Liraglutide Enhances Cell Viability and Reduces Oxidative Stress in Hyperglycemic H9c2 Cardiomyocytes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. MTT Assay and Cell Viability
2.3. Hyperglycemic Model and Experimental Grouping
2.4. Transmission Electron Microscopic Examination
2.5. Measurement of HIF-1α and Oxidative Stress Biomarkers
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
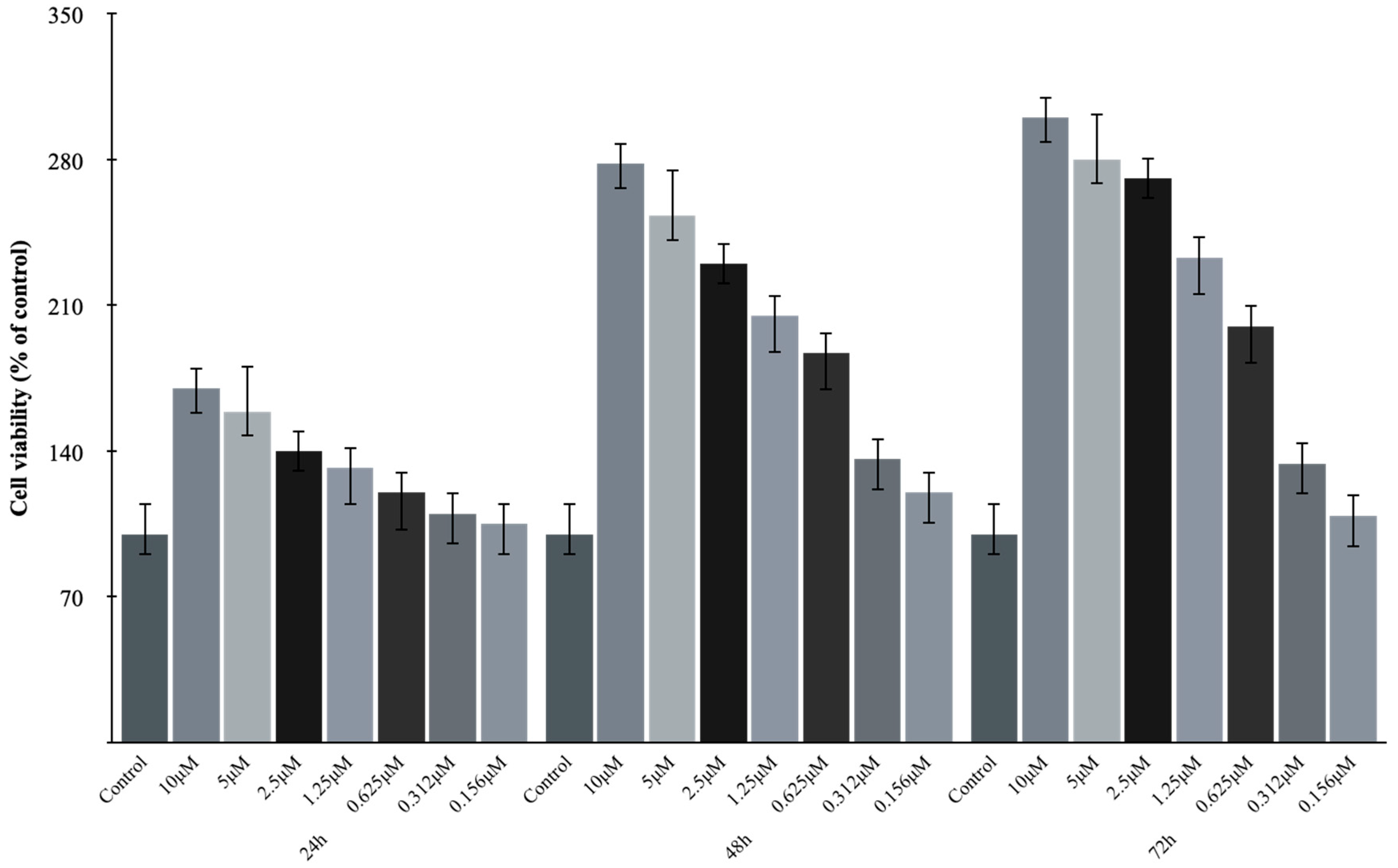
3.1. Lir Concentrations’ Effects on the Cell Viability of H9c2 Cells
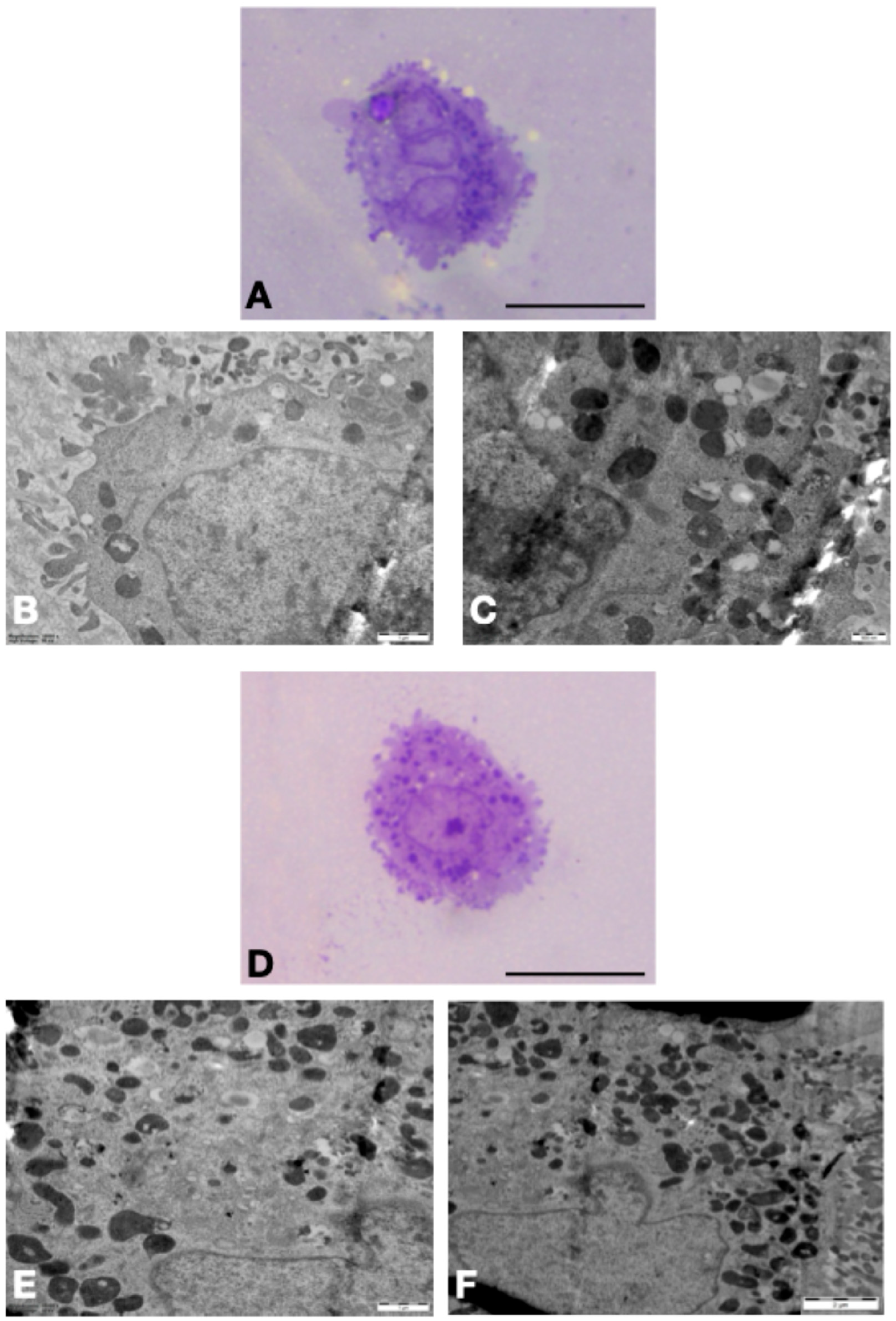
3.2. TEM Results in H9c2 Cells
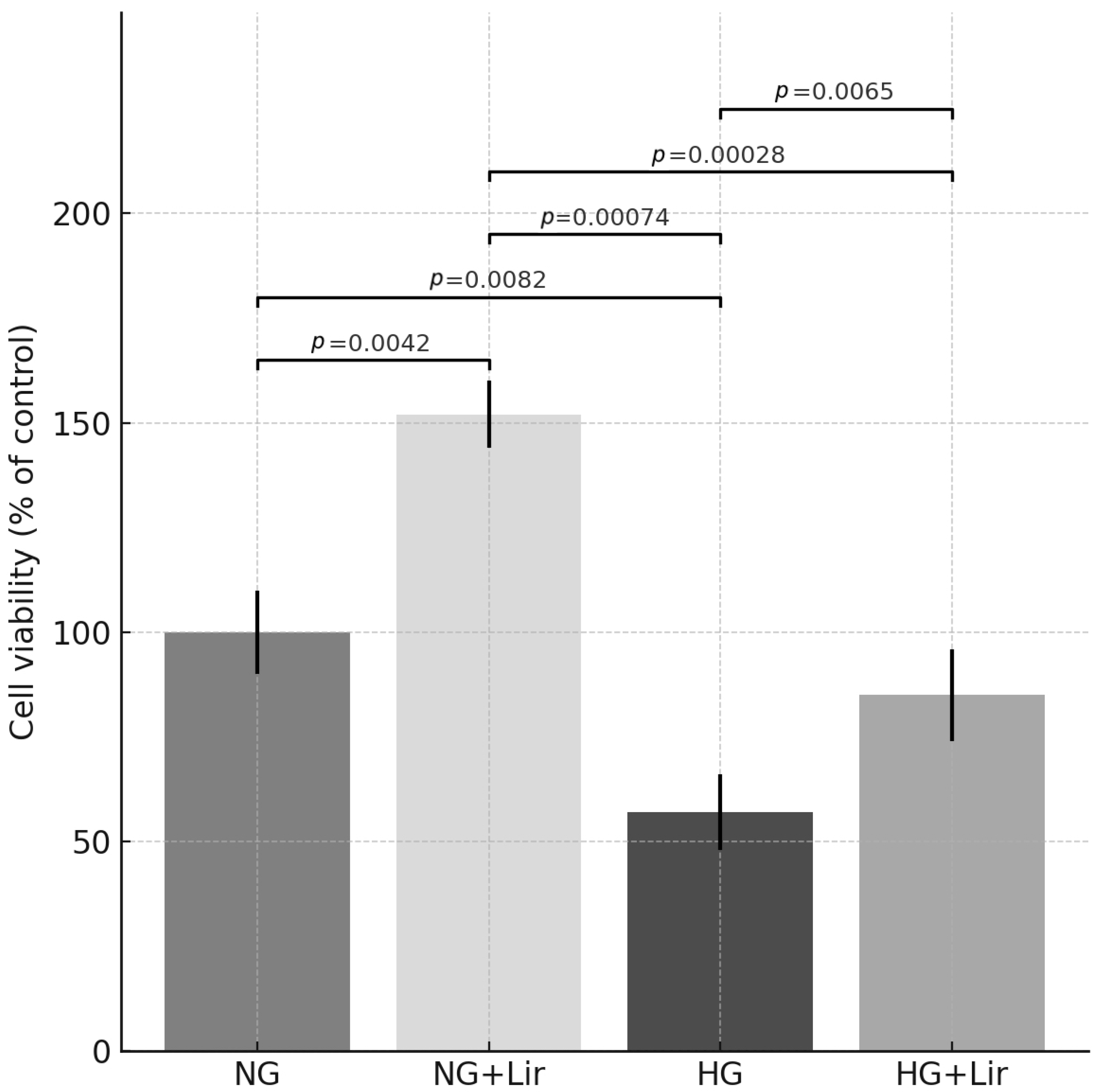
3.3. Effects of Lir on HIF-1α Levels and Oxidative Stress Biomarkers in H9c2 Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AOPP | Advanced oxidation protein products |
| DM | Diabetes mellitus |
| GLP-1 | Glucagon-like peptide-1 |
| GLP-1R | Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor |
| HG | Hyperglycemia |
| HIF-1α | Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α |
| Lir | Liraglutide |
| LOOH | Lipid hydroperoxides |
| MDA | Malondialdehyde |
| NG | Normoglycemia |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| SGLT2 | Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 |
| TAC | Total antioxidant capacity |
| T2DM | Type 2 diabetes mellitus |
References
- International Diabetes Federation IDF Diabetes Atlas: 11th Edition 2025. Available online: https://diabetesatlas.org/resources/idf-diabetes-atlas-2025/ (accessed on 7 May 2025).
- De Geest, B.; Mishra, M. Role of Oxidative Stress in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tangvarasittichai, S. Oxidative Stress, Insulin Resistance, Dyslipidemia and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. World J. Diabetes 2015, 6, 456–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvestrini, A.; Mancini, A. The Double-Edged Sword of Total Antioxidant Capacity: Clinical Significance and Personal Experience. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidari, F.; Rabizadeh, S.; Rajab, A.; Heidari, F.; Mouodi, M.; Mirmiranpour, H.; Esteghamati, A.; Nakhjavani, M. Advanced Glycation End-Products and Advanced Oxidation Protein Products Levels Are Correlates of Duration of Type 2 Diabetes. Life Sci. 2020, 260, 118422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mialet-Perez, J.; Belaidi, E. Interplay between Hypoxia Inducible Factor-1 and Mitochondria in Cardiac Diseases. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2024, 221, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myasoedova, V.A.; Bozzi, M.; Valerio, V.; Moschetta, D.; Massaiu, I.; Rusconi, V.; Di Napoli, D.; Ciccarelli, M.; Parisi, V.; Agostoni, P.; et al. Anti-Inflammation and Anti-Oxidation: The Key to Unlocking the Cardiovascular Potential of SGLT2 Inhibitors and GLP1 Receptor Agonists. Antioxidants 2023, 13, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcon, L.M.R.; Mazzieri, A. Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Oxidative Effects of GLP1-RAs and SGLT2i: The Guiding Star Towards Cardiovascular Protection in Type 2 Diabetes. Immuno 2025, 5, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Tian, J.; Diao, S.; Zhang, G.; Xiao, M.; Chang, D. GLP-1 Receptor Agonist Liraglutide Protects Cardiomyocytes from IL-1β-Induced Metabolic Disturbance and Mitochondrial Dysfunction. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2020, 332, 109252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Z.; Wang, T.; Li, Y.; Wang, L.; Yang, J.; Dong, H.; Li, S. Liraglutide Ameliorates COCl2-Induced Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis in H9C2 Cells via Regulating Cell Autophagy. Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 19, 3716–3722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamayo-Trujillo, R.; Ruiz-Pozo, V.A.; Cadena-Ullauri, S.; Guevara-Ramírez, P.; Paz-Cruz, E.; Zambrano-Villacres, R.; Simancas-Racines, D.; Zambrano, A.K. Molecular Mechanisms of Semaglutide and Liraglutide as a Therapeutic Option for Obesity. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1398059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skrobucha, A.; Pindlowski, P.; Krajewska, N.; Grabowski, M.; Jonik, S. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Glucagon-like Peptide-1 (GLP-1) in Coronary Artery Disease: A Comprehensive Review. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2024, 11, 1446468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eraky, S.M.; Ramadan, N.M.; Abo El-Magd, N.F. Antidiabetic Effects of Quercetin and Liraglutide Combination through Modulation of TXNIP/IRS-1/PI3K Pathway. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2022, 40, 90–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, C.-Y.; Tsou, S.-H.; Kornelius, E.; Chan, K.-C.; Chang, K.-W.; Li, J.-C.; Huang, C.-N.; Lin, C.-L. The Protective Effects of Liraglutide in Reducing Lipid Droplets Accumulation and Myocardial Fibrosis in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2025, 82, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, C.; Zhu, Q.; Li, N.; Zhou, H. Liraglutide, a Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Analog, Inhibits High Glucose-Induced Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis in Neonatal Rat Cardiomyocytes. Exp. Ther. Med. 2019, 17, 3734–3740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogan, Z.; Ergun, D.D.; Durmus, S.; Sahin, H.; Senturk, G.E.; Gelisgen, R.; Senyigit, A.; Uzun, H. Empagliflozin and Sacubitril/Valsartan Reverse Methotrexate Cardiotoxicity by Repressing Oxidative Stress and Hypoxia in Heart Embryonic H9c2 Cardiomyocytes—The Role of Morphology of Mitochondria Observed on Electron Microscopy. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2023, 27, 3979–3992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitirim, C.V.; Ozer, Z.B.; Aydos, D.; Genc, K.; Demirsoy, S.; Akcali, K.C.; Turan, B. Cardioprotective Effect of Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Ticagrelor-Pretreated Cardiomyocyte on Hyperglycemic Cardiomyocytes through Alleviation of Oxidative and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 5651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, A.; Sun, W.; Mou, F. lncRNA-MALAT1 Promotes High Glucose-induced H9C2 Cardiomyocyte Pyroptosis by Downregulating miR-141-3p Expression. Mol. Med. Rep. 2021, 23, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuamnaichati, N.; Mangmool, S.; Chattipakorn, N.; Parichatikanond, W. Stimulation of GLP-1 Receptor Inhibits Methylglyoxal-Induced Mitochondrial Dysfunctions in H9C2 Cardiomyoblasts: Potential Role of Epac/PI3K/Akt Pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, W.; Han, K.; Xie, M.; Li, S.; Chen, G.; Wang, Y.; Li, T. Mitochondrial Energy Metabolism in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy: Physiological Adaption, Pathogenesis, and Therapeutic Targets. Chin. Med. J. 2024, 137, 936–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catrina, S.-B.; Zheng, X. Hypoxia and Hypoxia-Inducible Factors in Diabetes and Its Complications. Diabetologia 2021, 64, 709–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramalho, A.R.; Toscano, A.; Pereira, P.; Girão, H.; Gonçalves, L.; Marques, C. Hyperglycemia-Induced Degradation of HIF-1α Contributes to Impaired Response of Cardiomyocytes to Hypoxia. Rev. Port. Cardiol. 2017, 36, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodd, M.S.; Sousa Fialho, M.d.L.; Montes Aparicio, C.N.; Kerr, M.; Timm, K.N.; Griffin, J.L.; Luiken, J.J.F.P.; Glatz, J.F.C.; Tyler, D.J.; Heather, L.C. Fatty Acids Prevent Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1α Signaling Through Decreased Succinate in Diabetes. JACC Basic. Transl. Sci. 2018, 3, 485–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langlois, A.; Mura, C.; Bietiger, W.; Seyfritz, E.; Dollinger, C.; Peronet, C.; Maillard, E.; Pinget, M.; Jeandidier, N.; Sigrist, S. In Vitro and In Vivo Investigation of the Angiogenic Effects of Liraglutide during Islet Transplantation. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0147068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waiz, M.; Alvi, S.S.; Khan, M.S. Association of Circulatory PCSK-9 with Biomarkers of Redox Imbalance and Inflammatory Cascades in the Prognosis of Diabetes and Associated Complications: A Pilot Study in the Indian Population. Free Radic. Res. 2023, 57, 294–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankaranarayanan, C.; Kalaivani, K. Isopulegol Mitigates Hyperglycemia Mediated Oxidative and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in HFD/STZ Induced Diabetic Rats. Arch. Med. Res. 2020, 51, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cessario, J.; Pierre-Louis, V.; Wahl, J.; Li, Z. Empagliflozin, Alone or in Combination with Liraglutide, Limits Cell Death in Vitro: Role of Oxidative Stress and Nitric Oxide. Pharmacol. Rep. 2021, 73, 858–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, J.-R.; Su, J.-N.; Sun, G.-Y.; Wang, Q.-F.; Fan, Y.-D.; Jiang, N.; Yang, Y.-F.; Shi, Y. Liraglutide Alleviates Cognitive Deficit in Db/Db Mice: Involvement in Oxidative Stress, Iron Overload, and Ferroptosis. Neurochem. Res. 2022, 47, 279–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonon Firmino, F.; Peixoto, P.; Batista, T.J.; Escouto, L.d.S.; Brasil, G.A.; Couto, M.D.R.; de Melo Júnior, A.F.; Bissoli, N.S. High Dose of Liraglutide Impairs Renal Function in Female Hypertensive Rats. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2025, 85, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaballah, H.H.; Zakaria, S.S.; Mwafy, S.E.; Tahoon, N.M.; Ebeid, A.M. Mechanistic Insights into the Effects of Quercetin and/or GLP-1 Analogue Liraglutide on High-Fat Diet/Streptozotocin-Induced Type 2 Diabetes in Rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 92, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, H.-X.; Dong, N.-X.; Zhou, C.-X.; Wang, F.-J.; Xing, N.; Ma, H.-F.; Hou, L. Liraglutide Attenuates Restenosis After Vascular Injury in Rabbits With Diabetes Via the TGF-β/Smad3 Signaling Pathway. Altern. Ther. Health Med. 2022, 28, 22–28. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, S.-Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, P.-J.; Zhou, H.; Chen, Y.-D. Liraglutide Directly Protects Cardiomyocytes against Reperfusion Injury Possibly via Modulation of Intracellular Calcium Homeostasis. J. Geriatr. Cardiol. 2017, 14, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, L.; Gao, R.; Chen, Z.; Lin, D.; Liu, Z.; Wang, L.; Lin, L.; Liu, X.; Liu, X.; Liu, L. Liraglutide Reduces Oxidative Stress and Improves Energy Metabolism in Methylglyoxal-Induced SH-SY5Y Cells. NeuroToxicology 2022, 92, 166–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Xiao, X.; Zheng, J.; Li, M.; Yu, M.; Ping, F.; Wang, T.; Wang, X. Liraglutide Protects Cardiac Function in Diabetic Rats through the PPARα Pathway. Biosci. Rep. 2018, 38, BSR20180059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Durmus, S.; Dogan, Z.; Ergun, D.D.; Ozdemir, M.; Sahin, H.; Senturk, G.E.; Gelisgen, R.; Uzun, H. Liraglutide Enhances Cell Viability and Reduces Oxidative Stress in Hyperglycemic H9c2 Cardiomyocytes. Medicina 2025, 61, 1754. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61101754
Durmus S, Dogan Z, Ergun DD, Ozdemir M, Sahin H, Senturk GE, Gelisgen R, Uzun H. Liraglutide Enhances Cell Viability and Reduces Oxidative Stress in Hyperglycemic H9c2 Cardiomyocytes. Medicina. 2025; 61(10):1754. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61101754
Chicago/Turabian StyleDurmus, Sinem, Zeki Dogan, Dilek Duzgun Ergun, Mahmut Ozdemir, Hakan Sahin, Gozde Erkanli Senturk, Remise Gelisgen, and Hafize Uzun. 2025. "Liraglutide Enhances Cell Viability and Reduces Oxidative Stress in Hyperglycemic H9c2 Cardiomyocytes" Medicina 61, no. 10: 1754. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61101754
APA StyleDurmus, S., Dogan, Z., Ergun, D. D., Ozdemir, M., Sahin, H., Senturk, G. E., Gelisgen, R., & Uzun, H. (2025). Liraglutide Enhances Cell Viability and Reduces Oxidative Stress in Hyperglycemic H9c2 Cardiomyocytes. Medicina, 61(10), 1754. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61101754





