Evaluation of TAM Receptor Targeting in Pathophysiology of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
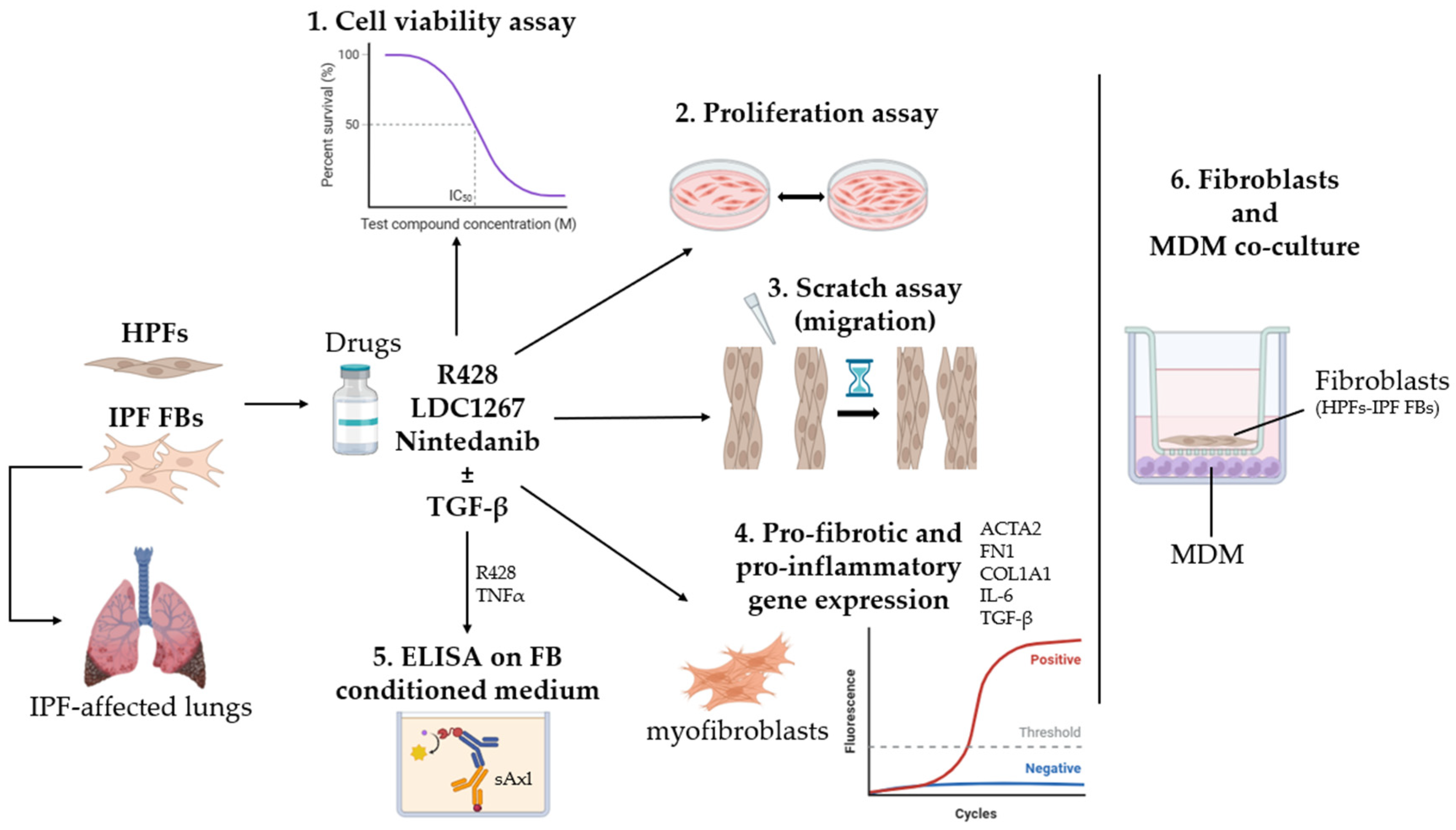
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. MTT Assay: Metabolic Cell Viability
2.3. Cell Proliferation
2.4. Wound Healing Scratch Assay
2.5. RNA Extraction, Reverse Transcription, and RT-qPCR
2.6. TNFα Treatment
2.7. ELISA Assay: sAxl
2.8. Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cell (PBMC) Isolation and Differentiation into Macrophages
2.9. Co-Culture: Fibroblasts and Macrophages
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
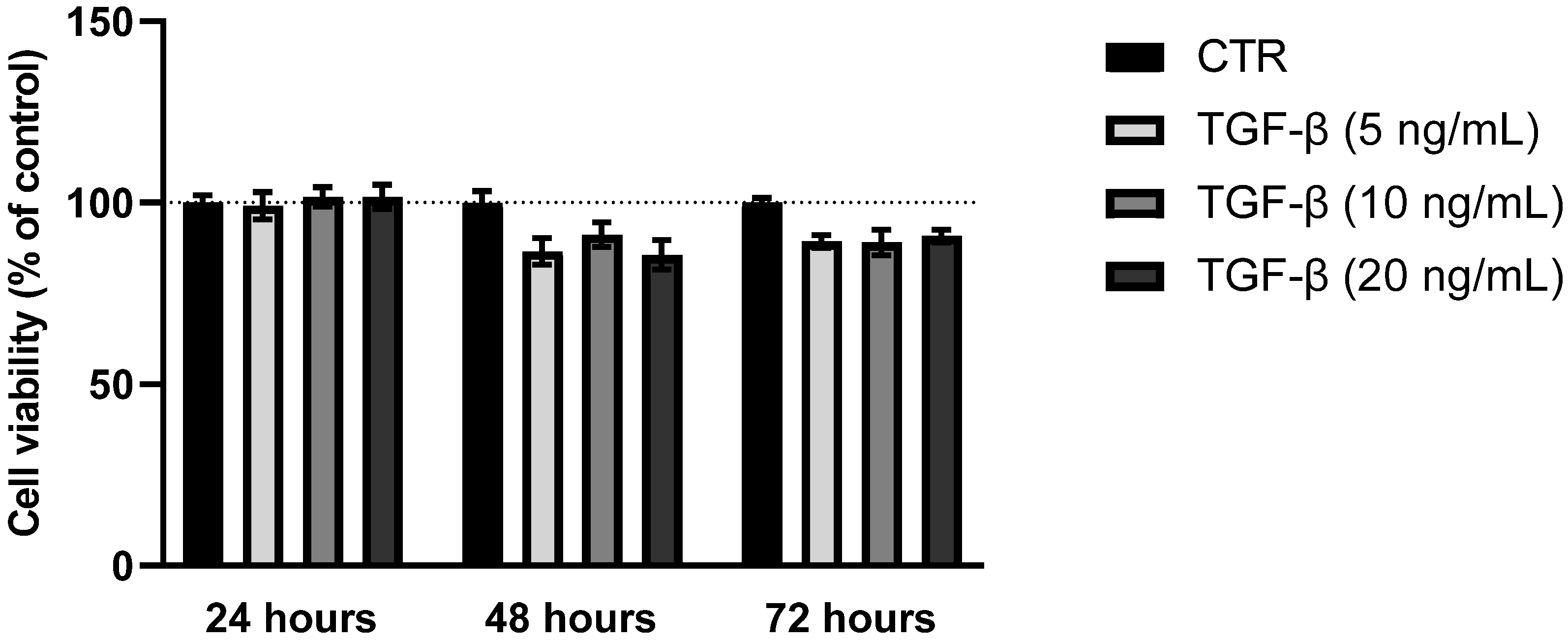
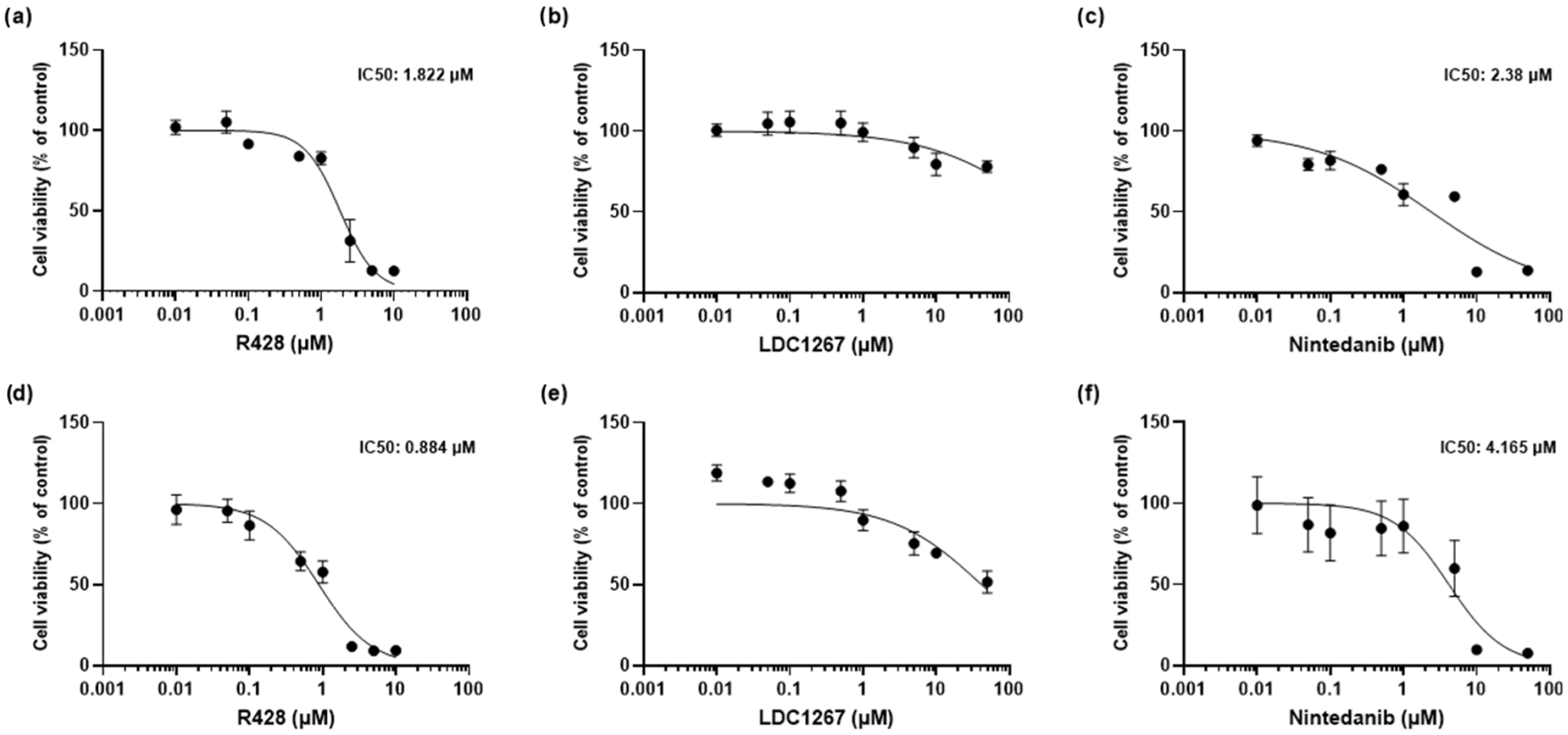
3.1. MTT Assay: Cytotoxicity of TAM Inhibitors, Nintedanib, and TGF-β
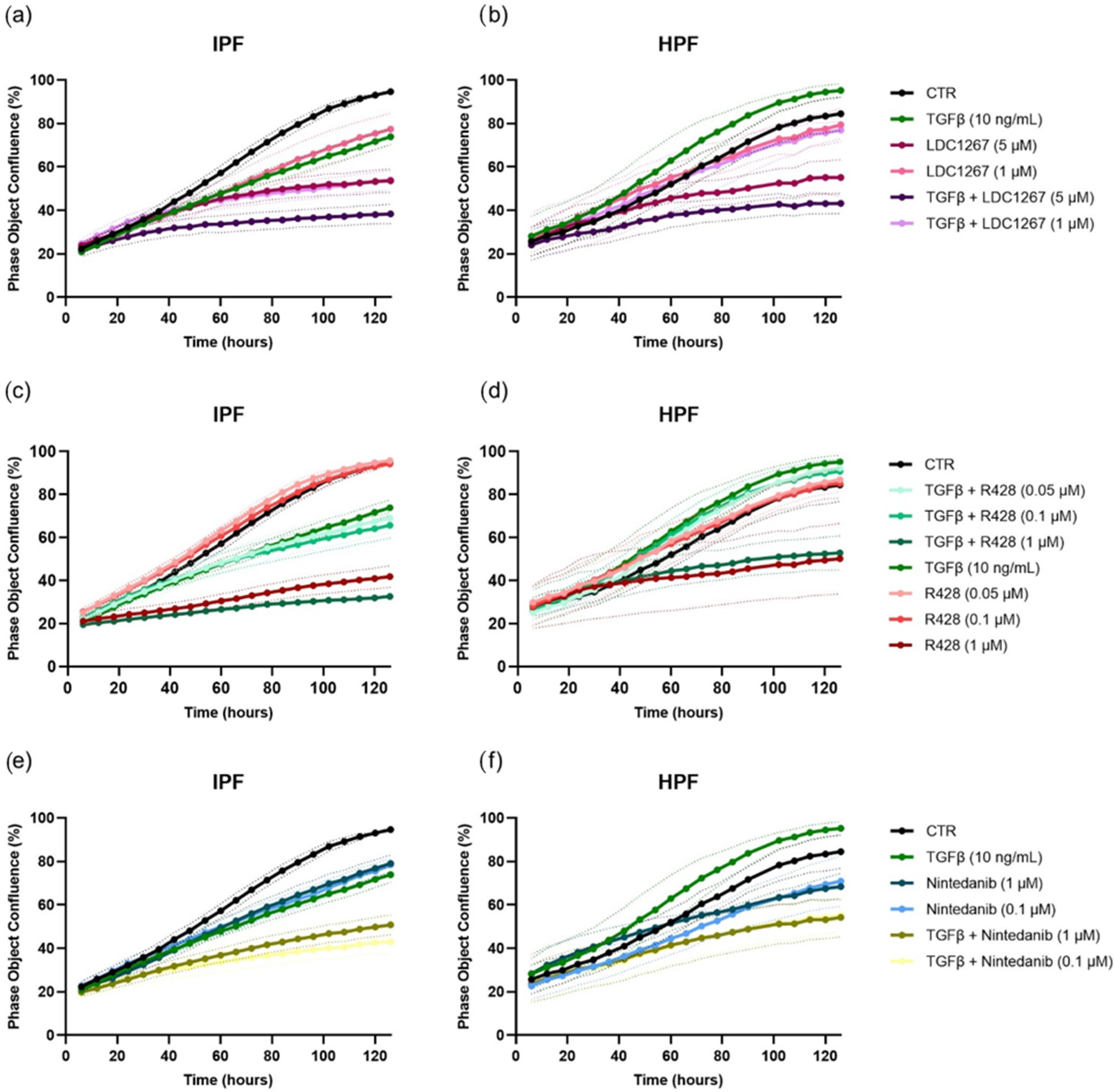
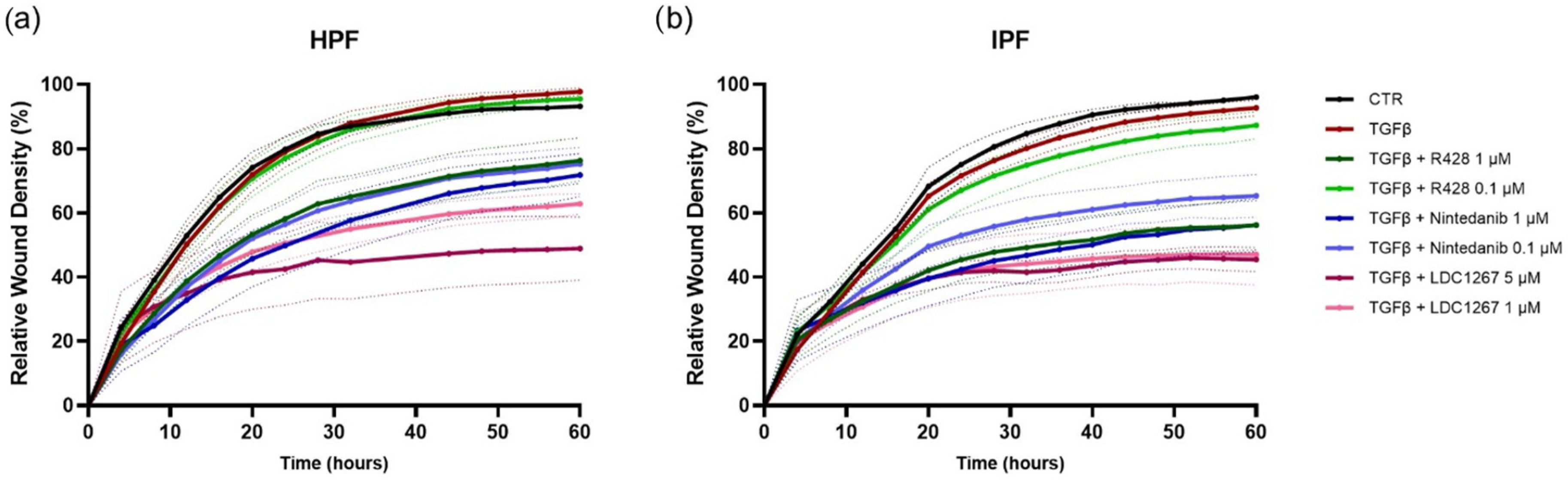
3.2. TAM Inhibitors: Effect on Cell Proliferation and Cell Migration
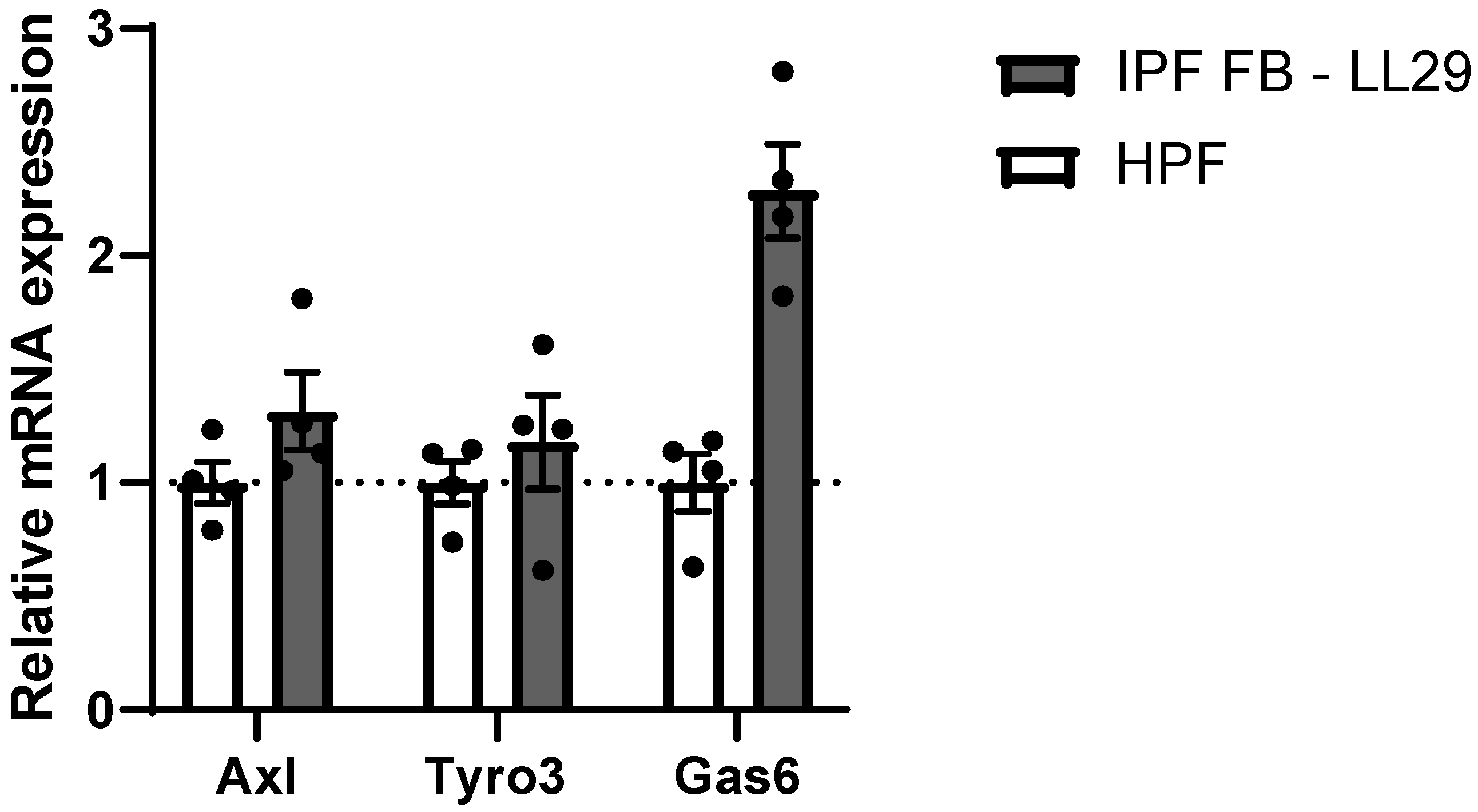
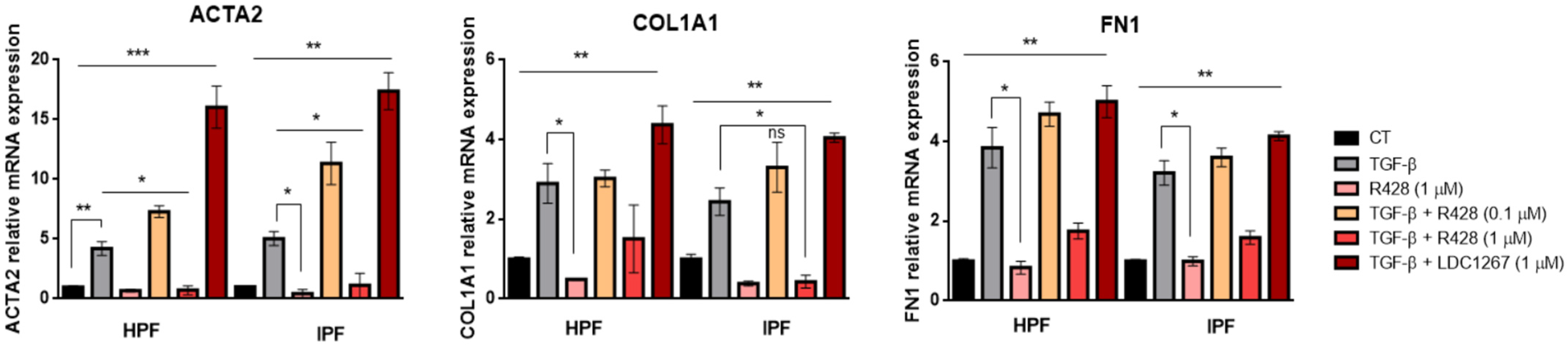
3.3. Expression of Fibrotic Genes in TGF-β-Induced Myofibroblasts: Effect of TAM Inhibitors
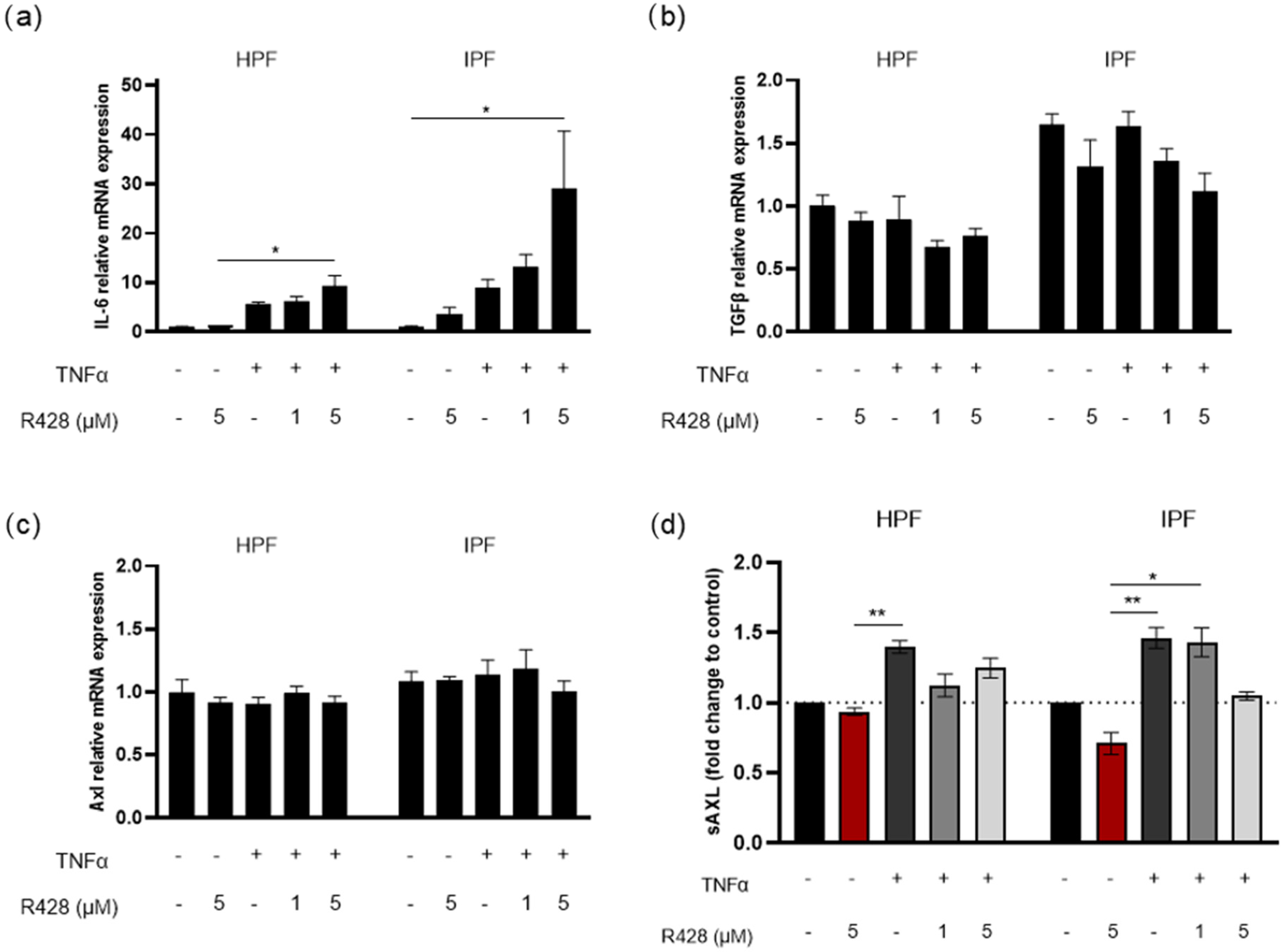
3.4. Effect of Axl Targeting on TNFα-Induced IL-6 and TGF-β Expression
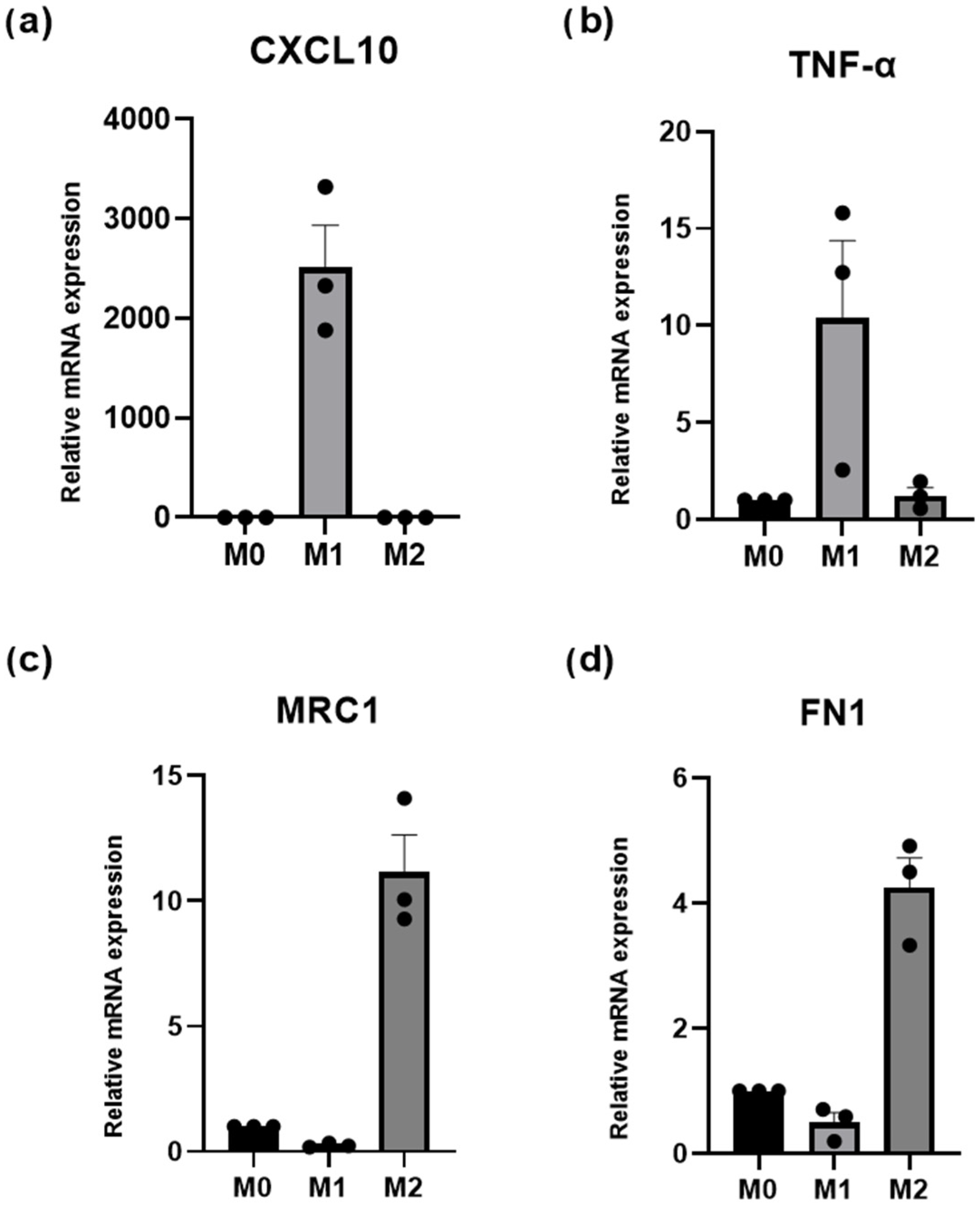
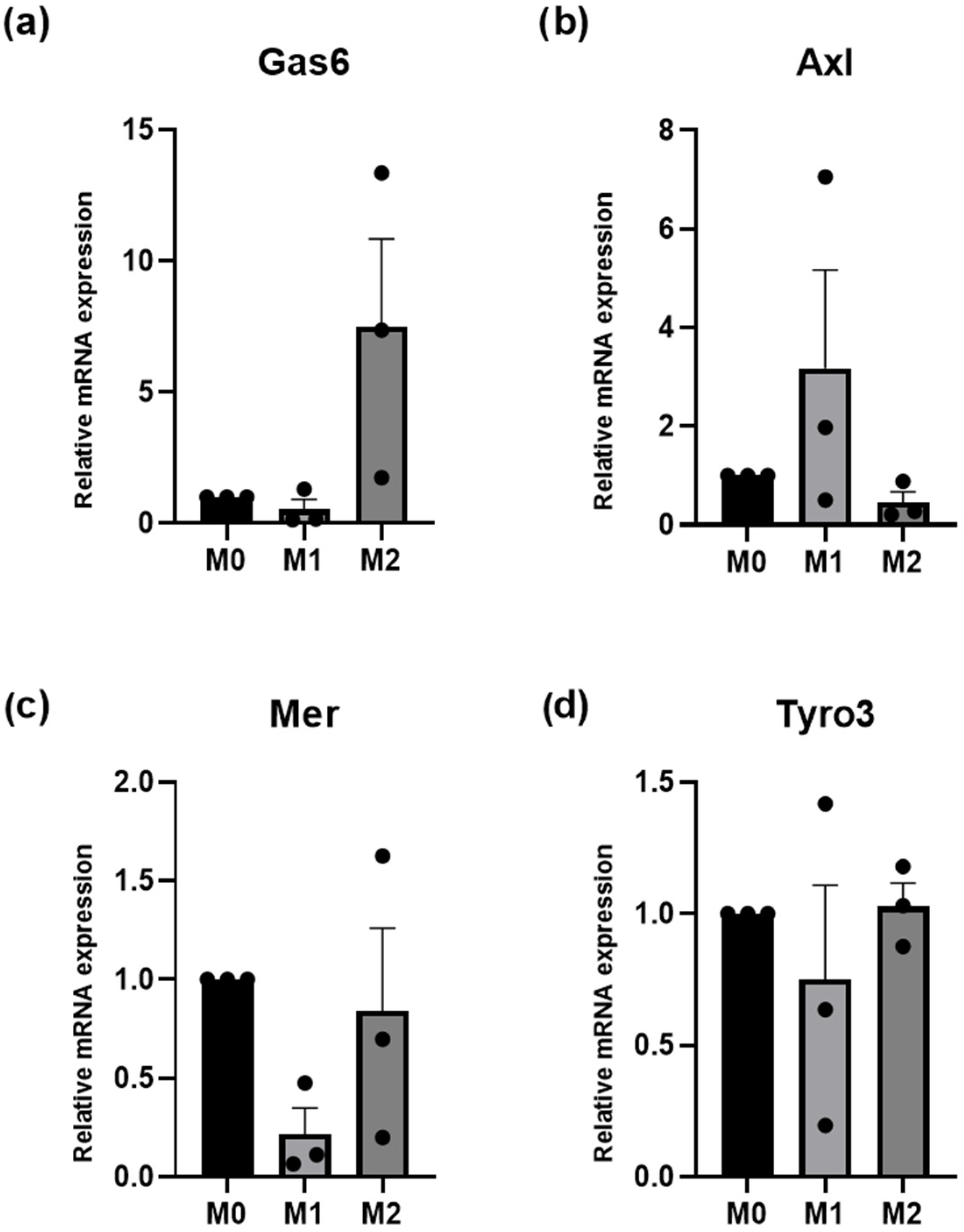
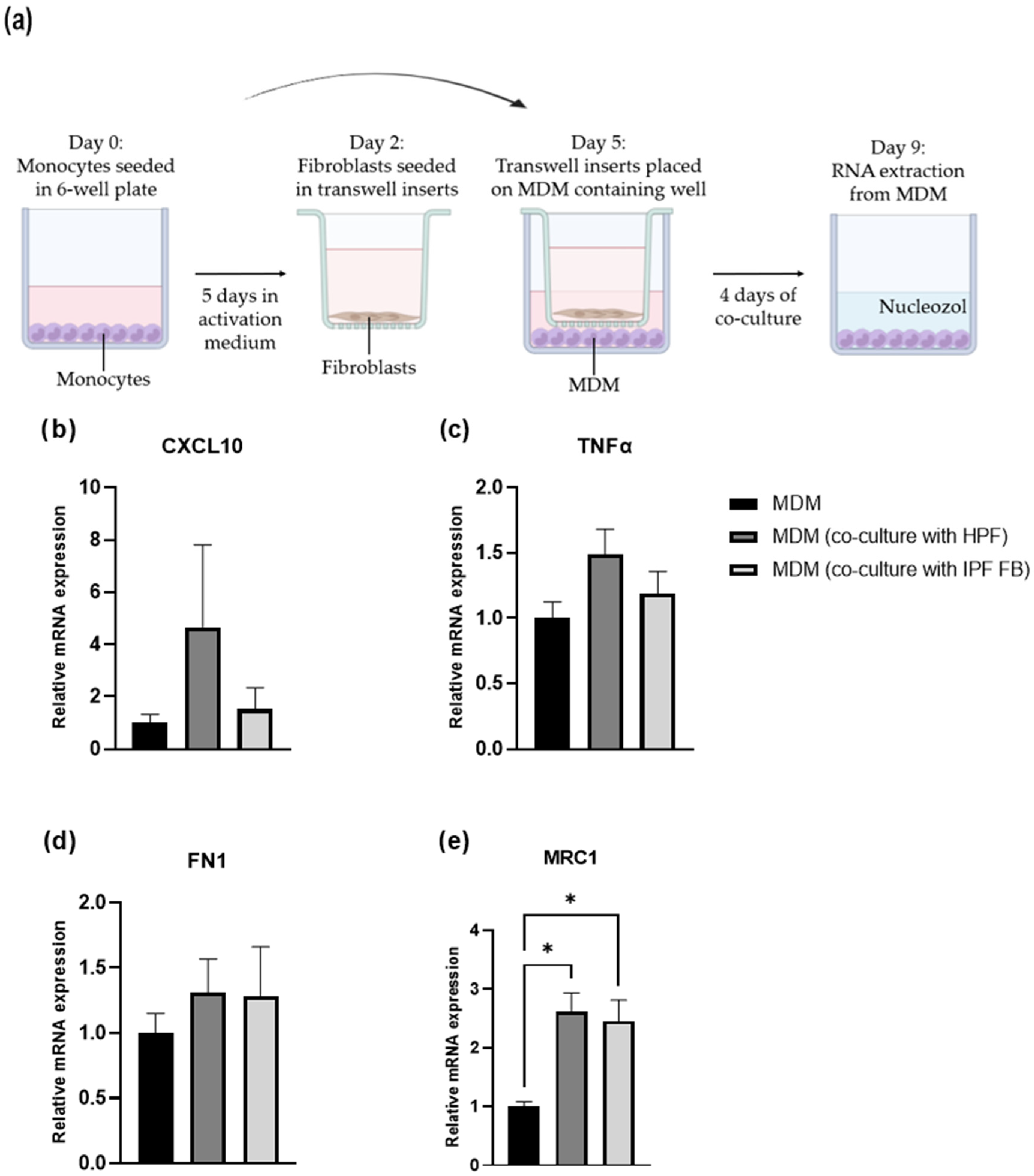
3.5. Macrophage Polarization: Fibroblast-Mediated Effects
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TAMs | Tyro3, Axl, and Mer receptors |
| Gas6 | Growth Arrest-Specific 6 |
| IPF | Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis |
| HPF | Human pulmonary fibroblast |
| IPF FBs | IPF fibroblasts |
| R428 | Bemcentinib (Axl-specific inhibitor) |
| LDC1267 | TAM inhibitor |
| TGF-β | Transforming Growth Factor Beta |
| ACTA2 | Actin Alpha 2, Smooth Muscle |
| FN1 | Fibronectin 1 |
| COL1A1 | Collagen Type I Alpha 1 Chain |
| MRC1 | Mannose Receptor C-Type 1 |
| TNFα | Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha |
| CXCL10 | C-X-C Motif Chemokine Ligand 10 |
| ILDs | Interstitial Lung Diseases |
| UIP | Usual Interstitial Pneumonia |
| IIPs | Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias |
| AEC2s | Type 2 alveolar epithelial cells |
| AEC1s | Type 1 alveolar epithelial cells |
| EMT | Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition |
| RTKs | tyrosine kinases receptors |
| ProS1 | Protein S |
| sTyro3 | soluble Tyro3 |
| sAxl | soluble Axl |
| sMer | soluble Mer |
| FBS | Fetal Bovine Serum |
| DMSO | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| PBS | Phosphate Buffered Saline |
| NTC | No template control |
| NRT | No reverse transcriptase control |
| HPRT | Hypoxanthine Phosphoribosyltransferase 1 |
| TBP | TATA-Box Binding Protein |
| PBMC | Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cell |
| M-CSF | Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor |
| GM-CSF | Granulocyte–Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor |
| MDM | Monocyte-derived macrophage |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| IFN-γ | Interferon-γ |
| IL-4 | Interleukin 4 |
| IL-10 | Interleukin 10 |
| IL-13 | Interleukin 13 |
| IC50 | Inhibitory Concentration 50 |
| SEM | Standard Error of the Mean |
| IL-6 | Interleukin 6 |
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration |
| α-SMA | α-smooth muscle actin |
| FGF-2 | Fibroblast Growth Factor 2 |
| ADAM10/17 | A Disintegrin And Metalloproteinase Domain 10/17 |
| TGM2 | Transglutaminase-2 |
| LOX | Lysyl oxidase |
| ECM | Extracellular matrix |
| Arg1 | Arginase 1 |
| MCP-1 | Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 |
| MIP-1α/β | Macrophage Inflammatory Protein 1α/β |
| CXCL9 | C-X-C Motif Chemokine Ligand 9 |
| PDGF | platelet-derived growth factor |
Appendix A
| Genes | Forward | Reverse |
|---|---|---|
| Axl | GGTGGCTGTGAAGACGATGA | CTCAGATACTCCATGCCACT |
| Mer | GCCCCATCAGTAGCACCTTT | TGCACGTAGCATTGTGGACT |
| Tyro3 | CAATGCAGTTGGCTGTGGAC | CGTTAGCACACCAAGGACCA |
| Gas6 | ACGACCCCGAGACGGATTAT | CTTCCTATCGCAGGGGTTGG |
| ACTA2 | AGCCAAGCACTGTCAGGAAT | TTGTCACACACCAAGGCAGT |
| COL1A1 | CAGGCTGGTGTGATGGGATT | GGGCCTTGTTCACCTCTCTC |
| FN1 | GGGTCTCCTCCCAGAGAAGT | GGAAGGGTTACCAGTTGGGG |
| IL-6 | TCACTGGTCTTTTGGAGTTTGA | AGAGCCCTCAGGCTGGACT |
| TFG-β | CCCAGCATCTGCAAAGCTC | GTCAATGTACAGCTGCCGCA |
| CXCL10 | GTGGATGTTCTGACCCTGCT | GGAGGATGGCAGTGGAAGTC |
| TNF-α | CCCAGGGACCTCTCTCTAATC | ATGGGCTACAGGCTTGTCACT |
| MRC1 | ACCTGCGACAGTAAACGAGG | TGTCTCCGCTTCATGCCATT |
| HPRT | GATTTGGAAAGGGTGTTTAT | TCCCATCTCCTTCATCACAT |
| TBP | TGTATCCACAGTGAATCTTGGTTG | GGTTCGTGGCTCTCTTATCCTC |
References
- Cottin, V.; Hirani, N.A.; Hotchkin, D.L.; Nambiar, A.M.; Ogura, T.; Otaola, M.; Skowasch, D.; Park, J.S.; Poonyagariyagorn, H.K.; Wuyts, W.; et al. Presentation, Diagnosis and Clinical Course of the Spectrum of Progressive-Fibrosing Interstitial Lung Diseases. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2018, 27, 180076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, J.; Costabel, U.; Cordier, J.F.; DoPico, G.A.; DuBois, R.M.; Lynch, D.; Lynch, J.P.; Myers, J.; Panos, R.; Raghu, G.; et al. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Diagnosis and Treatment: International Consensus Statement. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2000, 161, 646–664. [Google Scholar]
- Raghu, G.; Remy-Jardin, M.; Richeldi, L.; Thomson, C.C.; Antoniou, K.M.; Bissell, B.D.; Bouros, D.; Buendia-Roldan, I.; Caro, F.; Crestani, B.; et al. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (an Update) and Progressive Pulmonary Fibrosis in Adults: An Official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT Clinical Practice Guideline. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2022, 205, e18–e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, T.E. Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias: Progress in Classification, Diagnosis, Pathogenesis and Management. Trans. Am. Clin. Climatol. Assoc. 2004, 115, 43. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Richeldi, L.; Collard, H.R.; Jones, M.G. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Lancet 2017, 389, 1941–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewlett, J.C.; Kropski, J.A.; Blackwell, T.S. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Epithelial-Mesenchymal Interactions and Emerging Therapeutic Targets. Matrix Biol. 2018, 71–72, 112–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kletukhina, S.; Mutallapova, G.; Titova, A.; Gomzikova, M. Role of Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Extracellular Vesicles in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, T.; Liu, N.; Chen, H.; Geng, Y.; Kurkciyan, A.; Mena, J.M.; Stripp, B.R.; Jiang, D.; et al. Hyaluronan and TLR4 Promote Surfactant-Protein-C-Positive Alveolar Progenitor Cell Renewal and Prevent Severe Pulmonary Fibrosis in Mice. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 1285–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horowitz, J.C.; Thannickal, V.J. Epithelial-Mesenchymal Interactions in Pulmonary Fibrosis. Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 27, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, C.; Linn, G.; Chow, Y.H.; Kobayashi, A.; Mittelsteadt, K.; Altemeier, W.A.; Gharib, S.A.; Schnapp, L.M.; Duffield, J.S. Role of Lung Pericytes and Resident Fibroblasts in the Pathogenesis of Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 188, 820–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, M.; Yamauchi, K.; Chiba, R.; Iwama, N.; Date, F.; Shibata, N.; Kumagai, H.; Risteli, J.; Sato, S.; Takahashi, T.; et al. The Definition of Fibrogenic Processes in Fibroblastic Foci of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Based on Morphometric Quantification of Extracellular Matrices. Hum. Pathol. 2009, 40, 1278–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.H.; Yamauchi, K.; Uzuki, M.; Nakanishi, T.; Takigawa, M.; Inoue, H.; Sawai, T. Type II Alveolar Epithelial Cells and Interstitial Fibroblasts Express Connective Tissue Growth Factor in IPF. Eur. Respir. J. 2001, 17, 1220–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Epstein Shochet, G.; Brook, E.; Israeli-Shani, L.; Edelstein, E.; Shitrit, D. Fibroblast Paracrine TNF-α Signaling Elevates Integrin A5 Expression in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF). Respir. Res. 2017, 18, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadjicharalambous, M.R.; Lindsay, M.A. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Pathogenesis and the Emerging Role of Long Non-Coding RNAs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, C.M.; Fingerlin, T.E.; Schwarz, M.I.; Lynch, D.; Kurche, J.; Warg, L.; Yang, I.V.; Schwartz, D.A. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Genetic Disease That Involves Mucociliary Dysfunction of the Peripheral Airways. Physiol. Rev. 2016, 96, 1567–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wollin, L.; Wex, E.; Pautsch, A.; Schnapp, G.; Hostettler, K.E.; Stowasser, S.; Kolb, M. Mode of Action of Nintedanib in the Treatment of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Eur. Respir. J. 2015, 45, 1434–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richeldi, L.; du Bois, R.M.; Raghu, G.; Azuma, A.; Brown, K.K.; Costabel, U.; Cottin, V.; Flaherty, K.R.; Hansell, D.M.; Inoue, Y.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Nintedanib in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 2071–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto, A.L.; Lai, C. The TAM Subfamily of Receptor Tyrosine Kinases: The Early Years. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, B.; Kasikara, C. TAM Receptors and Their Ligand-Mediated Activation: Role in Atherosclerosis. Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol. 2020, 357, 21–33. [Google Scholar]
- Manfioletti, G.; Brancolini, C.; Avanzi, G.; Schneider’, C. The Protein Encoded by a Growth Arrest-Specific Gene (Gas6) Is a New Member of the Vitamin K-Dependent Proteins Related to Protein S, a Negative Coregulator in the Blood Coagulation Cascade. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1993, 13, 4976–4985. [Google Scholar]
- O’bryan, J.P.; Frye, R.A.; Cogswell, P.C.; Neubauer, A.; Kitch, B.; Prokop, C.; Espinosa, R., III; Le Beau, M.M.; Shelton Earp, H.; Liul, E.T. Axl, a Transforming Gene Isolated from Primary Human Myeloid Leukemia Cells, Encodes a Novel Receptor Tyrosine Kinase. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1991, 11, 5016–5031. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wium, M.; Paccez, J.D.; Zerbini, L.F. The Dual Role of TAM Receptors in Autoimmune Diseases and Cancer: An Overview. Cells 2018, 7, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tondo, G.; Perani, D.; Comi, C. TAM Receptor Pathways at the Crossroads of Neuroinflammation and Neurodegeneration. Dis. Markers 2019, 2019, 2387614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemke, G.; Lu, Q. Macrophage Regulation by Tyro 3 Family Receptors. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2003, 15, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellan, M.; Cittone, M.G.; Tonello, S.; Rigamonti, C.; Castello, L.M.; Gavelli, F.; Pirisi, M.; Sainaghi, P.P. Gas6/TAM System: A Key Modulator of the Interplay between Inflammation and Fibrosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espindola, M.S.; Habiel, D.M.; Narayanan, R.; Jones, I.; Coelho, A.L.; Murray, L.A.; Jiang, D.; Noble, P.W.; Hogaboam, C.M. Targeting of TAM Receptors Ameliorates Fibrotic Mechanisms in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 197, 1443–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tutusaus, A.; de Gregorio, E.; Cucarull, B.; Cristóbal, H.; Aresté, C.; Graupera, I.; Coll, M.; Colell, A.; Gausdal, G.; Lorens, J.B.; et al. A Functional Role of GAS6/TAM in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis Progression Implicates AXL as Therapeutic Target. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 9, 349–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, P.; Talwar, P. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF): Disease Pathophysiology, Targets, and Potential Therapeutic Interventions. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2024, 479, 2181–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartold, K.; Iskierko, Z.; Sharma, P.S.; Lin, H.Y.; Kutner, W. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF): Diagnostic Routes Using Novel Biomarkers. Biomed. J. 2024, 47, 100729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Chen, H.; Ke, S.; Mo, L.; Qiu, M.; Zhu, G.; Zhu, W.; Liu, L. Identifying Potential Biomarkers of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis through Machine Learning Analysis. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 16559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petnak, T.; Lertjitbanjong, P.; Thongprayoon, C.; Moua, T. Impact of Antifibrotic Therapy on Mortality and Acute Exacerbation in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Chest 2021, 160, 1751–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitre, T.; Mah, J.; Helmeczi, W.; Khalid, M.F.; Cui, S.; Zhang, M.; Husnudinov, R.; Su, J.; Banfield, L.; Guy, B.; et al. Medical Treatments for Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Thorax 2022, 77, 1243–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holland, S.J.; Pan, A.; Franci, C.; Hu, Y.; Chang, B.; Li, W.; Duan, M.; Torneros, A.; Yu, J.; Heckrodt, T.J.; et al. R428, a Selective Small Molecule Inhibitor of Axl Kinase, Blocks Tumor Spread and Prolongs Survival in Models of Metastatic Breast Cancer. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 1544–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Epstein, F.H.; Border, W.A.; Noble, N.A. Transforming Growth Factor β in Tissue Fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 1994, 331, 1286–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correll, K.A.; Edeen, K.E.; Redente, E.F.; Zemans, R.L.; Edelman, B.L.; Danhorn, T.; Curran-Everett, D.; Mikels-Vigdal, A.; Mason, R.J. TGF Beta Inhibits HGF, FGF7, and FGF10 Expression in Normal and IPF Lung Fibroblasts. Physiol. Rep. 2018, 6, e13794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, A.; Horie, M.; Nagase, T. TGF-β Signaling in Lung Health and Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lijnen, P.; Petrov, V. Transforming Growth Factor-Β1-Induced Collagen Production in Cultures of Cardiac Fibroblasts Is the Result of the Appearance of Myofibroblasts. Methods Find. Exp. Clin. Pharmacol. 2002, 24, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, N.; Xu, Y.D.; O’Connor, R.; Duronio, V. Proliferation of Pulmonary Interstitial Fibroblasts Is Mediated by Transforming Growth Factor-Β1-Induced Release of Extracellular Fibroblast Growth Factor-2 and Phosphorylation of P38 MAPK and JNK. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 43000–43009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Du, Y.; Shen, Y.; He, Y.; Zhao, H.; Li, Z. TGF-Beta 1 Induced Fibroblast Proliferation Is Mediated by the FGF-2/ERK Pathway. Front. Biosci. 2011, 17, 2667–2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.Q.; Nian, Y.; Zhu, T.J. Circ_PWWP2A Promotes Lung Fibroblast Proliferation and Fibrosis via the MiR-27b-3p/GATA3 Axis, Thereby Aggravating Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2023, 70, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez, D.; Cárdenes, N.; Sellarés, J.; Bueno, M.; Corey, C.; Hanumanthu, V.S.; Peng, Y.; D’Cunha, H.; Sembrat, J.; Nouraie, M.; et al. IPF Lung Fibroblasts Have a Senescent Phenotype. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2017, 313, L1164–L1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, P.D.; McCulloch, C.A.G. Dependence of Fibroblast Migration on Actin Severing Activity of Gelsolin. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 20516–20523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suganuma, H.; Sato, A.; Tamura, R.; Chida, K. Enhanced Migration of Fibroblasts Derived from Lungs with Fibrotic Lesions. Thorax 1995, 50, 984–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, C.A.; Rodansky, E.S.; Johnson, L.A.; Berinstein, J.A.; Cushing, K.C.; Huang, S.; Spence, J.R.; Higgins, P.D.R. AXL Is a Potential Target for the Treatment of Intestinal Fibrosis. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2021, 27, 303–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machahua, C.; Marti, T.M.; Dorn, P.; Funke-Chambour, M. Fibrosis in PCLS: Comparing TGF-β and Fibrotic Cocktail. Respir. Res. 2025, 26, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wynn, T.A.; Ramalingam, T.R. Mechanisms of Fibrosis: Therapeutic Translation for Fibrotic Disease. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 1028–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.C.; Lin, T.H.; Wu, M.Y.; Chiu, Y.C.; Tang, C.H.; Hour, M.J.; Liou, H.C.; Tu, H.J.; Yang, R.S.; Fu, W.M. 5-Lipoxygenase Inhibitors Attenuate TNF-α-Induced Inflammation in Human Synovial Fibroblasts. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahar, I.; Fireman, E.; Topilsky, M.; Grief, J.; Kivity, S.; Spirer, Z.; Ben Efraim, S. Effect of IL-6 on Alveolar Fibroblast Proliferation in Interstitial Lung Diseases. Clin. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1996, 79, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papiris, S.A.; Tomos, I.P.; Karakatsani, A.; Spathis, A.; Korbila, I.; Analitis, A.; Kolilekas, L.; Kagouridis, K.; Loukides, S.; Karakitsos, P.; et al. High Levels of IL-6 and IL-8 Characterize Early-on Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Acute Exacerbations. Cytokine 2018, 102, 168–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roofeh, D.; Lin, C.J.F.; Goldin, J.; Kim, G.H.; Furst, D.E.; Denton, C.P.; Huang, S.; Khanna, D. Tocilizumab Prevents Progression of Early Systemic Sclerosis–Associated Interstitial Lung Disease. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021, 73, 1301–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, D.; Lin, C.J.F.; Furst, D.E.; Goldin, J.; Kim, G.; Kuwana, M.; Allanore, Y.; Matucci-Cerinic, M.; Distler, O.; Shima, Y.; et al. Tocilizumab in Systemic Sclerosis: A Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 963–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.H.; Kim, H.C.; Im, K.; Baek, I.J.; Choi, Y.J.; Lee, H.; Kim, D.S.; Lee, C.W.; Jeong, J.Y.; Ban, K.; et al. Inhibition of AXL Ameliorates Pulmonary Fibrosis via Attenuation of M2 Macrophage Polarisation. Eur. Respir. J. 2025, 65, 2400615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.C.; Gu, S.; Li, J.M.; Hsu, S.W.; Chen, S.J.; Chang, W.H.; Chen, C.H. Targeting the AXL Receptor in Combating Smoking-Related Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2021, 64, 734–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, D.E.; Ferris, M.B.; Pociask, D.; Brody, A.R. Tumor Necrosis Factor-α Induces Transforming Growth Factor-Β1 Expression in Lung Fibroblasts through the Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase Pathway. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2005, 32, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Li, Y.; Yang, S.; Chen, Y.; Wu, K.; Geng, J.; Liu, P.; Wang, Z.; Dai, H.; Wang, C. Orderly Regulation of Macrophages and Fibroblasts by Axl in Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis in Mice. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2025, 29, e70321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajbakhsh, A.; Gheibi Hayat, S.M.; Butler, A.E.; Sahebkar, A. Effect of Soluble Cleavage Products of Important Receptors/Ligands on Efferocytosis: Their Role in Inflammatory, Autoimmune and Cardiovascular Disease. Ageing Res. Rev. 2019, 50, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.W.; Chun, W.; Lee, H.J.; Min, J.H.; Kim, S.M.; Seo, J.Y.; Ahn, K.S.; Oh, S.R. The Role of Macrophages in the Development of Acute and Chronic Inflammatory Lung Diseases. Cells 2021, 10, 897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Z.; Chen, Y.; Ma, L.; Hu, F.; Xie, L. Macrophage Polarization and Its Impact on Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1444964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzoni, G.; Mura, L.; Razzuoli, E.; De Ciucis, C.G.; Fruscione, F.; Dell’Anno, F.; Zinellu, S.; Carta, T.; Anfossi, A.G.; Dei Giudici, S.; et al. Heterogeneity of Phenotypic and Functional Changes to Porcine Monocyte-Derived Macrophages Triggered by Diverse Polarizing Factors In Vitro. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orecchioni, M.; Ghosheh, Y.; Pramod, A.B.; Ley, K. Macrophage Polarization: Different Gene Signatures in M1(Lps+) vs. Classically and M2(LPS-) vs. Alternatively Activated Macrophages. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, R.; Bing, R.; Gartling, G.J.; Branski, R.C. Macrophages Alter Inflammatory and Fibrotic Gene Expression in Human Vocal Fold Fibroblasts. Exp. Cell Res. 2022, 419, 113301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, D.J.; Chamberlain, L.M.; Grainger, D.W. Cell-Cell Signaling in Co-Cultures of Macrophages and Fibroblasts. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 9382–9394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donlin, L.T.; Jayatilleke, A.; Giannopoulou, E.G.; Kalliolias, G.D.; Ivashkiv, L.B. Modulation of TNF-Induced Macrophage Polarization by Synovial Fibroblasts. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 2373–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, P.; Ortega, J.G.; Tamaki, W.; Chien, C.; Chang, K.-C.; Biswas, N.; Pan, S.; Nilsson, J.; Yin, X.; Bhattacharyya, A.; et al. Myeloid-mesenchymal crosstalk drives ARG1-dependent profibrotic metabolism via ornithine in lung fibrosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2025, 28, e188734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novak, C.M.; Sethuraman, S.; Luikart, K.L.; Reader, B.F.; Wheat, J.S.; Whitson, B.; Ghadiali, S.N.; Ballinger, M.N. Alveolar Macrophages Drive Lung Fibroblast Function in Cocultures of IPF and Normal Patient Samples. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2023, 324, L507–L520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, R.; Valls, A.F.; Yerbes, R.; von Richter, S.; Kahlert, C.; Loges, S.; Weitz, J.; Schneider, M.; de Almodovar, C.R.; Ulrich, A.; et al. TAM Receptors Tyro3 and Mer as Novel Targets in Colorectal Cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 56355–56370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroder, K.; Irvine, K.M.; Taylor, M.S.; Bokil, N.J.; Le Cao, K.A.; Masterman, K.A.; Labzin, L.I.; Semple, C.A.; Kapetanovic, R.; Fairbairn, L.; et al. Conservation and Divergence in Toll-like Receptor 4-Regulated Gene Expression in Primary Human versus Mouse Macrophages. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, E944–E953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, F.O.; Helming, L.; Milde, R.; Varin, A.; Melgert, B.N.; Draijer, C.; Thomas, B.; Fabbri, M.; Crawshaw, A.; Ho, L.P.; et al. Genetic Programs Expressed in Resting and IL-4 Alternatively Activated Mouse and Human Macrophages: Similarities and Differences. Blood 2013, 121, e57–e69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Lan, P.; Wang, T. The Role of Immune Cells in the Pathogenesis of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Medicina 2023, 59, 1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vercellino, N.; Ferreira, L.L.; Zoppis, E.; Di Tizio, A.; Sabihi Ahvaz, Z.; Minisini, R.; Gavelli, F.; Sainaghi, P.P.; Patrucco, F.; Bellan, M. Evaluation of TAM Receptor Targeting in Pathophysiology of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Medicina 2025, 61, 1837. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61101837
Vercellino N, Ferreira LL, Zoppis E, Di Tizio A, Sabihi Ahvaz Z, Minisini R, Gavelli F, Sainaghi PP, Patrucco F, Bellan M. Evaluation of TAM Receptor Targeting in Pathophysiology of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Medicina. 2025; 61(10):1837. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61101837
Chicago/Turabian StyleVercellino, Nicole, Luciana L. Ferreira, Elisa Zoppis, Alice Di Tizio, Zohre Sabihi Ahvaz, Rosalba Minisini, Francesco Gavelli, Pier Paolo Sainaghi, Filippo Patrucco, and Mattia Bellan. 2025. "Evaluation of TAM Receptor Targeting in Pathophysiology of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis" Medicina 61, no. 10: 1837. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61101837
APA StyleVercellino, N., Ferreira, L. L., Zoppis, E., Di Tizio, A., Sabihi Ahvaz, Z., Minisini, R., Gavelli, F., Sainaghi, P. P., Patrucco, F., & Bellan, M. (2025). Evaluation of TAM Receptor Targeting in Pathophysiology of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Medicina, 61(10), 1837. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61101837






