A Multimodal Diagnostic Model for Breast Cancer Invasiveness Based on Ultrasound Imaging and Serum Biomarkers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
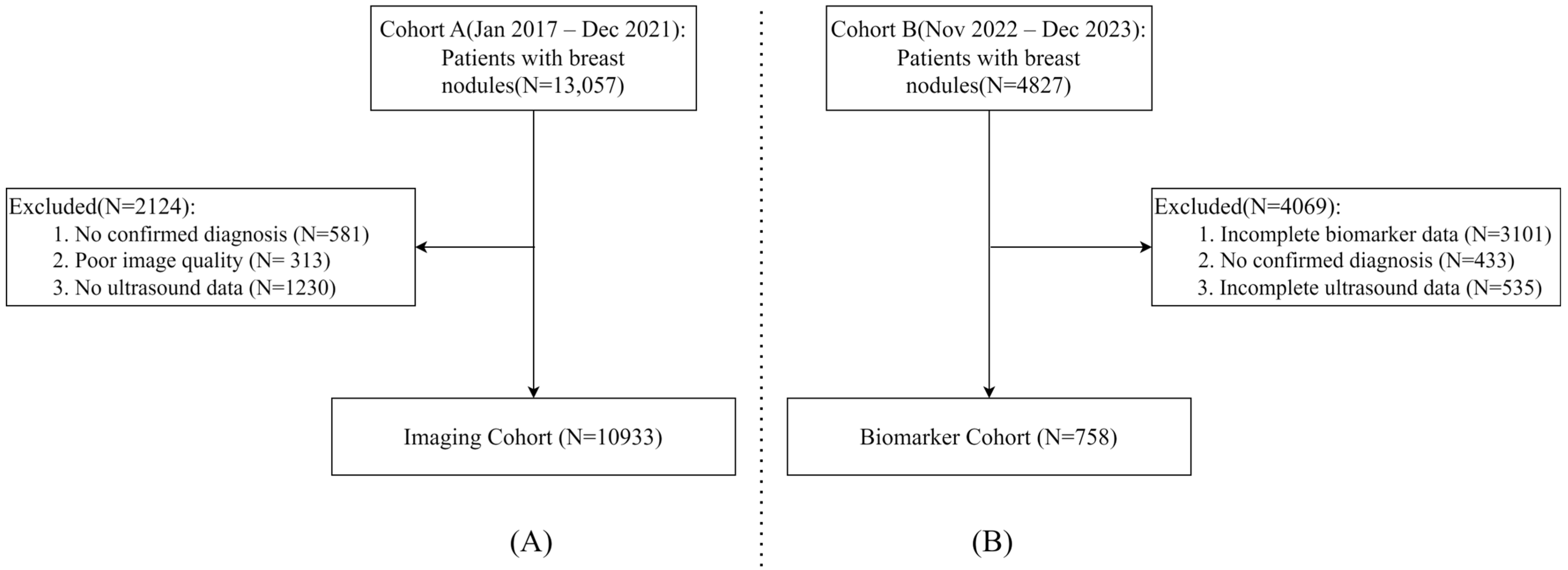
2.1. Study Population
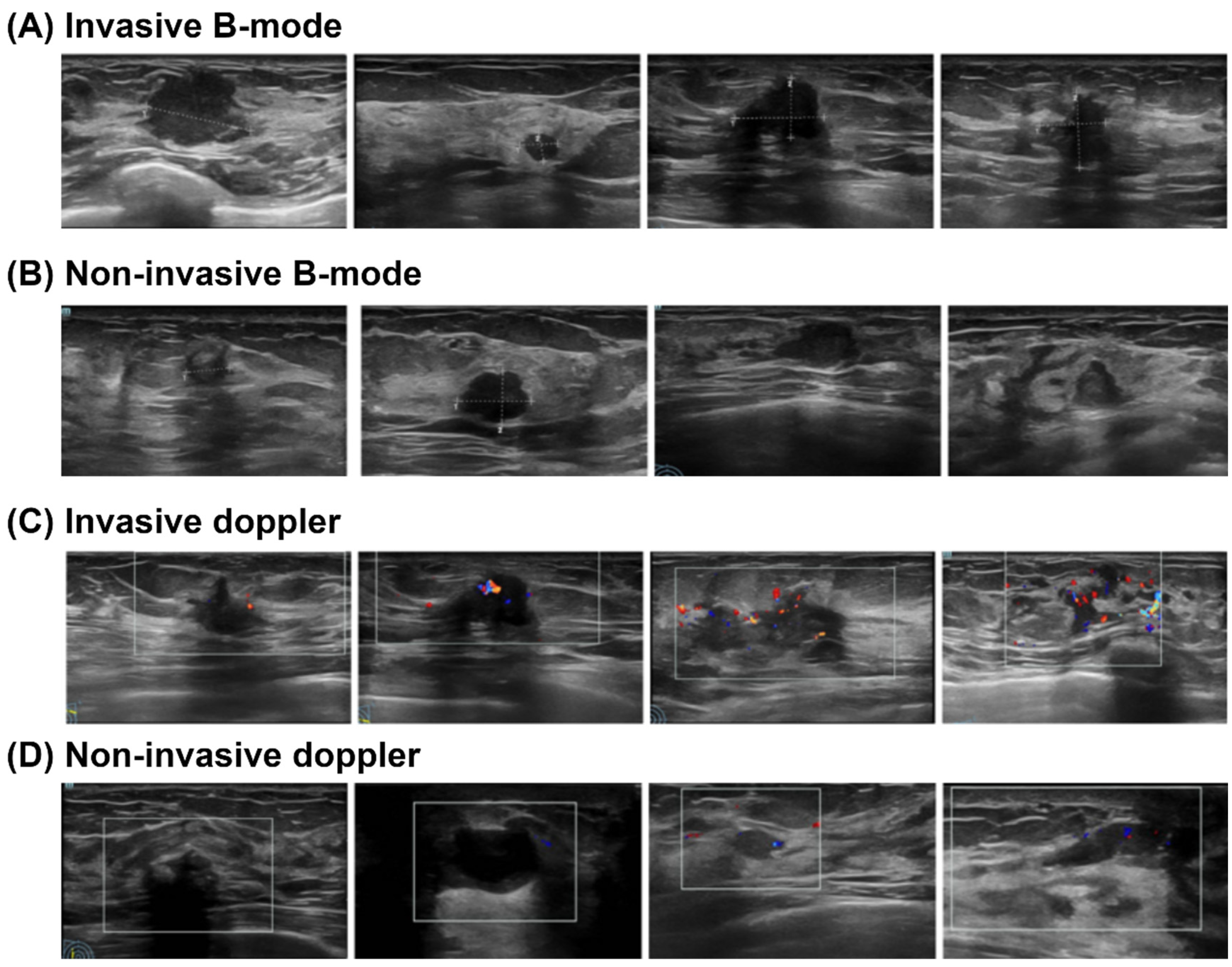
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Serum Biomarker Assays
2.4. Model Development
- Imaging Model: Deep learning models (including EfficientNet, ResNet101, and ViT) were developed and validated exclusively on Cohort A, utilizing the B-mode and Doppler ultrasound images. A weighted loss function was employed during training to mitigate the effects of class imbalance. This approach assigned higher penalties for misclassifying minority (invasive) class samples, thereby compelling the models to pay closer attention to these critical, less frequent instances.
- Biomarker Model: A separate predictive model was developed using the structured clinical biomarker data from Cohort B. Given the nature of tabular data, we employed XGBoost, which is well-suited for robust performance on such tasks. Feature selection was performed to identify the most informative serum markers for integration. This process involved first filtering biomarkers based on a univariate statistical significance threshold (p < 0.05). We then assessed multicollinearity among the significant features using the Variance Inflation Factor (VIF). All biomarkers retained for the final model had a VIF of less than 5, indicating acceptable levels of collinearity.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
3.2. Diagnostic Performance of Single-Modality Ultrasound
3.3. Diagnostic Performance of Multimodal Techniques
4. Discussion
4.1. Multimodal Advantage
4.2. Performance of Single-Modality Models
4.3. Comparative Analysis of Model Architectures
4.4. Practical and Clinical Implications
4.5. Limitations and Future Directions
4.6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Giaquinto, A.N.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2024. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 12–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santeramo, R.; Damiani, C.; Wei, J.; Montana, G.; Brentnall, A.R. Are better AI algorithms for breast cancer detection also better at predicting risk? A paired case-control study. Breast Cancer Res. 2024, 26, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hameed, Z.; Garcia-Zapirain, B.; Aguirre, J.J.; Isaza-Ruget, M.A. Multiclass classification of breast cancer histopathology images using multilevel features of deep convolutional neural network. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 15600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marmé, F.; Krieghoff-Henning, E.; Gerber, B.; Schmitt, M.; Zahm, D.-M.; Bauerschlag, D.; Forstbauer, H.; Hildebrandt, G.; Ataseven, B.; Brodkorb, T.; et al. Deep learning to predict breast cancer sentinel lymph node status on INSEMA histological images. Eur. J. Cancer 2023, 195, 113390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetstein, S.C.; de Jong, V.M.T.; Stathonikos, N.; Opdam, M.; Dackus, G.M.H.E.; Pluim, J.P.W.; van Diest, P.J.; Veta, M. Deep learning-based breast cancer grading and survival analysis on whole-slide histopathology images. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 15102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramanian, A.A.; Al-Heejawi, S.M.A.; Singh, A.; Breggia, A.; Ahmad, B.; Christman, R.; Ryan, S.T.; Amal, S. Ensemble Deep Learning-Based Image Classification for Breast Cancer Subtype and Invasiveness Diagnosis from Whole Slide Image Histopathology. Cancers 2024, 16, 2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, Z.; Zahia, S.; Garcia-Zapirain, B.; Javier Aguirre, J.; María Vanegas, A. Breast Cancer Histopathology Image Classification Using an Ensemble of Deep Learning Models. Sensors 2020, 20, 4373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Yang, Q.; Li, M.; Gu, J.; Du, C.; Chen, Y.; Li, B. Predicting HER2 Status in Breast Cancer on Ultrasound Images Using Deep Learning Method. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 829041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.-X.; Shi, J.; Ding, S.-S.; Zhang, H.-L.; Wang, X.-Y.; Lin, S.-Y.; Xu, Y.-F.; Wei, M.-J.; Liu, L.-Z.; Pei, X.-Q. Deep Learning Model Based on Dual-Modal Ultrasound and Molecular Data for Predicting Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Breast Cancer. Acad Radiol. 2023, 30 (Suppl. S2), S50–S61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.-X.; Wu, L.; Wang, X.-Y.; Lin, S.-Y.; Xu, Y.-F.; Wei, M.-J.; Pei, X.-Q. Delta Radiomics Based on Longitudinal Dual-modal Ultrasound Can Early Predict Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Breast Cancer Patients. Acad. Radiol. 2024, 31, 1738–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.-H.; Miao, S.-M.; Li, C.-Y.; Hang, J.; Deng, J.; Ye, X.-H.; Liu, Y. Pretreatment ultrasound-based deep learning radiomics model for the early prediction of pathologic response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer. Eur. Radiol. 2023, 33, 5634–5644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferro, A.; Bottosso, M.; Dieci, M.V.; Scagliori, E.; Miglietta, F.; Aldegheri, V.; Bonanno, L.; Caumo, F.; Guarneri, V.; Griguolo, G.; et al. Clinical applications of radiomics and deep learning in breast and lung cancer: A narrative literature review on current evidence and future perspectives. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2024, 203, 104479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.-J.; Su, G.-H.; You, C.; Zhang, X.; Xiao, Y.; Jiang, Y.-Z.; Shao, Z.-M. Radiomics in breast cancer: Current advances and future directions. Cell Rep. Med. 2024, 5, 101719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Park, H.; Ko, E.S. Radiomics in Breast Imaging from Techniques to Clinical Applications: A Review. Korean J. Radiol. 2020, 21, 779–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Hashemi, H.S.; Gordon, P.; Warren, L.; Wang, J.; Rohling, R.; Salcudean, S. Breast Cancer Detection Using Multimodal Time Series Features from Ultrasound Shear Wave Absolute Vibro-Elastography. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2022, 26, 704–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.M.; Won, J.-K.; Lee, K.-B.; Park, I.A.; Yi, A.; Moon, W.K. Comparison of shear-wave and strain ultrasound elastography in the differentiation of benign and malignant breast lesions. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2013, 201, W347–W356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, X.; Pei, J.; Zheng, H.; Xie, X.; Yan, L.; Zhang, H.; Han, C.; Gao, X.; Zhang, H.; Zheng, W.; et al. Prospective assessment of breast cancer risk from multimodal multiview ultrasound images via clinically applicable deep learning. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 5, 522–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eghtedari, M.; Chong, A.; Rakow-Penner, R.; Ojeda-Fournier, H. Current Status and Future of BI-RADS in Multimodality Imaging, From the AJR Special Series on Radiology Reporting and Data Systems. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2021, 216, 860–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Núñez, C. Blood-based protein biomarkers in breast cancer. Clin. Chim. Acta Int. J. Clin. Chem. 2019, 490, 113–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loke, S.Y.; Lee, A.S.G. The future of blood-based biomarkers for the early detection of breast cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 2018, 92, 54–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; An, R.; Yu, H.; Dai, Y.; Lou, L.; Quan, S.; Chen, R.; Ding, Y.; Zhao, H.; Wu, X.; et al. Largescale multicenter study of a serum metabolite biomarker panel for the diagnosis of breast cancer. iScience 2024, 27, 110345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, S.H.; Saadatpour, Z.; Salmaninejad, A.; Momeni, F.; Mokhtari, M.; Nahand, J.S.; Rahmati, M.; Mirzaei, H.; Kianmehr, M. Breast cancer diagnosis: Imaging techniques and biochemical markers. J. Cell Physiol. 2018, 233, 5200–5213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moar, K.; Pant, A.; Saini, V.; Pandey, M.; Maurya, P.K. Potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers for breast cancer: A compiled review. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2023, 251, 154893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Li, S.; Wu, C.; Wu, S.; Lin, Y.; Wei, D. Ultrasound-based deep learning radiomics nomogram for differentiating mass mastitis from invasive breast cancer. BMC Med. Imaging 2024, 24, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Zhou, W.; Lu, W.-W.; Qin, X.-C.; Zhang, X.-Y.; Wang, J.-L.; Wu, J.; Luo, Y.-H.; Duan, Y.-Y.; Zhang, C.-X. Ultrasound-Based Deep Learning Radiomics Nomogram for the Assessment of Lymphovascular Invasion in Invasive Breast Cancer: A Multicenter Study. Acad. Radiol. 2024, 31, 3917–3928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Lu, X.; Chen, Q.; Gong, H.; Lei, J. Multiphases DCE-MRI Radiomics Nomogram for Preoperative Prediction of Lymphovascular Invasion in Invasive Breast Cancer. Acad. Radiol. 2024, 31, 4743–4758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Ultrasound Modality | Invasive Images | Non-Invasive Images | Invasive Cases | Non-Invasive Cases |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| B-mode | 6602 | 26,400 | 1517 | 7222 |
| Doppler | 2967 | 12,452 | 1352 | 6930 |
| Marker | Invasive Mean | Non-Invasive Mean | p-Value | Significant |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CA125 | 26.10 | 23.31 | 0.03 | Yes |
| CA15-3 | 17.28 | 17.41 | 0.041 | Yes |
| CEA | 11.62 | 5.46 | 0.04 | Yes |
| CA19-9 | 67.99 | 34.71 | 0.03 | Yes |
| AFP | 2.44 | 2.55 | 0.73 | No |
| FSH | 29.69 | 32.92 | 0.542 | No |
| LH | 18.00 | 17.68 | 0.41 | No |
| PRL | 22.11 | 20.85 | 0.371 | No |
| P | 2.67 | 1.82 | 0.796 | No |
| T | 0.37 | 0.34 | 0.84 | No |
| E2 | 62.08 | 62.50 | 0.383 | No |
| Model | Accuracy (%) | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | F1-Score (%) | AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ResNet101 | 90.98 | 79.85 | 73.29 | 76.43 | 0.933 |
| ViT | 86.71 | 65.27 | 71.39 | 68.19 | 0.888 |
| EfficientNet | 91.12 | 78.15 | 77.02 | 77.58 | 0.937 |
| Model | Accuracy (%) | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | F1-Score (%) | AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ResNet101 | 84.87 | 61.47 | 56.21 | 58.72 | 0.861 |
| ViT | 75.40 | 37.08 | 40.94 | 38.92 | 0.691 |
| EfficientNet | 86.13 | 64.04 | 62.75 | 63.39 | 0.869 |
| Model | Accuracy (%) | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | F1-Score (%) | AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Logistic Regression | 85.53 | 89.47 | 87.63 | 88.54 | 0.909 |
| Random Forest | 86.09 | 87.88 | 90.62 | 89.23 | 0.898 |
| XGBoost | 87.50 | 90.62 | 89.69 | 90.16 | 0.894 |
| Model | Accuracy (%) | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | F1-Score (%) | AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Logistic Regression | 86.79 | 89.83 | 89.42 | 89.61 | 0.917 |
| Random Forest | 87.18 | 91.15 | 88.58 | 89.79 | 0.918 |
| XGBoost | 88.90 | 92.17 | 90.25 | 91.20 | 0.930 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tan, D.; Zhai, Y.; Hu, Z.; Sun, D.; Zheng, T. A Multimodal Diagnostic Model for Breast Cancer Invasiveness Based on Ultrasound Imaging and Serum Biomarkers. Medicina 2025, 61, 2010. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61112010
Tan D, Zhai Y, Hu Z, Sun D, Zheng T. A Multimodal Diagnostic Model for Breast Cancer Invasiveness Based on Ultrasound Imaging and Serum Biomarkers. Medicina. 2025; 61(11):2010. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61112010
Chicago/Turabian StyleTan, Dianhuan, Yue Zhai, Zhengming Hu, Desheng Sun, and Tingting Zheng. 2025. "A Multimodal Diagnostic Model for Breast Cancer Invasiveness Based on Ultrasound Imaging and Serum Biomarkers" Medicina 61, no. 11: 2010. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61112010
APA StyleTan, D., Zhai, Y., Hu, Z., Sun, D., & Zheng, T. (2025). A Multimodal Diagnostic Model for Breast Cancer Invasiveness Based on Ultrasound Imaging and Serum Biomarkers. Medicina, 61(11), 2010. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61112010







