Mental Illnesses in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: mens sana in corpore sano
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
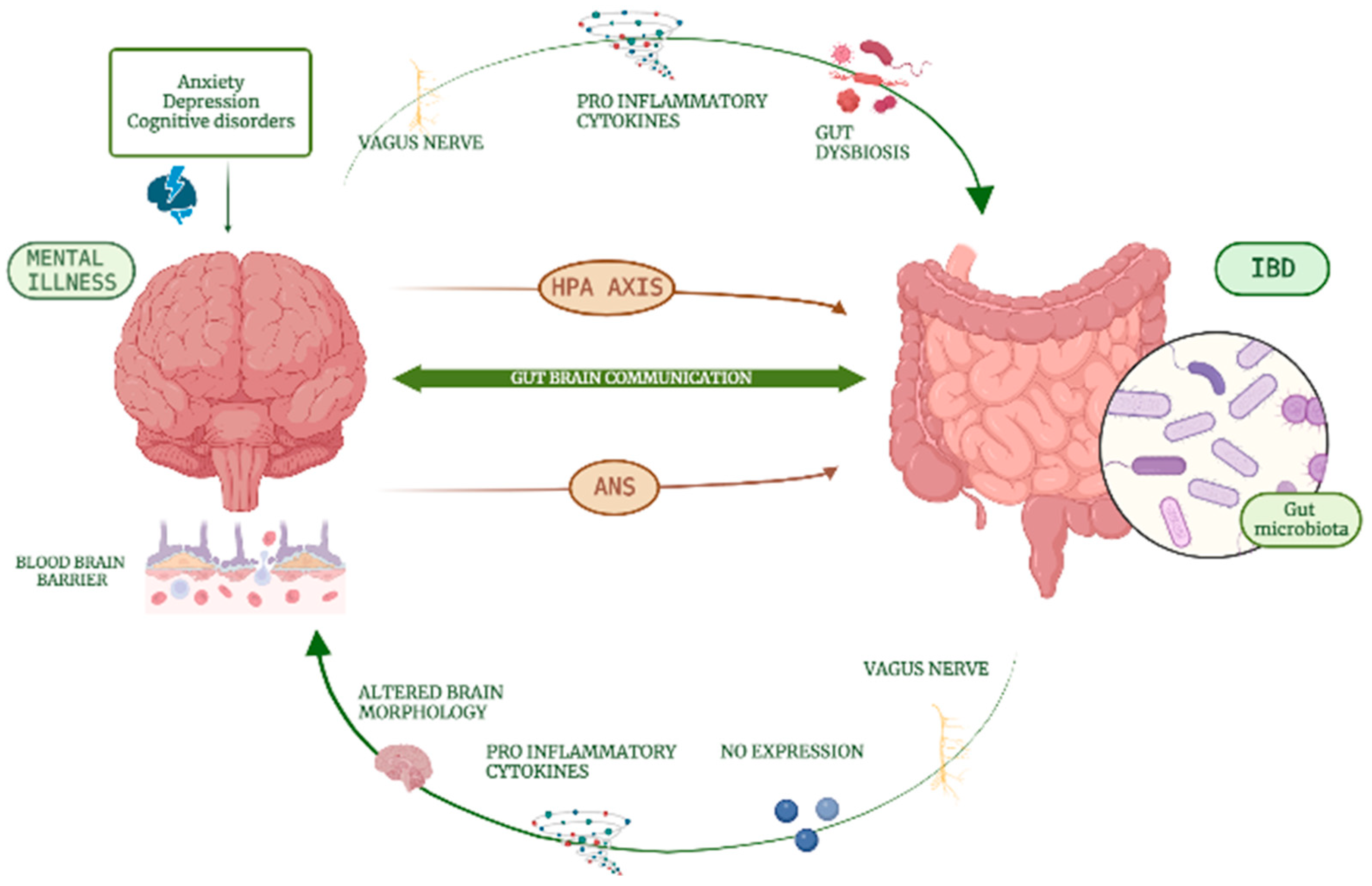
3. Neural Mechanisms Implied
4. Incidence and Prevalence
4.1. Depression
4.2. Anxiety
4.3. Bipolar Disorder
4.4. Cognitive Disorders
| Reference | Year | Study Design | Observation Time | Incidence/Prevalence of Depression | Incidence/Prevalence of Anxiety | Incidence/Prevalence of Bipolar Disorder | Incidence/Prevalence of Dementia |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Barberio et al. [5] | 2021 | Meta-analysis | Pooled prevalence of depressive symptoms: 25.2% | Pooled prevalence of anxiety symptoms: 32.1% | |||
| Mikocka-Walus et al. [37] | 2016 | Systematic review | Pooled prevalence of depression in IBD vs. healthy control: 21.2% vs. 13.4%, in active vs. inactive disease: 34.7% vs. 19.9% | Pooled prevalence of anxiety in IBD vs. healthy control: 19.1% vs. 9.6%, in active vs. inactive disease: 66.4% vs. 28.2% | |||
| Neuendorf et al. [38] | 2014 | Systematic review | Pooled prevalence of depression disorders: 15.2%, depressive symptoms: 21.6%, pooled prevalence of depressive symptoms in active vs. inactive disease: 40.7% vs. 16.5% | Pooled prevalence of anxiety disorders: 20.5%, anxiety symptoms: 35.1%, pooled prevalence of anxiety symptoms in active vs. inactive disease: 75.6% vs. 31.4% | |||
| Choi et al. [41] | 2019 | Cohort study | 6 years | Incidence rate (per 1000 persons/year) in CD vs. non-CD controls: 14.99 vs. 7.75 In UC vs. non-UC controls: 19.63 vs. 11.28 Prevalence in IBD vs. non-IBD controls: 8.0% vs. 3.7% | Incidence rate (per 1000 persons/year) in CD vs. non-CD controls: 20.88 vs. 14.31, in UC vs. non-UC controls: 31.19 vs. 21.55 Prevalence in IBD vs. non-IBD controls: 12.2% vs. 8.7% | ||
| Marrie et al. [42] | 2017 | Cohort study | 9.6 years | Incidence rate ratio of depression in IBD of 1.61 | Incidence rate ratio of anxiety in IBD of 1.37 | ||
| Walker et al. [43] | 2008 | Cohort study | Lifetime prevalence of major depressive disorder in IBD vs. control: 27.2% vs. 12.3% | Lifetime prevalence of any anxiety or mood disorder in IBD vs. control: 35.8% vs. 22.1% | |||
| Kao et al. [48] | 2019 | Population-based cohort study | Adjusted odds ratio of developing a bipolar disorder of 2.10 (95% CI 1.30–3.38) | ||||
| Bernstein et al. [50] | 2019 | Population-based cohort study | Incidence in the IBD group as compared to the matched cohort (3.80, 95% CI 2.29–6.30; vs. 1.56, 95% CI 1.09–2.23), higher incidence rate ratios (IRR, 1.82; 95% CI, 1.44–2.30) | ||||
| Zhang et al. [56] | 2021 | Cohort study | 16 years | Incidence (per 1700 persons) of dementia in IBD vs. healthy control: 5.5% vs. 1.4% |
4.5. Schizophrenia
5. Compliance to Therapy and Role of Psychotherapeutic Intervention
6. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Roda, G.; Chien, N.S.; Kotze, P.G.; Argollo, M.; Panaccione, R.; Spinelli, A.; Kaser, A.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L.; Danese, S. Crohn’s disease. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2020, 6, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, T.; Siegmund, B.; Le Berre, C.; Wei, S.C.; Ferrante, M.; Shen, B.; Bernstein, C.N.; Danese, S.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L.; Hibi, T. Ulcerative colitis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2020, 6, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ananthakrishnan, A.N.; Bernstein, C.N.; Iliopoulos, D.; Macpherson, A.; Neurath, M.F.; Ali, R.A.R.; Vavricka, S.R.; Fiocchi, C. Environmental triggers in IBD: A review of progress and evidence. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 15, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armuzzi, A.; Liguori, G. Quality of life in patients with moderate to severe ulcerative colitis and the impact of treatment: A narrative review. Dig. Liver Dis. 2021, 53, 803–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barberio, B.; Zamani, M.; Black, C.J.; Savarino, E.V.; Ford, A.C. Prevalence of symptoms of anxiety and depression in patients with inflammatory bowel disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 6, 359–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bisgaard, T.H.; Allin, K.H.; Keefer, L.; Ananthakrishnan, A.N.; Jess, T. Depression and anxiety in inflammatory bowel disease: Epidemiology, mechanisms and treatment. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 19, 717–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keefer, L.; Keshavarzian, A.; Mutlu, E. Reconsidering the methodology of “stress” research in inflammatory bowel disease. J. Crohns Colitis 2008, 2, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Mitchell, R. Impact of inflammatory bowel disease on quality of life: Results of the European Federationof Crohn’s and ulcerative colitis associations (EFCCA) patient survey. J. Crohns Colitis 2007, 1, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eugenicos, M.P.; Ferreira, N.B. Psychological factors associated with inflammatory bowel disease. Br. Med. Bull. 2021, 138, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.T.; Allen, J.I.; Meadows, P.; Szigethy, E.M.; Henrichsen, K.; Kim, S.C.; Lawton, R.C.; Murphy, S.M.; Regueiro, M.; Rubin, D.T.; et al. The Cost of Inflammatory Bowel Disease: An Initiative From the Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2020, 26, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Casati, J.; Toner, B.B. Psychosocial aspects of inflammatory bowel disease. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2000, 54, 388–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sewitch, M.J.; Abrahamowicz, M.; Bitton, A.; Daly, D.; Wild, G.E.; Cohen, A.; Katz, S.; Szego, P.L.; Dobkin, P.L. Psychological distress, social support, and disease activity in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2001, 96, 1470–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levenstein, S.; Prantera, C.; Varvo, V.; Scribano, M.L.; Andreoli, A.; Luzi, C.; Arcà, M.; Berto, E.; Milite, G.; Marcheggiano, A. Stress and exacerbation in ulcerative colitis: A prospective study of patients enrolled in remission. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2000, 95, 1213–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ananthakrishnan, A.N.; Gainer, V.S.; Perez, R.G.; Cai, T.; Cheng, S.C.; Savova, G.; Chen, P.; Szolovits, P.; Xia, Z.; De Jager, P.L.; et al. Psychiatric co-morbidity is associated with increased risk of surgery in Crohn’s disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 37, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oligschlaeger, Y.; Yadati, T.; Houben, T.; Condello Oliván, C.M.; Shiri-Sverdlov, R. Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Stressed “Gut/Feeling”. Cells 2019, 8, 659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navabi, S.; Gorrepati, V.S.; Yadav, S.; Chintanaboina, J.; Maher, S.; Demuth, P.; Stern, B.; Stuart, A.; Tinsley, A.; Clarke, K.; et al. Influences and Impact of Anxiety and Depression in the Setting of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2018, 24, 2303–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maunder, R.G.; Levenstein, S. The role of stress in the development and clinical course of inflammatory bowel disease: Epidemiological evidence. Curr. Mol. Med. 2008, 8, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gracie, D.J.; Hamlin, P.J.; Ford, A.C. The influence of the brain-gut axis in inflammatory bowel disease and possible implications for treatment. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 4, 632–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuart, M.J.; Baune, B.T. Chemokines and chemokine receptors in mood disorders, schizophrenia, and cognitive impairment: A systematic review of biomarker studies. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2014, 42, 93–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frolkis, A.D.; Vallerand, I.A.; Shaheen, A.A.; Lowerison, M.W.; Swain, M.G.; Barnabe, C.; Patten, S.B.; Kaplan, G.G. Depression increases the risk of inflammatory bowel disease, which may be mitigated by the use of antidepressants in the treatment of depression. Gut 2019, 68, 1606–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.; Saunders, P.R.; Hanssen, N.P.; Yang, P.C.; Yates, D.; Groot, J.A.; Perdue, M.H. Corticotropin-releasing hormone mimics stress-induced colonic epithelial pathophysiology in the rat. Am. J. Physiol. 1999, 277, G391–G399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, J.D.; Campisi, J.; Sharkey, C.M.; Kennedy, S.L.; Nickerson, M.; Greenwood, B.N.; Fleshner, M. Catecholamines mediate stress-induced increases in peripheral and central inflammatory cytokines. Neuroscience 2005, 135, 1295–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farhadi, A.; Keshavarzian, A.; Van de Kar, L.D.; Jakate, S.; Domm, A.; Zhang, L.; Shaikh, M.; Banan, A.; Fields, J.Z. Heightened responses to stressors in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2005, 100, 1796–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brzozowski, B.; Mazur-Bialy, A.; Pajdo, R.; Kwiecien, S.; Bilski, J.; Zwolinska-Wcislo, M.; Mach, T.; Brzozowski, T. Mechanisms by which Stress Affects the Experimental and Clinical Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD): Role of Brain-Gut Axis. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2016, 14, 892–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dal Buono, A.; Caldirola, D.; Allocca, M. Genetic susceptibility to inflammatory bowel disease: Should we be looking to the hypothalamus? Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2021, 17, 803–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murayama, S.; Kurganov, E.; Miyata, S. Activation of microglia and macrophages in the circumventricular organs of the mouse brain during TLR2-induced fever and sickness responses. J. Neuroimmunol. 2019, 334, 576973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCusker, R.H.; Kelley, K.W. Immune-neural connections: How the immune system’s response to infectious agents influences behavior. J. Exp. Biol. 2013, 216 Pt 1, 84–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornaro, R.; Actis, G.C.; Caviglia, G.P.; Pitoni, D.; Ribaldone, D.G. Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Role of Vagus Nerve Stimulation. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghia, J.E.; Blennerhassett, P.; Collins, S.M. Impaired parasympathetic function increases susceptibility to inflammatory bowel disease in a mouse model of depression. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 2209–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camilleri, M. Leaky gut: Mechanisms, measurement and clinical implications in humans. Gut 2019, 68, 1516–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haj-Mirzaian, A.; Amiri, S.; Amini-Khoei, H.; Hosseini, M.J.; Haj-Mirzaian, A.; Momeny, M.; Rahimi-Balaei, M.; Dehpour, A.R. Anxiety- and Depressive-Like Behaviors are Associated with Altered Hippocampal Energy and Inflammatory Status in a Mouse Model of Crohn’s Disease. Neuroscience 2017, 366, 124–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carloni, S.; Bertocchi, A.; Mancinelli, S.; Bellini, M.; Erreni, M.; Borreca, A.; Braga, D.; Giugliano, S.; Mozzarelli, A.M.; Manganaro, D.; et al. Identification of a choroid plexus vascular barrier closing during intestinal inflammation. Science 2021, 374, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zonis, S.; Pechnick, R.N.; Ljubimov, V.A.; Mahgerefteh, M.; Wawrowsky, K.; Michelsen, K.S.; Chesnokova, V. Chronic intestinal inflammation alters hippocampal neurogenesis. J. Neuroinflamm. 2015, 12, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitali, R.; Prioreschi, C.; Lorenzo Rebenaque, L.; Colantoni, E.; Giovannini, D.; Frusciante, S.; Diretto, G.; Marco-Jiménez, F.; Mancuso, M.; Casciati, A.; et al. Gut-Brain Axis: Insights from Hippocampal Neurogenesis and Brain Tumor Development in a Mouse Model of Experimental Colitis Induced by Dextran Sodium Sulfate. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Labus, J.S.; Griffin, F.; Gupta, A.; Bhatt, R.R.; Sauk, J.S.; Turkiewicz, J.; Bernstein, C.N.; Kornelsen, J.; Mayer, E.A. Functional brain rewiring and altered cortical stability in ulcerative colitis. Mol. Psychiatry 2022, 27, 1792–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, V.A.; Beniwal-Patel, P.; Mbah, I.; Young, B.M.; Prabhakaran, V.; Saha, S. Structural Imaging Changes and Behavioral Correlates in Patients with Crohn’s Disease in Remission. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikocka-Walus, A.; Knowles, S.R.; Keefer, L.; Graff, L. Controversies Revisited: A Systematic Review of the Comorbidity of Depression and Anxiety with Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2016, 22, 752–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuendorf, R.; Harding, A.; Stello, N.; Hanes, D.; Wahbeh, H. Depression and anxiety in patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A systematic review. J. Psychosom Res. 2016, 87, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panara, A.J.; Yarur, A.J.; Rieders, B.; Proksell, S.; Deshpande, A.R.; Abreu, M.T.; Sussman, D.A. The incidence and risk factors for developing depression after being diagnosed with inflammatory bowel disease: A cohort study. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 39, 802–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, G.; Rosenfeld, G.; Leung, Y.; Qian, H.; Raudzus, J.; Nunez, C.; Bressler, B. Prevalence of Anxiety and Depression in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Can. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 2017, 6496727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.; Chun, J.; Han, K.; Park, S.; Soh, H.; Kim, J.; Lee, J.; Lee, H.J.; Im, J.P.; Kim, J.S. Risk of Anxiety and Depression in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Nationwide, Population-Based Study. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marrie, R.A.; Walld, R.; Bolton, J.M.; Sareen, J.; Walker, J.R.; Patten, S.B.; Singer, A.; Lix, L.M.; Hitchon, C.A.; El-Gabalawy, R.; et al. Rising incidence of psychiatric disorders before diagnosis of immune-mediated inflammatory disease. Epidemiol. Psychiatr. Sci. 2019, 28, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marrie, R.A.; Walld, R.; Bolton, J.M.; Sareen, J.; Walker, J.R.; Patten, S.B.; Singer, A.; Lix, L.M.; Hitchon, C.A.; El-Gabalawy, R.; et al. Increased incidence of psychiatric disorders in immune-mediated inflammatory disease. J. Psychosom. Res. 2017, 101, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludvigsson, J.F.; Olén, O.; Larsson, H.; Halfvarson, J.; Almqvist, C.; Lichtenstein, P.; Butwicka, A. Association Between Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Psychiatric Morbidity and Suicide: A Swedish Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study With Sibling Comparisons. J. Crohns Colitis 2021, 15, 1824–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Q.; Tang, F.; Li, Y.; Xie, F.; Yuan, L.; Yao, C.; Wu, R.; Wang, J.; Wang, Q.; Feng, P. Association of inflammatory bowel disease with suicidal ideation, suicide attempts, and suicide: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Psychosom. Res. 2022, 160, 110983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butwicka, A.; Olén, O.; Larsson, H.; Halfvarson, J.; Almqvist, C.; Lichtenstein, P.; Serlachius, E.; Frisén, L.; Ludvigsson, J.F. Association of Childhood-Onset Inflammatory Bowel Disease With Risk of Psychiatric Disorders and Suicide Attempt. JAMA Pediatr. 2019, 173, 969–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, J.R.; Ediger, J.P.; Graff, L.A.; Greenfeld, J.M.; Clara, I.; Lix, L.; Rawsthorne, P.; Miller, N.; Rogala, L.; McPhail, C.M.; et al. The Manitoba IBD cohort study: A population-based study of the prevalence of lifetime and 12-month anxiety and mood disorders. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 103, 1989–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolova, V.L.; Pelton, L.; Moulton, C.D.; Zorzato, D.; Cleare, A.J.; Young, A.H.; Stone, J.M. The Prevalence and Incidence of Irritable Bowel Syndrome and Inflammatory Bowel Disease in Depression and Bipolar Disorder: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Psychosom. Med. 2022, 84, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, L.T.; Lin, H.C.; Lee, H.C. Inflammatory bowel disease and bipolar disorder: A population-based cross-sectional study. J. Affect. Disord. 2019, 247, 120–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstein, C.N.; Hitchon, C.A.; Walld, R.; Bolton, J.M.; Sareen, J.; Walker, J.R.; Graff, L.A.; Patten, S.B.; Singer, A.; Lix, L.M.; et al. Increased Burden of Psychiatric Disorders in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2019, 25, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachdev, P.S.; Blacker, D.; Blazer, D.G.; Ganguli, M.; Jeste, D.V.; Paulsen, J.S.; Petersen, R.C. Classifying neurocognitive disorders: The DSM-5 approach. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2014, 10, 634–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopkins, C.W.P.; Powell, N.; Norton, C.; Dumbrill, J.L.; Hayee, B.; Moulton, C.D. Cognitive Impairment in Adult Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Acad. Consult. Liaison Psychiatry 2021, 62, 387–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitehouse, C.E.; Fisk, J.D.; Bernstein, C.N.; Berrigan, L.I.; Bolton, J.M.; Graff, L.A.; Hitchon, C.A.; Marriott, J.J.; Peschken, C.A.; Sareen, J.; et al. Comorbid anxiety, depression, and cognition in MS and other immune-mediated disorders. Neurology 2019, 92, e406–e417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golan, D.; Gross, B.; Miller, A.; Klil-Drori, S.; Lavi, I.; Shiller, M.; Honigman, S.; Almog, R.; Segol, O. Cognitive Function of Patients with Crohn’s Disease is Associated with Intestinal Disease Activity. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2016, 22, 364–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, X.; Du, H. Inflammatory bowel disease: A potential pathogenic factor of Alzheimer’s disease. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2022, 119, 110610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Wang, H.E.; Bai, Y.M.; Tsai, S.J.; Su, T.P.; Chen, T.J.; Wang, Y.P.; Chen, M.H. Inflammatory bowel disease is associated with higher dementia risk: A nationwide longitudinal study. Gut 2021, 70, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Wang, Y.; He, L.; Sun, J.; Wang, X.; Li, H. Inflammatory bowel disease and risk of dementia: An updated meta-analysis. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 4, 962681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Su, B.; Karhunen, V.; Gill, D.; Zuber, V.; Ahola-Olli, A.; Palaniswamy, S.; Auvinen, J.; Herzig, K.H.; Keinänen-Kiukaanniemi, S.; et al. Inflammatory Diseases, Inflammatory Biomarkers, and Alzheimer Disease: An Observational Analysis and Mendelian Randomization. Neurology 2023, 100, e568–e581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, K.Y.; Zhang, B.; Wang, H.E.; Bai, Y.M.; Tsai, S.J.; Su, T.P.; Chen, T.J.; Hou, M.C.; Lu, C.L.; Wang, Y.P.; et al. Schizophrenia and risk of new-onset inflammatory bowel disease: A nationwide longitudinal study. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2022, 55, 1192–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, L.; He, X.; Gao, F.; Fan, Y.; Zhao, B.; Ma, Q.; Yan, B.; Wang, W.; Ma, X.; Yang, J. Estimation of the bidirectional relationship between schizophrenia and inflammatory bowel disease using the mendelian randomization approach. Schizophrenia 2022, 8, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, I.; Ogura, J.; Aizawa, E.; Ota, M.; Hidese, S.; Yomogida, Y.; Matsuo, J.; Yoshida, S.; Kunugi, H. Gut permeability and its clinical relevance in schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacol. Rep. 2022, 42, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gokulakrishnan, K.; Nikhil, J.; Vs, S.; Holla, B.; Thirumoorthy, C.; Sandhya, N.; Nichenametla, S.; Pathak, H.; Shivakumar, V.; Debnath, M.; et al. Altered Intestinal Permeability Biomarkers in Schizophrenia: A Possible Link with Subclinical Inflammation. Ann. Neurosci. 2022, 29, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maes, M.; Sirivichayakul, S.; Kanchanatawan, B.; Vodjani, A. Upregulation of the Intestinal Paracellular Pathway with Breakdown of Tight and Adherens Junctions in Deficit Schizophrenia. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 56, 7056–7073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usta, A.; Kılıç, F.; Demirdaş, A.; Işık, Ü.; Doğuç, D.K.; Bozkurt, M. Serum zonulin and claudin-5 levels in patients with schizophrenia. Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2021, 271, 767–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, C.A.; Clatworthy, J.; Robinson, A.; Horne, R. Factors associated with non-adherence to oral medication for inflammatory bowel disease: A systematic review. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 105, 525–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigro, G.; Angelini, G.; Grosso, S.B.; Caula, G.; Sategna-Guidetti, C. Psychiatric predictors of noncompliance in inflammatory bowel disease: Psychiatry and compliance. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2001, 32, 66–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolovich, C.; Bernstein, C.N.; Singh, H.; Nugent, Z.; Tennakoon, A.; Shafer, L.A.; Marrie, R.A.; Sareen, J.; Targownik, L.E. Anxiety and Depression Leads to Anti-Tumor Necrosis Factor Discontinuation in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 19, 1200–1208.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calloway, A.; Dalal, R.; Beaulieu, D.B.; Duley, C.; Annis, K.; Gaines, L.; Slaughter, C.; Schwartz, D.A.; Horst, S. Depressive Symptoms Predict Anti-tumor Necrosis Factor Therapy Noncompliance in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2017, 62, 3563–3567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kane, S.V.; Accortt, N.A.; Magowan, S.; Brixner, D. Predictors of persistence with 5-aminosalicylic acid therapy for ulcerative colitis. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2009, 29, 855–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shale, M.J.; Riley, S.A. Studies of compliance with delayed-release mesalazine therapy in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2003, 18, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodhand, J.R.; Kamperidis, N.; Sirwan, B.; Macken, L.; Tshuma, N.; Koodun, Y.; Chowdhury, F.A.; Croft, N.M.; Direkze, N.; Langmead, L.; et al. Factors associated with thiopurine non-adherence in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 38, 1097–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiao, D.K.; Chan, W.; Jeganathan, J.; Chan, J.T.; Perry, J.; Selinger, C.P.; Leong, R.W. Inflammatory Bowel Disease Pharmacist Adherence Counseling Improves Medication Adherence in Crohn’s Disease and Ulcerative Colitis. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2017, 23, 1257–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmer, A.; Preiss, J.C.; Motschall, E.; Rücker, G.; Jantschek, G.; Moser, G. Psychological interventions for treatment of inflammatory bowel disease. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Brink, G.; Stapersma, L.; Bom, A.S.; Rizopolous, D.; van der Woude, C.J.; Stuyt, R.J.L.; Hendriks, D.M.; van der Burg, J.A.T.; Beukers, R.; Korpershoek, T.A.; et al. Effect of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy on Clinical Disease Course in Adolescents and Young Adults With Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Subclinical Anxiety and/or Depression: Results of a Randomized Trial. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2019, 25, 1945–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hommel, K.A.; Hente, E.A.; Odell, S.; Herzer, M.; Ingerski, L.M.; Guilfoyle, S.M.; Denson, L.A. Evaluation of a group-based behavioral intervention to promote adherence in adolescents with inflammatory bowel disease. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 24, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gracie, D.J.; Irvine, A.J.; Sood, R.; Mikocka-Walus, A.; Hamlin, P.J.; Ford, A.C. Effect of psychological therapy on disease activity, psychological comorbidity, and quality of life in inflammatory bowel disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 2, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinelli, A.; Carvello, M.; D’Hoore, A.; Pagnini, F. Psychological perspectives of inflammatory bowel disease patients undergoing surgery: Rightful concerns and preconceptions. Curr. Drug Targets 2014, 15, 1074–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polidano, K.; Chew-Graham, C.A.; Farmer, A.D.; Saunders, B. Access to Psychological Support for Young People Following Stoma Surgery: Exploring Patients’ and Clinicians’ Perspectives. Qual. Health Res. 2021, 31, 535–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lores, T.; Goess, C.; Mikocka-Walus, A.; Collins, K.L.; Burke, A.L.J.; Chur-Hansen, A.; Delfabbro, P.; Andrews, J.M. Integrated Psychological Care Reduces Health Care Costs at a Hospital-Based Inflammatory Bowel Disease Service. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 19, 96–103.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jedel, S.; Hoffman, A.; Merriman, P.; Swanson, B.; Voigt, R.; Rajan, K.B.; Shaikh, M.; Li, H.; Keshavarzian, A. A randomized controlled trial of mindfulness-based stress reduction to prevent flare-up in patients with inactive ulcerative colitis. Digestion 2014, 89, 142–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neilson, K.; Ftanou, M.; Monshat, K.; Salzberg, M.; Bell, S.; Kamm, M.A.; Connell, W.; Knowles, S.R.; Sevar, K.; Mancuso, S.G.; et al. A Controlled Study of a Group Mindfulness Intervention for Individuals Living with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2016, 22, 694–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boye, B.; Lundin, K.E.; Jantschek, G.; Leganger, S.; Mokleby, K.; Tangen, T.; Jantschek, I.; Pripp, A.H.; Wojniusz, S.; Dahlstroem, A.; et al. INSPIRE study: Does stress management improve the course of inflammatory bowel disease and disease-specific quality of life in distressed patients with ulcerative colitis or Crohn’s disease? A randomized controlled trial. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2011, 17, 1863–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bartocci, B.; Dal Buono, A.; Gabbiadini, R.; Busacca, A.; Quadarella, A.; Repici, A.; Mencaglia, E.; Gasparini, L.; Armuzzi, A. Mental Illnesses in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: mens sana in corpore sano. Medicina 2023, 59, 682. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59040682
Bartocci B, Dal Buono A, Gabbiadini R, Busacca A, Quadarella A, Repici A, Mencaglia E, Gasparini L, Armuzzi A. Mental Illnesses in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: mens sana in corpore sano. Medicina. 2023; 59(4):682. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59040682
Chicago/Turabian StyleBartocci, Bianca, Arianna Dal Buono, Roberto Gabbiadini, Anita Busacca, Alessandro Quadarella, Alessandro Repici, Emanuela Mencaglia, Linda Gasparini, and Alessandro Armuzzi. 2023. "Mental Illnesses in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: mens sana in corpore sano" Medicina 59, no. 4: 682. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59040682
APA StyleBartocci, B., Dal Buono, A., Gabbiadini, R., Busacca, A., Quadarella, A., Repici, A., Mencaglia, E., Gasparini, L., & Armuzzi, A. (2023). Mental Illnesses in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: mens sana in corpore sano. Medicina, 59(4), 682. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59040682








