Evaluation of Hematological, Biochemical, and Coagulation Tests in Patients with Hepatitis C
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
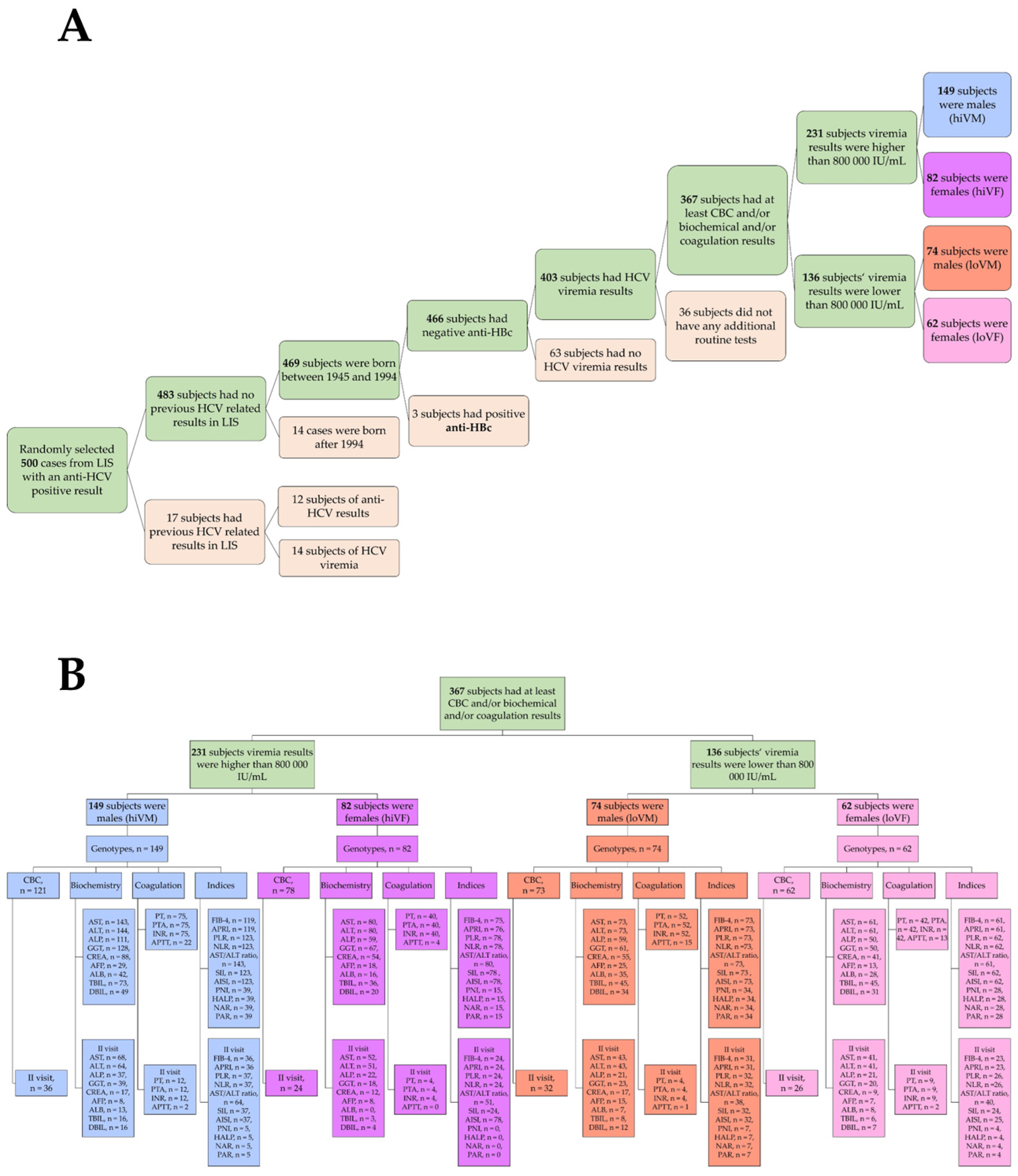
2.1. Course of the Study and Selection of Subjects
2.2. Detection of Hepatitis C Virus Antibodies
2.3. Determination of Viremia by the In Vitro Nucleic Acid Amplification Assay
2.4. HCV Genotyping
2.5. Hematological Examination
2.6. Biochemical Indicators
2.7. Coagulation Indicators
2.8. Non-Invasive Hematological and Inflammation-Based Indices
2.9. Statistical Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Study Subjects
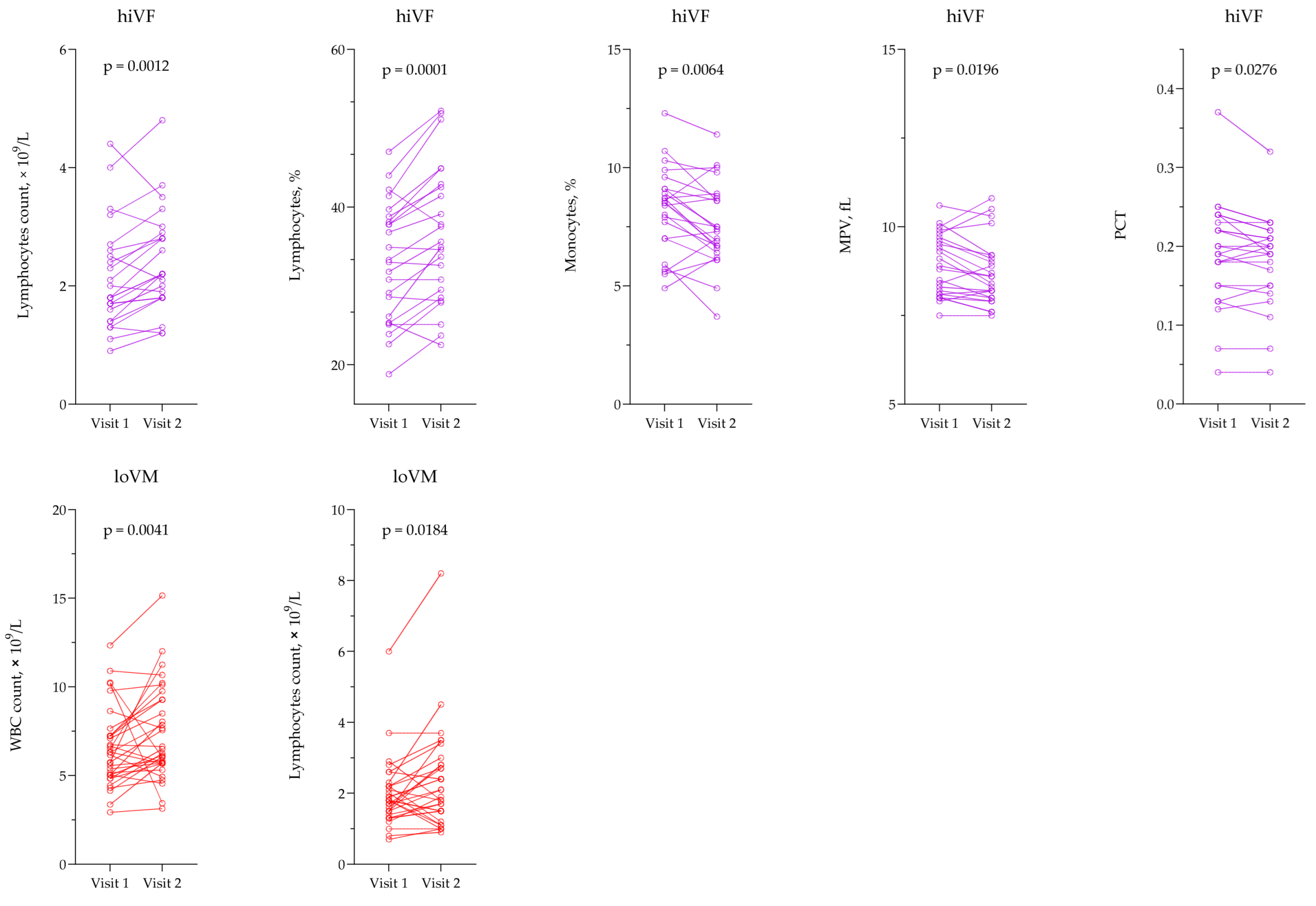
3.2. Evaluation of Hematological Testing
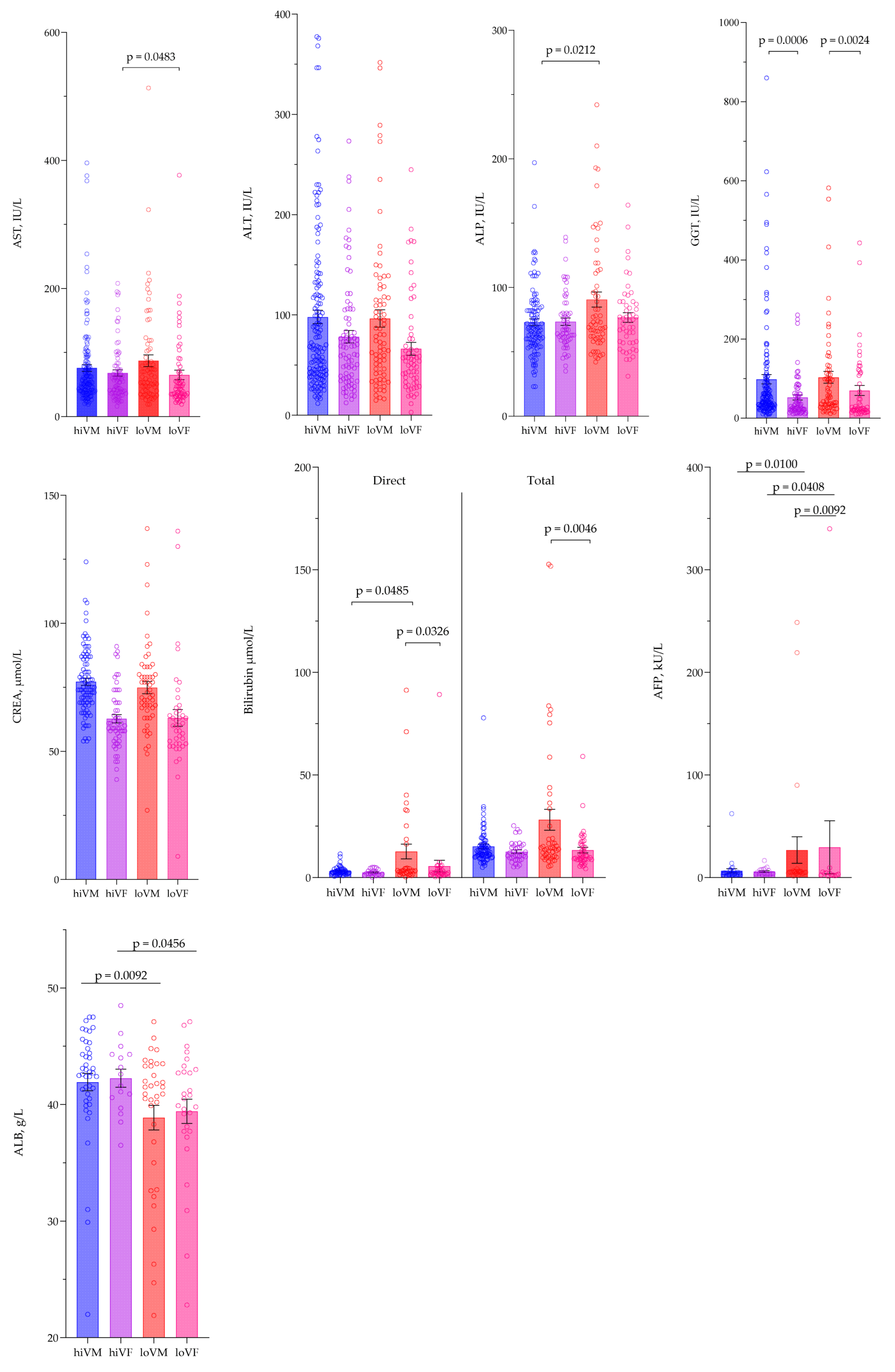
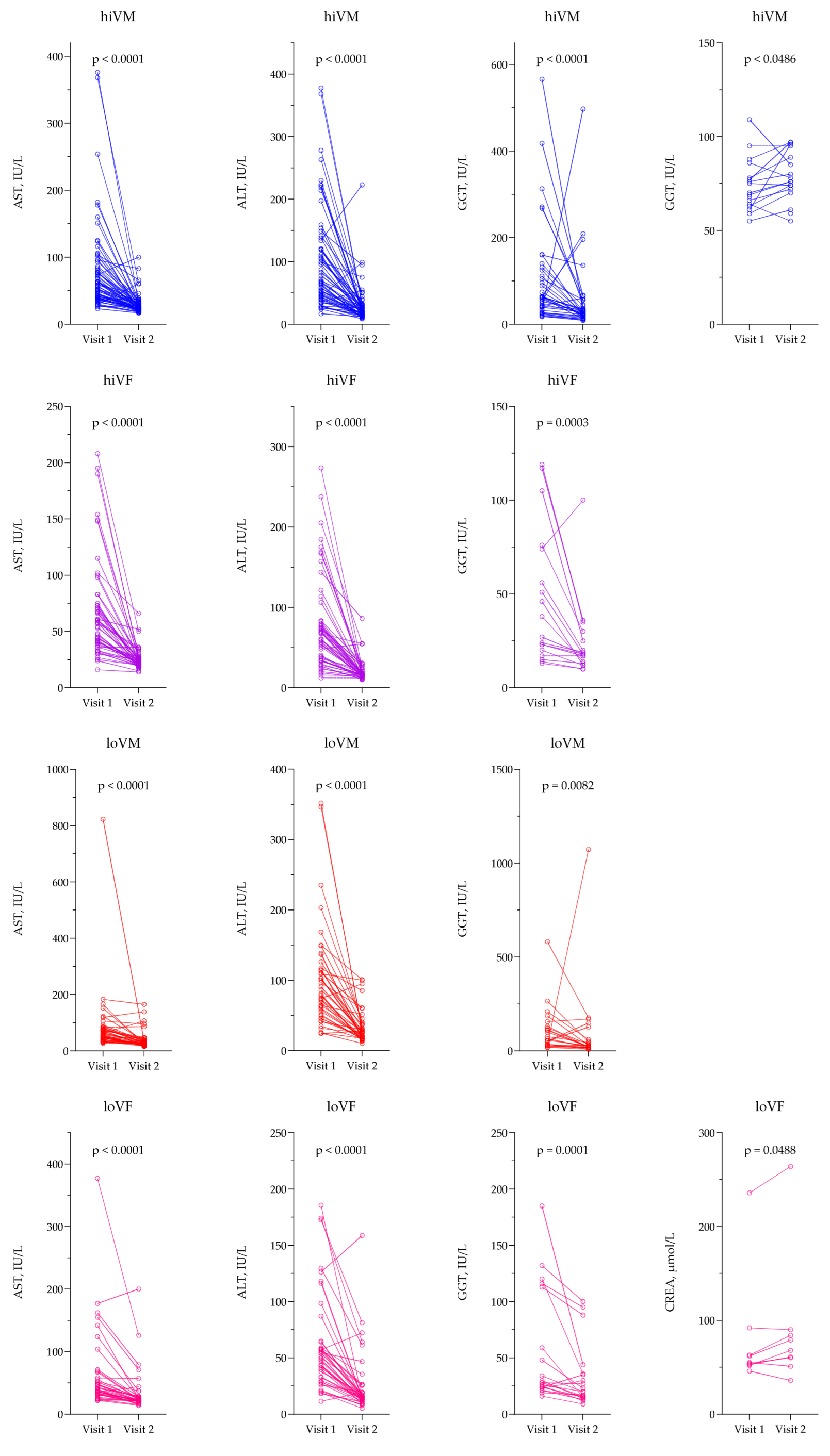
3.3. Evaluation of Biochemical Parameters
3.4. Evaluation of Coagulation Tests
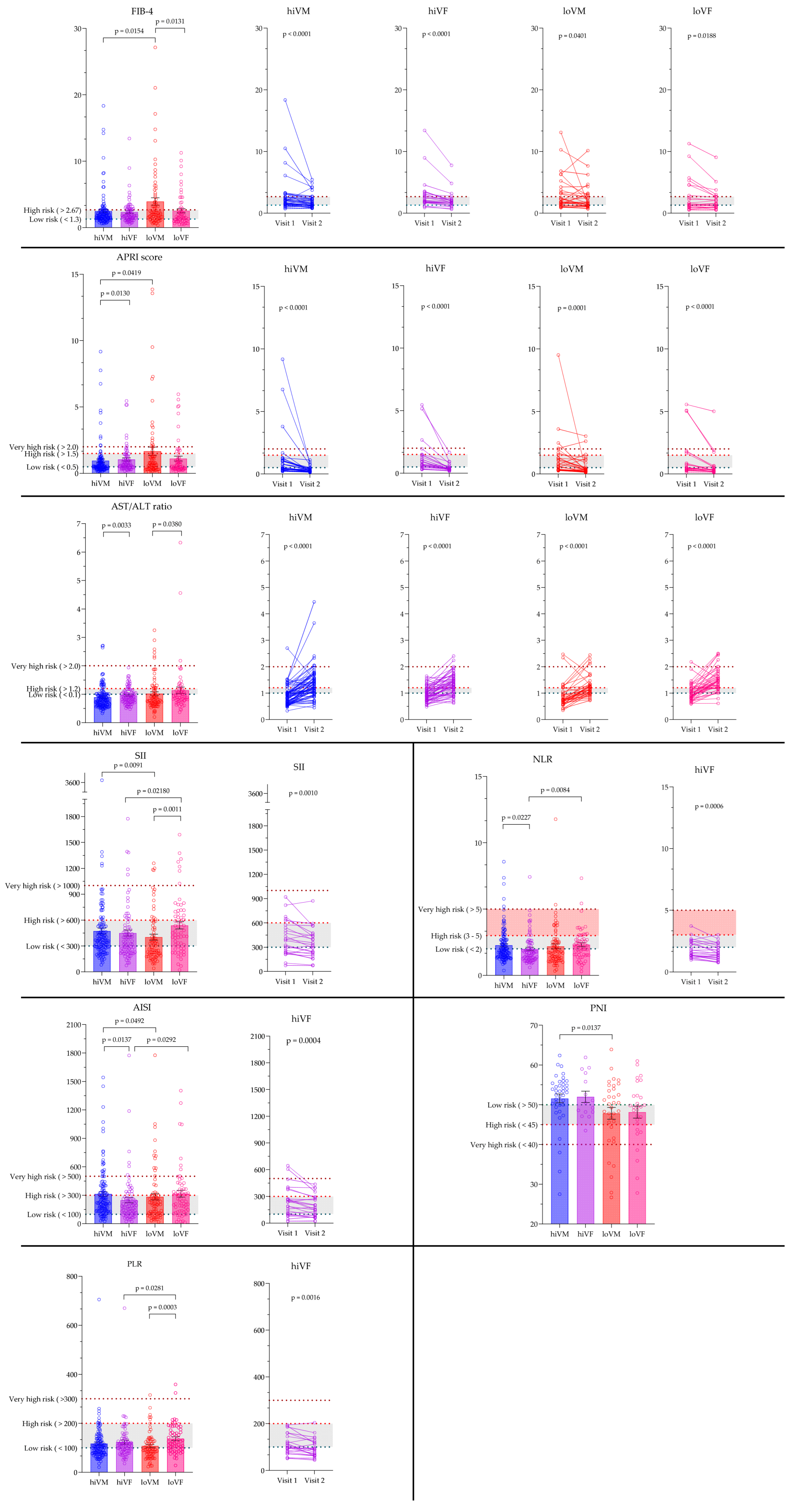
3.5. Evaluation of Non-Invasive Hematological and Inflammation-Based Indices
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AFP | α-fetoprotein |
| AISI | Aggregate index of systemic inflammation |
| ALB | Albumin |
| ALP | Alkaline phosphatase |
| ALT | Alanine aminotransferase |
| APRI | Aspartate aminotransferase to platelet ratio index |
| APTT | Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time |
| AST | Aspartate Aminotransferase |
| CREA | Creatinine |
| EASL | European Association for the Study of the Liver |
| FIB-4 | Fibrosis-4 index |
| GGT | γ-glutamyl transferase |
| HALP | Hemoglobin, albumin, lymphocytes, platelet index |
| HCC | Hepatocellular carcinoma |
| HCT | Hematocrit |
| HCV | Hepatitis C virus |
| HGB | Hemoglobin |
| hiVF | High viremia females |
| hiVM | High viremia males |
| INR | International Normalized Ratio |
| loVF | Low viremia females |
| loVM | Low viremia males |
| LUHS | Lithuanian University of Health Sciences |
| LYMPH | Lymphocytes |
| MONO | Monocytes |
| MPV | Mean platelet volume |
| NAR | Neutrophil–albumin ratio |
| NLR | Neutrophil–lymphocyte ratio |
| PAR | Platelet–albumin ratio |
| PCT | Plateletcrit |
| PLR | Platelets–lymphocytes ratio |
| PLT | Platelets |
| PNI | Prognostic nutritional index |
| PTA | Prothrombin time activity |
| PT | Prothrombin time |
| RBC | Red blood cells |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| SEM | Standard error of mean |
| SII | Systemic immune-inflammation index |
| WBC | White blood cells |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
Appendix A
| Males | Females | |
|---|---|---|
| Hematological tests | ||
| RBC, ×1012/L | 4.32–5.72 | 3.9–5.03 |
| HGB, g/L | 135–175 | 120–155 |
| HCT, % | 38.8–50 | 34.9–44.5 |
| WBC, ×109/L | 3.6–10.2 | 3.8–11.8 |
| Lymphocytes, ×109/L | 1–3.2 | 1.1–3.1 |
| Lymphocytes, % | 15.2–43.3 | 16–45.9 |
| Monocytes, ×109/L | 0.3–1.1 | 0.2–0.9 |
| Monocytes, % | 5.5–13.7 | 4.3–10.9 |
| PLT, ×109/L | 152–348 | 179–408 |
| MPV, fL | 7.4–11.4 | 7.9–10.8 |
| PCT, % | 0.15–0.35 | 0.15–0.35 |
| Biochemical tests | ||
| AST, IU/L | 0–50 | 0–35 |
| ALT, IU/L | 1–50 | 0–35 |
| CREA, μmol/L | 59–104 | 45–84 |
| ALP, IU/L | 30–120 | |
| AFP, kU/L | ||
| GGT, IU/L | 1–39 | |
| DBIL, μmol/L | 0–3.4 | |
| TBIL, μmol/L | 5–21 | |
| ALB, g/L | 35–52 | |
| Coagulation tests | ||
| PT, s | 19.8–25.8 | |
| PT, % | 70–130 | |
| INR | 0.9–1.2 | |
| APTT, s | 28–38 | |
| Statistical Parameters | hiVM | hiVF | loVM | loVF | p | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RBC, ×1012/L | ||||||||||
| Mean | n | 4.72 | 121 | 4.52 | 78 | 4.55 | 73 | 4.43 | 62 | 0.0001 * |
| SD | CI Lower | 0.507 | 4.62 | 0.332 | 4.38 | 0.574 | 4.51 | 0.484 | 4.38 | |
| SEM | CI Upper | 0.0461 | 4.90 | 0.0376 | 4.60 | 0.0672 | 4.78 | 0.0615 | 4.61 | |
| HGB, g/L | ||||||||||
| Mean | n | 149 | 121 | 139 | 78 | 144 | 73 | 134 | 62 | <0.0001 * |
| SD | CI Lower | 15.1 | 146 | 10.7 | 138 | 18.1 | 142 | 16.1 | 133 | |
| SEM | CI Upper | 1.37 | 156 | 1.21 | 143 | 2.12 | 153 | 2.04 | 140 | |
| HCT, % | ||||||||||
| Mean | n | 43.3 | 121 | 40.0 | 78 | 41.8 | 73 | 39.4 | 62 | <0.0001 * |
| SD | CI Lower | 4.11 | 42.8 | 5.07 | 40.0 | 4.91 | 41.2 | 4.40 | 38.9 | |
| SEM | CI Upper | 0.373 | 45.0 | 0.574 | 41.4 | 0.575 | 43.9 | 0.558 | 41.3 | |
| WBC, ×109/L | ||||||||||
| Mean | n | 5.964 | 121 | 6.247 | 78 | 6.409 | 73 | 6.251 | 62 | 0.0841 * |
| SD | CI Lower | 2.014 | 5.020 | 2.140 | 5.440 | 2.245 | 5.570 | 2.050 | 5.420 | |
| SEM | CI Upper | 0.1446 | 5.630 | 0.2423 | 6.340 | 0.2627 | 6.730 | 0.2603 | 6.210 | |
| Lymphocytes, % | ||||||||||
| Mean | n | 29.93 | 121 | 32.77 | 78 | 31.45 | 73 | 29.97 | 62 | 0.0861 * |
| SD | CI Lower | 9.293 | 33.1 | 8.844 | 30.1 | 10.59 | 27.5 | 9.667 | 25.8 | |
| SEM | CI Upper | 0.8448 | 27.8 | 1.001 | 36.8 | 1.239 | 34.5 | 1.228 | 31.6 | |
| Monocytes, % | ||||||||||
| Mean | n | 9.650 | 121 | 8.731 | 78 | 10.46 | 73 | 9.053 | 62 | 0.0058 * |
| SD | CI Lower | 2.976 | 8.70 | 2.134 | 8.00 | 3.290 | 9.10 | 2.967 | 7.70 | |
| SEM | CI Upper | 0.2706 | 10.0 | 0.2416 | 8.90 | 0.3851 | 11.3 | 0.3768 | 9.30 | |
| Lymphocytes, ×109/L | ||||||||||
| Mean | n | 2.04 | 121 | 2.00 | 78 | 1.97 | 73 | 1.80 | 62 | 0.3238 * |
| SD | CI Lower | 1.03 | 1.80 | 0.764 | 1.80 | 0.874 | 1.70 | 0.646 | 1.50 | |
| SEM | CI Upper | 0.0936 | 2.10 | 0.0865 | 2.00 | 0.102 | 2.10 | 0.0820 | 2.00 | |
| Monocytes, ×109/L | ||||||||||
| Mean | n | 0.631 | 121 | 0.527 | 78 | 0.649 | 73 | 0.544 | 62 | 0.0006 * |
| SD | CI Lower | 0.224 | 0.600 | 0.196 | 0.400 | 0.256 | 0.600 | 0.188 | 0.500 | |
| SEM | CI Upper | 0.0204 | 0.700 | 0.0222 | 0.600 | 0.0300 | 0.600 | 0.0239 | 0.600 | |
| PLT, ×109/L | ||||||||||
| Mean | n | 206 | 121 | 219 | 78 | 189 | 73 | 228 | 62 | 0.0013 * |
| SD | CI Lower | 66.1 | 191 | 66.0 | 202 | 76.5 | 165 | 79.4 | 212 | |
| SEM | CI Upper | 6.01 | 213 | 7.48 | 228 | 8.96 | 203 | 10.1 | 257 | |
| MPV, fL | ||||||||||
| Mean | n | 8.82 | 121 | 8.75 | 78 | 8.74 | 73 | 8.71 | 62 | 0.8955 * |
| SD | CI Lower | 1.09 | 8.50 | 0.818 | 8.30 | 1.07 | 8.20 | 0.911 | 8.30 | |
| SEM | CI Upper | 0.0990 | 9.00 | 0.0927 | 9.00 | 0.125 | 8.90 | 0.116 | 9.00 | |
| PCT, % | ||||||||||
| Mean | n | 0.178 | 121 | 0.190 | 78 | 0.163 | 73 | 0.194 | 62 | 0.0007 * |
| SD | CI Lower | 0.0481 | 0.170 | 0.0576 | 0.170 | 0.0637 | 0.150 | 0.0597 | 0.190 | |
| SEM | CI Upper | 0.00437 | 0.180 | 0.00652 | 0.200 | 0.00746 | 0.170 | 0.00758 | 0.220 | |
| AST, IU/L | ||||||||||
| Mean | n | 75.9 | 143 | 67.9 | 80 | 87.2 | 73 | 65.0 | 61 | 0.0509 * |
| SD | CI Lower | 63.0 | 50.0 | 44.0 | 44.0 | 77.9 | 51.0 | 58.2 | 36.0 | |
| SEM | CI Upper | 5.27 | 63.0 | 4.92 | 65.0 | 9.12 | 74.0 | 7.45 | 54.0 | |
| ALT, IU/L | ||||||||||
| Mean | n | 98.0 | 144 | 78.3 | 80 | 96.6 | 73 | 66.2 | 61 | 0.0139 * |
| SD | CI Lower | 79.2 | 57.8 | 55.8 | 50.6 | 74.1 | 60.4 | 49.4 | 43.1 | |
| SEM | CI Upper | 6.60 | 88.2 | 6.24 | 75.2 | 8.68 | 100 | 6.33 | 58.8 | |
| ALP, IU/L | ||||||||||
| Mean | n | 73.1 | 111 | 73.4 | 59 | 90.6 | 59 | 76.6 | 50 | 0.2075 |
| SD | CI Lower | 27.0 | 63.0 | 22.2 | 63.0 | 45.2 | 67.0 | 26.4 | 65.0 | |
| SEM | CI Upper | 2.56 | 74.0 | 2.90 | 76.0 | 5.89 | 89.0 | 3.73 | 82.0 | |
| GGT, IU/L | ||||||||||
| Mean | n | 98.50 | 128 | 52.48 | 67 | 103.5 | 61 | 70.12 | 50 | 0.0002 |
| SD | CI Lower | 133.9 | 40.00 | 53.24 | 24.00 | 118.1 | 39.00 | 89.76 | 21.00 | |
| SEM | CI Upper | 11.83 | 62.00 | 6.505 | 46.00 | 15.12 | 99.00 | 12.69 | 49.00 | |
| CREA, μmol/L | ||||||||||
| Mean | n | 77.22 | 88 | 62.72 | 54 | 74.93 | 55 | 63.07 | 41 | <0.0001 * |
| SD | CI Lower | 13.09 | 73.00 | 11.88 | 58.00 | 17.76 | 68.00 | 20.84 | 55.00 | |
| SEM | CI Upper | 1.396 | 78.00 | 1.617 | 63.00 | 2.395 | 79.00 | 3.254 | 64.00 | |
| Total bilirubin, μmol/L | ||||||||||
| Mean | n | 15.19 | 73 | 12.59 | 36 | 28.14 | 45 | 13.35 | 45 | 0.0235 |
| SD | CI Lower | 9.723 | 11.14 | 5.014 | 10.17 | 34.32 | 12.09 | 9.273 | 9.030 | |
| SEM | CI Upper | 1.138 | 14.58 | 0.8357 | 14.46 | 5.116 | 16.69 | 1.414 | 13.44 | |
| Direct bilirubin, μmol/L | ||||||||||
| Mean | n | 3.214 | 49 | 2.496 | 20 | 12.69 | 34 | 5.602 | 31 | 0.0744 |
| SD | CI Lower | 2.105 | 2.350 | 1.436 | 1.740 | 20.93 | 2.440 | 15.62 | 1.770 | |
| SEM | CI Upper | 0.3008 | 3.110 | 0.3210 | 3.140 | 3.590 | 4.500 | 2.805 | 3.470 | |
| AFP, kU/L | ||||||||||
| Mean | n | 6.603 | 29 | 5.923 | 18 | 26.77 | 25 | 29.50 | 13 | 0.0315 |
| SD | CI Lower | 11.05 | 2.850 | 3.502 | 3.600 | 64.79 | 4.830 | 93.34 | 2.320 | |
| SEM | CI Upper | 2.052 | 4.540 | 0.8255 | 7.830 | 12.96 | 6.170 | 25.89 | 5.300 | |
| ALB, g/L | ||||||||||
| Mean | n | 41.93 | 42 | 42.26 | 16 | 38.88 | 35 | 39.42 | 28 | 0.0273 |
| SD | CI Lower | 4.869 | 41.50 | 3.089 | 39.70 | 6.262 | 39.90 | 5.532 | 38.10 | |
| SEM | CI Upper | 0.7514 | 44.00 | 0.7723 | 44.30 | 1.058 | 42.00 | 1.045 | 42.70 | |
| PT, s | ||||||||||
| Mean | n | 25.93 | 75 | 25.57 | 40 | 32.00 | 52 | 26.08 | 42 | 0.0002 |
| SD | CI Lower | 3.533 | 24.60 | 8.521 | 23.00 | 17.57 | 25.10 | 5.055 | 23.50 | |
| SEM | CI Upper | 0.4080 | 26.30 | 1.347 | 24.80 | 2.436 | 28.60 | 0.7800 | 25.80 | |
| PTA, % | ||||||||||
| Mean | n | 85.51 | 75 | 94.88 | 40 | 73.06 | 52 | 88.10 | 42 | 0.0004 |
| SD | CI Lower | 19.67 | 80.00 | 21.46 | 89.00 | 26.66 | 66.00 | 24.32 | 77.00 | |
| SEM | CI Upper | 2.271 | 90.00 | 3.393 | 104.0 | 3.697 | 84.00 | 3.752 | 102.0 | |
| INR | ||||||||||
| Mean | n | 1.09 | 75 | 1.07 | 40 | 1.32 | 52 | 1.10 | 42 | 0.0004 |
| SD | CI Lower | 0.131 | 1.04 | 0.291 | 0.990 | 0.688 | 1.07 | 0.193 | 0.990 | |
| SEM | CI Upper | 0.0151 | 1.10 | 0.0461 | 1.05 | 0.0954 | 1.19 | 0.0297 | 1.11 | |
| APTT, s | ||||||||||
| Mean | n | 34.2 | 22 | 34.8 | 4 | 36.3 | 15 | 33.8 | 13 | 0.4536 |
| SD | CI Lower | 2.99 | 33.0 | 3.08 | 31.1 | 4.60 | 32.5 | 3.81 | 32.0 | |
| SEM | CI Upper | 0.637 | 35.9 | 1.54 | 38.5 | 1.19 | 41.3 | 1.06 | 36.3 | |
| FIB-4 | ||||||||||
| Mean | n | 2.49 | 119 | 2.37 | 75 | 3.95 | 73 | 2.54 | 61 | 0.0604 |
| SD | CI Lower | 2.66 | 1.54 | 1.88 | 1.60 | 4.77 | 1.74 | 2.43 | 1.33 | |
| SEM | CI Upper | 0.244 | 2.01 | 0.217 | 2.34 | 0.558 | 2.88 | 0.311 | 2.15 | |
| APRI | ||||||||||
| Mean | n | 0.960 | 119 | 1.05 | 75 | 1.67 | 73 | 1.12 | 61 | 0.1182 |
| SD | CI Lower | 1.36 | 0.470 | 1.03 | 0.590 | 2.67 | 0.560 | 1.39 | 0.420 | |
| SEM | CI Upper | 0.124 | 0.700 | 0.119 | 0.930 | 0.312 | 1.08 | 0.178 | 0.840 | |
| PLR | ||||||||||
| Mean | n | 117 | 123 | 124 | 78 | 107 | 73 | 137 | 62 | 0.0027 |
| SD | CI Lower | 70.9 | 94.4 | 75.8 | 98.5 | 56.0 | 85.0 | 59.2 | 107 | |
| SEM | CI Upper | 6.40 | 111 | 8.59 | 118 | 6.51 | 110 | 7.51 | 153 | |
| NLR | ||||||||||
| Mean | n | 2.27 | 123 | 2.00 | 78 | 2.18 | 73 | 2.32 | 62 | 0.0687 |
| SD | CI Lower | 1.28 | 1.71 | 1.11 | 1.39 | 1.56 | 1.46 | 1.16 | 1.95 | |
| SEM | CI Upper | 0.116 | 2.04 | 0.126 | 1.88 | 0.182 | 2.18 | 0.148 | 2.55 | |
| AST/ALT ratio | ||||||||||
| Mean | n | 0.894 | 143 | 0.959 | 80 | 1.02 | 73 | 1.14 | 61 | 0.0075 |
| SD | CI Lower | 0.391 | 0.750 | 0.286 | 0.850 | 0.595 | 0.730 | 0.884 | 0.840 | |
| SEM | CI Upper | 0.0324 | 0.880 | 0.0299 | 1.01 | 0.0678 | 0.920 | 0.112 | 1.05 | |
| SII | ||||||||||
| Mean | n | 472 | 123 | 450 | 78 | 402 | 73 | 540 | 61 | 0.0082 |
| SD | CI Lower | 383 | 344 | 314 | 291 | 294 | 229 | 337 | 399 | |
| SEM | CI Upper | 34.6 | 426 | 35.6 | 434 | 34.1 | 365 | 42.8 | 591 | |
| AISI | ||||||||||
| Mean | n | 313 | 123 | 248 | 78 | 283 | 73 | 316 | 61 | 0.0769 |
| SD | CI Lower | 269 | 207 | 252 | 150 | 290 | 137 | 280 | 189 | |
| SEM | CI Upper | 24.2 | 272 | 28.6 | 233 | 33.7 | 254 | 35.6 | 321 | |
| PNI | ||||||||||
| Mean | n | 51.6 | 39 | 52.0 | 15 | 47.8 | 34 | 48.2 | 28 | 0.0548 |
| SD | CI Lower | 6.85 | 50.6 | 5.50 | 48.2 | 8.70 | 45.8 | 7.88 | 46.2 | |
| SEM | CI Upper | 1.10 | 54.8 | 1.42 | 58.0 | 1.49 | 52.5 | 1.49 | 51.8 | |
| HALP | ||||||||||
| Mean | n | 66.7 | 39 | 61.0 | 15 | 61.2 | 34 | 53.9 | 28 | 0.2528 |
| SD | CI Lower | 32.8 | 46.3 | 27.2 | 46.1 | 25.4 | 46.8 | 33.0 | 39.4 | |
| SEM | CI Upper | 5.26 | 69.2 | 7.02 | 67.8 | 4.36 | 79.5 | 6.23 | 59.2 | |
| NAR | ||||||||||
| Mean | n | 0.100 | 39 | 0.0847 | 15 | 0.108 | 34 | 0.0875 | 28 | 0.4963 |
| SD | CI Lower | 0.0437 | 0.0700 | 0.0309 | 0.0600 | 0.105 | 0.0600 | 0.0551 | 0.0700 | |
| SEM | CI Upper | 0.00700 | 0.110 | 0.00798 | 0.0900 | 0.0179 | 0.110 | 0.0104 | 0.0900 | |
| PAR | ||||||||||
| Mean | n | 5.05 | 39 | 4.69 | 15 | 4.56 | 34 | 4.88 | 28 | 0.4486 |
| SD | CI Lower | 1.86 | 4.44 | 1.17 | 3.88 | 1.99 | 3.71 | 1.87 | 3.93 | |
| SEM | CI Upper | 0.297 | 5.27 | 0.303 | 5.15 | 0.341 | 4.98 | 0.353 | 5.88 | |
References
- Cooke, G.S.; Flower, B.; Cunningham, E.; Marshall, A.D.; Lazarus, J.V.; Palayew, A.; Jia, J.; Aggarwal, R.; Al-Mahtab, M.; Tanaka, Y.; et al. Progress towards elimination of viral hepatitis: A Lancet Gastroenterology & Hepatology Commission update. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 9, 346–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Global Health Sector Strategies on, Respectively, HIV, Viral Hepatitis and Sexually Transmitted Infections for the Period 2022–2030; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Bagheri, S.; Fard, G.B.; Talkhi, N.; Rashidi Zadeh, D.; Mobarra, N.; Mousavinezhad, S.; Khamse, F.M.; Hosseini Bafghi, M. Laboratory Biochemical and Hematological Parameters: Early Predictive Biomarkers for Diagnosing Hepatitis C Virus Infection. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2024, 38, e25127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasser Saud, M.D.; Khalid Mohammed, T.S.; Ali Yahya, H.M.; Jamilah Ali Ali, W.; Khulud Ali Ayeel, D.; Ali Hamoud Mohammad, M.; Hamad Ali, H.; Meshal Abdullah Ahmad, A.; Waad Faiz, S.A.; Alshehri, W.S.M. The Role of Laboratory Testing in Evaluating Immune Function in Chronic Illnesses. J. Int. Crisis Risk Commun. Res. 2023, 6, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, G.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Wu, J.; Gu, M. Inflammatory markers as predictors of liver fibrosis in type 2 diabetes patients with metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease. Front. Endocrinol. 2025, 16, 1556646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.O.; Sterling, R.K. Systematic review: Non-invasive methods of fibrosis analysis in chronic hepatitis C. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2009, 30, 557–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, K.M.; Delk, M.; Devuni, D.; Sarkar, M. Sex differences in chronic liver disease and benign liver lesions. JHEP Rep. 2023, 5, 100870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.H.; Chen, M.Y.; Yeh, C.T.; Lin, H.S.; Lin, M.S.; Huang, T.J.; Chang, M.L. Sexual Dimorphic Metabolic Alterations in Hepatitis C Virus-infected Patients: A Community-Based Study in a Hepatitis B/Hepatitis C Virus Hyperendemic Area. Medicine 2016, 95, e3546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, S.L.; Flanagan, K.L. Sex differences in immune responses. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 626–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, M.E.; Bartlett, S.R.; Yu, A.; Lamb, J.; Reitz, C.; Wong, S.; Alvarez, M.; Binka, M.; Velásquez Garcia, H.; Jeong, D.; et al. Women in the 2019 hepatitis C cascade of care: Findings from the British Columbia Hepatitis Testers cohort study. BMC Womens Health 2021, 21, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavon Lde, L.; Narciso-Schiavon, J.L.; de Carvalho-Filho, R.J. Non-invasive diagnosis of liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 2854–2866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterling, R.K.; Lissen, E.; Clumeck, N.; Sola, R.; Correa, M.C.; Montaner, J.; S Sulkowski, M.; Torriani, F.J.; Dieterich, D.T.; Thomas, D.L.; et al. Development of a simple noninvasive index to predict significant fibrosis in patients with HIV/HCV coinfection. Hepatology 2006, 43, 1317–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wai, C.T.; Greenson, J.K.; Fontana, R.J.; Kalbfleisch, J.D.; Marrero, J.A.; Conjeevaram, H.S.; Lok, A.S. A simple noninvasive index can predict both significant fibrosis and cirrhosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology 2003, 38, 518–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Yang, X.R.; Xu, Y.; Sun, Y.F.; Sun, C.; Guo, W.; Zhang, X.; Wang, W.M.; Qiu, S.J.; Zhou, J.; et al. Systemic immune-inflammation index predicts prognosis of patients after curative resection for hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 6212–6222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Hu, X.; Xiao, L.; Long, G.; Yao, L.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, L. Prognostic Nutritional Index and Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index Predict the Prognosis of Patients with HCC. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2021, 25, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EASL. Recommendations on Treatment of Hepatitis C 2018. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 461–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuh, B. The Natural History and Predictors of Liver Fibrosis Progression Using the Fib-4 Score Among HIV/HCV Co-Infected Adults in an Outpatient Clinic. Ph.D. Thesis, Yale University, New Haven, CT, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Zeng, J.; Guo, P.; Zeng, J.; Liu, J. Prognostic Significance of Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratio (PLR) in Extrahepatic Metastasis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma After Curative Resection. Cancer Manag. Res. 2021, 13, 1395–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiucă, O.M.; Morariu, S.H.; Mariean, C.R.; Tiucă, R.A.; Nicolescu, A.C.; Cotoi, O.S. Predictive Performances of Blood-Count-Derived Inflammatory Markers for Liver Fibrosis Severity in Psoriasis Vulgaris. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 16898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheth, S.G.; Flamm, S.L.; Gordon, F.D.; Chopra, S. AST/ALT ratio predicts cirrhosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1998, 93, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biyik, M.; Ucar, R.; Solak, Y.; Gungor, G.; Polat, I.; Gaipov, A.; Cakir, O.O.; Ataseven, H.; Demir, A.; Turk, S. Blood neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio independently predicts survival in patients with liver cirrhosis. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 25, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ustaoglu, M.; Aktas, G.; Kucukdemirci, O.; Goren, I.; Bas, B. Could a reduced hemoglobin, albumin, lymphocyte, and platelet (HALP) score predict autoimmune hepatitis and degree of liver fibrosis? Rev. Assoc. Med. Bras. 2024, 70, e20230905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, G.B.; Lu, Y.Y.; Liao, R.W.; Chen, Q.S.; Zhang, K.Q. Prognostic nutritional index predicts prognosis in patients with metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Onco Targets Ther. 2016, 9, 5955–5961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onodera, T.; Goseki, N.; Kosaki, G. Prognostic nutritional index in gastrointestinal surgery of malnourished cancer patients. Nihon Geka Gakkai Zasshi 1984, 85, 1001–1005. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.; He, Q.; Fisher, D.; Pronyuk, K.; Musabaev, E.; Zhao, L. Association of platelet to albumin ratio with metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease based on the National Health and Nutrition Survey 2017–2018. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 10573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Peng, W.; Zhang, X.Y.; Wen, T.F.; Chen, L.P. The preoperative platelet to albumin ratio predicts the prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma patients without portal hypertension after liver resection. Medicine 2019, 98, e17920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, B.; Xu, S.; Sun, P.; Zheng, L. Neutrophil to albumin ratio: A biomarker in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and with liver fibrosis. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1368459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saif-Al-Islam, M.; Mohamed, H.S.; Younis, M.A.; Abdelhamid, M.Y.; Ali, M.M.; Khalaf, S. Impact of gender difference on characteristics and outcome of chronic hepatitis C. Open J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 10, 281–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.C.; Verna, E.C.; Brown, R.S., Jr.; O’Leary, J.G.; Trotter, J.F.; Forman, L.M.; Duman, J.D.; Foster, R.G.; Stravitz, R.T.; Terrault, N.A. Hepatitis C virus-infected women have a higher risk of advanced fibrosis and graft loss after liver transplantation than men. Hepatology 2011, 54, 418–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontana, R.J.; Bonkovsky, H.L.; Naishadham, D.; Dienstag, J.L.; Sterling, R.K.; Lok, A.S.; Su, G.L. Serum fibrosis marker levels decrease after successful antiviral treatment in chronic hepatitis C patients with advanced fibrosis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2009, 7, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magri, A.; Manfredi, G.F.; Smirne, C.; Pigni, S.; Burlone, M.E.; Bellan, M.; Vercellino, N.; Minisini, R.; Pirisi, M. Impact of Age and Sex on Viral Load in Hepatitis C Virus Infection. Viruses 2024, 17, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guy, J.; Peters, M.G. Liver disease in women: The influence of gender on epidemiology, natural history, and patient outcomes. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 9, 633. [Google Scholar]
- Baranoski, A.S.; Cotton, D.; Heeren, T.; Nunes, D.; Kubiak, R.W.; Horsburgh, C.R., Jr. Clinical liver disease progression among hepatitis C-infected drug users with CD4 cell count less than 200 cells/mm3 is more pronounced among women than men. In Open Forum Infectious Diseases; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2016; p. ofv214. [Google Scholar]
- Desai, S.N.; Dodge, J.L.; Landay, A.L.; Glesby, M.J.; Latham, P.S.; Villacres, M.C.; French, A.L.; Gange, S.J.; Greenblatt, R.M.; Peters, M.G. Hepatic fibrosis and immune phenotype vary by HCV viremia in HCV/HIV co-infected subjects: A Women’s interagency HIV study. Medicine 2016, 95, e4483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salama, M.; Darwesh, N.; Elsabaawy, M.M.; Abdelsameea, E.; Gomaa, A.; Sabry, A. Long-Term Outcomes of Patients with Liver Cirrhosis After Eradication of Chronic Hepatitis C with Direct-Acting Antiviral Drugs (DAAs). J. Hepatocell. Carcinoma 2024, 11, 2115–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apol, Á.D.; Sølund, C.; Vinten, C.; Underwood, A.P.; Bukh, J.; Weis, N. Cure of chronic hepatitis C virus infection after DAA treatment only partially restores the functional capacity of exhausted T cell subsets: A systematic review. Front. Immunol. 2025, 16, 1546915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi-Sari, H.; Piggott, D.A.; Scully, E.P.; Ward, K.; Sutcliffe, C.G.; Sulkowski, M.; Falade-Nwulia, O. Changes in Inflammatory Cytokines After Chronic Hepatitis C Treatment Among People Living With HIV. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2024, 11, ofad623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soldera, J. Immunological crossroads: The intriguing dance between hepatitis C and autoimmune hepatitis. World J. Hepatol. 2024, 16, 867–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Index | Cut-Off Values (Risk Zones) | Formula | Clinical Relevance in HCV Patients | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FIB-4 (Fibrosis-4 Index) | <1.45 → low risk; 1.45–3.25 → intermediate; >3.25 → high risk of advanced fibrosis | (Age [years] × AST [U/L])/(PLT [109/L × √ALT[U/L]) | Non-invasive assessment of liver fibrosis reduces the need for biopsy | [5,12,17] |
| PLR (Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratio) | <100 → low; 100–200 → intermediate; >200 → high inflammation/fibrosis risk | PLT [×109/L]/LYMPH [×109/L] | Reflects systemic inflammation, associated with fibrosis progression in HCV | [5,18,19] |
| AST/ALT ratio | <1 → usually non-advanced disease; >1 → advanced fibrosis or cirrhosis | AST [U/L]/ALT [U/L] | Simple marker for disease severity; ratio >1 often indicates cirrhosis | [20] |
| NLR (Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio) | <2 → normal; 2–4 → intermediate; >4 → high inflammatory risk | NEUTRO [×109/L]/LYMPH [×109/L] | An indicator of systemic inflammation, it predicts the progression of fibrosis and the risk of HCC | [21,22] |
| APRI (AST to Platelet Ratio Index) | <0.5 → low risk; 0.5–1.5 → intermediate; >1.5 → high risk of significant fibrosis | [(AST [IU/L]/ upper limit of normal AST [IU/L])/PLT [×109/L]] × 100 | Widely used non-invasive tool for fibrosis and cirrhosis | [13,19] |
| SII (Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index) | <500 → low; 500–1000 → intermediate; >1000 → high risk | (PLT [×109/L] × NEUTRO [×109/L])/LYMPH [×109/L] | Captures systemic inflammation and immune status, linked to fibrosis progression | [14,19] |
| AISI (Aggregate Index of Systemic Inflammation) | No universal cut-offs; higher values = worse prognosis | (NEUTRO [×109/L ] × MONO [×109/L ] × PLT [×109/L])/LYMPH [×109/L] | Comprehensive inflammation index, explored for HCV outcomes | [19] |
| PNI (Prognostic Nutritional Index) | >45 → good; 40–45 → moderate; <40 → poor nutritional/immune status | 10 × ALB [g/L] + 0.005 × LYMPH [×109/L] | Reflects nutritional and immune reserve; predictive of chronic liver disease | [23,24] |
| HALP (Hemoglobin, Albumin, Lymphocyte, Platelet Index) | >30 → favorable; <30 → unfavorable prognosis | (HGB [g/L] × ALB [g/L] × LYMPH [×109/L])/PLT [×109/L] | Integrates inflammation and nutrition, associated with outcomes in HCV | [22] |
| PAR (Platelet-to-Albumin Ratio) | Higher ratio = worse fibrosis; no fixed cut-offs yet | PLT [×109/L]/ALB [g/L] | Reflects impaired albumin synthesis + thrombocytopenia in liver damage | [25,26] |
| NAR (Neutrophil-to-Albumin Ratio) | >0.15–0.20 → higher risk (study-dependent) | NEUTRO [×109/L]/ALB [g/L] | Combines inflammation and liver synthetic function, linked with poor outcomes | [27] |
| High Viremia | Low Viremia | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | 231 | 136 | ||
| Viremia, IU/ml | ≥800,000 | <800,000 | ||
| Gender (males/females) | 149 | 82 | 74 | 62 |
| Age (mean ± SD) | 53.48 ± 10.29 | 58.32 ± 10.63 | 55.01 ± 10.57 | 55.40 ± 13.78 |
| Viremia, Mean (95% CI of mean) | 8,867,906 (7,574,998–10,160,814) | 8,780,378 (5,076,277–12,484,479) | 204,336 (163,653–245,019) | 255,093 (206,549–303,637) |
| Time between I and II visit, mean ± SD (HCV RNA = 0 IU/mL) | 17 ± 4 | |||
| 1 | 1a | 1a/1b | 1b | 2 | 2a/2c | 3 | 3a | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | ||
| hiVM | 0 | 36 | 1 | 49 | 3 | 18 | 0 | 42 | 149 |
| (0.0) | (24.16) | (0.67) | (32.89) | (2.01) | (12.08) | (0.00) | (28.19) | ||
| hiVF | 0 | 7 | 0 | 45 | 2 | 6 | 1 | 21 | 82 |
| (0.00) | (8.54) | (0.00) | (54.88) | (2.44) | (7.32) | (1.22) | (25.61) | ||
| loVM | 3 | 10 | 2 | 31 | 1 | 5 | 1 | 21 | 74 |
| (4.05) | (13.51) | (2.70) | (41.89) | (1.35) | (6.76) | (1.35) | (28.38) | ||
| loVF | 0 | 2 | 0 | 30 | 6 | 2 | 0 | 22 | 62 |
| (0.00) | (3.23) | (0.00) | (48.99) | (9.68) | (3.23) | (0.00) | (35.48) | ||
| Total | 3 | 55 | 3 | 155 | 12 | 31 | 2 | 106 | 367 |
| (0.82) | (14.99) | (082) | (42.23) | (3.27) | (8.45) | (0.54) | (28.88) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Janulaityte, I.; Petkute, G.; Maciuliene, A.; Borodiciene, J.; Kareiva, J.; Vitkauskiene, A. Evaluation of Hematological, Biochemical, and Coagulation Tests in Patients with Hepatitis C. Medicina 2025, 61, 2049. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61112049
Janulaityte I, Petkute G, Maciuliene A, Borodiciene J, Kareiva J, Vitkauskiene A. Evaluation of Hematological, Biochemical, and Coagulation Tests in Patients with Hepatitis C. Medicina. 2025; 61(11):2049. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61112049
Chicago/Turabian StyleJanulaityte, Ieva, Gintare Petkute, Asta Maciuliene, Jurgita Borodiciene, Jokubas Kareiva, and Astra Vitkauskiene. 2025. "Evaluation of Hematological, Biochemical, and Coagulation Tests in Patients with Hepatitis C" Medicina 61, no. 11: 2049. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61112049
APA StyleJanulaityte, I., Petkute, G., Maciuliene, A., Borodiciene, J., Kareiva, J., & Vitkauskiene, A. (2025). Evaluation of Hematological, Biochemical, and Coagulation Tests in Patients with Hepatitis C. Medicina, 61(11), 2049. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61112049








