Effect of Infraorbital and/or Infratrochlear Nerve Blocks on Postoperative Care in Patients with Septorhinoplasty: A Meta-Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy and Study Selection
2.2. Data Extraction and Risk of Bias Assessment
2.3. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
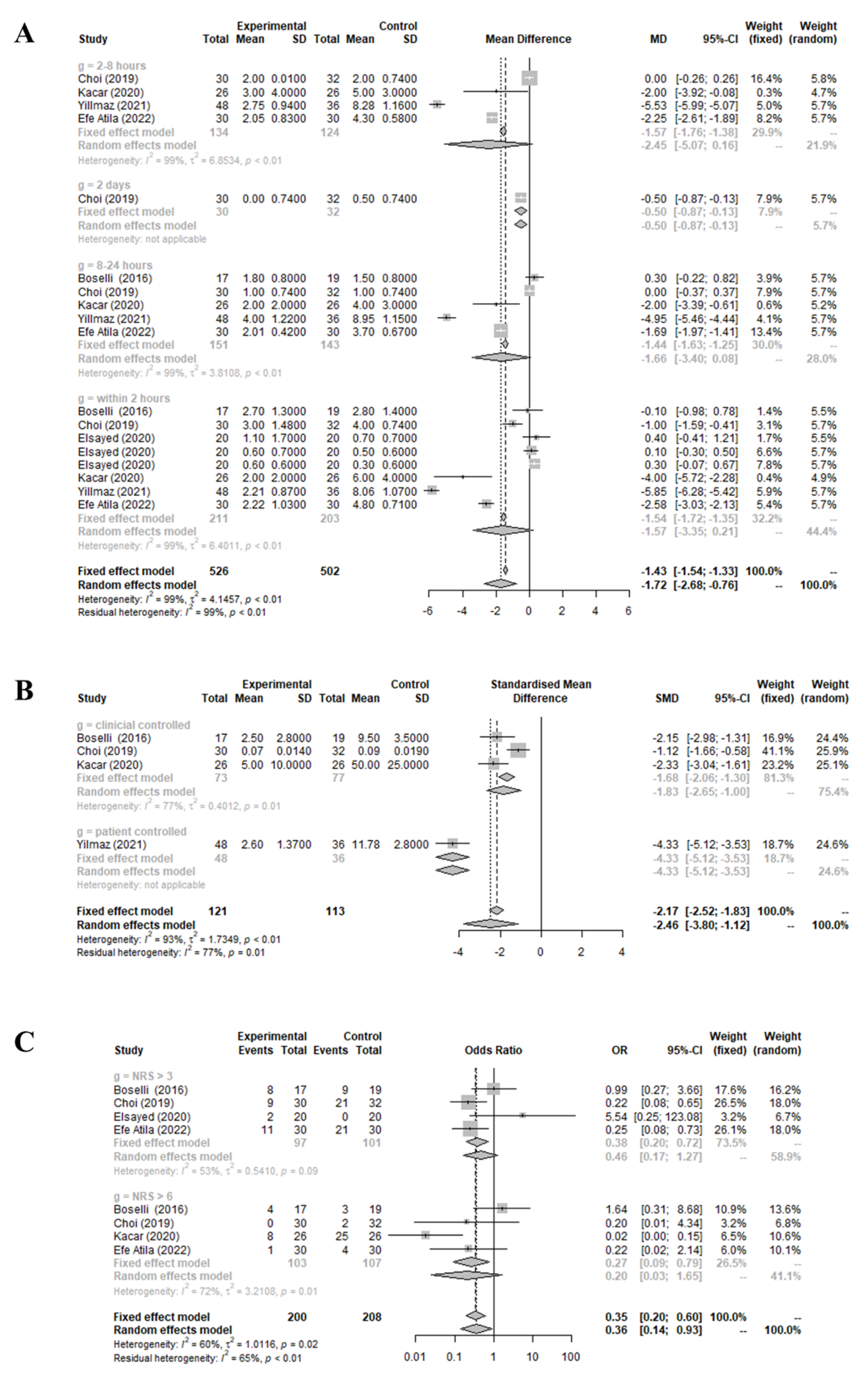
3.1. Effect of Preoperative Infraorbital and/or Infratrochlear Nerve Blocks on Patient-Reported Pain Score and the Quantity and Frequency of Administered Analgesic Medication Compared to the Control Group
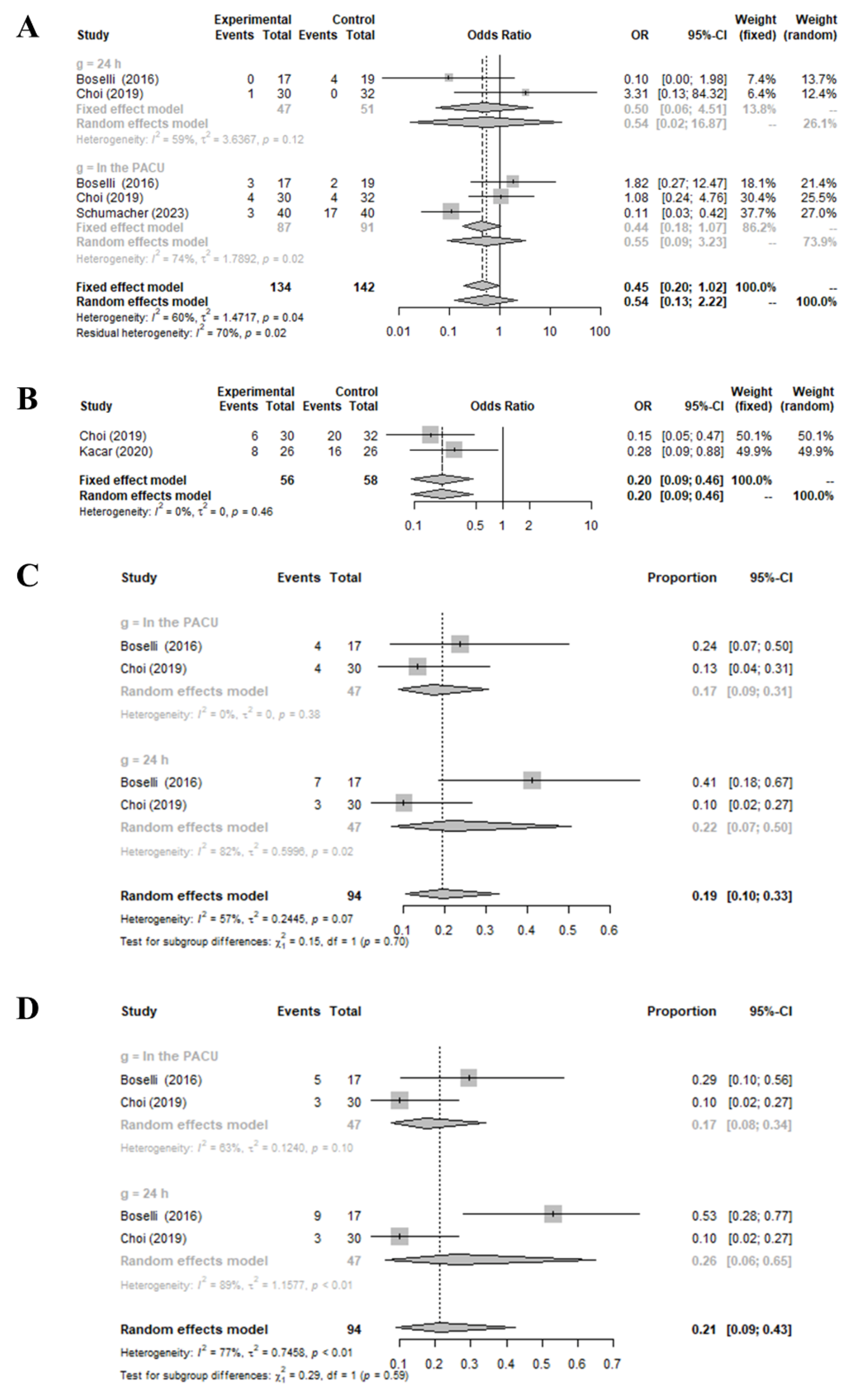
3.2. Effect of Preoperative Infraorbital and/or Infratrochlear Nerve Blocks on the Incidence of Postoperative Nausea and Vomiting, Emergence Agitation, and Occurrence of Side Effects Compared to the Control Group
3.3. Sensitivity Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, D.H.; Kang, H.; Jin, H.J.; Hwang, S.H. Effect of piezoelectric osteotomy on postoperative oedema and ecchymosis after rhinoplasty. Clin. Otolaryngol. 2019, 44, 968–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wittekindt, D.; Wittekindt, C.; Schneider, G.; Meissner, W.; Guntinas-Lichius, O. Postoperative pain assessment after septorhinoplasty. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2012, 269, 1613–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerbershagen, H.J.; Aduckathil, S.; van Wijck, A.J.; Peelen, L.M.; Kalkman, C.J.; Meissner, W. Pain intensity on the first day after surgery: A prospective cohort study comparing 179 surgical procedures. Anesthesiology 2013, 118, 934–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, R.; Gordon, D.B.; de Leon-Casasola, O.A.; Rosenberg, J.M.; Bickler, S.; Brennan, T.; Carter, T.; Cassidy, C.L.; Chittenden, E.H.; Degenhardt, E.; et al. Management of Postoperative Pain: A Clinical Practice Guideline from the American Pain Society, the American Society of Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine, and the American Society of Anesthesiologists’ Committee on Regional Anesthesia, Executive Committee, and Administrative Council. J. Pain 2016, 17, 131–157. [Google Scholar]
- Lam, D.M.H.; Choi, S.W.; Wong, S.S.C.; Irwin, M.G.; Cheung, C.W. Efficacy of Pregabalin in Acute Postoperative Pain Under Different Surgical Categories: A Meta-Analysis. Medicine 2015, 94, e1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, G.P. Putting it all together: Recommendations for improving pain management in plastic surgical procedures. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2014, 134, 94s–100s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cekic, B.; Geze, S.; Erturk, E.; Akdogan, A.; Eroglu, A. A comparison of levobupivacaine and levobupivacaine-tramadol combination in bilateral infraorbital nerve block for postoperative analgesia after nasal surgery. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2013, 70, 131–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.; Jung, S.H.; Hong, J.M.; Joo, Y.H.; Kim, Y.; Hong, S.H. Effects of Bilateral Infraorbital and Infratrochlear Nerve Block on Emergence Agitation after Septorhinoplasty: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boselli, E.; Bouvet, L.; Augris-Mathieu, C.; Bégou, G.; Diot-Junique, N.; Rahali, N.; Vertu-Ciolino, D.; Gérard, C.; Pivot, C.; Disant, F.; et al. Infraorbital and infratrochlear nerve blocks combined with general anaesthesia for outpatient rhinoseptoplasty: A prospective randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Anaesth. Crit. Care Pain Med. 2016, 35, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsayed, M.; Alosaimy, R.A.; Ali, N.Y.; Alshareef, M.A.; Althqafi, A.H.; Rajab, M.K.; Assalem, A.S.; Khiyami, A.J. Nerve Block for Septorhinoplasty: A Retrospective Observational Study of Postoperative Complications in 24 Hours. Cureus 2020, 12, e6961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaçar, C.K.; Uzundere, O.; Salık, F.; Akgündüz, M.; Bıçak, E.A.; Yektaş, A. Effects of Adding a Combined Infraorbital and Infratrochlear Nerve Block to General Anaesthesia in Septorhinoplasty. J. Pain Res. 2020, 13, 2599–2607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yılmaz, R.; Arıcan, Ş.; Hacıbeyoğlu, G.; Tuncer Uzun, S. Effects of Bilateral Infraorbital-Supraorbital Nerve Block on Postoperative Pain Control and Drug Consumption in Rhinoplasty. Eur. J. Ther. 2021, 27, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nihal, E.A.I. ATES Evaluation of Analgesic Effectivity of Infra Orbital Nerve Block in Open Septorhinoplasty Surgery: A Retrospective Study. New Trend Med. Sci. 2022, 3, 128–131. [Google Scholar]
- Schumacher, J.K.; Cristel, R.T.; Talugula, S.; Shah, A.R. The Use of Adjunctive Perioperative Nerve Blocks in Rhinoplasty in the Immediate Postoperative Period. Facial Plast. Surg. Aesthet. Med. 2023, 25, 361–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, G.; Fu, W.; Li, S.T. The effect of infraorbital nerve block on emergence agitation in children undergoing cleft lip surgery under general anesthesia with sevoflurane. Paediatr. Anaesth. 2015, 25, 906–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Kim, S.W.; Basurrah, M.A.; Hwang, S.H. Clinical and Laboratory Features of Various Criteria of Eosinophilic Chronic Rhinosinusitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Exp. Otorhinolaryngol. 2022, 15, 230–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.H.; Kim, S.W.; Basurrah, M.A.; Kim, D.H. Efficacy of Steroid-Impregnated Spacers After Endoscopic Sinus Surgery in Chronic Rhinosinusitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Exp. Otorhinolaryngol. 2023, 16, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Kim, D.H.; Hwang, S.H. Effectiveness of Dupilumab Treatment to Treat Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyposis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Rhinol. 2023, 30, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koputan, M.H.; Apan, A.; Oz, G.; Köse, E.A. The effects of tramadol and levobupivacaine infiltration on postoperative analgesia in functional endoscopic sinus surgery and septorhinoplasty. Balkan Med. J. 2012, 29, 391–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kehlet, H.; Dahl, J.B. Anaesthesia, surgery, and challenges in postoperative recovery. Lancet 2003, 362, 1921–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vahabi, S.; Kazemi, A.H. Effects of clonidine as premedication on plasma renin activity, serum and urine electrolytes and body fluids in general anesthesia. A randomized double blind placebo controlled clinical trial. Middle East J. Anaesthesiol. 2011, 21, 71–76. [Google Scholar]
- Vahabi, S.; Nadri, S.; Izadi, F. The effects of gabapentin on severity of post spinal anesthesia headache. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 27, 1203–1207. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lepousé, C.; Lautner, C.A.; Liu, L.; Gomis, P.; Leon, A. Emergence delirium in adults in the post-anaesthesia care unit. Br. J. Anaesth. 2006, 96, 747–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlajkovic, G.P.; Sindjelic, R.P. Emergence delirium in children: Many questions, few answers. Anesth. Analg. 2007, 104, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudek, K. Emergence delirium: A nursing perspective. AORN J. 2009, 89, 509–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aitkenhead, A.R. Injuries associated with anaesthesia. A global perspective. Br. J. Anaesth. 2005, 95, 95–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, M.S.; Petersen, E.E.; Dahl, J.B.; Wetterslev, J. Post-operative serious adverse events in a mixed surgical population—A retrospective register study. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 2016, 60, 1209–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiser, T.G.; Haynes, A.B.; Molina, G.; Lipsitz, S.R.; Esquivel, M.M.; Uribe-Leitz, T.; Fu, R.; Azad, T.; Chao, T.E.; Berry, W.R.; et al. Size and distribution of the global volume of surgery in 2012. Bull. World Health Organ. 2016, 94, 201–209f. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.; Elnabtity, A.M.; Keera, A. Efficacy of external nasal nerve block following nasal surgery: A randomized, controlled trial. Anaesthesist 2018, 67, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apfel, C.C.; Heidrich, F.M.; Jukar-Rao, S.; Jalota, L.; Hornuss, C.; Whelan, R.P.; Zhang, K.; Cakmakkaya, O.S. Evidence-based analysis of risk factors for postoperative nausea and vomiting. Br. J. Anaesth. 2012, 109, 742–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, G.W.; Bekker, T.B.; Carlsen, H.H.; Moffatt, C.H.; Slattery, P.J.; McClure, A.F. Postoperative nausea and vomiting are strongly influenced by postoperative opioid use in a dose-related manner. Anesth. Analg. 2005, 101, 1343–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gritsenko, K.; Khelemsky, Y.; Kaye, A.D.; Vadivelu, N.; Urman, R.D. Multimodal therapy in perioperative analgesia. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Anaesthesiol. 2014, 28, 59–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, C.K.; Seymour, R.A.; Lirk, P.; Merry, A.F. Combining paracetamol (acetaminophen) with nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs: A qualitative systematic review of analgesic efficacy for acute postoperative pain. Anesth. Analg. 2010, 110, 1170–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahl, J.B.; Nielsen, R.V.; Wetterslev, J.; Nikolajsen, L.; Hamunen, K.; Kontinen, V.K.; Hansen, M.S.; Kjer, J.J.; Mathiesen, O. Post-operative analgesic effects of paracetamol, NSAIDs, glucocorticoids, gabapentinoids and their combinations: A topical review. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 2014, 58, 1165–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aydil, U.; Yilmaz, M.; Akyildiz, I.; Bayazit, Y.; Keseroglu, K.; Ceylan, A. Pain and safety in otorhinolaryngologic procedures under local anesthesia. J. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2008, 37, 851–855. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Szychta, P.; Antoszewski, B. Assessment of early post-operative pain following septorhinoplasty. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2010, 124, 1194–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCamant, K.L. Peripheral nerve blocks: Understanding the nurse’s role. J. Perianesth. Nurs. 2006, 21, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanakaraj, M.; Shanmugasundaram, N.; Chandramohan, M.; Kannan, R.; Perumal, S.M.; Nagendran, J. Regional anesthesia in faciomaxillary and oral surgery. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2012, 4, S264–S269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moskovitz, J.B.; Sabatino, F. Regional nerve blocks of the face. Emerg. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2013, 31, 517–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalek, P.; Donaldson, W.; McAleavey, F.; Johnston, P.; Kiska, R. Ultrasound imaging of the infraorbital foramen and simulation of the ultrasound-guided infraorbital nerve block using a skull model. Surg. Radiol. Anat. 2013, 35, 319–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neagos, A.; Dumitru, M.; Vrinceanu, D.; Costache, A.; Marinescu, A.N.; Cergan, R. Ultrasonography used in the diagnosis of chronic rhinosinusitis: From experimental imaging to clinical practice. Exp. Ther. Med. 2021, 21, 611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apan, A.; Aykac, E.; Kazkayasi, M.; Doganci, N.; Tahran, F.D. Magnesium sulphate infusion is not effective on discomfort or emergence phenomenon in paediatric adenoidectomy/tonsillectomy. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2010, 74, 1367–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casati, A.; Putzu, M. Bupivacaine, levobupivacaine and ropivacaine: Are they clinically different? Best Pract. Res. Clin. Anaesthesiol. 2005, 19, 247–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Study (Year) | Study Design | Number of Patients | Sex (Male/Female) | Age, Median (Range) or Mean (SD), y | Nation | Procedure | Medication | Anesthesia | Medication | Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Choi (2019) [8] | RCT | 62 | NA | 21.97 ± 1.47 | Korea | bilateral infraorbital and infratrochlear nerve blocks | 0.5% ropivacaine | G/A | Isotonic saline | Postoperative pain score, used analgesic amount, frequency of used analgesic drug, incidence of postoperative nausea and vomiting, incidence of emergence agitation, incidence rate of edema and hematoma |
| Boselli (2016) [9] | RCT | 36 | 13/23 | 38 ± 14 | France | bilateral infraorbital and infratrochlear nerve blocks | 10 mL of 0.25% levobupivacaine | G/A | Isotonic saline | Postoperative pain score, used analgesic amount, frequency of used analgesic drug, incidence of postoperative nausea and vomiting, incidence rate of edema and hematoma |
| Kacar (2020) [11] | RCT | 52 | 24/28 | 27.38 ± 7.09 | Turkey | bilateral infraorbital and infratrochlear nerve blocks | 4 mL of 0.5% bupivacaine | G/A | G/A only | Postoperative pain score, used analgesic amount, frequency of used analgesic drug, incidence of emergence agitation |
| Elsayed (2020) [10] | Observational Study | 40 | 26/14 | 26 (8) | Saudi Arabia | bilateral infraorbital and infratrochlear nerve blocks | 5 mL of 0.25% levobupivacaine with 5 mL of diluted adrenaline 1:10,000 | G/A | G/A only | Frequency of used analgesic drug |
| Yılmaz (2021) [12] | Observational Study | 84 | 26/58 | 26.88 ± 5.45 | Turkey | bilateral infraorbital and supraorbital nerve blocks | 5 mg bupivacaine and 10 mg lidocaine for a total of 1.5 mL | G/A | G/A only | Postoperative pain score, used analgesic amount |
| Efe Atila (2022) [13] | Observational Study | 60 | 27/33 | 30.5 ± 4 | Turkey | bilateral infraorbital nerve blocks | 15 mg bupivacaine hydrochloride to infraorbital foramen | G/A | G/A only | Postoperative pain score, frequency of used analgesic drug |
| Schumacher (2023) [14] | Observational Study | 80 | NA | 27.6 | USA | bilateral infraorbital nerve blocks | 1.5 mL preoperative and postoperative bupivacaine | NA | NA | Incidence of postoperative nausea and vomiting |
| Study | Selection a | Comparability b | Exposure c | Newcastle–Ottawa Scale Score | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5A | 5B | 6 | 7 | 8 | ||
| Elsayed (2020) [10] | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | 6 |
| Yılmaz (2021) [12] | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | 7 |
| Efe Atila (2022) [13] | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | 6 |
| Schumacher (2023) [14] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | 7 |
| Study | Random Sequence Generation | Allocation Concealment | Blinding of Participants and Personnel | Blinding of Outcome Assessment | Incomplete Outcome Data Addressed | Free of Selective Reporting | Risk of Bias of Randomized Studies |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Choi (2019) [8] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Low |
| Boselli (2016) [9] | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Low |
| Kacar (2020) [11] | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | High |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, D.H.; Park, J.-B.; Kim, S.W.; Stybayeva, G.; Hwang, S.H. Effect of Infraorbital and/or Infratrochlear Nerve Blocks on Postoperative Care in Patients with Septorhinoplasty: A Meta-Analysis. Medicina 2023, 59, 1659. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59091659
Kim DH, Park J-B, Kim SW, Stybayeva G, Hwang SH. Effect of Infraorbital and/or Infratrochlear Nerve Blocks on Postoperative Care in Patients with Septorhinoplasty: A Meta-Analysis. Medicina. 2023; 59(9):1659. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59091659
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Do Hyun, Jun-Beom Park, Sung Won Kim, Gulnaz Stybayeva, and Se Hwan Hwang. 2023. "Effect of Infraorbital and/or Infratrochlear Nerve Blocks on Postoperative Care in Patients with Septorhinoplasty: A Meta-Analysis" Medicina 59, no. 9: 1659. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59091659
APA StyleKim, D. H., Park, J.-B., Kim, S. W., Stybayeva, G., & Hwang, S. H. (2023). Effect of Infraorbital and/or Infratrochlear Nerve Blocks on Postoperative Care in Patients with Septorhinoplasty: A Meta-Analysis. Medicina, 59(9), 1659. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59091659






