Causes and Clinical Outcomes of Acute Kidney Injury After Cardiac Arrest: A Retrospective Cohort Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Patient Population
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Treatment Protocol
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographics and Clinical and Treatment Data
3.2. Logistics Regression Analysis for AKI
3.3. Logistics Regression Analysis for Mortality
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gräsner, J.T.; Herlitz, J.; Tjelmeland, I.B.M.; Wnent, J.; Masterson, S.; Lilja, G.; Bein, B.; Böttiger, B.W.; Rosell-Ortiz, F.; Nolan, J.P.; et al. European Resuscitation Council Guidelines 2021: Epidemiology of cardiac arrest in Europe. Resuscitation 2021, 161, 61–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stirparo, G.; Andreassi, A.; Sechi, G.M.; Signorelli, C. Spring, it’s time to ROSC. J. Prev. Med. Hyg. 2023, 64, E87–E91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Nolan, J.P.; Sandroni, C.; Böttiger, B.W.; Cariou, A.; Cronberg, T.; Friberg, H.; Genbrugge, C.; Haywood, K.; Lilja, G.; Moulaert, V.R.M.; et al. European Resuscitation Council and European Society of Intensive Care Medicine guidelines 2021: Post-resuscitation care. Intensive Care Med. 2021, 47, 369–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kalogeris, T.; Baines, C.P.; Krenz, M.; Korthuis, R.J. Ischemia/Reperfusion. Compr. Physiol. 2016, 7, 113–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Jeppesen, K.K.; Rasmussen, S.B.; Kjaergaard, J.; Schmidt, H.; Mølstrøm, S.; Beske, R.P.; Grand, J.; Ravn, H.B.; Winther-Jensen, M.; Meyer, M.A.S.; et al. Acute kidney injury after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. Crit. Care 2024, 28, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDougal, W.S. Renal perfusion/reperfusion injuries. J. Urol. 1988, 140, 1325–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemiale, V.; Dumas, F.; Mongardon, N.; Giovanetti, O.; Charpentier, J.; Chiche, J.-D.; Carli, P.; Mira, J.-P.; Nolan, J.; Cariou, A. Intensive care unit mortality after cardiac arrest: The relative contribution of shock and brain injury in a large cohort. Intensive Care Med. 2013, 39, 1972–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adler, C.; Reuter, H.; Seck, C.; Hellmich, M.; Zobel, C. Fluid therapy and acute kidney injury in cardiogenic shock after cardiac arrest. Resuscitation 2013, 84, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khwaja, A. KDIGO clinical practice guidelines for acute kidney injury. Nephron Clin. Pract. 2012, 120, c179–c184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patyna, S.; Riekert, K.; Buettner, S.; Wagner, A.; Volk, J.; Weiler, H.; Erath-Honold, J.W.; Geiger, H.; Fichtlscherer, S.; Honold, J. Acute kidney injury after in-hospital cardiac arrest in a predominant internal medicine and cardiology patient population: Incidence, risk factors, and impact on survival. Ren. Fail. 2021, 43, 1163–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Tujjar, O.; Mineo, G.; Dell’Anna, A.; Poyatos-Robles, B.; Donadello, K.; Scolletta, S.; Vincent, J.-L.; Taccone, F.S. Acute kidney injury after cardiac arrest. Crit. Care 2015, 19, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sabaz, M.S.; Aşar, S.; Sertçakacılar, G.; Sabaz, N.; Çukurova, Z.; Hergünsel, G.O. The effect of body mass index on the development of acute kidney injury and mortality in intensive care unit: Is obesity paradox valid? Ren. Fail. 2021, 43, 543–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, S.; Lee, T.W.; Yoo, J.W.; Lee, S.J.; Cho, Y.J.; Jeong, Y.Y.; Lee, J.D.; Kim, J.-Y.; Lee, G.D.; Kim, H.C. Body Mass Index as a Predictor of Acute Kidney Injury in Critically Ill Patients: A Retrospective Single-Center Study. Tuberc. Respir. Dis. 2018, 81, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto, G.J.; Frank, A.J.; Christiani, D.C.; Gong, M.N. Body mass index and acute kidney injury in the acute respiratory distress syndrome. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 40, 2601–2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danziger, J.; Chen, K.P.; Lee, J.; Feng, M.; Mark, R.G.; Celi, L.A.; Mukamal, K.J. Obesity, Acute Kidney Injury, and Mortality in Critical Illness. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 44, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Adrie, C.; Adib-Conquy, M.; Laurent, I.; Monchi, M.; Vinsonneau, C.; Fitting, C.; Fraisse, F.; Dinh-Xuan, A.T.; Carli, P.; Cavaillon, J.-M.; et al. Successful cardiopulmonary resuscitation after cardiac arrest as a “sepsis-like” syndrome. Circulation 2002, 106, 562–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adrie, C.; Laurent, I.; Monchi, M.; Cariou, A.; Dhainaou, J.F.; Spaulding, C. Postresuscitation disease after cardiac arrest: A sepsis-like syndrome? Curr. Opin. Crit. Care 2004, 10, 208–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huet, O.; Dupic, L.; Batteux, F.; Matar, C.; Conti, M.; Chereau, C.; Lemiale, V.; Harrois, A.; Mira, J.-P.; Vicaut, E.; et al. Postresuscitation syndrome: Potential role of hydroxyl radical-induced endothelial cell damage. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 39, 1712–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cha, K.C.; Kim, H.I.; Kim, O.H.; Cha, Y.S.; Kim, H.; Lee, K.H.; Hwang, S.O. Echocardiographic patterns of postresuscitation myocardial dysfunction. Resuscitation 2018, 124, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stirparo, G.; Bellini, L.; Ristagno, G.; Bonora, R.; Pagliosa, A.; Migliari, M.; Andreassi, A.; Signorelli, C.; Sechi, G.M.; Fagoni, N. The Impact of COVID-19 on Lombardy Region ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction Emergency Medical System Network-A Three-Year Study. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rattka, M.; Dreyhaupt, J.; Winsauer, C.; Stuhler, L.; Baumhardt, M.; Thiessen, K.; Rottbauer, W.; Imhof, A. Effect of the COVID-19 pandemic on mortality of patients with STEMI: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Heart 2020, 107, 482–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadim, M.K.; Forni, L.G.; Mehta, R.L.; Connor, M.J., Jr.; Liu, K.D.; Ostermann, M.; Rimmelé, T.; Zarbock, A.; Bell, S.; Bihorac, A.; et al. COVID-19-Associated Acute Kidney Injury: Consensus Report of the 25th Acute Disease Quality Initiative (ADQI) Workgroup. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2020, 16, 747–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chávez-Valencia, V.; Orizaga-de-la-Cruz, C.; Lagunas-Rangel, F.A. Acute Kidney Injury in COVID-19 Patients: Pathogenesis, Clinical Characteristics, Therapy, and Mortality. Diseases 2022, 10, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Andersen, L.W.; Holmberg, M.J.; Berg, K.M.; Donnino, M.W.; Granfeldt, A. In-Hospital Cardiac Arrest: A Review. JAMA 2019, 321, 1200–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Stankovic, N.; Høybye, M.; Holmberg, M.J.; Lauridsen, K.G.; Andersen, L.W. Asger Granfeldt, Factors associated with shockable versus non-shockable rhythms in patients with in-hospital cardiac arrest. Resuscitation 2021, 158, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nabi, Z.; Anjum, N.; Rashid, R.M.; Zahideen, Z.U. Contrast Induced Nephropathy in High Risk Patients—Myth or Reality. J. Ayub Med. Coll. Abbottabad 2021, 33, 568–571. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Qiu, H.; Zhu, Y.; Shen, G.; Wang, Z.; Li, W.A. Predictive Model for Contrast-Induced Acute Kidney Injury After Percutaneous Coronary Intervention in Elderly Patients with ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction. Clin. Interv. Aging 2023, 18, 453–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Patil, V.P.; Salunke, B.G. Fluid Overload and Acute Kidney Injury. Indian J. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 24 (Suppl. S3), S94–S97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
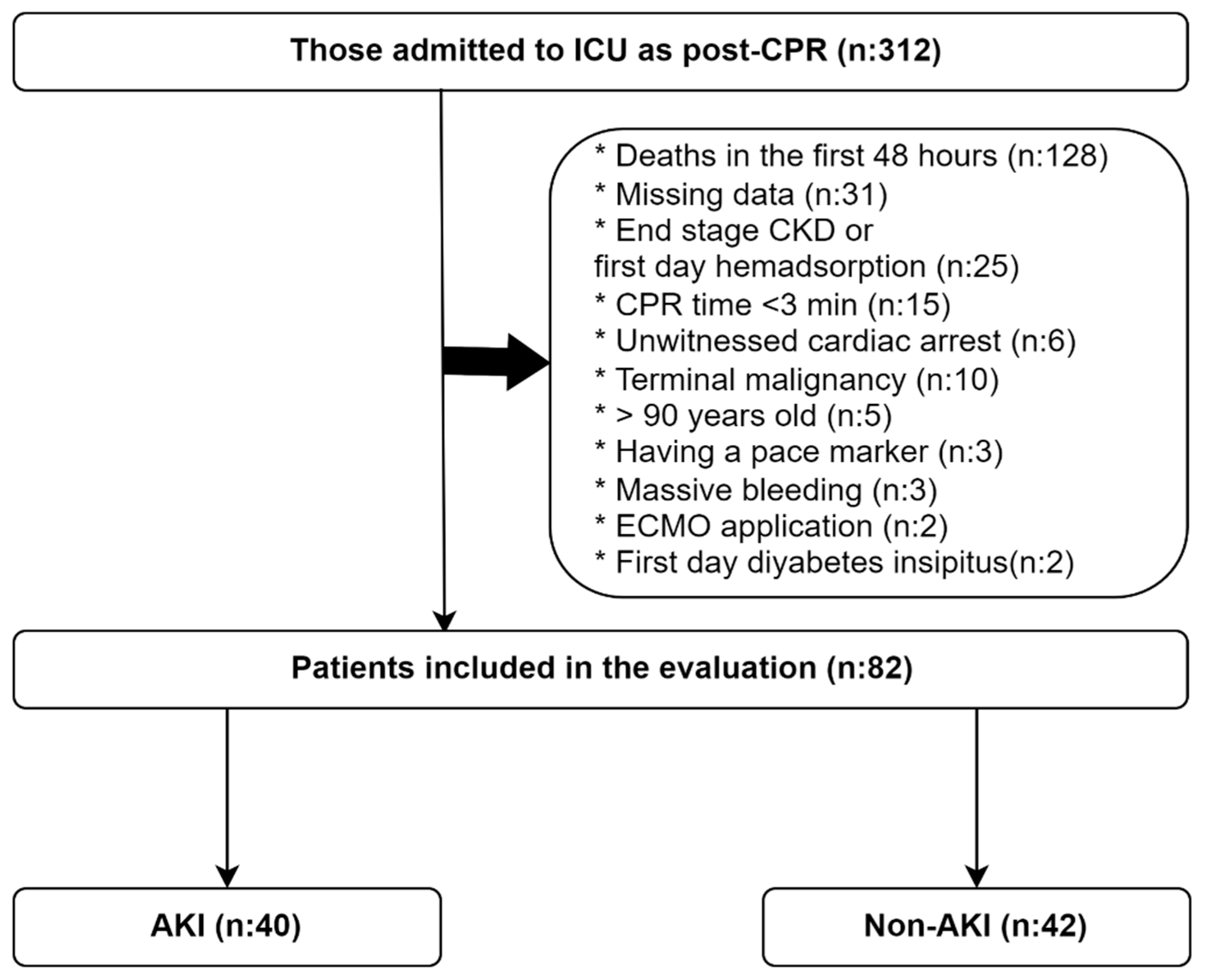
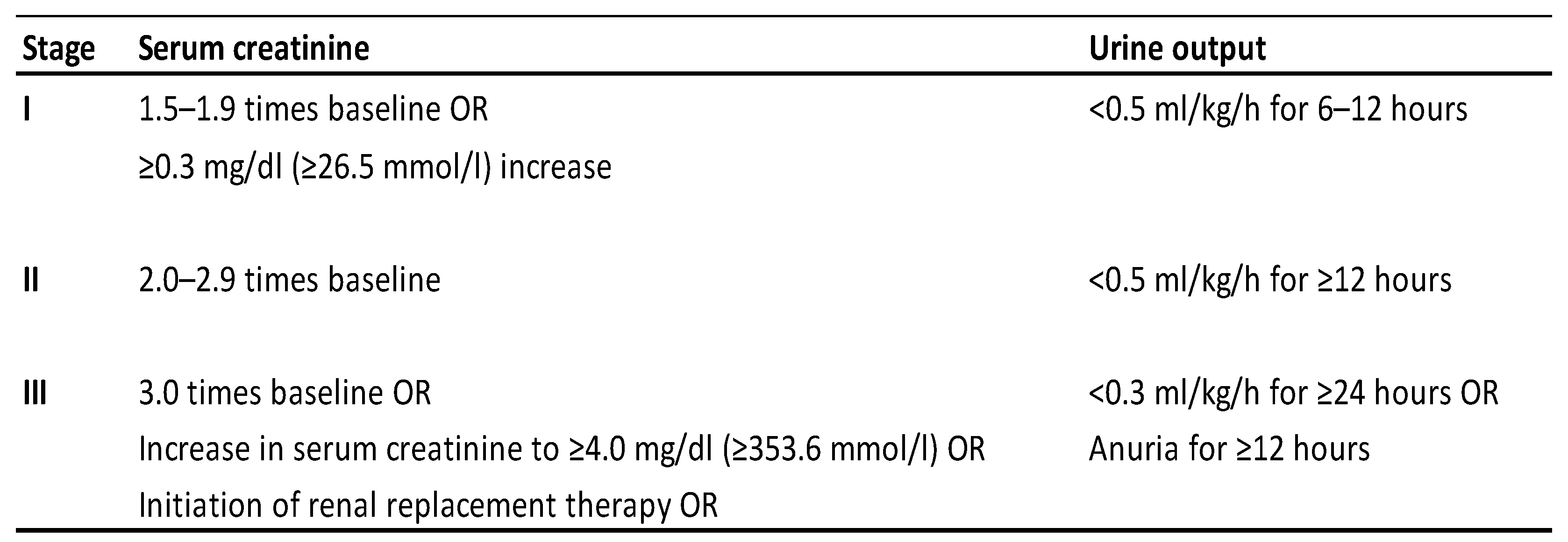
| AKI (n: 40) | non-AKI (n: 42) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cardiac arrest place (in-hospital), n (%) | 32 (80.0) | 30 (71.4) | 0.518 |
| ICU transfer place (emergency depart), n (%) | 26 (65.0) | 26 (61.9) | 0.951 |
| Cardiac arrest etiology, n (%) | |||
| Acute coronary syndrome | 20 (50.0) | 20 (47.6) | 1.000 |
| Respiratory (pneumonia, sepsis) | 15 (37.5) | 12 (28.6) | 0.947 |
| Neurological | 3 (7.5) | 4 (9.5) | |
| Heart failure | 1 (2.5) | 3 (7.1) | |
| Toxemia | 0 (0) | 2 (4.8) | |
| Pulmonary embolism | 1 (2.5) | 1 (2.4) | |
| COVID period, n (%) | 24 (60) | 15 (35.7) | 0.048 * |
| CPR time (minute), median (IQR) | 15 (10–22) | 15 (10–28) | 0.877 |
| AKI (n: 40) | non-AKI (n: 42) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, median (IQR) | 60 (52–71) | 60 (42–70) | 0.623 |
| Gender (male), n (%) | 24 (60.0) | 29 (69.0) | 0.532 |
| Body mass index, median (IQR) | 27.4 (24.7–34.0) | 24.2 (22.9–26.7) | 0.001 * |
| Charlson comorbidity index, median (IQR) | 3.0 (2.0–5.0) | 3.5 (2.0–5.0) | 0.948 |
| Heart rate (first 1 day average), median (IQR) | 85 (74–106) | 80 (70–96) | 0.199 |
| MAP (first 1 day average), median (IQR) | 78 (70–84) | 81 (71–88) | 0.285 |
| Admission APACHE-II score, median (IQR) | 28 (19–32) | 21 (17–26) | 0.003 * |
| Admission PaO2/FiO2 ratio, median (IQR) | 163 (108–300) | 206 (141–352) | 0.095 |
| Neurological evaluation (3–4. day), n (%) | |||
| GCS (motor < 4), | 22 (55.0) | 10 (23.8) | 0.008 * |
| Pupillary reflex negativity | 5 (12.5) | 4 (9.5) | 0.735 |
| Serum creatinine, median (IQR) | |||
| Basal level | 1.1 (0.8–1.3) | 1.0 (0.7–1.3) | 0.450 |
| After CPR (2 day after) | 1.8 (1.2–3.0) | 0.8 (0.6–1.0) | <0.001 |
| ICU Admission lab parameters, median (IQR) | |||
| pH | 7.18 (7.11–7.30) | 7.29 (7.16–7.36) | 0.015 * |
| pCO2 (mmHg) | 50 (39–66) | 45 (38–51) | 0.177 |
| HCO3− (mmol/L) | 17.5 (13.0–20.0) | 19.0 (16.0–23.0) | 0.042 * |
| Lactate (mmol/L) | 4.3 (3.2–6.7) | 3.3 (1.9–4.8) | 0.021 * |
| Phosphorus (mmol/L) | 5.3 (4.0–7.3) | 4.0 (3.0–5.3) | 0.005 * |
| Na (mmol/L) | 137 (134–139) | 137 (134–140) | 0.696 |
| K (mmol/L) | 4.3 (3.4–4.6) | 4.0 (3.7–4.5) | 0.967 |
| CI (mmol/L) | 102 (98–108) | 102 (99–107) | 0.967 |
| AST (U/L) | 197 (65–482) | 127 (54–240) | 0.180 |
| ALT (U/L) | 89 (34–243) | 74 (41–163) | 0.728 |
| WBC (×109/L) | 20.6 (13.3–27.4) | 15.5 (13.0–24.4) | 0.344 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 13.9 (10.9–14.8) | 12.8 (11.0–15.1) | 0.893 |
| Platelet (×109/L) | 283 (192–364) | 262 (226–354) | 0.735 |
| CRP (mg/L) | 11.4 (3.0–67.8) | 8.9 (1.5–76.6) | 0.578 |
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 250 (184–389) | 277 (168–321) | 0.384 |
| Creatine kinase (max within 48 h) | 708 (204–3104) | 495 (102–1892) | 0.168 |
| AKI (n: 40) | non-AKI (n: 52) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| After 24 h fluid status (Liter), median (IQR) | |||
| Input | 3.0 (1.7–4.4) | 3.0 (2.5–4.0) | 0.564 |
| Output | 1.0 (0.4–2.8) | 1.9 (1.4–2.7) | 0.001 * |
| Balance | 1.5 (0.9–3.1) | 0.9 (0.0–2.1) | 0.033 * |
| First 24 h VSP and/or INO need, n (%) | |||
| No VSP/INO | 1 (2.5) | 13 (31.0) | <0.001 * |
| VSP (n: 44) or INO (n: 4) | 24 (60.0) | 24 (57.1) | |
| VSP and INO | 15 (37.5) | 5 (11.9) | |
| First 24 h max body temperature, median (IQR) | 37.5 (37–38.4) | 37.4 (36.5–38.0) | 0.314 |
| TTM therapy, n (%) | 4 (10.0) | 9 (21.4) | 0.265 |
| Continuous RRT in-ICU | 7 (17.5) | 5 (11.9) | 0.686 |
| ICU LOS (day), median (IQR) | 5.6 (3.2–9.7) | 9.3 (5.7–16.0) | 0.020 * |
| In ICU mortality, n (%) | 26 (65.0) | 11 (26.2) | 0.001 * |
| OR (95%CI) | OR (95%CI) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Univariable Analysis | p | Multivariable Analysis | p | |
| Age | 1.015 (0.987–1.043) | 0.297 | ||
| Male gender | 0.672 (0.271–1.671) | 0.393 | ||
| BMI | 1.153 (1.038–1.280) | 0.008 * | 1.272 (1.089–1486) | 0.002 * |
| CCI | 1.037 (0.835–1.289) | 0.742 | ||
| CPR time | 1.001 (0.966–1.038) | 0.946 | ||
| Etiology | ||||
| The others (n: 42) | Reference category | |||
| ACS (n: 40) | 1.100 (0.462–2.616) | 0.829 | ||
| COVID-19 period | 2.700 (1.105–6.599) | 0.029 * | 2.801 (0.859–9.126) | 0.088 |
| Cardiac arrest place | ||||
| In-Hospital (n: 62) | Reference category | |||
| Out-of-Hospital (n: 20) | 0.625 (0.224–1.740) | 0.368 | ||
| HR (first 1 day average) | 1.014 (0.992–1037) | 0.210 | ||
| MAP (first 1 day average) | 0.977 (0.934–1021) | 0.291 | ||
| VSP and INO need | ||||
| No VSP or INO (n: 14) | Reference category | Reference category | ||
| VSP or INO (n: 48) | 13.000 (1.574–107.354) | 0.017 * | 14.225 (1.172–172.669) | 0.037 * |
| VSP and INO (n: 20) | 39.000 (4.022–378.199) | 0.002 * | 42.089 (2.683–660.201) | 0.008 * |
| TTM therapy | ||||
| Yes (n: 13) | Reference category | |||
| No (n: 79) | 2.455 (0.690–8.731) | 0.165 | ||
| Admission Lab Parameters | ||||
| Phosphorus | 1.367 (1.086–1.719) | 0.008 * | 1.237 (0.951–1.609) | 0.113 |
| Creatinine | 0.884 (0.251–2.223) | 0.793 | ||
| pH | 0.021 (0.001–0.641) | 0.027 * | ||
| Lactate | 1.263 (1.045–1.526) | 0.016 * | 1.161 (0.910–1.481) | 0.230 |
| WBC | 1.023 (0.978–1070) | 0.315 | ||
| Hemoglobin | 1.006 (0.857–1.181) | 0.942 | ||
| PaO2/FiO2 ratio | 0.998 (0.994–1.001) | 0.223 | ||
| Glucose | 1.001 (0.998–1.005) | 0.416 | ||
| Fluid Input | 0.993 (0.806–1.224) | 0.950 |
| OR (95%CI) | OR (95%CI) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Univariable Analysis | p | Multivariable Analysis | p | |
| Age | 0.989 (0.963–1.016) | 0.414 | ||
| Male Gender (n: 53) | 0.662 (0.266–1.646) | 0.375 | ||
| CCI | 0.819 (0.651–1.030) | 0.087 | ||
| BMI | 1.043 (0.983–1.107) | 0.160 | ||
| CPR time | 0.992 (0.957–1.029) | 0.681 | ||
| Cardiac arrest causes | ||||
| Non-ACS (n: 42) | Reference category | |||
| ACS (n: 40) | 0.545 (0.226–1.317) | 0.178 | ||
| Cardiac arrest place | ||||
| In-Hospital (n: 62) | Reference category | |||
| Out-of-Hospital (n: 20) | 1.741 (0.612–4.951) | 0.298 | ||
| HR (first 1 day average) | 1.032 (1007–1058) | 0.010* | ||
| MAP (first 1 day average) | 0.979 (0.937–1023) | 0.351 | ||
| VSP and INO need | ||||
| No VSP or INO | Reference category | |||
| VSP or INO | 4.667 (0.940–23.158) | 0.059 | 2.863 (0.497–16.495) | 0.239 |
| VSP and INO | 14.000 (2.370–82.717) | 0.004 * | 8.455 (1.132–63,160) | 0.037 * |
| AKI 1–3 | 5.234 (2.032–13.482) | 0.001 * | 2.194 (0.700–6.872) | 0.178 |
| GCS motor response < 4 | 5.133 (1.962–13.428) | 0.001 * | 5.004 (1.590–15.750) | 0.006 * |
| Pupillary reflex negativity | 12.138 (1.441–102.247) | 0.022 * | ||
| No TTM therapy | 3.238 (0.820–12.792) | 0.094 | ||
| Admission Lab Parameters | ||||
| Lactate | 1.239 (1.032–1.488) | 0.022 * | ||
| PaO2/FiO2 ratio | 0.995 (0.992–0.999) | 0.023 * | 0.995 (0.990–0.999) | 0.025 * |
| WBC | 1.005 (0.962–1.049) | 0.838 | ||
| Hemoglobin | 0.854 (0.721–1.011) | 0.066 | ||
| Glucose | 1.000 (0.996–1.003) | 0.982 | ||
| Fluid Input | 1.241 (0.965–1.594) | 0.092 | ||
| CRRT therapy | 2.828 (0.778–10.282) | 0.115 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aslan, M.; Yılmaz, R.; Birtane, D.; Çukurova, Z. Causes and Clinical Outcomes of Acute Kidney Injury After Cardiac Arrest: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Medicina 2025, 61, 338. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61020338
Aslan M, Yılmaz R, Birtane D, Çukurova Z. Causes and Clinical Outcomes of Acute Kidney Injury After Cardiac Arrest: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Medicina. 2025; 61(2):338. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61020338
Chicago/Turabian StyleAslan, Murat, Rabia Yılmaz, Dicle Birtane, and Zafer Çukurova. 2025. "Causes and Clinical Outcomes of Acute Kidney Injury After Cardiac Arrest: A Retrospective Cohort Study" Medicina 61, no. 2: 338. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61020338
APA StyleAslan, M., Yılmaz, R., Birtane, D., & Çukurova, Z. (2025). Causes and Clinical Outcomes of Acute Kidney Injury After Cardiac Arrest: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Medicina, 61(2), 338. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61020338








