PUM1 in Breast Cancer: Tumor Expression and Prognostic and Predictive Significance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. PUM1 Expression in Existing BC Datasets
2.2. PUM1 Expression in a New Cohort
2.3. IHC Staining for PUM1
2.4. IHC Assessment of PUM1 Expression
2.5. The Predictive Significance of PUM1 Expression
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. PUM1 mRNA Expression and Clinicopathological Parameters
3.2. PUM1 Protein Expression and Clinicopathological Parameters
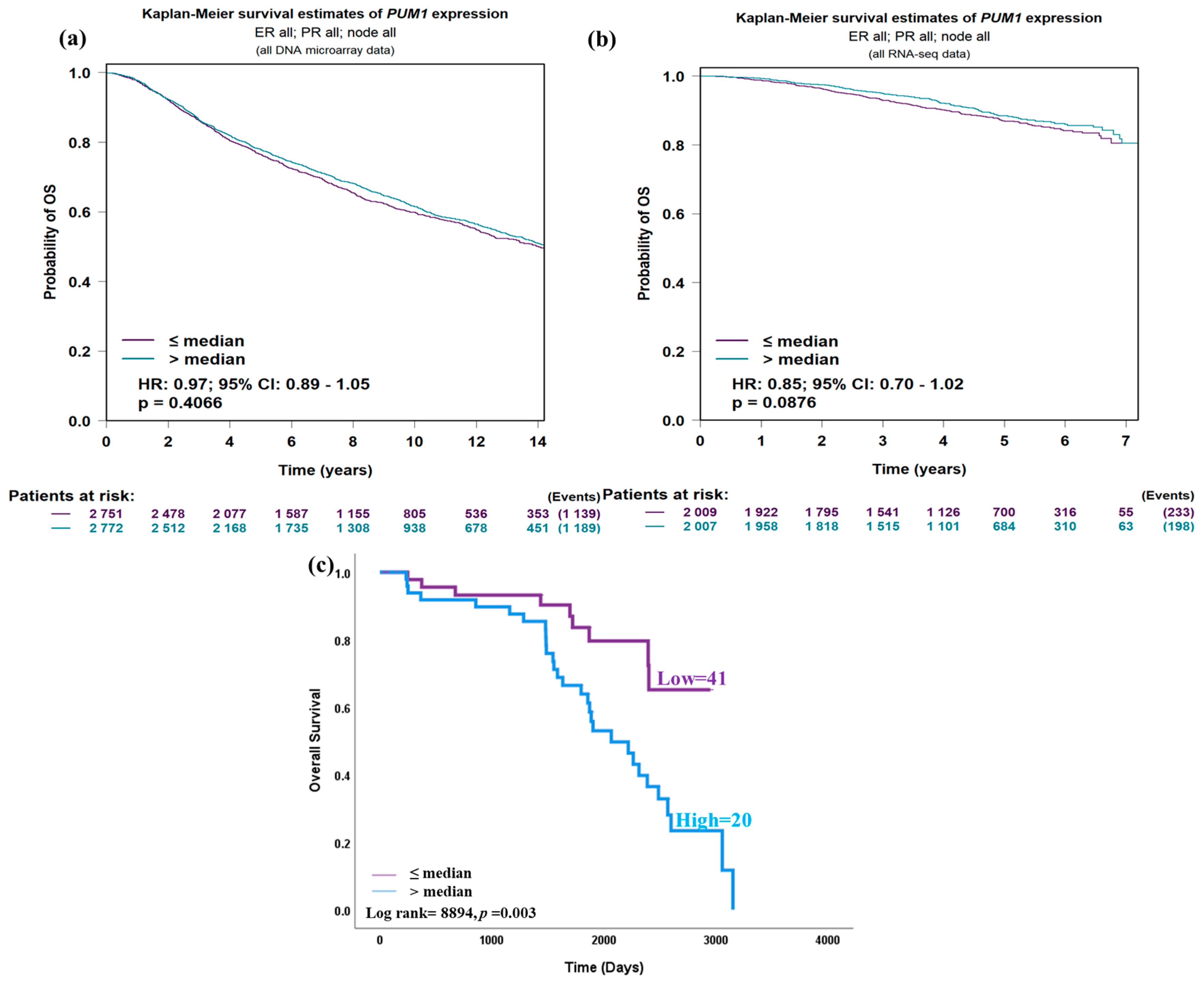
3.3. PUM1 Expression and Patient Outcomes
3.4. Predictive Value of PUM1 mRNA Expression
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, J.; Harper, A.; McCormack, V.; Sung, H.; Houssami, N.; Morgan, E.; Mutebi, M.; Garvey, G.; Soerjomataram, I.; Fidler-Benaoudia, M.M. Global patterns and trends in breast cancer incidence and mortality across 185 countries. Nat. Med. 2025, 31, 1154–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Yuan, Y.; Zeng, Q.; Xiong, J.; Gan, Y.; Jiang, K.; Xie, N. Plant protein-derived anti-breast cancer peptides: Sources, therapeutic approaches, mechanisms, and nanoparticle design. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1468977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Martinez, L.; Zhang, Y.; Nakata, Y.; Chan, H.L.; Morey, L. Epigenetic mechanisms in breast cancer therapy and resistance. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smialek, M.J.; Ilaslan, E.; Sajek, M.P.; Jaruzelska, J. Role of PUM RNA-binding proteins in cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, S.; Shingle, D.L.; Green, C.B. Post-transcriptional control of circadian rhythms. J. Cell Sci. 2011, 124, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.; Zagore, L.L.; Brister, M.M.; Ye, X.; Crespo-Hernández, C.E.; Licatalosi, D.D.; Jankowsky, E. The kinetic landscape of an RNA-binding protein in cells. Nature 2021, 591, 152–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstrohm, A.C.; Hall, T.M.T.; McKenney, K.M. Post-transcriptional regulatory functions of mammalian pumilio proteins. Trends Genet. 2018, 34, 972–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smialek, M.J.; Ilaslan, E.; Sajek, M.P.; Swiercz, A.; Janecki, D.M.; Kusz-Zamelczyk, K.; Wozniak, T.; Kotecki, M.; Handschuh, L.; Figlerowicz, M.; et al. Characterization of RNP networks of PUM1 and PUM2 post-transcriptional regulators in TCam-2 cells, a human male germ cell model. Cells 2020, 9, 984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quenault, T.; Lithgow, T.; Traven, A. PUF proteins: Repression, activation and mRNA localization. Trends Cell Biol. 2011, 21, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Chen, S.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L.-L.; Zhao, Y.; Zong, Z.-H. PUM1 promotes ovarian cancer proliferation, migration and invasion. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 497, 313–318. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, L.-H.; Yan, Q.-H.; Sun, O.-D.; Gao, Y.-P. MiR-411-5p acts as a tumor suppressor in non-small cell lung cancer through targeting PUM1. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 22, 5565–5574. [Google Scholar]
- Aljohani, A.; Toss, M.S.; El-Sharawy, K.A.; Mirza, S.; Ball, G.R.; Green, A.R.; Rakha, E.A. Upregulation of Cyclin B2 (CCNB2) in breast cancer contributes to the development of lymphovascular invasion. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2022, 12, 469–489. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jézéquel, P.; Gouraud, W.; Ben Azzouz, F.; Guérin-Charbonnel, C.; Juin, P.P.; Lasla, H.; Campone, M. bc-GenExMiner 4.5: New mining module computes breast cancer differential gene expression analyses. Database 2021 2021, baab007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunheri, B.; Raj, R.V.; Vijaykumar, D.; Pavithran, K. Impact of St. Gallen surrogate classification for intrinsic breast cancer sub-types on disease features, recurrence, and survival in South Indian patients. Indian J. Cancer 2020, 57, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gradishar, W.J.; Moran, M.S.; Abraham, J.; Abramson, V.; Aft, R.; Agnese, D.; Allison, K.H.; Anderson, B.; Burstein, H.J.; Chew, H.; et al. NCCN Guidelines® Insights: Breast Cancer, Version 4.2023. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2023, 21, 594–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, T.; Kim, A.; Kim, C. Automated immunohistochemical assessment ability to evaluate estrogen and progesterone receptor status compared with quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction in breast carcinoma patients. J. Pathol. Transl. Med. 2021, 55, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fekete, J.T.; Győrffy, B. ROCplot.org: Validating predictive biomarkers of chemotherapy/hormonal therapy/anti-HER2 therapy using transcriptomic data of 3,104 breast cancer patients. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 145, 3140–3151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popa, M.-T.; Noditi, A.; Peleaşa, T.-M.; Stoleru, S.; Blidaru, A. Breast Cancer: A Heterogeneous Pathology. Prognostic and Predictive Factors—A Narrative Review. Chirurgia 2025, 120, 32–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simms, L.; Barraclough, H.; Govindan, R. Biostatistics primer: What a clinician ought to know—prognostic and predictive factors. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2013, 8, 808–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krystel-Whittemore, M.; Tan, P.H.; Wen, H.Y. Predictive and prognostic biomarkers in breast tumours. Pathology 2024, 56, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, P.; Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Li, W.; Li, H.; Fu, P. Long non-coding RNA NORAD inhibition upregulates microRNA-323a-3p to suppress tumorigenesis and development of breast cancer through the PUM1/eIF2 axis. Cell Cycle 2021, 20, 1295–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.; Shen, K.; Yang, Y.; Su, X.; Luo, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Shuai, L.; Zheng, P.; Chen, Z.; Bie, P. PUM1 knockdown prevents tumor progression by activating the PERK/eIF2/ATF4 signaling pathway in pancreatic adenocarcinoma cells. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.; Liu, H.; Zhou, Z.; Xu, X.; Wang, P.; Chen, W.; Deng, G.; Wang, H.; Yu, H.; Gu, L.; et al. PUM1 promotes tumor progression by activating DEPTOR-mediated glycolysis in gastric cancer. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, 2301190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gor, R.; Sampath, S.S.; Lazer, L.M.; Ramalingam, S. RNA-binding protein PUM1 promotes colon cancer cell proliferation and migration. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 174, 549–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Zhang, J.; Ding, M.; Xu, K.; Li, L.; Mao, L.; Zheng, J. Ki67 targeted strategies for cancer therapy. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2018, 20, 570–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Beyer, A.; Aebersold, R. On the dependency of cellular protein levels on mRNA abundance. Cell 2016, 165, 535–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zerdes, I.; Karafousia, V.; Mezheyeuski, A.; Stogiannitsi, M.; Kuiper, R.; Ruiz, P.M.; Rassidakis, G.; Bergh, J.; Hatschek, T.; Foukakis, T.; et al. Discordance of PD-L1 expression at the protein and RNA levels in early breast cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 4655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swindell, W.R.; Remmer, H.A.; Sarkar, M.K.; Xing, X.; Barnes, D.H.; Wolterink, L.; Voorhees, J.J.; Nair, R.P.; Johnston, A.; Elder, J.T.; et al. Proteogenomic analysis of psoriasis reveals discordant and concordant changes in mRNA and protein abundance. Genome Med. 2015, 7, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Török, M.; Nagy, Á.; Cserni, G.; Karancsi, Z.; Gregus, B.; Nagy, D.H.; Árkosy, P.; Kovács, I.; Méhes, G.; Krenács, T. Prognostic potential of apoptosis-related biomarker expression in triple-negative breast cancers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anagnostou, V.K.; Welsh, A.W.; Giltnane, J.M.; Siddiqui, S.; Liceaga, C.; Gustavson, M.; Syrigos, K.N.; Reiter, J.L.; Rimm, D.L. Analytic variability in immunohistochemistry biomarker studies. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2010, 19, 982–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Su, X.; Shen, K.; Zhang, C.; Dai, H.; Ma, H.; Jiang, Y.; Shuai, L.; Liu, Z.; You, J.; et al. PUM1 is upregulated by DNA methylation to suppress antitumor immunity and results in poor prognosis in pancreatic cancer. Transl. Cancer Res. 2021, 10, 2153–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

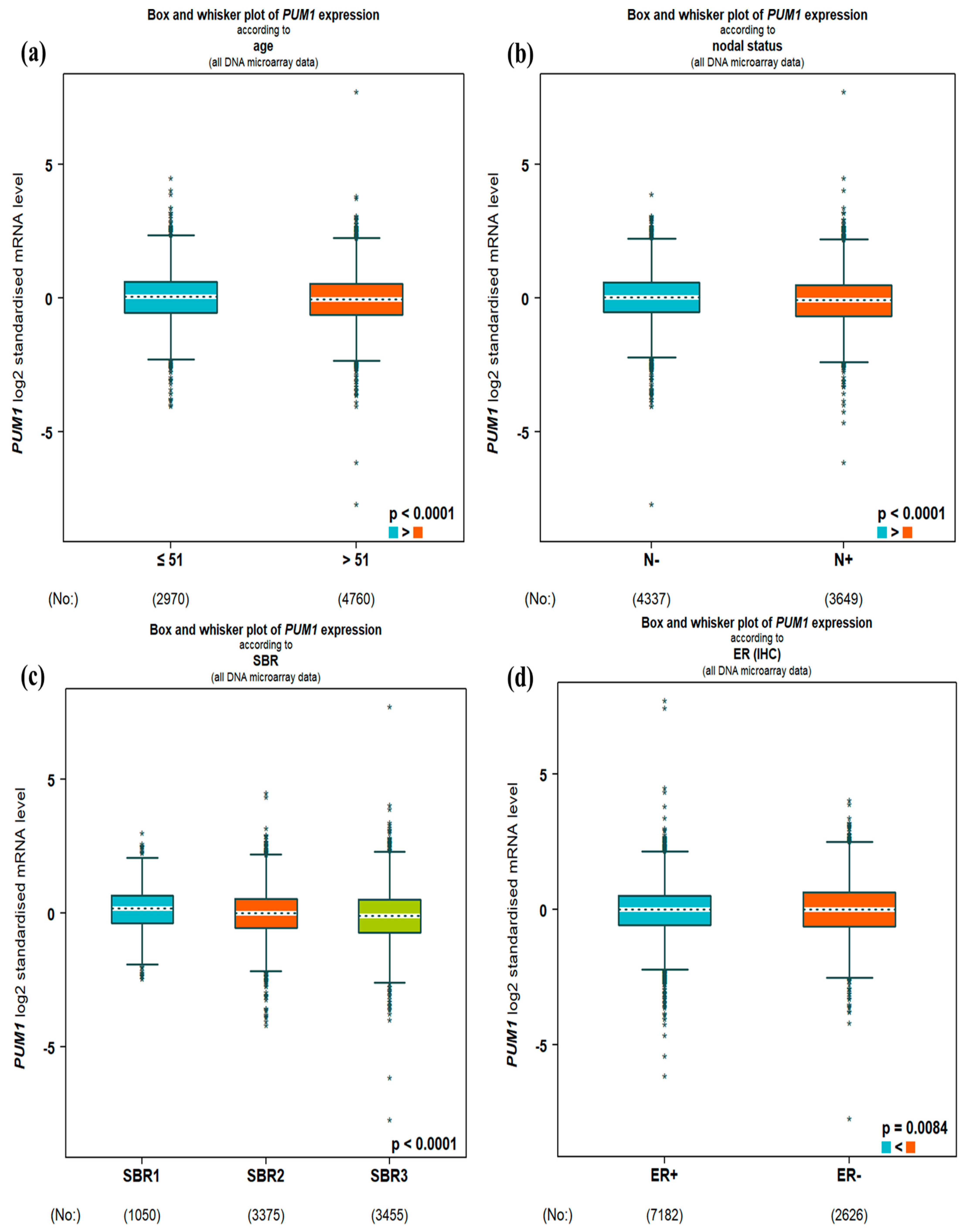
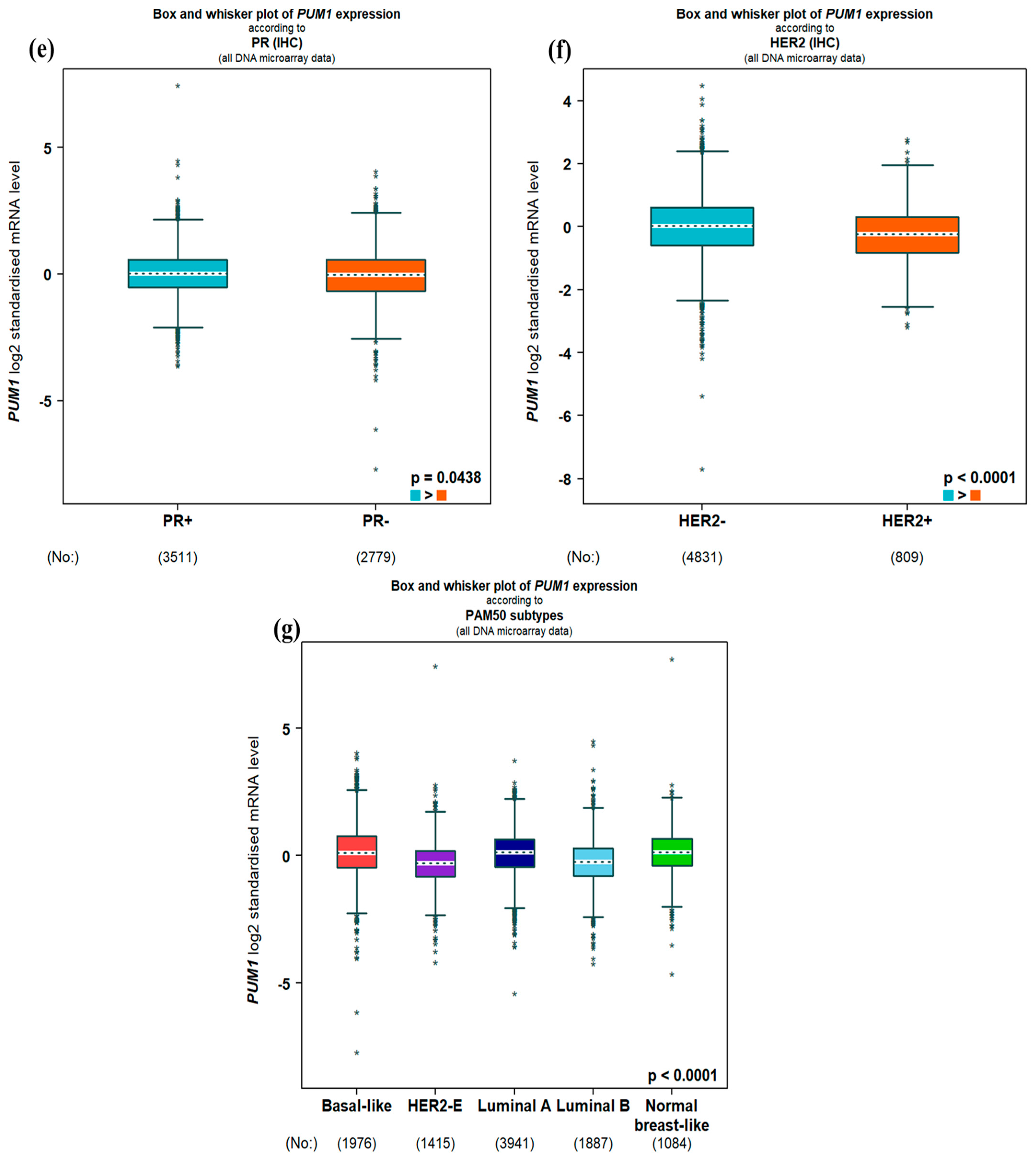
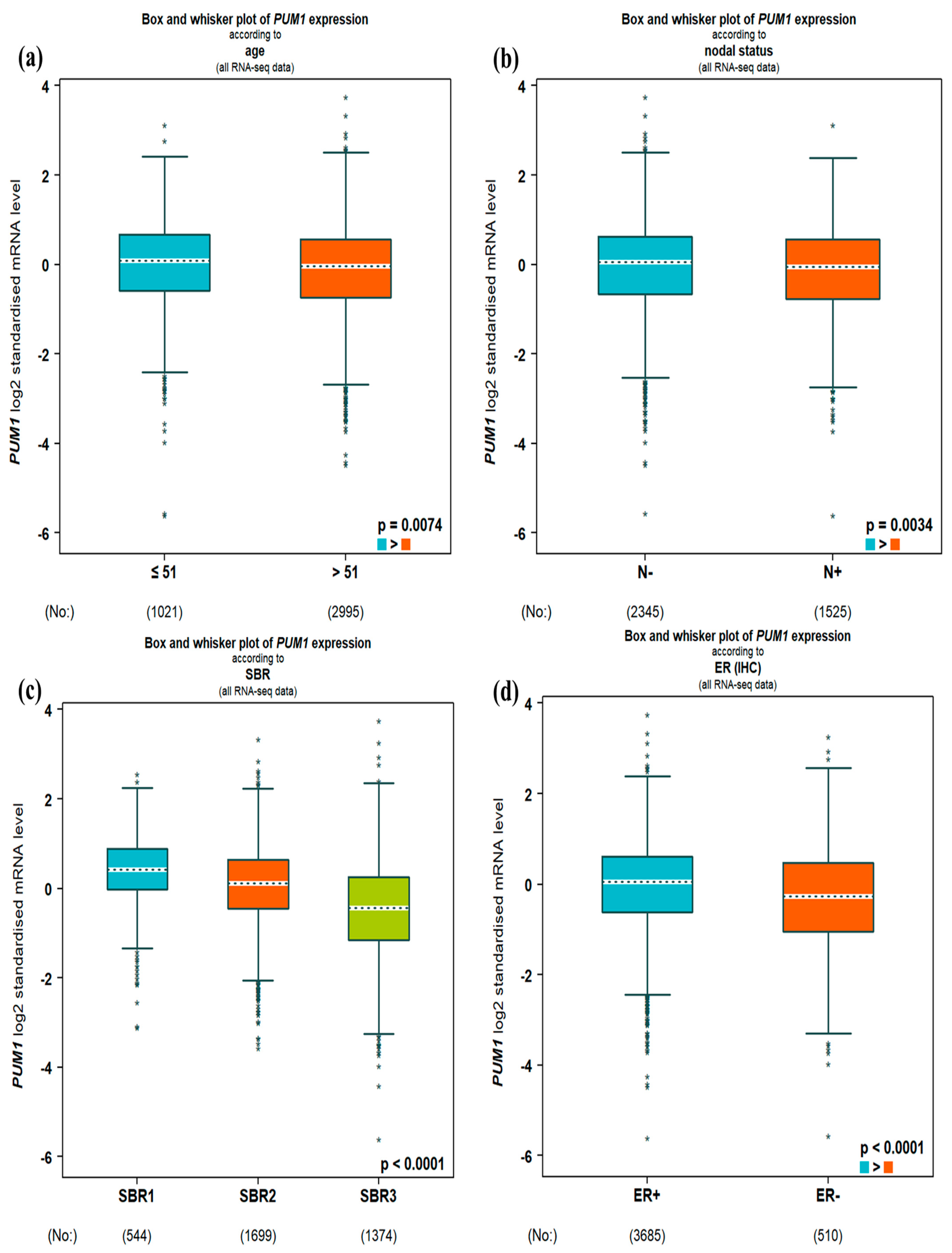
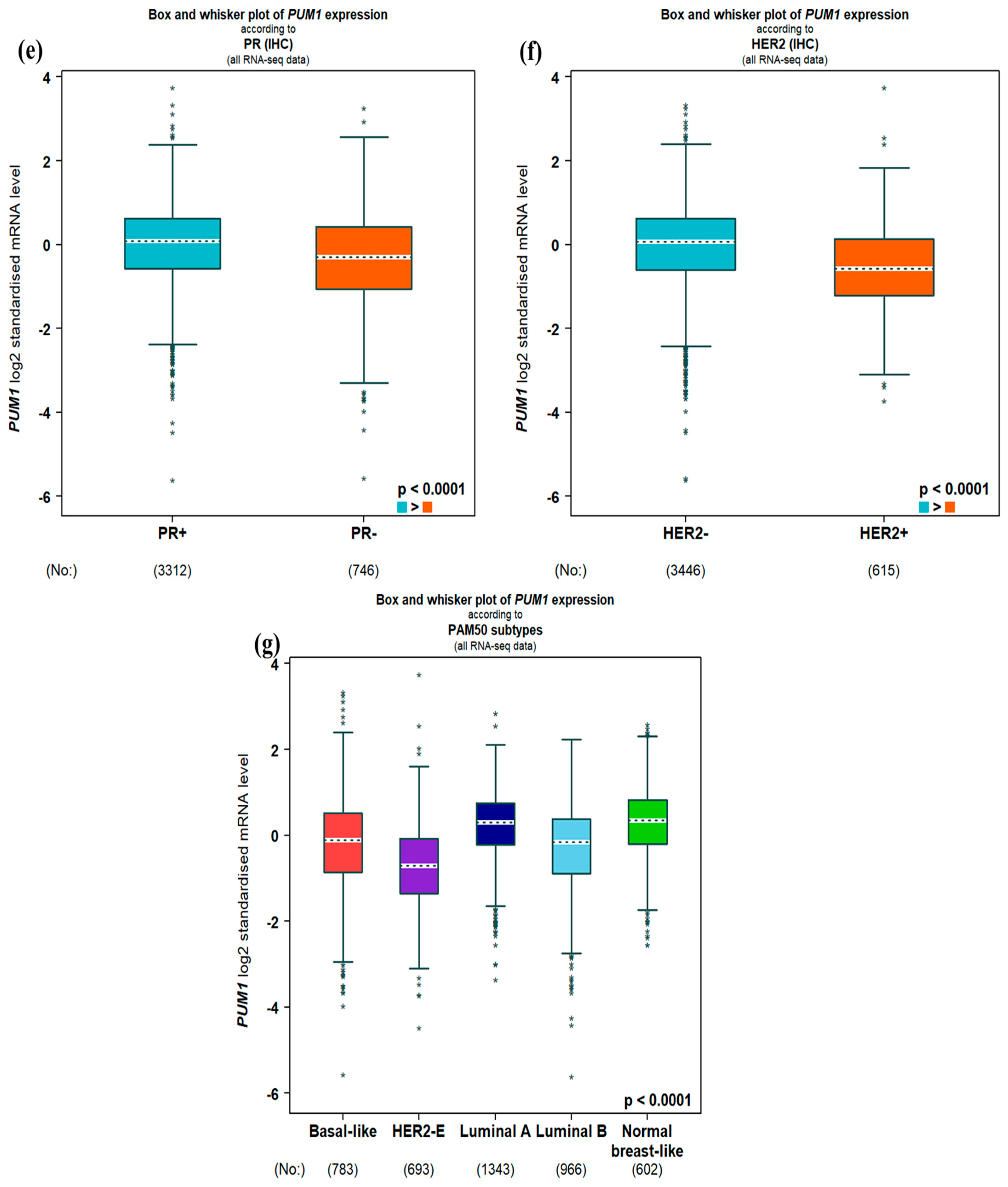

| Variable | PUM1 Expression | χ2 | p-Value | FDR Adjusted p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low (H-Score ≤ 125) | High (H-Score > 125) | ||||
| Age at diagnosis | |||||
| ≤50 years >50 years | 22 (46.8%) 28 (52.8%) | 25 (53.2%) 25 (47.2%) | 0.361 | 0.548 | 0.645 |
| Menopausal status | |||||
| Pre-menopausal Post-menopausal | 22 (46.8%) 28 (52.8%) | 25 (53.2%) 25 (47.2%) | 0.361 | 0.548 | 0.645 |
| Tumor size | |||||
| ≤10 mm >10 mm | 19 (61.3%) 12 (42.9%) | 12 (38.7%) 16 (57.1%) | 2.005 | 0.157 | 0.224 |
| Tumor grade | |||||
| I II III | 8 (88.9%) 38 (67.9%) 1 (3.3%) | 1 (11.1%) 18 (32.1%) 29 (96.7%) | 38.714 | <0.001 | 0.003 |
| Lymph node status | |||||
| Negative Positive | 15 (60.0%) 9 (34.6%) | 10 (40.0%) 17 (65.4%) | 3.296 | 0.069 | 0.115 |
| ER status | |||||
| Negative Positive | 5 (22.7%) 54 (58.4%) | 17 (77.3%) 32 (41.6%) | 8.731 | 0.003 | 0.006 |
| PR status | |||||
| Negative Positive | 6 (24.0%) 44 (59.5%) | 19 (76.0%) 30 (40.5%) | 9.400 | 0.002 | 0.005 |
| HER2 status | |||||
| Negative Positive | 36 (49.3%) 13 (52.0%) | 37 (50.7%) 12 (48.0%) | 0.054 | 0.817 | 0.817 |
| Ki-67 status | |||||
| Negative Positive | 27 (71.1%) 21 (36.8%) | 11 (28.9%) 36 (63.2%) | 10.675 | 0.001 | 0.003 |
| IHC subtype | |||||
| ER+/HER2− low proliferation ER+/HER2− high proliferation Triple-negative HER2+ | 29 (74.4%) 15 (41.7%) 1 (7.1%) 4 (50.0%) | 10 (25.6%) 21 (58.3%) 13 (92.9%) 4 (50.0%) | 20.534 | <0.001 | 0.003 |
| Parameters | Hazard Ratio (HR) | 95% Confidence Interval (CI) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | |||
| PUM 1 protein expression | 3.816 | 1.326 | 10.984 | 0.013 |
| Tumor grade | 0.749 | 0.374 | 1.498 | 0.414 |
| ER status | 0.753 | 0.190 | 2.988 | 0.687 |
| PR status | 0.530 | 0.130 | 2.154 | 0.374 |
| HER2 status | 1.233 | 0.517 | 2.941 | 0.636 |
| Ki-67 status | 0.677 | 0.296 | 1.549 | 0.355 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aljohani, A.I. PUM1 in Breast Cancer: Tumor Expression and Prognostic and Predictive Significance. Medicina 2025, 61, 1810. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61101810
Aljohani AI. PUM1 in Breast Cancer: Tumor Expression and Prognostic and Predictive Significance. Medicina. 2025; 61(10):1810. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61101810
Chicago/Turabian StyleAljohani, Abrar I. 2025. "PUM1 in Breast Cancer: Tumor Expression and Prognostic and Predictive Significance" Medicina 61, no. 10: 1810. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61101810
APA StyleAljohani, A. I. (2025). PUM1 in Breast Cancer: Tumor Expression and Prognostic and Predictive Significance. Medicina, 61(10), 1810. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61101810






