Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy Provides Limited Therapeutic Effects on Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.2. Search Strategy and Identification of Eligible Papers
2.3. Appraisal of Methodological Quality
2.4. Outcome
2.5. Data Extraction
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Study Selection
3.2. Methodological Quality of Included Studies
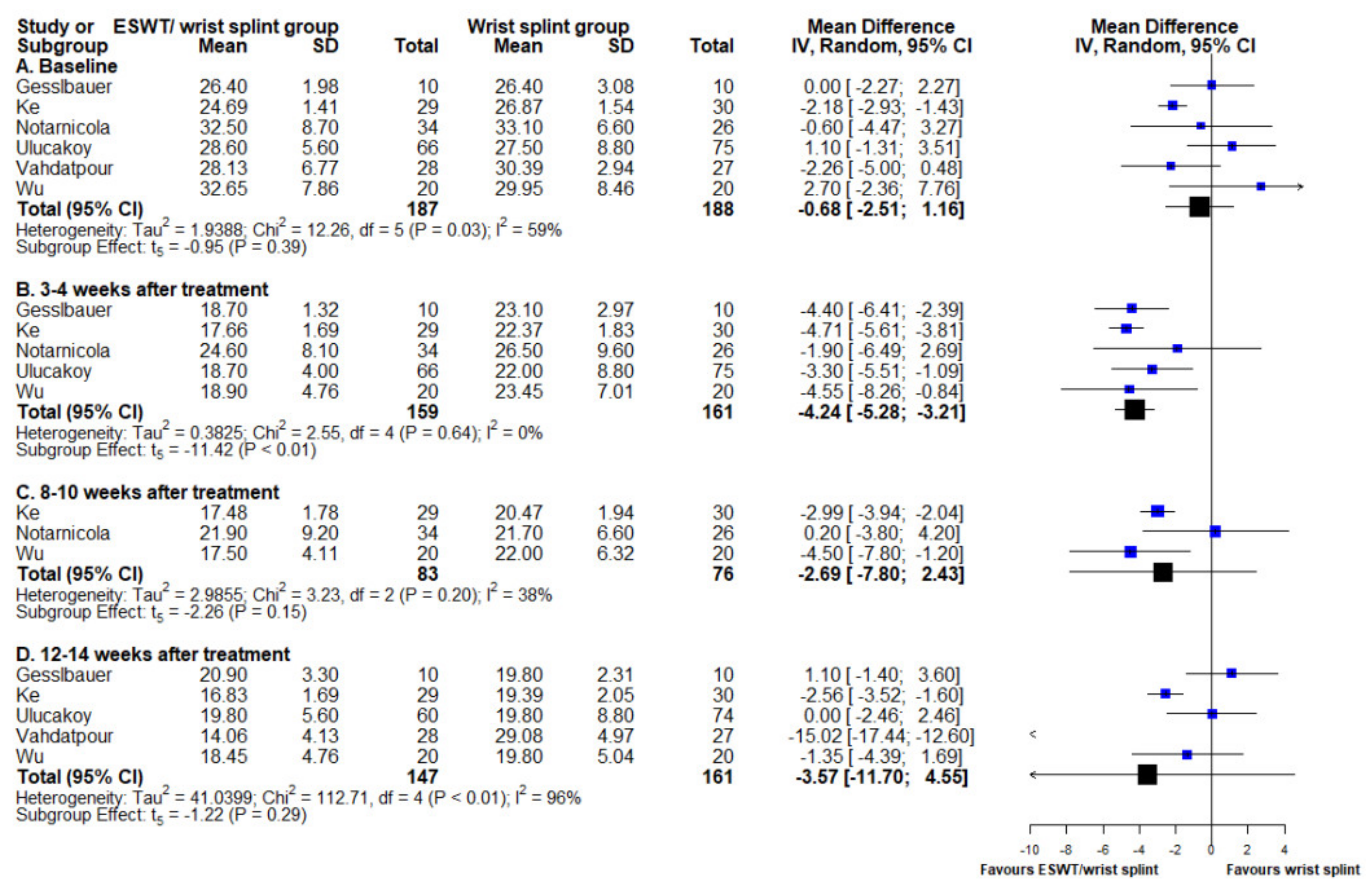
3.3. Boston Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Questionnaire Functional Subscale
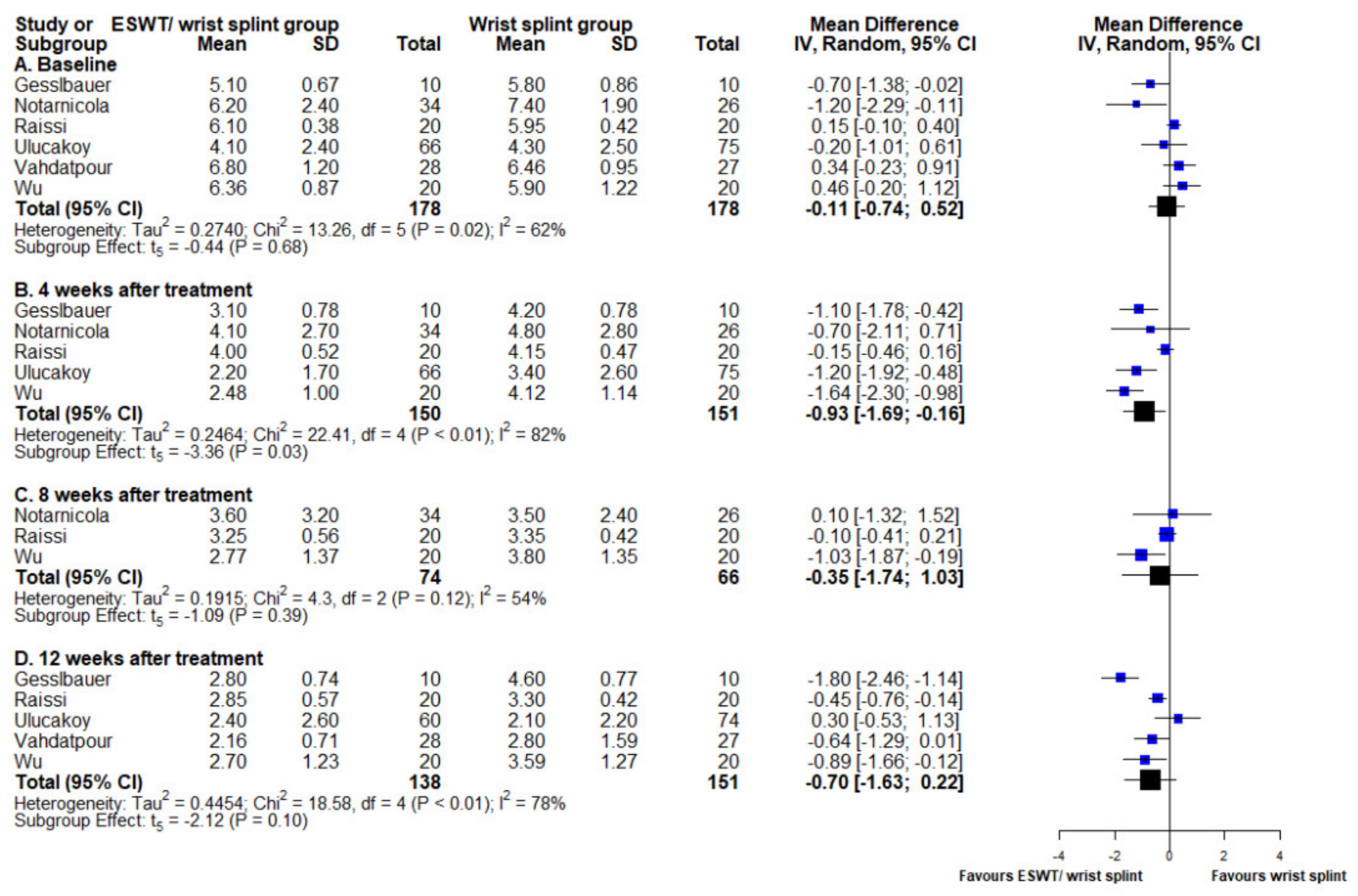
3.4. Boston Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Questionnaire Symptom Subscale
3.5. Visual Analogue Scale
3.6. Distal Motor Latency of Median Nerve and Sensory Nerve Conduction Velocity
3.7. Adverse Effects
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huisstede, B.M.; Brink, J.V.D.; Randsdorp, M.S.; Geelen, S.J.; Koes, B.W. Effectiveness of surgical and postsurgical interventions for carpal tunnel syndrome-A systematic review. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2018, 99, 1660–1680.e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urits, I.; Gress, K.; Charipova, K.; Orhurhu, V.; Kaye, A.D.; Viswanath, O. Recent advances in the understanding and management of carpal tunnel syndrome: A comprehensive review. Curr. Pain Headache Rep. 2019, 23, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huisstede, B.M.; Hoogvliet, P.; Randsdorp, M.S.; Glerum, S.; van Middelkoop, M.; Koes, B.W. Carpal tunnel syndrome. Part I: Effectiveness of nonsurgical treatments—A systematic review. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2010, 91, 981–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Agostino, M.; Craig, K.; Tibalt, E.; Respizzi, S. Shock wave as biological therapeutic tool: From mechanical stimulation to recovery and healing, through mechanotransduction. Int. J. Surg. 2015, 24 Pt B, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariotto, S.; de Prati, A.; Cavalieri, E.; Amelio, E.; Marlinghaus, E.; Suzuki, H. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy in inflammatory diseases: Molecular mechanism that triggers anti-inflammatory action. Curr. Med. Chem. 2009, 16, 2366–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yılmaz, G.D.; Aytekin, M.N.; Demir, Y.P.; Çırak, Y.; Dalkılınç, M.; Ağır, İ. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy in the treatment of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome; A novel technique and review of the literature. Nov. Sci. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2013, 2, 308–312. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.C.; Jung, S.H.; Lee, S.U.; Lee, S.Y. Effect of extracorporeal shockwave therapy on carpal tunnel syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Medicine 2019, 98, e16870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Higgins, J.; Thomas, J.; Cumpston, M.; Li, T.; Page, M.J.; Chandler, J.; Welch, V.A. (Eds.) Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Levine, D.W.; Simmons, B.P.; Koris, M.J.; Daltroy, L.H.; Hohl, G.G.; Fossel, A.H.; Katz, J.N. A self-administered questionnaire for the assessment of severity of symptoms and functional status in carpal tunnel syndrome. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 1993, 75, 1585–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Development Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Viechtbauer, W. Conducting Meta-Analyses in R with the metafor Package. J. Stat. Softw. 2010, 36, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Borenstein, M.; Hedges, L.V.; Higgins, J.P.T.; Rothstein, H.R. A basic introduction to fixed-effect and random-effects models for meta-analysis. Res. Synth. Methods 2010, 1, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, J.L.; Mengersen, K.L. Meta-analysis of repeated measures study designs. J. Eval. Clin. Pract. 2008, 14, 941–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, M.-J.; Chen, L.-C.; Chou, Y.-C.; Li, T.-Y.; Chu, H.-Y.; Tsai, C.-K.; Wu, Y.-T. The dose-dependent efficiency of radial shock wave therapy for patients with carpal tunnel syndrome: A prospective, randomized, single-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Notarnicola, A.; Maccagnano, G.; Tafuri, S.; Fiore, A.; Pesce, V.; Moretti, B. Comparison of shock wave therapy and nutraceutical composed of Echinacea angustifolia, alpha lipoic acid, conjugated linoleic acid and quercetin (perinerv) in patients with carpal tunnel syndrome. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2015, 28, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raissi, G.R.; Ghazaei, F.; Forogh, B.; Madani, S.P.; Daghaghzadeh, A.; Ahadi, T. The effectiveness of radial extracorporeal shock waves for treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome: A randomized clinical trial. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2017, 43, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vahdatpour, B.; Kiyani, A.; Dehghan, F. Effect of extracorporeal shock wave therapy on the treatment of patients with carpal tunnel syndrome. Adv. Biomed. Res. 2016, 5, 120. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.-T.; Ke, M.-J.; Chou, Y.-C.; Chang, C.-Y.; Lin, C.-Y.; Li, T.-Y.; Shih, F.-M.; Chen, L.-C. Effect of radial shock wave therapy for carpal tunnel syndrome: A prospective randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J. Orthop. Res. 2016, 34, 977–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gesslbauer, C.; Mickel, M.; Schuhfried, O.; Huber, D.; Keilani, M.; Crevenna, R. Effectiveness of focused extracorporeal shock wave therapy in the treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome: A randomized, placebo-controlled pilot study. Wien. Klin. Wochenschr. 2020, 133, 568–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karataş, Ö.; Çatal, S.; Gökmen, E.A.; Samanci, N. Treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome with eswt: A sham controlled double blinded randomised study. Ann. Clin. Anal. Med. 2020, 11, 166–170. [Google Scholar]
- Ulucaköy, R.K.; Yurdakul, F.G.; Bodur, H. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy as a conservative treatment option for carpal tunnel syndrome: A double-blind, prospective, randomized, placebo-controlled study. Turk. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2020, 66, 388–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Shindel, A.W.; Lin, G.; Lue, T.F. Cellular signaling pathways modulated by low-intensity extracorporeal shock wave therapy. Int. J. Impot. Res. 2019, 31, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGregor, C.E.; English, A.W. The role of BDNF in peripheral nerve regeneration: Activity-dependent treatments and Val66Met. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2019, 12, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, C.-Y.; Hung, S.-Y.; Chen, H.-T.; Tsou, H.-K.; Fong, Y.-C.; Wang, S.-W.; Tang, C.-H. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor increases vascular endothelial growth factor expression and enhances angiogenesis in human chondrosarcoma cells. Biochem. Pharm. 2014, 91, 522–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deasy, B.M.; Feduska, J.M.; Payne, T.R.; Li, Y.; Ambrosio, F.; Huard, J. Effect of VEGF on the regenerative capacity of muscle stem cells in dystrophic skeletal muscle. Mol. Ther. 2009, 17, 1788–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Ning, H.; Reed-Maldonado, A.B.; Zhou, J.; Ruan, Y.; Zhou, T.; Wang, H.S.; Oh, B.S.; Banie, L.; Lin, G.; et al. Low-Intensity extracorporeal shock wave therapy enhances brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression through PERK/ATF4 signaling pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Choi, G.H.; Wieland, L.S.; Lee, H.; Sim, H.; Lee, M.S.; Shin, B.C. Acupuncture and related interventions for the treatment of symptoms associated with carpal tunnel syndrome. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 12, CD011215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.T.; Ho, T.Y.; Chou, Y.C.; Ke, M.J.; Li, T.Y.; Huang, G.S.; Chen, L.C. Six-month efficacy of platelet-rich plasma for carpal tunnel syndrome: A prospective randomized, single-blind controlled trial. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uzun, H.; Bitik, O.; Uzun, Ö.; Ersoy, U.S.; Aktaş, E. Platelet-rich plasma versus corticosteroid injections for carpal tunnel syndrome. J. Plast. Surg. Hand Surg. 2017, 51, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Zhang, C.; Liang, B.; Wang, J.; Wang, L.; Wan, T.; Xu, F.; Lei, L. Effects of shock wave therapy in patients with carpal tunnel syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Disabil. Rehabil. 2020, 44, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Study | Inclusion Criteria | Patient Number, n, (Male, %) | Age, Years, Mean ± SD | Lesion Site, n | Symptom Duration, Months, Mean ± SD | Interventions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gesslbauer [Austria, 2020] | a. Electrophysiology study confirmed mild to moderate CTS | T: 10 (2) C:10 (4) | T: 55.8 ± 4.66 C: 54 ± 17.4 | NA | T: 29 ± 32.89 C: 33.6 ± 44.26 | T: One session/week of fESWT for 3 weeks, 500 shocks, 0.05 mJ/mm2 pressure + night wrist splint C: Sham ESWT + night wrist splint |
| Ke [Taiwan, 2016] | a. Disease duration > 3 months b. Tinel sign or Phalen test positive c. Electrophysiology study confirmed mild to moderate CTS | T: 29 (20.7) C: 30 (16.7) | T: 55.45 ± 1.38 C: 58.13 ± 1.13 | T: R15, L14 C: R16, L14 | T: 35.34 ± 7.45 C: 34.37 ± 5.42 | T: One session of rESWT for 2000 shocks, 4 bar pressure + night wrist splint C: Sham rESWT + night wrist splint during study period |
| Notarnicola [Italy, 2015] | a. Tinel sign and compression test positive b. Electrophysiology study confirmed CTS | T: 34 C: 26 | T: 57.1 ± 9.5 C: 60.2 ± 6.6 | Intergroup difference, p > 0.05 | NA | T: One session/week of ESWT for 3 weeks, 1600 shocks at 0.03 mJ/mm2 pressure + wrist splint C: Diet supplementary composed mainly of ALA, GLA, and Echinacea + wrist splint for 10 weeks |
| Raissi [Iran, 2016] | a. VAS ≥ 4 b. Disease duration > 1 month c. Tinel sign or Phalen test positived. Electrophysiology study confirmed mild to moderate CTS | T: 20 (10) C: 20 (5) | T: 46.1 ± 1.95 C: 46.65 ± 2.23 | T: R1, L5, B14 C: R3, L6, B11 | NA | T: One session/week of rESWT for 3 weeks, 1000 shocks, 1.5 bar pressure + night wrist splint C: Night wrist splint for 12 weeks |
| Ulucaköy [Turkey, 2020] | a. Electrophysiology study confirmed mild to moderate CTS | T: 47 (17) C: 50 (6) | T: 48.4 ± 10.1 C: 48.5 ± 9.8 | NA | T: 33.7 ± 38.1 C: 24.8 ± 31.5 | T: One session/week of rESWT for 3 weeks, 1000 shocks at 0.05 mJ/mm2 pressure + night wrist splint C: Night wrist splint for 12 weeks |
| Vahdatpour [Iran, 2016] | a. Tinel sign and compression test positive b. Electrophysiology study confirmed moderate CTS | Male: 9 Female: 51 (Intergroup difference, p > 0.05) | T: 51.5 ± 8.5 C: 49 ± 7.3 | NA | T: 3.5 ± 0.35 C: 3.72 ± 0.5 | T: One session/week of ESWT for 4 weeks with 800, 900,1000, and 1100 shocks, 0.05, 0.07, 0.1, and 0.15 bar pressure + night wrist splint C: Sham ESWT + night wrist splint for 3 months |
| Wu [Taiwan, 2016] | a. Tinel sign or Phalen test positive b. Numbness in at least two first, second, or third digits c. Electrophysiology study confirmed CTS | T: 20 (10) C: 20 (15) | T: 54.7 ± 7.96 C: 57.8 ± 6.51 | T: R9, L11 C: R11, L9 | T: 34.1 ± 33.11 C: 36.1 ± 30.8 | T: One session/week of rESWT for 3 weeks, 2000 shocks, 4 bar pressure + night wrist splint C: Sham rESWT + night wrist splint during study period |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, K.-T.; Chen, Y.-P.; Kuo, Y.-J.; Chiang, M.-H. Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy Provides Limited Therapeutic Effects on Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Medicina 2022, 58, 677. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58050677
Chen K-T, Chen Y-P, Kuo Y-J, Chiang M-H. Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy Provides Limited Therapeutic Effects on Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Medicina. 2022; 58(5):677. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58050677
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Ko-Ta, Yu-Pin Chen, Yi-Jie Kuo, and Ming-Hsiu Chiang. 2022. "Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy Provides Limited Therapeutic Effects on Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Medicina 58, no. 5: 677. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58050677
APA StyleChen, K.-T., Chen, Y.-P., Kuo, Y.-J., & Chiang, M.-H. (2022). Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy Provides Limited Therapeutic Effects on Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Medicina, 58(5), 677. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58050677






