Assessing the Influence of Proton Pump Inhibitors on Clinical Outcomes in Hormone Receptor-Positive Metastatic Breast Cancer Patients Receiving CDK4/6 Inhibitors: Evidence from a Ribociclib-Dominant Cohort
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AI | Aromatase inhibitor |
| CDK4/6 | Cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 |
| CDK4/6i | Cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitor(s) |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| CTCAE | Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events |
| CYP3A4 | Cytochrome P450 3A4 |
| DCR | Disease control rate |
| ECOG PS | Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Performance Status |
| ER | Estrogen receptor |
| ET | Endocrine therapy |
| GERD | Gastroesophageal reflux disease |
| HER2 | Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 |
| HR | Hazard ratio |
| HR+/HER2 | Hormone receptor–positive/HER2-negative |
| IHC | Immunohistochemistry |
| ISH | In situ hybridization |
| iDFS | Invasive disease-free survival |
| LHRH | Luteinizing hormone–releasing hormone |
| mBC | Metastatic breast cancer |
| ORR | Overall response rate |
| OS | Overall survival |
| OTC | Over-the-counter |
| PFS | Progression-free survival |
| PPI | Proton pump inhibitor |
| PK/PD | Pharmacokinetics/pharmacodynamics |
| SPSS | Statistical Package for the Social Sciences |
| C_ss/IC50 | Steady-state drug concentration to half-maximal inhibitory concentration ratio |
References
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Kratzer, T.B.; Giaquinto, A.N.; Sung, H.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2025. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2025, 75, 10–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Harper, A.; McCormack, V.; Sung, H.; Houssami, N.; Morgan, E.; Mutebi, M.; Garvey, G.; Soerjomataram, I.; Fidler-Benaoudia, M.M. Global patterns and trends in breast cancer incidence and mortality across 185 countries. Nat. Med. 2025, 31, 1154–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahraman, S.; Erul, E.; Gumusay, O.; Guven, D.C.; Aksoy, S.; Basaran, G.; Seyyar, M.; Sahin, E.; Cabuk, D.; Bayram, E.; et al. Real-World Treatment Efficacy of Ribociclib or Palbociclib Plus Fulvestrant in Hormone Receptor-Positive/HER2-Negative Metastatic Breast Cancer: Turkish Oncology Group (TOG) Study. Clin. Breast Cancer 2025, 25, e635–e644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathy, D.; Im, S.A.; Colleoni, M.; Franke, F.; Bardia, A.; Harbeck, N.; Hurvitz, S.A.; Chow, L.; Sohn, J.; Lee, K.S.; et al. Ribociclib plus endocrine therapy for premenopausal women with hormone-receptor-positive, advanced breast cancer (MONALEESA-7): A randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 904–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goetz, M.P.; Toi, M.; Campone, M.; Sohn, J.; Paluch-Shimon, S.; Huober, J.; Park, I.H.; Trédan, O.; Chen, S.C.; Manso, L.; et al. MONARCH 3: Abemaciclib As Initial Therapy for Advanced Breast Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 3638–3646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slamon, D.J.; Neven, P.; Chia, S.; Fasching, P.A.; De Laurentiis, M.; Im, S.A.; Petrakova, K.; Bianchi, G.V.; Esteva, F.J.; Martín, M.; et al. Overall Survival with Ribociclib plus Fulvestrant in Advanced Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 514–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, S.A.; Lu, Y.S.; Bardia, A.; Harbeck, N.; Colleoni, M.; Franke, F.; Chow, L.; Sohn, J.; Lee, K.S.; Campos-Gomez, S.; et al. Overall Survival with Ribociclib plus Endocrine Therapy in Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hortobagyi, G.N.; Stemmer, S.M.; Burris, H.A.; Yap, Y.S.; Sonke, G.S.; Paluch-Shimon, S.; Campone, M.; Blackwell, K.L.; André, F.; Winer, E.P.; et al. Ribociclib as First-Line Therapy for HR-Positive, Advanced Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1738–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, R.S.; Martin, M.; Rugo, H.S.; Jones, S.; Im, S.A.; Gelmon, K.; Harbeck, N.; Lipatov, O.N.; Walshe, J.M.; Moulder, S.; et al. Palbociclib and Letrozole in Advanced Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1925–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahin, T.K.; Kavgaci, G.; Guven, D.C.; Aksoy, S. Drug-Drug interactions and special considerations in breast cancer patients treated with CDK4/6 inhibitors: A comprehensive review. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2025, 137, 102956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strand, D.S.; Kim, D.; Peura, D.A. 25 Years of Proton Pump Inhibitors: A Comprehensive Review. Gut Liver 2017, 11, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Klamerus, K.J.; Yuhas, L.M.; Pawlak, S.; Plotka, A.; O’Gorman, M.; Kirkovsky, L.; Kosa, M.; Wang, D. Impact of Acid-Reducing Agents on the Pharmacokinetics of Palbociclib, a Weak Base With pH-Dependent Solubility, With Different Food Intake Conditions. Clin. Pharmacol. Drug Dev. 2017, 6, 614–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Moraes, F.C.A.; Pereira, C.R.M.; Sano, V.K.T.; Laia, E.A.; Stecca, C.; Burbano, R.M.R. Do proton pump inhibitors affect the effectiveness of cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitors in advanced HR positive, HER2 negative breast cancer? A meta-analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1352224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odabas, H.; Dogan, A.; Ozcelik, M.; Yildirim, S.; Ozkerim, U.; Turan, N.; Yildirim, M.E.; Gumus, M. Does Proton Pump Inhibitors Decrease the Efficacy of Palbociclib and Ribociclib in Patients with Metastatic Breast Cancer? Medicina 2023, 59, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Re, M.; Crucitta, S.; Omarini, C.; Bargagna, I.; Mongillo, M.; Palleschi, M.; Stucci, S.; Meattini, I.; D’Onofrio, R.; Lorenzini, G.; et al. Concomitant administration of proton pump inhibitors does not significantly affect clinical outcomes in metastatic breast cancer patients treated with ribociclib. Breast 2022, 66, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-E.; Kwon, S.-H.; Kwon, S.; Jung, H.-I.; Nam, J.H.; Lee, E.-K. Concomitant Use of Proton Pump Inhibitors and Palbociclib Among Patients With Breast Cancer. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, e2324852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eser, K.; Önder, A.H.; Sezer, E.; Çil, T.; İnal, A.; Öztürk, B.; Erçolak, V.; Duman, B.B.; Çelik, H.; Köşeci, T.; et al. Proton pump inhibitors may reduce the efficacy of ribociclib and palbociclib in metastatic breast cancer patients based on an observational study. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Allison, K.H.; Hammond, M.E.H.; Dowsett, M.; McKernin, S.E.; Carey, L.A.; Fitzgibbons, P.L.; Hayes, D.F.; Lakhani, S.R.; Chavez-MacGregor, M.; Perlmutter, J.; et al. Estrogen and Progesterone Receptor Testing in Breast Cancer: ASCO/CAP Guideline Update. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 1346–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolff, A.C.; Hammond, M.E.H.; Allison, K.H.; Harvey, B.E.; Mangu, P.B.; Bartlett, J.M.S.; Bilous, M.; Ellis, I.O.; Fitzgibbons, P.; Hanna, W.; et al. Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2 Testing in Breast Cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists Clinical Practice Guideline Focused Update. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 2105–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karacin, C.; Oksuzoglu, B.; Demirci, A.; Keskinkılıç, M.; Baytemür, N.K.; Yılmaz, F.; Selvi, O.; Erdem, D.; Avşar, E.; Paksoy, N.; et al. Efficacy of subsequent treatments in patients with hormone-positive advanced breast cancer who had disease progression under CDK 4/6 inhibitor therapy. BMC Cancer 2023, 23, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gennari, A.; André, F.; Barrios, C.H.; Cortés, J.; de Azambuja, E.; DeMichele, A.; Dent, R.; Fenlon, D.; Gligorov, J.; Hurvitz, S.A.; et al. ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline for the diagnosis, staging and treatment of patients with metastatic breast cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, 1475–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freites-Martinez, A.; Santana, N.; Arias-Santiago, S.; Viera, A. Using the Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE—Version 5.0) to Evaluate the Severity of Adverse Events of Anticancer Therapies. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2021, 112, 90–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bas, O.; Erul, E.; Guven, D.C.; Aksoy, S. Infectious complications of cyclin-dependent kinases 4 and 6 inhibitors in patients with hormone-receptor-positive metastatic breast cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Support. Care Cancer 2022, 30, 9071–9078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahraman, S.; Erul, E.; Seyyar, M.; Gumusay, O.; Bayram, E.; Demirel, B.C.; Acar, O.; Aksoy, S.; Baytemur, N.K.; Sahin, E.; et al. Treatment efficacy of ribociclib or palbociclib plus letrozole in hormone receptor-positive/HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer. Future Oncol. 2023, 19, 727–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, S.R.D.; Harbeck, N.; Hegg, R.; Toi, M.; Martin, M.; Shao, Z.M.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Martinez Rodriguez, J.L.; Campone, M.; Hamilton, E.; et al. Abemaciclib Combined With Endocrine Therapy for the Adjuvant Treatment of HR+, HER2-, Node-Positive, High-Risk, Early Breast Cancer (monarchE). J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 3987–3998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slamon, D.; Lipatov, O.; Nowecki, Z.; McAndrew, N.; Kukielka-Budny, B.; Stroyakovskiy, D.; Yardley, D.A.; Huang, C.S.; Fasching, P.A.; Crown, J.; et al. Ribociclib plus Endocrine Therapy in Early Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 390, 1080–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapagan, T.; Bulut, N.; Erdem, G.U. Polypharmacy and drug-drug interactions in metastatic breast cancer patients receiving cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) 4/6 inhibitors. J. Oncol. Pharm. Pract. 2024, 30, 1403–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çağlayan, D.; Koçak, M.Z.; Geredeli, Ç.; Tatlı, A.M.; Göksu, S.S.; Eryılmaz, M.K.; Araz, M.; Artaç, M. The effect of concomitant use of proton pump inhibitors with CDK 4/6 inhibitors on survival in metastatic breast cancer. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2023, 79, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Luo, M.; Cao, Y.; Lin, X.; Wu, Q.; Wang, S.; Wang, L.; Zhou, J. Efficacy of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors with concurrent proton pump inhibitors in patients with breast cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Oncologist 2025, 30, oyae320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raoul, J.L.; Moreau-Bachelard, C.; Gilabert, M.; Edeline, J.; Frénel, J.S. Drug-drug interactions with proton pump inhibitors in cancer patients: An underrecognized cause of treatment failure. ESMO Open 2023, 8, 100880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.C.; Song, J.; Chang, Y.; Huang, C.H.; Sudan, A.; Chen, P.C.; Chi, K.Y. The Association between Proton Pump Inhibitors and the Effectiveness of CDK Inhibitors in HR+/HER- Advanced Breast Cancer Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers 2023, 15, 5133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.; Uozumi, R.; Mukohara, T.; Hayashida, T.; Iwabe, M.; Iihara, H.; Kusuhara-Mamishin, K.; Kitagawa, Y.; Tsuchiya, M.; Kitahora, M.; et al. Proton Pump Inhibitors and Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 4/6 Inhibitors in Patients with Breast Cancer. Oncologist 2024, 29, e741–e749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Total (n = 92) | Concomitant Use of PPI | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yes (n = 31) | No (n = 61) | |||
| Age (years), median (range) | 59 (34–86) | 60 (34–84) | 58 (36–86) | 0.77 |
| ECOG PS, n (%) | ||||
| 0 | 33 (35.9) | 10 (32.3) | 23 (37.7) | 0.34 |
| 1 | 50 (58.7) | 16 (51.6) | 34 (55.7) | |
| 2–3 | 9 (7.6) | 5 (16.1) | 4 (6.6) | |
| CDK4/6 inhibitor type, n (%) | ||||
| Ribociclib | 86 (93.5) | 28 (90.3) | 58 (95.1) | 0.36 |
| Palbociclib | 6 (6.5) | 3 (9.7) | 3 (4.9) | |
| Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI) | ||||
| CCI ≤ 7 | 48 (52.2) | 16 (51.6) | 32 (52.5) | 1.00 |
| CCI > 7 | 44 (47.8) | 15 (48.4) | 29 (47.5) | |
| Polypharmacy | ||||
| <5 agents | 75 (81.5) | 24 (77.4) | 51 (83.6) | 0.661 |
| ≥5 agents | 17 (18.5) | 7 (22.6) | 10 (16.4) | |
| Menopausal status, n (%) * | ||||
| Premenopausal | 34 (37.0) | 10 (32.3) | 24 (39.3) | 0.48 |
| Postmenopausal | 58 (63.0) | 21 (67.7) | 37 (60.7) | 0.48 |
| Concomitant LH–RH agonist, n (%) | ||||
| None | 69 (75) | 22 (71) | 47 (77) | 0.09 |
| Goserelin acetate | 23 (25) | 9 (29) | 14 (23) | |
| Concomitant endocrine therapy, n (%) | ||||
| Anastrozole | 4 (4.3) | 4 (12.9) | 0 (0.0) | 0.43 |
| Exemestane | 3 (3.3) | 2 (6.5) | 1 (1.6) | |
| Letrozole | 49 (53.2) | 13 (41.9) | 36 (59.0) | |
| Fulvestrant | 36 (39.1) | 12 (38.7) | 24 (39.3) | |
| Endocrine sensitivity status of the disease, n (%) | ||||
| Sensitive | 68 (73.9) | 21 (67.7) | 47 (77) | 0.33 |
| Resistant | 24 (26.1) | 10 (32.3) | 14 (23) | |
| Type of disease, n (%) | ||||
| De novo | 44 (47.8) | 12 (38.7) | 32 (52.5) | 0.21 |
| Recurrent | 48 (52.2) | 19 (61.3) | 29 (47.5) | |
| Treatment line, n (%) | ||||
| 1st | 45 (48.9) | 10 (32.3) | 35 (57.4) | 0.057 |
| 2nd | 25 (27.2) | 10 (32.3) | 15 (24.6) | |
| ≥3rd | 22 (23.9) | 11 (35.5) | 11 (18) | |
| Metastatic pattern, n (%) | ||||
| Visceral involvement † | 56 (60.9) | 20 (64.5) | 36 (59.0) | 0.60 |
| Non-visceral | 36 (39.1) | 11 (35.5) | 25 (41) | |
| Lung | 39 (42.4) | 13 (41.9) | 26 (42.6) | 0.95 |
| Liver | 23 (25) | 9 (29) | 14 (23) | 0.52 |
| Lung+ liver | 10 (10.9) | 3 (9.7) | 7 (11.5) | 0.79 |
| Bone lesion only | 31 (33.7) | 10 (32.3) | 21 (34.4) | 0.83 |
| Number of metastatic sites, n (%) | ||||
| <3 | 63 (68.5) | 18 (58.1) | 45 (73.8) | 0.12 |
| ≥3 | 29 (31.5) | 13 (41.9) | 16 (26.2) | |
| Dose reduction, n (%) | 27 (29.3) | 9 (29) | 18 (29.5) | 0.96 |
| Ribociclib 400 mg | 20 (21.7) | 6 (19.4) | 14 (23) | |
| Ribociclib 200 mg | 4 (4.3) | 1 (3.2) | 3 (4.9) | |
| Palbociclib 100 mg | 2 (2.2) | 1 (3.2) | 1 (1.6) | |
| Palbociclib 75 mg | 1 (1.1) | 1 (3.2) | 0 (0.0) | |
| PPI used, n (%) | ||||
| Esomeprazole | 6 (19.4) | |||
| Lansoprazole | 12 (38.7) | |||
| Pantoprazole | 13 (41.9) | |||
| Univariate | Multivariate | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR (95%CI) | p-Value | HR (95%CI) | p-Value | |
| Age (years) | ||||
| ≤59 (ref) | 0.76 (0.45–1.27) | 0.29 | 1.49 (0.63–3.49) | 0.364 |
| >59 | ||||
| ECOG PS | ||||
| ECOG 0–1 (ref) | 2.1 (1.03–4.31) | 0.042 | 1.25 (0.48–3.22) | 0.651 |
| ECOG ≥ 2 | ||||
| Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI) | ||||
| CCI > 7 (ref) | 1.21 (0.72–2.02) | 0.47 | 0.74 (0.33–1.66) | 0.463 |
| CCI ≤ 7 | ||||
| Polypharmacy | ||||
| ≥5 chronic agents | 1.07 (0.57–2.01) | 0.84 | 1.66 (0.73–3.78) | 0.230 |
| <5 agents | ||||
| Menopausal status | ||||
| Premenopausal (ref) | 1.36 (0.71–2.63) | 0.35 | 1.02 (0.39–2.60) | 0.968 |
| Postmenopausal | ||||
| Endocrine sensitivity status of the disease | ||||
| Sensitive (ref) | 2.92 (1.71–4.98) | <0.001 | 2.50 (1.34–4.65) | 0.004 |
| Resistant | ||||
| Metastatic pattern | ||||
| Non-visceral (ref) | 1.60 (0.93–2.77) | 0.091 | 0.59 (0.26–1.31) | 0.198 |
| Visceral involvement | ||||
| Number of metastatic sites | ||||
| <3 (ref) | 2.65 (1.53–4.60) | <0.001 | 3.06 (1.39–6.76) | 0.005 |
| ≥3 | ||||
| Treatment line | ||||
| 1 L (ref) | ||||
| 2 L | 2.11 (1.15–3.86) | 0.015 | 2.04 (0.95–4.39) | 0.069 |
| ≥3 L | 2.42 (1.27–4.63) | 0.007 | 2.51 (1.12–5.63) | 0.026 |
| Dose reduction | ||||
| No (ref) | 0.78 (0.44–1.39) | 0.40 | 0.62 (0.33–1.18) | 0.147 |
| Yes | ||||
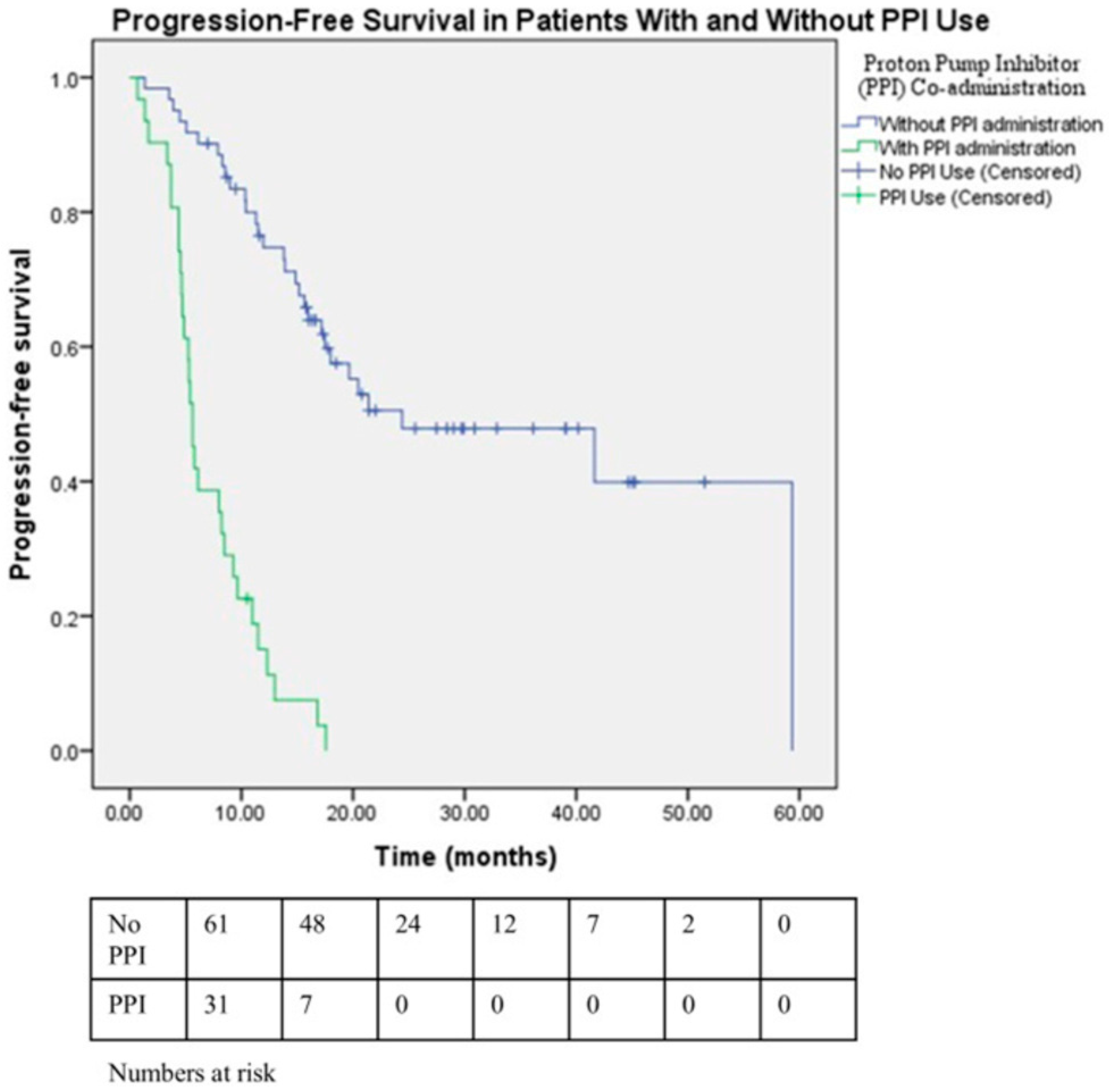
| Concomitant use of PPI | ||||
| No (ref) | 7.26 (4.04–13.06) | <0.001 | 6.82 (3.33–13.96) | <0.001 |
| Yes | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Erul, E.; Öksüz, N.E.; Akkus, E.; Tolunay, P.K.; Köksoy, E.B.; Yasar, H.A. Assessing the Influence of Proton Pump Inhibitors on Clinical Outcomes in Hormone Receptor-Positive Metastatic Breast Cancer Patients Receiving CDK4/6 Inhibitors: Evidence from a Ribociclib-Dominant Cohort. Medicina 2025, 61, 1960. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61111960
Erul E, Öksüz NE, Akkus E, Tolunay PK, Köksoy EB, Yasar HA. Assessing the Influence of Proton Pump Inhibitors on Clinical Outcomes in Hormone Receptor-Positive Metastatic Breast Cancer Patients Receiving CDK4/6 Inhibitors: Evidence from a Ribociclib-Dominant Cohort. Medicina. 2025; 61(11):1960. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61111960
Chicago/Turabian StyleErul, Enes, Nejat Emre Öksüz, Erman Akkus, Pınar Kubilay Tolunay, Elif Berna Köksoy, and Hatime Arzu Yasar. 2025. "Assessing the Influence of Proton Pump Inhibitors on Clinical Outcomes in Hormone Receptor-Positive Metastatic Breast Cancer Patients Receiving CDK4/6 Inhibitors: Evidence from a Ribociclib-Dominant Cohort" Medicina 61, no. 11: 1960. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61111960
APA StyleErul, E., Öksüz, N. E., Akkus, E., Tolunay, P. K., Köksoy, E. B., & Yasar, H. A. (2025). Assessing the Influence of Proton Pump Inhibitors on Clinical Outcomes in Hormone Receptor-Positive Metastatic Breast Cancer Patients Receiving CDK4/6 Inhibitors: Evidence from a Ribociclib-Dominant Cohort. Medicina, 61(11), 1960. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61111960








