M.; Seraidarian, P.I. Interdisciplinary Treatment of a C lass III Patient with Congenitally Absent Maxillary Lateral Incisors. J. Esthet. Restor. Dent. 2013, 25, 242–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westgate, E.; Waring, D.; Malik, O.; Darcey, J. Management of missing maxillary lateral incisors in general practice: Space opening versus space closure. Br. Dent. J. 2019, 226, 400–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicek, O.; Arslan, D. Investigation of the Mesiodistal Angulations of Maxillary Canines and Central Incisors for Missing Bilateral Maxillary Lateral Incisor. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borzabadi-Farahani, A.; Zadeh, H.H. Orthodontic therapy in implant dentistry: Orthodontic implant site development. In Vertical Alveolar Ridge Augmentation in Implant Dentistry: A Surgical Manual; Tolstunov, L., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 30–37. [Google Scholar]
- Jurado, C.; Fischer, N.G.; Fu, C.-C.; Tsujimoto, A.; Jurado, C.A. A multidisciplinary approach to congenitally missing central incisors: A case report. Cureus 2022, 14, e21911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimberg, L.; Arnrup, K.; Bondemark, L. The impact of malocclusion on the quality of life among children and adolescents: A systematic review of quantitative studies. Eur. J. Orthod. 2015, 37, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kragt, L.; Wolvius, E.B.; Jaddoe, V.W.; Tiemeier, H.; Ongkosuwito, E.M. Influence of self-esteem on perceived orthodontic treatment need and oral health-related quality of life in children: The Generation R Study. Eur. J. Orthod. 2018, 40, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, C.; Sheiham, A. Orthodontic treatment and its impact on oral health-related quality of life in Brazilian adolescents. J. Orthod. 2004, 31, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalaf, K.; Miskelly, J.; Voge, E.; Macfarlane, T.V. Prevalence of hypodontia and associated factors: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Orthod. 2014, 41, 299–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cocconi, R.; Rapa, S. Unilateral agenesis of the maxillary lateral incisor: Space closure versus space preservation in growing patients. Semin. Orthod. 2020, 26, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, T.M.; Kokich Sr, V.G. Postorthodontic root approximation after opening space for maxillary lateral incisor implants. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2010, 137, 158.e1–158.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proffit, W.R.; Fields, H.W.; Larson, B.E.; Sarver, D.M. Contemporary Orthodontics, 6th ed.; Elsevier Inc.: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Alkadhimi, A.; Razaghi, N.; Elder, A.; DiBiase, A.T. Camouflaging the permanent maxillary canine to substitute an absent lateral incisor-part 1: Assessment and management. Br. Dent. J. 2022, 232, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLaughlin, R.P.; Bennett, J.C.; Trevisi, H.J. Systemized Orthodontic Treatment Mechanics, 1st ed.; Mosby Ltd.: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Cicek, O.; Yilmaz, H.; Demir Cicek, B. Comparison of the mesiodistal angulations of canine and molar teeth in different types of orthodontic malocclusions: A retrospective study. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ülgen, M. Ortodonti: Anomaliler, Sefalometri, Etoloji, Büyüme ve Gelişim, Tanı, Ed. Yeditepe Üniversitesi: İstanbul, Türkiye, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Johal, A.; Huang, Y.; Toledano, S. Hypodontia and its impact on a young person’s quality of life, esthetics, and self-esteem. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2022, 161, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-Bassat, Y.; Brin, I. Skeletal and dental patterns in patients with severe congenital absence of teeth. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2009, 135, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vucic, S.; Dhamo, B.; Kuijpers, M.A.; Jaddoe, V.W.; Hofman, A.; Wolvius, E.B.; Ongkosuwito, E.M. Craniofacial characteristics of children with mild hypodontia. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2016, 150, 611–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demiröz, D. Investigation of Craniofacial Morphology of Individuals with Congenitally Missing Upper Lateral Incisors Through CBCT. Ph.D. Thesis, Atatürk University Faculty of Dentistry Department of Orthodontics, Erzurum, Turkey, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Tageldin, M.A.; Yacout, Y.M.; Marzouk, E.S. Skeletal and dentoalveolar characteristics of maxillary lateral incisor agenesis patients: A comparative cross-sectional study. BMC Oral Health 2022, 22, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öztürk, T.; Topsakal, K.G.; Yağcı, A. The Effect of Missing Lateral Incisor and Incisor Tooth Positions on Lower Front Face Soft Tisse Thickness. J. Health Sci. 2019, 28, 148–157. [Google Scholar]
- Kreczi, A.; Proff, P.; Reicheneder, C.; Faltermeier, A. Effects of hypodontia on craniofacial structures and mandibular growth pattern. Head Face Med. 2011, 7, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, T.; Ozoe, R.; Yoshino, S.; Shimooka, S. Hypodontia patterns and variations in craniofacial morphology in Japanese orthodontic patients. Angle Orthod. 2006, 76, 996–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motairi, M.; Jalal, R.; Afify, A. Skeletal facial pattern usually associated with congenitally missing upper lateral incisor in Saudi orthodontic patients Jeddah, KSA. Int. J. Oral Dent. Health 2022, 8, 139. [Google Scholar]
- Elias, M.; Kadkhodayan, S.; Pacheco-Pereira, C.; Vich, M.L. Incisors inclination in relation to lip parameters: A CBCT study. Dental Press. J. Orthod. 2024, 29, e2424130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapatki, B.G.; Baustert, D.; Schulte-Mönting, J.; Frucht, S.; Jonas, I.E. Lip-to-incisor relationship and postorthodontic long-term stability of cover-bite treatment. Angle Orthod. 2006, 76, 942–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiliaridis, S.; Sidira, M.; Kirmanidou, Y.; Michalakis, K. Treatment options for congenitally missing lateral incisors. Eur. J. Oral Implantol. 2016, 9, S5–S24. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Güngör, A.Y. Evalution of Craniofacial Characteristics of Patiens with Congenitally Missing Teeth. Ph.D. Thesis, Süleyman Demirel University, Institute of Health Sciences, Department of Orthodontics, Isparta, Turkey, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Fekonja, A. Hypodontia in orthodontically treated children. Eur. J. Orthod. 2005, 27, 457–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zachrisson, B.U.; Rosa, M.; Toreskog, S. Congenitally missing maxillary lateral incisors: Canine substitution. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2011, 139, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, L.L. Treatment planning in the presence of congenitally absent second premolars: A review of the literature. J. Clin. Pediatr. Dent. 2003, 27, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertsson, S.; Mohlin, B. The congenitally missing upper lateral incisor. A retrospective study of orthodontic space closure versus restorative treatment. Eur. J. Orthod. 2000, 22, 697–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldini, B.; Cavagnetto, D.; Baselli, G.; Sforza, C.; Tartaglia, G.M. Cephalometric measurements performed on CBCT and reconstructed lateral cephalograms: A cross-sectional study providing a quantitative approach of differences and bias. BMC Oral Health 2022, 22, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maspero, C.; Farronato, M.; Bellincioni, F.; Cavagnetto, D.; Abate, A. Assessing mandibular body changes in growing subjects: A comparison of CBCT and reconstructed lateral cephalogram measurements. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Study Groups (Space Opening and Closure) | Control Group |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
| Control | Space Opening | Space Closure | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (year) | Mean ± sd | 18.1 ± 4.1 | 15.4 ± 2.9 | 14.9 ± 2.9 |
| Gender | Female (n-%) | 15–83.3% | 14–77.8% | 14–82.4% |
| Male (n-%) | 3–16.7% | 4–22.2% | 3–17.6% | |
| Treatment duration (year) | 2.66 ± 1.07 | 3.41 ± 1.26 |
| Cephalometric Points | Definitions |
|---|---|
| Sella (S) | The geometric center of the sella turcica. |
| Nasion (N) | The most anterior and deepest point of the frontonasal suture. |
| A point (A) | The deepest point of the bony concavity on the anterior surface of the maxilla. |
| B point (B) | The deepest point of the bony concavity on the anterior surface of the mandible. |
| Porion (Po) | The uppermost point of the bony concavity that forms the external auditory canal. |
| Pogonion (Pog) | The most anterior point of the mandible in the sagittal plane. |
| Gnathion (Gn) | The most anterior and inferior point of the mandible. |
| Menton (Me) | The point where the lower border of the mandible meets the symphysis in the sagittal plane. |
| Gonion (Go) | The point where the bisector of the angle formed by the intersection of lines, drawn along the ramus and corpus of the mandible, cuts the ramus. |
| Maxillary incisor edge point | The point of the incisal edge of the most anteriorly positioned maxillary incisor. |
| Mandibular incisor edge point | The point of the incisal edge of the most anteriorly positioned mandibular incisor. |
| Subnasale (Sn) | The point of junction between the lower border of the nasal septum and the upper lip. |
| Labialis superior anterior (LSA) | The most anterior point of the upper lip in the sagittal plane. |
| Labialis inferior anterior (LIA) | The most anterior point of the lower lip in the sagittal plane. |
| Condylion (Co) | The most superoposterior point of the condyle in the sagittal plane. |
| Parameters | Definitions | |
|---|---|---|
| Angular measurements (°) | U1/SN | It is the angle that the axis inclination of the upper incisor makes with the SN plane. |
| U1/NA | The angle between the inclination of the upper incisor axis and the NA line. | |
| L1/NB | It is the angle between the lower incisor axis inclination and the NB line. | |
| Nasolabial | It is the angle formed by the intersection of the most anterior point of the upper lip and the tangent passing through the columella in the subnasale region. | |
| Labiomental | It is the angle formed at the intersection of the most anterior point of the lower lip, the supramentale, and the lines drawn from the soft tissue pogonion to the supramentale. | |
| Upper Lip | It is the angle formed between the line drawn from the most anterior point of the upper lip to the subnasale point and the GDS. | |
| U1-ANSPNS | The angle formed at the intersection of the upper incisal axis inclination and the spinalar plane. | |
| U1–Upper Occlusal Plane | The angle formed between the inclination of the upper incisor axis and the upper occlusal plane. | |
| Linear Measurements (mm) | U1/NA | The distance measured from the incisal of the upper incisor down to the NA line. |
| L1/NB | The distance measured from the incisal of the lower incisor to the NB line. | |
| A Nasion Perpendicular (N⊥A) | It is the distance between the perpendiculars, lowered from the points Nasion and A to the Frankfurt horizontal plane. | |
| Effective Maxillary Length | This is the distance between the Condylon point and point A. | |
| Upper Lip Length (Sn-ULI) | The distance between the subnasale point and the lowest point of the upper lip. | |
| Upper Lip Thickness | The distance between the most anterior part of the upper lip and the inner part. | |
| Upper Lip–E Line | The distance between the most anterior point of the upper lip and the E plane. | |
| Lower Lip–E Line | The distance between the most anterior point of the lower lip and the E plane. | |
| A’-TVL (mm) | The distance between the soft tissue point A and the true vertical line. | |
| Upper Incisor Incisal—TVL | The distance between the incisal point of the upper incisor and the true vertical line. | |
| Upper Lip Anterior Part—TVL | It is the distance between the most anterior point of the upper lip and the true vertical line. |
| Control 1 | Space Opening 2 | Space Closure 3 | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SNA | |||||
| T0 | Mean ± sd | 81.4 ± 1.4 | 81.6 ± 4.1 | 79.2 ± 2.8 1 | 0.036 *,K |
| T1 | Mean ± sd | 81.4 ± 1.4 | 81.8 ± 4.3 | 78.6 ± 2.9 1,2 | 0.006 *,K |
| T0/T1 Change | Mean ± sd | 0.2 ± 1.2 | −0.6 ± 1.3 | 0.077 M | |
| Intra Group Change p | 0.415 W | 0.093 W | |||
| SNB | |||||
| T0 | Mean ± sd | 79.2 ± 1.1 | 79.9 ± 3.4 | 77.3 ± 3.0 1,2 | 0.012 *,K |
| T1 | Mean ± sd | 79.2 ± 1.1 | 80.5 ± 3.7 | 76.8 ± 3.1 1,2 | 0.002 *,K |
| T0/T1 Change | Mean ± sd | 0.6 ± 1.3 | −0.5 ± 1.3 | 0.025 *,M | |
| Intra Group Change p | 0.092 W | 0.103 W | |||
| ANB | |||||
| T0 | Mean ± sd | 2.3 ± 1.0 | 1.6 ± 1.4 | 1.9 ± 1.2 | 0.224 K |
| T1 | Mean ± sd | 2.3 ± 1.0 | 1.4 ± 1.6 | 1.9 ± 1.5 | 0.183 K |
| T0/T1 Change | Mean ± sd | −0.2 ± 0.6 | −0.1 ± 0.6 | 0.397 M | |
| Intra Group Change p | 0.157 W | 0.655 W | |||
| GOGn/SN | |||||
| T0 | Mean ± sd | 33.7 ± 3.0 | 32.4 ± 4.2 | 35.3 ± 4.9 | 0.129 K |
| T1 | Mean ± sd | 33.7 ± 3.0 | 32.3 ± 4.6 | 35.9 ± 5.1 2 | 0.045 *,K |
| T0/T1 Change | Mean ± sd | −0.1 ± 2.4 | 0.6 ± 2.1 | 0.242 M | |
| Intra Group Change p | 0.905 W | 0.187 W | |||
| A-Nazion Perpendicular | |||||
| T0 | Mean ± sd | −1.4 ± 2.5 | −1.5 ± 4.2 | −3.5 ± 2.8 | 0.115 A |
| T1 | Mean ± sd | −1.4 ± 2.5 | −1.1 ± 4.8 | −3.7 ± 3.5 | 0.101 A |
| T0/T1 Change | Mean ± sd | 0.4 ± 2.4 | −0.2 ± 2.8 | 0.537 t | |
| Intra Group Change p | 0.500 P | 0.817 P | |||
| Effective Maxillar Length | |||||
| T0 | Mean ± sd | 87.7 ± 4.2 | 83.3 ± 3.61 | 81.4 ± 6.8 1 | 0.001 *,K |
| T1 | Mean ± sd | 87.7 ± 4.2 | 87.1 ± 3.2 | 83.8 ± 6.1 1 | <0.050 *,K |
| T0/T1 Change | Mean ± sd | 3.8 ± 3.4 | 2.4 ± 2.8 | 0.314 M | |
| Intra Group Change p | <0.001 *,W | <0.001 *,W | |||
| Control 1 | Space Opening 2 | Space Closure 3 | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| U1/SN | |||||
| T0 | Mean ± sd | 104.3 ± 3.1 | 100.2 ± 4.5 1 | 98.1 ± 7.5 1 | 0.004 *,A |
| T1 | Mean ± sd | 104.3 + 3.1 2 | 108.2 ± 3.2 | 100.0 ± 7.6 2 | <0.001 *,A |
| T0/T1 Change | Mean ± sd | 8.0 ± 5.7 | 1.9 ± 6.0 | 0.004 *,t | |
| Intra Group Change p | <0.001 *,P | 0.198 P | |||
| U1/NA | |||||
| T0 | Mean ± sd | 24.1 ± 3.6 | 20.2 ± 4.6 | 19.9 ± 6.6 1 | 0.031 *,A |
| T1 | Mean ± sd | 24.1 ± 3.6 | 27.2 ± 4.5 | 24.4 ± 5.7 | 0.099 A |
| T0/T1 Change | Mean ± sd | 7.0 ± 6.6 | 4.4 ± 7.9 | 0.300 t | |
| Intra Group Change p | <0.001 *,P | 0.035 *,P | |||
| U1-ANSPNS | |||||
| T0 | Mean ± sd | 113.7 ± 5.2 | 109.8 ± 5.5 | 107.8 ± 6.31 | 0.012 *,A |
| T1 | Mean ± sd | 113.7 ± 5.2 | 116.6 ± 4.3 | 110.6 ± 6.32 | 0.008 *,A |
| T0/T1 Change | Mean ± sd | 6.8 ± 6.0 | 2.8 ± 6.6 | 0.070 t | |
| Intra Group Change p | <0.001 *,P | 0.106 P | |||
| IMPA | |||||
| T0 | Mean ± sd | 91.5 ± 3.3 | 90.2 ± 5.5 | 86.4 ± 6.5 1 | 0.016 *,A |
| T1 | Mean ± sd | 91.5 ± 3.3 | 92.4 ± 7.2 | 86.9 ± 7.2 2 | 0.025 *,A |
| T0/T1 Change | Mean ± sd | 2.3 ± 4.6 | 0.6 ± 7.4 | 0419 t | |
| Intra Group Change p | 0.051 P | 0.746 P | |||
| Interincisal Angle | |||||
| T0 | Mean ± sd | 130.3 ± 6.5 | 136.9 ± 11.4 | 140.2 ± 9.6 1 | 0.010 *,A |
| T1 | Mean ± sd | 130.3 ± 6.5 | 129.8 ± 9.0 | 134.9 ± 10.7 | 0.194 A |
| T0/T1 Change | Mean ± sd | −7.1 ± 9.0 | −5.3 ± 11.0 | 0.597 t | |
| Intra Group Change p | 0.004 *,P | 0.066 P | |||
| U1–Upper Occlusal Plane | |||||
| T0 | Mean ± sd | 57.6 ± 3.0 | 59.8 ± 4.8 | 62.1 ± 6.3 1 | 0.016 *,A |
| T1 | Mean ± sd | 57.6 ± 3.0 | 55.2 ± 3.2 | 61.4 ± 5.7 1,2 | <0.001 *,A |
| T0/T1 Change | Mean ± sd | −4.6 ± 4.8 | −0.6 ± 7.0 | 0.057 t | |
| Intra Group Change p | 0.001 *,P | 0.707 P | |||
| U1-ANSPNS | |||||
| T0 | Mean ± sd | 113.7 ± 5.2 | 109.8 ± 5.5 | 107.8 ± 6.3 1 | 0.012 *,A |
| T1 | Mean ± sd | 113.7 ± 5.2 | 116.6 ± 4.3 | 110.6 ± 6.3 2 | 0.008 *,A |
| T0/T1 Change | Mean ± sd | 6.8 ± 6.0 | 2.8 ± 6.6 | 0.070 t | |
| Intra Group Change p | <0.001 *,P | 0.106 P | |||
| L1/NB | |||||
| T0 | Mean ± sd | 23.2 ± 4.8 | 20.9 ± 8.5 | 17.9 ± 7.1 | 0.086 A |
| T1 | Mean ± sd | 23.2 ± 4.8 | 21.7 ± 9.1 | 19.2 ± 7.9 | 0.283 A |
| T0/T1 Change | Mean ± sd | 0.8 ± 4.5 | 1.3 ± 7.3 | 0.801 t | |
| Intra Group Change p | 0.471 P | 0.474 P | |||
| Control 1 | Space Opening 2 | Space Closure 3 | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| U1/NA | |||||
| T0 | Mean ± sd | 5.2 ± 1.3 | 3.4 ± 1.9 1 | 3.5 ± 2.1 1 | 0.008 *,K |
| T1 | Mean ± sd | 5.2 ± 1.3 | 6.2 ± 1.8 | 4.5 ± 2.8 2 | 0.008 *,K |
| T0/T1 Change | Mean ± sd | 2.8 ± 2.7 | 1.0 ± 3.2 | 0.075 m | |
| Intra Group Change p | <0.001 *,W | 0.379 W | |||
| L1/NB | |||||
| T0 | Mean ± sd | 4.8 ± 1.6 | 3.1 ± 3.2 | 3.4 ± 2.5 | 0.112 A |
| T1 | Mean ± sd | 4.8 ± 1.6 | 4.0 ± 2.4 | 3.5 ± 2.6 | 0.260 A |
| T0/T1 Change | Mean ± sd | 0.9 ± 1.6 | 0.1 ± 2.1 | 0.207 t | |
| Intra Group Change p | 0.028 *,P | 0.876 P | |||
| Upper Incisor-TVL | |||||
| T0 | Mean ± sd | 12.7 ± 2.1 | 13.7 ± 2.3 | 11.8 ± 4.2 | 0.180 A |
| T1 | Mean ± sd | 12.7 ± 2.1 | 12.2 ± 2.7 | 13.4 ± 3.6 | 0.483 A |
| T0/T1 Change | Mean ± sd | −1.5 ± 2.2 | 1.6 ± 3.1 | 0.002 *,t | |
| Intra Group Change p | 0.011 *,P | <0.050 *,P | |||
| Overjet | |||||
| T0 | Mean ± sd | 3.3 ± 0.42 | 2.4 ± 0.8 | 3.2 ± 1.2 2 | 0.001 *,K |
| T1 | Mean ± sd | 3.3 ± 0.4 | 3.8 ± 0.8 | 3.2 ± 0.9 2 | 0.042 *,K |
| T0/T1 Change | Mean ± sd | 1.5 ± 0.8 | 0.0 ± 1.7 | <0.001 *,M | |
| Intra Group Change p | <0.001 *,W | 0.407 *,W | |||
| Overbite | |||||
| T0 | Mean ± sd | 2.5 ± 0.9 | 2.7 ± 1.4 | 3.1 ± 1.4 | 0.348 K |
| T1 | Mean ± sd | 2.5 ± 0.9 | 2.1 ± 0.9 | 2.4 ± 1.4 | 0.895 K |
| T0/T1 Change | Mean ± sd | −0.6 ± 1.3 | −0.6 ± 1.8 | 0.409 M | |
| Intra Group Change p | 0.067 W | 0.109 W | |||
| Control 1 | Space Opening 2 | Space Closure 3 | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nasolabial Angle | |||||
| T0 | Mean ± sd | 109.5 ± 7.7 | 108.9 ± 7.6 | 109.8 ± 10.2 | 0.953 A |
| T1 | Mean ± sd | 109.5 ± 7.7 | 105.0 ± 9.0 | 110.3 ± 10.3 | 0.180 A |
| T0/T1 Change | Mean ± sd | −3.9 ± 9.7 | 0.5± 10.1 | 0.196 t | |
| Intra Group Change p | 0.102 P | 0.850 P | |||
| Labiomental Angle | |||||
| T0 | Mean ± sd | 121.8 ± 10.3 | 125.2 ± 11.8 | 133.3 ± 16.5 1 | 0.036 *,A |
| T1 | Mean ± sd | 121.8 ± 10.3 | 120.8± 12.6 | 132.6 ± 11.7 1,2 | 0.007 *,A |
| T0/T1 Change | Mean ± sd | −4.4 ± 9.3 | −0.6 ± 13.4 | 0.341 t | |
| Intra Group Change p | 0.062 P | 0.844 P | |||
| Upper Lip Angle | |||||
| T0 | Mean ± sd | 5.1± 4.9 | 4.8 ± 5.7 | 8.2 ± 7.5 | 0.203 A |
| T1 | Mean ± sd | 5.1 ± 0.9 | 8.7 ± 6.0 | 3.8 ± 5.52 | 0.027 *,A |
| T0/T1 Change | Mean ± sd | 3.9 ± 4.5 | −4.4 ± 6.6 | <0.001 *,t | |
| Intra Group Change p | 0.002 *,P | 0.014 *,P | |||
| Upper Lip Length | |||||
| T0 | Mean ± sd | 18.2 ± 2.0 | 17.7 ± 1.3 | 18.0 ± 2.4 | 0.691 A |
| T1 | Mean ± sd | 18.2 ± 2.0 | 18.5 ± 1.9 | 18.6 ± 1.6 | 0.837 A |
| T0/T1 Change | Mean ± sd | 0.8 ± 1.7 | 0.6 ± 2.4 | 0.750 t | |
| Intra Group Change p | 0.062 P | 0.327 P | |||
| Upper Lip Thickness | |||||
| T0 | Mean ± sd | 12.9± 2.1 | 13.1 ± 1.7 | 12.6 ± 3.3 | 0.786 A |
| T1 | Mean ± sd | 12.9 ± 2.1 | 13.3 ± 2.3 | 13.2 ± 2.6 | 0.889 A |
| T0/T1 Change | Mean ± sd | 0.2 ± 1.3 | 0.6 ± 2.9 | 0.551 t | |
| Intra Group Change p | 0.625 P | 0.388 P | |||
| Anterior Upper Lip–TVL | |||||
| T0 | Mean ± sd | 1.4 ± 0.9 | 1.0 ± 1.2 | 1.9 ± 2.3 | 0.230 A |
| T1 | Mean ± sd | 1.4 ± 0.9 | 1.5 ± 1.3 | 1.0 ± 1.2 | 0.347 A |
| T0/T1 Change | Mean ± sd | 0.5 ± 1.3 | −0.9 ± 2.3 | 0.024 *,t | |
| Intra Group Change p | 0.106 P | 0.106 P | |||
| Upper Lip–E Line | |||||
| T0 | Mean ± sd | −4.3 ± 2.5 | −4.3 ± 2.9 | −4.2 ± 1.9 | 0.991 A |
| T1 | Mean ± sd | −4.3 ± 2.5 | −4.2 ± 3.8 | −4.4 ± 1.7 | 0.979 A |
| T0/T1 Change | Mean ± sd | 0.0 ± 2.3 | −0.2 ± 1.5 | 0.711 t | |
| Intra Group Change p | 0.992 P | 0.507 P | |||
| Lower Lip–E Line | |||||
| T0 | Mean ± sd | −2.8 ± 2.3 | −3.1 ± 3.5 | −1.7 ± 2.2 | 0.314 A |
| T1 | Mean ± sd | −2.8 ± 2.3 | −2.9 ± 3.5 | −2.3 ± 2.1 | 0.788 A |
| T0/T1 Change | Mean ± sd | 0.2 ± 1.6 | −0.6 ± 1.5 | 0.146 t | |
| Intra Group Change p | 0.544 P | 0.158 P | |||
| A’-TVL | |||||
| T0 | Mean ± sd | −1.9 ± 0.5 | −2.3 ± 0.7 | −1.2 ± 0.8 1,2 | <0.001 *,A |
| T1 | Mean ± sd | −1.9 ± 0.5 | −2.2 ± 0.9 | −2.1 ± 0.8 | 0.520 A |
| T0/T1 Change | Mean ± sd | 0.1 ± 1.0 | −0.9 ± 0.9 | 0.006 *,t | |
| Intra Group Change p | 0.695 P | 0.001 *,P | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Şenel, T.; Cicek, O. Comparison of Skeletal, Dental, and Soft Tissue Changes Before and After Orthodontic Treatment in Patients with Congenitally Missing Bilateral Maxillary Lateral Incisors. Medicina 2025, 61, 485. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61030485
Şenel T, Cicek O. Comparison of Skeletal, Dental, and Soft Tissue Changes Before and After Orthodontic Treatment in Patients with Congenitally Missing Bilateral Maxillary Lateral Incisors. Medicina. 2025; 61(3):485. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61030485
Chicago/Turabian StyleŞenel, Tuğba, and Orhan Cicek. 2025. "Comparison of Skeletal, Dental, and Soft Tissue Changes Before and After Orthodontic Treatment in Patients with Congenitally Missing Bilateral Maxillary Lateral Incisors" Medicina 61, no. 3: 485. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61030485
APA StyleŞenel, T., & Cicek, O. (2025). Comparison of Skeletal, Dental, and Soft Tissue Changes Before and After Orthodontic Treatment in Patients with Congenitally Missing Bilateral Maxillary Lateral Incisors. Medicina, 61(3), 485. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61030485







