Effects of Exercise on Sarcopenia and Frailty in Haemodialysis Patients: A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Search Strategy
2.3. Eligibility Criteria
- -
- Population: Participants with chronic kidney disease, over 18 years old and receiving haemodialysis treatment.
- -
- Intervention: Interventions that carried out intradialytic exercise programmes.
- -
- Comparison: Control groups where the participants continued with their haemodialysis treatment but did not performed exercise during haemodialysis.
- -
- Outcome measures: Variables measuring sarcopenia and frailty. Frailty was assessed using variables related to physical function, including the 6 min walk test (6 MWT), the Short Physical Performance Battery (SPPB), and gait speed. Sarcopenia was evaluated through body composition and strength-related measures, such as body mass index (BMI), handgrip strength, and lower limb strength. The sit-to-stand test was considered the most specific functional measure for sarcopenia, while also serving as an indicator of frailty.
- -
- Type of studies: clinical trials and randomized controlled trials published in the last 10 years in Spanish or English, which included at least two study outcome measures.
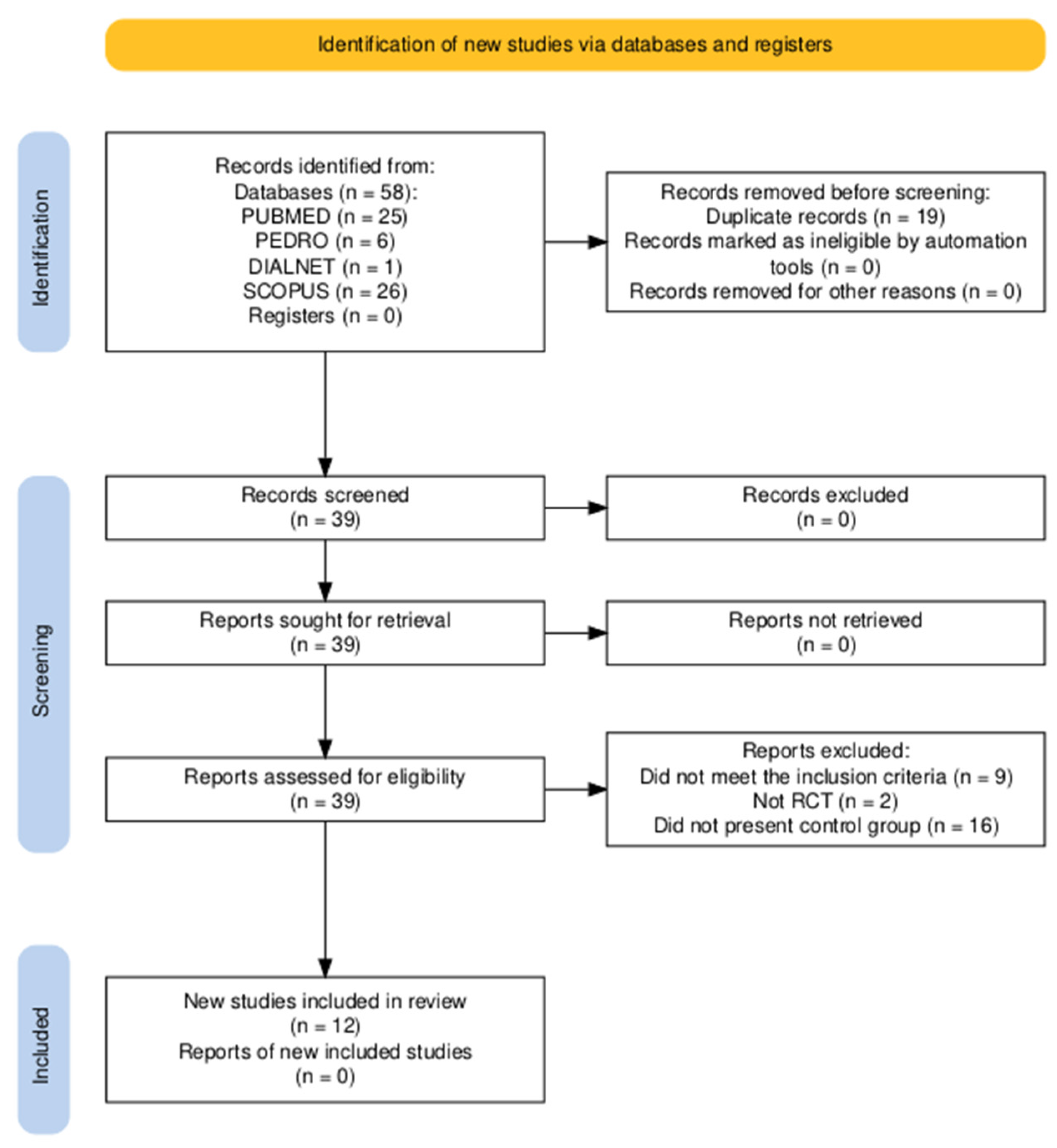
2.4. Selection of Studies
2.5. Methodological Quality Analysis
2.6. Risk of Bias Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Sociodemographic and Methodological Characteristics
3.2. Results Related to Variables and Study Outcomes
3.2.1. Physical Function
3.2.2. Muscle Strength
3.2.3. Frailty
3.3. Methodological Quality of the Articles
3.4. Risk of Bias
4. Discussion
Limitations of the Review
5. Conclusions
- Implementing intradialytic exercise programmes could be beneficial for patients with chronic kidney disease.
- Intradialytic exercise could improve frailty and sarcopenia in patients with chronic kidney disease.
- Intradialytic exercise programmes should be conducted two or three times per week, during 3 to 12 months and should include aerobic or resistance training to achieve better improvements.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gómez, M.F.L.; Gómez, P.F.; Núñez, J.F.M. Nefrología y Urología; Ediciones Universidad de Salamanca: Plaza de San Benito, Salamanca, 2021. Available online: https://dialnet.unirioja.es/servlet/libro?codigo=79383 (accessed on 30 August 2025).
- Arroyo, R.A.; Martínez, L.O.; González, A.O. Enfermedad renal crónica avanzada. Nefrología 2008, 28, 3–6. [Google Scholar]
- Ávila-Saldivar, M.N. Enfermedad renal crónica: Prevención y detección temprana en el primer nivel de atención. Med. Interna México 2013, 29, 148–153. [Google Scholar]
- Vaidya, S.R.; Aeddula, N.R. Chronic Kidney Disease. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK535404/ (accessed on 30 November 2024).
- Sánchez Tocino, M.L.; Cigarrán, S.; Ureña, P.; González Casaus, M.L.; Mas-Fontao, S.; Gracia Iguacel, C.; Ortízg, A.; Gonzalez Parra, E. Definición y evolución del concepto de sarcopenia. Nefrol. Publ. Soc. Esp. Nefrol. 2024, 44, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anker, S.D.; Morley, J.E.; von Haehling, S. Welcome to the ICD-10 code for sarcopenia. J. Cachex. Sarcopenia Muscle 2016, 7, 512–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Dominguez, B.; Lopez-Brull, A.; Perpiña-Martinez, S.; Casaña, J.; Rodriguez-Rodriguez, A.M.; Blanco-Diaz, M. A dataset of the effects of therapeutic exercise programs on physical function in patients undergoing hemodialysis. Data Brief 2023, 48, 109048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Sáez, M.J.; Gutiérrez-Dalmau, Á.; Moreso, F.; Mañas, L.R.; Pascual, J. La fragilidad en candidatos a trasplante renal. Nefrología 2021, 41, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, F.C.; Ranhoff, A.H. Frailty and Sarcopenia. In Orthogeriatrics: The Management of Older Patients with Fragility Fractures, 2nd ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK565582/ (accessed on 15 June 2025).
- Villanego, F.; Naranjo, J.; Vigara, L.A.; Cazorla, J.M.; Montero, M.E.; García, T.; Torrado, J.; Mazuecos, A. Impacto del ejercicio físico en pacientes con enfermedad renal crónica: Revisión sistemática y metaanálisis. Nefrología 2020, 40, 237–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, L.A.; March, D.S.; Wilkinson, T.J.; Billany, R.E.; Bishop, N.C.; Castle, E.M.; Chilcot, J.; Davies, M.D.; Graham-Brown, M.P.M.; Greenwood, S.A.; et al. Clinical practice guideline exercise and lifestyle in chronic kidney disease. BMC Nephrol. 2022, 23, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clyne, N.; Anding-Rost, K. Exercise training in chronic kidney disease-effects, expectations and adherence. Clin. Kidney J. 2021, 14, ii3–ii14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutton, B.; Catalá-López, F.; Moher, D. La extensión de la declaración PRISMA para revisiones sistemáticas que incorporan metaanálisis en red: PRISMA-NMA. Med. Clin. 2016, 147, 262–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-Y.; Han, H.-M.; Huang, M.-C.; Chen, Y.-M.; Yu, W.-P.; Weng, L.-C. Effect of qigong training on fatigue in haemodialysis patients: A non-randomized controlled trial. Complement. Ther. Med. 2014, 22, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escala PEDro. PEDro—Physiotherapy Evidence Database. PEDro. 2016. Available online: https://pedro.org.au/spanish/resources/pedro-scale/ (accessed on 24 July 2025).
- HHiggins, J.P.T.; Altman, D.G.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Jüni, P.; Moher, D.; Oxman, A.D.; Savović, J.; Schulz, K.F.; Weeks, L.; Sterne, J.A.C.; et al. The Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 2011, 343, d5928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardoso, R.K.; Araujo, A.M.; Del Vechio, F.B.; Bohlke, M.; Barcellos, F.C.; Oses, J.P.; de Freitas, M.P.; Rombaldi, A.J. Intradialytic exercise with blood flow restriction is more effective than conventional exercise in improving walking endurance in hemodialysis patients: A randomized controlled trial. Clin. Rehabilit. 2020, 34, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krase, A.A.; Terzis, G.; Giannaki, C.D.; Stasinaki, A.N.; Wilkinson, T.J.; Smith, A.C.; Zorz, C.; Karatzaferi, C.; Stefanidis, I.; Sakkas, G.K. Seven months of aerobic intradialytic exercise training can prevent muscle loss in haemodialysis patients: An ultrasonography study. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2022, 54, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhardjono; Umami, V.; Tedjasukmana, D.; Setiati, S. The effect of intradialytic exercise twice a week on the physical capacity, inflammation, and nutritional status of dialysis patients: A randomized controlled trial. Hemodial. Int. 2019, 23, 486–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yabe, H.; Kono, K.; Yamaguchi, T.; Yamada, N.; Ishikawa, Y.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Azekura, H. Effect of intradialytic exercise on geriatric issues in older patients undergoing hemodialysis: A single-center non-randomized controlled study. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2022, 54, 2939–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yabe, H.; Kono, K.; Yamaguchi, T.; Ishikawa, Y.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Azekura, H. Effects of intradialytic exercise for advanced-age patients undergoing hemodialysis: A randomized controlled trial. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0257918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Huang, L.; Wang, W.; Shen, Q.; Zhang, H. Effect of intradialytic progressive resistance exercise on physical fitness and quality of life in maintenance haemodialysis patients. Nurs. Open 2020, 7, 1945–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamshidpour, B.; Bahrpeyma, F.; Khatami, M.-R. The effect of aerobic and resistance exercise training on the health related quality of life, physical function, and muscle strength among hemodialysis patients with Type 2 diabetes. J. Bodyw. Mov. Ther. 2020, 24, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogiatzaki, E.; Michou, V.; Liakopoulos, V.; Roumeliotis, A.; Roumeliotis, S.; Kouidi, E.; Deligiannis, A. The effect of a 6-month intradialytic exercise program on hemodialysis adequacy and body composition: A randomized controlled trial. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2022, 54, 2983–2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assawasaksakul, N.; Sirichana, W.; Joosri, W.; Kulaputana, O.; Eksakulkla, S.; Ketanun, C.; Kittiskulnam, P.; Chantadisai, M.; Takkavatakarn, K.; Susantitaphong, P.; et al. Effects of intradialytic cycling exercise on daily physical activity, physical fitness, body composition, and clinical parameters in high-volume online hemodiafiltration patients: A pilot randomized-controlled trial. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2021, 53, 359–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michou, V.; Davioti, M.; Syrakou, N.; Liakopoulos, V.; Deligiannis, A.; Kouidi, E. Effects of a Combined Intradialytic Exercise Training Program on Functional Capacity and Body Composition in Kidney Transplant Candidates. J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2023, 8, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdo, A.L.; Sens, Y.A.D.S.; Miorin, L.A.; Xavier, V.B.; Fernandes, A.D.O.; Alves, V.L.D.S. Quadriceps muscle strength after training with a cycloergometer in patients on hemodialysis. Fisioter. Em Mov. 2019, 32, e003237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, M.-L.; Wang, M.-H.; Hsu, C.-C.; Liu, Y.-M. Twelve-week intradialytic cycling exercise improves physical functional performance with gain in muscle strength and endurance: A randomized controlled trial. Clin. Rehabilit. 2020, 34, 916–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Zhou, W.; Sun, Q.; Zhai, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Su, H.; Wang, Z. Effects of intradialytic resistance exercises on physical performance, nutrient intake and quality of life among haemodialysis people: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nurs. Open 2021, 8, 529–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bündchen, D.C.; Sousa, H.; Afreixo, V.; Frontini, R.; Ribeiro, O.; Figueiredo, D.; Costa, E. Intradialytic exercise in end-stage renal disease: An umbrella review of systematic reviews and/or meta-analytical studies. Clin. Rehabilit. 2021, 35, 812–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Park, H.J.; Yang, D.H. An intradialytic aerobic exercise program ameliorates frailty and improves dialysis adequacy and quality of life among hemodialysis patients: A randomized controlled trial. Kidney Res. Clin. Pract. 2022, 41, 462–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, E.; Aragoncillo, I.; Moreno, J.; Vega, A.; Abad, S.; García-Prieto, A.; Macias, N.; Hernandez, A.; Godino, M.T.; Luño, J. Exercise training during hemodialysis sessions: Physical and biochemical benefits. Ther. Apher. Dial. 2020, 24, 648–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaovarin, C.; Chaiprasert, A.; Satirapoj, B.; Nata, N.; Kaewput, W.; Tangwonglert, T.; Varothai, N.; Thimachai, P.; Tasanavipas, P.; Inkong, P.; et al. Effect of intradialytic weight resistance training exercise in sarcopenic hemodialysis patients: A randomized controlled trial. Ther. Apher. Dial. 2023, 28, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Database | Search Strategy |
|---|---|
| PubMed | Haemodialysis AND physiotherapy. Haemodialysis AND physiotherapy were combined with muscle strength, exercise using the operator AND. Haemodialysis combined using the operator AND with exercise, weakness, muscle strength, functional physical performance, chronic kidney disease, hand grip strength. End-stage renal disease AND exercise and physiotherapy. |
| Scopus | Haemodialysis combined with the operator AND with the following words: short physical performance, hand grip strength, body mass index, exercise frailty phenotype fried gait speed test, physical performance, and exercise. |
| PEDro | Haemodialysis AND physiotherapy. Haemodialysis AND physiotherapy were combined with muscle strength, exercise using the operator AND. Haemodialysis combined using the operator AND with exercise, weakness, muscle strength, functional physical performance, chronic kidney disease, hand grip strength. End-stage renal disease AND exercise and physiotherapy. |
| Author | Mean Age | Sample Size | Type of Intervention | Assessment Tools | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cardoso et al. [17] | CG = 49.4, GEA = 59.8, GEARF = 49.4 | N = 59. CG = 20 (11M, 9H). GEA = 20 (9M, 11H). GEARF = 19 (10M, 9H). | CG: HD without exercise. GEA: Intradialytic aerobic cycling with cycle ergometer. Duration: 3 months. Sessions: 20 min, 3×/week. GEARF: Same as GEA but with blood flow restriction. | 6 MWT. Static leg strength test. | Intradialytic cycling program with blood flow restriction produced a significant increase in distance walked in 6 min in the flow restriction group. |
| Krase et al. [18] | CG = 68.26, GEA = 66.24 | N = 44. CG = 23 (13M, 10H). GEA = 21 (5M, 16H). | CG: Standard HD care. GEA: Intradialytic aerobic cycling with cycle ergometer. Duration: 4 weeks. Sessions: 60 min, 3×/week. | 6 MWT. STS. Handgrip strength. Physical activity with pedometer. Muscle architecture with ultrasound. | Intradialytic cycling produced significant improvements in physical performance, 6 MWT, and handgrip strength in the exercise group. |
| Suhardjono et al. [19] | CG = 50.54, EG = 49.78, GEC = 46.38 | N = 123. CG = 41 (21M, 18H). GEA = 42 (14M, 28H). GEC = 40 (18M, 21H). | CG: HD treatment. GEA: Aerobic cycling program. GEC: Intradialytic aerobic cycling and resistance exercise. No follow-up post-program. | Upper limb muscle strength with hand dynamometer. Lower limb muscle strength with hand dynamometer; 4 m gait speed. Skeletal muscle mass index via bioimpedance. | Aerobic intradialytic cycling generated significant improvements in lower limb strength in the exercise groups. No significant differences between exercise groups. |
| Yabe et al. [20] | CG = 75.3, GEC = 74.3 | N = 83. CG = 19 (4M, 15H). GEC = 27 (13M, 14H). | CG: HD treatment. GEC: Aerobic exercise with cycle ergometer and resistance exercise with elastic bands. Duration: 1 year. Sessions: 30 min, 3×/week. No follow-up post-program. | Handgrip strength with dynamometer; 10 m gait speed. Lower limb strength with dynamometer. SPPB. GDS scale. Frailty: QMCOO questionnaire. | Control group experienced a significant decline in handgrip strength and gait speed. Exercise group showed no evidence of improvements in physical function. |
| Yabe et al. [21] | CG = 79, GEC = 78.7 | N = 84. CG = 40 (19M, 21H). GEC = 44 (18M, 26H). | CG: HD with standard care. GEC: Aerobic cycling and resistance exercise with bands. Duration: 6 months. Sessions: 30–40 min, 3×/week. No follow-up post-program. | Lower limb strength with dynamometer. SPPB; 10 m gait speed. | Significant improvements in physical performance were obtained in the exercise group. No significant improvements in strength and gait speed between groups. |
| Zhang et al. [22] | CG = 62, GER = 60 | N = 83. CG = 40 (16M, 27H). GER = 43 (18M, 26H). | CG: One HD session. GER: Progressive resistance exercises. Duration: 3 weeks. Sessions: 40–50 min, increased from 2 to 3×/week. No follow-up post-program. | 6 MWT. STS. Handgrip strength with dynamometer. | Significant improvements were obtained in all variables measuring physical function. |
| Jamidshpour et al. [23] | CG = 58.46, GEC = 64.93 | N = 28. CG = 13 (5M, 8H). GEC = 15 (3M, 12H). | CG: HD and habitual physical activity. GEC: Intradialytic aerobic cycling and moderate intradialytic resistance exercise. Duration: 2 months. Sessions: 1 h, 3×/week. No follow-up post-program. | 6 MWT. Lower limb strength with dynamometer. | Exercise group obtained significant improvements in 6 MWT, but hip abductor and flexor strength did not improve. Control group decreased significantly. |
| Vogiatzaki et al. [24] | CG = 57.4, GEA = 58.1 | N = 24. CG = 12 (4M, 8H). GEA = 12 (5M, 7H). | CG: HD and habitual physical activity. GEA: Intradialytic aerobic cycling. Duration: 6 months. Sessions: 1 h, 3×/week. No follow-up post-program. | BMI; 6 MWT. | Significant improvement in 6 MWT in the experimental group and compared to the control group. BMI showed no significant improvement. |
| Assawasaksakul et al. [25] | CG = 53.7, GEC = 52.5 | N = 12. CG = 6 (3M, 3H). GEC = 6 (4M, 2H). | CG: HD with standard care. GEC: Intradialytic aerobic and resistance exercise with cycle ergometer. Duration: 6 months. Sessions: 1 h, 3×/week. No follow-up post-program. | 6 MWT. Body composition: DXA. Daily activity measured with accelerometer. STS. | Physical activity increased in the experimental group compared to the control. Body mass did not increase in the exercise group but decreased in the control group. |
| Michou et al. [26] | CG = 54.5, GEC = 53.26 | N = 29. CG = 14 (14H). GEC = 15 (15H). | CG: HD standard care. GEC: Combined aerobic and resistance exercise. Duration: 4 months. Sessions: 80–100 min, 3×/week. | 6 MWT. STS. HGS. Body composition: BIA. | After the exercise program, significant improvements in strength, 6 MWT, and STS were evidenced. |
| Abdo et al. [27] | CG = 40, GEA = 40.5 | N = 42. CG = 20 (11M, 9H). GEA = 22 (12M, 10H). | CG: HD treatment. GEA: Intradialytic aerobic exercise with cycle ergometer. Duration: 2 months. Sessions: 40 min, 3×/week. | Quadriceps muscle strength with dynamometer. | Quadriceps strength increased in the exercise group compared to the control group. |
| Yeh et al. [28] | CG = 53.91, GEC = 57.87 | N = 62. CG = 32 (17M, 15H). GEC = 30 (11M, 19H). | CG: HD without exercise. GEC: Intradialytic exercise. Aerobic with cycle ergometer and resistance. Duration: 3 months. Sessions: 30 min, 3×/week. | 6 MWT. STS-10. STS-60. | Increase in distance walked during 6 MWT in the exercise group compared to control. STS decreased time and increased number of repetitions in the exercise group compared to control. |
| Authors | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | TOTAL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cardoso et al. [17] | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | N | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | 8 (good) |
| Krase et al. [18] | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | N | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | 7 (good) |
| Suhardjono et al. [19] | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | N | N | Y | N | Y | Y | 7 (good) |
| Yabe et al. [20] | Y | N | N | Y | N | N | N | N | N | Y | Y | 4 (fair) |
| Yabe et al. [21] | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | N | N | N | N | Y | Y | 6 (good) |
| Zhag et al. [22] | Y | Y | Y | N | N | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | 8 (good) |
| Assawasaksakul et al. [25] | Y | Y | Y | N | N | N | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | 6 (good) |
| Jamshidpour et al. [23] | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | N | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | 8 (good) |
| Vogiatzaki et al. [24] | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | N | Y | N | N | Y | Y | 7 (good) |
| Michou et al. [26] | Y | Y | N | Y | N | N | N | N | N | Y | Y | 5 (fair) |
| Abdo et al. [27] | Y | Y | N | Y | N | N | N | Y | N | Y | Y | 6 (good) |
| Yeh et al. [28] | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | N | Y | N | N | Y | Y | 7 (good) |
| B1 | B2 | B3 | B4 | B5 | B6 | B7 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cardoso et al. [17] | + | + | + | + | - | + | + |
| Krase et al. [18] | + | + | + | + | - | + | + |
| Suhardjono et al. [19] | + | + | + | U | U | + | + |
| Yabe et al. [20] | - | - | + | - | + | - | + |
| Yabe et al. [21] | + | - | - | - | - | + | + |
| Zhang et al. [22] | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| Assawasaksakul et al. [25] | + | + | + | U | + | + | + |
| Jamshidpour et al. [23] | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| Vogiatzaki et al. [24] | + | + | + | + | - | + | + |
| Michou et al. [26] | + | U | U | U | + | + | + |
| Abdo et al. [27] | + | U | U | + | + | + | + |
| Yeh et al. [28] | + | + | + | U | + | + | + |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Garrido-Ardila, E.M.; Castro Lemus, M.Á.; Ramírez-Durán, M.d.V.; Jiménez-Palomares, M.; Martín Hidalgo-Barquero, M.V.; González-Sánchez, B.; Rodríguez-Mansilla, J. Effects of Exercise on Sarcopenia and Frailty in Haemodialysis Patients: A Systematic Review. Medicina 2025, 61, 2204. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61122204
Garrido-Ardila EM, Castro Lemus MÁ, Ramírez-Durán MdV, Jiménez-Palomares M, Martín Hidalgo-Barquero MV, González-Sánchez B, Rodríguez-Mansilla J. Effects of Exercise on Sarcopenia and Frailty in Haemodialysis Patients: A Systematic Review. Medicina. 2025; 61(12):2204. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61122204
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarrido-Ardila, Elisa María, Miguel Ángel Castro Lemus, María del Valle Ramírez-Durán, María Jiménez-Palomares, María Victoria Martín Hidalgo-Barquero, Blanca González-Sánchez, and Juan Rodríguez-Mansilla. 2025. "Effects of Exercise on Sarcopenia and Frailty in Haemodialysis Patients: A Systematic Review" Medicina 61, no. 12: 2204. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61122204
APA StyleGarrido-Ardila, E. M., Castro Lemus, M. Á., Ramírez-Durán, M. d. V., Jiménez-Palomares, M., Martín Hidalgo-Barquero, M. V., González-Sánchez, B., & Rodríguez-Mansilla, J. (2025). Effects of Exercise on Sarcopenia and Frailty in Haemodialysis Patients: A Systematic Review. Medicina, 61(12), 2204. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61122204









