Abstract
Recent advances in genetics and epigenetics have provided critical insights into the pathogenesis of both idiopathic and non-idiopathic interstitial lung diseases (ILDs). Mutations in telomere-related genes and surfactant proteins have been linked to familial pulmonary fibrosis, while variants in MUC5B and TOLLIP increase the risk of ILD, including idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and rheumatoid arthritis-associated ILD. Epigenetic mechanisms, such as DNA methylation, histone modifications, and non-coding RNAs such as miR-21 and miR-29, regulate fibrotic pathways, influencing disease onset and progression. Although no standardized genetic panel for ILD exists, understanding the interplay of genetic mutations and epigenetic alterations could aid in the development of personalized therapeutic approaches. This review highlights the genetic and epigenetic factors driving ILD, emphasizing their potential for refining diagnosis and treatment.
1. Introduction
Interstitial lung disease (ILD) encompasses a broad spectrum of pulmonary disorders characterized by inflammation and/or fibrosis within the alveolar interstitium of the lungs []. These diseases are rare, with a population prevalence of less than 0.05 percent, but they share common clinical, radiological, and physiological features []. The development of pulmonary fibrosis involves multiple risk factors, which can be categorized as environmental and genetic. Environmental factors include advanced age, smoking, respiratory infections, gastroesophageal reflux, and occupational or environmental exposures [,]. On the genetic side, specific genetic variants and epigenetic modifications have been implicated in the disease’s pathogenesis [,]. The strongest evidence for a genetic predisposition to ILD comes from its clustering in families, particularly in homozygous twins raised apart [], multigenerational families [,], and genetically related relatives []. Based on etiology, ILDs can be divided into idiopathic forms (idiopathic interstitial pneumonia, IIP) and those with known causes, such as connective tissue diseases (CTD-ILDs) or secondary to environmental exposures, radiation, or drug use. Among the idiopathic forms, idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is the most prevalent, accounting for 20–50% of all diffuse infiltrative lung diseases. IPF is a progressive fibrosing condition that, without antifibrotic therapy, leads to respiratory failure and death within 3–5 years of diagnosis. According to guidelines, IPF diagnosis requires excluding other known causes of ILD and identifying the high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) pattern of usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP) or specific combinations of HRCT and histopathology findings from lung tissue samples. Figure 1 illustrates the classification and subdivision of ILD types and subtypes.
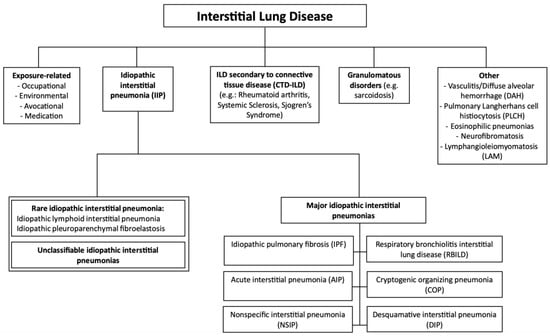
Figure 1.
Classification of interstitial lung diseases.
Within idiopathic forms of ILD, IPF can be further classified into sporadic, familial, and syndromic forms. Familial IPF (f-IPF), which accounts for 20% of IPF cases, is diagnosed when at least two biological family members exhibit the clinical and histological features of IPF. Familial pulmonary fibrosis (FPF) refers to the presence of any fibrosing ILD in two or more first- or second-degree relatives []. Familial forms tend to have an earlier onset and faster progression toward fibrosing ILD compared with sporadic cases. Among relatives with FPF, UIP is the most frequent phenotype; however, more than 50% of affected families exhibit multiple ILD phenotypes, including nonspecific interstitial pneumonia (NSIP), hypersensitivity pneumonitis (HP), and rheumatoid arthritis-associated ILD (RA-ILD) []. In contrast, sporadic IPF (s-IPF) has a multifactorial etiology, with environmental factors sometimes interacting with genetic variants.
Both idiopathic and non-idiopathic forms of ILD share a common genetic background [,,,]. Genetic mutations, occurring at frequencies below 1% in the general population, differ from common variants, which have frequencies greater than 1%. Mutations in telomere maintenance genes (telomerase reverse transcriptase [TERT], telomerase RNA component [TERC], Poly (A)-specific ribonuclease [PARN], regulator of telomere length 1 [RTEL1]) lead to telomere shortening, accelerated cellular aging, and abnormal epithelial repair [], while mutations in surfactant protein (SP)-encoding genes (SFTPA1, SFTPA2, SFTPC, ABCA3) are also implicated. On the other hand, variants in the Mucin 5 b (MUC5B) gene, which regulates mucosal defense, and the Toll-interacting protein (TOLLIP) gene also contribute to disease susceptibility. This review highlights the key genetic risk factors identified in ILDs, emphasizing the similarities and differences between idiopathic and non-idiopathic forms. Gene mutations and variants associated with ILDs are summarized in Table 1. Furthermore, epigenetic alterations, including histone modifications, DNA methylation, and non-coding RNA-mediated gene silencing, which play a significant role in ILD pathogenesis, are thoroughly examined.

Table 1.
Mutations and variants associated with interstitial lung diseases.
2. Telomere Dysfunction
Telomeres, the terminal regions of eukaryotic chromosomes, consist of tandem DNA repeats and play a vital role in the cell division cycle. During DNA replication, the inability to fully replicate the ends of chromosomes results in the progressive shortening of telomeres over time []. To mitigate this, the enzyme telomerase extends telomeres by adding repetitive DNA sequences to the chromosomal ends, thereby preserving their length []. Telomerase comprises two main subunits: telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT), which serves as the catalytic component responsible for telomere elongation, and telomerase RNA component (TERC), a non-coding RNA that provides the structural framework for the telomerase complex. Additionally, RTEL1, a DNA helicase, contributes to maintaining telomere integrity, while PARN, an enzyme involved in mRNA regulation during development, plays a critical role in sustaining telomere length in fibroblasts and facilitating the induction of pluripotent stem cells [,]; however, telomerase activity is not universally expressed. It is active in proliferating cells, such as stem cells, progenitors, and precursors, but absent in most terminally differentiated or quiescent cells, such as somatic cells [].
Mutations in telomere-related genes (TRG) can disrupt the maintenance of telomere length, resulting in progressive shortening. Once this shortening reaches a critical threshold, DNA damage occurs, leading to cellular apoptosis []. Telomere length is considered short when it falls below the 10th percentile for a given age group []. The measurement of telomere length in peripheral blood cells is often used as a proxy for detecting telomere mutations []. Notably, telomere shortening is closely linked to aging and age-related diseases, as it tends to decrease with age [,]. Mutations in TRG were initially identified in patients with dyskeratosis congenita (DKC) and later in those suffering from bone marrow failure syndromes, pulmonary fibrosis, and liver disease []. Although the exact mechanisms driving ILD pathogenesis remain unclear, there is growing evidence that telomere shortening and genetic instability—hallmarks of early cellular aging—play a key role in the fibrotic process [,]. Telomere dysfunction is thought to induce senescence and apoptosis, particularly in alveolar stem cells (alveolar epithelial type 2 cells, or AEC type 2) []. This, in turn, contributes to pulmonary fibrosis through two main pathways: first, it impairs the regeneration of functional alveolar tissue [], and second, it triggers a cytokine cascade that recruits inflammatory cells, including fibroblasts and myofibroblasts [,,].
2.1. Telomere Dysfunction in IPF and FPF
IPF accounts for more than 70% of all cases of IIPs []. IPF manifests in both sporadic and familial forms, with mutations in telomere-related genes (TRG) identified in both TRG mutations have been found in approximately 25% of f-IPF cases and 1–3% of sporadic cases []. Among familial IPF patients with telomere mutations, half have mutations in the TERT or TERC genes [], while the other half may carry mutations in other telomere-related genes such as RTEL1 or PARN. Mutations in TERT, TERC, PARN, and RTEL1 impair telomerase activity, accelerating telomere shortening (Table 1) []. Sporadic IPF is multifactorial, involving environmental risk factors that sometimes interact with variant in numerous genes. These patients show shorter blood leukocyte telomeres—ranging from 5.71% to 68.2% shorter than controls—without the presence of a clear TRG mutation. In sporadic IPF, short telomeres are associated with worse survival outcomes [], suggesting that the pathways involved in familial disease related to telomere dysfunction (even in the absence of genetic mutations) may also contribute to sporadic forms of the disease [,]. Silencing TERT expression results in telomerase inactivation []. As a result, mutations in TERT are linked to short telomere syndromes and can present a broad spectrum of clinical phenotypes []. Families with TERT mutations tend to have an earlier onset of pulmonary fibrosis, typically occurring between the ages of 60 and 70 []. In a study by Alder et al., 45 individuals from 10 families with known TRG mutations were screened. Comparisons between mutation carriers and their non-carrier first-degree relatives revealed that individuals with TRG mutations had significantly shorter telomeres (p < 0.0001) []. Despite this, identifying TRG mutations in patients with sporadic forms of idiopathic interstitial pneumonia (IIP) remains rare []. For example, Tsakari et al. identified only one hTERT mutation among 44 sporadic IPF cases []. Armanios et al. evaluated 73 families with familial pulmonary fibrosis (FPF) and found that six of them had shorter telomeres in peripheral blood leukocytes than their peers. These families also carried TERT/TERC heterozygous mutations that code for RNA ligands of the telomerase complex, expressed in an autosomal dominant pattern [,]. Mutations in RTEL1 lead to the loss of telomeric repeats, which results in telomere shortening []. Telomere lengths in RTEL1 mutation carriers are similar to those in patients with TERT or TERC mutations, particularly in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) []. Rare RTEL1 mutations have been associated with familial ILD, especially in patients with short telomeres in PBMCs []. The exact mechanism linking PARN mutations to telomere shortening remains unclear [,]. In a study by Stuart et al., leukocyte telomere lengths in participants with PARN and RTEL1 mutations were significantly shorter compared with those in unrelated kindreds (p < 0.001 for both genes) [].
2.2. Telomere Dysfunction in RA-ILD
RA is a systemic inflammatory and autoimmune disorder, with extra-articular involvement occurring in nearly 50% of patients. The lungs are frequently affected, often presenting as ILD, with the UIP pattern being the most common [,]. Despite its prevalence and significant prognostic impact, much remains unknown about the pathogenesis of RA-ILD []. ILD is one of the leading causes of mortality in RA, accounting for 10% to 20% of deaths []. In fact, mortality rates are notably higher in patients with RA-ILD compared with those without ILD []. IPF, FPF, and RA-ILD share common risk factors, including cigarette smoking and male sex [,]. Due to these shared factors, it has been hypothesized that these disorders may also share genetic risk factors, such as telomere mutations. In a groundbreaking study, Juge et al. [] conducted whole exome sequencing (WES) on patients with RA-ILD to investigate the potential involvement of FPF-linked genes. The study identified heterozygous mutations in telomere-maintenance genes in 12 out of 101 RA-ILD patients, specifically in TERT, RTEL1, and PARN. Notably, no mutations were detected in TERC []. Importantly, no other clinical manifestations related to telomere syndromes were observed in mutation carriers. Additionally, pulmonary function tests and HRCT chest scans did not show significant differences between carriers and non-carriers; however, the mean age of ILD onset was significantly earlier in patients with TRG mutations compared with those without []. These findings confirm that RA-ILD and FPF share genetic risk factors, suggesting common pathogenic pathways. In terms of telomere lengths, chromosomes isolated from circulating leukocytes in telomere-mutation carriers were significantly shorter than those in controls, highlighting the detrimental effects of these mutations on telomere maintenance. Notably, three of the twelve mutation carriers had a family history of ILD, with PARN mutation carriers exhibiting the shortest telomeres, underscoring the crucial role of PARN in telomere maintenance. Furthermore, ILD onset occurred earlier in patients with RTEL1 and TERT mutations compared with controls. These results are consistent with previous studies and support the concept of genetic anticipation, which is commonly observed in telomere-mediated disorders.
2.3. Telomere Dysfunction in Chronic HP
HP is a form of ILD that develops following repeated exposure to environmental inhalant antigens. The condition is characterized by alveolitis and granuloma formation and, in some cases, may progress to chronic fibrotic disease []. Emerging evidence suggests that telomere dysfunction plays a role in the pathogenesis and prognosis of patients with chronic HP (CHP) []; however, the mechanisms driving fibrosis in HP remain poorly understood. In a subset of CHP patients, shorter telomere lengths in peripheral blood leukocytes (PBLs) have been observed, along with the identification of rare variants in telomere-related genes (TRG) [,]. CHP patients carrying telomere mutations tend to have more severe lung fibrosis, often presenting with the UIP pattern, and experience worse survival outcomes []. Ley and colleagues investigated the prevalence of TRG mutations in patients with CHP. They analyzed two CHP cohorts to identify variants in genes such as TERT, TERC, RTEL1, and PARN. Their findings revealed that a significant number of patients were carriers of TRG variants, which was associated with shorter telomere lengths in PBLs and a markedly reduced transplant-free survival rate [].
2.4. Telomere Dysfunction in Other ILDs
In systemic sclerosis-associated ILD (SSc-ILD), telomere shortening has been directly linked to more severe pulmonary fibrosis and worse clinical outcomes, underscoring its role in disease progression []. While telomere biology in sarcoidosis is less well understood, evidence suggests that shortened telomeres may contribute to chronic granulomatous inflammation and fibrotic remodeling in advanced or progressive disease forms []. In anti-synthetase syndrome-associated ILD (ASSD-ILD) and myositis-associated ILD, although specific studies are lacking, it is plausible that telomere attrition exacerbates autoimmune-driven inflammation and fibrosis, amplifying disease severity. These findings emphasize the need for further research to clarify the role of telomere dysfunction and explore therapeutic strategies targeting telomere-related mechanisms, with the potential to address overlapping pathogenic processes and improve patient outcomes.
3. Surfactant-Related Genes
A surfactant is a complex mixture of lipids, phospholipids, fatty acids, and proteins that coats the inner surface of the alveoli. Its primary function is to reduce surface tension in the peripheral airways, thereby stabilizing the alveoli and preventing collapse during expiration. Surfactant is produced by type II pneumocytes, where its components are stored within lamellar bodies in the endoplasmic reticulum and secreted into the airways through exocytosis []. Once in the airways, a surfactant is either recycled by type II cells or catabolized by alveolar macrophages, maintaining the system’s homeostasis []. Beyond its role in maintaining alveolar stability, surfactant also serves as a key player in immune defense, regulating both immune responses and lung inflammation. Surfactant proteins constitute up to 10% of surfactant weight and include four types: SP-A1 and A2, SP-B, SP-C, and SP-D, each encoded by their respective genes—SFTPA1, SFTPA2, SFTPB, SFTPC, and SFTPD. The hydrophilic proteins SP-A and SP-D play defensive roles by interacting with various pathogens, promoting their uptake, and regulating the activity of innate and adaptive immune cells such as macrophages, dendritic cells, neutrophils, and T cells []. In contrast, the hydrophobic proteins SP-B and SP-C are involved in the mechanical functions of surfactants, with SP-B being particularly crucial for the processing of SP-C within lamellar bodies. Mutations in SFTPA1, SFTPA2, SFTPB, and SFTPC—excluding SFTPD—are recognized as monogenic causes of interstitial lung disease. SFTPB mutations are most associated with severe respiratory failure in newborns, while mutations in the other surfactant-related genes are implicated in both adult and pediatric forms of interstitial lung disease, particularly pulmonary fibrosis []. Additionally, mutations in genes involved in the transport of surfactant lipids within lamellar bodies, such as ABCA3 (ATP binding cassette subfamily A member 3), and in regulatory genes such as NKX2-1 (encoding the thyroid transcription factor 1, TTF1), which controls the transcription of surfactant proteins and ABCA3, have also been identified []; therefore, disruptions in the factors responsible for surfactant system homeostasis are now recognized as monogenic causes of interstitial lung disease [].
3.1. Mutations in SFTPC and ABCA3 in FPF
In major cohorts of patients with FPF, mutations in surfactant-related genes rank second, contributing up to 8% of genetic involvement, following telomere-related alterations. To date, at least 26 mutations in SFTPC (up to 3.6%) have been identified in FPF patients, all presenting in heterozygosity and transmitted in an autosomal dominant manner []. These mutations often manifest as single nucleotide variants, predominantly occurring in the C-terminal BRICHOS domain of the pro-protein SP-C. This domain plays a crucial role in the processing and proper folding of pro-SPC []. Such mutations have been primarily observed in unrelated children presenting with severe acute respiratory failure at birth. Among these, the I73T mutation—where threonine replaces isoleucine at codon 73—is the most well-known. In a study conducted by Bullard et al., the genomes of 325 children were analyzed, revealing 55 carriers of SFTPC mutations, 19 of whom harbored the I73T variant. This substitution was associated with a broad spectrum of respiratory manifestations, ranging from neonatal death to the onset of symptoms within a few months of life or the development of pulmonary fibrosis in the fifth to sixth decade []. In a study led by Van Moorsel, the genetic contributions of SFTPC and ABCA3 were examined in a cohort of 229 patients with IIP. Among 20 unrelated adult FPF patients, SFTPC sequencing revealed mutations in five cases, with I73T being the most frequent. Two other cases involved previously unknown mutations, M71V and IVS412. Notably, no mutations were identified in the control cohort or among patients with sporadic pulmonary fibrosis (n = 20). Furthermore, some FPF patients were found to harbor ABCA3 variants []. The ABCA3 gene encodes a protein localized to the limiting membrane of lamellar bodies, where it is essential for surfactant storage and lamellar body biogenesis. Mutations in ABCA3, such as the autosomal recessive E292V variant, result in severe neonatal acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) or adult-onset interstitial lung disease. The presence of ABCA3 mutations appears to modulate disease severity and increase penetrance in individuals with the same sporadic SFTPC mutation [].
In 2011, a study of a Japanese family spanning three generations and comprising six individuals affected by pulmonary fibrosis with a UIP pattern led to the discovery of a significant mutation in the SP-C promoter, termed G100S. This mutation was found to induce endoplasmic reticulum stress within pneumocytes, leading to apoptosis in affected individuals []. Additionally, mutations affecting the SP-C promoter have been associated with its degradation, resulting in a deficit or absence of SP-C, which likely contributes to the pathogenesis of pulmonary fibrosis [].
In contrast to familial forms of pulmonary fibrosis, the findings in sporadic cases have been less significant. A 2004 American study conducted genetic sequencing of SFTPC in 89 patients with a sporadic UIP pattern, 46 with an NSIP pattern, and 104 healthy controls. Although some genetic variants were identified in patients with IPF, only the I73T variant was found to result in a significant alteration of the surfactant protein []. Similarly, a 2007 German study analyzed SFTPC in 35 patients with sporadic IPF (25) and NSIP (10). This study identified only two allelic variants that led to the same amino acid change, yet these variants were found at comparable frequencies in healthy controls. As a result, de novo mutations in the SFTPC gene are considered rare contributors to the pathogenesis of sporadic pulmonary fibrosis [].
3.2. Mutations in SFTPA1 and SFTPA2 in IPF and FPF
Although less frequently studied, mutations in surfactant protein A (SP-A) have also been investigated (Table 1). There are two isoforms, SP-A1 and SP-A2, with mutations in SFTPA1 being associated with endoplasmic reticulum stress. This stress can trigger a cellular response to misfolded proteins, leading to apoptosis and promoting epithelial-mesenchymal transformation, ultimately contributing to the development of pulmonary fibrosis []. Mutations in the gene encoding SP-A1 have been identified in patients from three Asian families with FPF, specifically affecting exon 6 []. Additionally, Takezaki and colleagues reported a homozygous mutation in two Japanese FPF patients, which resulted in decreased secretion of SP-A and increased susceptibility to influenza virus, potentially accelerating disease progression []. Wang and colleagues identified seven variants in exon 6 of the gene encoding SP-A2 in the sequencing of SFTPA2 from individuals in two families with pulmonary fibrosis []. A Dutch group replicated this sequencing in FPF patients, who were unrelated, as well as in patients with sporadic pulmonary fibrosis, excluding those with known mutations in SFTPC and telomere-related genes. They identified three novel variants of the N210T mutation in exon 6 among three FPF patients and one patient with sporadic pulmonary fibrosis. Exon 6 appears to be a critical region for SFTPA2 mutations, as it encodes a carbohydrate recognition domain involved in pathogen defense. Similar to SFTPC, mutations in SFTPA2 seem to induce endoplasmic reticulum stress, which is also expressed in club cells [].
3.3. Mutations of SP Related Genes in RA-ILD
A multicenter French study conducted comprehensive genetic sequencing in patients with RA-ILD, focusing on genes linked to IPF, particularly SFTPC. This study identified mutations such as I73T and a mutation affecting intracellular transport in the SP-C promoter among RA patients. This study was the first to demonstrate that IPF and RA-associated ILD share common genetic mutations involved in their pathogenesis [].
3.4. Mutations of SP Related Genes in CHP
Since HP involves an abnormal immune response to inhaled antigens, it has been hypothesized that alterations in surfactant proteins, which play a key role in immune defense and regulation, may contribute to its pathogenesis; however, research in this area remains limited, with only a few studies conducted on small populations, and the available evidence is not robust. The findings primarily focus on interactions between single SNV) and haplotypes in surfactant protein genes. A notable study was conducted in a Mexican population, including 75 HP patients with known antigen exposure, 64 exposed individuals without HP, and 194 unexposed healthy controls. Seventeen SNVs in surfactant proteins were analyzed, with a specific focus on the interaction between two or three SNVs and their potential impact on the risk of developing HP []. In the one- and two-SNV models, no significant association between surfactant protein gene SNVs and HP was observed when compared with exposed controls; however, in the three-SNV model, 25 significant interactions were identified, 16 of which were associated with an increased risk of HP. Furthermore, SNV interactions in hydrophilic surfactant protein genes such as SFTPA1, SFTPA2, and SFTPD were linked to an elevated risk of HP.
In 2022, the same research group expanded their analysis by studying SNV associations in the Mexican population, aiming to compare the genetic correlations with the development of similar fibrosing patterns in pulmonary fibrosis. This study involved 84 patients with IPF and 75 with HP. Among the SNVs analyzed, three in SFTPA1 and one in SFTPB were found to be associated with a decreased risk of IPF but an increased risk of HP. Many of the SNV-SNV interactions were shared between IPF and HP, although one three-SNV interaction involving SFTPA1, SFTPA2, and SFTPD was disease-specific, being linked to a decreased risk in HP and an increased risk in IPF [].
3.5. Mutations of SP-Related Genes in Other ILDs
Although there is currently no direct evidence linking SP gene mutations to sarcoidosis, myositis-associated ILD, anti-synthetase syndrome-associated ILD, or SSc-ILD, their potential role in these conditions represents a promising avenue for future research. Indeed, mutations in SP genes disrupt surfactant production and processing, leading to alveolar epithelial cell dysfunction, endoplasmic reticulum stress, and impaired immune regulation—processes that overlap with the pathophysiology of these ILDs []. For instance, in sarcoidosis, SP dysfunction could theoretically contribute to persistent granulomatous inflammation and fibrosis. Similarly, in autoimmune-mediated ILDs, SP mutations might exacerbate chronic inflammation and fibrotic remodeling. In SSc-ILD, where alveolar epithelial injury is a hallmark, studying SP-related mechanisms could enhance understanding of fibrosis progression. While no direct associations have been identified, exploring SP gene mutations in these diseases may uncover novel insights into shared pathways of immune dysregulation and fibrosis, potentially leading to targeted therapeutic strategies.
4. MUC5B
Mucins are key components of mucus, a gel-like material composed of 97% water and 3% solids, primarily proteins, salts, and cellular debris []. The human genome contains 17 genes encoding mucins, with MUC5AC and MUC5B being the most prominently expressed in the airways []. MUC5B is located on chromosome 11 and encodes Mucin 5 subtype B, a glycoprotein secreted by submucosal glands and airway secretory cells []. This glycoprotein plays a crucial role in mucus production, mucociliary clearance, infection control, and maintaining homeostasis within the airways and lungs []. MUC5B is implicated in several pulmonary diseases, including chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), asthma, cystic fibrosis [], and severe community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) []. A specific single nucleotide variant (SNV), rs35705950, located in the MUC5B promoter, is associated with increased promoter activity, leading to MUC5B overexpression []. The excessive production of MUC5B can result in its accumulation in the distal airways, impairing mucociliary clearance. This accumulation allows inhaled particles—such as those from cigarette smoke or air pollution, both known risk factors for IPF—to persist in the lungs, contributing to tissue injury. Furthermore, MUC5B overexpression and its accumulation in the distal airways may interfere with alveolar repair mechanisms by disrupting surfactant function and impairing type II epithelial cells []. This chain of events leads to lung injury, which in turn triggers chronic fibroproliferation and the formation of honeycomb cysts, characteristic features of progressive pulmonary fibrosis [].
4.1. MUC5B in IPF and FPF
In 2011, Seibold et al. were the first to demonstrate that the T minor allele of the single nucleotide variant (SNV) rs35705950 in the promoter region of MUC5B is associated with an increased risk of developing both FPF and IPF []. The major allele of this SNV is guanine (G), while the minor allele is thymine (T) []. Subsequent studies confirmed the association between the MUC5B variant and sporadic IPF across multiple populations, including European Caucasian [,], American [], and Chinese populations [,]; however, the frequency of the T minor allele varies among different populations. While it appears to be similar between American and European cohorts [,,,], its prevalence is significantly lower in the Chinese population [] (Table 2).

Table 2.
Frequency of the T minor allele.
Notably, the risk of developing IPF in carriers of rs35705950 is dose-dependent: homozygous individuals (with two copies of the T allele, genotype TT) face a higher risk of developing IPF compared with heterozygous individuals (with one copy of the T allele, genotype GT) [,,,,] (Table 3). Moreover, Chung et al. found that the rs35705950 variant is linked to distinct HRCT patterns of fibrosis. Specifically, carriers of the T minor allele more frequently exhibit a UIP pattern with a subpleural distribution and are less likely to present ground glass opacities (GGO) compared with carriers of the G major allele [].

Table 3.
Odds Ratio for IPF based on MUC5B Variant of Allele T.
The MUC5B variant is not only a genetic risk factor for IPF but also serves as a prognostic marker. Peljto et al. demonstrated in two independent cohorts of IPF patients that individuals carrying the GT and TT genotypes had a lower risk of mortality compared with those with the GG genotype []. The longer survival associated with the T allele was further confirmed in patients receiving antifibrotic therapy, regardless of whether the T allele was present in a homozygous or heterozygous form []. Additionally, Stock et al. reported a slower decline in forced vital capacity (FVC) in IPF patients with the MUC5B variant []; however, contrasting findings were reported by Jiang and colleagues, who observed in a Chinese cohort that the T allele was associated with worse survival outcomes, along with a greater decline in FVC and Diffusion of Lung Carbon Monoxide (DLCO) [].
4.2. MUC5B in RA-ILD
In 2018, Juge et al. first demonstrated that the MUC5B promoter variant significantly increases the risk of developing ILD in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), particularly in those with a UIP pattern []. This finding was later corroborated by Palomäki et al. in a Finnish study, which reported a tenfold increase in the risk of ILD among RA patients carrying the MUC5B variant compared with the general population []. Notably, Palomäki et al. also observed an increased risk of RA itself in individuals with the MUC5B variant, a relationship not identified by Juge et al., likely due to the smaller sample size in their study []. Further insights were provided by McDermott et al., who linked the MUC5B promoter variant to early onset RA-ILD, often manifesting before or within two years of RA diagnosis []; however, the MUC5B rs35705950 variant was not associated with the rate of pulmonary function decline in RA-ILD patients [].
4.3. MUC5B in CHP
The MUC5B promoter variant is also associated with HP. A retrospective case-control study by Furusawa et al. demonstrated that common genetic risk factors for IPF, including the MUC5B variant, were also linked to the fibrotic form of HP []. Similarly, Ley et al. found that in patients with fibrotic HP, the MUC5B variant was associated with HRCT evidence of moderate-to-severe fibrosis and traction bronchiectasis []. Regarding the prognostic role of the MUC5B variant in HP patients, it has been shown that the variant is associated with poorer survival outcomes, a finding that contrasts with the survival advantage observed in IPF patients carrying the same variant []. Additionally, a recent study reported that carriers of the MUC5B minor allele had significantly lower baseline FVC, experienced a greater decline in FVC over time, and exhibited a worse response to immunosuppressive therapy compared with individuals with the GG genotype [].
4.4. MUC5B in Other ILDs
The absence of an association between the MUC5B promoter variant and SSc-ILD has been observed in several studies conducted in both UK Caucasian populations [,] and an American cohort []. The lack of association between the MUC5B rs35705950 minor allele and lung fibrosis in SSc suggests that this variant may be specific to IPF or the UIP pattern. Notably, SSc-ILD is typically characterized by an NSIP pattern, while both IPF and RA-ILD are radiologically and pathologically defined by the UIP pattern. Supporting this, studies have demonstrated that in the lungs of IPF and RA-ILD patients, MUC5B expression is localized to areas of microscopic honeycombing [,]. The MUC5B variant is also not considered a risk factor in ASSD [], myositis [], or sarcoidosis []; however, the MUC5B rs35705950 promoter variant appears to be associated with asbestosis [], potentially due to the fact that asbestosis shares radiological and pathological UIP features with IPF.
5. Toll-Interacting Protein
TOLLIP is a protein-coding gene that encodes a ubiquitin-binding protein involved in multiple aspects of the Toll-like receptor (TLR) signaling pathway. Four isoforms of TOLLIP (A, B, C, D) have been identified, with three expressed in human mononuclear cells, where they play a crucial role in innate immune responses and lung epithelial cell apoptosis. TOLLIP modulates the interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β) signaling pathway by inhibiting IRAK-1 (IL-1 receptor–associated kinase-1) autophosphorylation, promoting receptor degradation, and negatively regulating NF-kB activation [,]. Furthermore, it interferes with the release of IFN1 in respiratory tract cells. TOLLIP plays a central role in both acute and chronic inflammatory processes []. It is involved in immune-cell activation, cellular survival mechanisms, and defense against pathogens, particularly at the frontline of host defenses. Additionally, TOLLIP facilitates the clearance of damaged mitochondria through autophagosome-lysosome fusion [,]. By reducing mitochondrial reactive oxygen species and enhancing autophagy, TOLLIP suppresses mitochondrial apoptosis. As TOLLIP expression levels vary across cell types and disease stages, its downregulation accelerates apoptosis, contributing to early IPF development, while its upregulation in atypical epithelial cells drives fibrosis progression in late-stage IPF [].
In pulmonary fibrosis, molecular mediators such as IL-6, MMP-7, and TGF-β secreted by lung epithelial cells exacerbate inflammation [,,]. Given its role in inflammation regulation, autophagy, and vacuolar transport, TOLLIP is implicated in numerous pulmonary diseases, including IPF, COPD, asthma, and infectious diseases [].
TOLLIP is ubiquitously expressed in lung cells (monocytes, macrophages, T-regulatory cells, and alveolar type 1 epithelial cells) in both healthy individuals and IPF patients []. Reduced or suppressed TOLLIP expression can lead to infectious and obstructive lung diseases by interfering with these cellular groups. Additionally, TOLLIP regulation may be altered by microRNAs, particularly the down-regulation of miR-31 (a tumor suppressor) in pulmonary diseases such as IPF [].
In IPF, certain single nucleotide variants (SNVs) in the TOLLIP locus on chromosome 11 are linked to disease susceptibility and prognosis []. Specifically, the minor alleles G in SNV rs111521887, SNV rs5743894, and SNV rs5743890 correlate with reduced TOLLIP expression. The first two, in linkage disequilibrium, increase susceptibility to IPF but do not correlate with mortality, while rs5743890 appears to have a protective effect against IPF onset, although carriers exhibit a higher risk of rapid disease progression and mortality [,]. Moreover, the minor allele T of SNV rs3750920 is marginally associated with IPF susceptibility, progression, and survival, while SNV rs5743899 minor allele G is associated with other non-infectious pulmonary diseases (e.g., asthma) and infectious diseases such as tuberculosis and respiratory viral infections [].
In CHP, the TOLLIP rs5743890 minor allele does not appear to be significantly associated with disease development compared with healthy individuals; however, patients with the TOLLIP rs5743899 GG genotype, associated with lower TOLLIP transcription-translation levels, exhibited rapid declines in FVC and increased Smad2 phosphorylation and inhibitor of NF-kB activity in lung tissues. Elevated serum levels of periostin, IL-1α, IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8, TNF-α, and IFN-γ were also observed, correlating with a significant annual decline in FVC in these patients []. A study by Kubbara et al. utilizing blood samples from the International Lung Disease database at the University of Minnesota evaluated the efficacy of pirfenidone in 56 IPF patients. The findings indicated that patients with TOLLIP rs5743890 genotypes CC and CT, along with TGF-β rs1800470, had improved survival with prolonged therapy []. In a post-hoc analysis of the PHANTER-IPF clinical trial, Oldham et al. reported that N-acetylcysteine (NAC) provided benefits to IPF patients carrying the TOLLIP rs3750920 TT genotype (present in approximately 25% of IPF patients), whereas patients with the CC genotype showed an increased risk of hospitalization. Nonetheless, genotype-stratified clinical trials are required before considering the off-label use of NAC in IPF treatment []. A study on Japanese patients with ILD found that the minor allele T of rs3750920 was less frequent in Japanese IPF patients compared with the European population from the PHANTER trial. Non-IPF patients exhibited an even lower prevalence of this allele, and those carrying the minor allele demonstrated better survival rates than non-carriers []. Finally, the PRECISIONS clinical trial (Prospective Treatment Efficacy in IPF Using Genotype for NAC Selection) has shown the potential for personalized medicine in IPF treatment, using molecular techniques to identify patients who may benefit from NAC therapy. This trial is currently in phase III, and further studies are required to confirm these findings [].
The list of key studies on gene variants in ILDs, based on the updated literature, is presented in Table 4, while Table 5 provides the list of genes expressed by the different lung cell populations.

Table 4.
List of key studies on gene variants in ILDs.

Table 5.
List of genes expressed by different lung cell populations.
6. Epigenetic
In recent years, the critical role of epigenetics in regulating gene expression across various diseases has been increasingly recognized. In the context of pulmonary fibrosis, significant findings have emerged, particularly in IPF and secondary forms such as RA-ILD and SSc-ILD. Epigenetic modifications influence gene transcription by activating or silencing specific genes without altering the underlying DNA sequence. In pulmonary fibrosis, these modifications primarily affect genes encoding proteins involved in fibrogenesis signaling pathways [].
Environmental factors, developmental processes, and aging are known to trigger these epigenetic changes. Among environmental influences, exposure to inhalants has been strongly linked to the development of IPF, with cigarette smoke being the most prominent risk factor for both IPF and FPF [].
The main epigenetic modifications observed in pulmonary fibrosis include DNA methylation, histone modifications, and the regulation of gene expression by non-coding RNAs, such as microRNAs and long non-coding RNAs [].
6.1. DNA Methylation
DNA methylation occurs at cytosine–guanine (C-G) sites, predominantly located in gene promoter regions, through the action of DNA methyltransferases (DNMTs), which add a methyl group to cytosine. This process leads to chromatin condensation, preventing the binding of the RNA polymerase complex to the promoter, thereby silencing gene expression. The degree of chromatin condensation induced by DNA methylation is directly linked to varying levels of gene expression. In general, hypermethylation of the promoter reduces target gene expression, while hypomethylation results in increased expression []. In IPF, genome-wide methylation studies have identified differentially methylated regions (DMRs) that are absent in healthy controls. These DMRs can be located within or outside the promoter regions of certain genes. Among the most studied genes are MUC5B, prostaglandin E receptor 2 (PTGER2), and THY1 cell surface antigen [].
The MUC5B gene contains a highly conserved enhancer region, including the genetic variant rs35705950, which appears differentially methylated. This enhancer plays a crucial role in regulating MUC5B expression by dynamically binding the transcription factor FOXA2 and RNA polymerase II. Increased methylation of this enhancer region is associated with elevated MUC5B expression and the presence of the T allele at rs35705950, contributing to an increased risk of IPF []. Similarly, the PTGER2 promoter, which encodes the PGE2 receptor, has been found to be hypermethylated in IPF, leading to a reduction in PGE2 receptor expression. This results in resistance to prostaglandin E2, a molecule that normally regulates fibroblast homeostasis and apoptosis []. The THY1 promoter, which encodes a differentiation antigen of thymocytes, is also hypermethylated in IPF fibroblasts, leading to a loss of Thy-1 expression and abnormal myofibroblast differentiation [,]. Notably, Robinson and colleagues demonstrated that this process also occurs in healthy fibroblasts under hypoxic conditions [].
Another molecular study identified additional significant DMRs in IPF involving genes such as CXCL10, CCL2, FOXP1, and miR21 []. In the context of FPF, the role of DNA methylation remains poorly understood; however, there is evidence suggesting that environmental exposure can influence the methylation of specific genes, potentially contributing to disease development in genetically predisposed individuals with FPF [].
To date, there is no evidence supporting the involvement of this epigenetic mechanism in secondary forms of interstitial lung disease.
6.2. Histone Modifications
Histone modifications, such as DNA methylation, induce changes in chromatin conformation, resulting in varying levels of gene expression. Among these modifications, acetylation is particularly significant. It involves the addition of an acetyl group to the N-terminal acetyl-CoA of histones, leading to a relaxed chromatin state known as euchromatin, which permits gene transcription. In contrast, deacetylation, mediated by histone deacetylase (HDAC) enzymes, compacts chromatin into heterochromatin, thereby preventing gene expression.
In IPF, a marked imbalance in HDAC enzyme activity has been observed in the affected cells. Specifically, an abnormal increase in HDAC expression, particularly in classes I and II, has been detected in fibroblasts/myofibroblasts and bronchial basal cells. Conversely, alveolar type II epithelial cells show a depletion of HDAC enzymes attributable to endoplasmic reticulum stress, senescence, and apoptosis []. Key enzymatic alterations in IPF include upregulation of EP300, a histone acetyltransferase involved in cell proliferation and differentiation []; reduced activity of acetyltransferases (HATs), leading to decreased prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) expression due to diminished COX2 expression []; and reduced acetylation of histones H3 and H4 at the Thy-1 promoter, resulting in gene silencing, as well as at the Fas promoter, contributing to fibroblast resistance to apoptosis [].
6.3. miRNAs
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are non-coding RNAs composed of 15–27 nucleotides that bind to the 3′ end of messenger RNAs (mRNAs), leading to their inhibition or degradation and resulting in gene silencing. Each miRNA can regulate multiple genes, and each gene can be influenced by several miRNAs. In epigenetic studies on IPF, it has been shown that miRNAs can be differentially up- or downregulated during fibrogenesis, modulating key signaling pathways, such as the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) pathways (both Smad-dependent and non-Smad-dependent), the TGF-beta signaling pathway, the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway, and the PI3K-Akt pathway. Consequently, miRNAs can be categorized as either profibrotic or antifibrotic based on their activity []. In IPF, the most relevant overexpressed miRNAs include miR-21, miR-199-5p, miR-200c, and miR-34, while miR-29, miR-31, let-7a, and let-7d are downregulated [,]. Of these, miR-21 stands out as the primary profibrotic miRNA, with its expression directly induced by TGF-beta. It facilitates the EMT process and collagen deposition by inhibiting Smad7 in the Smad2/3 fibrotic pathway.
Among the antifibrotic miRNAs, the miR-29 family is the most significant, and its downregulation in IPF promotes fibrogenesis. These miRNAs play a role in apoptosis regulation and control of collagen and extracellular matrix (ECM) gene expression. Given that both miR-21 and miR-29 exert their effects primarily on fibroblasts by targeting Smad3, it has been hypothesized that the balance between these two miRNAs may decisively influence pulmonary fibrogenesis []. Elevated serum levels of specific miRNAs have been identified in IPF, with miR-21-5p being particularly relevant. This miRNA is associated with increased lung damage, reflected in altered FVC and radiological deterioration, particularly in rapidly progressing IPF [,,,]. In progressive forms of IPF, lung biopsy studies have identified overexpression of miR-302c, miR-423-5p, miR-210, miR-376c, and miR-185, which are linked to rapid disease progression, while lower levels of miR-423-3p are observed in more stable cases [,]; however, it is important to note that most studies have not focused on fibrotic foci, which are central to the pathogenesis of IPF. In a study by Sabater and colleagues, miRNA expression in fibrotic foci was compared with that in fibroblast cultures and IPF-affected lung tissue. The results revealed significant differences and some overlap in the composition of miRNAs [].
Dissimilar to IPF, few studies have investigated miRNAs in familial forms of pulmonary fibrosis (FPF). It is hypothesized that miRNAs, along with environmental exposures, may influence the onset and severity of pulmonary fibrosis in genetically predisposed individuals with FPF []. In secondary forms of pulmonary fibrosis, miRNAs have been extensively studied in systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease (SSc-ILD). Comparisons between IPF and SSc-ILD have identified similarities, such as the overexpression of miR-21-5p and miR-92a-3p (profibrotic) and the downregulation of the miR-29 family, miR-26a-5p, and let-7d-5p (antifibrotic) [,]. In patients with SSc-ILD, elevated levels of miR-200c have been detected in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs), particularly in those with more severe fibrotic patterns, suggesting a potential prognostic role for this miRNA []. Additionally, miRNA-320a appears to regulate type I collagen expression. It is downregulated in the serum and PBMCs of patients with SSc-ILD but is upregulated by TGF-beta []. In RA-ILD, studies have shown significantly higher plasma levels of hsa-miR-214-5p and hsa-miR-7-5p in patients with RA-ILD compared with those with RA without ILD. This association is exclusive to patients with a UIP radiological pattern, and dissimilar to IPF patients, no increase in miR-21 levels was observed in RA-ILD patients [].
6.4. Long Non-Coding RNAs (LncRNAs)
Among non-coding RNAs, long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) play a crucial role in mediating RNA–RNA, RNA–protein, and RNA–DNA interactions, as well as in regulating gene expression at both the transcriptional and post-transcriptional levels. LncRNAs are classified based on their proximity to protein-coding genes and their regulatory functions. Specifically, lncRNAs are categorized as cis if they regulate the expression of nearby genes and trans if they leave the transcriptional site and perform their function elsewhere within the cell. LncRNAs can also induce direct modifications, such as phosphorylation, or act as competitive inhibitors of specific miRNAs, thereby regulating the expression of their target genes []. In pulmonary fibrosis, several studies, some ongoing, have revealed promising results, particularly in IPF and SSc-ILD. In IPF, the two most studied lncRNAs involved in the fibrogenesis process are DNM3OS and FENDRR [].
DNM3OS is a fibroblast-specific lncRNA that regulates the activation of myofibroblasts induced by TGF-beta through certain profibrotic miRNAs, including miR-199a-5p/3p and miR-214-3p, within both Smad-dependent and non-Smad-dependent TGF-beta signaling pathways []. Conversely, FENDRR is a lncRNA that is downregulated in IPF fibroblasts and functions to inhibit fibroblast activation through multiple mechanisms, including reducing iron concentration by interacting with IRP1 and competing with miR-214, a known profibrotic miRNA []. In SSc, lncRNAs have been observed to modulate various pathogenetic phases, particularly the fibrotic phase. Among the lncRNAs studied, those most noteworthy for their roles in fibrogenesis include TSIX, H19X, HOTAIR, CTBP1, AGAP1, and ncRNA00201. TSIX influences chromatin remodeling and gene silencing, thereby affecting the expression of genes involved in extracellular matrix production. H19X contributes to fibrogenesis by acting as a molecular sponge for microRNAs that suppress pro-fibrotic pathways, leading to increased fibroblast activation and collagen synthesis. HOTAIR facilitates fibrosis by recruiting polycomb repressive complex 2 (PRC2) to target genes, inducing epigenetic modifications that promote myofibroblast differentiation. CTBP1 and AGAP1 regulate transcription factors and signaling pathways critical for fibroblast proliferation and extracellular matrix deposition, while ncRNA00201 interacts with pro-fibrotic signaling cascades, such as TGF-β, to amplify the fibrotic response [].
7. Conclusions
Genetics and epigenetics have significantly advanced our understanding of the etiology and progression of both idiopathic and non-idiopathic ILDs. Key genetic factors, such as TRG mutations, SP variants, and the MUC5B promoter variant, have been linked to disease susceptibility, earlier onset, and more severe prognoses. These genetic pathways often intersect with epigenetic modifications, further modulating disease risk, and prognosis through environmental triggers. Despite these advancements, there remains no universally accepted genetic panel to guide the identification of relevant mutations in individuals with a family history of pulmonary fibrosis, and the impact of these genetic factors on treatment responses is largely unexplored. Addressing this gap represents a critical area for future research. Understanding how these genetic and epigenetic alterations influence therapeutic outcomes has the potential to drive the development of precision medicine approaches, ultimately improving individualized care and outcomes for ILD patients.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization and supervision, S.C.; data curation, E.M., O.N, L.P., L.R. and M.G.T.; writing original draft, S.C., E.M., O.N., L.P., L.R. and M.G.T.; writing, review and editing, S.C., A.V.S., G.R., D.A., F.G., B.B., E.C. and R.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The realization of this project produced as part of the research program at Experimental Pneumology, University of Modena and Reggio Emilia (www.experimentalpneumology.unimore.it) was carried out within the framework of the HEAL Italia project funded by the PNRR. The research leading to these results has received funding from the European Union-NextGenerationEU through the Italian Ministry of University and Research under PNRR-M4C2-l1.3 Project PE_00000019 “HEAL ITALIA” to prof. Enrico Clini, CUP E93C22001860006. The views and opinions expressed are those of the authors only and do not necessarily reflect those of the European Union or the European Commission. Neither the European Union nor the European Commission can be held responsible for them.
Acknowledgments
We thank “Federazione Italiana Malattie dell’Apparato Respiratorio (FIMARP), AMA Fuori dal Buio, Modena Golf Country Club, AMMI (Associazione Mogli di Medici Italiani), Gruppo Cremonini and B-PER Banca for the valuable contribution.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Maher, T.M. Interstitial Lung Disease: A Review. JAMA 2024, 331, 1655–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travis, W.D.; Costabel, U.; Hansell, D.M.; King, T.E.; Lynch, D.A.; Nicholson, A.G.; Ryerson, C.J.; Ryu, J.H.; Selman, M.; Wells, A.U.; et al. An official American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society statement: Update of the international multidisciplinary classification of the idiopathic interstitial pneumonias. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 188, 733–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirelli, C.; Pesenti, C.; Miozzo, M.; Mondoni, M.; Fontana, L.; Centanni, S. The Genetic and Epigenetic Footprint in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis and Familial Pulmonary Fibrosis: A State-of-the-Art Review. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molyneaux, P.L.; Maher, T.M. The role of infection in the pathogenesis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2013, 22, 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spagnolo, P.; Grunewald, J.; Du Bois, R.M. Genetic determinants of pulmonary fibrosis: Evolving concepts. Lancet Respir. Med. 2014, 2, 416–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kropski, J.A. Familial Interstitial Lung Disease. Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 41, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juge, P.A.; Lee, J.S.; Ebstein, E.; Furukawa, H.; Dobrinskikh, E.; Gazal, S.; Kannengiesser, C.; Ottaviani, S.; Oka, S.; Tohma, S.; et al. MUC5B Promoter Variant and Rheumatoid Arthritis with Interstitial Lung Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 2209–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borie, R.; Kannengiesser, C.; Antoniou, K.; Bonella, F.; Crestani, B.; Fabre, A.; Froidure, A.; Galvin, L.; Griese, M.; Grutters, J.C.; et al. European Respiratory Society statement on familial pulmonary fibrosis. Eur. Respir. J. 2023, 61, 2201383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juge, P.A.; Borie, R.; Kannengiesser, C.; Gazal, S.; Revy, P.; Wemeau-Stervinou, L.; Debray, M.P.; Ottaviani, S.; Marchand-Adam, S.; Nathan, N.; et al. Shared genetic predisposition in rheumatoid arthritis-interstitial lung disease and familial pulmonary fibrosis. Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 49, 1602314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ley, B.; Newton, C.A.; Arnould, I.; Elicker, B.M.; Henry, T.S.; Vittinghoff, E.; Golden, J.A.; Jones, K.D.; Batra, K.; Torrealba, J.; et al. The MUC5B promoter polymorphism and telomere length in patients with chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis: An observational cohort-control study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2017, 5, 639–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platenburg, M.G.J.P.; Wiertz, I.A.; van der Vis, J.J.; Crestani, B.; Borie, R.; Dieude, P.; Kannengiesser, C.; Burgers, J.A.; Grutters, J.C.; van Moorsel, C.H.M. The MUC5B promoter risk allele for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis predisposes to asbestosis. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 55, 1902361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podolanczuk, A.J.; Thomson, C.C.; Remy-Jardin, M.; Richeldi, L.; Martinez, F.J.; Kolb, M.; Raghu, G. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: State of the art for 2023. Eur. Respir. J. 2023, 61, 2200957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz de Leon, A.; Cronkhite, J.T.; Katzenstein, A.L.A.; Godwin, J.D.; Raghu, G.; Glazer, C.S.; Rosenblatt, R.L.; Girod, C.E.; Garrity, E.R.; Xing, C.; et al. Telomere lengths, pulmonary fibrosis and telomerase (TERT) Mutations. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greider, C.W.; Blackburn, E.H. Identification of a Specific Telomere Terminal Transferase Activity in Tetrahymena Extracts. Cell 1985, 43, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Funk, W.D.; Wang, S.S.; Weinrich, S.L.; Avilion, A.A.; Chiu, C.P.; Adams, R.R.; Chang, E.; Allsopp, R.C.; Yu, J.; et al. The RNA Component of Human Telomerase. Science 1995, 269, 1236–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blasco, M.A.; Rizen, M.; Greider, C.W.; Hanahan, D. Differential regulation of telomerase activity and telomerase RNA during multi-stage tumorigenesis. Nat. Genet. 1996, 12, 200–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Batenburg, A.A.; Kazemier, K.M.; van Oosterhout, M.F.M.; van der Vis, J.J.; Grutters, J.C.; Goldschmeding, R.; van Moorsel, C.H.M. Telomere shortening and dna damage in culprit cells of different types of progressive fibrosing interstitial lung disease. ERJ Open Res. 2021, 7, 00691–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spagnolo, P.; Lee, J.S. Recent advances in the genetics of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2023, 29, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alder, J.K.; Chen, J.J.L.; Lancaster, L.; Danoff, S.; Su, S.C.; Cogan, J.D.; Vulto, I.; Xie, M.; Qi, X.; Tuder, R.M.; et al. Short telomeres are a risk factor for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 13051–13056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackburn, E.H.; Epel, E.S.; Lin, J. Human telomere biology: A contributory and interactive factor in aging, disease risks, and protection. Science 2015, 350, 1193–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, K.J.; Vasu, V.; Griffin, D.K. Telomere biology and human phenotype. Cells 2019, 8, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, F.J.; Collard, H.R.; Pardo, A.; Raghu, G.; Richeldi, L.; Selman, M.; Swigris, J.; Taniguchi, H.; Wells, A.U. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selman, M.; López-Otín, C.; Pardo, A. Age-driven developmental drift in the pathogenesis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Eur. Respir. J. 2016, 48, 538–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Xu, L.; Cong, Y.S. Telomere dysfunction in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 739810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Yu, Y.; Huang, H.; Hu, Y.; Fu, S.; Wang, Z.; Shi, M.; Zhao, X.; Yuan, J.; Li, J.; et al. Progressive pulmonary fibrosis is caused by elevated mechanical tension on alveolar stem cells. Cell 2020, 180, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amsellem, V.; Gary-Bobo, G.; Marcos, E.; Maitre, B.; Chaar, V.; Validire, P.; Stern, J.B.; Noureddine, H.; Sapin, E.; Rideau, D.; et al. Telomere dysfunction causes sustained inflammation in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 184, 1358–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alder, J.K.; Barkauskas, C.E.; Limjunyawong, N.; Stanley, S.E.; Kembou, F.; Tuder, R.M.; Hogan, B.L.M.; Mitzner, W.; Armanios, M. Telomere dysfunction causes alveolar stem cell failure. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 5099–5104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, P.; Li, S.; Chen, H. Macrophages in lung injury, repair and fibrosis. Cells 2021, 10, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Travis, W.D.; King, T.E.; Bateman, E.D.; Lynch, D.A.; Capron, F.; Center, D.; Colby, T.V.; Cordier, J.F.; DuBois, R.M.; Galvin, J.; et al. American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society International Multidisciplinary Consensus Classification of the Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 165, 277–304. [Google Scholar]
- Kannengiesser, C.; Borie, R.; Ménard, C.; Réocreux, M.; Nitschké, P.; Gazal, S.; Mal, H.; Taillé, C.; Cadranel, J.; Nunes, H.; et al. Heterozygous RTEL1 mutations are associated with familial pulmonary fibrosis. Eur. Respir. J. 2015, 46, 474–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armanios, M.Y.; Chen, J.J.L.; Cogan, J.D.; Alder, J.K.; Ingersoll, R.G.; Markin, C.; Lawson, W.E.; Xie, M.; Vulto, I.; Phillips 3rd, J.A.; et al. Telomerase mutations in families with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 356, 1317–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stuart, B.D.; Lee, J.S.; Kozlitina, J.; Noth, I.; Devine, M.S.; Glazer, C.S.; Torres, F.; Kaza, V.; Girod, C.E.; Jones, K.D.; et al. Effect of telomere length on survival in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: An observational cohort study with independent validation. Lancet Respir. Med. 2014, 2, 557–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Planas-Cerezales, L.; Arias-Salgado, E.G.; Buendia-Roldán, I.; Montes-Worboys, A.; López, C.E.; Vicens-Zygmunt, V.; Hernaiz, P.L.; Sanuy, R.L.; Leiro-Fernandez, V.; Vilarnau, E.B.; et al. Predictive factors and prognostic effect of telomere shortening in pulmonary fibrosis. Respirology 2019, 24, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsakiri, K.D.; Cronkhite, J.T.; Kuan, P.J.; Xing, C.; Raghu, G.; Weissler, J.C.; Rosenblatt, R.L.; Shay J., W.; Garcia, C.K. Adult-onset pulmonary fibrosis caused by mutations in telomerase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 7552–7557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulaner, G.A.; Hu, J.F.; Vu, T.H.; Giudice, L.C.; Hoffman, A.R. Telomerase activity in human development is regulated by human telomerase reverse transcriptase (hTERT) transcription and by alternate splicing of hTERT transcripts. Cancer Res. 1998, 58, 4168–4172. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Armanios, M.; Chen, J.L.; Chang, Y.P.C.; Brodsky, R.A.; Hawkins, A.; Griffin, C.A.; Eshleman, J.R.; Cohen, A.R.; Chakravarti, A.; Hamosh, A.; et al. Haploinsufficiency of telomerase reverse transcriptase leads to anticipation in autosomal dominant dyskeratosis congenita. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 15960–15964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newton, C.A.; Batra, K.; Torrealba, J.; Kozlitina, J.; Glazer, C.S.; Aravena, C.; Meyer, K.; Raghu, G.; Collard, H.R.; Garcia, C.K. Telomere-related lung fibrosis is diagnostically heterogeneous but uniformly progressive. Eur. Respir. J. 2016, 48, 1710–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cogan, J.D.; Kropski, J.A.; Zhao, M.; Mitchell, D.B.; Rives, L.; Markin, C.; Garnett, E.T.; Montgomery, K.H.; Mason, W.R.; McKean, D.F.; et al. Rare variants in RTEL1 are associated with familial interstitial pneumonia. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 191, 646–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vannier, J.B.; Pavicic-Kaltenbrunner, V.; Petalcorin, M.I.R.; Ding, H.; Boulton, S.J. RTEL1 dismantles T loops and counteracts telomeric G4-DNA to maintain telomere integrity. Cell 2012, 149, 795–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vannier, J.B.; Sarek, G.; Boulton, S.J. RTEL1: Functions of a disease-associated helicase. Trends Cell Biol. 2014, 24, 416–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dehlin, E.; Wormington, M.; Körner, C.G.; Wahle, E. Cap-dependent deadenylation of mRNA. EMBO J. 2000, 19, 1079–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, D.H.; Segal, M.; Boyraz, B.; Guinan, E.; Hofmann, I.; Cahan, P.; Tai, A.K.; Agarwal, S. Poly(A)-specific ribonuclease (PARN) mediates 3′-end maturation of the telomerase RNA component. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 1482–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stuart, B.D.; Choi, J.; Zaidi, S.; Xing, C.; Holohan, B.; Chen, R.; Choi, M.; Dharwadkar, P.; Torres, F.; Girod, C.E.; et al. Exome sequencing links mutations in PARN and RTEL1 with familial pulmonary fibrosis and telomere shortening. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 512–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turesson, C.; O’Fallon, W.M.; Crowson, C.S.; Gabriel, S.E.; Matteson, E.L. Occurrence of extraarticular disease manifestations is associated with excess mortality in a community-based cohort of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J. Rheumatol. 2002, 29, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.J.; Collard, H.R.; King, T.E. Rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease: The relevance of histopathologic and radiographic pattern. Chest 2009, 136, 1397–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doyle, T.J.; Lee, J.S.; Dellaripa, P.F.; Lederer, J.A.; Matteson, E.L.; Fischer, A.; Ascherman, D.P.; Glassberg, M.K.; Ryu, J.H.; Danoff, S.K.; et al. A roadmap to promote clinical and translational research in rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease. Chest 2014, 145, 454–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bongartz, T.; Nannini, C.; Medina-Velasquez, Y.F.; Achenbach, S.J.; Crowson, C.S.; Ryu, J.H.; Vassallo, R.; Gabriel, S.E.; Matteson, E.L. Incidence and mortality of interstitial lung disease in rheumatoid arthritis: A population-based study. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 1583–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assayag, D.; Lubin, M.; Lee, J.S.; King, T.E.; Collard, H.R.; Ryerson, C.J. Predictors of mortality in rheumatoid arthritis-related interstitial lung disease. Respirology 2014, 19, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, C.A.; Saravanan, V.; Nisar, M.; Arthanari, S.; Woodhead, F.A.; Price-Forbes, A.N.; Dawson, J.; Sathi, N.; Ahmad, Y.; Koduri, G.; et al. Rheumatoid arthritis-related interstitial lung disease: Associations, prognostic factors and physiological and radiological characteristics—A large multicentre UK study. Rheumatology 2014, 53, 1676–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouros, D.; Tzouvelekis, A. Telomeropathy in chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 200, 1086–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ley, B.; Torgerson, D.G.; Oldham, J.M.; Adegunsoye, A.; Liu, S.; Li, J.; Elicker, B.M.; Henry, T.S.; Golden, J.A.; Jones, K.D.; et al. Rare protein-altering telomere-related gene variants in patients with chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 200, 1154–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Chung, M.P.; Ley, B.; French, S.; Elicker, B.M.; Fiorentino, D.F.; Chung, L.S.; Boin, F.; Wolters, P.J. Peripheral blood leucocyte telomere length is associated with progression of interstitial lung disease in systemic sclerosis. Thorax 2021, 76, 1186–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Hao, Z.; Chen, Q.; Liu, X.; Wu, W.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, F. Casual effects of telomere length on sarcoidosis: A bidirectional Mendelian randomization analysis. Front. Med. 2024, 11, 1408980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Moorsel, C.H.M.; van der Vis, J.J.; Grutters, J.C. Genetic disorders of the surfactant system: Focus on adult disease. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2021, 30, 200085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitsett, J.A.; Wert, S.E.; Weaver, T.E. Alveolar surfactant homeostasis and the pathogenesis of pulmonary disease. Annu. Rev. Med. 2010, 61, 105–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, J.R. Immunoregulatory functions of surfactant proteins. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 5, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markart, P.; Ruppert, C.; Wygrecka, M.; Schmidt, R.; Korfei, M.; Harbach, H.; Theruvath, I.; Pison, U.; Seeger, W.; Guenther, A.; et al. Surfactant protein C mutations in sporadic forms of idiopathic interstitial pneumonias. Eur. Respir. J. 2006, 29, 134–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bullard, J.E.; Nogee, L.M. Heterozygosity for ABCA3 mutations modifies the severity of lung disease associated with a surfactant protein C gene (SFTPC) mutation. Pediatr. Res. 2007, 62, 176–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Moorsel, C.H.M.; van Oosterhout, M.F.M.; Barlo, N.P.; de Jong, P.A.; van der Vis, J.J.; Ruven, H.J.T.; van Es, H.W.; van den Bosch, J.M.M.; Grutters, J.C. Surfactant protein C mutations are the basis of a significant portion of adult familial pulmonary fibrosis in a Dutch cohort. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2010, 182, 1419–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, S.; Tanaka, T.; Ishida, M.; Kinoshita, A.; Fukuoka, J.; Takaki, M.; Sakamoto, N.; Ishimatsu, Y.; Kohno, S.; Hayashi, T.; et al. Surfactant protein C G100S mutation causes familial pulmonary fibrosis in Japanese kindred. Eur. Respir. J. 2011, 38, 861–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawson, W.E.; Grant, S.W.; Ambrosini, V.; Womble, K.E.; Dawson, E.P.; Lane, K.B.; Markin, C.; Renzoni, E.; Lympany, P.; Thomas, A.Q.; et al. Genetic mutations in surfactant protein C are a rare cause of sporadic cases of IPF. Thorax 2004, 59, 977–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, D.; Gao, R.; Xue, Q.; Luan, R.; Yang, J. Genomic fingerprint associated with familial idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A review. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2023, 20, 329–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doubková, M.; Staňo Kozubík, K.; Radová, L.; Pešová, M.; Trizuljak, J.; Pál, K.; Svobodová, K.; Réblová, K.; Svozilová, H.; Vrzalová, Z.; et al. A novel germline mutation of the SFTPA1 gene in familial interstitial pneumonia. Hum. Genome Var. 2019, 6, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takezaki, A.; Tsukumo, S.; Setoguchi, Y.; Ledford, J.G.; Goto, H.; Hosomichi, K.; Uehara, H.; Nishioka, Y.; Yasutomo, K. A homozygous SFTPA1 mutation drives necroptosis of type II alveolar epithelial cells in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. J. Exp. Med. 2019, 216, 2724–2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Kuan, P.J.; Xing, C.; Cronkhite, J.T.; Torres, F.; Rosenblatt, R.L.; DiMaio, J.M.; Kinch, L.N.; Grishin, N.V.; Garcia, C.K. Genetic defects in surfactant protein A2 are associated with pulmonary fibrosis and lung cancer. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2009, 84, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Moorsel, C.H.M.; ten Klooster, L.; van Oosterhout, M.F.M.; de Jong, P.A.; Adams, H.; Wouter van Es, H.; Ruven, H.J.T.; van der Vis, J.J.; Grutters, J.C. SFTPA2 mutations in familial and sporadic idiopathic interstitial pneumonia. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 192, 1249–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, C.K.; Chen, C.; Amatya, S.; Yang, L.; Fu, C.; Zhou, S.; Wu, R.; Buendia-Roldan, I.; Selman, M.; Pardo, A.; et al. SNP and haplotype interaction models reveal association of surfactant protein gene polymorphisms with hypersensitivity pneumonitis of Mexican population. Front. Med. 2021, 7, 588404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbasi, A.; Chen, C.; Gandhi, C.K.; Wu, R.; Pardo, A.; Selman, M.; Floros, J. Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP) and SNP-SNP interactions of the surfactant protein genes are associated with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis in a Mexican study group; Comparison with hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 842745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fahy, J.V.; Dickey, B.F. Airway mucus function and dysfunction. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 2233–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, M.G.; Livraghi-Butrico, A.; Fletcher, A.A.; McElwee, M.M.; Evans, S.E.; Boerner, R.M.; Alexander, S.N.; Bellinghausen, L.K.; Song, A.S.; Petrova, Y.M.; et al. Muc5b is required for airway defence. Nature 2014, 505, 412–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, O.W.; Sharafkhaneh, A.; Kim, V.; Dickey, B.F.; Evans, C.M. Airway mucus: From production to secretion. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2006, 34, 527–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, L.; Lu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Y.; Sun, H.; Zhang, J. Respiratory MUC5B disproportion is involved in severe community-acquired pneumonia. BMC Pulm. Med. 2022, 22, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakano, Y.; Yang, I.V.; Walts, A.D.; Watson, A.M.; Helling, B.A.; Fletcher, A.A.; Lara, A.R.; Schwarz, M.I.; Evans, C.M.; Schwartz, D.A. MUC5B promoter variant rs35705950 affects MUC5B expression in the distal airways in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 193, 464–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seibold, M.A.; Wise, A.L.; Speer, M.C.; Steele, M.P.; Brown, K.K.; Loyd, J.E.; Fingerlin, T.E.; Zhang, W.; Gudmundsson, G.; Groshong, S.D.; et al. A common MUC5B promoter polymorphism and pulmonary fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 1503–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biondini, D.; Cocconcelli, E.; Bernardinello, N.; Lorenzoni, G.; Rigobello, C.; Lococo, S.; Castelli, G.; Baraldo, S.; Cosio, M.G.; Gregori, D.; et al. Prognostic role of MUC5B rs35705950 genotype in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) on antifibrotic treatment. Respir. Res. 2021, 22, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stock, C.J.; Sato, H.; Fonseca, C.; Banya, W.A.S.; Molyneaux, P.L.; Adamali, H.; Russel, A.M.; Denton, C.P.; Abraham, D.J.; Hansell, D.M.; et al. Mucin 5B promoter polymorphism is associated with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis but not with development of lung fibrosis in systemic sclerosis or sarcoidosis. Thorax 2013, 68, 436–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borie, R.; Crestani, B.; Dieude, P.; Nunes, H.; Allanore, Y.; Kannengiesser, C.; Airo, P.; Matucci-Cerinic, M.; Wallaert, B.; Israel-Biet, D.; et al. The MUC5B variant is associated with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis but not with systemic sclerosis interstitial lung disease in the European Caucasian population. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Noth, I.; Garcia, J.G.N.; Kaminski, N. A variant in the promoter of MUC5B and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 1576–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Zhuang, Y.; Guo, W.; Cao, L.; Zhang, H.; Xu, L.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, D.; Wang, Y. Mucin 5B promoter polymorphism is associated with susceptibility to interstitial lung diseases in Chinese males. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e104919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Hu, Y.; Shang, L.; Li, Y.; Yang, L.; Chen, Y. Association between MUC5B polymorphism and susceptibility and severity of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 14953–14958. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Li, W.; Luo, Z.; Chen, Y. The minor T allele of the MUC5B promoter rs35705950 associated with susceptibility to idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 24007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, J.H.; Peljto, A.L.; Chawla, A.; Talbert, J.L.; McKean, D.F.; Rho, B.H.; Fingerlin, T.E.; Schwarz, M.I.; Schwartz, D.A.; Lynch, D.A. CT imaging phenotypes of pulmonary fibrosis in the MUC5B promoter site polymorphism. Chest 2016, 149, 1215–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peljto, A.L.; Zhang, Y.; Fingerlin, T.E.; Ma, S.-F.; Garcia, J.G.N.; Richards, T.J.; Richards, T.J.; Silveira, L.J.; Lindell, K.O.; Steele, M.P.; et al. Association between the MUC5B promoter polymorphism and survival in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. JAMA 2013, 309, 2232–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomäki, A.; Palotie, A.; Koskela, J.; Eklund, K.K.; Pirinen, M.; Ripatti, S.; Laitinen, T.; Mars, N. Lifetime risk of rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease in MUC5B mutation carriers. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2021, 80, 1530–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDermott, G.; Gill, R.; Gagne, S.; Byrne, S.; Huang, W.; Cui, J.; Prisco, L.; Zaccardelli, A.; Martin, L.; Kronzer, V.L.; et al. Associations of the MUC5B promoter variant with timing of interstitial lung disease and rheumatoid arthritis onset. Rheumatology 2022, 61, 4915–4923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juge, P.A.; Solomon, J.J.; van Moorsel, C.H.M.; Garofoli, R.; Lee, J.S.; Louis-Sydney, F.; Rojas-Serrano, J.; González-Pérez, M.I.; Mejia, M.; Buendia-Roldán, I.; et al. MUC5B promoter variant rs35705950 and rheumatoid arthritis associated interstitial lung disease survival and progression. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2021, 51, 996–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furusawa, H.; Peljto, A.L.; Walts, A.D.; Cardwell, J.; Molyneaux, P.L.; Lee, J.S.; Fernández Pérez, E.R.; Wolters, P.J.; Yang, I.V.; Schwartz, D.A. Common idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis risk variants are associated with hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Thorax 2022, 77, 508–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewandowska, K.B.; Szturmowicz, M.; Lechowicz, U.; Franczuk, M.; Błasińska, K.; Falis, M.; Błaszczyk, K.; Sobiecka, M.; Wyrostkiewicz, D.; Siemion-Szcześniak, I.; et al. The presence of T allele (rs35705950) of the MUC5B gene predicts lower baseline forced vital capacity and its subsequent decline in patients with hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Mejías, R.; Remuzgo-Martínez, S.; Genre, F.; Pulito-Cueto, V.; Rozas, S.M.F.; Llorca, J.; Fernández, D.I.; Cuesta, V.M.M.; Ortego-Centeno, N.; Gómez, N.P.; et al. Influence of MUC5B gene on antisynthetase syndrome. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, C.; Rosen, P.; Lloyd, T.; Horton, M.; Christopher-Stine, L.; Oddis, C.V.; Mammen, A.L.; Danoff, S.K. Exploration of the MUC5B promoter variant and ILD risk in patients with autoimmune myositis. Respir. Med. 2017, 130, 52–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burns, K.; Clatworthy, J.; Martin, L.; Martinon, F.; Plumpton, C.; Maschera, B.; Lewis, A.; Ray, K.; Tschopp, J.; Volpe, F. Tollip, a new component of the IL-1RI pathway, links IRAK to the IL-1 receptor. Nat. Cell Biol. 2000, 2, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brissoni, B.; Agostini, L.; Kropf, M.; Martinon, F.; Swoboda, V.; Lippens, S.; Everett, H.; Aebi, N.; Janssens, S.; Meylan, E.; et al. Intracellular trafficking of interleukin-1 receptor I requires Tollip. Curr. Biol. 2006, 16, 2265–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capelluto, D.G.S. Tollip: A multitasking protein in innate immunity and protein trafficking. Microbes Infect. 2012, 14, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, T.A.; Phillips, E.O.; Collier, C.L.; Robinson, J.B.; Routledge, D.; Wood, R.E.; Assar, E.A.; Tumbarello, D.A. Tollip coordinates Parkin-dependent trafficking of mitochondrial-derived vesicles. EMBO J. 2020, 39, e102539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Goobie, G.C.; Gregory, A.D.; Kass, D.J.; Zhang, Y. Toll-interacting protein in pulmonary diseases abiding by the Goldilocks principle. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2021, 64, 536–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aumiller, V.; Balsara, N.; Wilhelm, J.; Günther, A.; Königshoff, M. WNT/β-catenin signaling induces IL-1β expression by alveolar epithelial cells in pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2013, 49, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, T.S.; Schupp, J.C.; Poli, S.; Ayaub, E.A.; Neumark, N.; Ahangari, F.; Chu, S.G.; Raby, B.A.; Delullis, G.; Januszyk, M.; et al. Single-cell RNA-seq reveals ectopic and aberrant lung-resident cell populations in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaba1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Upagupta, C.; Shimbori, C.; Alsilmi, R.; Kolb, M. Matrix abnormalities in pulmonary fibrosis. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2018, 27, 180033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Yang, L.; Wang, W.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Xu, Z. Discovery and validation of extracellular/circulating microRNAs during idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis disease progression. Gene 2015, 562, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noth, I.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, S.F.; Flores, C.; Barber, M.; Huang, Y.; Broderick, S.M.; Wade, M.S.; Hysi, P.; Scuirba, J.; et al. Genetic variants associated with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis susceptibility and mortality: A genome-wide association study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2013, 1, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katayanagi, S.; Setoguchi, Y.; Kitagawa, S.; Okamoto, T.; Miyazaki, Y. Alternative gene expression by TOLLIP variant is associated with lung function in chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Chest 2022, 161, 458–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubbara, A.; Amundson, W.H.; Herman, A.; Lee, A.M.; Bishop, J.R.; Kim, H.J. Genetic variations in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and patient response to pirfenidone. Heliyon 2023, 9, e18573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldham, J.M.; Ma, S.F.; Martinez, F.J.; Anstrom, K.J.; Raghu, G.; Schwartz, D.A.; Valenzi, E.; Witt, L.; Lee, C.; Vij, R.; et al. TOLLIP, MUC5B, and the response to N-acetylcysteine among individuals with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 192, 1475–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isshiki, T.; Koyama, K.; Homma, S.; Sakamoto, S.; Yamasaki, A.; Shimizu, H.; Miyoshi, S.; Nakamura, Y.; Kishi, K. Association of rs3750920 polymorphism in TOLLIP with clinical characteristics of fibrosing interstitial lung diseases in Japanese. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 16250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Podolanczuk, A.J.; Kim, J.S.; Cooper, C.B.; Lasky, J.A.; Murray, S.; Oldham, J.M.; Raghu, G.; Flaherty, K.R.; Spino, C.; Noth, I.; et al. Design and rationale for the prospective treatment efficacy in IPF using genotype for NAC selection (PRECISIONS) clinical trial. BMC Pulm. Med. 2022, 22, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steele, M.P.; Speer, M.C.; Loyd, J.E.; Brown, K.K.; Herron, A.; Slifer, S.H.; Burch, L.H.; Wahidi, M.M.; Phillips, J.A., 3rd; Sporn, T.A.; et al. Clinical and pathologic features of familial interstitial pneumonia. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 172, 1146–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartczak, K.; Białas, A.J.; Kotecki, M.J.; Górski, P.; Piotrowski, W.J. More than a genetic code: Epigenetics of lung fibrosis. Mol. Diagn. Ther. 2020, 24, 665–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helling, B.A.; Gerber, A.N.; Kadiyala, V.; Sasse, S.K.; Pedersen, B.S.; Sparks, L.; Nakano, Y.; Okamoto, T.; Evans, C.M.; Yang, I.V.; et al. Regulation of MUC5B expression in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2017, 57, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.K.; Fisher, A.S.; Scruggs, A.M.; White, E.S.; Hogaboam, C.M.; Richardson, B.C.; Peters-Golden, M. Hypermethylation of PTGER2 confers prostaglandin E2 resistance in fibrotic fibroblasts from humans and mice. Am. J. Pathol. 2010, 177, 2245–2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagood, J.S.; Prabhakaran, P.; Kumbla, P.; Salazar, L.; MacEwen, M.W.; Barker, T.H.; Ortiz, L.A.; Schoeb, T.; Siegal, G.P.; Alexander, C.B.; et al. Loss of fibroblast Thy-1 expression correlates with lung fibrogenesis. Am. J. Pathol. 2005, 167, 365–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanders, Y.Y.; Pardo, A.; Selman, M.; Nuovo, G.J.; Tollefsbol, T.O.; Siegal, G.P.; Hagood, J.S. Thy-1 promoter hypermethylation: A novel epigenetic pathogenic mechanism in pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2008, 39, 610–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, C.M.; Neary, R.; Levendale, A.; Watson, C.J.; Baugh, J.A. Hypoxia-induced DNA hypermethylation in human pulmonary fibroblasts is associated with Thy-1 promoter methylation and the development of a pro-fibrotic phenotype. Respir. Res. 2012, 13, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konigsberg, I.R.; Borie, R.; Walts, A.D.; Cardwell, J.; Rojas, M.; Metzger, F.; Hauck, S.M.; Fingerlin, T.E.; Yang, I.V.; Schwartz, D.A. Molecular signatures of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2021, 65, 430–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korfei, M.; Mahavadi, P.; Guenther, A. Targeting histone deacetylases in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A future therapeutic option. Cells 2022, 11, 1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagnato, G.; Roberts, W.N.; Roman, J.; Gangemi, S. A systematic review of overlapping microRNA patterns in systemic sclerosis and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2017, 26, 160125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montgomery, R.L.; Yu, G.; Latimer, P.A.; Stack, C.; Robinson, K.; Dalby, C.M.; Kaminski, N.; van Rooij, E. MicroRNA mimicry blocks pulmonary fibrosis. EMBO Mol. Med. 2014, 6, 1347–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Luo, H.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Chai, J.; Xiao, X.; You, Y.; Zuo, X. MicroRNA-21 in scleroderma fibrosis and its function in TGF-β-regulated fibrosis-related gene expression. J. Clin. Immunol. 2013, 33, 1100–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oak, S.R.; Murray, L.; Herath, A.; Sleeman, M.; Anderson, I.; Joshi, A.D.; Coelho, A.L.; Flaherty, K.R.; Toews, G.B.; Knight, D.; et al. A micro RNA processing defect in rapidly progressing idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e21253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabater, L.; Gossart, J.B.; Hernandez, I.; Rico, D.; Blanchard, A.; Borthwick, L.A.; Fisher, A.J.; Majo, J.; Jiwa, K.; Collins, A.; et al. miRNA expression in fibroblastic foci within idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis lungs reveals novel disease-relevant pathways. Am. J. Pathol. 2023, 193, 417–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szabo, I.; Muntean, L.; Crisan, T.; Rednic, V.; Sirbe, C.; Rednic, S. Novel concepts in systemic sclerosis pathogenesis: Role for miRNAs. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Tao, J.H.; Zuo, T.; Li, X.M.; Wang, G.S.; Fang, X.; Xu, X.L.; Li, X.P. The correlation between miR-200c and the severity of interstitial lung disease associated with different connective tissue diseases. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2017, 46, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Huang, J.; Hu, C.; Zhou, J.; Xu, D.; Hou, Y.; Wu, C.; Zhao, J.; Li, M.; Zeng, X.; et al. MicroRNA-320a: An important regulator in the fibrotic process in interstitial lung disease of systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2021, 23, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oka, S.; Furukawa, H.; Shimada, K.; Hashimoto, A.; Komiya, A.; Fukui, N.; Tsuchiya, N.; Tohma, S. Plasma miRNA expression profiles in rheumatoid arthritis associated interstitial lung disease. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2017, 18, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rusek, M.; Krasowska, D. Non-coding RNA in systemic sclerosis: A valuable tool for translational and personalized medicine. Genes. 2021. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savary, G.; Dewaeles, E.; Diazzi, S.; Buscot, M.; Nottet, N.; Fassy, J.; Courcot, E.; Henaoui, I.S.; Lemaire, J.; Martis, N.; et al. The long noncoding RNA DNM3OS is a reservoir of fibromirs with major functions in lung fibroblast response to TGF-β and pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 200, 184–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Liang, Y.; Zeng, X.; Yang, X.; Xu, D.; Gou, X.; Sathiaseelan, R.; Senavirathna, L.K.; Wang, P.; Liu, L.; et al. Long noncoding RNA FENDRR exhibits antifibrotic activity in pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2020, 62, 440–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).