Are Intravenous Immunoglobulins Effective in Preventing Primary EBV Infection in Pediatric Kidney Transplant Recipients?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
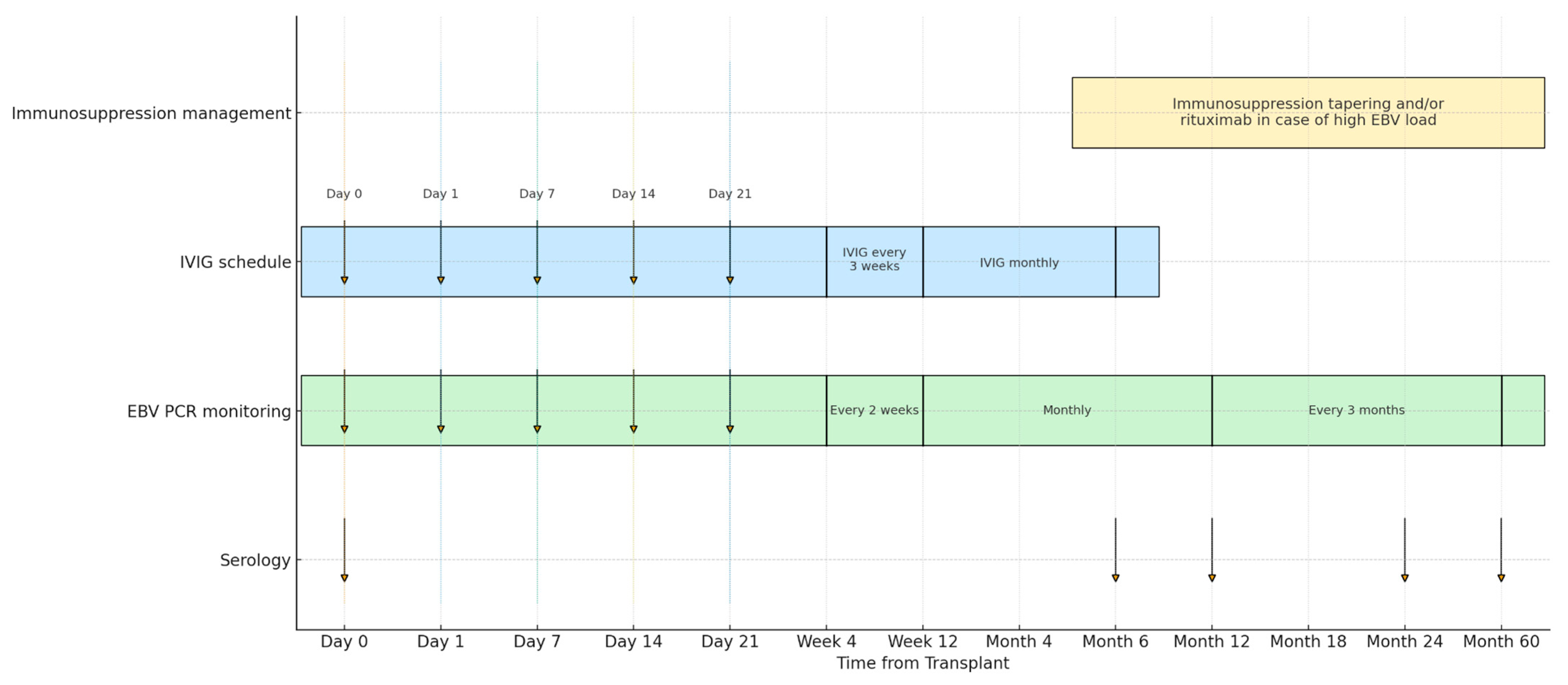
2.1. Study Design and Subjects
2.2. Endpoints
2.3. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Population Characteristics
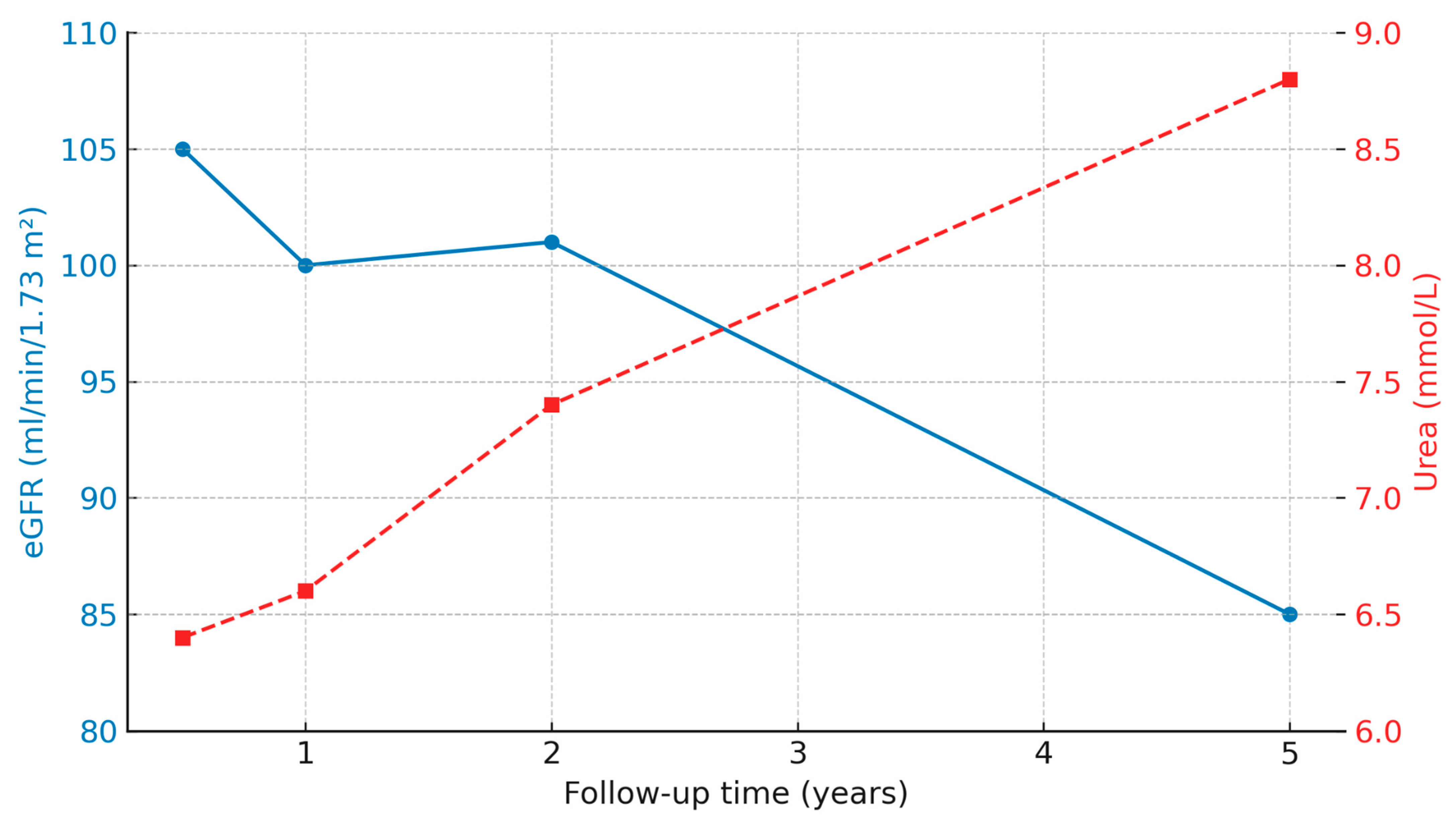
3.2. Kidney Function and Laboratory Test over Time
3.3. EBV Viremia and Seroconversion After Transplantation
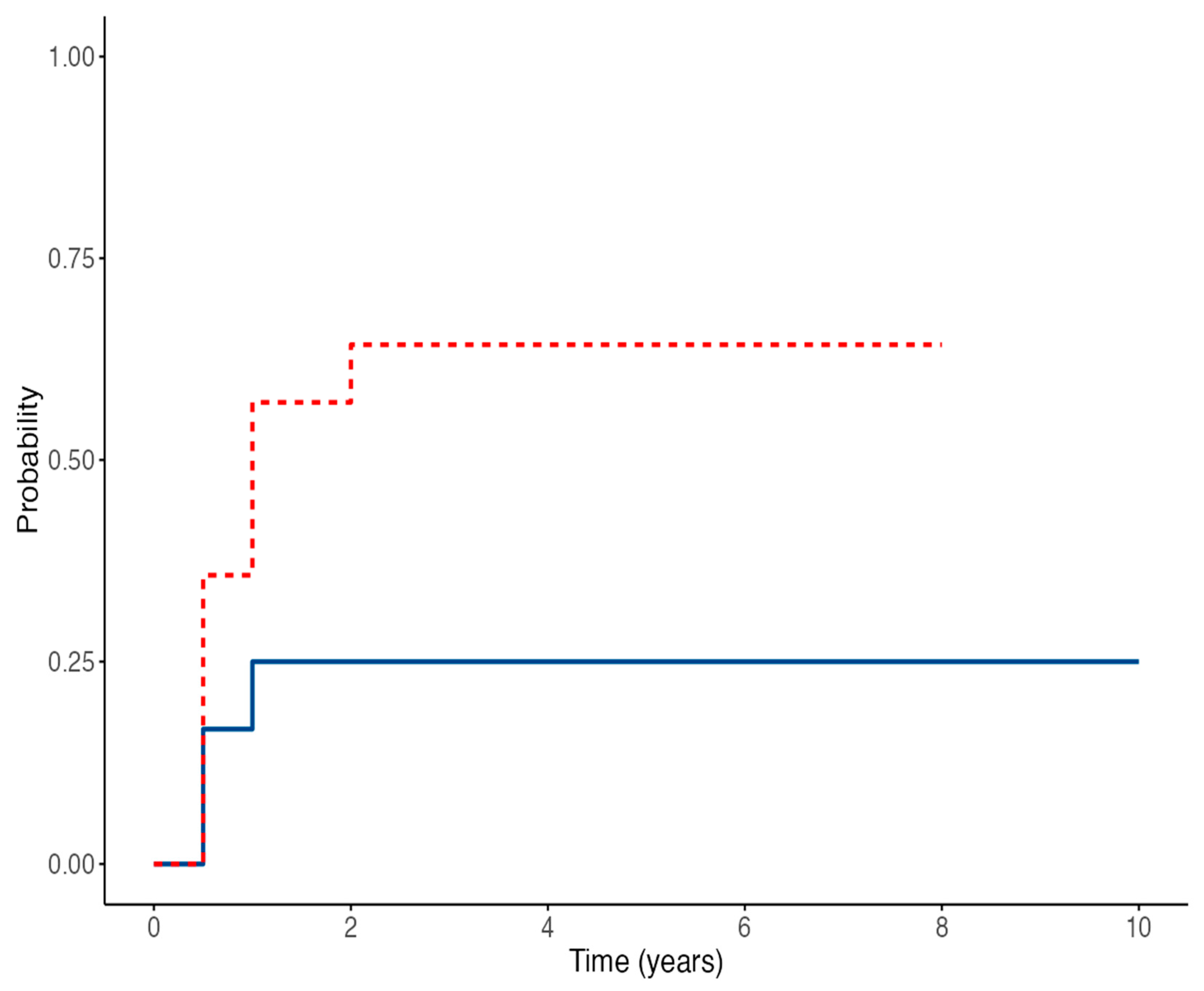
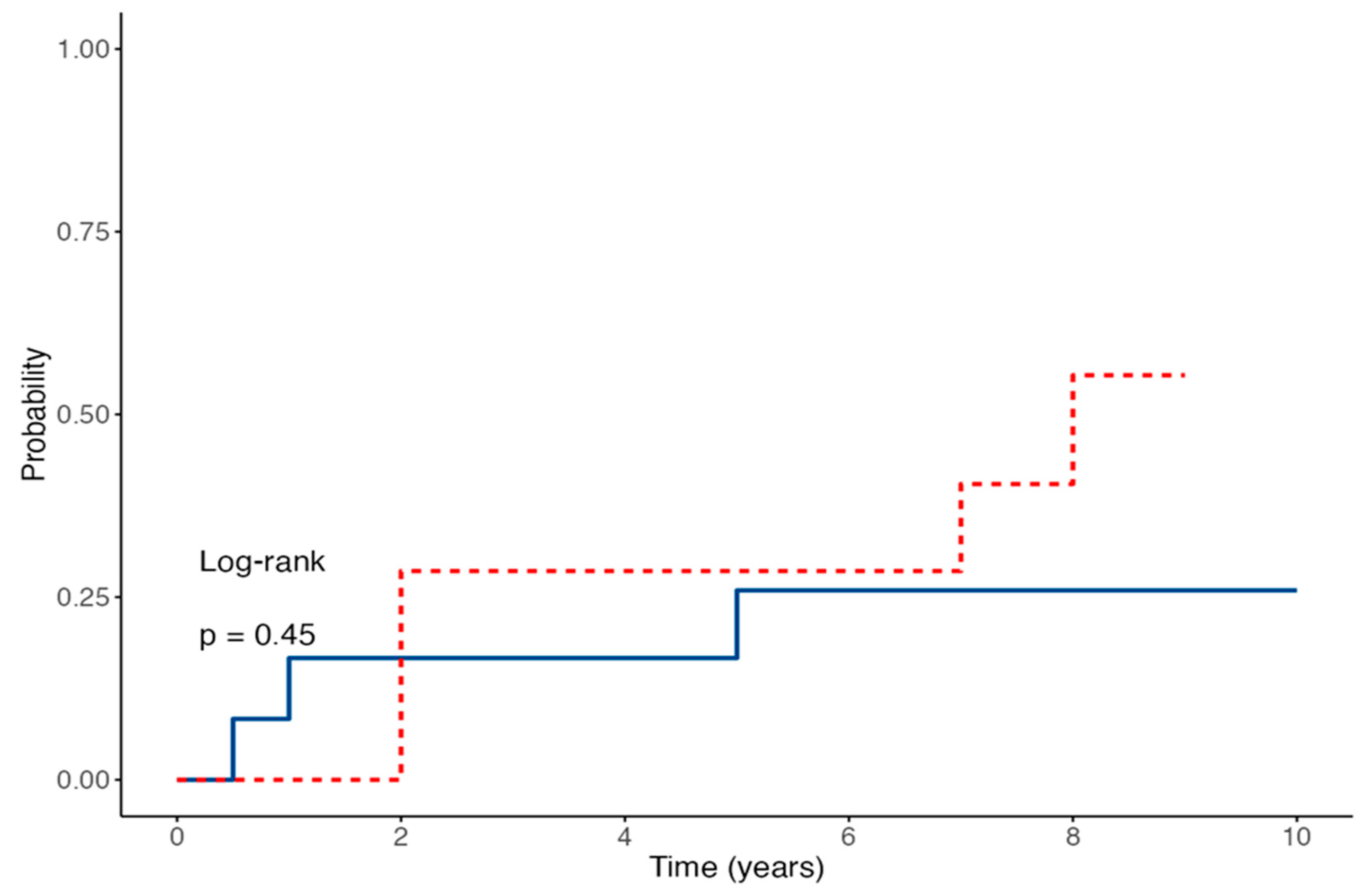
3.4. Time-to-Event Outcomes for EBV Viremia and Seroconversion in Children Receiving IVIG Prophylaxis After Kidney Transplantation
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EBV | Epstein–Barr virus |
| D/R | Donor/Recipient |
| PTLD | Post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder |
| IVIG | Intravenous immunoglobulins |
| HR | Hazard Ratio |
| EBNA-IgG | Epstein–Barr Nuclear Antigen-Immunoglobulin G |
| PCR | Polymerase chain reaction |
| HLA | Human Leucocyte Antigens |
| VCA | Viral Capsid Antigen |
| EA | Early Antigen |
| ATG | Anti-thymocyte globulin |
| CNI | Calcineurin inhibitor |
| CMV | Cytomegalovirus |
| ELISA | Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| IR | Interquartile range |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| CAKUT | Congenital anomalies of the kidney and the urinary tract |
References
- Dunmire, S.K.; Verghese, P.S.; Balfour, H.H., Jr. Primary Epstein-Barr virus infection. J. Clin. Virol. 2018, 102, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, U.D.; Preiksaitis, J.K. AST Infectious Diseases Community of Practice. Post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorders, Epstein-Barr virus infection, and disease in solid organ transplantation: Guidelines from the American Society of Transplantation Infectious Diseases Community of Practice. Clin. Transplant. 2019, 33, e13652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, A.; Frauca Remacha, E.; Torres Canizales, J.; Bravo-Gallego, L.Y.; Fitzpatrick, E.; Alonso Melgar, A.; Muñoz Bartolo, G.; Garcia Guereta, L.; Ramos Boluda, E.; Mozo, Y.; et al. Current Practices on Diagnosis, Prevention and Treatment of Post-Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disorder in Pediatric Patients after Solid Organ Transplantation: Results of ERN TransplantChild Healthcare Working Group Survey. Children 2021, 8, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, K.H.; Tam, J.S.; Peiris, J.S.; Seto, W.H.; Ng, M.H. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection in infancy. J. Clin. Virol. 2001, 21, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuri, A.; Jacobs, B.M.; Vickaryous, N.; Pakpoor, J.; Middeldorp, J.; Giovannoni, G.; Dobson, R. Epidemiology of Epstein-Barr virus infection and infectious mononucleosis in the United Kingdom. BMC Public Health 2020, 20, 912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollack, S.; Plonsky, M.; Tibi, R.; Libinson-Zebegret, I.; Yakobov, R.; Eisenstein, I.; Magen, D. Prevention of post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder in pediatric kidney transplant recipients. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2025, 40, 829–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, M.; Reyes, J.; Webber, S.; Rowe, D. The role of antiviral and immunoglobulin therapy in the prevention of Epstein-Barr virus infection and post-transplant lymphoproliferative disease following solid organ transplantation. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2001, 3, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, M.; Michaels, M.G.; Katz, B.Z.; Burroughs, M.; Gerber, D.; Shneider, B.L.; Newell, K.; Rowe, D.; Reyes, J. CMV-IVIG for prevention of Epstein Barr virus disease and posttransplant lymphoproliferative disease in pediatric liver transplant recipients. Am. J. Transplant. 2006, 6, 1906–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, G.J.; Muñoz, A.; Schneider, M.F.; Mak, R.H.; Kaskel, F.; Warady, B.A.; Furth, S.L. New equations to estimate GFR in children with CKD. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 20, 629–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roufosse, C.; Simmonds, N.; Clahsen-van Groningen, M.; Haas, M.; Henriksen, K.J.; Horsfield, C.; Loupy, A.; Mengel, M.; Perkowska-Ptasińska, A.; Rabant, M.; et al. A 2018 reference guide to the Banff classification of renal allograft pathology. Transplantation 2018, 102, 1795–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaudry, W.; Ettenger, R.; Jara, P.; Varela-Fascinetto, G.; Bouw, M.R.; Ives, J.; Walker, R.; Valcyte WV16726 Study Group. Valganciclovir dosing according to body surface area and renal function in pediatric solid organ transplant recipients. Am. J. Transplant. 2009, 9, 636–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razonable, R.R.; Humar, A. Cytomegalovirus in solid organ transplant recipients: Guidelines of the American Society of Transplantation Infectious Diseases Community of Practice. Clin. Transplant. 2019, 33, e13512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertazza Partigiani, N.; Negrisolo, S.; Carraro, A.; Marzenta, D.; Manaresi, E.; Gallinella, G.; Barzon, L.; Benetti, E. Pre-Existing Intrarenal Parvovirus B19 Infection May Relate to Antibody-Mediated Rejection in Pediatric Kidney Transplant Patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preiksaitis, J.; Allen, U.; Bollard, C.M.; Green, M.; Squires, J.E.; Chinnok, R.; Comoli, P.; Danziger-Isakov, L.; Dulek, D.E.; Esquivel, C.O.; et al. The IPTA Nashville Consensus Conference on post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorders after solid organ transplantation in children: III—Consensus guidelines for Epstein-Barr virus load and other biomarker monitoring. Pediatr. Transplant. 2019, 23, e13591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dharnidharka, V.R.; Lamb, K.E.; Gregg, J.A.; Meier-Kriesche, H.U. Associations between EBV serostatus and organ transplant type in PTLD risk: An analysis of the SRTR National Registry Data in the United States. Am. J. Transplant. 2012, 12, 976–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferla, V.; Rossi, F.G.; Goldaniga, M.C.; Baldini, L. Biological Difference Between Epstein-Barr Virus Positive and Negative Post-transplant Lymphoproliferative Disorders and Their Clinical Impact. Front Oncol. 2020, 10, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, J.I. Epstein-Barr virus infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 343, 481–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dharnidharka, V.R.; Webster, A.C.; Martinez, O.M.; Preiksaitis, J.K.; Leblond, V.; Choquet, S. Post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorders. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2016, 2, 15088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, A.K.C.; Lam, J.M.; Barankin, B. Infectious Mononucleosis: An Updated Review. Curr. Pediatr. Rev. 2024, 20, 305–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, S.; Stagno, S.; Whitley, R. Transfusion-associated viral infections. Curr. Probl. Pediatr. 1987, 17, 391–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enok Bonong, P.R.; Buteau, C.; Delage, G.; Tanner, J.E.; Lacroix, J.; Duval, M.; Laporte, L.; Tucci, M.; Robitaille, N.; Spinella, P.C.; et al. Transfusion-related Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection: A multicenter prospective cohort study among pediatric recipients of hematopoietic stem cell transplants (TREASuRE study). Transfusion 2021, 61, 144–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trottier, H.; Buteau, C.; Robitaille, N.; Duval, M.; Tucci, M.; Lacroix, J.; Alfieri, C. Transfusion-related Epstein-Barr virus infection among stem cell transplant recipients: A retrospective cohort study in children. Transfusion 2012, 52, 2653–2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babel, N.; Gabdrakhmanova, L.; Hammer, M.; Rosenberger, C.; Oppert, M.; Volk, H.D.; Reinke, P. Induction of pre-transplant Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection by donor blood transfusion in EBV-seronegative recipients may reduce risk of post-transplant lymphoproliferative disease in adolescent renal transplant patients: Report of two cases. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2005, 7, 133–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheyssac, E.; Savadogo, H.; Lagoutte, N.; Baudouin, V.; Charbit, M.; Novo, R.; Sellier-Leclerc, A.L.; Fila, M.; Decramer, S.; Merieau, E.; et al. Valganciclovir is not associated with decreased EBV infection rate in pediatric kidney transplantation. Front. Pediatr. 2023, 10, 1085101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paulsen, G.; Cumagun, P.; Mixon, E.; Fowler, K.; Feig, D.; Shimamura, M. Cytomegalovirus and Epstein-Barr virus infections among pediatric kidney transplant recipients at a center using universal Valganciclovir Prophylaxis. Pediatr. Transplant. 2019, 23, e13382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, M.; Squires, J.E.; Chinnock, R.E.; Comoli, P.; Danziger-Isakov, L.; Dulek, D.E.; Esquivel, C.O.; Höcker, B.; L’HUillier, A.G.; Mazariegos, G.V.; et al. The IPTA Nashville consensus conference on post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorders after solid organ transplantation in children: II-consensus guidelines for prevention. Pediatr. Transplant. 2022, 26, e14350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlDabbagh, M.A.; Gitman, M.R.; Kumar, D.; Humar, A.; Rotstein, C.; Husain, S. The role of antiviral prophylaxis for the prevention of Epstein-Barr virus-associated posttransplant lymphoproliferative disease in solid organ transplant recipients: A systematic review. Am. J. Transplant. 2017, 17, 770–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schachtner, T.; Reinke, P. Pretransplant prophylactic rituximab to prevent Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) viremia in EBV-seronegative kidney transplant recipients from EBV-seropositive donors: Results of a pilot study. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2016, 18, 881–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashoor, I.F.; Al-Akash, S.; Kizilbash, S.; Moudgil, A.; Puliyanda, D.; Ranabothu, S.; Shi, Y.; Dharnidharka, V. Effect of pre-emptive rituximab on EBV DNA levels and prevention of post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder in pediatric kidney transplant recipients: A case series from the pediatric nephrology research consortium. Pediatr. Transplant. 2024, 28, e14743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puliyanda, D.P.; Jordan, S.C.; Kim, I.K.; Patel, M.; Murthy, A.; Huang, E.; Zhang, X.; Reinsmoen, N.; Kamil, E.S.; Toyoda, M. Use of Rituximab for persistent EBV DNAemia, and Its effect on donor-specific antibody development in pediatric renal transplant recipients: A case series. Pediatr. Transplant. 2021, 25, e14113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marjańska, A.; Pogorzała, M.; Dziedzic, M.; Czyżewski, K.; Richert-Przygońska, M.; Dębski, R.; Bogiel, T.; Styczyński, J. Impact of prophylaxis with rituximab on EBV-related complications after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation in children. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1427637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | IVIG Group (n = 14) | Control Group (n = 12) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age at transplant (years) (range) | 4.1 (2.3–7.0) | 8.2 (7.0–12.1) | 0.008 |
| Sex (male) (%) | 9 (64) | 8 (67) | 0.919 |
| Weight at transplant (kg) (range) | 10.9 (5.7–28.5) | 21.0 (19.4–44.0) | 0.084 |
| Number of second transplants (n) (%) | 0 (0) | 3 (25) | 0.098 |
| Mismatch (n) (range) | 4 (2–5) | 3 (2–4) | 0.255 |
| Living donor transplant (n) (%) | 4 (29) | 4 (33) | 0.796 |
| ATG * (n) (%) | 1 (7) | 3 (25) | 0.272 |
| Tacrolimus (n) (%) | 7 (50) | 6 (50) | 1.000 |
| PTLD * (n) (%) | 1 (7) | 0 (0) | 0.619 |
| Valganciclovir (n) (%) | 11 (79) | 8 (67) | 0.523 |
| Rituximab (n) (%) | 1 (7) | 0 (0) | 0.619 |
| Transfusion of blood, platelet or plasma (n) (%) | 8 (57) | 6 (50) | 0.732 |
| Pre-emptive transplant (n) (%) | 1 (7) | 5 (42) | 0.070 |
| Peritoneal dialysis (n) (%) | 9 (64) | 6 (50) | 0.460 |
| Hemodialysis (n) (%) | 0 (0) | 1 (8) | 0.471 |
| Hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis (n) (%) | 4 (29) | 0 (0) | 0.080 |
| CAKUT * (n) (%) | 9 (64) | 7 (58) | 0.826 |
| Glomerulopathy (n) (%) | 1 (7) | 3 (25) | 0.218 |
| Ciliopathy (n) (%) | 3 (21) | 1 (8) | 0.381 |
| Asphyxia (n) (%) | 1 (7) | 1 (8) | 1.000 |
| Parameter | Time Point | N | Control Group Median [IQR] | IVIG Group Median [IQR] | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 6 months | 26 | 104.8 [84.9–118.0] | 108.0 [102.0–118.5] | 0.35 |
| 12 months | 25 | 97.8 [89.1–122.3] | 106.0 [100.0–131.3] | 0.24 | |
| 24 months | 25 | 95.8 [70.7–117.3] | 102.5 [92.0–114.2] | 0.33 | |
| 60 months | 23 | 50.8 [48.3–94.8] | 84.5 [63.0–97.9] | 1.00 | |
| Urea (mmol/L) | 6 months | 26 | 4.9 [4.8–7.6] | 6.2 [6.2–6.6] | 0.42 |
| 12 months | 25 | 5.2 [5.5–8.2] | 6.6 [6.6–8.4] | 0.94 | |
| 24 months | 26 | 5.3 [5.7–9.8] | 7.5 [6.9–9.1] | 0.84 | |
| 60 months | 23 | 6.2 [7.0–12.3] | 9.2 [8.1–11.7] | 0.72 | |
| Uric acid (mmol/L) | 6 months | 26 | 0.3 [0.3–0.3] | 0.3 [0.3–0.4] | 0.96 |
| 12 months | 25 | 0.2 [0.2–0.4] | 0.3 [0.3–0.4] | 0.79 | |
| 24 months | 26 | 0.2 [0.3–0.4] | 0.3 [0.3–0.4] | 0.19 | |
| 60 months | 23 | 0.3 [0.3–0.3] | 0.3 [0.3–0.4] | 0.40 | |
| Tacrolimus (ng/mL) | 6 months | 10 | 5.0 [6.3–9.0] | 7.2 [7.8–8.0] | 0.75 |
| 12 months | 13 | 2.3 [5.6–7.0] | 5.3 [6.7–7.6] | 0.58 | |
| 24 months | 19 | 4.3 [5.3–6.3] | 6.2 [6.1–6.9] | 0.94 | |
| 60 months | 17 | 5.3 [4.9–7.1] | 6.8 [6.5–7.2] | 0.68 | |
| Cyclosporine (C2, ng/mL) | 6 months | 16 | 524.8 [512.7–748.0] | 647.0 [674.0–825.2] | 0.87 |
| 12 months | 12 | 314.6 [579.9–708.0] | 579.5 [653.0–739.2] | 0.63 | |
| 24 months | 7 | 513.3 [420.0–626.0] | 730.0 [523.0–781.3] | 0.28 | |
| 60 months | 5 | 398.2 [577.0–714.0] | 494.0 [645.5–879.0] | 0.64 |
| Category | Time-Point | IVIG Group | Control Group | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EBV-DNA | 6 months | 8/14 (57%) | 3/12 (25%) | 0.11 |
| 12 months | 8/14 (57%) | 3/12 (25%) | 0.11 | |
| 24 months | 7/14 (50%) | 3/12 (25%) | 0.22 | |
| 60 months | 4/14 (28%) | 2/12 (17%) | 0.38 | |
| Ever positive | 9/14 (64%) | 3/12 (25%) | 0.047 * | |
| Anti-EBNA IgG | 6 months | 9/14 (64%) | 2/12 (17%) | 0.012 * |
| 12 months | 0/14 (0%) | 2/12 (17%) | 0.23 | |
| 24 months | 3/14 (21%) | 3/12 (25%) | 0.83 | |
| 60 months | 5/14 (36%) | 2/12 (17%) | 0.15 | |
| Ever positive | 6/14 (43%) | 3/12 (25%) | 0.38 |
| Variable | Category | n (%) | HR (Univariable) | HR (Multivariable) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Outcome (Case/Control) | 0 (Control) | 12 (46.2) | – | – |
| 1 (Case) | 14 (53.8) | 3.24 (0.87–12.01), p = 0.079 | 1.50 (0.33–6.73), p = 0.599 | |
| Tacrolimus | 0 (No) | 13 (50.0) | – | – |
| 1 (Yes) | 13 (50.0) | 0.44 (0.13–1.46), p = 0.181 | 0.30 (0.08–1.14), p = 0.078 | |
| Primary cause of CKD | CAKUT | 16 (61.5) | – | – |
| Asphyxia | 2 (7.7) | 1.21 (0.15–9.69), p = 0.857 | 1.88 (0.19–18.41), p = 0.587 | |
| Ciliopathy | 4 (15.4) | 2.05 (0.54–7.77), p = 0.292 | 3.65 (0.81–16.57), p = 0.093 | |
| Glomerulopathy | 4 (15.4) | 0.00 (0.00–Inf), p = 0.998 | 0.00 (0.00–Inf), p = 0.998 | |
| Age at transplant (years) | Mean (SD) | 6.9 (4.9) | 0.88 (0.75–1.04), p = 0.131 | 0.90 (0.75–1.07), p = 0.238 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bertazza Partigiani, N.; Bertozzi, V.; Sangermano, M.; Benetti, E. Are Intravenous Immunoglobulins Effective in Preventing Primary EBV Infection in Pediatric Kidney Transplant Recipients? Medicina 2025, 61, 1967. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61111967
Bertazza Partigiani N, Bertozzi V, Sangermano M, Benetti E. Are Intravenous Immunoglobulins Effective in Preventing Primary EBV Infection in Pediatric Kidney Transplant Recipients? Medicina. 2025; 61(11):1967. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61111967
Chicago/Turabian StyleBertazza Partigiani, Nicola, Veronica Bertozzi, Maria Sangermano, and Elisa Benetti. 2025. "Are Intravenous Immunoglobulins Effective in Preventing Primary EBV Infection in Pediatric Kidney Transplant Recipients?" Medicina 61, no. 11: 1967. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61111967
APA StyleBertazza Partigiani, N., Bertozzi, V., Sangermano, M., & Benetti, E. (2025). Are Intravenous Immunoglobulins Effective in Preventing Primary EBV Infection in Pediatric Kidney Transplant Recipients? Medicina, 61(11), 1967. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61111967






