The Effect of Hippotherapy Simulator-Assisted Therapy on Motor and Functional Outcomes in Children with Cerebral Palsy
Abstract
1. Introduction
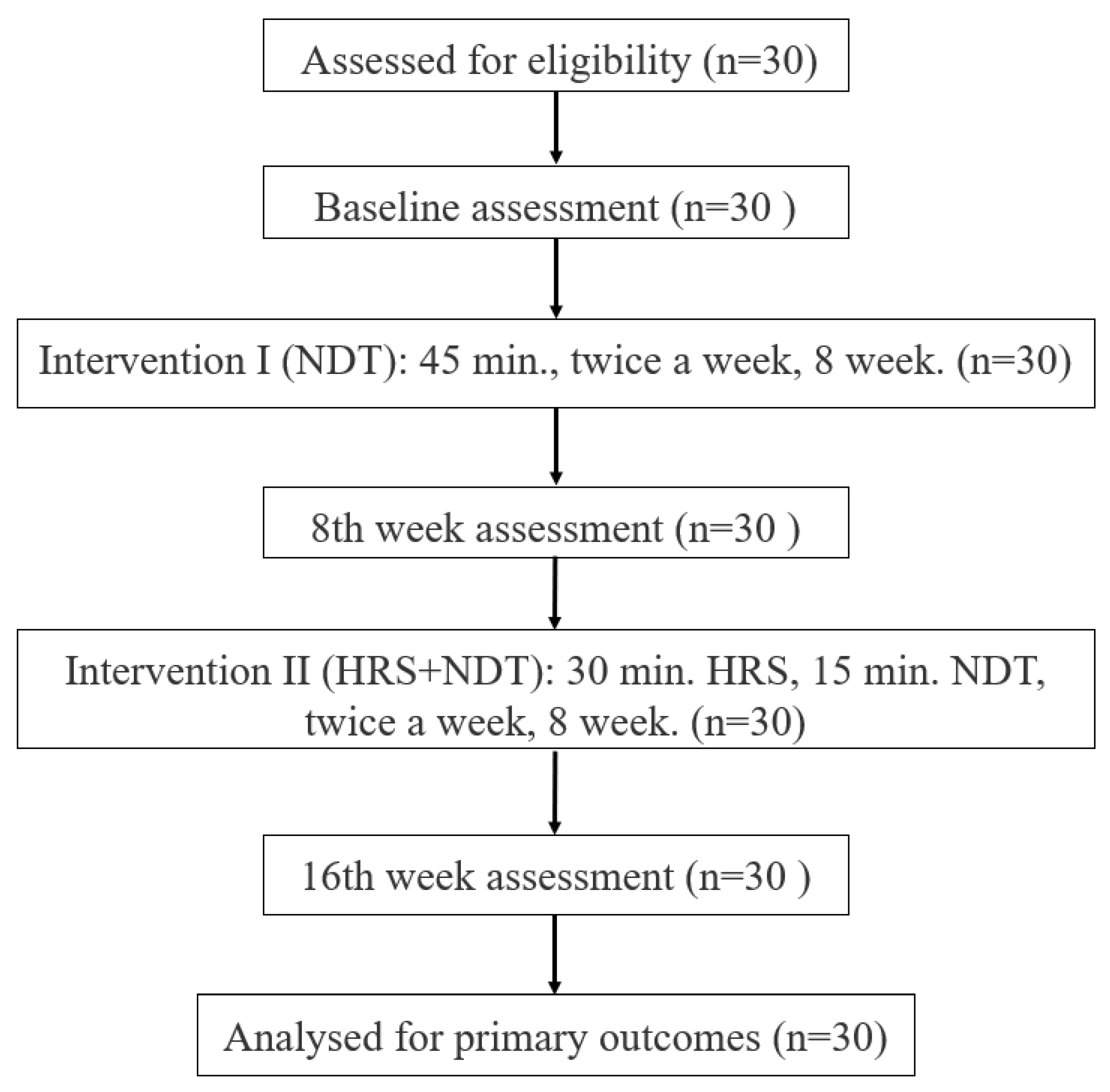
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Ethical Approval
2.3. Sample Size
2.4. Interventions
2.5. Neurodevelopmental Therapy (NDT)
2.6. Horse-Riding Simulator (HRS)
2.7. Outcome Measures
2.8. Modified Ashworth Scale (MAS)
2.9. Myoton®PRO
2.10. Gross Motor Function Measures (GMFM)-88
2.11. Pediatric Balance Scale (PBS)
2.12. Trunk Impairment Scale (TIS)
2.13. Pedalo® Sensamove Balance Test (Pedalo® SBT)
2.14. Gait Analysis with Win-Track
2.15. Functional Independence Measure (WeeFIM)
2.16. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. Lower Extremity Muscle Tone
3.3. Myoton®PRO Results
3.4. Gross Motor Functions
3.5. Functional Independence
3.6. Trunk Postural Control
3.7. Balance Function
3.8. Gait Parameters
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rosenbaum, P.; Paneth, N.; Leviton, A.; Goldstein, M.; Bax, M.; Damiano, D.; Dan, B.; Jacobsson, B. A report: The definition and classification of cerebral palsy April 2006. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. Suppl. 2007, 109 (Suppl. S109), 8–14. [Google Scholar]
- Vitrikas, K.; Dalton, H.; Breish, D. Cerebral palsy: An overview. Am. Fam. Physician 2020, 101, 213–220. [Google Scholar]
- Viruega, H.; Gaillard, I.; Carr, J.; Greenwood, B.; Gaviria, M. Short-and mid-term improvement of postural balance after a neurorehabilitation program via hippotherapy in patients with sensorimotor impairment after cerebral palsy: A preliminary kinetic approach. Brain Sci. 2019, 9, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novak, I.; Morgan, C.; Adde, L.; Blackman, J.; Boyd, R.N.; Brunstrom-Hernandez, J.; Cioni, G.; Damiano, D.; Darrah, J.; Eliasson, A.C.; et al. Early, accurate diagnosis and early intervention in cerebral palsy: Advances in diagnosis and treatment. JAMA Pediatr. 2017, 171, 897–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novak, I.; Morgan, C.; Fahey, M.; Finch-Edmondson, M.; Galea, C.; Hines, A.; Langdon, K.; Namara, M.M.; Paton, M.C.; Popat, H.; et al. State of the evidence traffic lights 2019: Systematic review of interventions for preventing and treating children with cerebral palsy. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2020, 20, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanon, M.A.; Pacheco, R.L.; Latorraca, C.d.O.C.; Martimbianco, A.L.C.; Pachito, D.V.; Riera, R. Neurodevelopmental treatment (Bobath) for children with cerebral palsy: A systematic review. J. Child Neurol. 2019, 34, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obrero-Gaitan, E.; Montoro-Cardenas, D.; Cortes-Perez, I.; Osuna-Pérez, M.C. Effectiveness of Mechanical Horse-Riding Simulator-Based Interventions in Patients with Cerebral Palsy—A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sterba, J.A. Does horseback riding therapy or therapist-directed hippotherapy rehabilitate children with cerebral palsy? Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2007, 49, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Guindos-Sanchez, L.; Lucena-Anton, D.; Moral-Munoz, J.A.; Salazar, A.; Carmona-Barrientos, I. The effectiveness of hippotherapy to recover gross motor function in children with cerebral palsy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Children 2020, 7, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadnikar, M.; Kastrin, A. Effects of hippotherapy and therapeutic horseback riding on postural control or balance in children with cerebral palsy: A meta-analysis. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2011, 53, 684–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín-Valero, R.; Vega-Ballón, J.; Pérez-Cabezas, V. Benefits of hippotherapy in children with cerebral palsy: A narrative review. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2018, 22, 1150–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.R.; Lee, N.G.; Cha, H.J.; O, Y.S.; You, S.J.H.; Oh, J.H.; Bang, H.S. The effect of robo-horseback riding therapy on spinal alignment and associated muscle size in MRI for a child with neuromuscular scoliosis: An experimenter-blind study. NeuroRehabilitation 2011, 29, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Temcharoensuk, P.; Lekskulchai, R.; Akamanon, C.; Ritruechai, P.; Sutcharitpongsa, S. Effect of horseback riding versus a dynamic and static horse riding simulator on sitting ability of children with cerebral palsy: A randomized controlled trial. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2015, 27, 273–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez-Romero, J.G.; Molina-Aroca, A.; Moral-Munoz, J.A.; Luque-Moreno, C.; Lucena-Anton, D. Effectiveness of mechanical horse-riding simulators on postural balance in neurological rehabilitation: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewar, R.; Love, S.; Johnston, L.M. Exercise interventions improve postural control in children with cerebral palsy: A systematic review. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2015, 57, 504–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.J.; Kim, T.; Oh, S.; Yoon, B. Equine exercise in younger and older adults: Simulated versus real horseback riding. Percept. Mot. Ski. 2018, 125, 93–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.J.; Jung, Y.G.; Park, Y.S.; O, S.H.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, C.W. Virtual reality-incorporated horse riding simulator to improve motor function and balance in children with cerebral palsy: A pilot study. Sensors 2021, 21, 6394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, M.B.S.; Werneck, M.J.d.S.; Silva MdLd Gandolfi, L.; Pratesi, R. Therapeutic effects of a horse riding simulator in children with cerebral palsy. Arq. De Neuro-Psiquiatr. 2011, 69, 799–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrero, P.; Gómez-Trullén, E.M.; Asensio, Á.; García, E.; Casas, R.; Monserrat, E.; Pandyan, A. Study of the therapeutic effects of a hippotherapy simulator in children with cerebral palsy: A stratified single-blind randomized controlled trial. Clin. Rehabil. 2012, 26, 1105–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.W.; Nam, K.S.; Son, S.M. Effects of virtual reality horse riding simulator training using a head-mounted display on balance and gait functions in children with cerebral palsy: A preliminary pilot study. J. Korean Phys. Ther. 2019, 31, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinniah, H.; Natarajan, M.; Ramanathan, R.; Ambrose, J.W.F. Effects of horse riding simulator on sitting motor function in children with spastic cerebral palsy. Physiother. Res. Int. 2020, 25, e1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega-Cruz, A.; Sánchez-Silverio, V.; Riquelme-Aguado, V.; Alonso-Perez, J.L.; Abuín-Porras, V.; Villafañe, J.H. Effects of Hippotherapy and Horse-Riding Simulators on Gross Motor Function in Children with Cerebral Palsy: A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, L.; Shamseer, L.; Altman, D.G.; Weeks, L.; Peters, J.; Kober, T.; Dias, S.; Schulz, K.F.; Plint, A.C.; Moher, D. Consolidated standards of reporting trials (CONSORT) and the completeness of reporting of randomised controlled trials (RCTs) published in medical journals. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2012, MR000030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faul, F.; Erdfelder, E.; Lang, A.-G.; Buchner, A. G*Power 3: A flexible statistical power analysis program for the social, behavioral, and biomedical sciences. Behav. Res. Methods 2007, 39, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mutlu, A.; Livanelioglu, A.; Gunel, M.K. Reliability of Ashworth and Modified Ashworth scales in children with spastic cerebral palsy. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2008, 9, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Park, S.; Kim, J. Effect of Walking with Combat Boots on the Muscle Tone and Stiffness of Lower Extremity. J. Int. Acad. Phys. Ther. Res. 2020, 11, 2221–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palisano, R.J.; Hanna, S.E.; Rosenbaum, P.L.; Russell, D.J.; Walter, S.D.; Wood, E.P.; Raina, P.S.; Galuppi, B.E. Validation of a model of gross motor function for children with cerebral palsy. Phys. Ther. 2000, 80, 974–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franjoine, M.R.; Gunther, J.S.; Taylor, M.J. Pediatric balance scale: A modified version of the berg balance scale for the school-age child with mild to moderate motor impairment. Pediatr. Phys. Ther. 2003, 15, 114–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saether, R.; Helbostad, J.L.; Adde, L.; Jørgensen, L.; Vik, T. Reliability and validity of the Trunk Impairment Scale in children and adolescents with cerebral palsy. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2013, 34, 2075–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, I.; Noohu, M.M.; Verma, S.; Azharuddin, M.; Hussain, M. Validity and Responsiveness of Balance Measures using Pedalo®-Sensomove Balance Device in Patients with Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2019, 13, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandra, P.; Maiya, A.G.; Kumar, P. Test-retest reliability of the Win-Track platform in analyzing the gait parameters and plantar pressures during barefoot walking in healthy adults. Foot Ankle Spec. 2012, 5, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tur, B.S.; Küçükdeveci, A.A.; Kutlay, Ş.; Yavuzer, G.; Elhan, A.H.; Tennant, A. Psychometric properties of the WeeFIM in children with cerebral palsy in Turkey. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2009, 51, 732–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakens, D. Calculating and reporting effect sizes to facilitate cumulative science: A practical primer for t-tests and ANOVAs. Front. Psychol. 2013, 4, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGibbon, N.H.; Benda, W.; Duncan, B.R.; Silkwood-Sherer, D. Immediate and long-term effects of hippotherapy on symmetry of adductor muscle activity and functional ability in children with spastic cerebral palsy. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2009, 90, 966–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemachithra, C.; Meena, N.; Ramanathan, R.; Felix, A. Immediate effect of horse riding simulator on adductor spasticity in children with cerebral palsy: A randomized controlled trial. Physiother. Res. Int. 2020, 25, e1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benda, W.; McGibbon, N.H.; Grant, K.L. Improvements in muscle symmetry in children with cerebral palsy after equine-assisted therapy (hippotherapy). J. Altern. Complement. Med. 2003, 9, 817–825. [Google Scholar]
- Lucena-Antón, D.; Rosety-Rodríguez, I.; Moral-Munoz, J.A. Effects of a hippotherapy intervention on muscle spasticity in children with cerebral palsy: A randomized controlled trial. Complement. Ther. Clin. Pract. 2018, 31, 188–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alemdaroğlu, E.; Yanıkoğlu, İ.; Öken, Ö.; Uçan, H.; Ersöz, M.; Köseoğlu, B.F.; Kapıcıoğlu, M.İ.S. Horseback riding therapy in addition to conventional rehabilitation program decreases spasticity in children with cerebral palsy: A small sample study. Complement. Ther. Clin. Pract. 2016, 23, 26–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silkwood-Sherer, D.; Warmbier, H. Effects of hippotherapy on postural stability, in persons with multiple sclerosis: A pilot study. J. Neurol. Phys. Ther. 2007, 31, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrero, P.; Asensio, Á.; García, E.; Marco, Á.; Oliván, B.; Ibarz, A.; Gómez-Trullén, E.M.; Casas, R. Study of the therapeutic effects of an advanced hippotherapy simulator in children with cerebral palsy: A randomised controlled trial. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2010, 11, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshafey, M.A. Hippotherapy simulator as alternative method for hippotherapy treatment in hemiplegic children. Int. J. Physiother. Res. 2014, 2, 435–441. [Google Scholar]
- Whalen, C.N.; Case-Smith, J. Therapeutic effects of horseback riding therapy on gross motor function in children with cerebral palsy: A systematic review. Phys. Occup. Ther. Pediatr. 2012, 32, 229–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, S.-H.; Chen, H.-C.; Tam, K.-W. Systematic review and meta-analysis of the effect of equine assisted activities and therapies on gross motor outcome in children with cerebral palsy. Disabil. Rehabil. 2013, 35, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterba, J.A.; Rogers, B.T.; France, A.P.; Vokes, D.A. Horseback riding in children with cerebral palsy: Effect on gross motor function. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2002, 44, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casady, R.L.; Nichols-Larsen, D.S. The effect of hippotherapy on ten children with cerebral palsy. Pediatr. Phys. Ther. 2004, 16, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, E.S.; Rha, D.-W.; Shin, J.S.; Kim, S.; Jung, S. Effects of hippotherapy on gross motor function and functional performance of children with cerebral palsy. Yonsei Med. J. 2014, 55, 1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, J.-Y.; Chang, H.J.; Yi, S.-H.; Lee, J.Y.; Shin, H.-Y.; Kim, Y.-H. Effect of hippotherapy on gross motor function in children with cerebral palsy: A randomized controlled trial. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 2015, 21, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quint, C.; Toomey, M. Powered saddle and pelvic mobility: An investigation into the effects on pelvic mobility of children with cerebral palsy of a powered saddle which imitates the movements of a walking horse. Physiotherapy 1998, 84, 376–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuczyński, M.; Słonka, K. Influence of artificial saddle riding on postural stability in children with cerebral palsy. Gait Posture 1999, 10, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-W.; Kim, S.G.; Na, S.S. The effects of hippotherapy and a horse riding simulator on the balance of children with cerebral palsy. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2014, 26, 423–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Choi, H.-J.; Kim, K.-J.; Nam, K.-W. The effects of a horseback riding simulation exercise on the spinal alignment of children with cerebral palsy. J. Korean Phys. Ther. 2014, 26, 209–215. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Choi, H.-J.; Nam, K.-W. The effect of horseback riding simulator on static balance of cerebral palsy. J. Korean Phys. Ther. 2014, 26, 269–273. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Park, J.-H.; You, J.H. Innovative robotic hippotherapy improves postural muscle size and postural stability during the quiet stance and gait initiation in a child with cerebral palsy: A single case study. NeuroRehabilitation 2018, 42, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, C.E.; MacDonald, J.R.; Gnip, C. Counting repetitions: An observational study of outpatient therapy for people with hemiparesis post-stroke. J. Neurol. Phys. Ther. 2007, 31, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, J.-Y.; Chang, H.J.; Lee, J.Y.; Ha, Y.; Lee, P.K.; Kim, Y.-H. Effects of hippotherapy on gait parameters in children with bilateral spastic cerebral palsy. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2011, 92, 774–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, H.G.; Lee, B.J.; Lee, W.H. The effects of horse riding simulation exercise with blindfolding on healthy subjects’ balance and gait. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2016, 28, 3165–3167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, F.N.; do Pinho, A.S.; Kleiner, A.F.R.; Salazar, A.P.; Eltz, G.D.; de Oliveira Junior, A.A.; Cechetti, F.; Galli, M.; Pagnussat, A.S. Different horse’s paces during hippotherapy on spatio-temporal parameters of gait in children with bilateral spastic cerebral palsy: A feasibility study. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2016, 59, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| n = 30 | Mean ± SD or n (%) |
|---|---|
| Age (year) | 9.3 ± 3.2 (5–15) |
| Female | 17 (56.7%) |
| Male | 13 (43.3%) |
| Height (cm) | 131.7 ± 19.1 |
| Weight (kg) | 33.6 ± 13.4 |
| Body Mass Index (kg/m2) | 18.5 ± 3.37 |
| CP topography | |
| Hemiparetic | 17 (56.7%) |
| Diparetic | 13 (43.3%) |
| GMFCS Level (Hemiparetic) | |
| Grade 1 | 13 (76.5%) |
| Grade 2 | 4 (23.5%) |
| GMFCS Level (Diparetic) | |
| Grade 1 | 0 (0%) |
| Grade 2 | 5 (38.5%) |
| Grade 3 | 8 (61.5%) |
| Variables | Baseline Mean ± SD Median (min–max) | Intervention I Mean ± SD Median (min–max) | Intervention II Mean ± SD Median (min–max) | p a T0–T1–T2 | Z | p b T0–T1 T0–T2 T1–T2 | ES T0–T1 T0–T2 T1–T2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hemiparetic CP (n = 17) (affected side) | |||||||
| Hip adductors | 1.71 ± 0.98 2.00 (0–3) | 1.41 ± 0.87 1.00 (0–3) | 1.24 ± 0.70 1.00 (0–2) | <0.001 | −2.236 −3.286 −3.606 | 0.025 <0.001 <0.001 | 0.542 0.797 ** 0.874 ** |
| Hamstring | 2.35 ± 0.60 2.00 (1–3) | 2.29 ± 0.58 2.00 (1–3) | 1.82 ± 0.80 2.00 (1–3) | <0.001 | −1.000 −3.000 −2.828 | 0.317 0.003 0.005 | 0.243 0.728 ** 0.686 ** |
| Gastrocnemius | 2.65 ± 0.60 3.00 (1–3) | 2.58 ± 0.71 3.00 (1–3) | 1.76 ± 0.83 2.00 (0–3) | <0.001 | −1.000 −3.419 −3.276 | 0.317 <0.001 <0.001 | 0.243 0.829 ** 0.795 ** |
| Soleus | 2.00 ± 0.79 2.00 (0–3) | 1.70 ± 0.91 2.00 (0–3) | 1.17 ± 0.80 1.00 (0–2) | <0.001 | −2.236 −3.276 −3.000 | 0.025 <0.001 0.003 | 0.542 0.795 ** 0.728 ** |
| Diparetic CP (n = 13) (Right side) | |||||||
| Hip adductors | 2.54 ± 0.66 3.00 (1–3) | 2.15 ± 0.89 2.00 (0–3) | 1.31 ± 0.63 1.00 (0–2) | <0.001 | −2.236 −3.358 −3.317 | 0.025 <0.001 <0.001 | 0.620 0.931 ** 0.920 ** |
| Hamstring | 3.54 ± 0.51 4.00 (3–4) | 2.92 ± 0.27 3.00 (2–3) | 2.54 ± 0.27 3.00 (2–3) | <0.001 | −2.828 −3.357 −2.236 | 0.005 <0.001 0.025 | 0.784 ** 0.930 ** 0.620 |
| Gastrocnemius | 3.31 ± 0.48 3.00 (3–4) | 3.15 ± 0.37 3.00 (3–4) | 2.69 ± 0.48 3.00 (2–3) | <0.001 | −1.414 −2.828 −2.449 | 0.157 0.005 0.014 | 0.392 0.784 ** 0.679 ** |
| Soleus | 2.85 ± 0.37 3.00 (2–3) | 2.38 ± 0.65 3.00 (1–3) | 1.92 ± 0.64 2.00 (1–3) | <0.001 | −2.449 −3.207 −2.449 | 0.014 <0.001 0.014 | 0.679 ** 0.889 ** 0.679 ** |
| Diparetic CP (n = 13) (Left side) | |||||||
| Hip adductors | 2.77 ± 0.59 3.00 (1–3) | 2.38 ± 0.76 3.00 (1–3) | 1.31 ± 0.48 1.00 (1–2) | <0.001 | −2.236 −3.153 −2.889 | 0.025 0.002 0.004 | 0.620 0.874 ** 0.801 ** |
| Hamstring | 3.69 ± 0.48 4.00 (3–4) | 2.85 ± 0.37 3.00 (2–3) | 2.69 ± 0.37 3.00 (2–3) | <0.001 | −3.317 −3.127 −1.414 | 0.001 < 0.002 0.157 | 0.920 ** 0.867 ** 0.392 |
| Gastrocnemius | 3.38 ± 0.50 3.00 (3–4) | 2.92 ± 0.27 3.00 (2–3) | 2.69 ± 0.48 3.00 (2–3) | <0.001 | −2.449 −2.460 −1.732 | 0.014 0.014 0.083 | 0.679 ** 0.682 ** 0.480 |
| Soleus | 2.85 ± 0.37 3.00 (2–3) | 2.23 ± 0.43 2.00 (2–3) | 1.69 ± 0.48 2.00 (1–2) | <0.001 | −2.828 −3.035 −2.646 | 0.005 0.002 0.008 | 0.784 ** 0.842 ** 0.733 ** |
| Variables n = 17 | Baseline Mean ± SD Median (min–max) | Intervention I Mean ± SD Median (min–max) | Intervention II Mean ± SD Median (min–max) | p a T0–T1–T2 | Z | p b T0–T1 T0–T2 T1–T2 | ES T0–T1 T0–T2 T1–T2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hip adductors | |||||||
| F (Hz) | 12.24 ± 0.60 12.15 (11.15–13.50) | 12.43 ± 0.72 12.40 (11.45–14.15) | 12.17 ± 1.02 11.80 (10.65–14.05) | 0.320 | −0.829 −0.310 −1.224 | 0.407 0.756 0.221 | 0.201 0.075 0.297 |
| S (N/m) | 168.53 ± 19.13 220 (142.50–209) | 171.09 ± 23.73 205 (134.50–209) | 167.50 ± 29.76 203 (128–237.50) | 0.943 | −0.379 −0.047 −0.781 | 0.705 0.962 0.435 | 0.092 0.011 0.189 |
| D | 0.94 ± 0.14 0.98 (0.77–1.41) | 0.93 ± 0.15 0.90 (0.70–1.12) | 0.91 ± 0.13 0.88 (0.68–1.13) | 0.943 | −0.000 −0.734 −0.521 | 1.000 0.463 0.603 | 0.000 0.178 0.126 |
| Hamstring | |||||||
| F (Hz) | 14.17 ± 1.06 14.90 (12.53–16.03) | 14.16 ± 1.18 14.86 (12.47–15.82) | 14.19 ± 1.11 14.10 (12.50–14.37) | 0.327 | −1.492 −0.024 −1.444 | 0.136 0.981 0.149 | 0.362 0.006 0.350 |
| S (N/m) | 234.73 ± 43.82 224.66 (165–329.33) | 232.10 ± 48.50 222.33 (151.3–324.3) | 226.29 ± 41.70 220.33 (150.6–290.3) | 0.193 | −1.775 −0.284 −1.538 | 0.076 0.776 0.124 | 0.430 0.069 0.373 |
| D | 1.11 ± 0.14 1.11 (0.88–1.37) | 1.11 ± 0.12 1.09 (0.91–1.33) | 1.08 ± 0.16 1.09 (0.77–1.40) | 0.838 | −0.142 −0.687 −0.758 | 0.887 0.492 0.449 | 0.034 0.167 0.184 |
| Gastrocnemius | |||||||
| F (Hz) | 14.59 ± 1.00 14.65 (12.90–16.30) | 14.80 ± 1.02 14.45 (12.88–15.30) | 14.11 ± 0.92 14.38 (12.92–15.34) | 0.101 | −0.639 −1.681 −1.491 | 0.523 0.093 0.232 | 0.155 0.408 0.362 |
| S (N/m) | 250.79 ± 33.40 248.50 (194–300) | 250.76 ± 28.76 242.50 (190.5–299.5) | 232.65 ± 33.28 228.00 (186.50–301) | 0.047 | −0.071 −1.941 −2.770 | 0.943 0.052 0.006 | 0.017 0.471 0.672 ** |
| D | 1.10 ± 0.17 1.10 (0.81–1.46) | 1.06 ± 0.18 1.01 (0.72–1.46) | 1.08 ± 0.13 1.09 (0.68–1.27) | 0.465 | −1.302 −0.474 −0.734 | 0.193 0.636 0.463 | 0.316 0.115 0.178 |
| Soleus | |||||||
| F (Hz) | 16.33 ± 1.43 16.40 (14.20–19.00) | 15.35 ± 1.79 15.60 (11.20–18.80) | 15.76 ± 1.24 15.50 (14.05–18.60) | 0.011 | −2.369 −1.897 −0.968 | 0.016 0.058 0.333 | 0.575 ** 0.460 0.235 |
| S (N/m) | 308.29 ± 54.17 301.00 (222–409) | 279.71 ± 44.33 282.00 (200–364) | 278.71 ± 41.54 274.00 (203–373) | 0.004 | −2.604 −2.368 −0.213 | 0.011 0.016 0.723 | 0.632 ** 0.574 ** 0.052 |
| D | 1.02 ± 0.16 0.97 (0.81–1.33) | 0.97 ± 0.15 0.96 (0.73–1.28) | 0.97 ± 0.13 0.95 (0.73–1.22) | 0.575 | −2.557 −2.368 −0.355 | 0.098 0.393 0.918 | 0.620 0.574 0.086 |
| Variables n = 13 | Baseline Mean ± SD Median (min–max) | Intervention I Mean ± SD Median (min–max) | Intervention II Mean ± SD Median (min–max) | p a T0–T1–T2 | Z | p b T0–T1 T0–T2 T1–T2 | ES T0–T1 T0–T2 T1–T2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hip adductors (R) | |||||||
| F (Hz) | 11.45 ± 0.81 11.50 (10.25–13.00) | 11.51 ± 0.74 11.60 (10.40–12.65) | 11.37 ± 0.58 11.50 (10.45–12.40) | 0.383 | −0.236 −0.455 −1.438 | 0.814 0.649 0.150 | 0.065 0.126 0.399 |
| S (N/m) | 162.31 ± 28.42 164.50 (120.5–206.0) | 158.54 ± 17.72 161.00 (124–186.50) | 151.42 ± 17.68 147.00 (120–178) | 0.219 | −0.889 −1.712 −2.308 | 0.374 0.087 0.021 | 0.247 0.475 0.640 |
| D | 1.01 ± 0.16 0.96 0.77–1.33 | 1.00 ± 0.16 1.02 (0.80–1.32) | 1.02 ± 0.24 0.98 (0.75–1.64) | 0.981 | −0.784 −0.175 −0.140 | 0.433 0.861 0.889 | 0.217 0.049 0.039 |
| Hip adductors (L) | |||||||
| F (Hz) | 11.52 ± 0.87 11.40 (10.25–12.90) | 11.75 ± 0.87 12.00 (10.35–13.10) | 11.41 ± 0.83 11.40 (10.20–13.10) | 0.101 | −0.157 −0.804 −1.893 | 0.875 0.421 0.058 | 0.044 0.223 0.525 |
| S (N/m) | 165.31 ± 31.49 171.00 (125.5–218.5) | 164.19 ± 17.71 172.00 (125.50–188) | 151.50 ± 23.27 149.00 (117.5–215.5) | 0.050 | −0.314 −1.433 −2.342 | 0.754 0.152 0.014 | 0.087 0.397 0.649 ** |
| D | 1.02 ± 0.16 0.98 (0.74–1.35) | 1.00 ± 0.13 0.98 (0.84–1.32) | 1.02 ± 0.20 1.01 (0.78–1.46) | 0.353 | −0.802 −0.350 −0.524 | 0.422 0.727 0.600 | 0.222 0.097 0.145 |
| Hamstring (R) | |||||||
| F (Hz) | 13.91 ± 1.68 13.53 (11.4–16.13) | 13.64 ± 1.59 14.00 (11.60–15.23) | 13.40 ± 1.02 13.53 (11.67–15.33) | 0.101 | −1.177 −1.503 −1.573 | 0.239 0.133 0.116 | 0.326 0.417 0.436 |
| S (N/m) | 228.1 ± 57.4 225.66 (139–315.67) | 216.15 ± 38.39 216.33 (146.67–279) | 204.44 ± 34.89 204.00 (145.67–267) | 0.055 | −1.490 −1.712 −1.992 | 0.136 0.087 0.046 | 0.413 0.475 0.552 |
| D | 1.12 ± 0.15 1.07 (0.86–1.36) | 1.10 ± 0.12 1.14 (0.92–1.31) | 1.08 ± 0.16 1.06 (0.90–1.45) | 0.127 | −1.179 −1.398 −1.295 | 0.239 0.162 0.195 | 0.327 0.388 0.359 |
| Hamstring (L) | |||||||
| F (Hz) | 13.86 ± 1.62 13.33 (11.8–16.33) | 13.71 ± 1.38 14.10 (11.83–15.80) | 13.66 ± 1.14 13.93 (11.80–15.33) | 0.239 | −1.060 −0.874 −1.223 | 0.239 0.382 0.221 | 0.294 0.242 0.339 |
| S (N/m) | 226.64 ± 60.58 204.33 (143–333.67) | 213.51 ± 47.82 212.00 (146–292.67) | 208.59 ± 35.87 221.33 (157–258.33) | 0.239 | −1.726 −1.503 −0.979 | 0.084 0.133 0.328 | 0.479 0.417 0.271 |
| D | 1.17 ± 0.22 1.18 (0.76–1.55) | 1.15 ± 0.17 1.16 (0.91–1.44) | 1.11 ± 0.15 1.08 (0.86–1.41) | 0.545 | −0.785 −1.154 −1.713 | 0.432 0.249 0.087 | 0.218 0.320 0.475 |
| Gastrocnemius (R) | |||||||
| F (Hz) | 14.41 ± 1.58 13.90 (12–17.25) | 14.33 ± 1.55 14.65 (11.60–17.25) | 14.03 ± 1.53 13.70 (11.50–16.60) | 0.025 | −0.890 −1.162 −2.098 | 0.373 0.107 0.016 | 0.247 0.322 0.582 ** |
| S (N/m) | 256.96 ± 60.0 243.00 (183.50–392) | 254.31 ± 54.87 205.50 (174–352) | 239.19 ± 50.23 224.00 (183.50–392) | 0.023 | −0.942 −1.748 −2.201 | 0.346 0.080 0.012 | 0.261 0.485 0.610 ** |
| D | 1.01 ± 0.16 0.96 (0.83–1.40) | 1.02 ± 0.19 0.99 (0.78–1.44) | 0.97 ± 0.14 0.95 (0.76–1.27) | 0.484 | −1.021 −1.014 −0.979 | 0.307 0.310 0.327 | 0.283 0.281 0.271 |
| Gastrocnemius (L) | |||||||
| F (Hz) | 14.33 ± 1.35 14.05 (12.35–16.50) | 14.18 ± 1.42 14.65 (11.85–16.35) | 13.60 ± 1.17 13.95 (11.85–15.40) | <0.001 | −1.217 −3.113 −3.065 | 0.224 0.002 0.002 | 0.338 0.863 ** 0.850 ** |
| S (N/m) | 250.31 ± 50.63 233.50 (183–353) | 238.27 ± 47.17 231.00 (168–324) | 217.65 ± 47.41 224.50 (165.50–303) | <0.001 | −1.804 −2.761 −3.185 | 0.071 0.006 < 0.001 | 0.500 0.766 ** 0.884 ** |
| D | 1.08 ± 0.19 1.02 (0.87–1.46) | 1.01 ± 0.18 0.95 (0.76–1.38) | 1.00 ± 0.19 0.94 (0.79–1.33) | 0.538 | −2.001 −1.255 −0.489 | 0.045 0.209 0.625 | 0.555 0.348 0.136 |
| Soleus (R) | |||||||
| F (Hz) | 15.80 ± 2.54 15.80 (12.10–22.30) | 15.46 ± 2.18 15.80 (11.90–20.70) | 14.74 ± 1.63 14.80 (11.40–17.70) | <0.001 | −1.780 −2.482 −2.484 | 0.075 0.013 0.013 | 0.494 0.688 ** 0.689 ** |
| S (N/m) | 306.92 ± 76.89 290.00 (196–417) | 293.38 ± 66.50 280.00 (212–388) | 266.85 ± 66.10 242.00 (189–388) | <0.001 | −2.120 −2.667 −2.201 | 0.041 0.005 0.002 | 0.588 0.739 ** 0.610 ** |
| D | 1.03 ± 0.20 1.02 (0.85–1.62) | 1.05 ± 0.33 0.97 (0.76–1.96) | 0.93 ± 0.14 0.94 (0.75–1.32) | <0.001 | −1.452 −2.269 −2.201 | 0.146 0.013 0.014 | 0.403 0.629 ** 0.610 ** |
| Soleus (L) | |||||||
| F (Hz) | 15.76 ± 1.36 15.80 (12.60–17.70) | 15.11 ± 1.54 15.80 (11.70–17.00) | 14.47 ± 1.44 14.90 (12.20–16.10) | <0.001 | −2.356 −3.112 −2.345 | 0.016 0.002 0.015 | 0.653 ** 0.863 ** 0.650 ** |
| S (N/m) | 311.15 ± 53.68 290.00 (213–378) | 287.92 ± 67.43 280.00 (170–396) | 251.85 ± 54.86 242.00 (183–332) | <0.001 | −1.374 −3.118 −2.901 | 0.169 0.002 0.004 | 0.381 0.865 ** 0.805 ** |
| D | 1.04 ± 0.17 0.99 (0.87–1.50) | 0.94 ± 0.11 0.93 (0.74–1.14) | 0.94 ± 0.15 0.91 (0.62–1.17) | 0.044 | −2.493 −1.820 −0.771 | 0.013 0.069 0.441 | 0.691 ** 0.505 0.214 |
| Variables n = 30 | Baseline Mean ± SD Median (min–max) | Intervention I Mean ± SD Median (min–max) | Intervention II Mean ± SD Median (min–max) | p a T0–T1–T2 | Z | p b T0–T1 T0–T2 T1–T2 | ES T0–T1 T0–T2 T1–T2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GMFM-88 | |||||||
| B | 69.83 ± 16.62 69.16 (38.33–93.33) | 75.5 ± 14.97 74.16 (43.33–96.67) | 81.44 ± 12.40 78.33 (60.00–98.33) | <0.001 | −4.807 −4.786 −4.731 | <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 | 0.878 ** 0.874 ** 0.864 ** |
| D | 56.5 ± 26.20 60.25 (20.51–92.31) | 61.70 ± 25.96 66.67 (23.08–94.87) | 67.24 ± 25.65 73.07 (25.64–97.44) | <0.001 | −3.918 −4.754 −4.713 | <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 | 0.715 ** 0.868 ** 0.860 ** |
| E | 54.68 ± 29.08 59.02 (13.89–91.67) | 58.85 ± 28.43 63.19 (16.66–94.44) | 62.26 ± 28.26 65.97 (18.05–97.22) | <0.001 | −4.219 −4.517 −4.715 | <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 | 0.770 ** 0.825 ** 0.860 ** |
| Total | 60.34 ± 23.42 62.52 (25.17–91.88) | 65.03 ± 22.43 67.01 (29.27–95.33) | 70.32 ± 21.75 71.71 (35.12–97.66) | <0.001 | −4.556 −4.762 −4.783 | <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 | 0.832 ** 0.869 ** 0.873 ** |
| Wee-FIM | |||||||
| Self-care | 38.70 ± 7.61 40.00 (16–51) | 40.23 ± 7.13 41.00 (19–52) | 42.06 ± 7.04 43.50 (21–53) | <0.001 | −4.444 −4.813 −4.799 | <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 | 0.811 ** 0.879 ** 0.876 ** |
| Mobility | 25.73 ± 6.94 26.00 (14–34) | 26.66 ± 6.58 27.00 (15–35) | 28.00 ± 6.06 28.50 (17–35) | <0.001 | −4.315 −4.573 −4.585 | <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 | 0.788 ** 0.835 ** 0.837 ** |
| Cognition | 29.26 ± 4.00 30.00 (22–35) | 29.60 ± 4.08 30.50 (22–35) | 30.03 ± 4.02 31.00 (22–35) | <0.001 | −3.162 −1.782 −3.127 | <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 | 0.577 ** 0.325 * 0.571 ** |
| Total | 93.70 ± 15.86 95.50 (61–117) | 96.50 ± 15.03 101.00 (66–119) | 100.10 ± 14.61 106.50 (69–121) | <0.001 | −4.642 −4.789 −4.803 | <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 | 0.848 ** 0.874 ** 0.877 ** |
| TIS | |||||||
| Static | 4.73 ± 1.91 6.00 (2.00–7.00) | 5.06 ± 1.79 6.00 (2.00–7.00) | 5.66 ± 1.56 6.00 (2.00–7.00) | <0.001 | −2.428 −4.563 −4.243 | 0.015 <0.001 <0.001 | 0.443 * 0.833 ** 0.775 ** |
| Dynamic | 4.63 ± 1.58 5.00 (2.00–8.00) | 5.83 ± 1.41 6.00 (3.00–9.00) | 7.03 ± 1.56 7.00 (4.00–10.00) | <0.001 | −4.617 −4.775 −4.617 | <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 | 0.843 ** 0.872 ** 0.843 ** |
| Coordination | 0.77 ± 0.67 1.00 (0.00–3.00) | 1.23 ± 0.81 1.00 (0.00–4.00) | 2.40 ± 0.89 2.00 (1.00–5.00) | <0.001 | −3.742 −4.904 −5.152 | <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 | 0.683 ** 0.895 ** 0.941 ** |
| Total | 10.13 ± 3.55 10.00 (4.00–18.00) | 12.07 ± 3.47 13.00 6.00–20.00 | 14.80 ± 3.66 15.50 (9.00–22.00) | <0.001 | −4.851 −4.529 −4.224 | <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 | 0.886 ** 0.827 ** 0.771 ** |
| Pedalo® SBT | |||||||
| Sitting balance | 87.20 ± 9.89 91.00 (67–98) | 89.27 ± 7.52 91.50 (75–98) | 92.33 ± 6.76 95.00 (67–99) | <0.001 | −2.228 −3.295 −3.037 | 0.026 <0.001 0.002 | 0.407 * 0.602 ** 0.555 ** |
| Sitting proprioception | 81.57 ± 13.53 87.00 (54–98) | 85.07 ± 9.60 88.00 (66–98) | 88.70 ± 7.23 91.50 (74–97) | <0.001 | −2.093 −3.280 −3.250 | 0.036 <0.001 <0.001 | 0.382 * 0.599 ** 0.593 ** |
| PBS | 36.80 ± 13.75 43.00 (15–51) | 39.37 ± 12.69 46.00 (18.52) | 42.50 ± 12.06 49.00 (22–55) | <0.001 | −4.649 −4.795 −4.816 | <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 | 0.849 ** 0.875 ** 0.879 ** |
| Outcome Measures | Baseline Mean ± SD Median (min–max) | Intervention I Mean ± SD Median (min–max) | Intervention II Mean ± SD Median (min–max) | p a T0–T1–T2 | Z | p b T0–T1 T0–T2 T1–T2 | ES T0–T1 T0–T2 T1–T2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hemiparetic CP (n = 17) | |||||||
| Walking speed (m/s) | 0.59 ± 0.22 0.52 (0.32–1.22) | 0.72 ± 0.25 0.69 (0.40–1.45) | 0.83 ± 0.27 0.74 (0.49–1.62) | <0.001 | −3.621 −3.621 −3.621 | <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 | 0.878 ** 0.878 ** 0.878 ** |
| Cadence (steps/min) | 90.71 ± 12.56 90.90 (71.40–120) | 104.21 ± 14.13 105.30 (69–135.50) | 113.86 ± 15.59 115.40 (76–145.50) | <0.001 | −3.527 −3.575 −3.528 | <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 | 0.855 ** 0.867 ** 0.855 ** |
| Stride length (m) | 0.77 ± 0.21 0.72 (0.44–1.22) | 0.83 ± 0.20 0.80 (0.49–1.28) | 0.87 ± 0.21 0.85 (0.55–1.34) | <0.001 | −3.628 −3.624 −3.637 | <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 | 0.880 ** 0.879 ** 0.882 ** |
| Stride time (s) | 1.98 ± 0.25 1.95 (1.53–2.35) | 1.91 ± 0.22 1.84 (1.63–2.44) | 1.84 ± 0.21 1.78 (1.55–2.35) | 0.013 | −1.303 −2.522 −1.941 | 0.193 0.016 0.052 | 0.316 0.612 ** 0.471 |
| Diparetic CP (n = 13) | |||||||
| Walking speed (m/s) | 0.22 ± 0.17 0.14 (0.07–0.60) | 0.28 ± 0.19 0.19 (0.09–0.68) | 0.33 ± 0.21 0.26 (0.11–0.75) | <0.001 | −3.180 −3.180 −3.110 | <0.001 <0.001 0.002 | 0.882 ** 0.882 ** 0.863 ** |
| Cadence (steps/min) | 50.16 ± 23.3 42.50 (28.3–95.2) | 57.93 ± 23.85 57.20 (32.30–100) | 64.68 ± 24.71 63.70 (35.30–105.30) | <0.001 | −3.181 −3.180 −3.184 | <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 | 0.882 ** 0.882 ** 0.883 ** |
| Stride length (m) | 0.48 ± 0.16 0.44 (0.30–0.76) | 0.52 ± 0.16 0.48 (0.34–0.83) | 0.56 ± 0.16 0.51 (0.37–0.86) | <0.001 | −3.055 −3.011 −2.497 | 0.002 0.003 0.014 | 0.848 ** 0.835 ** 0.692 ** |
| Stride time (s) | 4.55 ± 2.02 4.82 (1.89–6.86) | 4.18 ± 1,76 4.48 (1.80–6.16) | 3.85 ± 1.55 3.81 (1.87–5.68) | <0.001 | −3.041 −3.040 −2.901 | 0.002 0.002 0.004 | 0.843 ** 0.843 ** 0.805 ** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Günay Yazıcı, C.; Özden, F.; Çoban, O.; Tarakçı, D.; Aydoğdu, O.; Sarı, Z. The Effect of Hippotherapy Simulator-Assisted Therapy on Motor and Functional Outcomes in Children with Cerebral Palsy. Medicina 2025, 61, 1811. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61101811
Günay Yazıcı C, Özden F, Çoban O, Tarakçı D, Aydoğdu O, Sarı Z. The Effect of Hippotherapy Simulator-Assisted Therapy on Motor and Functional Outcomes in Children with Cerebral Palsy. Medicina. 2025; 61(10):1811. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61101811
Chicago/Turabian StyleGünay Yazıcı, Canan, Fatih Özden, Osman Çoban, Devrim Tarakçı, Onur Aydoğdu, and Zübeyir Sarı. 2025. "The Effect of Hippotherapy Simulator-Assisted Therapy on Motor and Functional Outcomes in Children with Cerebral Palsy" Medicina 61, no. 10: 1811. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61101811
APA StyleGünay Yazıcı, C., Özden, F., Çoban, O., Tarakçı, D., Aydoğdu, O., & Sarı, Z. (2025). The Effect of Hippotherapy Simulator-Assisted Therapy on Motor and Functional Outcomes in Children with Cerebral Palsy. Medicina, 61(10), 1811. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61101811






