Pregnancy Complications and Outcomes in Obese Women with Gestational Diabetes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Diagnostic Criteria and Classification of Hyperglycemia First Detected in Pregnancy. 2013. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/85975 (accessed on 16 November 2020).
- Law, K.P.; Zhang, H. The pathogenesis and pathophysiology of gestational diabetes mellitus: Deductions from a three-part longitudinal metabolomics study in China. Clin. Chim. Acta 2017, 468, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ministry of Health of the Republic of Lithuania. Guidelines and Protocols of Diagnostics and Treatment in Obstetrics “Nesciuju Diabetas”. 2019. Available online: https://sam.lrv.lt/uploads/sam/documents/files/Akušerinė%20metodika_Nėščiųjų%20diabetas_SAM_2019-07-20.pdf (accessed on 16 December 2020).
- Quintanilla Rodriguez, B.S.; Vadakekut, E.S.; Mahdy, H. Gestational Diabetes. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Zhou, Y.; Zhong, J.; Wang, K.; Ding, Y.; Li, L. Current guidelines on the management of gestational diabetes mellitus: A content analysis and appraisal. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2019, 19, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macrì, F.; Pitocco, D.; di Pasquo, E.; Salvi, S.; Rizzi, A.; Di Leo, M.; Tartaglione, L.; Di Stasio, E.; Lanzone, A.; De Carolis, S. Gestational weight gain as an independent risk factor for adverse pregnancy outcomes in women with gestational diabetes. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 22, 4403–4410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aaron, B.C.; Erika, F.W.; Vanessa, A.B.; FACOG. Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: Obstetric Issues and Management. UpToDate 2019 October. Available online: https://www-uptodate-com.ezproxy.dbazes.lsmuni.lt/contents/gestational-diabetes-mellitus-obstetric-issues-and-management?search=gestationaldiabetes&source=search_result&selectedTitle=1~150&usage_type=default&display_rank=1 (accessed on 25 November 2020).
- Plows, J.F.; Stanley, J.L.; Baker, P.N.; Reynolds, C.M.; Vickers, M.H. The Pathophysiology of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catalano, P.M. Management of Obesity in Pregnancy. Obstet. Gynecol. 2007, 109 Pt 1, 419–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisonkova, S.; Muraca, G.M.; Potts, J.; Liauw, J.; Chan, W.S.; Skoll, A.; Lim, K.I. Association Between Prepregnancy Body Mass Index and Severe Maternal Morbidity. JAMA 2017, 318, 1777–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiteman, V.E.; Salemi, J.L.; Mejia De Grubb, M.C.; Ashley Cain, M.; Mogos, M.F.; Zoorob, R.J.; Salihu, H.M. Additive effects of pre-pregnancy body mass index and gestational diabetes on health outcomes and costs. Obesity 2015, 23, 2299–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Chen, H.; Hsu, H. Maternal Prepregnancy Body Mass Index, Gestational Weight Gain, and Risk of Adverse Perinatal Outcomes in Taiwan: A Population-Based Birth Cohort Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metzger, B.E.; Buchanan, T.A.; Coustan, D.R.; De Leiva, A.; Dunger, D.B.; Hadden, D.R.; Hod, M.; Kitzmiller, J.L.; Kjos, S.L.; Oats, J.N.; et al. Summary and recommendations of the Fifth International Workshop-Conference on Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Care 2007, 30 (Suppl. S2), S251–S260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, J.C. Maternal Obesity, Metabolism, and Pregnancy Outcomes. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2006, 26, 271–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaillard, R. Maternal obesity during pregnancy and cardiovascular development and disease in the offspring. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2015, 30, 1141–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Underweight and Obesity in Lithuania. 2022. Available online: https://ncdrisc.org/downloads/country-pdf/double-burden/NCD-RisC%20country%20factsheet%20Lithuania.pdf (accessed on 12 November 2024).
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Defining Adult Overweight and Obesity. 2017. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/nccdphp/dnpao/data-trends-maps/help/npao_dtm/definitions.html (accessed on 25 November 2020).
- ACOG. Practice Bulletin No. 190: Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Obstet. Gynecol. 2018, 131, e49–e64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machado, C.; Monteiro, S.; Oliveira, M.J. Impact of overweight and obesity on pregnancy outcomes in women with gestational diabetes—Results from a retrospective multicenter study. Arch. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 64, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baliutavičienė, D.; Buinauskienė, J.B.; Petrenko, V.; Danytė, E.; Žalinkevičius, R. Gestational Diabetes, Obesity, and Metabolic Syndrome Diagnosed During Pregnancy. Metab. Syndr. Relat. Disord. 2012, 10, 214–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiyama, T.; Nagao, K.; Metoki, H.; Nishigori, H.; Saito, M.; Tokunaga, H.; Nagase, S.; Sugawara, J.; Watanabe, Y.; Yaegashi, N.; et al. Pregnancy outcomes of gestational diabetes mellitus according to pre-gestational BMI in a retrospective multi-institutional study in Japan. Endocr. J. 2014, 61, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wahabi, H.A.; Fayed, A.A.; Alzeidan, R.A.; Mandil, A.A. The independent effects of maternal obesity and gestational diabetes on the pregnancy outcomes. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2014, 14, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, M.; Dai, M.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, F.; Guo, X.; Sun, G. Influence of maternal overweight, obesity and gestational weight gain on the perinatal outcomes in women with gestational diabetes mellitus. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 305–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huet, J.; Beucher, G.; Rod, A.; Morello, R.; Dreyfus, M. Joint impact of gestational diabetes and obesity on perinatal outcomes. J. Gynecol. Obstet. Hum. Reprod. 2018, 47, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, D.; Li, F.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, X. Associations of the pre-pregnancy BMI and gestational BMI gain with pregnancy outcomes in Chinese women with gestational diabetes mellitus. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2014, 7, 5784–5789. [Google Scholar]
- Sabolović Rudman, S.; Djaković, I.; Gall, V.; Djaković, Ž.; Košec, V. Pregnancy outcome in gestational diabetes compared to body mass index. Acta Clin. Croat. 2019, 58, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennedy, M.C.; Dunne, F. The maternal and fetal impacts of obesity and gestational diabetes on pregnancy outcome. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 24, 573–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Criteria | Women of Normal Weight | Obese Women | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n = 381 (%) | n = 202 (%) | |||
| Age (years) 1 | 31.04 ± 5.4 | 32.22 ± 5.3 | p = 0.012 | |
| Type of GD 2 | A1 | 271 (71.1) | 104 (51.4) | p < 0.05 |
| A2 | 110 (28.9) | 98 (48.5) | ||
| Place of residence 2 | City | 270 (70.9) | 126 (62.4) | p = 0.041 |
| Countryside | 111 (29.1) | 76 (37.6) | ||
| Weeks of gestation 3 | 39 (24–41; 38.63) | 39 (22–41; 38.47) | p = 0.140 | |
| Criteria | Women of Normal Weight | Obese Women | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n = 381(%) | n = 202 (%) | ||||
| The number of pregnancies 2 | 2 (1–6; 1.98) | 2 (1–9; 2.58) | p < 0.001 | ||
| The number of pregnancies according to type of GD 1 | A1 | First | 122 (45.0) | 39 (37.5) | p = 0.150 |
| Second | 86 (32.0) | 31 (29.8) | |||
| Third or more | 63 (23.0) | 34 (32.7) | |||
| A2 | First | 39 (35.5) | 17 (17.3) | p = 0.009 | |
| Second | 35 (31.8) | 34 (34.7) | |||
| Third or more | 36 (32.7) | 47 (48.0) | |||
| The number of deliveries 2 | 2 (1–6; 1.72) | 2 (1–9; 2.06) | p < 0.001 | ||
| The number of deliveries according to type of GD 2 | A1 | First | 140 (51.7) | 55 (52.9) | p = 0.303 |
| Second | 95 (35.0) | 30 (28.8) | |||
| Third or more | 36 (13.3) | 19 (18.3) | |||
| A2 | First | 49 (44.5) | 21 (21.4) | p = 0.002 | |
| Second | 38 (34.5) | 47 (48.0) | |||
| Third or more | 23 (20.9) | 30 (30.6) | |||
| Test | Normal Body Weight n = 381 (%) | Obesity n = 202 (%) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Venous plasma glucose level (mmol/L), (n = 224) | 5.49 (5–8; 5.56) | 5.67 (5–7; 5.78) | p < 0.001 | |
| Venous plasma glucose level according to type of GD (mmol/L) | A1 | 5.49 (5–8; 5.56) | 5.62 (5–7; 5.71) | p = 0.106 |
| A2 | 5.48 (5–7; 5.58) | 5.69 (5–7; 5.86) | p = 0.006 | |
| OGTT I point (0 min) (mmol/L), (n = 359) | 5.20 (3–8; 5.19) | 5.45 (3–8; 5.52) | p < 0.001 | |
| OGTT I point (0 min) according to type of GD (mmol/L) | A1 | 5.20 (3–8; 5.09) | 5.42 (3–7; 5.40) | p < 0.001 |
| A2 | 5.26 (4–8; 5.41) | 5.52 (4–8; 5.58) | p = 0.025 | |
| OGTT II point (60 min) (mmol/L), (n = 359) | 8.10 (4–14; 8.28) | 8.29 (3–13; 8.48) | p = 0.105 | |
| OGTT II point (0 min) according to type of GD (mmol/L) | A1 | 8.00 (4–14; 8.25) | 7.80 (3–13; 8.02) | p = 0.550 |
| A2 | 8.15 (4–14; 8.38) | 8.75 (5–13; 8.97) | p = 0.071 | |
| OGTT III point (120 min), (mmol/L), (n = 359) | 7.40 (4–15; 7.56) | 7.39 (3–11; 7.33) | p = 0.453 | |
| OGTT III point (0 min) according to type of GD (mmol/L) | A1 | 7.56 (4–15; 7.77) | 7.10 (3–10; 7.08) | p = 0.037 |
| A2 | 7.10 (4–13; 7.10) | 7.64 (5–11; 7.58) | p = 0.104 | |
| Pregnancy Complication | Normal Body Weight n = 126 (%) | Obesity n = 173 (%) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary hypertension | 11 (2.9) | 38 (18.8) | p < 0.001 | |
| Primary hypertension according to type of GD | A1 | 6 (2.2) | 15 (14.4) | p < 0.001 |
| A2 | 5 (4.5) | 23 (23.5) | p < 0.001 | |
| Hypertensive disorders in pregnancy | 72 (19.0) | 96 (47.5) | p < 0.001 | |
| Hypertensive disorders in pregnancy according to type of GD | A1 | 51 (19.0) | 44 (42.3) | p < 0.001 |
| A2 | 21 (19.1) | 52 (53.1) | p < 0.001 | |
| Gestational anemia | 37 (9.8) | 26 (12.9) | p = 0.251 | |
| Gestational anemia according to type of GD | A1 | 24 (8.9) | 12 (11.5) | p = 0.443 |
| A2 | 13 (11.8) | 14 (14.3) | p = 0.597 | |
| Cholestasis of pregnancy | 6 (1.6) | 13 (6.4) | p = 0.002 | |
| Cholestasis of pregnancy according to type of GD | A1 | 5 (1.9) | 8 (7.7) | p = 0.006 |
| A2 | 1 (0.9) | 5 (5.1) | p = 0.071 | |
| Type of GD | Amount of Amniotic Fluid | Normal Body Weight n = 381, n (%) | Obesity n = 202, n (%) | Statistics |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | Normal | 240 (88.5) | 77 (74.0) | p = 0.003 |
| Polyhydramnios | 17 (6.3) | 16 (15.4) 1 | ||
| Oligohydramnios | 12 (4.5) | 11 (10.6) 1 | ||
| A2 | Normal | 102 (92.7) | 69 (23.7) 2 | p < 0.001 |
| Polyhydramnios | 4 (3.6) | 23 (23.7) 2 | ||
| Oligohydramnios | 4 (3.6) | 5 (5.2) |
| Criteria | Normal Body Weight n = 340(%) | Obesity n = 179(%) | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spontaneous onset of labour | 189 (55.6) | 44 (24.6) | p < 0.001 | ||
| Induced labour | Amniotomy Mechanical methods Using drugs | 126 (83.4) 9(6.0) 42 (27.8) | 111 (82.2) 13 (9.7) 45 (33.3) | p > 0.001 | |
| Labour according to the type of GD | A1 | Spontaneous | 143 (59.1) | 27 (29.7) | p < 0.001 |
| Induced | 99 (40.9) | 64 (70.3) | |||
| A2 | Spontaneous | 46 (46.9) | 17 (19.3) | p < 0.001 | |
| Induced | 52 (53.1) | 71 (80.7) | |||
| Criteria | Normal Body Weight n (%) | Obesity n (%) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type of delivery (n = 583) | Vaginal | 319 (83.5) | 152 (75.2) | p = 0.015 |
| CS | 62 (16.5) | 50 (24.8) | ||
| Urgency of CS (n = 112) | Planned | 36 (58.1) | 17 (34.0) | p = 0.011 |
| Emergency | 26 (41.9) | 33 (66.0) | ||
| Complications of Delivery | Normal Body Weight n = 151 (%) | Obesity n = 135 (%) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical narrow pelvis | 9 (2.4) | 4 (2.0) | p = 0.759 | |
| Distribution of clinical narrow pelvis according to the type of GD | A1 | 7 (2.6) | 3 (2.9) | p = 0.880 |
| A2 | 2 (1.8) | 1 (1.0) | p = 0.630 | |
| Foetal distress | 4 (1.1) | 8 (4.0) | p = 0.019 | |
| Distribution of foetal distress according to the type of GD | A1 | 2 (0.7) | 5 (4.8) | p = 0.009 |
| A2 | 2 (1.8) | 3 (3.1) | p = 0.559 | |
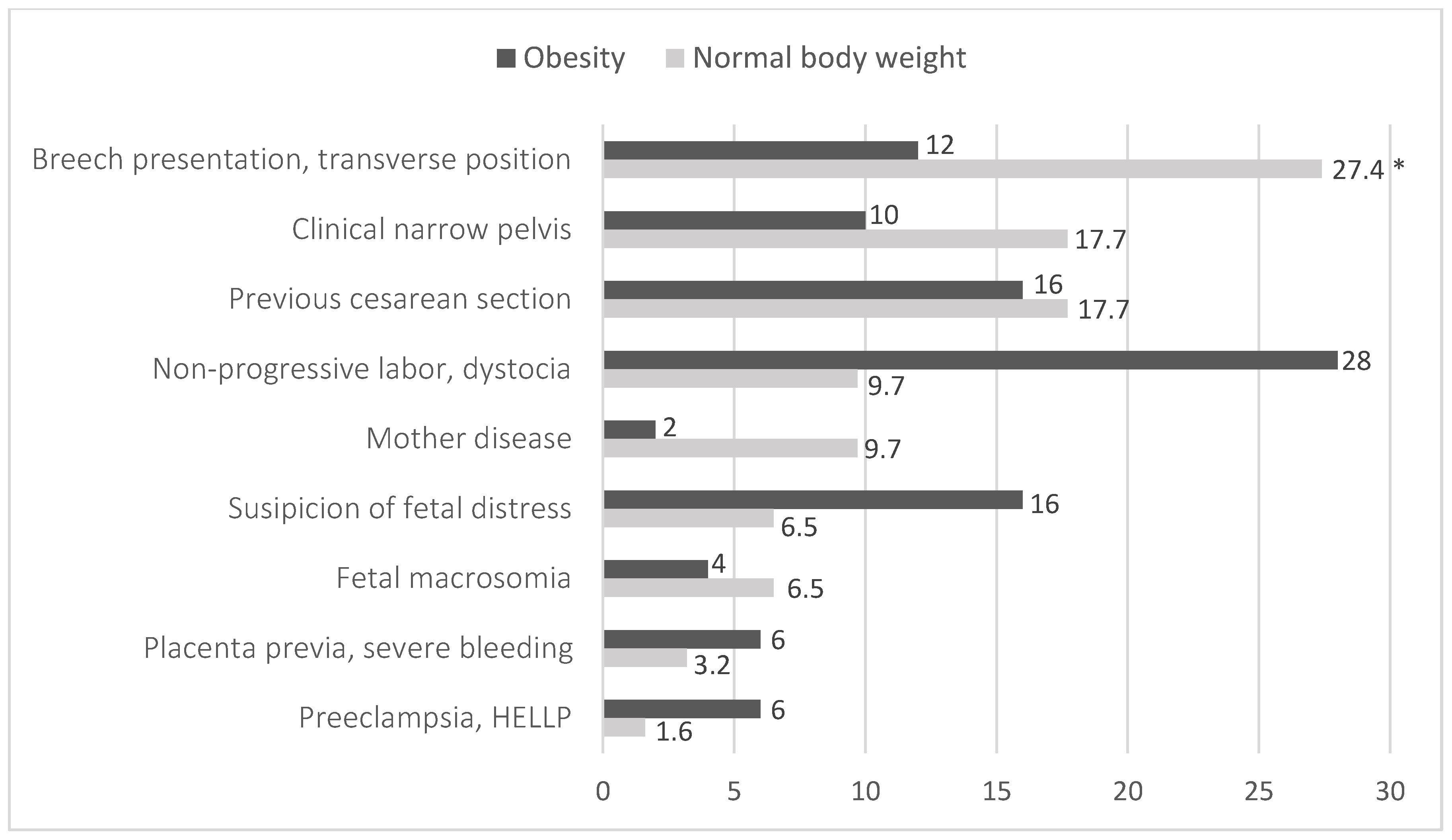
| Dystocia | 13 (3.4) | 19 (9.4) | p = 0.003 | |
| Distribution of dystocia according to the type of GD | A1 | 10 (3.7) | 7 (6.7) | p = 0.211 |
| A2 | 3 (2.7) | 12 (12.2) | p = 0.008 | |
| Abnormal foetus position | 17 (4.5) | 6 (3.0) | p = 0.372 | |
| Distribution of abnormal foetus position according to the type of GD | A1 | 14 (5.2) | 3 (2.9) | p = 0.335 |
| A2 | 3 (2.7) | 3 (3.1) | p = 0.886 | |
| Chorioamnionitis | 16 (4.2) | 8 (4.0) | p = 0.880 | |
| Distribution of chorioamnionitis according to the type of GD | A1 | 12 (4.5) | 7 (6.7) | p = 0.371 |
| A2 | 4 (3.6) | 1 (1.0) | p = 0.219 | |
| Preterm delivery | 27 (7.1) | 14 (6.9) | p = 0.931 | |
| Distribution of preterm delivery according to the type of GD | A1 | 20 (7.4) | 10 (9.6) | p = 0.487 |
| A2 | 7 (6.4) | 4 (4.1) | p = 0.463 | |
| Duration of Delivery | Normal Body Weight n = 381 | Obesity n = 202 | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 500 (10–1764; 582.76) | 420 (69–1850; 558.80) | p = 0.495 | |
| Total, according to the type of GD | A1 | 493 (60–1764; 595.41) | 524 (69–1850; 644.80) | p = 0.343 |
| A2 | 525 (10–1465; 551.78) | 342 (81–1610; 466.58) | p = 0.094 | |
| I stage of labour | 430 (4–1740; 502.45) | 360 (5–1590; 466.6) | p = 0.279 | |
| I stage of labour according to the type of GD | A1 | 425 (25–1740; 513.65) | 465 (5–1590; 559.63) | p = 0.323 |
| A2 | 450 (4–1320; 475.12) | 310 (40–1530; 367.55) | p = 0.017 | |
| II stage of labour | 30 (24–310; 61.89) | 24 (2–310; 47.70) | p = 0.030 | |
| II stage of labour according to the type of GD | A1 | 31 (1–314; 62.14) | 30 (2–268; 54.74) | p = 0.378 |
| A2 | 27 (1–288; 57.82) | 18 (2–310; 39.79) | p = 0.070 | |
| Criteria | Normal Body Weight | Obesity | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean of neonate weight (g±SD), (n = 583) 1 | 3343 ± 617 | 3444 ± 694 | p = 0.074 | |
| Distribution of the mean of neonates weight according to the type of mother’s GD, (g ± SD) 1 | A1 | 3337 ± 648 | 3314 ± 827 | p = 0.002 |
| A2 | 3357 ± 537 | 3581 ± 484 | p = 0.002 | |
| Mean of Apgar scores after 1 min., (n =583) 2 | 9 (3–10; 9.06) | 9 (2–10; 8.9) | p = 0.024 | |
| Distribution of the mean of Apgar scores after 1 min according to the type of mother’s GD, (scores±SD) 2 | A1 | 9 (4–10; 8.99) | 9 (2–10; 8.66) | p = 0.027 |
| A2 | 9 (3–10; 9.23) | 9 (5–10; 9.15) | p = 0.537 | |
| Mean of Apgar scores after 5 min., (n = 583) 2 | 10 (6–10; 9.66) | 10 (6–10; 9.52) | p = 0.024 | |
| Distribution of the mean of Apgar scores after 5 min according to the type of mother’s GD 2 | A1 | 10 (6–10; 9.65) | 10 (6–10; 9.38) | p = 0.537 |
| A2 | 10 (8–10; 9.7) | 10 (8–10; 9.67) | p = 0.725 | |
| Macrosomia, (n = 84) 3 | 38 (10.0) | 46 (22.8) | p < 0.001 | |
| Distribution of macrosomia according to the type of mother’s GD 3 | A1 | 28 (10.4) | 23 (22.1) | p = 0.003 |
| A2 | 10 (9.1) | 23 (23.5) | p = 0.005 | |
| Foetal growth restriction (n = 83) 3 | 51 (13.5) | 32 (15.8) | p = 0.434 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ramonienė, G.; Malakauskienė, L.; Savukynė, E.; Maleckienė, L.; Gruzdaitė, G. Pregnancy Complications and Outcomes in Obese Women with Gestational Diabetes. Medicina 2025, 61, 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61010051
Ramonienė G, Malakauskienė L, Savukynė E, Maleckienė L, Gruzdaitė G. Pregnancy Complications and Outcomes in Obese Women with Gestational Diabetes. Medicina. 2025; 61(1):51. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61010051
Chicago/Turabian StyleRamonienė, Gitana, Laura Malakauskienė, Eglė Savukynė, Laima Maleckienė, and Greta Gruzdaitė. 2025. "Pregnancy Complications and Outcomes in Obese Women with Gestational Diabetes" Medicina 61, no. 1: 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61010051
APA StyleRamonienė, G., Malakauskienė, L., Savukynė, E., Maleckienė, L., & Gruzdaitė, G. (2025). Pregnancy Complications and Outcomes in Obese Women with Gestational Diabetes. Medicina, 61(1), 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61010051







