The Status of Metabolic Control in Patients with Diabetes Attending Primary Care Clinics in Madinah, Saudi Arabia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Sample Collection
2.2. Ethical Approval
2.3. Methods
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DM | Diabetes mellitus |
| PCCs | Primary care centers |
| HDL | High-density lipoprotein |
| LDL | Low-density lipoprotein |
| BMI | Body mass index |
References
- Hu, H.; Hori, A.; Nishiura, C.; Sasaki, N.; Okazaki, H.; Nakagawa, T.; Honda, T.; Yamamoto, S.; Tomita, K.; Miyamoto, T.; et al. Hba1c, blood pressure, and lipid control in people with diabetes: Japan epidemiology collaboration on occupational health study. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0159071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhter, J.; Ahmed, A.; Mawani, M.; Lakhani, L.; Kalsekar, A.; Tabassum, S.; Islam, N. Patterns, control and complications of diabetes from a hospital based registry established in a low income country. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2017, 17, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noor, S.K.; Elmadhoun, W.M.; Bushara, S.O.; Almobarak, A.O.; Salim, R.S.; Forawi, S.A.; Awadallah, H.; Elwali, E.S.; Ahmed, M.H. Glycaemic control in Sudanese individuals with type 2 diabetes: Population based study. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev. 2017, 11, S147–S151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qaddoumi, M.; Al-Khamis, Y.; Channanath, A.; Tuomilehto, J.; Badawi, D. The status of metabolic control in patients with type 2 diabetes attending Dasman Diabetes Institute, Kuwait. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khunti, K.; Ceriello, A.; Cos, X.; De Block, C. Achievement of guideline targets for blood pressure, lipid, and glycaemic control in type 2 diabetes: A meta-analysis. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2018, 137, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, N.C.; Beck, R.W.; Miller, K.M.; Clements, M.A.; Rickels, M.R.; DiMeglio, L.A.; Maahs, D.M.; Tamborlane, W.V.; Bergenstal, R.; Smith, E.; et al. State of type 1 diabetes management and outcomes from the T1D Exchange in 2016–2018. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2019, 21, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahraz, S.; Pittas, A.G.; Saadati, M.; Thomas, C.P.; Lundquist, C.M.; Kent, D.M. Change in testing, awareness of hemoglobin A1c result, and glycemic control in US adults, 2007–2014. JAMA 2017, 318, 1825–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Diabetes Federation. Diabetes in MENA. Available online: https://idf.org/our-network/regions-and-members/middle-east-and-north-africa/ (accessed on 28 June 2021).
- Almetwazi, M.; Alwhaibi, M.; Balkhi, B.; Almohaini, H.; Alturki, H.; Alhawassi, T.; Ata, S.; AlQahtani, N.; Mahmoud, M.; Alshammari, T. Factors associated with glycemic control in type 2 diabetic patients in Saudi Arabia. Saudi Pharm. J. 2019, 27, 384–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Rowais, N.A. Glycemic control in diabetic patients in King Khalid University Hospital (KKUH)—Riyadh—Saudi Arabia. Saudi Pharm. J. 2014, 22, 203–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alzaheb, R.A.; Altemani, A.H. The prevalence and determinants of poor glycemic control among adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Saudi Arabia. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2018, 11, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almutairi, M.A.; Said, S.M.; Zainuddin, H. Predictors of poor glycemic control among type two diabetic patients. Am. J. Med. Med. Sci. 2013, 3, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alramadan, M.J.; Magliano, D.J.; Almigbal, T.H.; Batais, M.A.; Afroz, A.; Alramadhan, H.J.; Mahfoud, W.F.; Alragas, A.M.; Billah, B. Glycaemic control for people with type 2 diabetes in Saudi Arabia—an urgent need for a review of management plan. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2018, 18, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes Association. Standards of medical care in diabetes—2016 abridged for primary care providers. Clin. Diabetes 2016, 34, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Rasheedi, M.; Alhazmi, Y.; AlDaiji, L.A.; AlDaiji, L.A.; Mobarki, F.I.; Almuhaysini, K.M.; Alshammari, J.S.; Almistadi, N.A.; Yoldash, S.A.; Almaqwashi, N.; et al. Status of diabetes mellitus in different regions of KSA and update on its management. Front. Clin. Diabetes Healthc. 2024, 5, 1482090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khattab, M.; Khader, Y.S.; Al-Khawaldeh, A.; Ajlouni, K. Factors associated with poor glycemic control among patients with type 2 diabetes. J. Diabetes Its Complicat. 2010, 24, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanal, T.S.; Nair, N.S.; Adhikari, P. Factors associated with poor control of type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Diabetol. 2021, 2, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBrien, K.A.; Manns, B.J.; Hemmelgarn, B.R.; Weaver, R.; Edwards, A.L.; Ivers, N.; Rabi, D.; Lewanczuk, R.; Braun, T.; Naugler, C.; et al. The association between sociodemographic and clinical characteristics and poor glycaemic control: A longitudinal cohort study. Diabet. Med. 2016, 33, 1499–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alramadan, M.J.; Afroz, A.; Hussain, S.M.; Batais, M.A.; Almigbal, T.H.; Al-Humrani, H.A.; Albaloshi, A.; Romero, L.; Magliano, D.J.; Billah, B. Patient-related determinants of glycaemic control in people with type 2 diabetes in the Gulf Cooperation Council countries: A systematic review. J. Diabetes Res. 2018, 2018, 9389265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haghighatpanah, M.; Nejad, A.S.M.; Haghighatpanah, M.; Thunga, G.; Mallayasamy, S. Factors that correlate with poor glycemic control in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with complications. Osong Public Health Res. Perspect. 2018, 9, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cagliero, E.; Levina, E.V.; Nathan, D.M. Immediate feedback of HbA1c levels improves glycemic control in type 1 and insulin-treated type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Care 1999, 22, 1785–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levetan, C.S.; Dawn, K.R.; Robbins, D.C.; Ratner, R.E. Impact of computer-generated personalized goals on HbA(1c). Diabetes Care 2002, 25, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gæde, P.; Vedel, P.; Larsen, N.; Jensen, G.V.H.; Parving, H.H.; Pedersen, O. Multifactorial intervention and cardiovascular disease in patients with type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 383–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gæde, P.; Lund-Andersen, H.; Parving, H.-H.; Pedersen, O. Effect of a multifactorial intervention on mortality in type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 580–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gæde, P.; Pedersen, O. Intensive integrated therapy of type 2 diabetes: Implications for long-term prognosis. Diabetes 2004, 53 (Suppl. S3), S39–S47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | Total (n = 692) (Mean ± SD) | Males (n = 183) (Mean ± SD) | Females (n = 509) (Mean ± SD) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 55.1 ± 11.6 | 56.3 ± 12.9 | 54.7 ± 11.1 | 0.270 |
| Weight (kg) | 79.4 ± 17.6 | 80.9 ± 17.5 | 78.9 ± 17.7 | 0.207 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 32.1 ± 7.0 | 29.4 ± 6.0 | 33.1 ± 7.1 | 0.001 |
| Duration of diabetes (years) | 11.0 ± 7.8 | 12.7 ± 7.9 | 10.4 ± 7.8 | 0.002 |
| HbA1c (%) | 8.3 ± 1.7 | 8.5 ± 1.8 | 8.4 ± 1.9 | 0.505 |
| Fasting glucose (mmol/L) | 9.7 ± 4.2 | 10.0 ± 4.7 | 9.6 ± 4.0 | 0.314 |
| LDL (mmol/L) | 2.8 ± 1.04 | 2.8 ± 1.0 | 2.9 ± 1.0 | 0.319 |
| HDL (mmol/L) | 1.1 ± 0.4 | 1.1 ± 0.4 | 1.8 ± 0.4 | 0.018 |
| Triglyceride (mmol/L) | 1.7 ± 0.9 | 1.8 ± 1.2 | 1.6 ± 0.8 | 0.017 |
| SBP (mm Hg) | 132.3 ± 20.3 | 131.1 ± 21.6 | 132.7 ± 19.8 | 0.372 |
| DBP (mm Hg) | 74.3 ± 11.6 | 78.1 ± 11.7 | 73.1 ± 12.0 | <0.001 |
| Variable | Total (%) | Males (%) | Females (%) | p-value |
| Diabetic retinopathy | 17.9 | 19.1 | 17.5 | 0.590 |
| Diabetic nephropathy | 8.5 | 8.7 | 8.4 | 0.890 |
| Diabetic neuropathy | 23.3 | 25.1 | 22.6 | 0.480 |
| Hypertension | 61.2 | 83.9 | 55.1 | 0.001 |
| Dyslipidemia | 44.5 | 41.0 | 45.8 | 0.280 |
| Ischemic heart disease | 10.4 | 13.1 | 9.4 | 0.004 |
| Smoking | 6.8 | 24.0 | 0.6 | 0.001 |
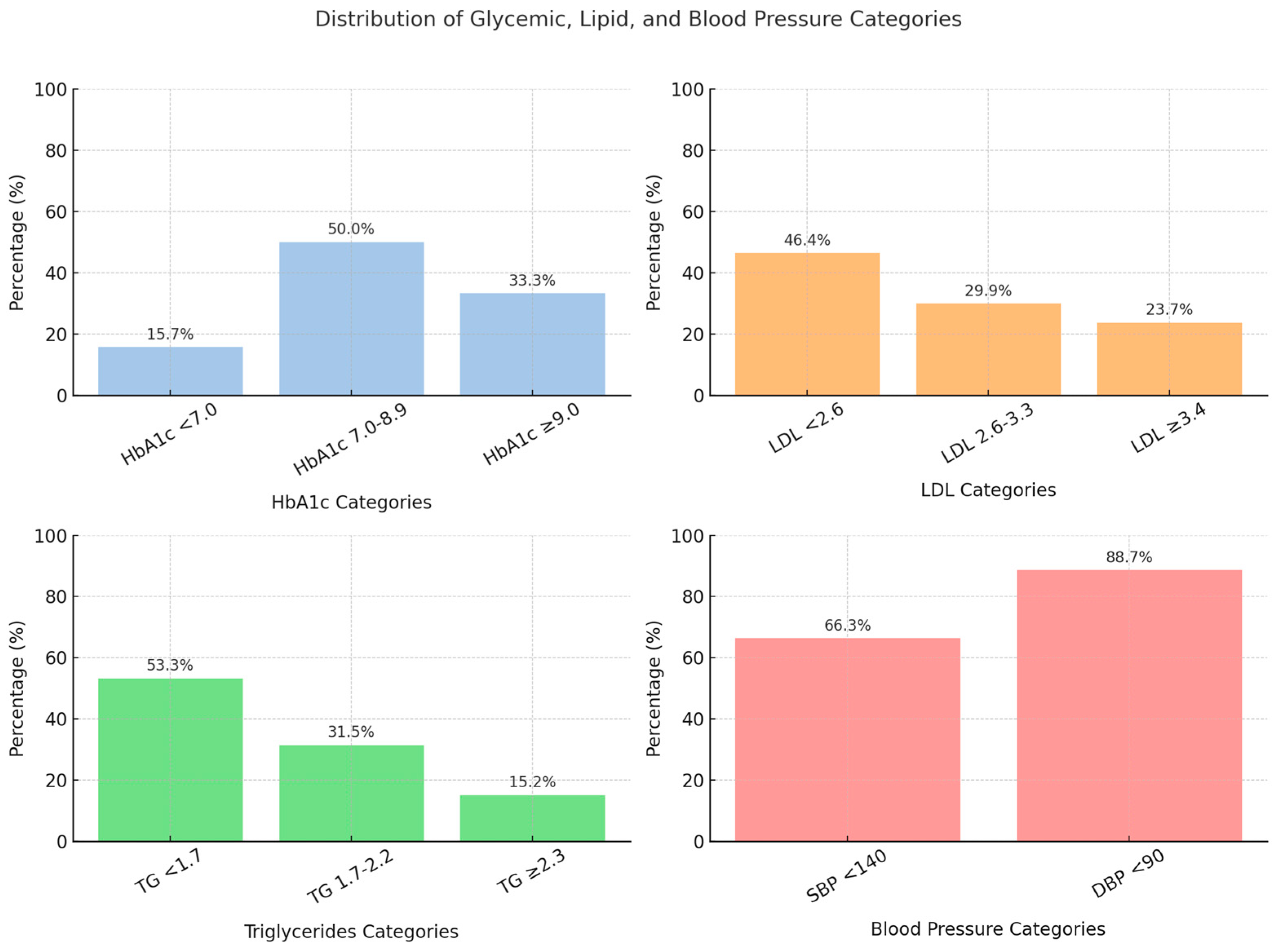
| Parameters | Percentages (%) |
|---|---|
| HbA1C < 7% | 15.7 |
| LDL < 2.6 mmol/L | 46.4 |
| Triglyceride < 1.7 mmol/L | 53.3 |
| HDL >1 mmol/L | 70.8 |
| SBP <140 mmHg | 66.3 |
| DBP <90 mmHg | 88.7 |
| Variable | Patients with A1c < 7 | Patients with A1c ≥ 7 | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD | |||
| Age (years) | 57.2 ± 12.4 | 54.6 ± 11.7 | 0.037 |
| Duration of diabetes (years) | 8.3 ± 7.4 | 11.3 ± 7.7 | 0.000 |
| Weight | 80.5 ± 18.2 | 79.2 ± 17.5 | 0.501 |
| BMI | 32.4 ± 6.8 | 32.0 ± 7.0 | 0.599 |
| Height | 157.5 ± 9.4 | 157.5 ± 9.0 | 0.969 |
| Systolic BP | 131.1 ± 20.8 | 132.2 ± 20.1 | 0.621 |
| Diastolic BP | 74.0 ± 11.9 | 74.2 ± 12.0 | 0.843 |
| Fasting glucose | 8.0 ± 3.7 | 10.0 ± 4.2 | 0.000 |
| HbA1C | 6.2 ± 0.5 | 8.8 ± 1.7 | 0.000 |
| Total cholesterol | 4.7 ± 1.1 | 4.8 ± 1.1 | 0.617 |
| LDL | 2.6 ± 1.0 | 2.9 ± 1.0 | 0.045 |
| Triglyceride | 1.6 ± 0.6 | 1.7 ± 1.0 | 0.176 |
| HDL | 1.1 ± 0.3 | 1.1 ± 0.4 | 0.764 |
| Serum creatinine | 77.6 ± 42 | 75.1 ± 42 | 0.521 |
| Percentages (%) | |||
| Sex: male/female | 18.1/16.3 | 81.9/83.7 | 0.633 |
| LDL < 2.6 mmol/L | 28.7 | 18.5 | 0.025 |
| HDL > 1 mmol/L | 66.7 | 69.9 | 0.292 |
| Triglyceride < 1.7 mmol/L | 64.8 | 59.6 | 0.181 |
| SBP < 140 mmHg | 71.3 | 68.4 | 0.315 |
| DBP < 90 mmHg | 89.8 | 89.5 | 1.00 |
| Variable | Adjusted OR (95% CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| Age (per 10 years ↑) | 0.82 (0.70–0.96) | 0.012 |
| Diabetes duration (years) | 1.15 (1.05–1.26) | 0.003 |
| BMI (per 5 kg/m2 ↑) | 1.21 (1.02–1.43) | 0.027 |
| LDL ≥ 2.6 mmol/L | 1.38 (1.10–1.75) | 0.006 |
| Male sex | 1.08 (0.79–1.47) | 0.624 |
| Hypertension | 0.92 (0.69–1.22) | 0.580 |
| Dyslipidemia | 1.17 (0.89–1.54) | 0.260 |
| Smoking | 1.41 (0.89–2.25) | 0.136 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alfadhli, E.; Surrati, A.M.Q.; Masoud, R.S.; Gadi, Y.A.; Alahmadi, W.A.; Turkistani, M.K. The Status of Metabolic Control in Patients with Diabetes Attending Primary Care Clinics in Madinah, Saudi Arabia. Medicina 2025, 61, 1856. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61101856
Alfadhli E, Surrati AMQ, Masoud RS, Gadi YA, Alahmadi WA, Turkistani MK. The Status of Metabolic Control in Patients with Diabetes Attending Primary Care Clinics in Madinah, Saudi Arabia. Medicina. 2025; 61(10):1856. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61101856
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlfadhli, Eman, Amal M. Qasem Surrati, Ruqaya Saleh Masoud, Yaseera Ali Gadi, Walaa A. Alahmadi, and Mohammed Khalid Turkistani. 2025. "The Status of Metabolic Control in Patients with Diabetes Attending Primary Care Clinics in Madinah, Saudi Arabia" Medicina 61, no. 10: 1856. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61101856
APA StyleAlfadhli, E., Surrati, A. M. Q., Masoud, R. S., Gadi, Y. A., Alahmadi, W. A., & Turkistani, M. K. (2025). The Status of Metabolic Control in Patients with Diabetes Attending Primary Care Clinics in Madinah, Saudi Arabia. Medicina, 61(10), 1856. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61101856





