Mental Health and Age-Related Differences in Community During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Cross-Sectional Study from Southeastern Türkiye
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design
2.2. Sample Size and Participants
2.3. Ethical Considerations and Consent Statement
2.4. Data Collection Tools
2.5. The Hospital Anxiety Depression Scale (HADS)
2.6. The Coping Flexibility Scale (CFS)
2.7. The Perceived Stress Scale (PSS)
2.8. Multidimensional Perceived Social Support Scale (MPSSS)
2.9. Data Analysis
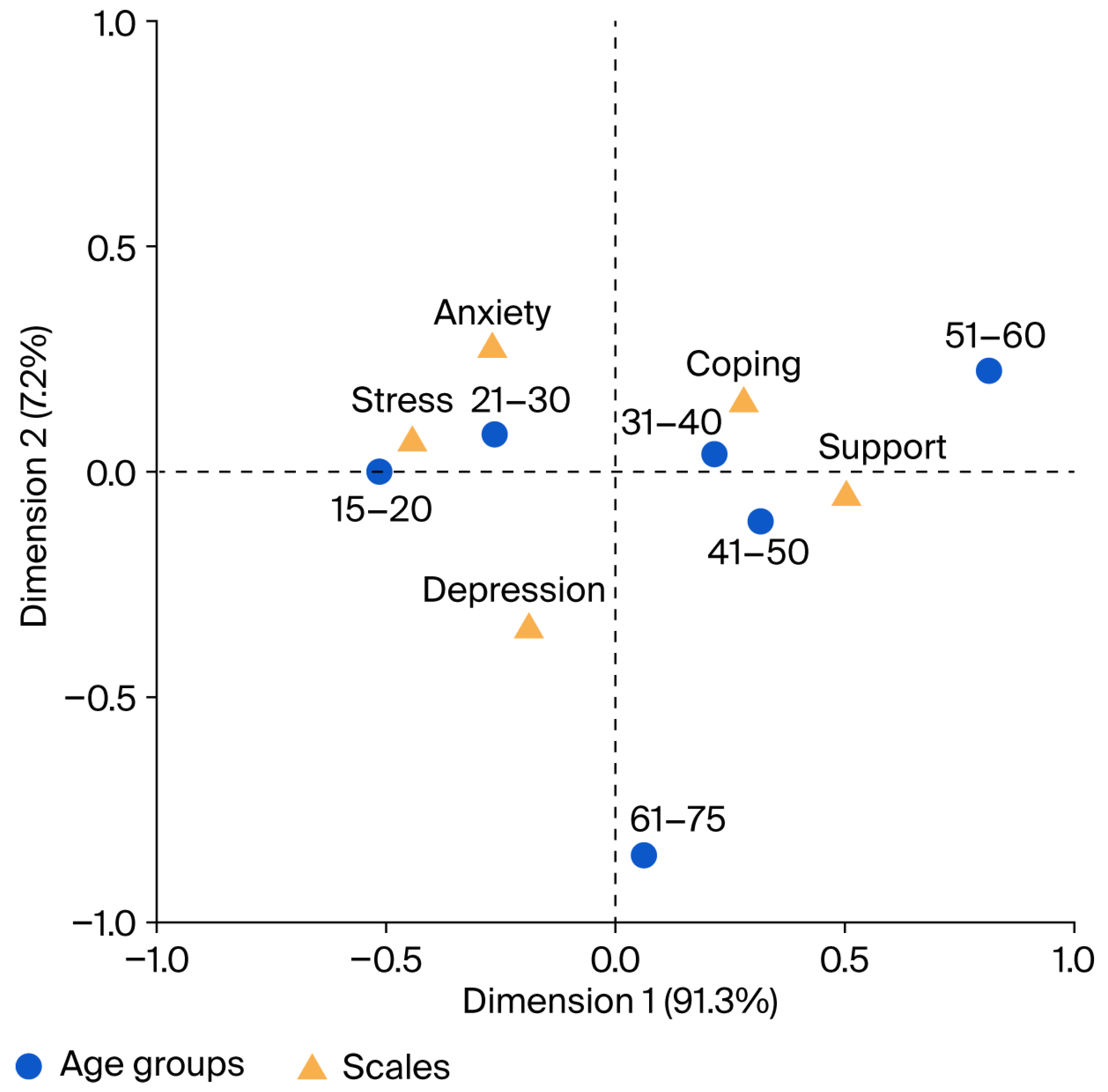
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boden, M.; Zimmerman, L.; Azevedo, K.J.; Ruzek, J.I.; Gala, S.; Magid, H.S.A.; Cohen, N.; Walser, R.; Mahtani, N.D.; Hoggatt, K.J.; et al. Addressing the mental health impact of COVID-19 through population health. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 2021, 85, 102006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- COVID-19 Pandemic Timeline. Northwestern Medicine. Available online: https://www.nm.org/healthbeat/medical-advances/new-therapies-and-drug-trials/covid-19-pandemic-timeline (accessed on 31 July 2025).
- Xiong, J.; Lipsitz, O.; Nasri, F.; Lui, L.M.W.; Gill, H.; Phan, L.; Chen-Li, D.; Iacobucci, M.; Ho, R.; Majeed, A.; et al. Impact of COVID-19 pandemic on mental health in the general population: A systematic review. J. Affect. Disord. 2020, 277, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santomauro, D.F.; Herrera, A.M.M.; Shadid, J.; Zheng, P.; Ashbaugh, C.; Pigott, D.M.; Abbafati, C.; Adolph, C.; Amlag, J.O.; Aravkin, A.Y.; et al. Global prevalence and burden of depressive and anxiety disorders in 204 countries and territories in 2020 due to the COVID-19 pandemic. Lancet 2021, 398, 1700–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borja, J.B.; Patten, S.B. Differential Effects of Pandemic-Related Stressors on Mental Health by Age and Sex. Healthcare 2025, 13, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salari, N.; Hosseinian-Far, A.; Jalali, R.; Vaisi-Raygani, A.; Rasoulpoor, S.; Mohammadi, M.; Rasoulpoor, S.; Khaledi-Paveh, B. Prevalence of stress, anxiety, depression among the general population during the COVID-19 pandemic: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Glob. Health 2020, 16, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Kakade, M.; Fuller, C.J.; Fan, B.; Fang, Y.; Kong, J.; Guan, Z.; Wu, P. Depression after exposure to stressful events: Lessons learned from the severe acute respiratory syndrome epidemic. Compr. Psychiatry 2012, 53, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Kala, M.P.; Jafar, T.H. Factors associated with psychological distress during the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic on the predominantly general population: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0244630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favaretto, E.; Bedani, F.; Brancati, G.E.; De Berardis, D.; Giovannini, S.; Scarcella, L.; Martiadis, V.; Martini, A.; Pampaloni, I.; Perugi, G.; et al. Synthesising 30 years of clinical experience and scientific insight on affective temperaments in psychiatric disorders: State of the art. J. Affect. Disord. 2024, 362, 406–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorillo, A.; Demyttenaere, K.; Martiadis, V.; Martinotti, G. Editorial: Treatment resistant depression (TRD): Epidemiology, clinic, burden and treatment. Front. Psychiatry 2025, 16, 1588902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmati, M.; Lee, S.; Yon, D.K.; Lee, S.W.; Udeh, R.; McEvoy, M.; Oh, H.; Butler, L.; Keyes, H.; Barnett, Y.; et al. Physical activity and prevention of mental health complications: An umbrella review. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2024, 160, 105641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Chai, Y.; Yang, X.; Wang, M.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y. Psychosocial and mental health status among older adults in China during the COVID-19 pandemic: A cross-sectional study. Acta Psychol. 2024, 252, 104651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bucaktepe, P.G.E.; Akgül, F.; Çelïk, S.B. Evaluation of the effects of pandemic-related fears on anxiety and depression: The mediating roles of traumatic stress and loneliness. BMC Psychol. 2024, 12, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, C.M.C.; Ho, M.K.; Bharwani, A.A.; Cogo-Moreira, H.; Wang, Y.; Chow, M.S.C.; Fan, X.; Galea, S.; Leung, G.M.; Ni, M.Y. Mental disorders following COVID-19 and other epidemics: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Transl. Psychiatry 2022, 12, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, K.S.; Mamun, M.A.; Griffiths, M.D.; Ullah, I. The Mental Health Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic Across Different Cohorts. Int. J. Ment. Health Addict. 2020, 20, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Su, X.; Si, M.; Xiao, W.; Wang, H.; Wang, W.; Gu, X.; Ma, L.; Li, J.; Zhang, S.; et al. The impacts of coping style and perceived social support on the mental health of undergraduate students during the early phases of the COVID-19 pandemic in China: A multicenter survey. BMC Psychiatry 2021, 21, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Lau, H.-P.B.; Chan, M.-P.S. Coping flexibility and psychological adjustment to stressful life changes: A meta-analytic review. Psychol. Bull. 2014, 140, 1582–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Wang, H.-Y.; Ebrahimi, O.V. Adjustment to a “New Normal:” Coping Flexibility and Mental Health Issues During the COVID-19 Pandemic. Front. Psychiatry 2021, 12, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raffone, F.; Atripaldi, D.; Barone, E.; Marone, L.; Carfagno, M.; Mancini, F.; Saliani, A.M.; Martiadis, V. Exploring the role of guilt in eating disorders: A pilot study. Clin. Pract. 2025, 15, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martiadis, V.; Pessina, E.; Raffone, F.; Iniziato, V.; Martini, A.; Scognamiglio, P. Metacognition in schizophrenia: A practical overview of psychometric metacognition assessment tools for researchers and clinicians. Front. Psychiatry 2023, 14, 1155321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suhail, A.; Dar, K.A.; Iqbal, N. COVID-19 related fear and mental health in Indian sample: The buffering effect of support system. Curr. Psychol. 2021, 41, 480–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, A.W.; Swana, S.; Sarma, M.S. Evaluating the Buffering Role of Perceived Social Support and Coping Resources Against the Adult Mental Health Impacts of COVID-19 Psychosocial Stress: A Cross-Sectional Study in South Africa. Advers. Resil. Sci. 2025, 6, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, L.; Yang, L.; Mezo, P.G.; Liu, R. Age disparities in mental health during the COVID19 pandemic: The roles of resilience and coping. Soc. Sci. Med. 2022, 305, 115031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambin, M.; Sękowski, M.; Woźniak-Prus, M.; Wnuk, A.; Oleksy, T.; Cudo, A.; Hansen, K.; Huflejt-Łukasik, M.; Kubicka, K.; Łyś, A.E.; et al. Generalized anxiety and depressive symptoms in various age groups during the COVID-19 lockdown in Poland. Specific predictors and differences in symptoms severity. Compr. Psychiatry 2021, 105, 152222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, H.T.M.; Nguyen, H.V.; Zouini, B.; Senhaji, M.; Bador, K.; Meszaros, Z.S.; Stevanovic, D.; Kerekes, N. The COVID-19 pandemic and adolescents’ psychological distress: A multinational cross-sectional study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 8261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uribe-Restrepo, J.M.; Waich-Cohen, A.; Ospina-Pinillos, L.; Rivera, A.M.; Castro-Díaz, S.; Patiño-Trejos, J.A.; Sepúlveda, M.A.R.; Ariza-Salazar, K.; Cardona-Porras, L.F.; Gómez-Restrepo, C.; et al. Mental health and psychosocial impact of the COVID-19 pandemic and social distancing measures among young adults in Bogotá, Colombia. AIMS Public Health 2022, 9, 630–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betancourt-Ocampo, D.; Toledo-Fernández, A.; González-González, A. Mental health changes in older adults in response to the COVID-19 Pandemic: A longitudinal study in Mexico. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 848635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özdemir, P.A.; Çelen, H.N. Social loneliness and perceived stress among middle-aged and older adults during the COVID-19 pandemic. Curr. Psychol. 2024, 43, 12198–12207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flesia, L.; Monaro, M.; Mazza, C.; Fietta, V.; Colicino, E.; Segatto, B.; Roma, P. Predicting Perceived Stress Related to the COVID-19 Outbreak through Stable Psychological Traits and Machine Learning Models. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, S.X.; Wang, Y.; Afshar Jahanshahi, A.; Mokhtari Dinani, M.; Nazarian Madavani, A.; Nawaser, K. The relationship between age and mental health among adults in iran during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Int. J. Ment. Health. Addict. 2022, 20, 3162–3177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Egger, M.; Pocock, S.J.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Vandenbroucke, J.P. STROBE Initiative. Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement: Guidelines for reporting observational studies. BMJ 2007, 335, 806–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, S.; Fuchs, X.; Schakib-Ekbatan, K.; Schweiker, M. What does “moderate pain” mean? Subgroups holding different conceptions of rating scales evaluate experimental pain differently. Eur. J. Pain 2019, 24, 625–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zigmond, A.S.; Snaith, R.P. The Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 1983, 67, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aydemir, Ö. Reliability and validity of the Turkish version of Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale. Turk. J. Psychiatry 1997, 8, 280–287. [Google Scholar]
- Kato, T. Development of the Coping Flexibility Scale: Evidence for the coping flexibility hypothesis. J. Couns. Psychol. 2012, 59, 262–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akın, A.; Aşut, S.; Toprak, H.; Çardak, M.; Özdemir, E.; Sariçam, H.; Kaya, Ç. The validity and reliability of the Coping Flexibility Scale Turkish Form. In Proceedings of the 5th National Postgraduate Education Symposium, Sakarya, Turkey, 10–11 May 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, S.; Kamarck, T.; Mermelstein, R. A Global Measure of Perceived Stress. J. Health Soc. Behav. 1983, 24, 385–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskin, M.; Harlak, H.; Demirkıran, F.; Dereboy, Ç. The adaptation of the Perceived Stress Scale into Turkish: A reliability and validity analysis. New/Yeni Symp. J. 2013, 51, 132–140. [Google Scholar]
- Zimet, G.D.; Powell, S.S.; Farley, G.K.; Werkman, S.; Berkoff, K.A. Psychometric characteristics of the Multidimensional Scale of Perceived Social Support. J. Personal. Assess. 1990, 55, 610–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eker, D.; Arkar, H. Factorial structure, validity, and reliability of the Multidimensional Scale of Perceived Social Support. Turk Psikoloji Derg. 1995, 10, 45–55. [Google Scholar]
- Özdin, S.; Bayrak Özdin, Ş. Levels and predictors of anxiety, depression and health anxiety during COVID-19 pandemic in Turkish society: The importance of gender. Int. J. Soc. Psychiatry 2020, 66, 504–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydın, K.; Yıldız, N.G.; Aydin, H.Z.; Karaboğa, H.A.; Kahraman Güloğlu, F.; Phiri, Y.V.A.; Yıldız, H. Prevalence of depressive symptoms and related factors in Türkiye: Results of the 2016 and 2019 Turkish Health Survey. Turk. J. Psychiatry. 2024, 36, 204–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Guo, L.; Yu, M.; Jiang, W.; Wang, H. The psychological and mental impact of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) on medical staff and general public—A systematic review and meta-analysis. Psychiatry Res. 2020, 291, 113190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosen, I.; Al-Mamun, F.; Mamun, M.A. Prevalence and risk factors of the symptoms of depression, anxiety, and stress during the COVID-19 pandemic in Bangladesh: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Glob. Ment. Health 2021, 8, e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhang, M.; Álvarez-Aguado, I.; Celis Correa, J.; Toffoletto, M.C.; Rosello-Peñaloza, M.; Miranda-Castillo, C. Effects of Anxiety, Stress and Perceived Social Support on Depression and Loneliness Among Older People During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Cross-Sectional Path Analysis. Inquiry 2024, 61, 469580241273187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erten Bucaktepe, P.G.; Bulut Çelik, S.; Çelik, F.; Demir Pervane, V.; Aydın, M.; Altınbaş, K. Mental Health of Primary Care Workers During COVID-19 Pandemic: A Cross-Sectional Study TJFMPC. Turk. J. Fam. Med. Prim. Care 2025, 19, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, J.; Helter, T.M.; White, R.G.; van der Boor, C.; Łaszewska, A. Impacts of the COVID-19 lockdown and relevant vulnerabilities on capability well-being, mental health and social support: An Austrian survey study. BMC Public Health 2021, 21, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palgi, Y.; Shrira, A.; Ring, L.; Bodner, E.; Avidor, S.; Bergman, Y.; Cohen-Fridel, S.; Keisari, S.; Hoffman, Y. The loneliness pandemic: Loneliness and other concomitants of depression, anxiety and their comorbidity during the COVID-19 outbreak. J. Affect. Disord. 2020, 275, 109–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Li, M.; Li, Z.; Xiang, W.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, Z.; Xiong, Z. Coping style, social support and psychological distress in the general Chinese population in the early stages of the COVID-19 epidemic. BMC Psychiatry 2020, 20, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzahrani, F.; Alshahrani, N.Z.; Abu Sabah, A.; Zarbah, A.; Abu Sabah, S.; Mamun, M.A. Prevalence and factors associated with mental health problems in Saudi general population during the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PsyCh J. 2022, 11, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ames-Guerrero, R.J.; Barreda-Parra, V.A.; Huamani-Cahua, J.C.; Banaszak-Holl, J. Self-reported psychological problems and coping strategies: A web-based study in Peruvian population during COVID-19 pandemic. BMC Psychiatry 2021, 21, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaniasty, K.; van der Meulen, E.; Mahmoud, A.B. Impact of COVID-19 on psychological distress in subsequent stages of the pandemic: The role of received social support. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0310734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glowacz, F.; Schmits, E. Psychological distress during the COVID-19 lockdown: The young adults most at risk. Psychiatry Res. 2020, 293, 113486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varma, P.; Junge, M.; Meaklim, H.; Jackson, M.L. Younger people are more vulnerable to stress, anxiety and depression during COVID-19 pandemic: A global cross-sectional survey. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2021, 109, 110236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carstensen, L.L.; Turan, B.; Scheibe, S.; Ram, N.; Ersner-Hershfield, H.; Samanez-Larkin, G.R.; Brooks, K.P.; Nesselroade, J.R. Emotional experience improves with age: Evidence based on over 10 years of experience sampling. Psychol. Aging 2011, 26, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carstensen, L.L.; Shavit, Y.Z.; Barnes, J.T. Age Advantages in Emotional Experience Persist Even Under Threat From the COVID-19 Pandemic. Psychol. Sci. 2020, 31, 1374–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Castro, L.L.P.T.; Walsh, H.P.; Accioly, M.F.; Martins, L.J.P.; Oliveira, A.C.O.; Graffitti, L.P.M.; Pegorari, M.S.; de Walsh, I.A.P. Healthy lifestyle as predictors of common mental disorder during coronavirus disease. Front. Public Health 2024, 70, e20231004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Liu, L.; Liang, S.; Chen, J.; Zhao, J. Longitudinal changes in fear and anxiety among Chinese college students during the COVID-19 pandemic: A one-year follow-up study. Curr. Psychol. 2024, 43, 13887–13896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, Q.; Jeong, W.; Lee, S.W. Explainable AI in Clinical Decision Support Systems: A Meta-Analysis of Methods, Applications, and Usability Challenges. Healthcare 2025, 13, 2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarus, R.S.; Folkman, S. Stress, Appraisal and Coping; Springer Publishing Company: New York, NY, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Drazich, B.F.; Li, Q.; Perrin, N.A.; Szanton, S.L.; Lee, J.W.; Huang, C.-M.; Carlson, M.C.; Samuel, L.J.; Regier, N.G.; Rebok, G.W.; et al. The relationship between older adults’ technology use, in-person engagement, and pandemic-related mental health. Aging Ment. Health 2023, 27, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahar, C.J.; Nadeau, A.L.; Violette, J.; Roberts, S.; Reindl, D. Socio-Emotional Resilience Among Older Adults During the COVID-19 Pandemic. J. South Carol. Acad. Sci. 2023, 21, 23–27. [Google Scholar]

| Sociodemographic Features | n | % |
|---|---|---|
| Gender | ||
| Female | 986 | 58.0 |
| Male | 713 | 42.0 |
| Age | ||
| 15–20 | 215 | 12.7 |
| 21–30 | 612 | 36.0 |
| 31–40 | 368 | 21.7 |
| 41–50 | 282 | 16.6 |
| 51–60 | 143 | 8.4 |
| 61–75 | 79 | 4.6 |
| Marital Status | ||
| Single | 840 | 49.4 |
| Married | 793 | 46.7 |
| Divorcee/widow | 66 | 3.9 |
| Education | ||
| High school or less | 349 | 20.5 |
| Bachelor or more | 1350 | 79.5 |
| Employment | ||
| No | 206 | 12.1 |
| Yes | 892 | 52.5 |
| Student | 516 | 30.4 |
| Retired | 85 | 5.0 |
| Chronic Disease | ||
| No | 1430 | 84.2 |
| Yes | 269 | 15.8 |
| Chronic Patient at Home | ||
| No | 1131 | 66.6 |
| Yes | 568 | 33.4 |
| Easy Access to Personal Protective Equipment | ||
| No | 243 | 14.3 |
| Yes | 1456 | 85.7 |
| Having Been Quarantined | ||
| No | 982 | 57.8 |
| Yes | 717 | 42.2 |
| Need for Psychologic Support | ||
| No | 1257 | 74.0 |
| Yes | 442 | 26.0 |
| Anxiety Symptoms | ||
| No | 1282 | 75.5 |
| Yes | 417 | 24.5 |
| Depressive Symptoms | ||
| No | 983 | 57.9 |
| Yes | 716 | 42.1 |
| CFS | PSS | MPSSS | HADS-A | HADS-D | Mean ± SD (Min–Max) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 0.033 | −0.229 ** | 0.136 ** | −0.113 ** | −0.085 ** | 34.1 ± 13.1 (15–75) |
| No. of household members | −0.095 ** | 0.126 ** | −0.181 ** | 0.096 ** | 0.087 ** | 4.3 ± 1.9 (1–16) |
| Feeling lonely | −0.214 ** | 0.428 ** | −0.249 ** | 0.462 ** | 0.443 ** | 2.5 ± 1.2 (1–5) |
| Feeling distant from others | −0.145 ** | 0.362 ** | −0.154 ** | 0.404 ** | 0.373 ** | 2.8 ± 1.2 (1–5) |
| Feeling of losing control over life | −0.210 ** | 0.482 ** | −0.207 ** | 0.504 ** | 0.462 ** | 2.5 ± 1.3 (1–5) |
| Feeling ostracised | −0.223 ** | 0.357 ** | −0.182 ** | 0.449 ** | 0.417 ** | 1.9 ± 1.2 (1–5) |
| Sleep problems | −0.177 ** | 0.388 ** | −0.167 ** | 0.470 ** | 0.425 ** | 2.5 ± 1.3 (1–5) |
| Concentration problems | −0.198 ** | 0.447 ** | −0.188 ** | 0.510 ** | 0.462 ** | 2.5 ± 1.3 (1–5) |
| Fear of contracting COVID-19 | −0.098 ** | 0.244 ** | 0.048 * | 0.380 ** | 0.229 ** | 5.7 ± 2.9 (0–10) |
| Fear of dying from COVID-19 | −0.073 ** | 0.242 ** | 0.057 * | 0.380 ** | 0.216 ** | 5.3 ± 3.3 (0–10) |
| CFS | −0.412 ** | 0.362 ** | −0.356 ** | −0.398 ** | 20.4 ± 5.4 (2–30) | |
| PSS | −0.362 ** | 0.619 ** | 0.599 ** | 27.4 ± 7.6 (0–56) | ||
| MPSSS | −0.238 ** | −0.331 ** | 60.6 ± 17.4 (12–84) | |||
| HADS-A | 0.699 ** | 8.5 ± 4.5 (0–21) | ||||
| HADS-D | 7.8 ± 4.1 (0–21) |
| Sociodemographic Variables | CFS Mean ± SD | PSS Mean ± SD | MPSSS Mean ± SD | HADS-A Mean ± SD | HADS-D Mean ± SD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | |||||
| Female | 20.3 ± 5.5 | 28.8 ± 7.4 | 61.1 ± 17.7 | 9.3 ± 4.5 | 8.1 ± 4.2 |
| Male | 20.5 ± 5.1 | 25.5 ± 7.6 | 59.9 ± 17.0 | 7.3 ± 4.2 | 7.2 ± 4.0 |
| t | −0.667 | 8.868 ** | 1.450 | 9.263 ** | 3.604 ** |
| ES † | −0.033 | 0.436 | 0.071 | 0.455 | 0.177 |
| Age | |||||
| 15–20 ① | 19.8 ± 5.5 | 29.1 ± 8.3 | 54.4 ± 18.0 | 9.2 ± 4.4 | 8.4 ± 4.2 |
| 21–30 ② | 20.2 ± 5.4 | 29.1 ± 7.3 | 59.1 ± 17.2 | 8.8 ± 4.5 | 8.0 ± 4.1 |
| 31–40 ③ | 20.7 ± 5.2 | 26.8 ± 6.8 | 64.0 ± 16.5 | 8.4 ± 4.4 | 7.6 ± 4.1 |
| 41–50 ④ | 20.6 ± 5.3 | 25.4 ± 8.3 | 62.2 ± 17.2 | 8.0 ± 4.6 | 7.2 ± 4.2 |
| 51–60 ⑤ | 21.4 ± 5.5 | 23.9 ± 7.3 | 64.5 ± 17.8 | 7.5 ± 4.3 | 6.8 ± 3.9 |
| 61–75 ⑥ | 19.0 ± 5.3 | 25.5 ± 5.1 | 60.6 ± 16.2 | 7.9 ± 3.6 | 8.2 ± 4.0 |
| F | 2.997 * | 20.819 ** | 11.337 ** | 4.288 ** | 4.336 ** |
| ES ‡ | 0.009 | 0.058 | 0.032 | 0.013 | 0.013 |
| Post hoc test | ⑤ > ⑥ | ①, ② > ③, ④, ⑤, ⑥; ③ > ⑤ | ① < ②, ③, ④, ⑤; ② < ③, ⑤ | ① > ④, ⑤; ② > ⑤ | ① > ④, ⑤; ② > ⑤ |
| Marital Status | |||||
| Single ① | 20.1 ± 5.5 | 28.9 ± 7.8 | 57.4 ± 17.6 | 8.9 ± 4.5 | 8.1 ± 4.1 |
| Married ② | 20.5 ± 5.3 | 25.9 ± 7.4 | 64.1 ± 16.7 | 8.1 ± 4.4 | 7.4 ± 4.1 |
| Divorced/widow ③ | 21.8 ± 5.3 | 25.8 ± 7.6 | 59.8 ± 15.9 | 7.9 ± 4.0 | 7.5 ± 4.5 |
| F | 3.488 * | 35.120 ** | 31.669 ** | 6.572 ** | 5.380 ** |
| ES ‡ | 0.004 | 0.040 | 0.036 | 0.008 | 0.006 |
| Post hoc test | ③ > ① | ① > ②, ③ | ② > ① | ① > ② | ① > ② |
| Education | |||||
| High school or less | 19.6 ± 5.26 | 27.5 ± 6.7 | 58.6 ± 18.0 | 8.9 ± 4.3 | 8.2 ± 4.0 |
| Bachelor or more | 20.6 ± 5.4 | 27.4 ± 7.9 | 61.1 ± 17.2 | 8.4 ± 4.5 | 7.6 ± 4.2 |
| t | −3.147 ** | 0.280 | −2.348 * | 2.017 * | 2.358 * |
| ES † | −0.189 | 0.017 | −0.142 | 0.121 | 0.142 |
| Employment | |||||
| No ① | 20.1 ± 4.9 | 27.5 ± 6.5 | 62.0 ± 18.1 | 8.9 ± 4.5 | 7.9 ± 3.7 |
| Yes ② | 20.8 ± 5.4 | 26.6 ± 7.8 | 63.1 ± 16.9 | 8.2 ± 4.5 | 7.3 ± 4.2 |
| Student ③ | 19.7 ± 5.4 | 29.4 ± 7.8 | 55.2 ± 17.0 | 9.1 ± 4.4 | 8.4 ± 4.1 |
| Retired ④ | 20.1 ± 5.8 | 23.8 ± 6.2 | 63.9 ± 16.2 | 7.3 ± 3.8 | 7.7 ± 4.2 |
| F | 4.991 ** | 24.968 ** | 25.462 ** | 7.229 ** | 7.506 ** |
| ES ‡ | 0.009 | 0.038 | 0.043 | 0.013 | 0.013 |
| Post hoc test | ② > ③ | ③ > ①, ②, ④; ① > ④ | ③ < ①, ②, ④ | ① > ④; ③ > ②, ④ | ③ > ② |
| Chronic Disease | |||||
| No | 20.5 ± 5.3 | 27.4 ± 7.7 | 60.7 ± 17.3 | 8.4 ± 4.5 | 7.7 ± 4.2 |
| Yes | 19.9 ± 5.6 | 27.2 ± 7.5 | 60.2 ± 18.1 | 8.8 ± 4.3 | 7.8 ± 4.0 |
| t | 1.626 | 0.549 | 0.440 | −1.159 | −0.304 |
| ES † | 0.108 | 0.036 | 0.029 | −0.077 | −0.020 |
| Chronic Patient at Home | |||||
| No | 20.6 ± 5.3 | 26.6 ± 7.9 | 61.6 ± 17.1 | 8.0 ± 4.5 | 7.4 ± 4.1 |
| Yes | 19.8 ± 5.4 | 29.0 ± 6.9 | 58.6 ± 17.9 | 9.5 ± 4.3 | 8.5 ± 4.1 |
| t | 2.982 ** | −6.415 ** | 3.427 ** | −6.444 ** | −5.131 ** |
| ES † | 0.153 | −0.316 | 0.176 | −0.331 | −0.264 |
| Easy Access to PPE | |||||
| No | 19.0 ± 5.1 | 28.8 ± 6.5 | 55.8 ± 16.2 | 9.6 ± 4.2 | 9.1 ± 4.0 |
| Yes | 20.6 ± 5.4 | 27.2 ± 7.8 | 61.4 ± 17.5 | 8.3 ± 4.5 | 7.5 ± 4.1 |
| t | −4.255 ** | 2.654 ** | −4.960 ** | 4.235 ** | 5.415 ** |
| ES † | −0.295 | 0.162 | −0.325 | 0.293 | 0.375 |
| Having Been Quarantined | |||||
| No | 20.5 ± 5.3 | 26.6 ± 7.3 | 61.7 ± 17.0 | 8.2 ± 4.4 | 7.5 ± 4.0 |
| Yes | 20.1 ± 5.5 | 28.5 ± 8.0 | 59.0 ± 18.0 | 8.9 ± 4.6 | 8.1 ± 4.3 |
| t | 1.545 | −5.181 ** | 3.125 ** | −3.305 ** | −3.038 ** |
| ES † | 0.076 | −0.255 | 0.155 | −0.162 | −0.149 |
| Need for Psychological Support | |||||
| No | 20.8 ± 5.2 | 25.9 ± 7.4 | 62.2 ± 16.9 | 7.3 ± 4.1 | 6.8 ± 3.8 |
| Yes | 19.2 ± 5.6 | 31.7 ± 6.7 | 56.1 ± 18.1 | 11.8 ± 3.9 | 10.4 ± 3.9 |
| t | 5.303 ** | −14.737 ** | 6.361 ** | −19.917 ** | −16.874 ** |
| ES † | 0.293 | −0.815 | 0.352 | −1.101 | −0.933 |
| Anxiety Symptoms | |||||
| No | 21.2 ± 5.1 | 25.5 ± 7.1 | 62.3 ± 16.9 | - | 6.6 ± 3.6 |
| Yes | 17.8 ± 5.4 | 33.1 ± 6.4 | 55.3 ± 18.0 | - | 11.4 ± 3.6 |
| t | 11.701 ** | −20.425 ** | 7.287 ** | - | −23.941 ** |
| ES † | 0.660 | −1.090 | 0.411 | - | −1.350 |
| Depressive Symptoms | |||||
| No | 21.8 ± 5.0 | 24.4 ± 7.2 | 64.6 ± 16.3 | 6.4 ± 3.7 | - |
| Yes | 18.4 ± 5.3 | 31.5 ± 6.1 | 55.1 ± 17.5 | 11.4 ± 3.71 | - |
| t | 13.516 ** | −21.238 ** | 11.576 ** | −27.277 ** | - |
| ES † | 0.664 | −1.043 | 0.569 | −1.340 | - |
| Model Variables | Anxiety Symptoms | Depressive Symptoms | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B (SE) | %95 CI for B | β | B (SE) | %95 CI for B | β | |
| Age | −0.004 (0.005) | −0.015; 0.006 | −0.013 | 0.014 ** (0.005) | 0.004; 0.025 | 0.045 |
| No. of household members | 0.092 * (0.036) | 0.021; 0.162 | 0.040 | −0.023 (0.036) | −0.094; 0.048 | −0.011 |
| Feeling lonely | 0.048 (0.083) | −0.015; 0.210 | 0.013 | 0.119 (0.083) | −0.044; 0.281 | 0.035 |
| Feeling distant from others | −0.008 (0.075) | −0.155; 0.140 | −0.002 | 0.042 (0.075) | −0.106; 0.190 | 0.013 |
| Feeling of losing control over life | 0.156 * (0.075) | 0.009; 0.303 | 0.045 | 0.094 (0.075) | −0.052; 0.241 | 0.030 |
| Feeling ostracised | 0.273 ** (0.075) | 0.126; 0.421 | 0.073 | 0.119 (0.075) | −0.029; 0.267 | 0.034 |
| Sleep problems | 0.201 ** (0.071) | 0.063; 0.340 | 0.059 | 0.116 (0.071) | −0.023; 0.254 | 0.037 |
| Concentration problems | 0.282 ** (0.078) | 0.128; 0.435 | 0.079 | 0.149 (0.079) | −0.005; 0.303 | 0.045 |
| Fear of contracting COVID-19 | 0.149 ** (0.033) | 0.083; 0.214 | 0.097 | −0.021 (0.033) | −0.087; 0.044 | −0.015 |
| Fear of dying from COVID-19 | 0.171 ** (0.029) | 0.114; 0.228 | 0.126 | −0.048 (0.029) | −0.105; 0.010 | −0.038 |
| Coping flexibility | −0.042 ** (0.014) | −0.070; −0.014 | −0.050 | −0.071 ** (0.014) | −0.099; −0.043 | −0.092 |
| Perceived stress | 0.115 ** (0.012) | 0.091; 0.139 | 0.197 | 0.101 ** (0.012) | 0.077; 0.125 | 0.187 |
| Perceived social support | 0.008 (0.004) | −0.001; 0.016 | 0.031 | −0.021 ** (0.004) | −0.029; −0.012 | −0.087 |
| Anxiety symptoms | - | - | - | 0.430 ** (0.022) | 0.387; 0.474 | 0.464 |
| Depressive symptoms | 0.431 ** (0.022) | 0.387; 0.474 | 0.399 | - | - | - |
| Model [F(df); p] | 205.025(14); <0.001 | 159.412(14); <0.001 | ||||
| Adjusted R2 | 0.627 | 0.566 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bucaktepe, P.G.E.; Demir Pervane, V.; Göcen, Ö.; Çelik, S.B.; Çelik, F.; Batmaz, Ö.U.; Yılmaz, A.; Çelepkolu, T.; Altınbaş, K. Mental Health and Age-Related Differences in Community During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Cross-Sectional Study from Southeastern Türkiye. Medicina 2025, 61, 1840. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61101840
Bucaktepe PGE, Demir Pervane V, Göcen Ö, Çelik SB, Çelik F, Batmaz ÖU, Yılmaz A, Çelepkolu T, Altınbaş K. Mental Health and Age-Related Differences in Community During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Cross-Sectional Study from Southeastern Türkiye. Medicina. 2025; 61(10):1840. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61101840
Chicago/Turabian StyleBucaktepe, Pakize Gamze Erten, Vasfiye Demir Pervane, Ömer Göcen, Sercan Bulut Çelik, Fatima Çelik, Öznur Uysal Batmaz, Ahmet Yılmaz, Tahsin Çelepkolu, and Kürşat Altınbaş. 2025. "Mental Health and Age-Related Differences in Community During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Cross-Sectional Study from Southeastern Türkiye" Medicina 61, no. 10: 1840. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61101840
APA StyleBucaktepe, P. G. E., Demir Pervane, V., Göcen, Ö., Çelik, S. B., Çelik, F., Batmaz, Ö. U., Yılmaz, A., Çelepkolu, T., & Altınbaş, K. (2025). Mental Health and Age-Related Differences in Community During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Cross-Sectional Study from Southeastern Türkiye. Medicina, 61(10), 1840. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61101840







